Variety-Dependent Yield and Physiological Responses to Combined Inorganic and Organic Sources of Nitrogen in Wheat
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Sampling and Measurements
2.3. Calculations and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Yield and Yield Components
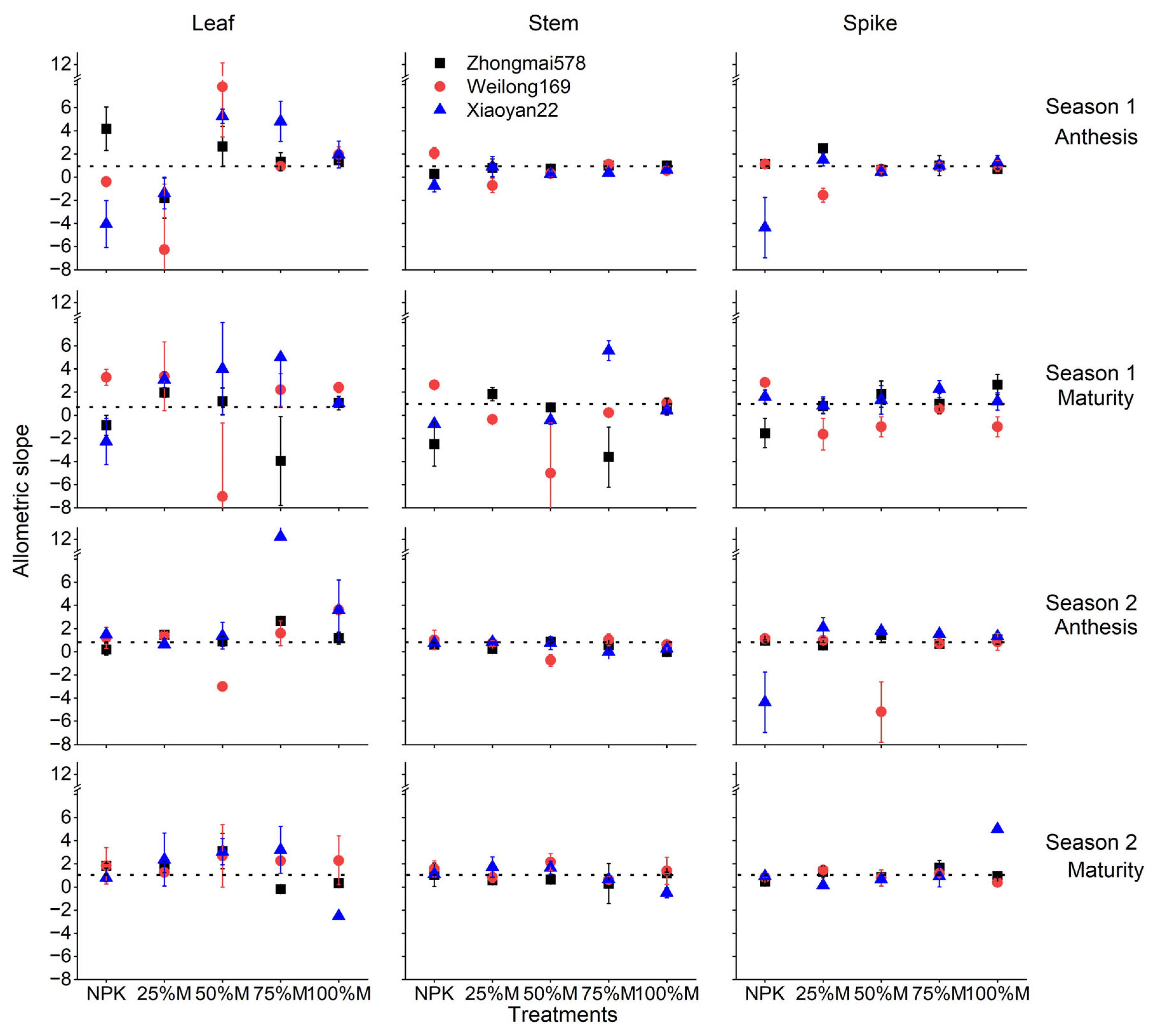
3.2. Allometric Coefficients
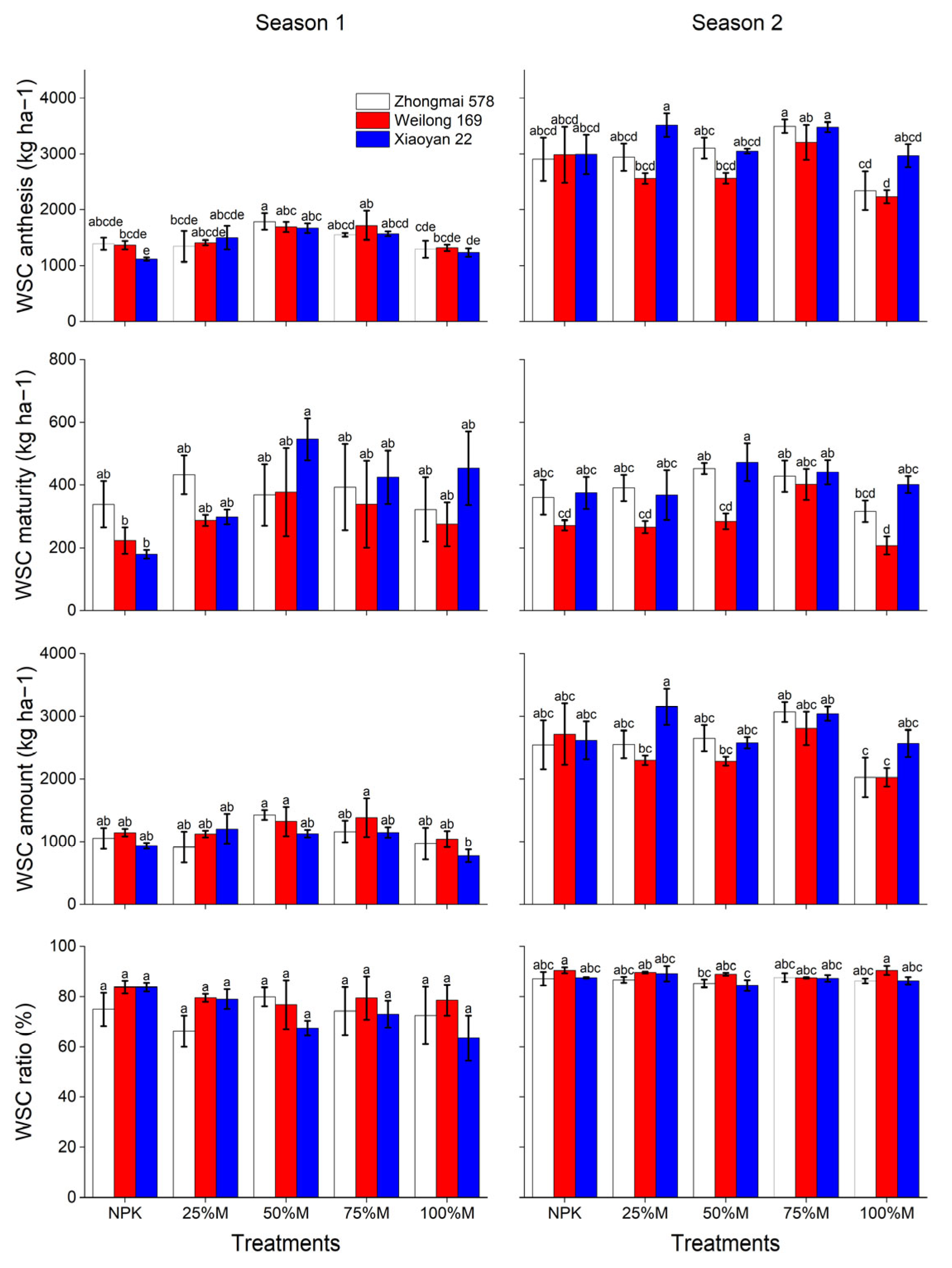
3.3. Water-Soluble Carbohydrates
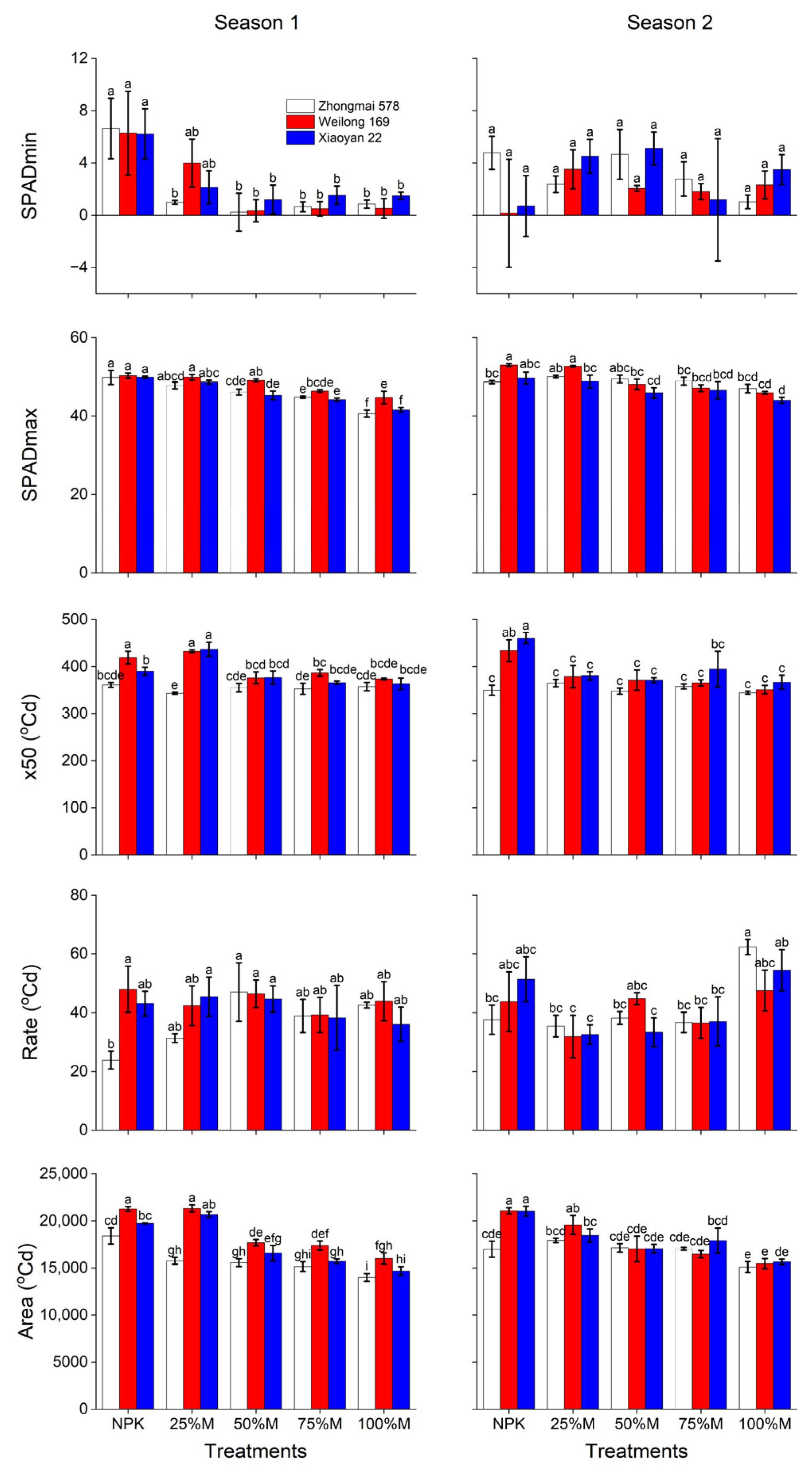
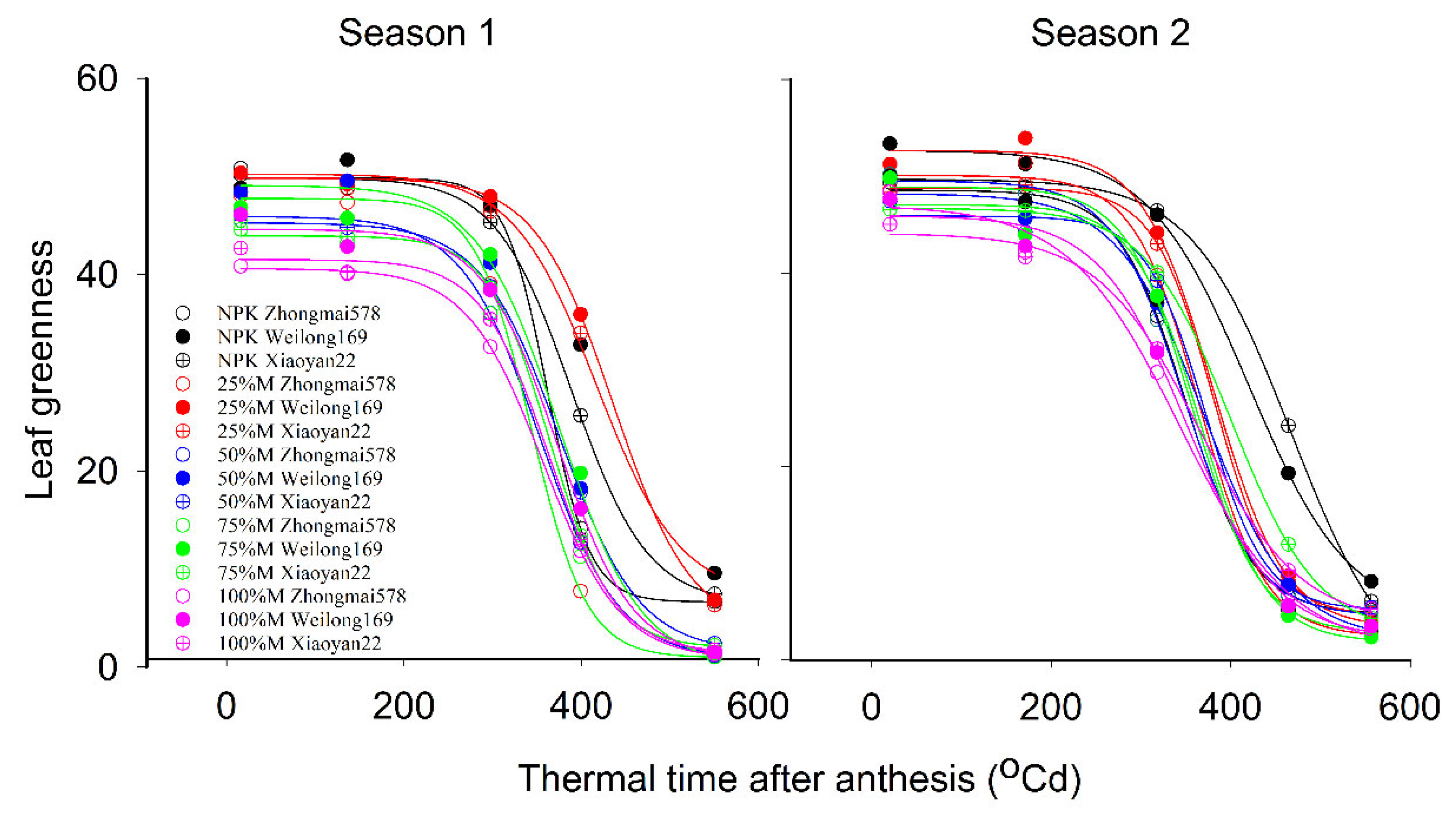
3.4. Flag Leaf Senescence
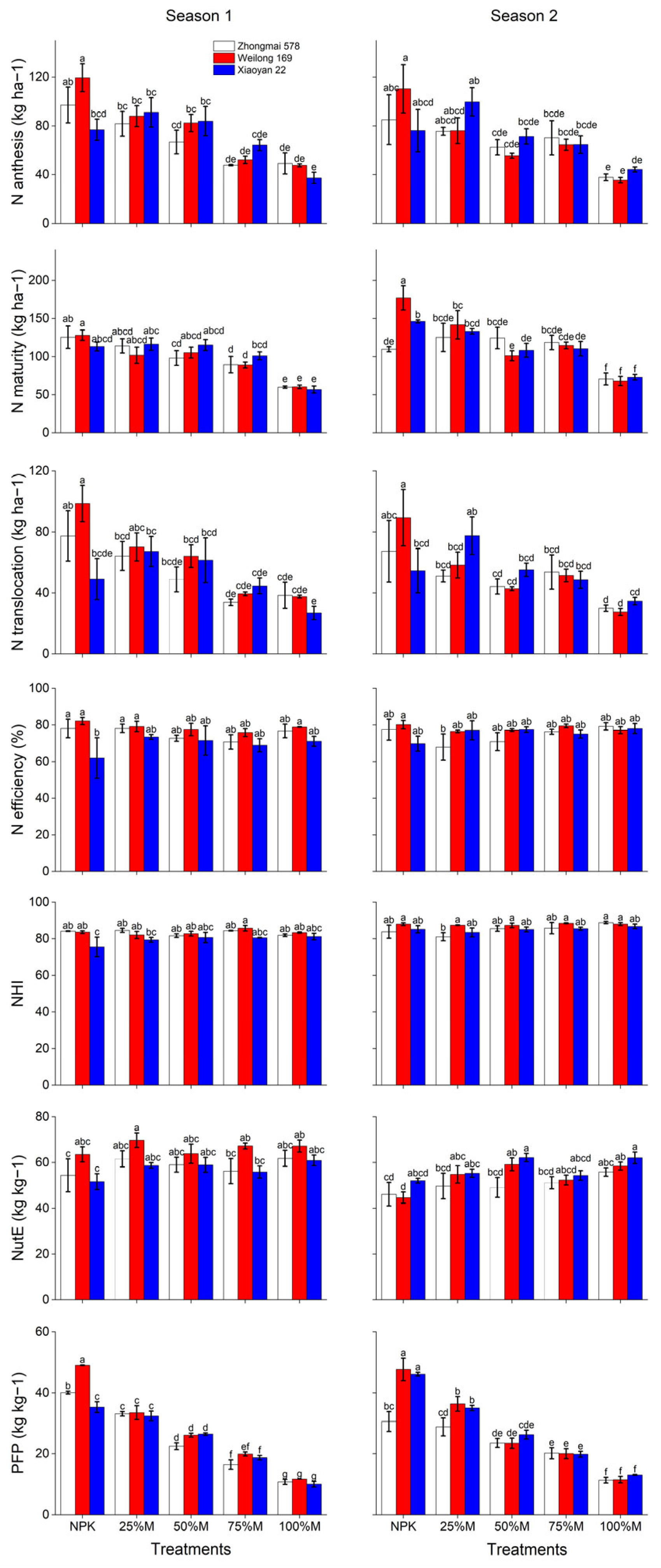
3.5. Nitrogen Traits
3.6. Correlations Between Traits
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Fertilization and Variety on Wheat Yield
- (1)
- (2)
- N mineralization of different manure types varies with the content of N and lignin, C/N ratio, and lignin/N ratio [45], and the mineralized N from manure correlates negatively with C/N ratio. The amendments with C/N ratios > 19:1 immobilized N, whereas amendments with C/N ratios < 14:1 mineralized N [46]. In our study, we used manure with a C/N ratio of 17 and 24 over two seasons, which implied that mineralization was limited to a certain extent;
- (3)
- Temperature affects mineralization: N mineralization was minimal during the winter when the temperature was low (~10 °C) but likely increased in spring and summer with higher temperatures (25–30 °C) [47]. Mean daily air temperature from sowing to anthesis was −7.1 to 22.4 °C and −4.2 to 21.3 °C over two seasons in our study.
