The Mechanism of an Fe-Based MOF Material as a Foliar Inhibitor and Its Co-Mitigation Effects on Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of MIL-88@SA
2.2. Experimental Site
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Analytical Methods
2.4.1. Determination of the As and Cd Contents in the Soil
2.4.2. Methods for Determining the Structure and Properties of MIL-88@SA
2.4.3. Methods for the Analysis of Plants in the Field Experiment
2.5. Data Processing and Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
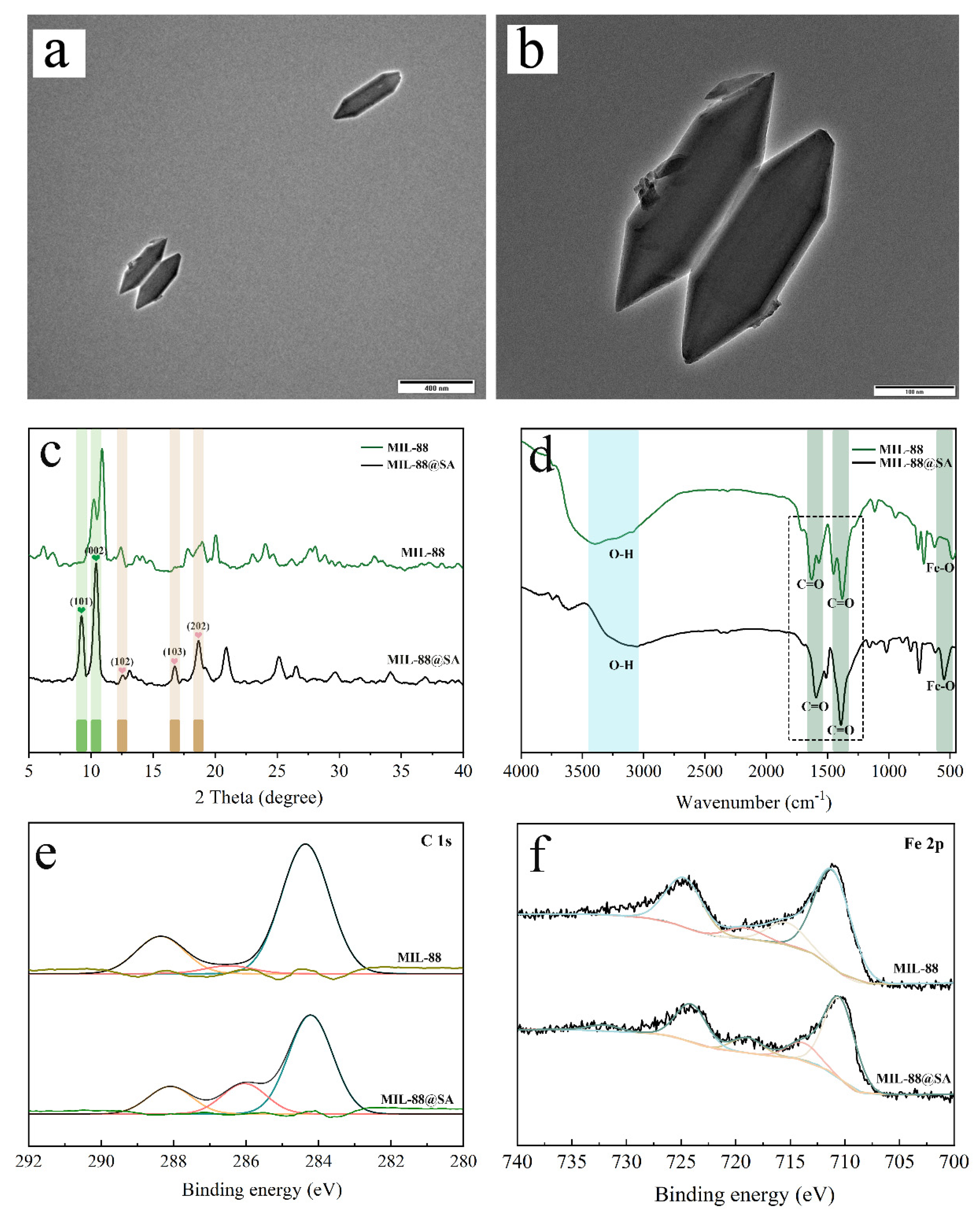
3.1. Characterization of MIL-88@SA
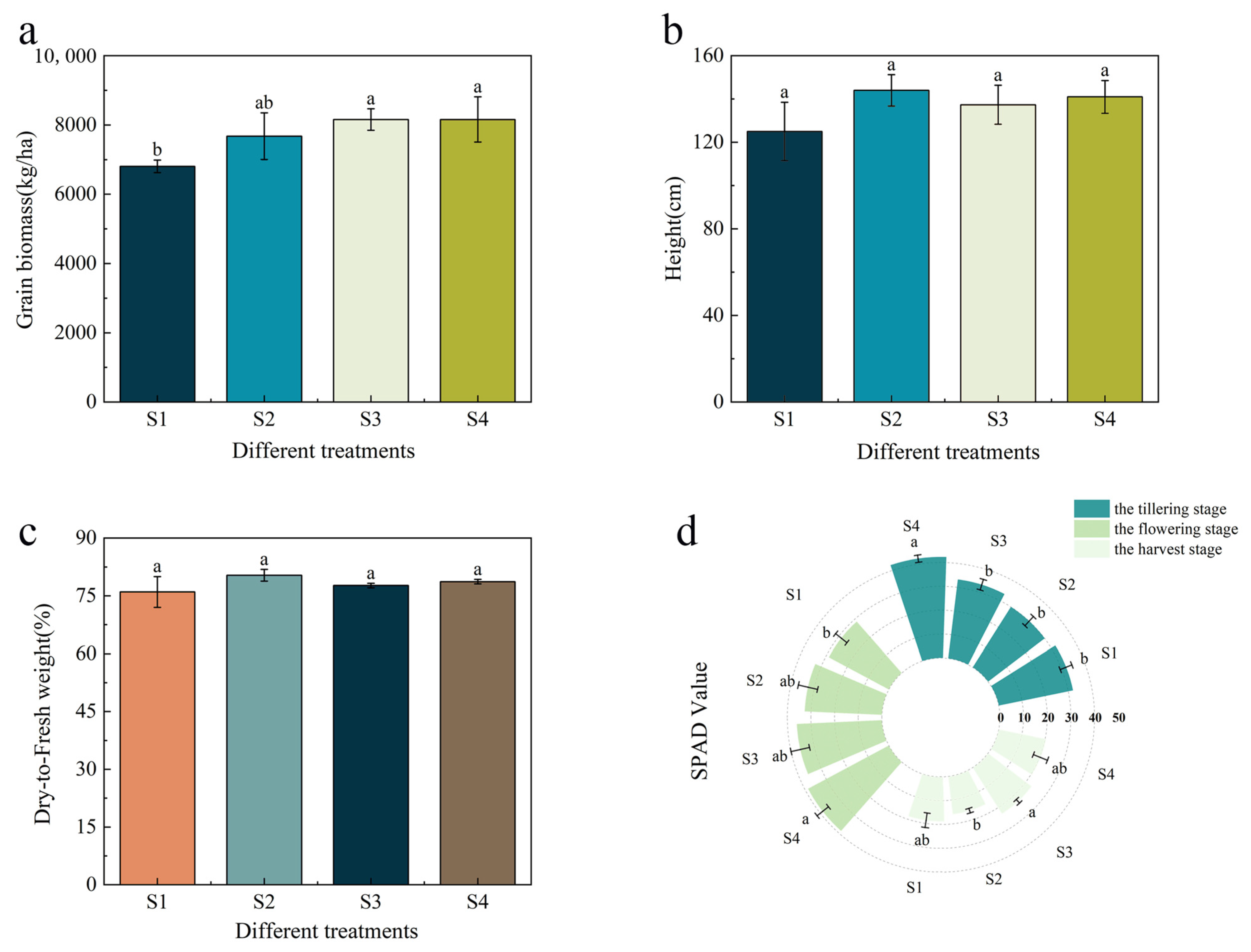
3.2. Effects on Rice Yield and Biomass
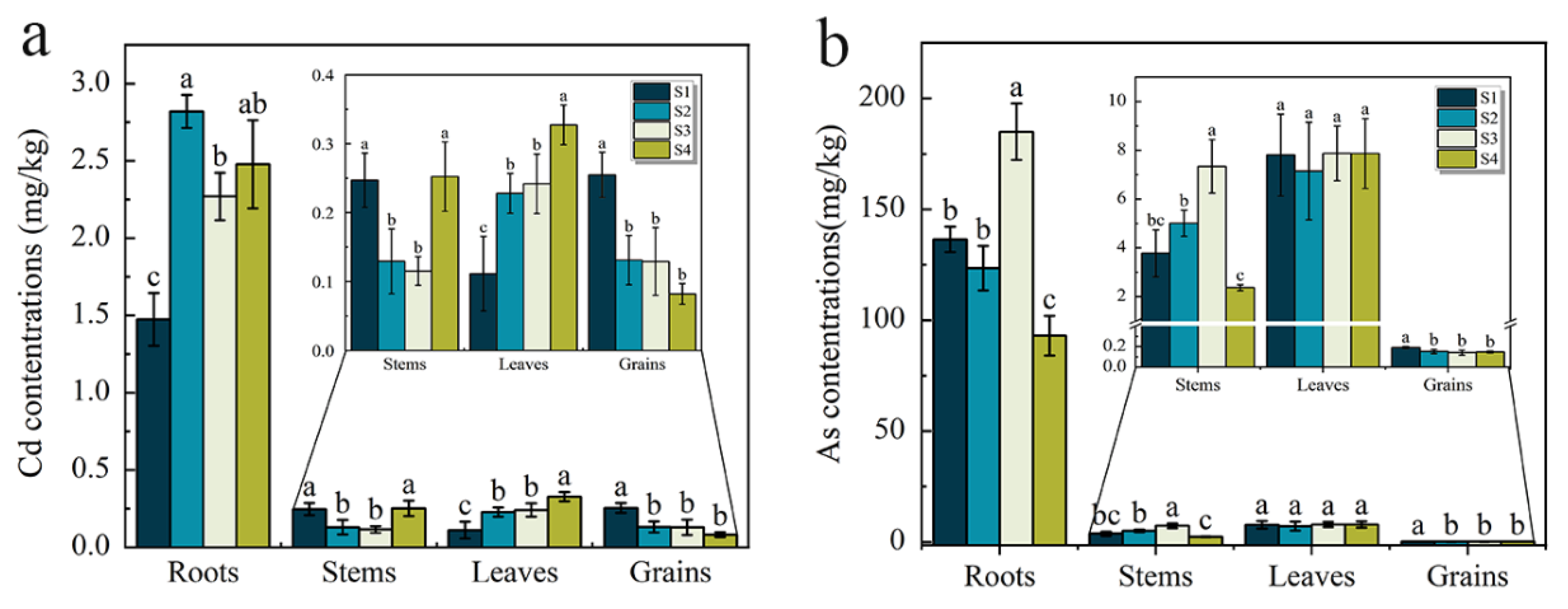
3.3. Distribution of As and Cd in Different Tissues of Rice Plants
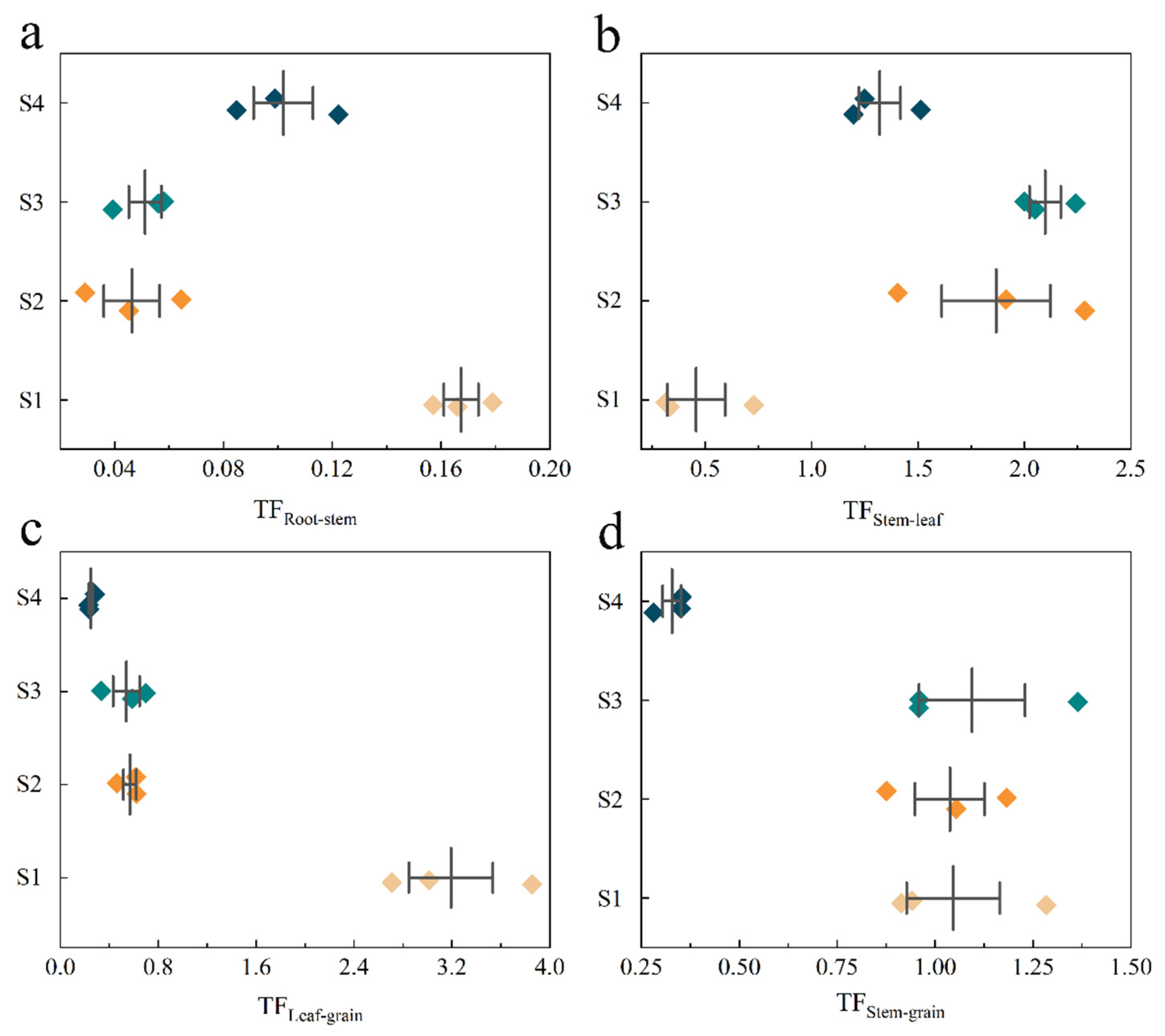
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Elements in Rice Tissue
3.5. Mechanisms by Which Foliar Inhibitors Mitigate As and Cd Accumulation in Rice
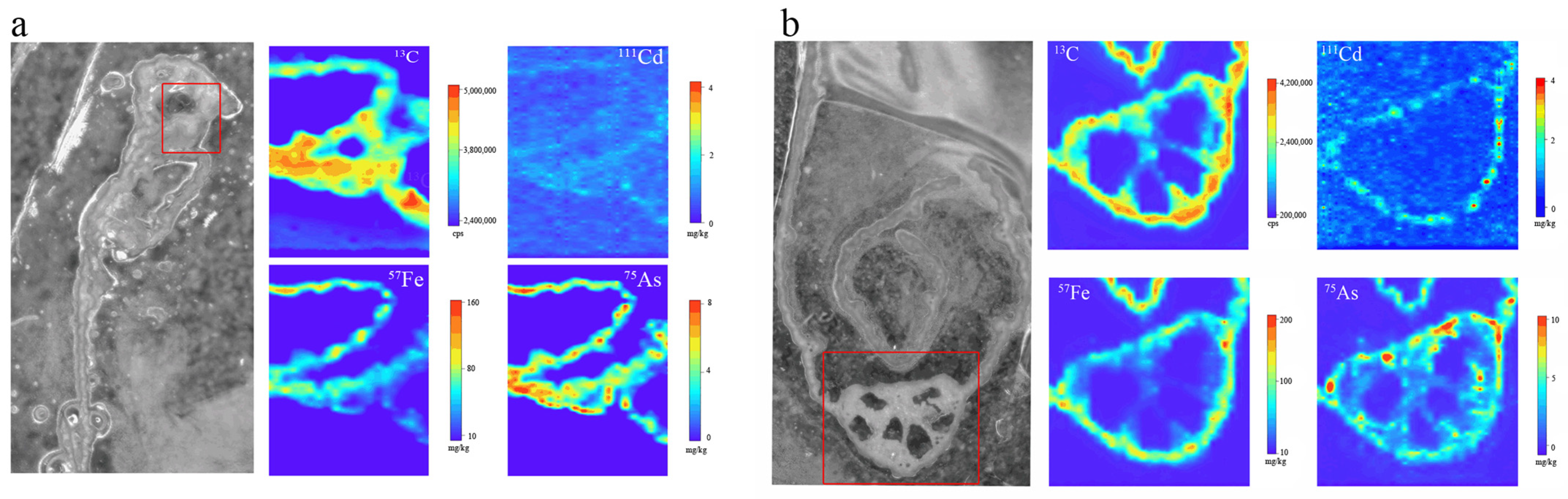
3.5.1. Mechanisms of As Mitigation in Rice Plants
3.5.2. Mechanisms of Cd Mitigation in Rice Plants
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hussain, B.; Umer, M.J.; Li, J.; Ma, Y.; Abbas, Y.; Ashraf, M.N.; Tahir, N.; Ullah, A.; Gogoi, N.; Farooq, M. Strategies for reducing cadmium accumulation in rice grains. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 286, 125557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Rahman, S.U.; Qiu, Z.; Shahzad, S.M.; Nawaz, M.F.; Huang, J.; Naveed, S.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Cheng, H. Toxic effects of cadmium on the physiological and biochemical attributes of plants, and phytoremediation strategies: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 325, 121433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, T.; Khan, S.; Muhammad, S.; Amin, S. Arsenic speciation, mechanisms, and factors affecting rice uptake and potential human health risk: A systematic review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, X.; Tang, J.; Tang, J.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhuang, X.; Feng, G.; Tang, L. Research progress on the environmental risk assessment and remediation technologies of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 149, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Huang, S.-Y.; Kong, L.-X.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, H.-F.; Wan, Y.-N. The risks of sulfur addition on cadmium accumulation in paddy rice under different water-management conditions. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 118, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Yang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, D.; Zeng, Q. Cichorium intybus L. is a potential Cd-accumulator for phytoremediation of agricultural soil with strong tolerance and detoxification to Cd. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 451, 131182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Guan, Q.; Kong, L.; Yang, R.; Liu, X.; Qu, J.; Jin, Y. Composite organic amendment boosts soil remediation and Cd detoxification to rape under different nitrogen level. