Organic Manure with Chemical Fertilizers Improves Rice Productivity and Decreases N2O Emissions by Increasing Soil Nitrogen Sequestration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
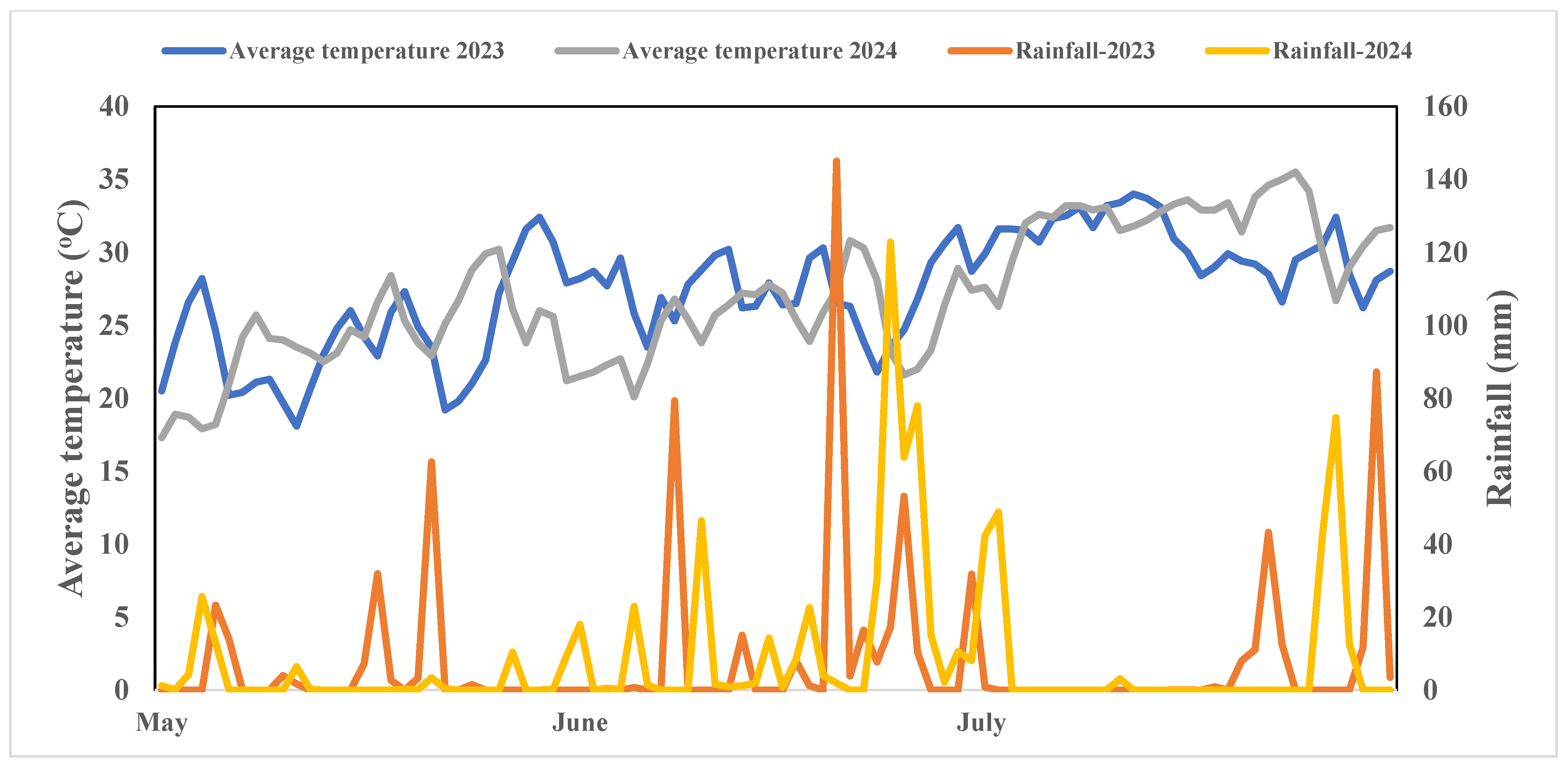
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design and Field Management
2.3. N2O Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Nitrogen and Carbon Metabolism Enzymes
2.5. Soil Sampling
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
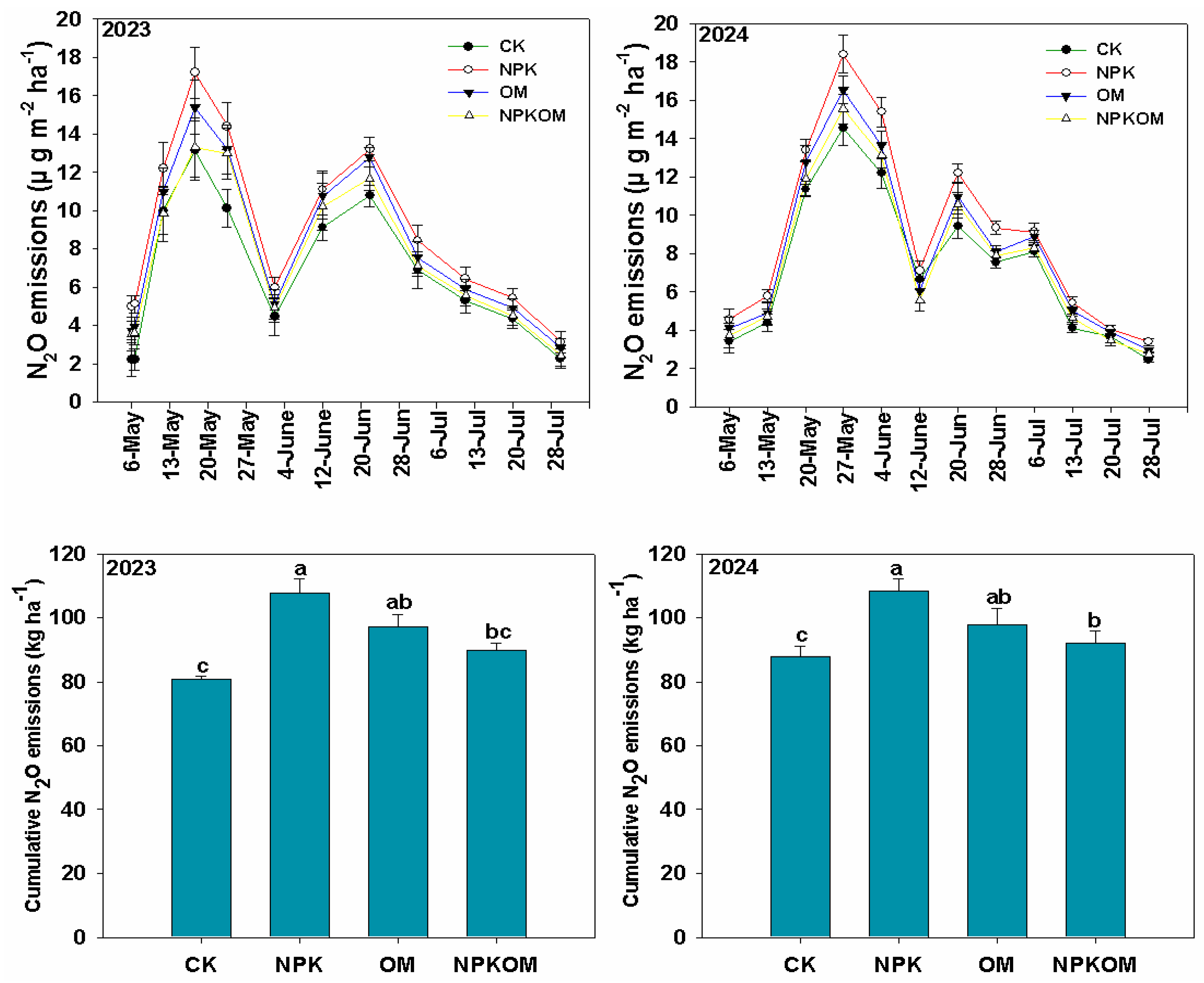
3.1. Effect of Different Fertilizations on Soil N2O Emissions
3.2. Effect of Different Fertilizations on Soil Properties
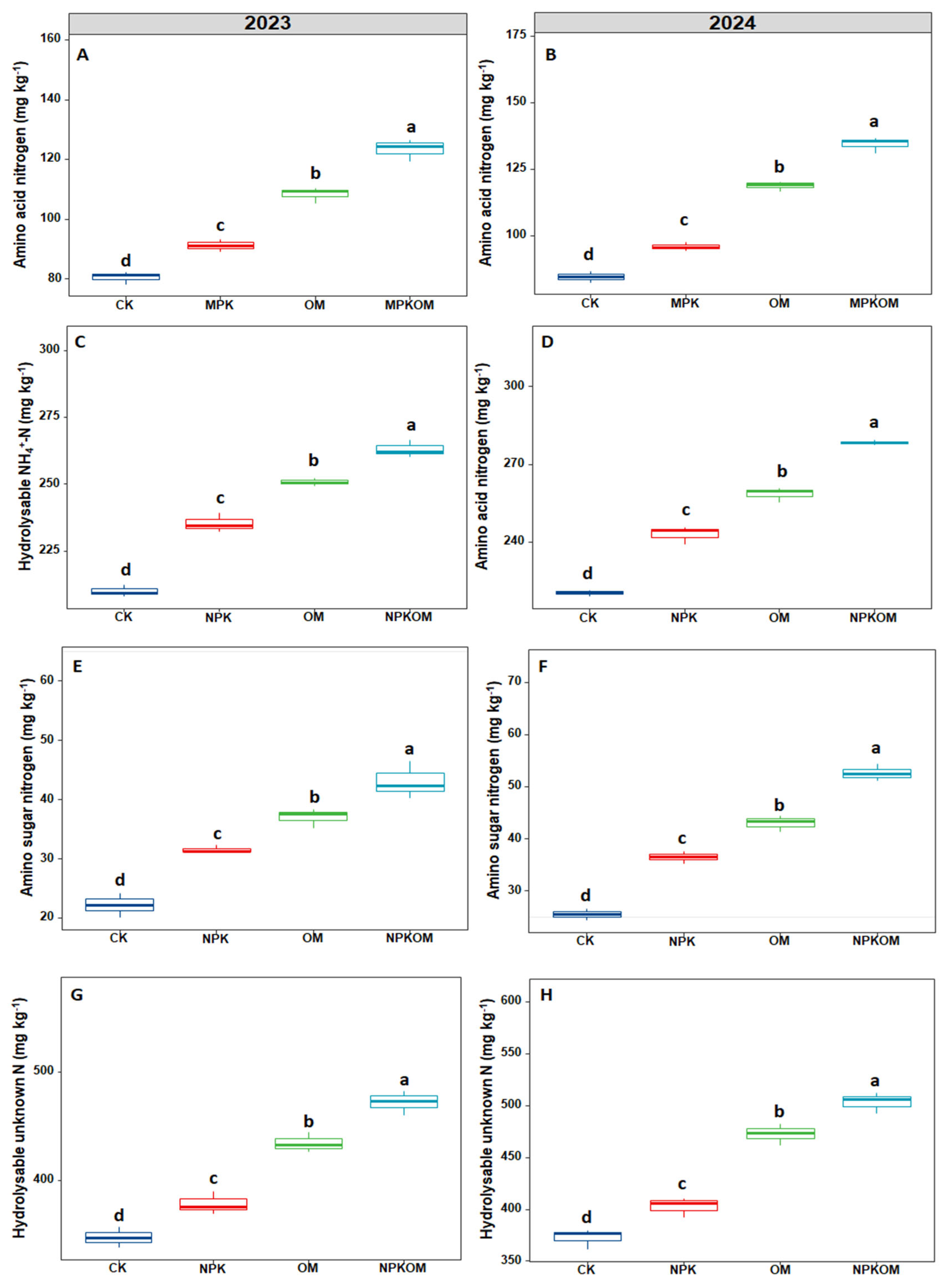
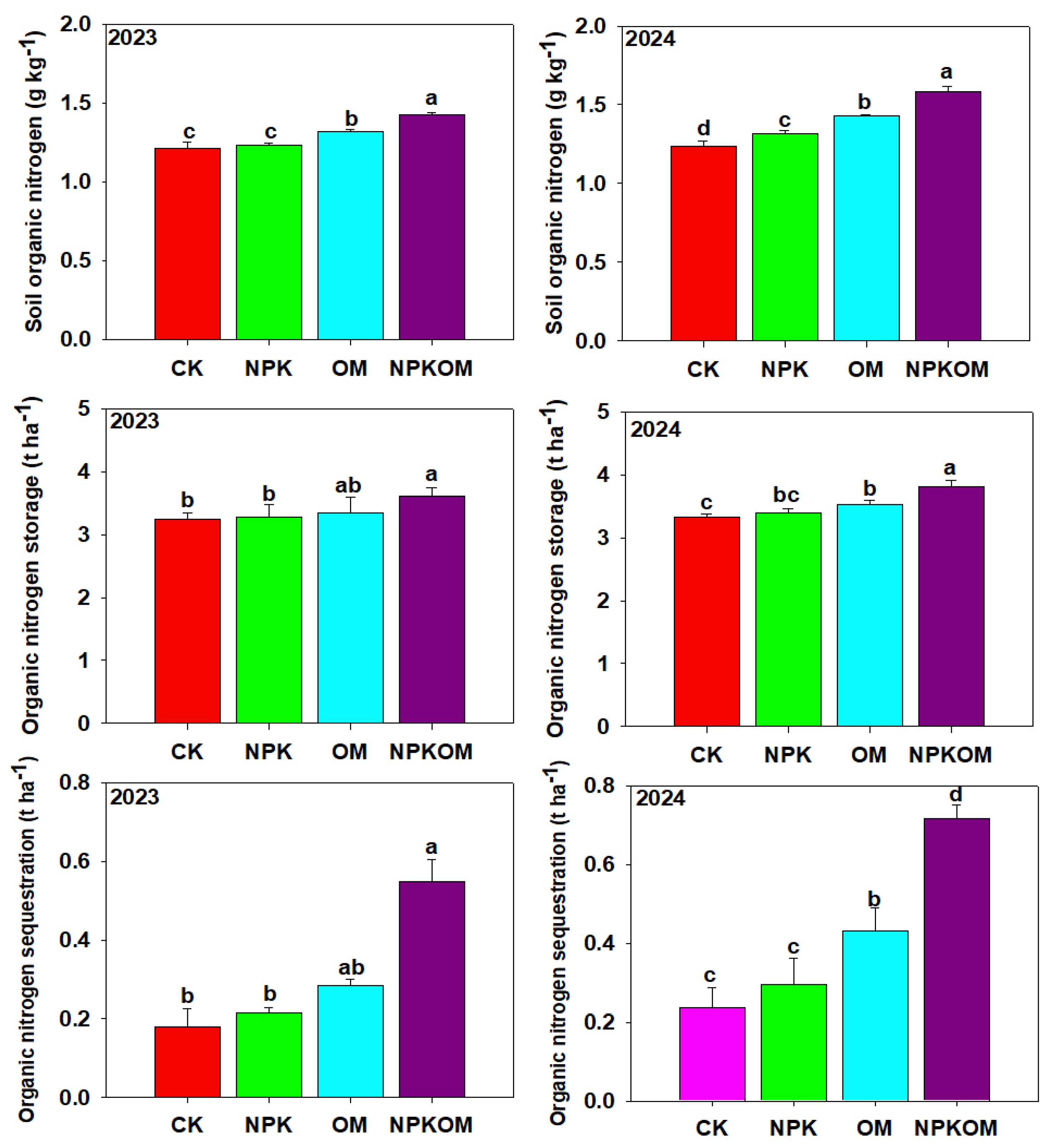
3.3. Effect of Different Fertilizations on Nitrogen Fractions and Nitrogen Storage and Sequestration
3.4. Effect of Different Fertilizations on Particulate and Mineral-Associated Organic Nitrogen
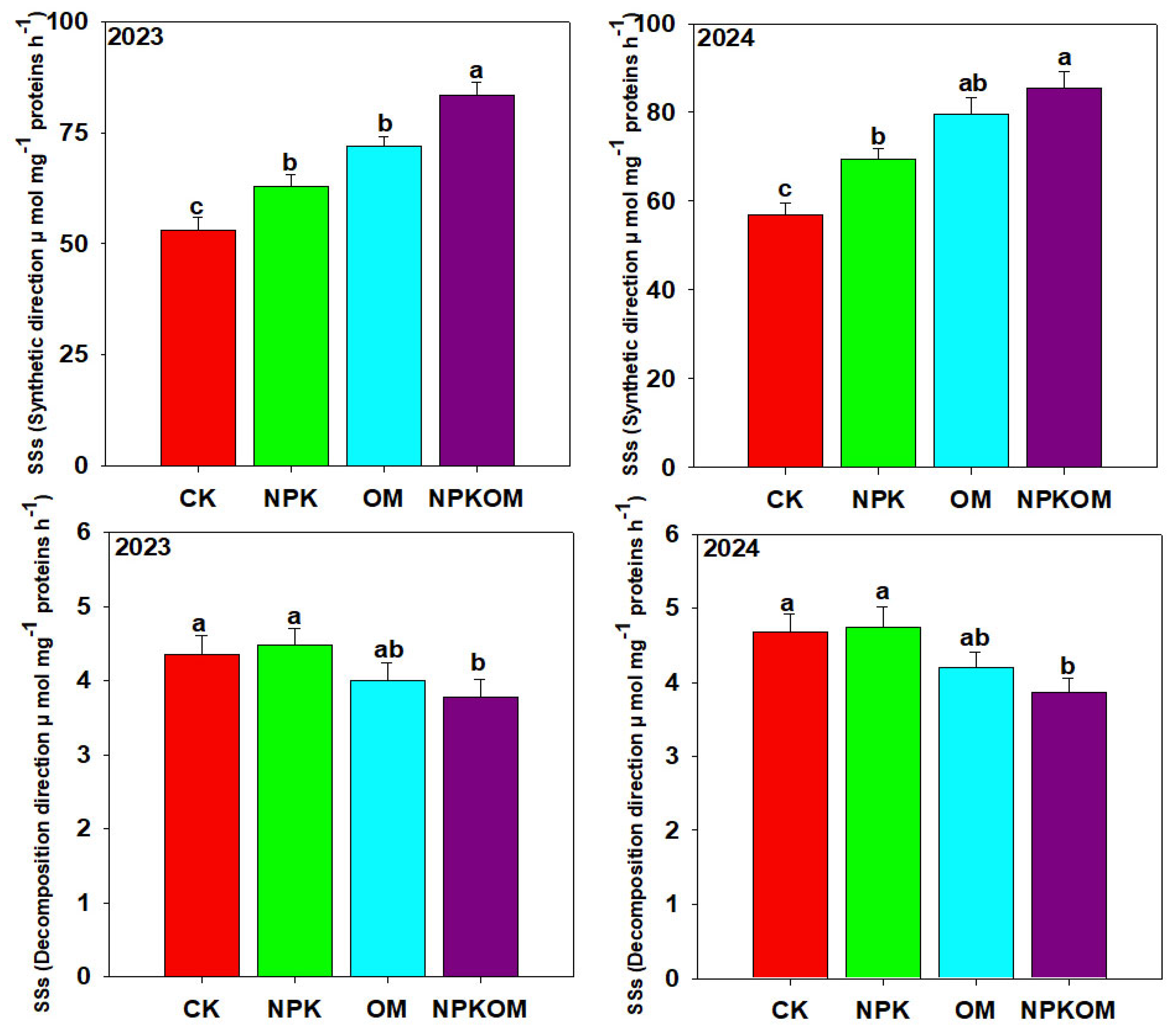
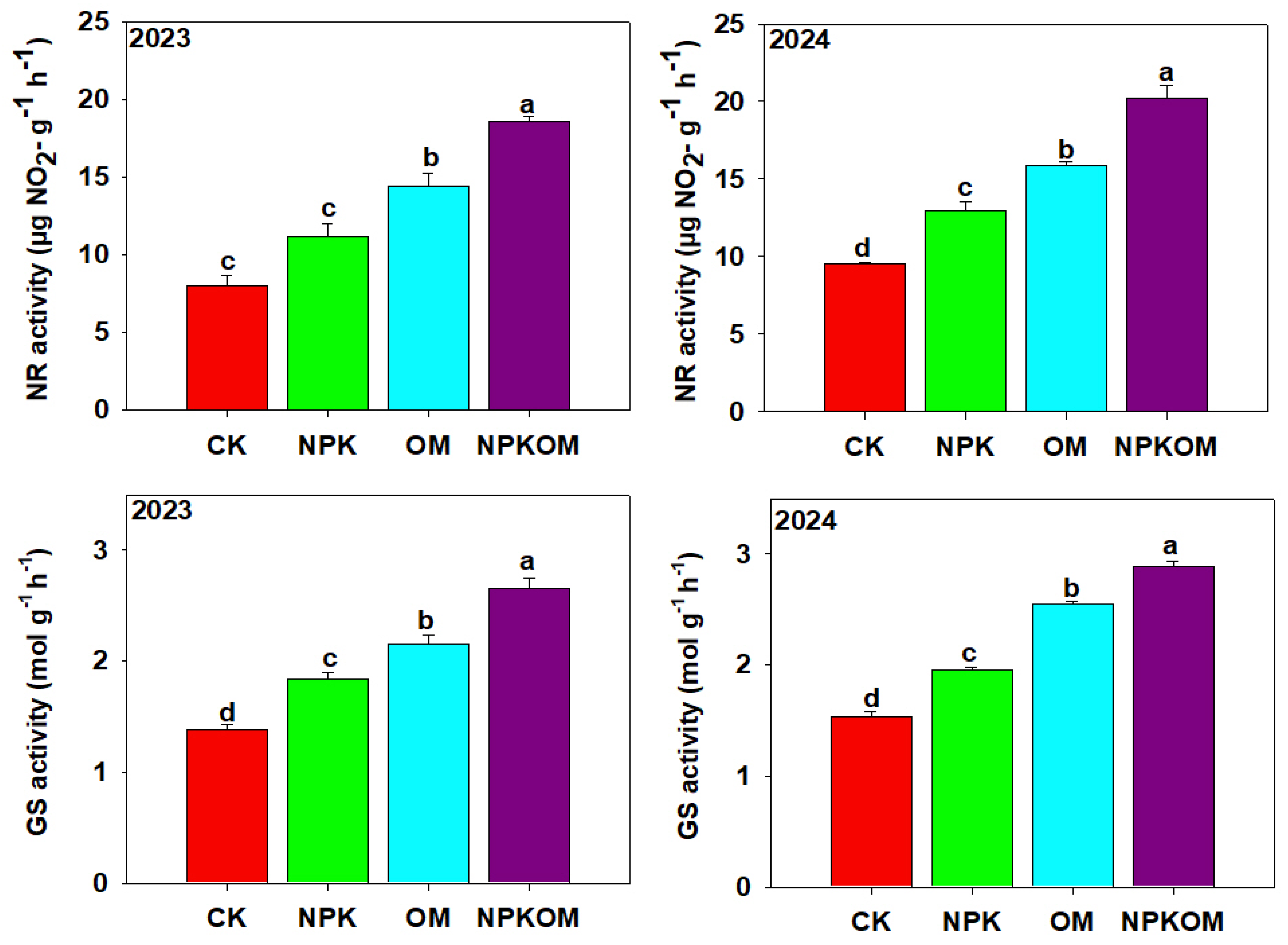
3.5. Effect of Different Fertilizations on Carbon and Nitrogen Metabolism-Related Enzymes in Rice
3.6. Effect of Different Fertilizations on Rice Yield Traits and Grain Protein Contents
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Geng, T.; Jia, F.; Cai, W.; Wu, L.; Gan, B.; Jing, Z.; Li, S.; McPhaden, M.J. Increased occurrences of consecutive La Niña events under global warming. Nature 2023, 619, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, P.; Bowler, D.E.; Baker, N.J.; Bonada, N.; Domisch, S.; Garcia Marquez, J.R.; Heino, J.; Hering, D.; Jähnig, S.C.; Schmidt-Kloiber, A. The recovery of European freshwater biodiversity has come to a halt. Nature 2023, 620, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abebaw, S.E. A Global Review of the Impacts of Climate Change and Variability on Agricultural Productivity and Farmers’ Adaptation Strategies. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 13, e70260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicuso, D.; Previti, A.; Pugliese, M. Climate change impacts on livestock and resulting effects on animal health: Current challenges in food safety, consumer protection, and animal welfare. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2025, 20, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Jia, X.; Ma, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Shangguan, Z.; Yan, W. Effects of warming and precipitation changes on soil GHG fluxes: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 827, 154351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filonchyk, M.; Peterson, M.P.; Zhang, L.; Hurynovich, V.; He, Y. Greenhouse gases emissions and global climate change: Examining the influence of CO2, CH4, and N2O. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 885, 173359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; Solazzo, E.; Guizzardi, D.; Monforti-Ferrario, F.; Tubiello, F.N.; Leip, A. Food systems are responsible for a third of global anthropogenic GHG emissions. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenet, B.; Gabrielle, B.; Chenu, C.; Arrouays, D.; Balesdent, J.; Bernoux, M.; Bruni, E.; Caliman, J.P.; Cardinael, R.; Chen, S. Can N2O emissions offset the benefits from soil organic carbon storage? Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapov, P.; Turubanova, S.; Hansen, M.C.; Tyukavina, A.; Zalles, V.; Khan, A.; Song, X.-P.; Pickens, A.; Shen, Q.; Cortez, J. Global maps of cropland extent and change show accelerated cropland expansion in the twenty-first century. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurek, M.; Hebinck, A.; Selomane, O. Climate change and the urgency to transform food systems. Science 2022, 376, 1416–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yang, W.; Li, M.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z. Prediction of total nitrogen content in different soil types based on spectroscopy. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandy, A.S.; Daly, A.B.; Bowles, T.M.; Gaudin, A.C.; Jilling, A.; Leptin, A.; McDaniel, M.D.; Wade, J.; Waterhouse, H. The nitrogen gap in soil health concepts and fertility measurements. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 175, 108856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, M.; Feizienė, D.; Tilvikienė, V.; Feiza, V.; Baltrėnaitė-Gedienė, E.; Ullah, S. Biochar with inorganic nitrogen fertilizer reduces direct greenhouse gas emission flux from soil. Plants 2023, 12, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farzadfar, S.; Knight, J.D.; Congreves, K.A. Soil organic nitrogen: An overlooked but potentially significant contribution to crop nutrition. Plant Soil 2021, 462, 7–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilling, A.; Kane, D.; Williams, A.; Yannarell, A.C.; Davis, A.; Jordan, N.R.; Koide, R.T.; Mortensen, D.A.; Smith, R.G.; Snapp, S.S. Rapid and distinct responses of particulate and mineral-associated organic nitrogen to conservation tillage and cover crops. Geoderma 2020, 359, 114001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zheng, H.; He, S.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer by organic fertilizer increases yield, quality and nitrogen utilization of Dioscorea polystachya. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, 0301108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, W.; Shao, S.; He, H.; Zhang, X. Comparing microbial transformation of maize residue-N and fertilizer-N in soil using amino sugar-specific 15N analysis. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 71, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, C.; Zhang, Y.; McLaughlin, N.B.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, D.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; et al. Changes in soil total nitrogen induced by crop residue return: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 230, 105712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Xu, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cao, W.; Zhai, B.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; et al. Leguminous green manure enhances the soil organic nitrogen pool of cropland via disproportionate increase of nitrogen in particulate organic matter fractions. Catena 2021, 207, 105574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathan, J.; Singh, A.; Ranjan, A. Sucrose transport and metabolism control carbon partitioning between stem and grain in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 4355–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Wen, F.; Li, F.; Chen, T.; Feng, B.; Xiong, J.; Fu, G.; Qin, Y.; Wang, W. Analysis of the Relationship Between Assimilate Production and Allocation and the Formation of Rice Quality. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamoud, Y.A.