Integrating Both Driving and Response Environmental Variables to Enhance Soil Salinity Inversion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
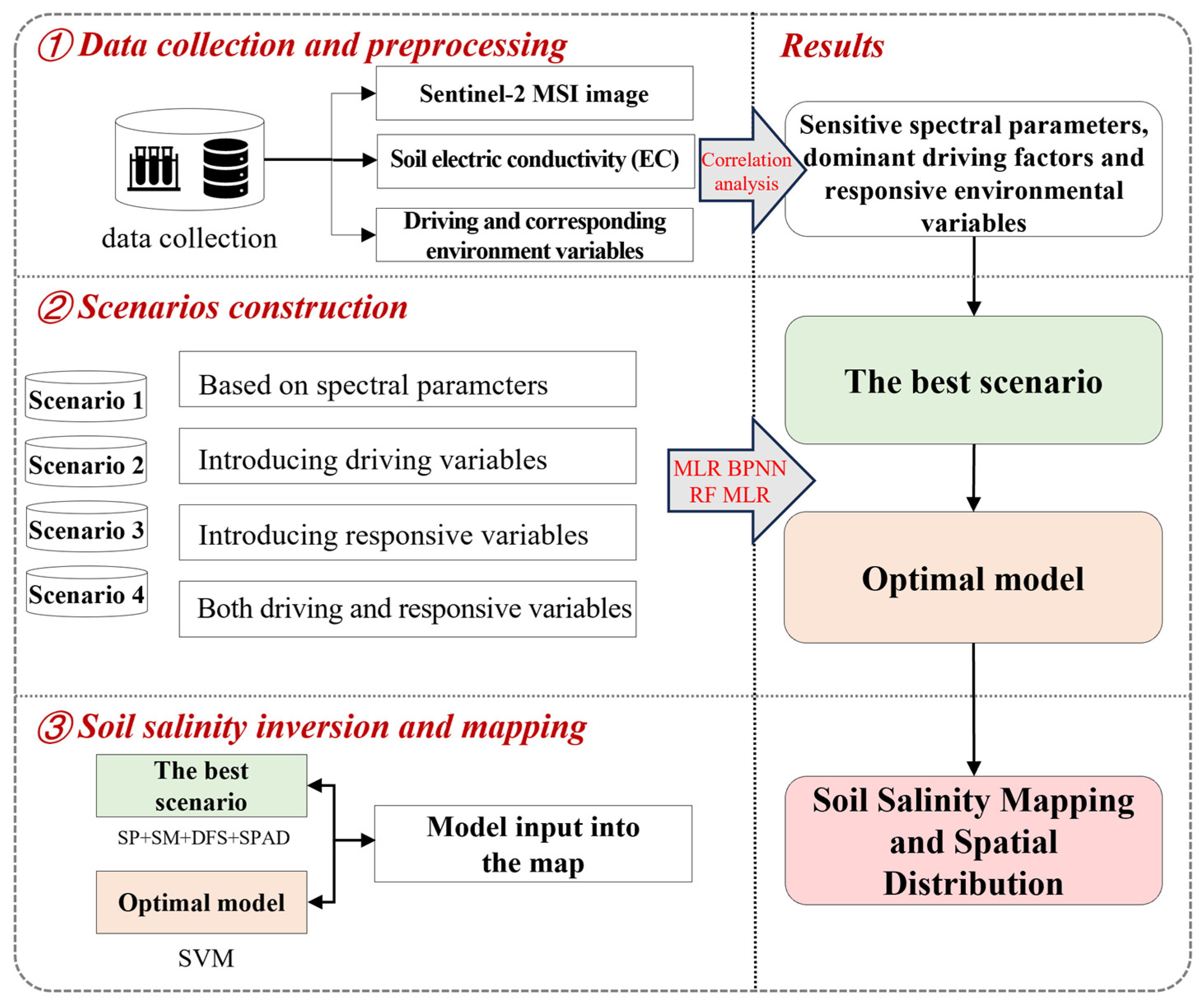
2.1. Research Scenario and Procedures
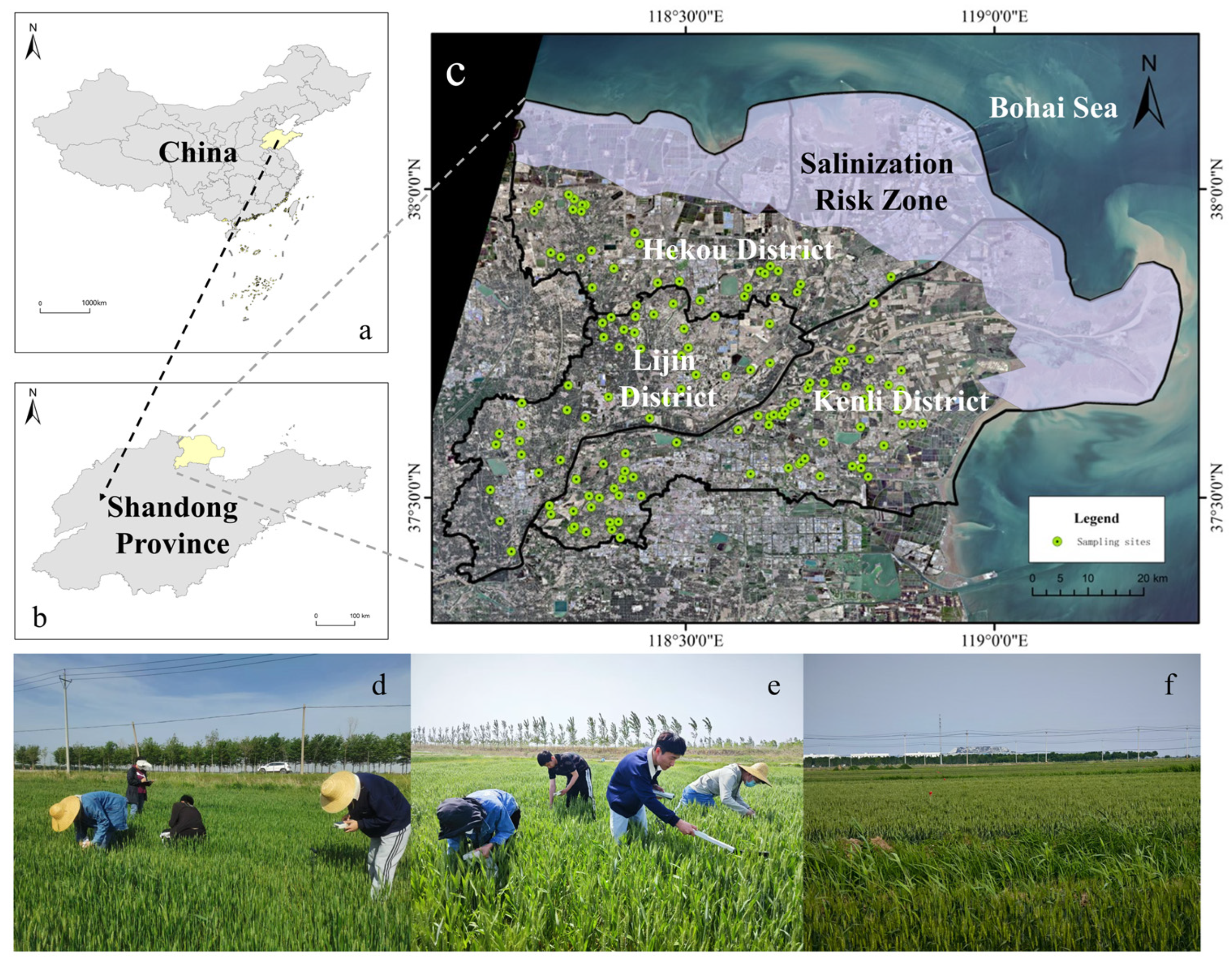
2.2. Study Area
2.3. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.3.1. Field Sampling and Soil Salinity Measurement
2.3.2. Acquisition of Driving Variables
2.3.3. Measurement of Response Variables
2.3.4. Acquisition and Preprocessing of Sentinel-2 MSI Imagery
2.4. Methodology
2.4.1. Analysis of Soil Salinity Sensitive Bands and Spectral Parameters
2.4.2. Analysis of Dominant Environmental Variables for Soil Salinity
2.4.3. Construction and Validation of Soil Salinity Inversion Models
Model Construction
Model Validation
2.4.4. Spatial Distribution Inversion and Accuracy Analysis of Soil Salinity in the Study Area
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Salinity Data of the Soil Samples
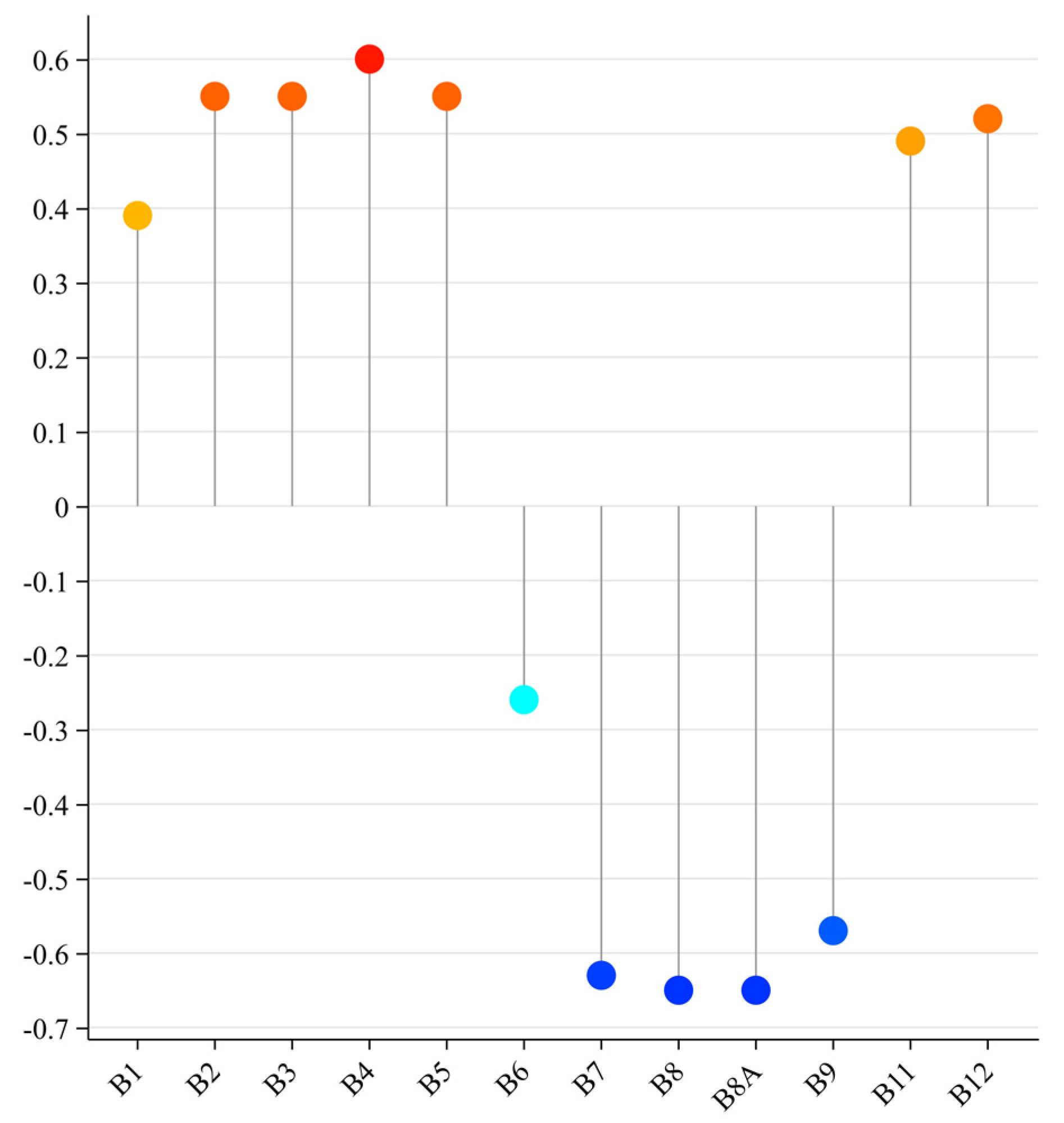
3.2. Sensitive Bands and Spectral Parameters of Soil Salinity
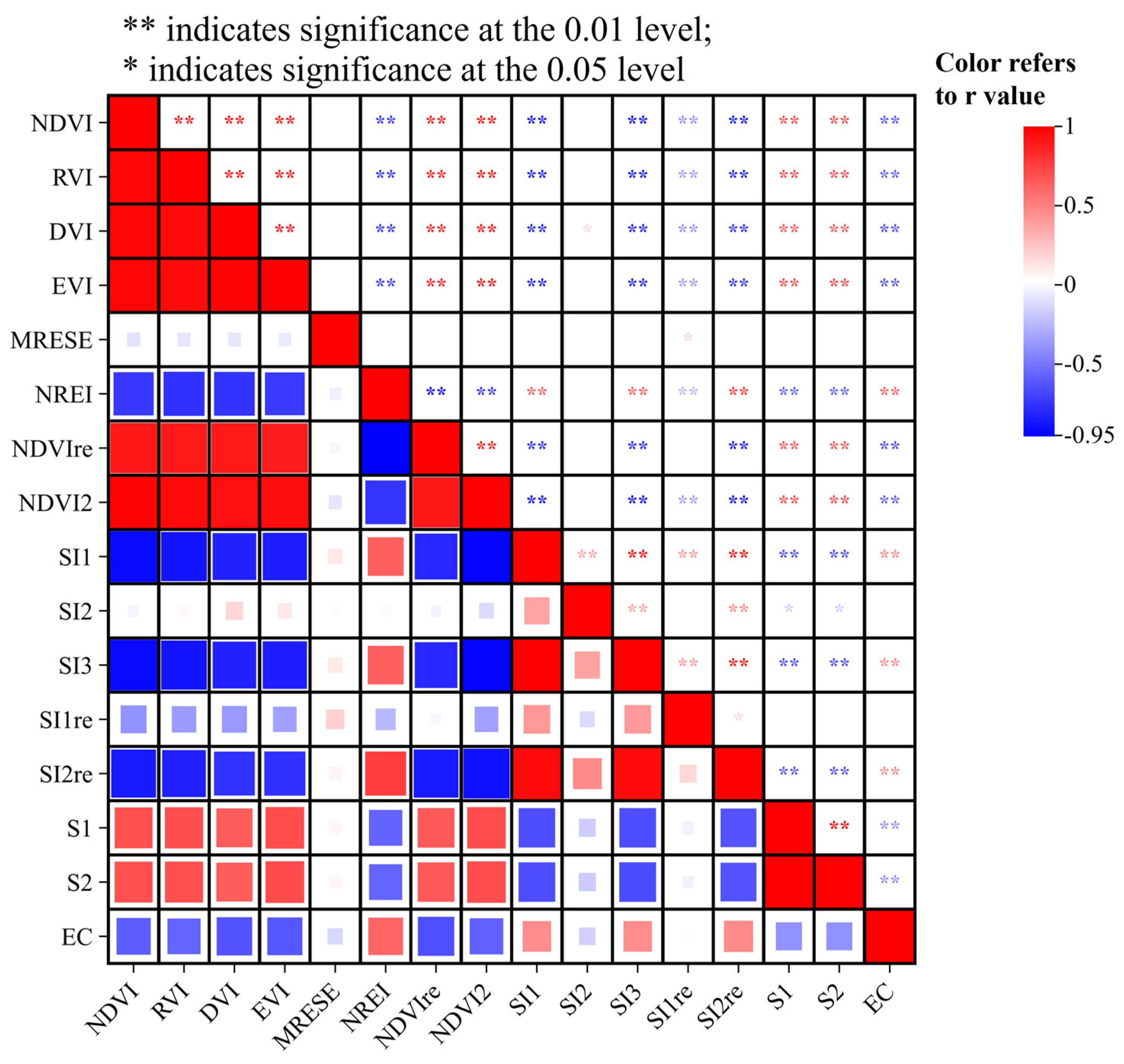
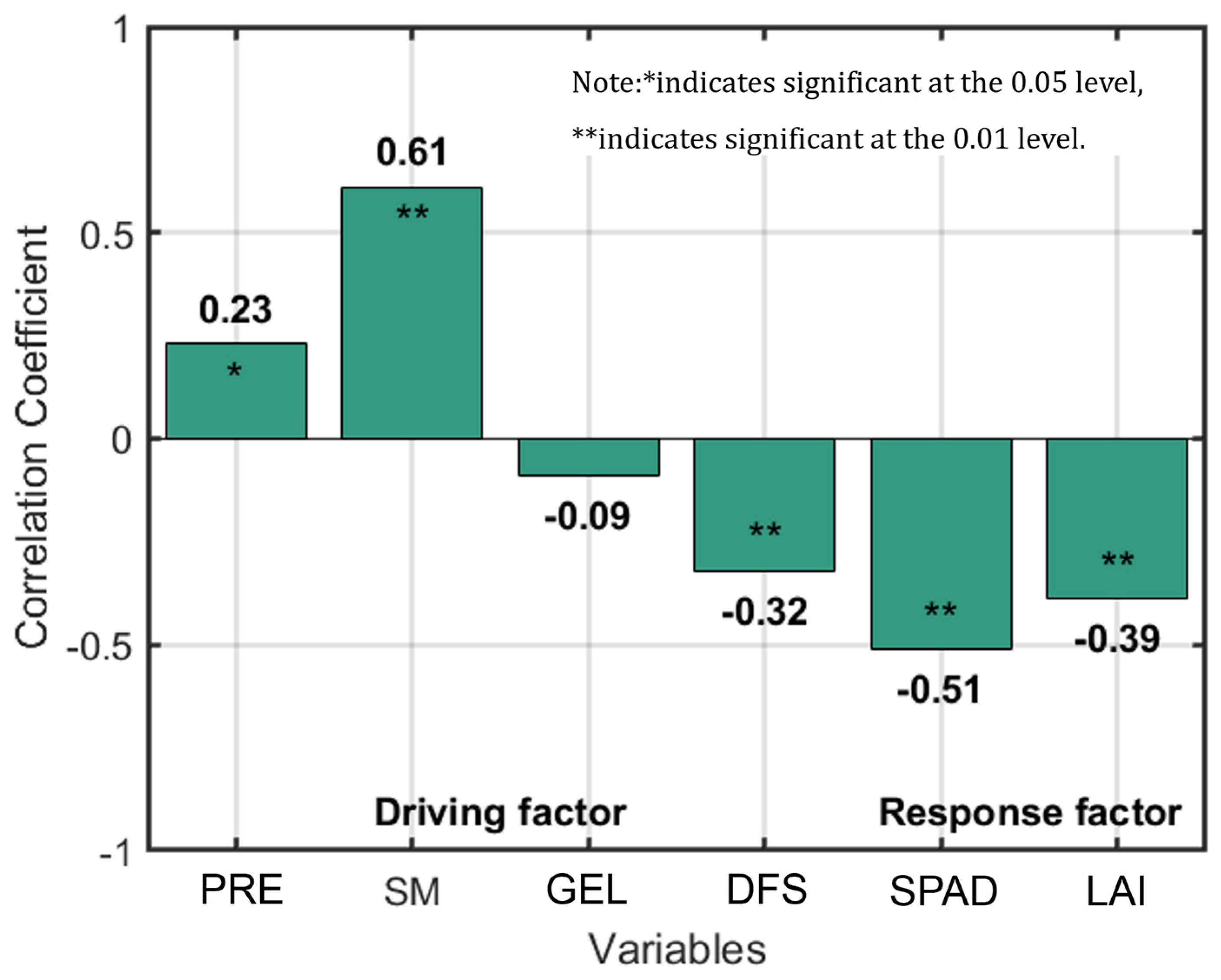
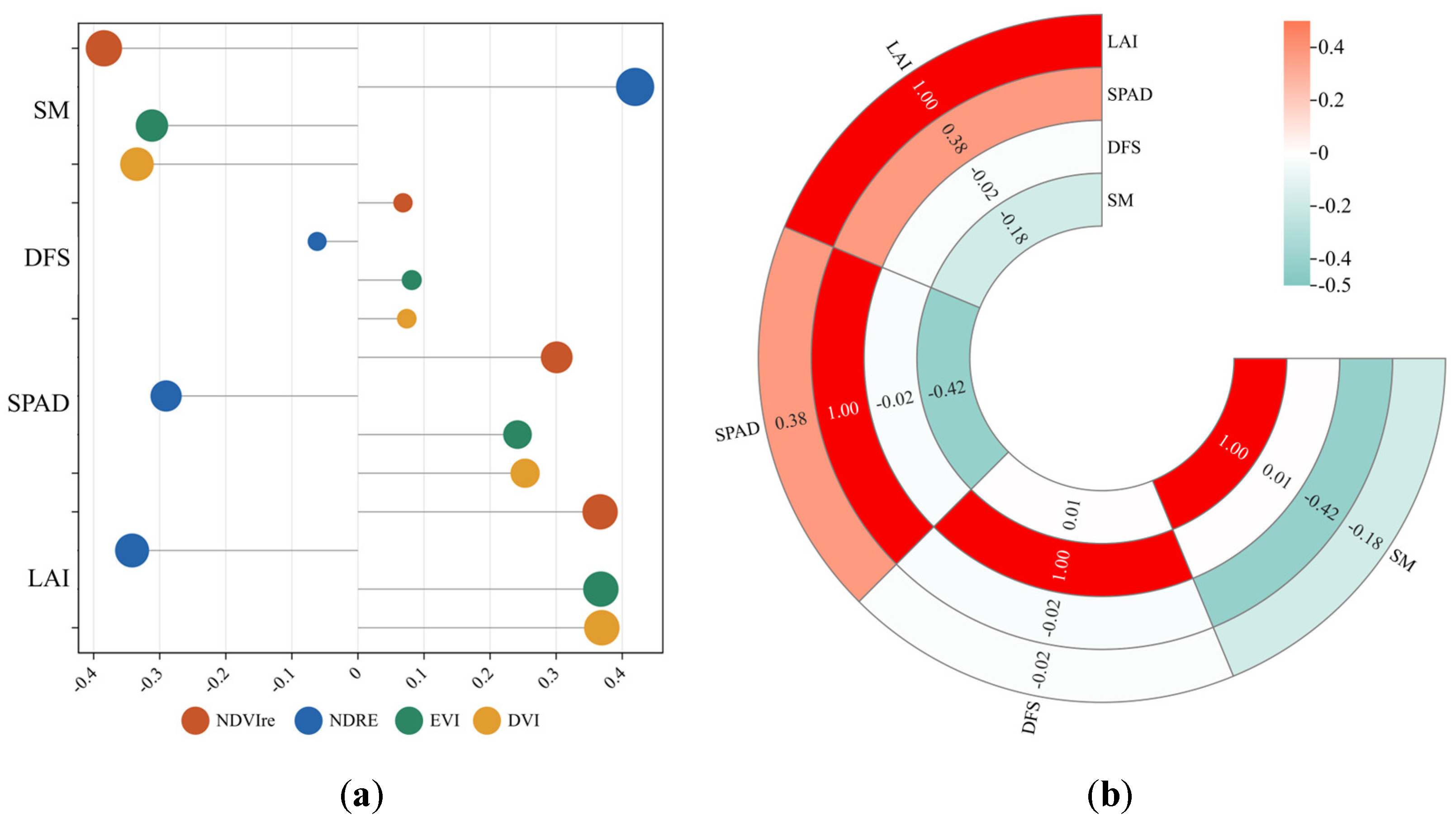
3.3. Selection of Dominant Environmental Variables of Soil Salinity
3.4. Quantitative Inversion Models of Soil Salinity
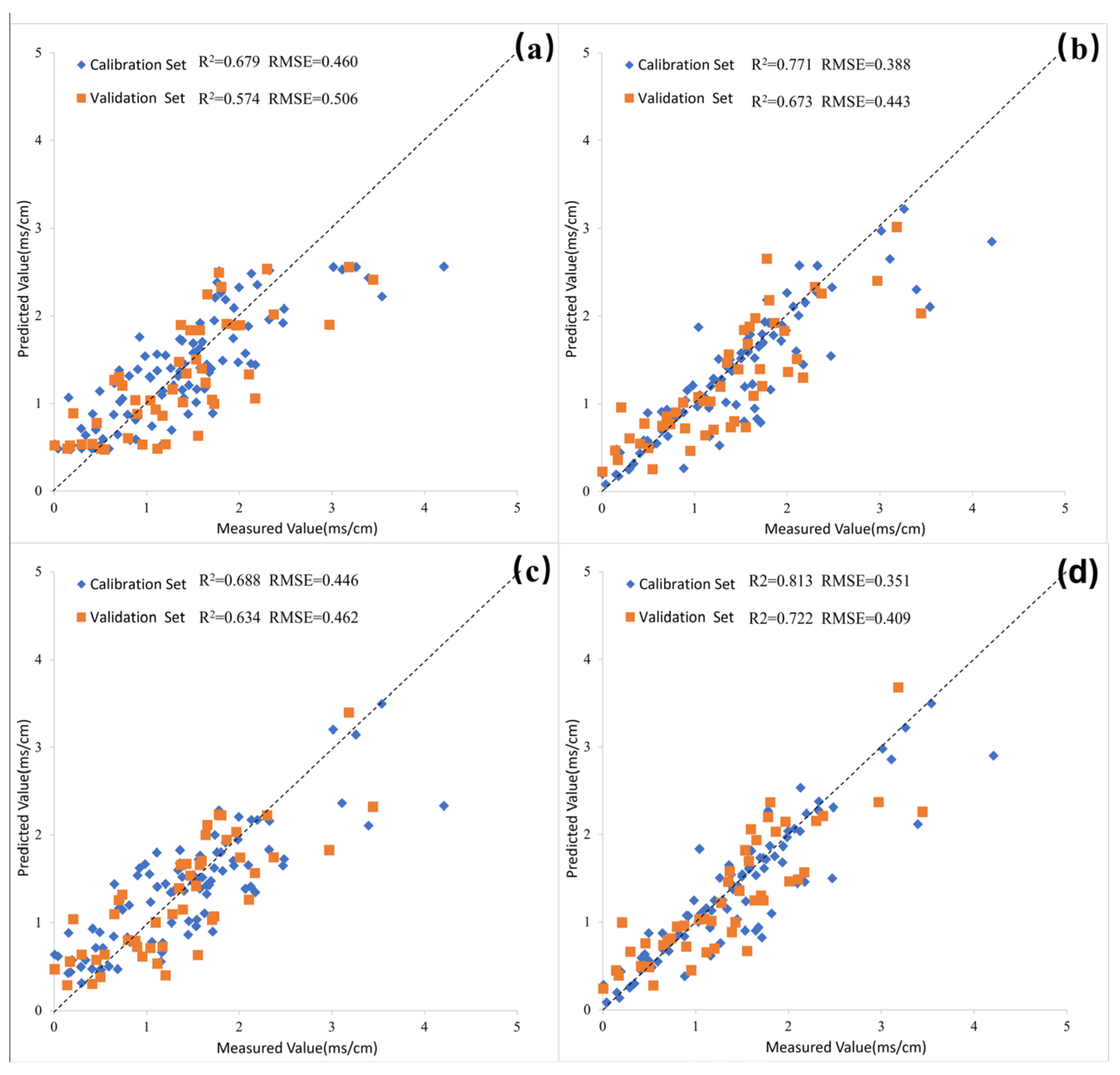
3.4.1. Soil Salinity Inversion Models Based on Scenario 1 (Only on Spectral Parameters)
3.4.2. Soil Salinity Inversion Models Based on Scenario 2 (Spectral Parameters in Combination with Driving Variables)
3.4.3. Soil Salinity Inversion Model Based on Scenario 3 (Spectral Parameters in Combination with Response Variables)
3.4.4. Soil Salinity Inversion Model Based on Scenario 4 (Spectral Parameters in Combination with Both Driving and Response Variables)
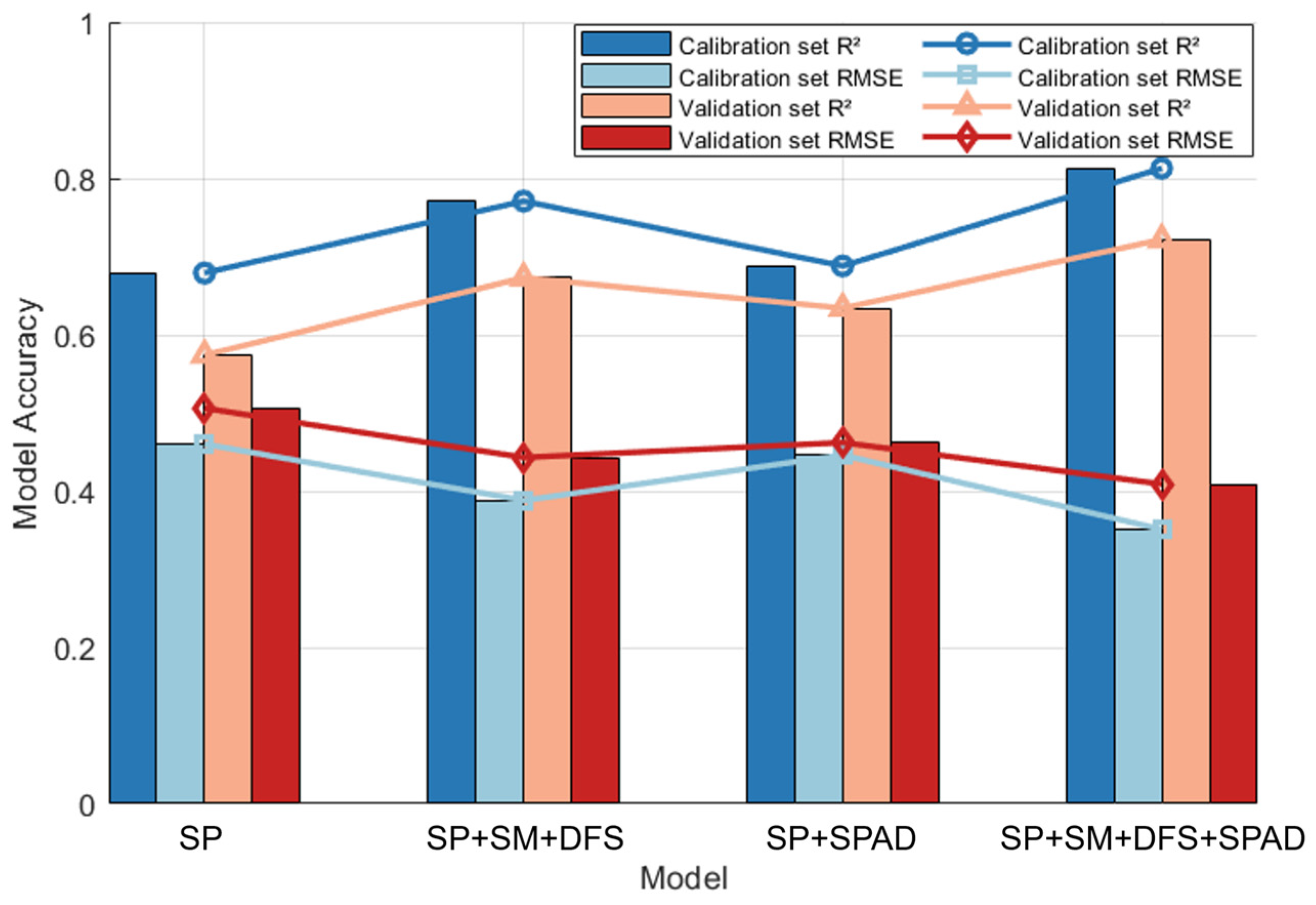
3.4.5. Model Comparison and Optimization
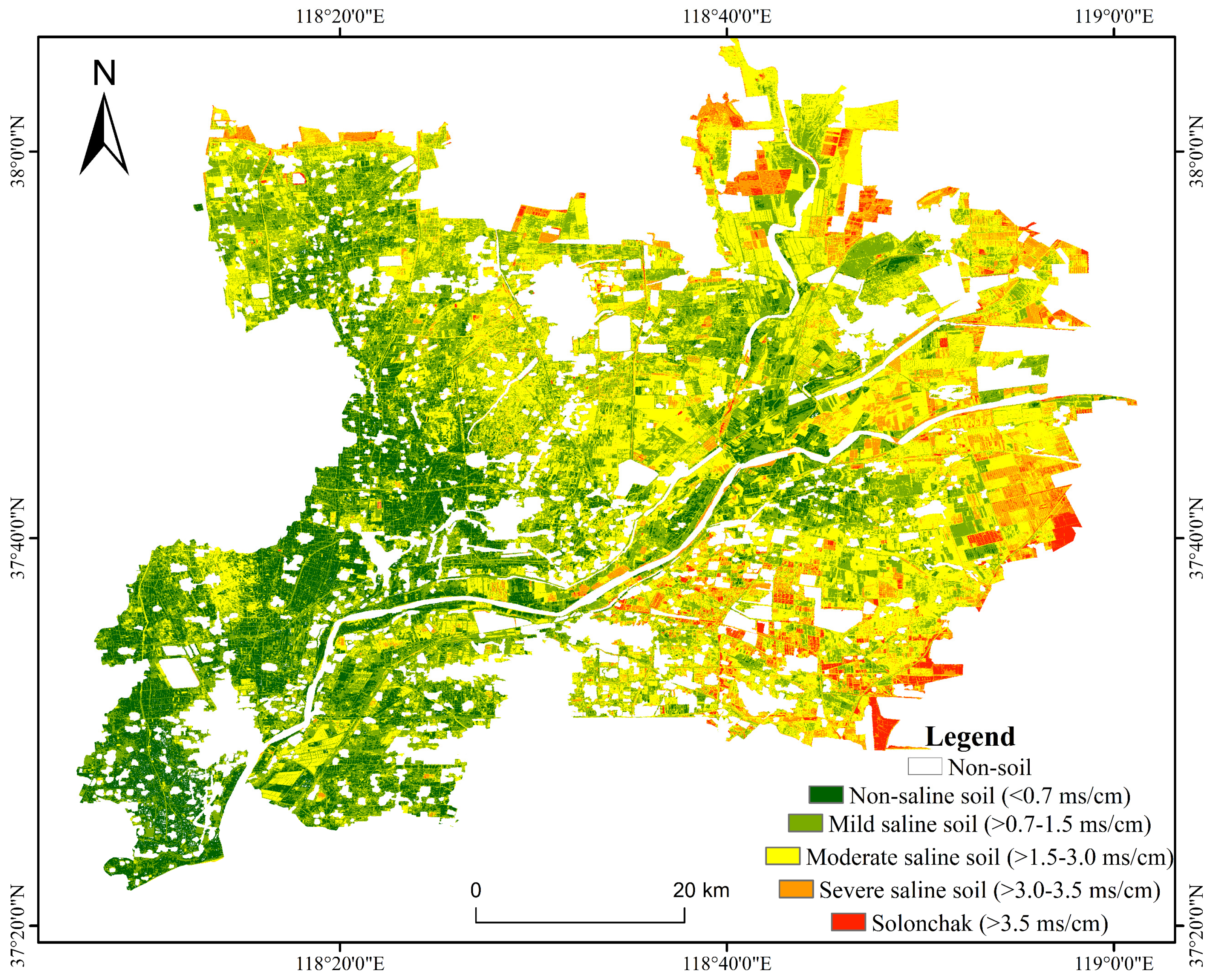
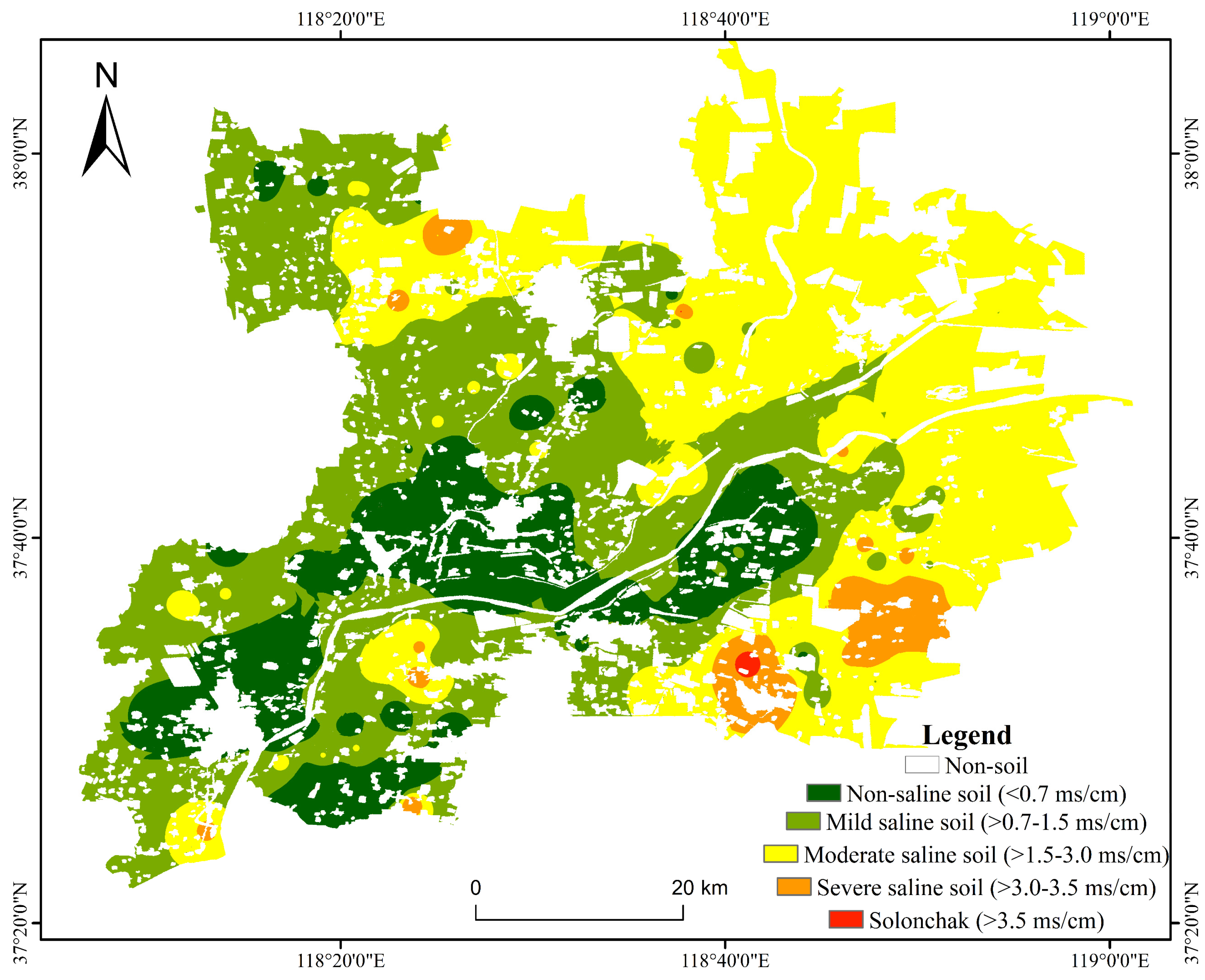
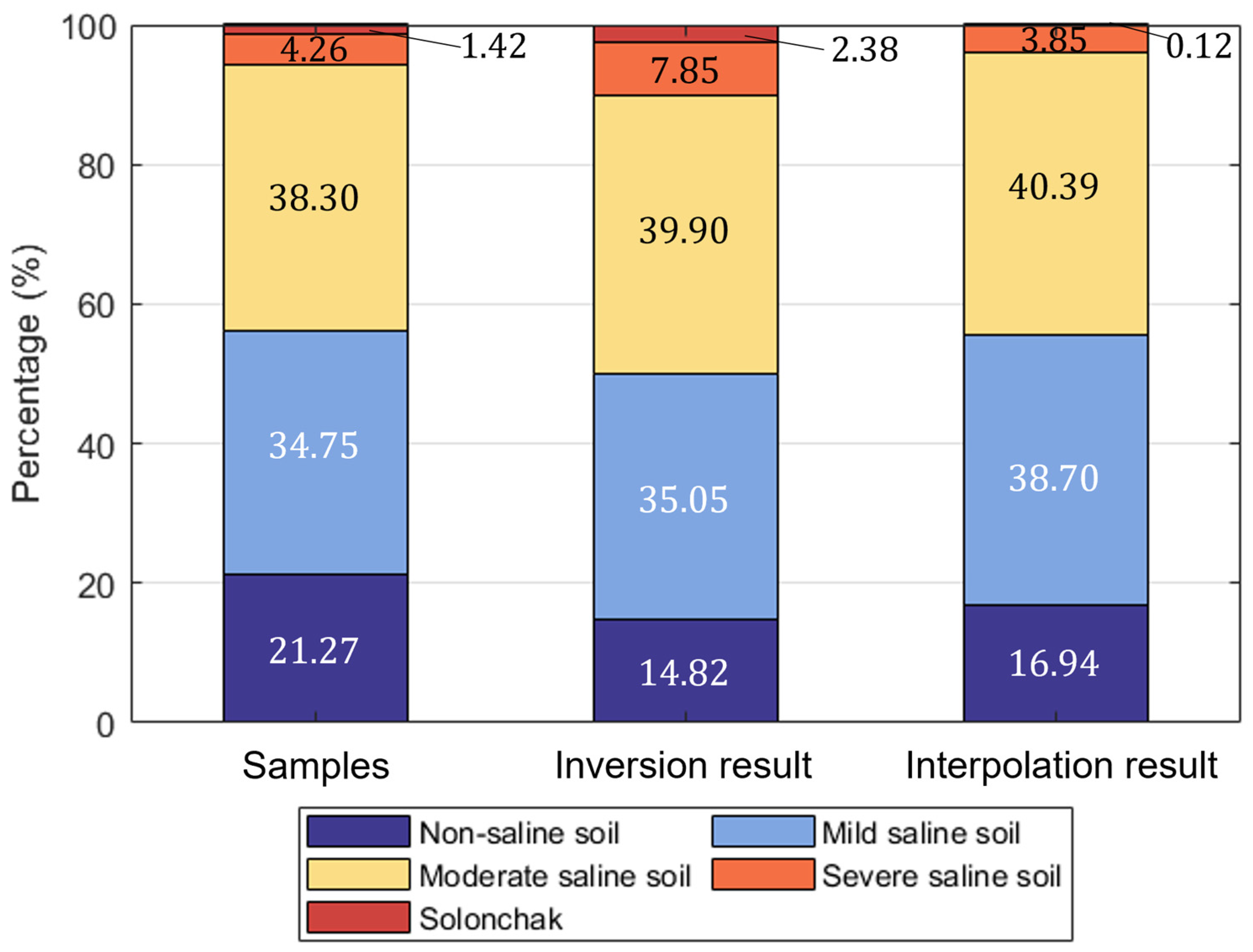
3.5. Soil Salinity Spatial Distribution Inversion and Accuracy Validation
3.6. Characteristics of Soil Salinity Spatial Distribution
4. Discussion
4.1. Effectiveness of the Models Introducing Environmental Variables Under Various Scenarios
4.2. Dominant Environmental Variables of Soil Salinity
4.3. Limitations and Outlook
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, J.-K.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of Plant Responses and Adaptation to Soil Salinity. Innovation 2020, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Ma, Y. Monitoring the Seasonal Dynamics of Soil Salinization in the Yellow River Delta of China Using Landsat Data. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 19, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouri, H.; Borujeni, S.C.; Nirola, R.; Hassanli, A.; Beecham, S.; Alaghmand, S.; Saint, C.; Mulcahy, D. Application of Green Remediation on Soil Salinity Treatment: A Review on Halophytoremediation. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 107, 94–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Predicting Long-Term Dynamics of Soil Salinity and Sodicity on a Global Scale. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 33017–33027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Gao, M.; Chang, C. Spatial Variability of Soil Salinity in Coastal Saline Soil at Different Scales in the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hamid, H.T.; Hong, G. Hyperspectral Remote Sensing for Extraction of Soil Salinization in the Northern Region of Ningxia. Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 6, 2487–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliakopoulos, I.N.; Tsanis, I.K.; Koutroulis, A.; Kourgialas, N.N.; Varouchakis, A.E.; Karatzas, G.P.; Ritsema, C.J. The Threat of Soil Salinity: A European Scale Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 727–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Shen, F.; Meadows, M.E.; Zhou, C. Hydrology, Vegetation, and Soil Properties as Key Drivers of Soil Organic Carbon in Coastal Wetlands: A High-Resolution Study. Environ. Sci. Ecotechnol. 2025, 23, 100482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghadosi, M.M.; Hasanlou, M.; Eftekhari, K. Retrieval of Soil Salinity from Sentinel-2 Multispectral Imagery. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2019, 52, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Deng, C.; Liu, Y.; Niu, Z.; Li, Y. Identifying Change in Spatial Accumulation of Soil Salinity in an Inland River Watershed, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 621, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswar, D.; Karuppusamy, R.; Chellamuthu, S. Drivers of Soil Salinity and Their Correlation with Climate Change. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2021, 50, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, L.T.; Mele, P.M.; Annett, S.; Kasel, S. Examining Links between Soil Management, Soil Health, and Public Benefits in Agricultural Landscapes: An Australian Perspective. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 139, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-X.; Song, Y.-T.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Li, X.-J.; Niu, B.-B. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Soil Salinity in the Yellow River Delta under the Impacts of Hydrology and Climate. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao= J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 32, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar]
- Letey, J.; Hoffman, G.J.; Hopmans, J.W.; Grattan, S.R.; Suarez, D.; Corwin, D.L.; Oster, J.D.; Wu, L.; Amrhein, C. Evaluation of Soil Salinity Leaching Requirement Guidelines. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawar, S.; Buddenbaum, H.; Hill, J.; Kozak, J. Modeling and Mapping of Soil Salinity with Reflectance Spectroscopy and Landsat Data Using Two Quantitative Methods (PLSR and MARS). Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 10813–10834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Shi, Z.; Biswas, A.; Yang, S.; Ding, J. Multi-Algorithm Comparison for Predicting Soil Salinity. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corwin, D.L. Climate Change Impacts on Soil Salinity in Agricultural Areas. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 842–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultanov, M.; Ibrakhimov, M.; Akramkhanov, A.; Bauer, C.; Conrad, C. Modelling End-of-Season Soil Salinity in Irrigated Agriculture through Multi-Temporal Optical Remote Sensing, Environmental Parameters, and in Situ Information. PFG–J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2018, 86, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Hu, J.; Hu, B.; Shi, Z. Estimating Soil Salinity from Remote Sensing and Terrain Data in Southern Xinjiang Province, China. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tong, Z.; Ren, Z.; Xie, Y. Digital Mapping of Soil pH and Driving Factor Analysis Based on Environmental Variable Screening. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, L.; Dai, X.; Zang, D.; Qi, B.; Meng, X.; Mei, X.; Luo, C.; Liu, H. Systematic Identification of Factors Influencing the Spatial Distribution of Soil Organic Matter in Croplands within the Black Soil Region of Northeastern China across Multiple Scales. Catena 2025, 249, 108633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Gao, B.; Ou, C.; Du, Z.; Yang, J.; Batsaikhan, B.; Dorjgotov, B.; Yun, W.; Zhu, D. A Quantitative Analysis of Factors Influencing Organic Matter Concentration in the Topsoil of Black Soil in Northeast China Based on Spatial Heterogeneous Patterns. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R.; Cramer, G.R.; Ball, M.C. Interactions between Rising CO2, Soil Salinity, and Plant Growth. In Carbon Dioxide and Environmental Stress; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; pp. 139–167. [Google Scholar]
- Darwish, T.; Atallah, T.; El Moujabber, M.; Khatib, N. Salinity Evolution and Crop Response to Secondary Soil Salinity in Two Agro-Climatic Zones in Lebanon. Agric. Water Manag. 2005, 78, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj-Amor, Z.; Araya, T.; Kim, D.-G.; Bouri, S.; Lee, J.; Ghiloufi, W.; Yang, Y.; Kang, H.; Jhariya, M.K.; Banerjee, A.; et al. Soil Salinity and Its Associated Effects on Soil Microorganisms, Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Crop Yield, Biodiversity and Desertification: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 156946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahab, S.; Suhani, I.; Srivastava, V.; Chauhan, P.S.; Singh, R.P.; Prasad, V. Potential Risk Assessment of Soil Salinity to Agroecosystem Sustainability: Current Status and Management Strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 764, 144164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Song, J.; Wang, H.; Lv, X.; Tian, T.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Zhong, M.; Jiang, M. Improving the Monitoring of Root Zone Soil Salinity under Vegetation Cover Conditions by Combining Canopy Spectral Information and Crop Growth Parameters. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1171594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scudiero, E.; Skaggs, T.H.; Corwin, D.L. Regional-Scale Soil Salinity Assessment Using Landsat ETM+ Canopy Reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munns, R. Comparative Physiology of Salt and Water Stress. Plant Cell Environ. 