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2023, 114, 103463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-T.; Yan, B.-F.; Cai, X.; Zheng, H.-X.; Qiu, R.-L.; Tang, Y.-T. Foliar-applied zinc promotes cadmium allocation from leaf surfaces to grains in rice. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 151, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Shi, D.; Wang, C.; Sun, G.; Li, H.; Hu, Y.; Li, X.; Hou, Y.; Zheng, R. Pristine/magnesium-loaded biochar and ZVI affect rice grain arsenic speciation and cadmium accumulation through different pathways in an alkaline paddy soil. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, M.M.; Okal, E.J.; Waseem, M. Cadmium toxicity impacts plant growth and plant remediation strategies. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 99, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Sun, J.; Shaghaleh, H.; Jiang, X.; Yu, H.; Zhai, S.; Hamoud, Y.A. Environmental Assessment of Soils and Crops Based on Heavy Metal Risk Analysis in Southeastern China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Liang, J.; Zhou, J. Foliar spraying with silicon and selenium reduces cadmium uptake and mitigates cadmium toxicity in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 1100–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, G.-L.; Hu, Y.; Liu, W.-J.; Kneer, R.; Zhao, F.-J.; Zhu, Y.-G. Evidence for a role of phytochelatins in regulating arsenic accumulation in rice grain. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2011, 71, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Li, F.; Fang, L.; Pang, T.; Wu, W.; Liu, C.; Chen, L. Unique feature of Fe-OM complexes for limiting Cd accumulation in grains by target-regulating gene expression in rice tissues. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.Y.; Sun, M.Q.; Chen, Z.L.; Xiao, Y.T.; Wei, H.; Zhang, J.Q.; Huang, L.; Zou, Q. Effect of foliage applied chitosan-based silicon nanoparticles on arsenic uptake and translocation in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 433, 124432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, S.; Shuai, H.; Xu, C.; Lv, G.; Zhu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Conde-Cid, M.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Foliar application of Zn reduces Cd accumulation in grains of late rice by regulating the antioxidant system, enhancing Cd chelation onto cell wall of leaves, and inhibiting Cd translocation in rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 770, 145302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Geng, L.; Fan, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Q.; Xue, P.; Liu, W. Spraying silicon to decrease inorganic arsenic accumulation in rice grain from arsenic-contaminated paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avellan, A.; Yun, J.; Morais, B.P.; Clement, E.T.; Rodrigues, S.M.; Lowry, G.V. Critical Review: Role of Inorganic Nanoparticle Properties on Their Foliar Uptake and in Planta Translocation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 13417–13431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kah, M.; Navarro, D.; Kookana, R.S.; Kirby, J.K.; Santra, S.; Ozcan, A.; Kabiri, S. Impact of (nano)formulations on the distribution and wash-off of copper pesticides and fertilisers applied on citrus leaves. Environ. Chem. 2019, 16, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, T.; Hong, J.; Lei, L.; Wei, S. Uptake And Translocation Of ZnO Nanoparticles In Rice Tissues Studied By Single Particle-ICP-MS. At. Spectrosc. 