4.2. Effect of Fertilization and Variety on N Use Efficiency
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IFA. Fertilizer Use by Crop and Country for the 2017–2018 Period; International Fertilizer Association (IFA): Paris, France, 2022; Available online: https://www.ifastat.org/consumption/fertilizeruse-by-crop (accessed on 14 September 2023).
- Fischer, R.A. Farming Systems of Australia. In Crop Physiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 22–54. ISBN 978-0-12-374431-9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xiong, W.; Mottaleb, K.A.; Krupnik, T.J.; Burgueño, J.; Pequeno, D.N.L.; Wu, W. Contrasting Contributions of Five Factors to Wheat Yield Growth in China by Process-Based and Statistical Models. Eur. J. Agron. 2021, 130, 126370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadras, V.O.; Hayman, P.T.; Rodriguez, D.; Monjardino, M.; Bielich, M.; Unkovich, M.; Mudge, B.; Wang, E. Interactions between Water and Nitrogen in Australian Cropping Systems: Physiological, Agronomic, Economic, Breeding and Modelling Perspectives. Crop Pasture Sci. 2016, 67, 1019–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Sadras, V.O.; Xu, J.; Hu, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S. Genetic Improvement of Crop Yield, Grain Protein and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Wheat, Rice and Maize in China. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 168, pp. 203–252. ISBN 978-0-12-824589-7. [Google Scholar]
- Angus, J.F.; Grace, P.R. Nitrogen Balance in Australia and Nitrogen Use Efficiency on Australian Farms. Soil Res. 2017, 55, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing Nitrogen for Sustainable Development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Xu, X.; Zhou, W.; Smith, W.; He, W.; Grant, B.; Ding, W.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, S. Ensuring Future Agricultural Sustainability in China Utilizing an Observationally Validated Nutrient Recommendation Approach. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 132, 126409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, C.; Xu, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, L. Farmland Scale and Chemical Fertilizer Use in Rural China: New Evidence from the Perspective of Nutrient Elements. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 376, 134278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Ying, H.; Zhang, F.; Cui, Z. Comprehensive Assessment of the Utilization of Manure in China’s Croplands Based on National Farmer Survey Data. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Cui, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Niu, W. Effects of Manure Fertilizer on Crop Yield and Soil Properties in China: A Meta-Analysis. CATENA 2020, 193, 104617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Ma, L.; Jin, S.; Ma, W.; Velthof, G.L.; Oenema, O.; Liu, L.; Chadwick, D.; Zhang, F. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium Flows through the Manure Management Chain in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 13409–13418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Sharma, V.; Shukla, A.K.; Verma, V.; Kaur, M.; Singh, P.; Gaber, A.; Hossain, A. Effect of Addition of Organic Manures on Basmati Yield, Nutrient Content and Soil Fertility Status in North-Western India. Heliyon 2023, 9, e14514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; De Jonge, L.W.; Moldrup, P.; Paradelo, M.; Arthur, E. Improvements in Soil Physical Properties after Long-Term Manure Addition Depend on Soil and Crop Type. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; He, X.; Evgenia, B. Improved Nitrogen Use Efficiency, Carbon Sequestration and Reduced Environmental Contamination under a Gradient of Manure Application. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Lei, T.; Du, W.; Liang, C.L.; Li, H.D.; Lv, J.L. Substituting Chemical Fertilizer Nitrogen with Organic Manure and Comparing Their Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Winter Wheat Yield. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 158, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Kalkhajeh, Y.K.; Hu, H. Partial Substitution of Chemical N with Solid Cow Manure Improved Soil Ecological Indicators and Crop Yield in a Wheat–Rice Rotation System. Agronomy 2024, 14, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B.; Mei, X. Grain Yield and Water Productivity of Winter Wheat Controlled by Irrigation Regime and Manure Substitution in the North China Plain. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 295, 108731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Saeed, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, R.; Liu, L.; Lv, F.; Xu, J.; Han, Y.; Zhang, P.; Hu, C.; et al. Manure Replacing Synthetic Fertilizer Improves Crop Yield Sustainability and Reduces Carbon Footprint under Winter Wheat–Summer Maize Cropping System. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 358, 120936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.; Hou, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, W. Partial Substitution of Urea Fertilizers by Manure Increases Crop Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of a Wheat–Maize Double Cropping System. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2022, 127, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yang, S.; Luan, C.; Wu, Q.; Lin, L.; Li, X.; Che, Z.; Zhou, D.; Dong, Z.; Song, H. Partial Organic Substitution for Synthetic Fertilizer Improves Soil Fertility and Crop Yields While Mitigating N2O Emissions in Wheat-Maize Rotation System. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 154, 127077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitonyo, O.M.; Sadras, V.O.; Zhou, Y.; Denton, M.D. Evaluation of Historic Australian Wheat Varieties Reveals Increased Grain Yield and Changes in Senescence Patterns but Limited Adaptation to Tillage Systems. Field Crops Res. 2017, 206, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Xie, Y.; Hu, L.; Feng, B.; Li, S. Remobilization of Vegetative Nitrogen to Developing Grain in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Wu, X.; Li, C.; Li, M.; Xiong, T.; Tang, Y. Dry Matter and Nitrogen Accumulation, Partitioning, and Translocation in Synthetic-Derived Wheat Cultivars under Nitrogen Deficiency at the Post-Jointing Stage. Field Crops Res. 2020, 248, 107720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaju, O.; Allard, V.; Martre, P.; Le Gouis, J.; Moreau, D.; Bogard, M.; Hubbart, S.; Foulkes, M.J. Nitrogen Partitioning and Remobilization in Relation to Leaf Senescence, Grain Yield and Grain Nitrogen Concentration in Wheat Cultivars. Field Crops Res. 2014, 155, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; He, L.; Ali, I.; Ullah, S.; Khan, A.; Akhtar, K.; Wei, S.; Fahad, S.; Khan, R.; Jiang, L. Co-Incorporation of Manure and Inorganic Fertilizer Improves Leaf Physiological Traits, Rice Production and Soil Functionality in a Paddy Field. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Han, G.; He, H.; Westcott, M. Yield, Protein, and Remobilization of Water Soluble Carbohydrate and Nitrogen of Three Spring Wheat Cultivars as Influenced by Nitrogen Input. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, G.F.; Bélanger, G.; Drapeau, R. Nitrogen Fertilizer Application and Developmental Stage Affect Silage Quality of Timothy (Phleum pratense L.). Grass Forage Sci. 2005, 60, 337–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beche, E.; Benin, G.; Da Silva, C.L.; Munaro, L.B.; Marchese, J.A. Genetic Gain in Yield and Changes Associated with Physiological Traits in Brazilian Wheat during the 20th Century. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 61, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Deng, A.; Zhang, W.; Li, W.; Qiao, Y.; Yang, T.; Zheng, C.; Cao, C.; Chen, F. Long-Term Inorganic plus Organic Fertilization Increases Yield and Yield Stability of Winter Wheat. Crop J. 2018, 6, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabato, W.; Ergudo, T.; Mutum, L.; Janda, T.; Molnár, Z. Response of Wheat to Combined Application of Nitrogen and Phosphorus along with Compost. J. Crop Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 25, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Song, J.; Giltrap, D.