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z.; Shaghaleh, H.; Chen, S.; Hassan, A.; Bakour, A. Effects of irrigation regime and soil clay content and their interaction on the biological yield, nitrogen uptake and nitrogen-use efficiency of rice grown in southern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 934–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pede, V.O.; Valera, H.G.; Mishra, A.K.; Balié, J. Future of Rice in Asia: Perspectives and Opportunities, 2050; Food Security Issues in Asia; World Scientific Publishing Co.: Singapore, 2024; p. 108. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.R.; Cao, P.P.; Yang, K.; Lyu, C.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Sun, W.J.; Yu, L.F.; Hu, Z.H.; Huang, Y. Effects of source-sink manipulation on the accumulation and translocation of non-structural carbohydrates in stems and sheaths of Japonica rice under elevated CO2 concentration and different nitrogen fertilization levels. Chin. J. Ecol. 2021, 40, 615. [Google Scholar]
- Bharali, A.; Baruah, K.K. Effects of integrated nutrient management on sucrose phosphate synthase enzyme activity and grain quality traits in rice. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2022, 28, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, J.; Guo, X.; Gong, H.; Ouyang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Mathijs, E. Excessive synthetic fertilizers elevate greenhouse gas emissions of smallholder-scale staple grain production in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 430, 139720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zou, J.; Cao, L.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.X. Melatonin regulates material transport to reduce carbon emissions and increase yield under different nitrogen in rice. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 342, 108235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Duan, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Ju, W.; Chen, H.; Yue, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, S.; et al. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry reveals microbial phosphorus limitation decreases the nitrogen cycling potential of soils in semi-arid agricultural ecosystems. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, X.; Xia, L.; Wang, M.; Xiang, J.; Ma, T. Co-application of organic phosphate fertilizer, manure, and biochar synergistically improves chemical and biological properties of Pb-Zn mine tailings: Insights from a pot trial. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 292, 117984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.; Sommers, L.; Page, A. Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 2 Chemical and Microbiological Properties of Phosphorus; ASA Monograph 9; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 403–430. [Google Scholar]
- Helmke, P.A.; Sparks, D.L. Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidium, and Cesium. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Book Series No. 5. Soil Science Society of America; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 551–573. [Google Scholar]
- Shaaban, M.; Peng, Q.-A.; Hu, R.; Wu, Y.; Lin, S.; Zhao, J. Dolomite application to acidic soils: A promising option for mitigating N2O emissions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 19961–19970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S. Experimental Principle and Technology of Plant Physiology and Biochemistry; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 123–124. [Google Scholar]
- Lea, P.J.; Blackwell, R.D.; Chen, F.-L.; Hecht, U. Enzymes of Ammonium Assimilation. In Methods in Plant Biochemistry; Dey, P.M., Harborne, J.B., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1990; pp. 257–276. [Google Scholar]