2023, 44, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunkunle, C.O.; Balogun, G.Y.; Olatunji, O.A.; Han, Z.; Adeleye, A.S.; Awe, A.A.; Fatoba, P.O. Foliar application of nanoceria attenuated cadmium stress in okra (Abelmoschus esculentus L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durgude, S.A.; Ram, S.; Kumar, R.; Singh, S.V.; Singh, V.; Durgude, A.G.; Pramanick, B.; Maitra, S.; Gaber, A.; Hossain, A. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica and Graphene-Based FeO and ZnO Nanocomposites for Nutritional Biofortification and Sustained the Productivity of Rice. J. Nanomater. 2022, 2022, 5120307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z. Foliar application with nano-silicon reduced cadmium accumulation in grains by inhibiting cadmium translocation in rice plants. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 2361–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Husted, S.; Minutello, F.; Pinna, A.; Tougaard, S.L.; Møs, P.; Kopittke, P.M. What is missing to advance foliar fertilization using nanotechnology? Trends Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, N.T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.T.; Nguyen, D.T.C.; Tran, T.V. Functionalization strategies of metal-organic frameworks for biomedical applications and treatment of emerging pollutants: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Cao, L.; Liu, T.; Chen, H.; Li, Y. pH-responsive copper-doped ZIF-8 MOF nanoparticles for enhancing the delivery and translocation of pesticides in wheat plants. Environ. Sci. Nano 2023, 10, 2578–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Cai, M.; Fu, T.; Yin, D.; Peng, H.; Liao, S.; Du, Y.; Kong, J.; Ni, J.; Yin, X. Fe-Based Metal Organic Frameworks (Fe-MOFs) for Bio-Related Applications. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Xu, X.; Ma, F.; Du, C. Fe-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Controlled Release of Fertilizer Nutrients. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 35970–35980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, P.; Lan, W.; Xie, J. Modification on sodium alginate for food preservation: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 143, 104217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, R.; Li, H.; Guo, W.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Q.; Jin, L.; Hu, S. Determination of REEs in Seawater RMs (NASS-7, CASS-6, and NMIJ 7204-A) Using Online Automated Separation ICP-MS Analysis System. At. Spectrosc. 2024, 45, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Guo, W.; Jin, L.; Peng, Y.e.; Hu, S. Elemental screening of plant-based foods by slurry nebulization ICP-MS. J. Anal. At. Spectrom. 