2002, 25, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Guo, B.; Zang, W.; Ge, D.; Luo, W.; Zhao, H. Desertification Detection Model in Naiman Banner Based on the Albedo-Modified Soil Adjusted Vegetation Index Feature Space Using the Landsat8 OLI Images. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2020, 11, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Pan, F.; Xiao, X.; Hu, L.; Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, S.; Tian, B.; Yu, H.; Lan, Y. Summer Maize Growth Estimation Based on Near-Surface Multi-Source Data. Agronomy 2023, 13, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Li, N.; Cui, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H. Study on Monitoring SPAD Values for Multispatial Spatial Vertical Scales of Summer Maize Based on UAV Multispectral Remote Sensing. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Cao, Q.; Zhang, K.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Liu, X. Optimal Leaf Positions for SPAD Meter Measurement in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pattey, E.; Admiral, S. Assessment of in Situ Crop LAI Measurement Using Unidirectional View Digital Photography. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 169, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, K.; Zhu, D.; Huang, J.; Wang, P. Atmospheric Correction Method for Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery. Acta Opt. Sin. 2018, 38, 0128001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, C.; Zang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Q.; Wu, Y. Remote Sensing of Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in the Wuyu’er-Shuangyang River Basin, Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Liu, M.; Du, B.; Wang, Z.; Hu, L.; Zhang, B. Mapping Soil Salinity/Sodicity by Using Landsat OLI Imagery and PLSR Algorithm over Semiarid West Jilin Province, China. Sensors 2018, 18, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Yang, J.; Xie, J.; Sun, Z. Feature Selection and Regression Models for Multisource Data-Based Soil Salinity Prediction: A Case Study of Minqin Oasis in Arid China. Land 2024, 13, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J. Red and Photographic Infrared Linear Combinations for Monitoring Vegetation. Remote Sens. Environ. 1979, 8, 127–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G.M.; Cutler, M.E.; McMorrow, J.; Pelz, D.; Tangki, H.; Boyd, D.S.; Douglas, I. Mapping the Biomass of Bornean Tropical Rain Forest from Remotely Sensed Data. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2001, 10, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaglio Laurin, G.; Francini, S.; Luti, T.; Chirici, G.; Pirotti, F.; Papale, D. Satellite Open Data to Monitor Forest Damage Caused by Extreme Climate-Induced Events: A Case Study of the Vaia Storm in Northern Italy. For. Int. J. For. Res. 2021, 94, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanke, Y.; Tubaña, B.; Dalen, M.; Harrell, D. Evaluation of Red and Red-Edge Reflectance-Based Vegetation Indices for Rice Biomass and Grain Yield Prediction Models in Paddy Fields. Precis. Agric. 