- Wardlaw, I.F.; Willenbrink, J. Carbohydrate storage and mobilisation by the culm of wheat between heading and grain maturity: The relation to sucrose synthase and sucrose-phosphate synthase. Funct. Plant Biol. 1994, 21, 255–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathalie, G.; Christine, H.F.; Erik, M.; Rhu, A.; Paul, Q.; Toni, A.V.; Catherine, T.; Gerard, L.; Thomas, B. Effects of light and atmospheric carbon dioxide enrichment on photosynthesis and carbon partitioning in the leaves of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.) plants over-expressing sucrose phosphate synthase. J. Exper. Bot. 1995, 46, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Çavuşoğlu, K.; Kılıç, S.; Kabar, K. Some morphological and anatomical observations during alleviation of salinity (NaCl) stress on seed germination and seedling growth of barley by polyamines. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2007, 29, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadamma, S.; Steinweg, J.M.; Mayes, M.A.; Wang, G.; Post, W.M. Decomposition of added and native organic carbon from physically separated fractions of diverse soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2014, 50, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J. Nitrogen-organic forms. In Methods of Soil Analysis: Part 3 Chemical Methods; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; Volume 5, pp. 1185–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.; Wei, C.; Yang, P. Variation in soil nitrous oxide emission with nitrogen application rates under reclaimed water irrigation. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 13, 1510520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, H. Greenhouse gas emissions of rice straw return varies with return depth and soil type in paddy systems of Northeast China. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2021, 67, 1591–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, C.; Siddique, K.H.; Ju, X. Enhanced efficiency nitrogen fertilizers maintain yields and mitigate global warming potential in an intensified spring wheat system. Field Crops Res. 2019, 244, 107624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.Q.; Liu, J.; Jiang, P.K.; Wu, J.S.; Li, Y.F.; Li, S.H. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer management on CH4 and N2O emissions in paddy field. Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 2171–2181. [Google Scholar]
- Hayatu, N.G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Han, T.; Khan, M.N.; Daba, N.A.; Noma, S.S.; Lv, Z.; Hou, H.; et al. Long-Term organic manure substitution increases yield and phosphorus use efficiency in a double-rice system by altering soil phosphorus uptake and apparent balance. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Chen, H.; Tang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Xiao, X. Combination of nitrogen and organic fertilizers reduce N2O emissions while increasing winter wheat grain yields and quality in China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1485043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Cai, T.; Wu, X.; Luo, Y.; Liao, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, G.; Hu, R.; Luo, Y.; et al. A combination of organic fertilizers partially substitution with alternate wet and dry irrigation could further reduce greenhouse gases emission in rice field. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhi, J.; Wang, H.; Shen, Q.; Zou, J.; Li, S. Decreased nitrous oxide emissions associated with functional microbial genes under bio-organic fertilizer application in vegetable fields. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilecco, G.E.; Chantigny, M.H.; Weiler, D.A.; Aita, C.; Thivierge, M.N.; Schmatz, R.; Chaves, B.; Giacomini, S.J. Greenhouse gas emissions and global warming potential from biofuel cropping systems fertilized with mineral and organic nitrogen sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 138767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, N.; Jiang, H.; Chen, L. Effects of long-term no-tillage with different residue application rates on soil nitrogen cycling. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Ding, F.; Dijkstra, F.A.; Jia, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, J. Crop residue decomposition and nutrient release are independently affected by nitrogen fertilization, plastic film mulching, and residue type. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 138, 126535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Wei, K.; Condron, L.M.; Chen, Z.; Xu, Z.; Feng, J.; Chen, L. Effects of elevated nitrogen and precipitation on soil organic nitrogen fractions and nitrogen-mineralizing enzymes in semi-arid steppe and abandoned cropland. Plant Soil 2017, 417, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, G.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, N.; Qiu, W.; Chen, L. Effects of different maize residue managements on soil organic nitrogen cycling in different soil layers in northeast China. GCB Bioenergy 2024, 16, e13123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Li, H.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C. Effects of organic fertilizers via quick artificial decomposition on crop growth. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ren, T.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cong, R.; Li, X.; Lu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Lu, J. Soil organic nitrogen sequestrated more in oilseed rape–rice rotation than in wheat-rice rotation under different fertilizations. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 381, 109445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Nie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, H.; Li, Y. Characteristics of greenhouse gas emissions from yellow paddy soils under long-term organic fertilizer application. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Molin, S.J.; Ernani, P.R.; Gerber, J.M. Soil Acidification and Nitrogen Release Following Application of Nitrogen Fertilizers. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 2551–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xiong, H.; Jiang, T. Influence of nitrogen fertilizer application on soil acidification characteristics of tea plantations in karst areas of southwest China. Agriculture 2023, 13, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; He, P.; Li, S.; Liang, G.; Zhou, W.; et al. The stronger impact of inorganic nitrogen fertilization on soil bacterial community than organic fertilization in short-term condition. Geoderma 2021, 382, 114752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Sheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, G.; Zheng, J. Organic fertilizer substitution increased soil organic carbon through the association of microbial necromass C with iron oxides. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Cheng, H.; Peng, Y.; Sun, T.; Gao, Y.; Wang, R.; Ma, Y.; Yang, J.