Abstract
In a greenhouse experiment, we examined the behavior of biochar in arable soil to demonstrate that these supplements can boost soil carbon storage, as well as to track changes in microbial biomass and identify the microbial communities that use these biochars. In order to ascertain if biochar can consistently alter soil microbial activities, we studied the impact of biochar combination treatments on 16S rRNA gene diversity. In soil treated with biochar, there was a rise in the relative abundance of taxa belonging to the phyla Actinobacteria and Gemmatimonadetes, despite the overall diversity decreasing with biochar addition. According to all of these observations, pyrogenic carbon has a major effect on the composition of the soil microbial community and enriches keystone taxa within the parent soil microbial community. Certain species experienced increases throughout the biochar-amended incubation period, despite the total diversity declining following biochar amendments. The phyla Actinobacteria and Gemmatimonadetes increased in the relative abundance of bacteria in soil treated with biochar, according to DNA sequencing of these species. In summary, these findings show that biochar significantly impacts the constitution and composition of the soil microbial community and enriches important taxa within the parent soil microbial community.
1. Introduction
The employment of biochar as a soil additive sets it apart from charcoal. Biochar is a carbon-rich porous material produced by the high-temperature pyrolysis of biomass under anaerobic conditions, and its recalcitrant carbon content is generally between 50% and 95% [1]. The sources of biomass are diverse. For instance, various plant residues, woody biomass, animal manure, and sludge can all be used to produce biochar [2]. The carbon component in biochar is relatively stable. Therefore, biochar was initially proposed as a soil conditioner to store carbon in the soil, thereby promoting soil carbon sequestration. However, research shows that biochar now has multiple functional values in environmental cleaning and agriculture, exceeding its original uses. Studies show that biochar can be used to restore contaminated soil, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, enhance soil fertility, and provide other ecosystem services [3]. Nkoh et al.’s research indicates that the unique porous structure of biochar can adsorb and chelate organic pollutants or heavy metals in the soil, which is conducive to the remediation of contaminated soil [4]. In addition, the porosity of biochar and its carbon-rich nature can help capture and store greenhouse gases (GHGs), enabling biochar to exist as a carbon sink in the soil. Meanwhile, altering the physicochemical properties of biochar can enhance its ability to act as a greenhouse gas sink and catalyst [5]. As a soil conditioner, it can improve soil properties, processes, and health, thereby enhancing productivity [6]. In this regard, biochars have drawn a lot of attention in recent years, primarily with an emphasis on their application to soils, where they may improve the soil’s biological and physical characteristics in addition to increasing the nutrient availability of plants [7,8,9]. Generally speaking, biochar has the potential to increase soil fertility over a prolonged period of time. A small part of this is due to the direct release of nutrients, mostly caused by indirect impacts, which include increased surface area, capacity for cation exchange, and retention of water in soil pores, all of which reduce nutrient leaching [10,11]. These positive outcomes are quite promising and may have a significant impact on how we manage our agroecosystems.
Soil microbial communities play a crucial role in farmland ecosystems and can promote sustainable crop production [12]. Studies have shown that soil microbial communities are highly sensitive to biochar. Compared with soil without biochar, the addition of biochar can effectively increase the diversity and richness of soil microorganisms [13]. Although most scholars agree that microbes cannot utilize most of the carbon in biochar [14], it is nonetheless clear that biochar increases soil microbial biomass, growth, and activity [15,16]. The microbial community constitution has been shown to be significantly impacted by the existence of black carbon using a culturing method and by screening cultured isolates [17]. This is the most comprehensive description of the shift in bacterial communities that has been published to date on anthrosols (Amazonian dark earth soils containing high levels of black carbon) compared to adjacent soils. Steinbeiss et al. [18] found that phospholipid fatty acid (PLFA) analysis of biochar-amended soils demonstrated a great change in fungus and Gram-negative bacteria abundance based on the feedstock used for charring. In a different study, biochar promoted arbuscular mycorrhizal colonization of plant roots while concurrently inhibiting plant growth [19]. Studies have shown that the addition of biochar to red soil reduces the microbial activity of phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) in Gram-positive bacteria and fungi, while the addition of biochar to black soil increases the proportion of PLFA in fungi/bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, and active bacteria [20]. There is little data on the association between microbial community migration and size change following biochar application, and these techniques have only disclosed the dominant microorganisms in the soil. However, high-throughput sequencing, more precisely and with higher classification resolution, describes the microbial diversity of soil microorganisms (bacteria and fungi) and better demonstrates the impact of biochar addition on the composition of soil microbial communities.
According to Hammond et al. [21], the two main applications of biochar are probably in agricultural fields and biomass plantations. In both settings, regularly added labile organic materials will include fall foliage and agricultural leftovers that are left in the field after harvest. The way that biochar influences the breakdown of these inputs is poorly understood. It has been shown that the breakdown of labile organic matter may be both reduced and promoted by using a variety of labile materials, such as straw and manure [22]. This can be an indication of intricate relationships. It has also been necessary to assess a mixture of commercial manure and straw owing to the ongoing dispute about enriching biochar with microbes and nutrients by co-composting it with fresh biomass.
Thus, a controlled pot experiment was established to study shifts over time in the soil bacterial community using high-throughput sequencing to analyze the 16S rRNA gene and physiochemical parameters of soils under straw and manure addition with/without biochar. The main objectives of this study are as follows: (i) to investigate the effect of adding biochar on the soil chemical properties of soil substrates mixed with different organic materials (straw or manure); (ii) to investigate the effect of adding biochar to different substrates on soil bacterial communities using high-throughput sequencing.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Collection
Soil from Xiping County (33°38′ N, 114°02′ E) in Zhumadian City, in the Chinese state of Henan, was utilized for the incubation experiment. This region has a temperate and monsoonal climate, as evidenced by an average annual temperature of 15 °C and precipitation of 900 mm. The experimental soil was lime concretion black soil, with the texture of clay loam. The soil had an initial pH (H2O) of 6.04; organic carbon content of 27.43 g·kg−1; and accessible N, P, and K concentrations of 116.90 mg·kg−1, 28.49 mg·kg−1, and 189.62 mg·kg−1, respectively, at the beginning of the experiment. Anaerobic heating at 500 °C for four hours produced peanut charcoal (Henan Shangqiu Sanli New Energy Co., Shangqiu, China). The resulting product had a pH of 9.16, organic carbon content of 647.16 g/kg, and a C/N ratio of 42.52. The C content of the maize straw we utilized was 432 g/kg, and the C/N ratio was 44.74. Commercial chicken dung with a pH of 8.16, an organic C content of 332 g/kg, and a C/N ratio of 11.57 was applied.