2020, 35, 592–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lux, A.; Morita, S.; Abe, J.U.N.; Ito, K. An Improved Method for Clearing and Staining Free-hand Sections and Whole-mount Samples. Ann. Bot. 2005, 96, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Yang, J.; Deng, J.; Wang, W.; Ke, Y.; Sun, Y.; Spectroscopy, A. Influence of Spot Size on LA-ICP-MS Ablation Behavior for Synthetic Calcium Tungstate and Silicate Glass Reference Material NIST SRM 610. At. Spectrosc. 2021, 42, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ni, X.; Fu, J.; Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Jin, L.; Peng, Y.; Hu, S. Quantitation and Imaging Analysis of Biological Samples by LA-ICP-MS. At. Spectrosc. 2021, 42, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zango, Z.U.; Jumbri, K.; Sambudi, N.S.; Hanif Abu Bakar, N.H.; Fathihah Abdullah, N.A.; Basheer, C.; Saad, B. Removal of anthracene in water by MIL-88(Fe), NH2-MIL-88(Fe), and mixed-MIL-88(Fe) metal–organic frameworks. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 41490–41501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zango, Z.U.; Abu Bakar, N.H.H.; Sambudi, N.S.; Jumbri, K.; Abdullah, N.A.F.; Kadir, E.A.; Saad, B. Adsorption of chrysene in aqueous solution onto MIL-88(Fe) and NH2-MIL-88(Fe) metal-organic frameworks: Kinetics, isotherms, thermodynamics and docking simulation studies. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, R.; Liu, H. Fe-based MOFs for efficient adsorption and degradation of acid orange 7 in aqueous solution via persulfate activation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 369, 130–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, S.; Shaji, S.; Pathiraja, G.; Mo, Y.; Rathnayake, H. Molecular magnetism in nanodomains of isoreticular MIL-88(Fe)-MOFs. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 21677–21689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chen, H.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, S.; Huang, S.; Cheng, D.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Z. Pectin-Coated Iron-Based Metal–Organic Framework Nanoparticles for Enhanced Foliar Adhesion and Targeted Delivery of Fungicides. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 6533–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizwan, M.; Noureen, S.; Ali, S.; Anwar, S.; Rehman, M.Z.u.; Qayyum, M.F.; Hussain, A. Influence of biochar amendment and foliar application of iron oxide nanoparticles on growth, photosynthesis, and cadmium accumulation in rice biomass. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 3749–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Deng, S.; Zhou, Y.; Long, J.; Ding, D.; Du, H.; Lei, M.; Chen, C.; Tie, B.Q. Application of different foliar iron fertilizers for enhancing the growth and antioxidant capacity of rice and minimizing cadmium accumulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 7828–7839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashir, A.; Rizwan, M.; Ali, S.; Zia ur Rehman, M.; Ishaque, W.; Atif Riaz, M.; Maqbool, A. Effect of foliar-applied iron complexed with lysine on growth and cadmium (Cd) uptake in rice under Cd stress. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 20691–20699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Grossart, H.