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, H.; et al. Relative role of soil nutrients vs. carbon availability on soil carbon mineralization in grassland receiving long-term N addition. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Sheoran, S.; Prakash, D.; Yadav, D.B.; Yadav, P.K.; Jat, M.K. Long-term application of organic manures and chemical fertilizers improve the organic carbon and microbiological properties of soil under pearl millet-wheat cropping system in North-Western India. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Chen, M.; Feng, H.; Wei, M.; Song, F.; Lou, Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, H.; Zhuge, Y. Organic and inorganic fertilizers respectively drive bacterial and fungal community compositions in a fluvo-aquic soil in northern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rambaut, L.A.E.; Vayssières, J.; Versini, A.; Salgado, P.; Lecomte, P.; Tillard, E. 15-year fertilization increased soil organic carbon stock even in systems reputed to be saturated like permanent grassland on andosols. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, X.; Bailey, L.S.; Kamat, M.N.; Basso, K.B. Identification and characterization of proteins, lipids, and metabolites in two organic fertilizer products derived from different nutrient sources. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2021, 64, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; DeLuca, T.H. Biochar alters nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in a western rangeland ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xiong, X.; He, M.; Xu, Z.; Hou, D.; Zhang, W.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Wang, L.; Tsang, D.C. Roles of biochar-derived dissolved organic matter in soil amendment and environmental remediation: A critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 424, 130387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiya, N.; Asano, A.; Peter, M.A.; Gichuhi, E.W.; Menge, D.M.; Kikuta, M.; Kondo, M.; Makihara, D. Effects of nitrogen application in upland rice cultivars: Balancing sink-source relationships for sustainable yield in water-limited environments. Field Crops Res. 2025, 332, 110012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, X.; Tian, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, W.; Yang, N.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, H.; et al. Auxin regulates source-sink carbohydrate partitioning and reproductive organ development in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2121671119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Huang, L. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer application rate on nitrate reductase activity in maize. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2020, 18, 2879–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.D.; Hu, Z.Y.; Hao, Z.Y.; Li, J.H.; Wang, Q.; Meng, X.X.; Zhou, Y.F.; Huang, R.D. Effect of nitrogen on the metabolic enzyme activity of leaves, protein content and yield of sorghum (Sorghum Bicolor [L.] moench) IN Northern China. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2021, 19, 3467–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, M. Chemical fertilizer reduction with organic fertilizer effectively improve soil fertility and microbial community from newly cultivated land in the Loess Plateau of China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 165, 103966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, H.; Liu, H.; Yang, L.; Mi, G.; Wang, P. Enhancing Crop Nitrogen Efficiency: The Role of Mixed Nitrate and Ammonium Supply in Plant Growth and Development. Biology 2025, 14, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, H.; Gong, Y.; Yang, J.