2016, 17, 507–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk, J.; Osberger, A. Red-Edge Vegetation Indices for Detecting and Assessing Disturbances in Norway Spruce Dominated Mountain Forests. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 37, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.P.; Prasad, R.; Bala, R.; Srivastava, P.K. Assessment of Red-Edge Vegetation Descriptors in a Modified Water Cloud Model for Forward Modelling Using Sentinel—1A and Sentinel—2 Satellite Data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delegido, J.; Verrelst, J.; Alonso, L.; Moreno, J. Evaluation of Sentinel-2 Red-Edge Bands for Empirical Estimation of Green LAI and Chlorophyll Content. Sensors 2011, 11, 7063–7081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolas, H.; Walter, C. Detecting Salinity Hazards within a Semiarid Context by Means of Combining Soil and Remote-Sensing Data. Geoderma 2006, 134, 217–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Yu, D.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ge, X.; Teng, D.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Lizaga, I.; et al. Capability of Sentinel-2 MSI Data for Monitoring and Mapping of Soil Salinity in Dry and Wet Seasons in the Ebinur Lake Region, Xinjiang, China. Geoderma 2019, 353, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Ma, F.; Yu, H.; Li, Z. Inversion Model of Salt Content in Alfalfa-Covered Soil Based on a Combination of UAV Spectral and Texture Information. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavi, I.; Thevs, N.; Priori, S. Soil Salinity and Sodicity in Drylands: A Review of Causes, Effects, Monitoring, and Restoration Measures. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 712831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Hao, Y.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Xiu, L.; Gao, Q. Soil Salinity Estimation by 3D Spectral Space Optimization and Deep Soil Investigation in the Songnen Plain, Northeast China. Sustainability 2024, 16, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerardo, R.; de Lima, I.P. Sentinel-2 Satellite Imagery-Based Assessment of Soil Salinity in Irrigated Rice Fields in Portugal. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Frédéric, B.; Gu, X.; Tong, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, B. Relating Soil Surface Moisture to Reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 238–246. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmati, M.; Amelung, W.; Brogi, C.; Dari, J.; Flammini, A.; Bogena, H.; Brocca, L.; Chen, H.; Groh, J.; Koster, R.D.; et al. Soil Moisture Memory: State-of-the-art and the Way Forward. Rev. Geophys. 2024, 62, e2023RG000828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, D.; Song, X.; Zhu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Soil Moisture Variability and Its Driving Factor. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nick, S.M.; Copty, N.K.; Saygın, S.D.; Öztürk, H.S.; Demirel, B.; Emadian, S.M.; Erpul, G.; Sedighi, M.; Babaei, M. Impact of Soil Compaction and Irrigation Practices on Salt Dynamics in the Presence of a Saline Shallow Groundwater: An Experimental and Modelling Study. Hydrol. Process. 