2.2. Incubation Experiment
An investigation of the impact of various biochar amendments on the soil nutrient and microbial community composition was carried out through a 12-month incubation experiment. A control (CK, nutrient-free charcoal), 1.5% straw addition (S), 3% manure addition (M), 5% biochar addition (B), 5% biochar and 1.5% straw addition (BS), and 5% biochar and 3% manure addition (BM) were the six treatments, in that order. The prior proportion represented the mass percentage of extra additions, and the calculated C inputs of the S and M treatments were the same. Each treatment was designed with three replicates. First, 500 g of air-dried soils that were less than 2 mm in weight were combined with straw and sieved biochar in a plastic drum in accordance with the experiment design. To allow for aeration, a polyethylene film with three pin-sized perforations was used to seal each individual container. The temperature of the culture containers was kept at 25 ± 1 °C, and the soil moisture content was adjusted every three days to maintain it at roughly 70% of its water-holding capacity. The method to control soil moisture content is as follows: Every three days at 17:00 in the afternoon, the soil moisture content was measured by the weighing method. Based on the measurement results and the weight of the soil, if the soil moisture content was less than the set range, water was replenished into the pot in time to keep the soil moisture content at around 70%. Twelve months later, the soils were taken and kept at ambient temperatures for chemical examination and at −80 °C for molecular analysis.
2.3. Soil Properties
A compound electrode was used to test soil pH at a soil-to-water ratio of 1:2.5 [23]. Dichromate oxidation was used to calculate the soil organic carbon (SOC) [24], and the procedures of Roberts et al. [25] were used to test the available N (AN). The Olsen technique [26] was used to calculate available P (AP), and ammonium substitution exchangeable cations were used to examine available K (AK) [27].
2.4. DNA Extraction and High Through-Put Sequencing
Utilizing a Fast DNA SPIN Kit for soil (MP Biomedicals, Illkirch, France) and according to the guidelines provided by the manufacturer, the whole DNA of the soil was extracted from 0.5 g of fresh soil. Ultimately, 100 μL of the kit’s DNA elution solution was used to elute the DNA. Electrophoresis on 1% (w/v) agarose gels was used to determine whether DNA extraction was successful. The PCR products obtained from amplification were quantitatively sequenced using the QuantiFluor-ST blue fluorescence detection system, with 3 replicates for each treatment. Biological sequencing was performed using the Illumina MiSeq PE 300 high-throughput sequencer (Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China).
In order to generate bacterial fragments of the proper size for Miseq, primers that target the V3-V4 hypervariable regions of bacterial 16S rRNA genes, 314F (5′-CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG-3′) and 805R (GACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC), were chosen. Both forward and reverse primers were supplemented with adaptor, pad, and linker sequences in order to pool several samples for a single MiSeq sequencing run. Three minutes at 94 °C; five cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 45 °C for 20 s, and 65 °C for 30 s; twenty cycles of 94 °C for 20 s, 55 °C for 20 s, and 72 °C for 30 s; and finally, five minutes at 72 °C were the PCR conditions. Three separate PCR assays were run for each sample. For sequencing from the adaptor, an equal quantity of purified PCR products within each sample was combined in a single tube. The Illumina MiSeq PE 300 platform was utilized to sequence the 16S rRNA gene fragments.
2.5. Bioinformatic Analyses of 16S rRNA Gene Sequences
The resultant sequences were retrieved, trimmed, quality verified, and aligned using Usearch (version 7.1 http://drive5.com/uparse/ (accessed on 10 January 2022). Fadrosh et al. [28] state that the QIIME program should be used to perform sequence analysis. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were categorized at a distinction of 0.03, and each phylotype presentative sequence was aligned by using a threshold of 80% of the bootstrap value within the Ribosomal Database Project Reference file [29]. With accession number PRJNA809782, the results were added to the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) collection at the NCBI. Utilizing the Mothur 1.30.2 software, estimates of bacterial diversity and richness were computed by rarefaction curves (Figure A1), Shannon diversity indices, and Chao and ACE richness estimators (Table A1) [30].
2.6. Statistical Analyses
To assess the data for each variable and identify significant differences between treatment means, a one-way ANOVA using SAS 9.1 was performed utilizing Fisher’s least significant differences (LSD, p < 0.05). The “vegan” package of the R software (version 3.2.1) was utilized to carry out principal coordinates analysis (PCoA), and a weighted UniFrac distance matrix derived from the relative abundance of OTUs found from MiSeq sequencing was utilized. As implemented in Canoco for Windows version 5, redundancy analysis (RDA) using the Monte Carlo permutation test (499 permutations) was carried out to ascertain whether variations in physicochemical parameters were connected to the composition of the soil microbial community (weighted UniFrac distance matrix). Using the SAS software, Pearson’s correlation analyses were also utilized to investigate the connections between soil parameters and community composition at the phylum and class levels of bacteria.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
Compared with the CK treatment, the B treatment significantly increased the pH value and SOC, AP, and AK contents in the soil. The addition of biochar increased the available N content in the soil by 5.86%, which did not reach a significant level (Table 1). Compared with the S treatment, the BS treatment reduced the AN content by 3.44% but showed no significant difference. The addition of biochar significantly increased the SOC, AP, and AK contents and pH value, with the increase rates being 115.14%, 107.14%, 95.43%, and 24.55%, respectively (Table 1). Compared with the M treatment, the BM treatment significantly increased the SOC, AP, and AK contents and pH value, with the increases being 61.58%, 12.58%, 33.83%, and 6.85%, respectively. The addition of biochar significantly reduced the soil AN content by 18.15% (Table 1).

Table 1.
Properties of soil samples under different fertilizer treatments.
3.2. Bacterial α-Diversity
pH was significantly positively correlated with SOC, AP, AK, OUT, ACE, Chao1, and Shannon (Table 2). In addition, SOC was significantly positively correlated with AK, OUT, ACE, and Chao1. AP was significantly positively correlated with OUT, ACE, Chao1, and Shannon. AK was significantly positively correlated with OUT (Table 2). OUT was significantly positively correlated with ACE, Chao1, and Shannon. ACE was significantly positively correlated with Chao1 and Shannon. Chao1 was significantly positively correlated with Shannon (Table 2). Among them, in the Pearson correlation coefficient of soil chemical properties, the correlation between SOC and AP was the greatest, with a correlation coefficient of 0.95. Among the Pearson correlation coefficients between soil chemical properties and soil microbial α-diversity, AP had the greatest correlation with Chao1, which was 0.78. Among the Pearson correlation coefficients of soil microbial α-diversity, the ACE index had the greatest correlation with the Chao1 index, with a correlation coefficient of 0.98.