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ye, N. Expression profile of the carbon reserve remobilization from the source to sink in rice in response to soil drying during grain filling. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zeng, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, W. SlSPS, a sucrose phosphate synthase gene, mediates plant growth and thermotolerance in tomato. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Zhang, T.; Lei, X.Y.; Cui, X.W.; Lu, Y.X.; Fan, P.F.; Long, S.P.; Huang, J.; Gao, J.S.; Zhang, Z.H.; et al. Improvement of soil fertility and rice yield after long-term application of cow manure combined with inorganic fertilizers. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.; He, H.; Cheng, L.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Yu, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. Combined application of chemical and organic fertilizers: Effects on yield and soil nutrients in spring wheat under drip irrigation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Q.; Huang, J.; Waqas, A.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Cai, A.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. Yield sustainability, soil organic carbon sequestration and nutrients balance under long-term combined application of manure and inorganic fertilizers in acidic paddy soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, E.; Yadavi, A.; Balouchi, H.; Dehnavi, M.M.; Piri, R.; Mastinu, A. Improving the physiological properties and yield of safflower by combining organic and chemical nitrogen in different irrigation cut-off conditions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 222, 119601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamuye, M.; Nebiyu, A.; Elias, E.; Berecha, G. Combined Use of Organic and Inorganic Nutrient Sources Improved Maize Productivity and Soil Fertility in Southwestern Ethiopia. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2021, 15, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zong, J.; Ma, J.; Li, C. Changes in soil organic carbon fractions and bacterial community composition under different tillage and organic fertiliser application in a maize–wheat rotation system. Acta Agric. Sci. B Soil Plant Sci. 2020, 70, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | Soil pH | Total Nitrogen (g kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg kg−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| CK | 6.47 b | 6.51 d | 1.27 c | 1.29 d | 27.47 b | 27.56 d | 40.30 d | 41.90 d |
| NPK | 6.40 b | 6.41 c | 1.30 c | 1.39 c | 30.30 b | 32.97 c | 44.74 c | 50.95 c |
| OM | 6.64 a | 6.71 b | 1.40 b | 1.51 b | 35.11 a | 36.90 b | 50.77 b | 57.63 b |
| NPKOM | 6.69 a | 6.80 a | 1.49 a | 1.65 a | 37.87 a | 41.40 a | 57.55 a | 63.17 a |
| LSD (p ≤ 0.05) | 0.089 | 0.072 | 0.074 | 0.049 | 4.15 | 2.23 | 2.42 | 3.65 |
| Treatments | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | SOC (mg kg−1) | MBC (mg kg−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| CK | 30.28 c | 31.43 c | 27.09 d | 27.96 d | 10.48 d | 10.61 d | 308 c | 313 c |
| NPK | 42.08 a | 44.40 a | 37.20 a | 39.80 a | 11.50 c | 11.76 c | 316 c | 323 c |
| OM | 38.27 b | 39.32 b | 32.67 b | 33.62 b | 14.77 b | 15.15 b | 351 b | 358 b |
| NPKOM | 37.49 b | 38.26 b | 30.83 c | 31.61 c | 17.39 a | 17.82 a | 363 a | 379 a |