2024, 38, e15135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelln, C.; Barbour, S.L.; Qualizza, C. Controls on the spatial distribution of soil moisture and solute transport in a sloping reclamation cover. Can. Geotech. J. 2008, 45, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhu, Y.; Ye, M.; Yang, Y.; Yang, J.; Mao, W.; Wu, J. Regional Soil Salinity Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Improved Temporal Stability Analysis in Arid Agricultural Areas. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 272–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurtseven, I.; Randhir, T.O. Multivariate Assessment of Spatial and Temporal Variations in Irrigation Water Quality in Lake Uluabat Watershed of Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xi, H.; Yu, T.; Cheng, W.; Chen, Y. Spatio-Temporal Variation in Soil Salinity and Its Influencing Factors in Desert Natural Protected Forest Areas. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 5054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.; Houborg, R.; McCabe, M.F. Response of Chlorophyll, Carotenoid and SPAD-502 Measurement to Salinity and Nutrient Stress in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Agronomy 2017, 7, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Volk, T.A.; Im, J. Forest and Crop Leaf Area Index Estimation Using Remote Sensing: Research Trends and Future Directions. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishzadeh, R.; Skidmore, A.; Atzberger, C.; van Wieren, S. Estimation of Vegetation LAI from Hyperspectral Reflectance Data: Effects of Soil Type and Plant Architecture. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2008, 10, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulig, B.; Lepiarczyk, A.; Oleksy, A.; Kołodziejczyk, M. The Effect of Tillage System and Forecrop on the Yield and Values of LAI and SPAD Indices of Spring Wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 2010, 33, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaan, R.L.; Taylor, G.R. Field-Derived Spectra of Salinized Soils and Vegetation as Indicators of Irrigation-Induced Soil Salinization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zheng, B.; Zhong, W.; Xu, J.; Nie, W.; Sun, Y.; Guan, Z. Infiltration and Leaching Characteristics of Soils with Different Salinity under Fertilizer Irrigation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Shang, X.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y.; Tian, B. Soil Salinity Inversion in Yellow River Delta by Regularized Extreme Learning Machine Based on ICOA. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkov, V.; Beilby, M.J. Salinity Tolerance in Plants: Mechanisms and Regulation of Ion Transport. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote Sensing of Soil Salinity: Potentials and Constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, T.J.; Colmer, T.D. Salinity Tolerance in Halophytes. New Phytol. 2008, 945–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, Q.; Yang, X.