Table 2.
Pearson’s correlation coefficients between soil properties and α-diversity.
3.3. Bacterial Community Composition
The dominant bacterial phyla (relative abundance > 1%) of each treatment were Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, Bacteroidetes, Verrucomicrobia, Firmicutes, Planctomycetes, Nitrospira, TM7, and OD1 (Figure 1). The phyla Proteobacteria, Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Gemmatimonadetes occupied 76.37–80.84% of the bacterial sequences under different fertilizer treatments, followed by Bacteroidetes (3.54–6.40%) and Verrucomicrobia (4.27–5.68%).
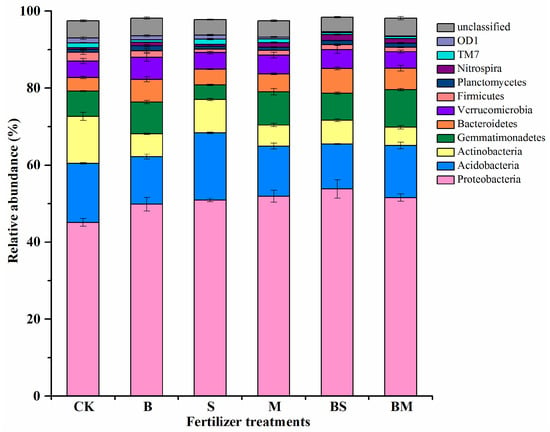
Figure 1.
Relative abundance of the abundant phyla across soils from different fertilizer treatments of total redundant sequences (>1%). Error bars indicate the standard error of relative abundance between three replicate samples.
The associations between environmental parameters and abundant phyla (i.e., abundance > 1%) were assessed using Pearson’s correlation coefficient (Table 3). Most of the abundant phyla, except Planctomyctes and Gemmatimonadetes, showed a strong correlation with pH, SOC, and accessible K, among other environmental parameters. The detected significant correlations between the relative abundance of Bacteroidetes, Planctomycetes, Nitrospira, Proteobacteria, and Gemmatimonadetes with soil pH, SOC, available P, and available K were positive, whereas Acidobacteria, TM7, OD1, and Actinobacteria were negative (Table 3).

Table 3.
Pearson’s correlation coefficients between soil characteristics and abundant phyla (relative abundance >1%).
No statistically significant effect of different substrate additions on abundant classes Subdivison3, Sphingobacteria, α-proteobacteria, or Deltaproteobacteria was observed, but there were noteworthy differences among treatments for β-proteobacteria, Acidobacteria_Gp1, Actinobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, γ-proteobacteria, Acidobacteria_Gp3, Acidobacteria_Gp6, and Spartobacteria (Figure 2). The addition of biocarbon can reduce the relative abundance of β-proteobacteria, Acidobacteria_Gp1, and Actinobacteria bacterial groups to varying degrees. The relative abundance of Acidobacteria_Gp6 and Gemmatimonadetes increased to varying degrees. Compared with the CK treatment, the B treatment could increase the relative abundance of γ-proteobacteria. However, compared with the S and M treatments, the addition of biochar reduced the relative abundance of γ-proteobacteria. Compared with the CK and S treatments, the addition of biochar reduced the relative abundance of Acidobacteria_Gp3, but compared with the M treatment, the BM treatment increased the relative abundance of Acidobacteria_Gp3. The changing trend of the relative abundance of Spartobacteria with the addition of biochar is opposite to that of Acidobacteria_Gp3.
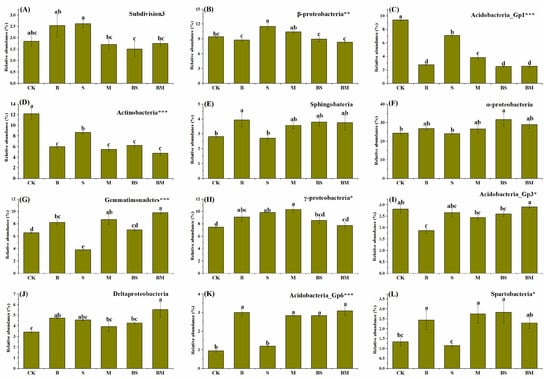
Figure 2.
Relative abundance of the twelve most abundant classes under different fertilizer treatments. Error bars indicate the standard error of relative abundance between three replications. *, ** and *** indicate whether there are differences in relative abundance among different bacterial phyla, where * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.0001. (A) The relative abundance of Subdivison3 under different treatments. (B) The relative abundance of β-proteobacteria under different treatments. (C) The relative abundance of Acidobacteria_Gp1 under different treatments. (D) The relative abundance of Actinobacteria under different treatments. (E) The relative abundance of Spartobacteria under different treatments. (F) The relative abundance of α-proteobacteria under different treatments. (G) The relative abundance of Gemmatimonadetes under different treatments. (H) The relative abundance of γ-proteobacteria under different treatments. (I) The relative abundance of Acidobacteria_Gp3 under different treatments. (J) The relative abundance of Deltaproteobacteria under different treatments. (K) The relative abundance of Acidobacteria_Gp6 under different treatments. (L) The relative abundance of Spartobacteria under different treatments. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) among the six fertilizer treatments (Fisher’s LSD test).
Associations between the physicochemical characteristics of the soil and the prevailing class abundance were discovered using Pearson’s correlation analysis (Table 4). The majority of the classes exhibited significant correlations with pH, SOC, available P, and available K. There was a correlation between β-proteobacteria and γ-proteobacteria and available N. The relative abundance of β-proteobacteria, Acidobacteria_Gp1, and Actinobacteria was negatively correlated with most soil characteristics. However, Sphingobacteria, Acidobacteria_Gp6, α-proteobacteria, Deltaproteobacteria, Spartobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, and γ-proteobacteria showed the opposite trend.

Table 4.
Pearson’s correlation coefficients between soil characteristics and abundant classes (relative abundance > 1%).
3.4. Bacterial β-Diversity
According to Figure 3A, the first three principal coordinates (PC1, PC2, and PC3) accounted for 49.3%, 12.7%, and 7.5%, respectively, of the alterations in bacterial communities. All the biochar and manure addition treatments (M, B, BS, and BM) were obviously separated from the CK and S treatments. Meanwhile, the combined biochar treatments (BS and BM) were separated from the B and M treatments in PC2.