-P. Enhancing crop yield and microbial diversity in saline-affected paddy soil through biochar amendment under aquaculture wastewater irrigation. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2024, 123, 103681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y. Mechanisms and uncertainties of Zn supply on regulating rice Cd uptake. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 253, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarwar, N.; Saifullah; Malhi, S.S.; Zia, M.H.; Naeem, A.; Bibi, S.; Farid, G. Role of mineral nutrition in minimizing cadmium accumulation by plants. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Chang, J.; Chen, R.; Li, H.; Lu, H.; Tao, L.; Xiong, J. Comparison on cellular mechanisms of iron and cadmium accumulation in rice: Prospects for cultivating Fe-rich but Cd-free rice. Rice 2016, 9, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, G. Iron uptake, signaling, and sensing in plants. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pournaghshband, A.; Sadeghi, M.; Nilouyal, S.; Muchtar, A.; Huang, G.; Ito, M.; Yamaguchi, D.; Sivaniah, E.; Ghalei, B. Tuning the Morphology of Segmented Block copolymers with Zr-MOF nanoparticles for Durable and Efficient Hydrocarbon Separation Membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 9382–9391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sun, W.; Zhang, S.; Sharifan, H.; Ma, X. Elucidating the Effects of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles and Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Arsenic Uptake and Speciation in Rice (Oryza sativa) in a Hydroponic System. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10040–10047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Christie, P.; Zhang, F. Influence of iron plaque on uptake and accumulation of Cd by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings grown in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 394, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Liu, Z.; Sun, G.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, M.; Tu, S.; Xiong, S. Simultaneous reduction in cadmium and arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by iron/iron-manganese modified sepiolite. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-Y.; Zhou, H.; Gu, J.-F.; Huang, F.; Yang, W.-J.; Wang, S.-L.; Yuan, T.-Y.; Liao, B.-H. Effects of nano-Fe3O4-modified biochar on iron plaque formation and Cd accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 113970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Tang, S.; Huang, S.; Lei, L.; Jiang, Z.; Li, L.; Wei, S. Simultaneous mitigation of arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice grains by foliar inhibitor with ZIF-8@Ge-132. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 860, 160307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, C.; Huang, Y.; Liu, B.; Liu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, C. Foliar application of the sulfhydryl compound 2,3-dimercaptosuccinic acid inhibits cadmium, lead, and arsenic accumulation in rice grains by promoting heavy metal immobilization in flag leaves. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 285, 117355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Fernandez, A.; Cai, Y. Complexation of Arsenite with Humic Acid in the Presence of Ferric Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3210–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Huang, G.; Yi, J.; Cui, J.; Liu, C.; Li, F.; Li, X. Foliar application of silica nanoparticles alleviates arsenic accumulation in rice grain: Co-localization of silicon and arsenic in nodes. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Han, L.; Chao, D.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R.; Guo, J.; Feng, R.; Xu, Y.; Ding, Y.; et al. Ionomic and transcriptomic analysis provides new insight into the distribution and transport of cadmium and arsenic in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, G.; He, X.; Zeng, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L. Ionome profiling and arsenic speciation provide evidence of arsenite detoxification in rice by phosphate and arsenite-oxidizing bacteria. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 128, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Shen, L.; Feng, C.; Yang, R.; Qu, J.; Ju, H.; Zhang, Y. Distribution of rare earth elements (REEs) and their roles in plant growth: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 298, 118540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, G. Rare-earth element yttrium enhances the tolerance of curly-leaf pondweed (Potamogeton crispus) to acute nickel toxicity. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Guo, Z.; Monikh, F.A.; Lynch, I.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Zhang, Z. Growing Rice (Oryza sativa) Aerobically Reduces Phytotoxicity, Uptake, and Transformation of CeO2 Nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8654–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaibur, M.R.; Sera, K.; Kawai, S. Effect of arsenic on concentrations and translocations of mineral elements in the xylem of rice. J. Plant Nutr. 2016, 39, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.L.; Fan, S.K.; Zhu, J.; Guan, M.Y.; Liu, X.X.; Zhang, Y.S.; Jin, C.W. Iron supply prevents Cd uptake in Arabidopsis by inhibiting IRT1 expression and favoring competition between Fe and Cd uptake. Plant Soil 2017, 416, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uraguchi, S.; Fujiwara, T. Cadmium transport and tolerance in rice: Perspectives for reducing grain cadmium accumulation. Rice 2012, 5, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, D.; Gu, X. How Fe-bearing materials affect soil arsenic bioavailability to rice: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, D.; Kong, S.; Shao, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, R.; Wei, X.; Bai, B.; Werner, D.; Gao, X.; Li, C. Mobilization of arsenic from As-containing iron minerals under irrigation: Effects of exogenous substances, redox condition, and intermittent flow. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 440, 129736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Xu, G.; Xu, C.; Zhou, G.; Wei, S. Competitive mechanism for capturing heavy metal contamination by iron-based porous composite particles for soil remediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 424, 138896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wei, L.; Zhang, S.; Xu, X.; Li, F. Effects of nanoscale silica sol foliar application on arsenic uptake, distribution and oxidative damage defense in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under arsenic stress. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 57227–57234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panthri, M.; Gupta, M. An insight into the act of iron to impede arsenic toxicity in paddy agro-system. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Di, X.; Norton, G.J.; Beesley, L.; Yin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhi, S. Selenite Foliar Application Alleviates Arsenic Uptake, Accumulation, Migration and Increases Photosynthesis of Different Upland Rice Varieties. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawia, A.M.; Hui, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Tabassum, J.; Lai, C.; Wang, J.; Shao, G.; Wei, X.; Tang, S.; et al. Inorganic arsenic toxicity and alleviation strategies in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Huang, C.; Li, R.; Li, Y. The bHLH Transcription Factor PhbHLH121 Regulates Response to Iron Deficiency in Petunia hybrida. Plants 2024, 13, 3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaji, N.; Ma, J.F. Metalloid transporters and their regulation in plants. Plant Physiol. 2021, 187, 1929–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y.; Liao, Y.; Xie, X.; Xiao, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, F.; Yuan, H.; et al. Combined Utilization of Chinese Milk Vetch, Rice Straw, and Lime Reduces Soil Available Cd and Cd Accumulation in Rice Grains. Agronomy 2023, 13, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Cai, Y.; Pan, B.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Cai, K.; Wang, W. Significant Synergy Effects of Biochar Combined with Topdressing Silicon on Cd Reduction and Yield Increase of Rice in Cd-Contaminated Paddy Soil. Agronomy 2024, 14, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, D.; Xu, C.; Zhu, H.; Feng, R.-W.; Zhu, Q. Fe fortification limits rice Cd accumulation by promoting root cell wall chelation and reducing the mobility of Cd in xylem. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 240, 113700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Zhang, P.; He, M.; Cao, Y.; Adeel, M.; Shakoor, N.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; et al. Iron-based nanomaterials reduce cadmium toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.) by modulating phytohormones, phytochelatin, cadmium transport genes and iron plaque formation. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 320, 121063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Chai, G.; Lu, M.; Xiao, R.; Xie, Q.; Luo, L. A new insight into the role of iron plaque in arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 254, 114714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Tong, H.; Zhao, Z.; Cheng, N.; Wu, P. Effects of Fe oxides and their redox cycling on Cd activity in paddy soils: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 456, 131665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Guo, W.; Hu, Z.; Jin, L.; Hu, S.; Guo, Q. Method Development for Direct Multielement Quantification by LA-ICP-MS in Food Samples. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Ma, L.; Tang, L.; Huang, F.; Xiao, N.; Zhang, L.; Song, B. Key Factors Controlling Cadmium and Lead Contents in Rice Grains of Plants Grown in Soil with Different Cadmium Levels from an Area with Typical Karst Geology. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.S.; Kaul, S.; Metwally, A.; Goyal, K.C.; Finkemeier, I.; Dietz, K.J. Cadmium toxicity to barley as affected by varying Fe nutritional status. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.K.; Noman, A.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Chen, C.; Shang, J. Goethite modified biochar simultaneously mitigates the arsenic and cadmium accumulation in paddy rice (Oryza sativa) L. Environ. Res. 2022, 206, 112238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.X.; Zhu, X.F.; Xue, D.W.; Zheng, S.J.; Jin, C.W. Beyond iron-storage pool: Functions of plant apoplastic iron during stress. Trends Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, G.H.; Huang, R.N.; Hong, L.H.; Xu, J.X.; Hong, Y.G.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, W.W. The transcription factor NAC102 confers cadmium tolerance by regulating WAKL11 expression and cell wall pectin metabolism in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 2262–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Mao, X.; Pan, Y.; Sun, W.; Zhao, X. Quantitative Determination of Cd Using Energy Dispersion XRF Based on Gaussian Mixture Clustering-Multilevel Model Recalibration. At. Spectrosc. 2024, 45, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Paddy Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Cd, mg·kg−1 | 0.72 ± 0.078 |
| Total As, mg·kg−1 | 18.24 ± 1.625 |
| DTPA-extractable As, mg·kg−1 | 4.93 ± 0.786 |
| DTPA-extractable Cd, mg·kg−1 | 0.55 ± 0.070 |
| pH | 6.02 ± 0.637 |
| Soil organic matter, % | 2.26 ± 0.482 |
| Total nitrogen, g·kg−1 | 2.64 ± 0.123 |
| Total phosphorus, g·kg−1 | 0.37 ± 0.040 |
| Available K, mg·kg−1 | 132.33 ± 1.528 |
| Cation exchange capacity (CEC), cmol·kg−1 | 5.71 ± 0.051 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; Cui, H.; Li, W.; Jiang, Z.; Li, L.; Lei, L.; Wei, S. The Mechanism of an Fe-Based MOF Material as a Foliar Inhibitor and Its Co-Mitigation Effects on Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071710
Wang T, Cui H, Li W, Jiang Z, Li L, Lei L, Wei S. The Mechanism of an Fe-Based MOF Material as a Foliar Inhibitor and Its Co-Mitigation Effects on Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071710
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tianyu, Hao Cui, Weijie Li, Zhenmao Jiang, Lei Li, Lidan Lei, and Shiqiang Wei. 2025. "The Mechanism of an Fe-Based MOF Material as a Foliar Inhibitor and Its Co-Mitigation Effects on Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071710
APA StyleWang, T., Cui, H., Li, W., Jiang, Z., Li, L., Lei, L., & Wei, S. (2025). The Mechanism of an Fe-Based MOF Material as a Foliar Inhibitor and Its Co-Mitigation Effects on Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains. Agronomy, 15(7), 1710. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071710