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Tang, Z.; Jiang, D.; Peng, C.; He, Y. Hyperspectral Imaging Combined with Machine Learning as a Tool to Obtain High-throughput Plant Salt-stress Phenotyping. Plant J. 2020, 101, 1448–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, T.A.; Khan, A.; Skalicky, M.; Wasaya, A.; Rehmani, M.I.A.; Sarwar, N.; Mubeen, K.; Aziz, M.; Hassan, M.M.; Hassan, F.A.; et al. Exogenous Sodium Nitroprusside Mitigates Salt Stress in Lentil (Lens culinaris Medik.) by Affecting the Growth, Yield, and Biochemical Properties. Molecules 2021, 26, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Bengio, S.; Hardt, M.; Recht, B.; Vinyals, O. Understanding Deep Learning (Still) Requires Rethinking Generalization. Commun. ACM 2021, 64, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menghani, G. Efficient Deep Learning: A Survey on Making Deep Learning Models Smaller, Faster, and Better. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chu, D.; Hu, H.; Deng, W.; Chen, J.; Guo, S. Effects of Land-Use Type and Salinity on Soil Carbon Mineralization in Coastal Areas of Northern Jiangsu Province. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | Data Source and Processing | Resolution |
|---|---|---|
| PRE | OpenLandMap (https://openlandmap.org, accessed on 9 September 2023) | 1000 m |
| SM | Field survey data, interpolated using IDW | 10 m |
| GEL | Copernicus DEM | 30 m |
| DFS | Calculated in ArcGIS from coastline (coastline from National Earth System Science Data Center) | 10 m |
| SPAD | Field survey data, interpolated using IDW | 10 m |
| LAI | Field survey data, interpolated using IDW | 10 m |
| Number | Spectral Parameter | Formula | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | NDVI | [39] | |
| 2 | RVI | [40] | |
| 3 | DVI | [41] | |
| 4 | EVI | ||
| 5 | MRESR | [42] | |
| 6 | NREI | [43] | |
| 7 | NDVIre | [44] | |
| 8 | NDVI2 | [45] | |
| 9 | SI1 | [46] | |
| 10 | SI2 | ||
| 11 | SI3 | ||
| 12 | SI1re | [19] | |
| 13 | SI2re | ||
| 14 | S1 | [47] | |
| 15 | S2 |
| Statistical Indicators | All Samples | Calibration Samples | Validation Samples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quantity | 141 | 94 | 47 |
| AVG (ms/cm) | 1.37 | 1.39 | 1.35 |
| MAX (ms/cm) | 4.21 | 4.21 | 3.45 |
| MIN (ms/cm) | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| SD (ms/cm) | 0.80 | 0.82 | 0.78 |
| CV | 1.37 | 1.39 | 1.35 |
| Statistical Indicators | Calibration Set | Validation Set | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | |
| MLR | 0.573 | 0.530 | 0.567 | 0.510 |
| BPNN | 0.600 | 0.503 | 0.579 | 0.513 |
| RF | 0.679 | 0.460 | 0.574 | 0.506 |
| SVM | 0.594 | 0.517 | 0.574 | 0.506 |
| Modeling Variable | Modeling Method | Calibration Set | Validation Set | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Improvement | Performance | Improvement | ||||||
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | ||
| SP + SM | MLR | 0.646 | 0.465 | 0.073 | −0.065 | 0.640 | 0.501 | 0.073 | −0.009 |
| BPNN | 0.653 | 0.460 | 0.053 | −0.043 | 0.641 | 0.500 | 0.062 | −0.013 | |
| RF | 0.696 | 0.430 | 0.017 | −0.03 | 0.653 | 0.492 | 0.079 | −0.014 | |
| SVM | 0.637 | 0.470 | 0.043 | −0.047 | 0.601 | 0.527 | 0.027 | \ | |
| SP + DFS | MLR | 0.667 | 0.458 | 0.094 | −0.072 | 0.656 | 0.482 | 0.089 | −0.028 |
| BPNN | 0.623 | 0.508 | 0.023 | \ | 0.629 | 0.479 | 0.05 | −0.034 | |