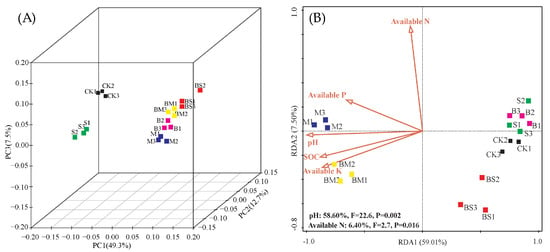
Figure 3.
Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) and redundancy analysis (RDA). (A) PCoA of the pyrosequencing reads obtained from soils subjected to different fertilizer treatments based on the weighted UniFrac metric. The first three axes are drawn, and the percent of variance explained by each axis is noted. (B) Redundancy analysis of soil bacterial communities and soil characteristics for individual samples.
In the RDA analysis of bacterial communities and soil environmental factor indicators, the first ranking axis explained 36.16% of the variations in the samples, and the second ranking axis explained 17.55% of the relationship between bacterial communities and soil environmental factors (Figure 3B). Based on the Monte Carlo displacement test, the influence of soil environmental factors on the changes in microbial communities was ranked as follows: pH > AN > AK > SOC > AP.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Combined Biochar Fertilization on Soil Chemical Properties
Previous studies have shown that biochar can improve soil permeability, agglomeration, and water retention [31]. Moreover, biochar has been shown to increase the availability of nutrients in nutrient-limited agroecosystems and the pH of acid soil due to its impact on physiochemical and biological characteristics [32]. In our study, pH generally ranged from 5.13 to 6.86 with significant increases under substrate addition compared with the control. Among different substrate combinations, substrates with biochar addition (BS and BM) showed the highest pH improvement, followed by biochar alone (B). Indeed, a pH increase through the postulated processes of the liming effect is the main explanation for the beneficial influences of biochar on agricultural productivity and soil fertility in acidic soils [11]. The results of biochar tests showed varying degrees of the liming effect, and the pH of the soil before and after amendment was recorded. An earlier investigation found that applying 0.5% biochar raised pH only when combined with litter; in this instance, the biochar buffered the trend of pH decline caused by the addition of litter [33]. In addition, biochar can also increase the available soil carbon (C) and nitrogen (N) pools. Yan et al.’s research shows that adding biochar can effectively increase total organic C (TOC) and organic carbon components (such as easily oxidizable carbon (EOC)). The total nitrogen (TN), available nitrogen (AN), and mineral N content of the soil also increased significantly [34]. Determining the direction and strength of these interacting impacts probably depends heavily on the nature of both biochar and organic materials. Due to the differences in the raw materials and production conditions of biochar, the changes in soil carbon and nitrogen contents caused by biochar often vary [1]. Undoubtedly, because of the higher carbon input, the biochar-containing treatments (B, BS, and BM) showed a significant increase in SOC compared with the other treatments, which was about twice that of the S and M treatments. Conversely, compared with CK, the biochar addition treatments did not improve the available N concentration to a significant level, but straw or manure applications (S and M) significantly improved soil available N content. However, this has also been demonstrated to cause nutrient declines, most notably in N availability [35]. Ash, labile or leachable C, and moderately recalcitrant C make up the bulk of biochar. Biochar differs greatly from other organic matter chemically because of its high levels of aromatic C and, more specifically, its fused aromatic C structures, which are the major cause of the great stability of biochars [36]. Because of the high chemical stability of a certain portion of the biochar material, microbes are not able to easily use the C or N in the structure as an energy source, or perhaps other nutrients. This might partially explain the unexpected reduction in available N content after biochar incorporation compared with the S and M treatments. Except for the S treatment, the other organic amendments increased available P, with the highest value under the BM treatment and a higher value under the M treatment, agreeing with previous findings [37]. Compared with the CK treatment, available K under different fertilizer treatments was significantly increased, especially under the biochar incorporation treatments (B, BS, and BM), with the highest concentration under BS treatment, which might be because of the extra K input along with straw incorporation [38].
4.2. Effects of Biochar Combined Fertilization on Bacterial α-Diversity
Although the beneficial effects of biochar incorporation on crop yield and soil fertility are well recognized, little is known about how biochar addition affects soil biodiversity, especially the biodiversity of microbial communities [13]. This study conducted microbiota detection on 18 soil samples and identified 493,724 high-quality sequences. In our study, each sample was classified into an average of 27,429 classifiable sequences per sample analyzed (range: 18,782–34,505), and their length was 413 bp on average. With a 97% similarity criterion, Good’s coverage values ranged from 0.84 to 0.90, demonstrating that the number of sequence reads available at the time was sufficient to capture the variety of bacteria found in these soils. Based on Mothur clustering, each soil sample’s OTU count varied between 3930 and 7421 for the five organic treatments and the control; CK had the lowest overall OTU count, and BM had the highest.
Significant variations in microbial diversity and richness (p < 0.05) were observed using culture-dependent methods for ACE, Chao 1, and OTUs but not for Shannon (Table 1). This is consistent with Xu’s research results. He pointed out that although the abundance of Chao1 and OTU increased with the increase in biochar, the Shannon diversity did not change [39]. This difference might be caused by the uniformity of different bacterial taxa. Shannon diversity reflects the richness and uniformity of classification, while the ACE, Chao1, and OTU indices are more influenced by richness. Therefore, biochar may increase the number of bacteria, while the relatively dominant bacterial phyla or bacterial categories may remain unchanged. Indices that showed significant variation (ACE, Chao 1, and OTUs) were all highest under BM treatment, which indicated that a combined treatment with biochar and manure can significantly enhance the diversity of soil bacteria [40]. Bacterial multiformity was higher in the BM and B treatments according to rarefaction analysis (Figure A1). Table 2 displays the correlation between α-diversity and soil characteristics. Significant relationships between the OTUs, ACE, Chao1, and Shannon index values and soil pH, SOC, and available P were observed, except for the Shannon index with SOC. In addition, OTU numbers across different fertilizer treatments showed a significant relationship with the content of available potassium. These significant correlations implied that the addition of biochar can affect the physical and chemical properties of soil and thereby influence the diversity of microbial populations. These changes are related to the properties of biochar and its impact on soil conditions, indicating that the influence of biochar on soil microbial diversity can be managed through its properties [39].