| LSD (p ≤ 0.05) | 0.69 | 2.74 | 1.73 | 0.96 | 1.28 | 0.26 | 10.61 | 11.85 |
| Treatments | Non-Structural Carbohydrates (mg g−1) | Soluble Sugars (mg g−1) | Starch Contents (mg g−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| CK | 78.70 c | 81.90 c | 8.27 c | 8.63 b | 25.77 b | 30.28 c |
| NPK | 104.10 a | 117.07 a | 8.83 bc | 9.22 b | 28.32 b | 32.30 c |
| OM | 94.03 b | 103.53 b | 9.55 ab | 9.89 ab | 31.30 ab | 36.60 b |
| NPKOM | 89.97 b | 98.00 b | 10.30 a | 11.01 a | 36.10 a | 40.32 a |
| LSD (p ≤ 0.05) | 7.49 | 10.63 | 0.96 | 1.26 | 6.01 | 2.93 |
| Treatments | Sucrose Phosphate Synthase (µ mol mg−1 Protein h−1) | α-Amylase (mg mg−1 Protein h−1) | β-Amylase (mg mg−1 Protein h−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| CK | 1.14 d | 1.24 c | 5.83 b | 5.98 d | 0.85 b | 1.05 b |
| NPK | 1.44 c | 1.56 c | 6.90 b | 7.42 c | 1.15 b | 1.25 b |
| OM | 1.80 b | 1.96 b | 8.25 a | 9.00 b | 1.83 a | 2.35 a |
| NPKOM | 2.04 a | 2.45 a | 9.41 a | 10.63 a | 2.05 a | 2.68 a |
| LSD (p ≤ 0.05) | 0.21 | 0.32 | 1.28 | 0.91 | 0.39 | 0.42 |
| Treatments | Plant Height (cm) | Productive Tillers (m2) | Panicle Length (cm) | Panicles/Plant | 1000 Grain Weight (g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| CK | 84 b | 88 b | 225 c | 245 c | 11.79 c | 12.18 c | 12 c | 13 b | 19.40 c | 20.58 d |
| NPK | 88 ab | 99 ab | 241 b | 252 bc | 13.86 b | 14.95 b | 13 bc | 14 b | 21.33 bc | 23.03 c |
| OM | 92 ab | 102 a | 251 ab | 265 ab | 14.31 b | 15.63 a | 15 b | 16 ab | 23.32 ab | 24.61 b |
| NPKOM | 95 a | 108 a | 261 a | 275 a | 14.95 a | 16.22 a | 17 a | 20 a | 25.48 a | 27.21 a |
| LSD (p ≤ 0.05) | 8.27 | 11.34 | 12.77 | 15.13 | 0.59 | 0.63 | 1.94 | 4.39 | 2.40 | 1.29 |
| Treatments | Grain Yield (t ha−1) | Biomass Yield (t ha−1) | Harvest Index (%) | Grain Protein (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | 2023 | 2024 | |
| CK | 3.07 d | 3.22 d | 14.67 d | 16.15 d | 20.47 c | 19.96 c | 8.82 d | 9.05 d |
| NPK | 5.96 c | 6.26 c | 17.29 c | 17.99 c | 34.66 b | 34.83 b | 9.34 c | 9.58 c |
| OM | 6.93 b | 7.25 b | 18.71 b | 19.93 b | 36.88 ab | 36.38 b | 9.62 b | 9.83 b |
| NPKOM | 7.89 a | 8.82 a | 20.63 a | 22.79 a | 38.47 a | 40.17 a | 10.05 a | 10.23 a |
| LSD (p ≤ 0.05) | 0.32 | 0.30 | 0.96 | 0.81 | 2.51 | 3.60 | 0.24 | 0.19 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Xiao, J.; Lan, X.; Ji, J.; Hou, H.; Chen, L.; Lv, Z. Organic Manure with Chemical Fertilizers Improves Rice Productivity and Decreases N2O Emissions by Increasing Soil Nitrogen Sequestration. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081783
Liu Y, Xiao J, Lan X, Ji J, Hou H, Chen L, Lv Z. Organic Manure with Chemical Fertilizers Improves Rice Productivity and Decreases N2O Emissions by Increasing Soil Nitrogen Sequestration. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081783
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yiren, Jingshang Xiao, Xianjin Lan, Jianhua Ji, Hongqian Hou, Liumeng Chen, and Zhenzhen Lv. 2025. "Organic Manure with Chemical Fertilizers Improves Rice Productivity and Decreases N2O Emissions by Increasing Soil Nitrogen Sequestration" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081783
APA StyleLiu, Y., Xiao, J., Lan, X., Ji, J., Hou, H., Chen, L., & Lv, Z. (2025). Organic Manure with Chemical Fertilizers Improves Rice Productivity and Decreases N2O Emissions by Increasing Soil Nitrogen Sequestration. Agronomy, 15(8), 1783. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15081783