| RF | 0.637 | 0.471 | \ | \ | 0.633 | 0.506 | 0.059 | \ | |
| SVM | 0.667 | 0.468 | 0.073 | −0.049 | 0.628 | 0.473 | 0.054 | −0.033 | |
| SP + SM + DFS | MLR | 0.743 | 0.423 | 0.17 | −0.107 | 0.729 | 0.407 | 0.162 | −0.103 |
| BPNN | 0.691 | 0.434 | 0.091 | −0.069 | 0.643 | 0.498 | 0.064 | −0.015 | |
| RF | 0.723 | 0.411 | 0.044 | −0.049 | 0.663 | 0.485 | 0.089 | −0.021 | |
| SVM | 0.771 | 0.388 | 0.177 | −0.129 | 0.673 | 0.443 | 0.099 | −0.063 | |
| Modeling Variable | Modeling Method | Calibration Set | Validation Set | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Improvement | Performance | Improvement | ||||||
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | ||
| SP + SPAD | MLR | 0.657 | 0.457 | 0.084 | −0.073 | 0.578 | 0.542 | 0.011 | \ |
| BPNN | 0.685 | 0.438 | 0.085 | −0.065 | 0.580 | 0.541 | 0.001 | \ | |
| RF | 0.682 | 0.440 | 0.003 | −0.02 | 0.651 | 0.493 | 0.077 | −0.013 | |
| SVM | 0.688 | 0.446 | 0.094 | −0.071 | 0.634 | 0.462 | 0.06 | −0.044 | |
| SP + LAI | MLR | 0.606 | 0.509 | 0.033 | −0.021 | 0.575 | 0.524 | 0.008 | \ |
| BPNN | 0.622 | 0.480 | 0.022 | −0.023 | 0.568 | 0.548 | \ | \ | |
| RF | 0.627 | 0.477 | \ | \ | 0.626 | 0.510 | 0.052 | \ | |
| SVM | 0.654 | 0.477 | 0.06 | −0.04 | 0.544 | 0.523 | \ | \ | |
| SP + SPAD + LAI | MLR | 0.657 | 0.457 | 0.084 | −0.073 | 0.574 | 0.545 | 0.007 | \ |
| BPNN | 0.660 | 0.487 | 0.06 | −0.016 | 0.625 | 0.478 | 0.046 | −0.035 | |
| RF | 0.690 | 0.435 | 0.011 | −0.025 | 0.656 | 0.490 | 0.082 | −0.016 | |
| SVM | 0.668 | 0.450 | 0.074 | −0.067 | 0.645 | 0.497 | 0.071 | −0.009 | |
| Modeling Variable | Modeling Approach | Calibration Set | Validation Set | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | Improvement | Performance | Improvement | ||||||
| R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | R2 | RMSE | ||
| SP + SM + SD + SPAD | MLR | 0.778 | 0.368 | 0.205 | −0.162 | 0.716 | 0.445 | 0.149 | −0.065 |
| BPNN | 0.779 | 0.367 | 0.179 | −0.136 | 0.650 | 0.494 | 0.071 | −0.019 | |
| RF | 0.750 | 0.390 | 0.071 | −0.07 | 0.703 | 0.455 | 0.129 | −0.051 | |
| SVM | 0.813 | 0.351 | 0.219 | −0.166 | 0.722 | 0.409 | 0.148 | −0.097 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.; Chen, H.; Liu, P. Integrating Both Driving and Response Environmental Variables to Enhance Soil Salinity Inversion. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081995
Zhou Q, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Wang D, Chen H, Liu P. Integrating Both Driving and Response Environmental Variables to Enhance Soil Salinity Inversion. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081995
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Qizhuo, Yong Zhang, Zheng Liu, Danyang Wang, Hongyan Chen, and Peng Liu. 2025. "Integrating Both Driving and Response Environmental Variables to Enhance Soil Salinity Inversion" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081995
APA StyleZhou, Q., Zhang, Y., Liu, Z., Wang, D., Chen, H., & Liu, P. (2025). Integrating Both Driving and Response Environmental Variables to Enhance Soil Salinity Inversion. Agronomy, 15(8), 1995. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081995