4.3. Effects of Biochar Combined Fertilization on Bacterial Community Composition
Wang et al. [41] pointed out that after adding biochar, the relative abundance of the dominant bacterial phyla showed an upward trend. The dominant bacterial phyla were mainly Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Firmicutes, with a relative abundance exceeding 70%. Similarly, taxon shifts caused by treatments with biochar combined with organic fertilizer were also observed in our study. Based on the alignment of the obtained sequences, we compared the relative abundances of different phyla across different incubated pots (Figure 1). Proteobacteria sequences made up the majority of the bacterial sequences in every soil sample, with percentages ranging from 45.12 to 53.83 (Figure 1). Various fertilization regimes significantly influenced the dominant phyla, except Verrucomicrobia and Firmicutes (Figure 1 and Table 2). This contradicts previous studies that linked the pattern of Verrucomicrobia abundance in grassland soil to low nutrient availability [42]. This might be because it is generally believed that the members of the Verruccomicrobial genus are oligotrophic [43]. The relative abundance of the most dominant Proteobacteria phylum microbes was enhanced under all the fertilizer treatments, especially under the S, M, BS, and BM treatments (p < 0.05), but proportions of the phyla Actinobacteria and Firmicutes were reduced with organic substrate additions. Another study found that biochar increased the abundance of Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Planctomycetes; however, these increases were dependent on the type of biochar employed [44]. Higher abundance of Proteobacterial groups was formerly linked to both higher pH and the availability of C [45,46], which is confirmed by the correlation analysis in our study (Table 3) by the higher nutrient levels and pH in the biochar and manure treatment. Meanwhile, the relative abundance of Gemmatimonadetes, Bacteroidetes, and Nitrospira only showed improvement with biochar or manure addition. As previously mentioned, when N fertilizer was added to soil, the relative abundance of the Gemmatimonadetes phylum increased; however, when P fertilizer was added, the relative abundance of Gemmatimonadetes dropped [43]. One possible explanation is that Gemmatimonadetes can make good use of the nitrogen resources provided by biochar. Copiotrophic taxa are those that grow quite quickly and do well in environments where the availability of carbon is increased. These include Bacteroidetes and many of the dominant Proteobacterial groups that grow in relative abundance with the incorporation of a substrate [42]. Previous studies covering a range of soil types and biomes discovered significant positive correlations between the relative abundance of Bacteriodetes and Actinobacteria and rising pH [47]. The relative abundance of Acidobacteria was only significantly elevated when straw (S) was added; it was lowered when other substrates were added, and it was, significantly, the lowest under the BM treatments (Table 2). Research looking at how the bacterial population responds to the addition of more substrate has also revealed similar taxon changes to ours. For example, it has been demonstrated that Acidobacteria’s relative abundance increases with decreasing pH [48]. In fertilized plots, Acidobacteria were found to be relatively less abundant, whereas Proteobacteria, especially γ-proteobacteria, were more abundant. This pattern was also noted by Wessen et al. [49], perhaps because Acidobacteria have been associated with the decomposition of biopolymers and exopolysaccharide secretions, and they are oligotrophic flora. The growth rate is relatively slow, but it can effectively metabolize maltrophic and stubborn C substrates. Therefore, adding biochar to the soil can significantly increase the relative abundance of Actinobacteria [39]. In contrast, after a year of incubation, the addition of charcoal or dung reduced the proliferation of microorganisms belonging to the TM7 and OD1 phyla.
Notably, various Acidobacterial groups’ relative abundances reacted differently to different fertilizer regimes. The addition of substrate dramatically reduced the relative abundance of Acidobacteria_Gp1 when contrasted with CK. All fertilized soils had higher relative abundances of the Acidobacteria_Gp3 and Acidobacteria_Gp6 classes, with the maximum abundances occurring under BM treatments. The positive consequences of biochar or manure addition in the expansion of Acidobacteria_Gp6 reached a significant level, while the relative abundance of the Acidobacteria_Gp3 class showed a significant reduction under the B treatment. It has also generally been demonstrated that pH has a significant and varied impact on subgroups within the phylum Acidobacteria. The findings of this investigation support earlier findings showing that Acidobacteria_Gp1, the most active group, is negatively dependent on pH [48,50]. Nevertheless, according to a prior analysis, Acidobacteria_Gp6 has been observed to favorably correspond to an increase in pH [51]. Regarding the proteobacterial classes, it was only with the BS treatment that the relative abundance of α-proteobacteria increased. Under the S and M treatments, as well as the B, S, and M treatments, the proliferation of β-proteobacteria and γ-proteobacteria was boosted. The α-proteobacteria and γ-proteobacteria classes are regarded as organotrophic; they can grow in nutrient-rich soils and use reduced inorganic substances as energy sources, such as ammonia, nitrite, or nitrate [52]. There are further observations indicating that as soil pH rises, the relative abundance of α-proteobacteria and γ-proteobacteria rises [51]. According to earlier research, long-term fertilized soils have a higher abundance of γ-proteobacteria than control soils [40]. Furthermore, the relative abundance of the Sphingobacteria, Gemmatimonadetes, and Spartobacteria classes showed similar patterns across different fertilizer treatments, which were all significantly reduced under the S treatment but increased under the B treatment compared with CK. Meanwhile, addition (M and BM) could strongly improve the relative abundance of the Gemmatimonadetes class (Figure 2G). In addition, compared with the treatment with increased biochar, the relative abundance of Actinobacteria without added biochar increased, while the abundance of Gemmatimonadetes decreased. This might be due to synergistic effects, such as similar response patterns to biological, chemical, or physical variables, that is, competing for similar ecological niche spaces [53]. The M and BS treatments also significantly increased Spartobacteria (Figure 2L). Sphingomonadales are capable of breaking down macromolecules and inhibiting phytopathogens [54]. Having glycosphingolipids in their cell envelope is a unique feature that sets many Sphingomonadetes species apart. According to Gupta and Mok [55], this group comprises phototrophic species like Erythrobacter litoralis, which may obtain a substantial portion of their energy metabolism from photosynthesis without oxygen.
4.4. Effects of Combined Biochar Fertilization on OTU-Level Bacterial β-Diversity
The findings revealed that adding biochar altered the characteristics of the soil and, in some cases, promoted community resemblance. Santos et al. [56] discovered that utilizing biochar may alter the soil microbial population composition. As biochar matures in the soil, the causes influencing community changes also change over time [57]. The key elements impacting the short-term shifts in microbial community constitution when biochar is introduced to soil are likely to be the unstable components included in the biochar, adsorbed volatile organic substances, and pH. The forward-selection option in CANOCO indicated that the two main factors influencing the variations in bacterial populations were soil pH (F = 22.6, p = 0.002) and soil available N alteration (F = 2.7, p = 0.016), which together accounted for 58.60% and 6.40% of the variation, respectively. Geisseler et al. found that the pH of soil is an excellent indicator of the makeup of bacterial populations and has a major impact on the makeup of microbial communities in soil [58]. Similarly, Rousk et al. [51] proposed that soil pH significantly affected bacterial communities because the majority of bacterial species show relatively narrow growth tolerances. The results of this study are consistent with those of previous studies but different from those of Wang et al. [59]. It is speculated that the reason might be the different properties of the soil. Wang et al. [59] believe that AK, OM, and TN are environmental factors that significantly affect the composition of bacterial communities. This might be because the soil tested by Wang et al. [59] was saline–alkali soil with a pH of 8.54, which is alkaline soil, while the soil used in this study was lime concretion black soil with a pH of 6.04, which is acidic soil.
The variety and leading taxa in soil microbial populations are impacted by biochar amendments, and a subset of the parent soil microbial population is enriched, despite the fact that investigations of microbial taxon changes during incubation with biochar and manure or straw in soils are not yet comprehensive. However, based on this research, we were still unable to determine whether the enhancement was caused by the extra nutrients that the biochar supplied or the acceleration of the natural nutrient cycle in the soil. In-depth research using sensitive analytical techniques like stable isotope labeling (SIP) at the DNA or RNA level could be helpful in deciphering the complex web of microbial pathways behind the nutrient transformation of biochar-amended soil in agroecosystems. According to [60], the incorporation of biochar had toxic effects on some microbial communities; enriched opportunistic taxa capable of metabolizing the carbon in biochar or additional nutrients that the biochar supplements; and led to variations in the pH, mineral content, pore and particle size, and availability of water and nutrients, among other physical and chemical aspects of the soil environment. The above factors may give rise to shifts in the relative abundance of taxa in soil and affect the bacterial population’s composition. Further research will be necessary to ascertain the relative significance of these variables in modifying microbial community composition as a result of soil biochar amendments, as well as the possible influence of these modifications on improving soil fertility and the long-term influence of biochar on the composition and constitution of microbial communities.
In addition, this study was a greenhouse cultivation experiment with a relatively short observation period. Research indicates that the impact of biochar on microbial communities may be influenced by climate, environmental factors, soil texture, soil physical and chemical properties, etc. [61,62,63]. Therefore, the results of this study still need to be further verified in field experiments. According to the research results, it was found that soil available nitrogen also has a relatively high impact on the bacterial microbial community. Meanwhile, Ji et al. [64] demonstrated that biochar can reduce the relative abundance of Flavobacterium, Enterobacter, and Devosia related to the nitrogen cycle in soil. However, the effects of different blending substrates on the microbial population of the nitrogen cycle under the experimental conditions of this study need further investigation.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the addition of biochar had a significant impact on soil properties. Compared with the CK, S, and M treatments without biochar, the B, BS, and BM treatments could significantly increase the pH value in the soil, as well as the levels of SOC, AP, and AK. Meanwhile, it can be said that the addition of biochar can increase microbial diversity and richness, and there are significant differences in the composition of soil microbial communities among different biochar treatments. Compared with the BS treatment, the BM treatment significantly increased the relative abundance of Acidobacteria and Gemmatimonadetes, which may contribute to soil carbon and nitrogen nutrient cycling. The correlation analysis of soil environmental factors with microbial diversity and community composition indicates that the soil pH value seems to have a major influence on the size and composition of bacterial communities. In conclusion, the BM treatment might be an effective fertilization solution for enhancing fertility and increasing the activity of bacteria and microorganisms in lime concretion black soil.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.Z., T.G., P.L. and Y.H.; methodology, T.G., P.L. and Y.H.; validation, M.W. (Mengyuan Wang) and W.S.; formal analysis, M.W. (Mengyuan Wang); investigation, M.W. (Mingyu Wu) and W.S.; resources, P.L., Y.H. and H.L.; data curation, M.W. (Mingyu Wu), M.W. (Mengyuan Wang), W.S., Q.Z. and H.L.; writing—original draft preparation, M.W. (Mingyu Wu); writing—review and editing, M.W. (Mengyuan Wang), Q.Z., T.G., P.L. and H.L.; visualization, M.W. (Mengyuan Wang) and W.S.; supervision, M.W. (Mingyu Wu), T.G., P.L., Y.H. and H.L.; project administration, M.W. (Mingyu Wu), Q.Z., T.G., and Y.H.; funding acquisition, H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research and APC were funded by [Science and Technology Research Project of Henan Province] grant number [242102320261].
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
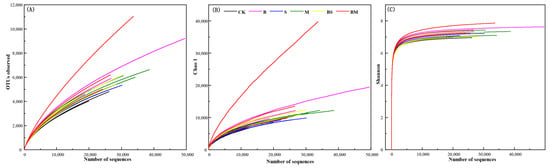
Figure A1.
Rarefaction curves showing the relationships between bacterial α-diversity and the number of randomly sampled sequences. (A) Numbers of OTUs observed experimentally; (B) richness predicted by Chao1; (C) diversity predicted by Shannon index.

Table A1.
Sequence number, OTUs, coverage, richness, and diversity of different fertilizer treatments.
Table A1.
Sequence number, OTUs, coverage, richness, and diversity of different fertilizer treatments.
| Richness | Diversity | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatments | Sequence Number | OTUs | Coverage | ACE | Chao1 | Shannon |
| CK | 18,782 ± 1290 c | 3930 ± 90 e | 0.87 ± 0.02 a | 13,139 ± 236 d | 9986 ± 758 c | 6.93 ± 0.04 c |
| B | 26,024 ± 2292 bc | 6573 ± 379 ab | 0.88 ± 0.01 a | 20,108 ± 290 b | 12,438 ± 535 b | 7.37 ± 0.14 ab |
| S | 35,053 ± 3458 a | 4943 ± 221 d | 0.90 ± 0.01 a | 13,143 ± 194 d | 9461 ± 210 c | 7.18 ± 0.05 abc |
| M | 31,172 ± 1638 ab | 6255 ± 191 bc | 0.90 ± 0.00 a | 16,403 ± 481 c | 11,932 ± 266 b | 7.29 ± 0.10 abc |
| BS | 25,362 ± 3858 bc | 5336 ± 469 cd | 0.87 ± 0.02 a | 16,715 ± 672 c | 11,218 ± 604 bc | 7.12 ± 0.10 bc |
| BM | 28,181 ± 2846 ab | 7421 ± 320 a | 0.84± 0.04 a | 36,981 ± 740 a | 21,044 ± 789 a | 7.51 ± 0.19 a |
| ANOVA p-values | 0.07 | 0.0004 | 0.54 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.10 |
Note: OTUs: operational taxonomic units (97% similarity). Coverage: Good’s non-parametric coverage estimator. Based on Chao1 and abundance-based coverage estimator (ACE) richness indices. Based on Shannon and Simpson diversity indices. Data are mean ± standard error (n = 3). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) among the six fertilizer treatments (Fisher’s LSD test).
References
- Deshoux, M.; Sadet-Bourgeteau, S.; Gentil, S.; Prévost-Bouré, N.C. Effects of biochar on soil microbial communities: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 166079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Wang, Z.Y.; Bolan, N.S.; Wang, H.L.; Wang, Y.J.; Chen, W.F. Visualizing the development trend and research frontiers of biochar in 2020: A scientometric perspective. Biochar 2021, 3, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Hoang, S.A.; Beiyuan, J.; Gupta, S.; Hou, D.; Karakoti, A.; Joseph, S.; Jung, S.; Kim, K.H.; Kirkham, M.B.; et al. Multifunctional applications of biochar beyond carbon storage. Int. Mater. Rev. 2022, 67, 150–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkoh, J.N.; Ajibade, F.O.; Atakpa, E.O.; Abdulaha-Al Baquy, M.; Mia, S.; Odii, E.C.; Xu, R. Reduction of heavy metal uptake from polluted soils and associated health risks through biochar amendment: A critical synthesis. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 6, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, H.; Zhang, H.; Chu, M.; Zhang, C.; Tang, J.; Chang, S.X.; Mašek, O.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar affects greenhouse gas emissions in various environments: A critical review. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 3327–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palansooriya, K.N.; Wong, J.T.F.; Hashimoto, Y.; Huang, L.; Rinklebe, J.; Chang, S.X.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H.; Ok, Y.S. Response of microbial communities to biochar-amended soils: A critical review. Biochar 2019, 1, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suddick, E.C.; Six, J. An estimation of annual nitrous oxide emissions and soil quality following the amendment of high temperature walnut shell biochar and compost to a small scale vegetable crop rotation. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, D.A.; Fleming, P.; Davis, D.D.; Horton, R.; Wang, B.; Karlen, D.L. Impact of biochar amendments on the quality of a typical Midwestern agricultural soil. Geoderma 2010, 158, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rondon, M.A.; Lehmann, J.; Ramírez, J.; Hurtado, M. Biological nitrogen fixation by common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) increases with bio-char additions. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 43, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Solomon, D.; Kinyangi, J.; Grossman, J.; O’Neill, B.; Skjemstad, J.O.; Thies, J.; Luizão, F.J.; Petersen, J.; et al. Black carbon increases cation exchange capacity in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 1719–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zwieten, L.; Kimber, S.; Morris, S.; Chan, K.Y.; Downie, A.; Rust, J.; Joseph, S.; Cowie, A. Effects of biochar from slow pyrolysis of papermill waste on agronomic performance and soil fertility. Plant Soil 2010, 327, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fan, W.; Xu, G.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hao, S.; Deng, B.; Ren, S.; Hu, S. Bio-organic fertilizers improve Dendrocalamus farinosus growth by remolding the soil microbiome and metabolome. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1117355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Jin, P.H.; Wang, H.; Hu, T.L.; Lin, X.W.; Xie, Z.B. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals stronger microbial carbon and nitrogen limitation in biochar amendment soils: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thies, J.E.; Rillig, M.C. Characteristics of biochar: Biological properties. In Biochar for Environmental Management; Routledge: Oxfordshire, UK, 2012; pp. 117–138. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Lehmann, J.; Sohi, S.P.; Thies, J.E.; O’Neill, B.; Trujillo, L.; Gaunt, J.; Solomon, D.; Grossman, J.; Neves, E.G.; et al. Black carbon affects the cycling of non-black carbon in soil. Org. Geochem. 2010, 41, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, C.; Das, K.C.; Garcia, M.; Förster, B.; Zech, W. Charcoal and smoke extract stimulate the soil microbial community in a highly weathered xanthic Ferralsol. Pedobiologia 2008, 51, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, B.; Grossman, J.; Tsai, M.; Gomes, J.E.; Lehmann, J.; Peterson, J.; Neves, E.; Thies, J.E. Bacterial community composition in Brazilian Anthrosols and adjacent soils characterized using culturing and molecular identification. Microb. Ecol. 2009, 58, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbeiss, S.; Gleixner, G.; Antonietti, M. Effect of biochar amendment on soil carbon balance and soil microbial activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1301–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Wagner, M.; Salem, M.; Antunes, P.M.; George, C.; Ramke, H.G.; Titirici, M.M.; Antonietti, M. Material derived from hydrothermal carbonization: Effects on plant growth and arbuscular mycorrhiza. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.; Di, H.; He, Y.; Xu, J. Influence of black carbon addition on phenanthrene dissipation and microbial community structure in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 161, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, J.; Shackley, S.; Sohi, S.; Brownsort, P. Prospective life cycle carbon abatement for pyrolysis biochar systems in the UK. Energy Policy 2011, 39, 2646–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, A.R. Abiotic and microbial oxidation of laboratory-produced black carbon (biochar). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 1295–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, C.; Liang, G.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, W. Responses of extracellular enzyme activities and microbial community in both the rhizosphere and bulk soil to long-term fertilization practices in a fluvo-aquic soil. Geoderma 2012, 173, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalembasa, S.J.; Jenkinson, D.S. A comparative study of titrimetric and gravimetric methods for the determination of organic carbon in soil. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1973, 24, 1085–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.L.; Ross, W.J.; Norman, R.J.; Slaton, N.A.; Wilson, C.E., Jr. Predicting nitrogen fertilizer needs for rice in Arkansas using alkaline hydrolyzable-nitrogen. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1161–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R.; Sommers, L.E. Phosphorus. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2. Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Gu, T.; Wang, W.; Zhang, B.; Lin, X.; Huang, Q.; Shen, W. The effects of mineral fertilizer and organic manure on soil microbial community and diversity. Plant Soil 2010, 326, 511–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadrosh, D.W.; Ma, B.; Gajer, P.; Sengamalay, N.; Ott, S.; Brotman, R.M.; Ravel, J. An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16S rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2014, 2, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodenhausen, N.; Horton, M.W.; Bergelson, J. Bacterial communities associated with the leaves and the roots of Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, B.; Sanadhya, P.; Keshri, J.; Jha, B. Comparative molecular analysis of chemolithoautotrophic bacterial diversity and community structure from coastal saline soils, Gujarat, India. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Luo, X.; Wang, Z.; Xing, B. Biochar-induced negative carbon mineralization priming effects in a coastal wetland soil: Roles of soil aggregation and microbial modulation. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 951–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, S.; Verheijen, F.G.; van der Velde, M.; Bastos, A.C. A quantitative review of the effects of biochar application to soils on crop productivity using meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 144, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prayogo, C.; Jones, J.E.; Baeyens, J.; Bending, G.D. Impact of biochar on mineralisation of C and N from soil and willow litter and its relationship with microbial community biomass and structure. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, P.; Cai, X.; Wang, C.; Van Zwieten, L.; Wang, H.; Yin, Q.; Liu, G.; Ren, T. Biochar-based fertilizer enhanced tobacco yield and quality by improving soil quality and soil microbial community. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 103964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Pereira da Silva, J.; Steiner, C.; Nehls, T.; Zech, W.; Glaser, B. Nutrient availability and leaching in an archaeological Anthrosol and a Ferralsol of the Central Amazon basin: Fertilizer, manure and charcoal amendments. Plant Soil 2003, 249, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Lim, J.E.; Zhang, M.; Bolan, N.; Mohan, D.; Withanage, M.; Lee, S.S.; Ok, Y.S. Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: A review. Chemosphere 2014, 99, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Liang, A.; Li, Y.; Song, Q.; Li, X.; Li, D.; Hou, N. Insight into the soil aggregate-mediated restoration mechanism of degraded black soil via biochar addition: Emphasizing the driving role of core microbial communities and nutrient cycling. Environ. Res. 2023, 228, 115895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Liang, G.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; He, P.; Li, L. Effects of different organic manures on the biochemical and microbial characteristics of albic paddy soil in a short-term experiment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Xu, H.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Gundale, M.J.; Zou, X.; Ruan, H. Global meta-analysis reveals positive effects of biochar on soil microbial diversity. Geoderma 2023, 436, 116528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangid, K.; Williams, M.A.; Franzluebbers, A.J.; Sanderlin, J.S.; Reeves, J.H.; Jenkins, M.B.; Endale, D.M.; Coleman, D.C.; Whitman, W.B. Relative impacts of land-use, management intensity and fertilization upon soil microbial community structure in agricultural systems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 2843–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yang, T.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, T.; Zheng, C. Effects of biochar carried microbial agent on compost quality, greenhouse gas emission and bacterial community during sheep manure composting. Biochar 2023, 5, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemergut, D.R.; Townsend, A.R.; Sattin, S.R.; Freeman, K.R.; Fierer, N.; Neff, J.C.; Bowman, W.D.; Schadt, C.W.; Weintrabu, M.N.; Schmidt, S.K. The effects of chronic nitrogen fertilization on alpine tundra soil microbial communities: Implications for carbon and nitrogen cycling. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 10, 3093–3105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.; Khan, S.; Yao, H.; Wang, J. Biochars reduced the bioaccessibility and (bio) uptake of organochlorine pesticides and changed the microbial community dynamics in agricultural soils. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 805–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazi, S.; Amalfitano, S.; Pernthaler, J.; Puddu, A. Bacterial communities associated with benthic organic matter in headwater stream microhabitats. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchman, D.L. The ecology of Cytophaga–Flavobacteria in aquatic environments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2002, 39, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 5111–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R.T.; Robeson, M.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Hamady, M.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. A comprehensive survey of soil acidobacterial diversity using pyrosequencing and clone library analyses. ISME J. 2009, 3, 442–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessén, E.; Nyberg, K.; Jansson, J.K.; Hallin, S. Responses of bacterial and archaeal ammonia oxidizers to soil organic and fertilizer amendments under long-term management. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriu, P.A.; Grayston, S.J. Relationship between soil properties and patterns of bacterial β-diversity across reclaimed and natural boreal forest soils. Microb. Ecol. 2010, 59, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousk, J.; Bååth, E.; Brookes, P.C.; Lauber, C.L.; Lozupone, C.; Caporaso, J.G.; Knight, R.; Fierer, N. Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J. 2010, 4, 1340–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; Kim, B.Y.; Song, J.; Weon, H.Y. Effects of PCR cycle number and DNA polymerase type on the 16S rRNA gene pyrosequencing analysis of bacterial communities. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, S.; Minchin, T.; Kimber, S.; van Zwieten, L.; Gilbert, J.; Munroe, P.; Joseph, S.; Thomas, T. Comparative analysis of the microbial communities in agricultural soil amended with enhanced biochars or traditional fertilisers. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Guan, T.; Wang, X.Y.; Zhu, Y.J.; Guo, T.C. Effects of combined application of biogas slurry and chemical fertilizer on winter wheat rhizosphere soil microorganisms and enzyme activities. Yingyong Shengtai Xuebao 2011, 22, 1007. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.S.; Mok, A. Phylogenomics and signature proteins for the alpha proteobacteria and its main groups. BMC Microbiol. 2007, 7, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, F.; Torn, M.S.; Bird, J.A. Biological degradation of pyrogenic organic matter in temperate forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 51, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Rillig, M.C.; Thies, J.; Masiello, C.A.; Hockaday, W.C.; Crowley, D. Biochar effects on soil biota–a review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1812–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Scow, K.M. Long-term effects of mineral fertilizers on soil microorganisms–A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 75, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Riaz, M.; Babar, S.; Eldesouki, Z.; Liu, B.; Xia, H.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, J.Y.; Xia, X.X.; Jiang, C.C. Alterations in the composition and metabolite profiles of the saline-alkali soil microbial community through biochar application. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 352, 120033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, J.K.; Campbell, L.; Rooney, D.; Clipson, N.; Gleeson, D.B. Minerals in soil select distinct bacterial communities in their microhabitats. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2009, 67, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, J.R.; Viger, M.; Arnold, E.C.; Harris, Z.M.; Ventura, M.; Miglietta, F.; Girardin, C.; Edwards, R.J.; Rumpel, F.; Fornasier, F.; et al. Biochar alters the soil microbiome and soil function: Results of next-generation amplicon sequencing across Europe. GCB Bioenergy 2017, 9, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Sun, D.; Yang, F. Insight into the correlation between biochar amendment and shifts in bacterial community 4 years after a single incorporation in soybean-and maize-planted soils in northeastern China. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.N.; Wallace, H.M.; Xu, C.Y.; Zwieten, L.V.; Weng, Z.H.; Xu, Z.H.; Che, R.X.; Tahmasbian, I.; Hu, H.W.; Bai, S.H. The effects of short term, long term and reapplication of biochar on soil bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Qin, Z.; Cai, W.; Yang, Y.; Yan, S.; Guo, X. Effects of adding lignocellulose-degrading microbial agents and biochar on nitrogen metabolism and microbial community succession during pig manure composting. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).