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S. Crop Yield and N2O Emission Affected by Long-Term Organic Manure Substitution Fertilizer under Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Cropping System. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Song, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, G.; Abbott, L.K.; Zhang, F.; Li, F.-M. Yield Benefits from Joint Application of Manure and Inorganic Fertilizer in a Long-Term Field Pea, Wheat and Potato Crop Rotation. Field Crops Res. 2023, 294, 108873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A Decimal Code for the Growth Stages of Cereals. Weed Res. 1974, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemm, E.W.; Willis, A.J. The Estimation of Carbohydrates in Plant Extracts by Anthrone. Biochem. J. 1954, 57, 508–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fan, H.; Wen, X.; Han, J.; Liao, Y. Optimizing Planting Pattern and Nitrogen Application Rate Improves Grain Yield and Water Use Efficiency for Rain-Fed Spring Maize by Promoting Root Growth and Reducing Redundant Root Growth. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasko, T.; Pyda, S.; Ivanova, I. Effect of Living Mulch on Soil Conditions and Morphometrical Indices of Sweet Cherry Trees. Int. J. Appl. Agric. Sci. 2021, 7, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearsall, W.H. Growth Studies VI. On the Relative Sizes of Growing Plant Organs. Ann. Bot. 1927, 41, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, J.T.; Veyradier, M.; Borrell, A.K.; Harvey, G.; Fletcher, S.; Chenu, K. Phenotyping Novel Stay-Green Traits to Capture Genetic Variation in Senescence Dynamics. Funct. Plant Biol. 2014, 41, 1035–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Sadras, V.O.; Lu, G.; Zhang, R.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S. Root Pruning Enhances Wheat Yield, Harvest Index and Water-Use Efficiency in Semiarid Area. Field Crops Res. 2019, 230, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Nelson, P.N.; Bird, M.I. The Effects of Biochar, Compost and Their Mixture and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Barley Grown on a Nitisol in the Highlands of Ethiopia. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 869–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatholahi, S.; Ehsanzadeh, P.; Karimmojeni, H. Ancient and Improved Wheats Are Discrepant in Nitrogen Uptake, Remobilization, and Use Efficiency yet Comparable in Nitrogen Assimilating Enzymes Capabilities. Field Crops Res. 2020, 249, 107761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchmann, H.; Kätterer, T.; Bergström, L.; Börjesson, G.; Bolinder, M.A. Flaws and Criteria for Design and Evaluation of Comparative Organic and Conventional Cropping Systems. Field Crops Res. 2016, 186, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Pu, S.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Razavi, B.S. Impact of Manure on Soil Biochemical Properties: A Global Synthesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubarak, A.R.; Gali, E.A.M.; Mohamed, A.G.; Steffens, D.; Awadelkarim, A.H. Nitrogen Mineralization from Five Manures as Influenced by Chemical Composition and Soil Type. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2010, 41, 1903–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazicki, P.; Geisseler, D.; Lloyd, M. Nitrogen Mineralization from Organic Amendments Is Variable but Predictable. J. Environ. Qual. 2020, 49, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watts, D.B.; Torbert, H.A.; Prior, S.A. Soil Property and Landscape Position Effects on Seasonal Nitrogen Mineralization of Composted Dairy Manure. Soil Sci. 2010, 175, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Gao, P.; Tong, Y.; Norse, D.; Lu, Y.; Powlson, D. Overcoming Nitrogen Fertilizer Over-Use through Technical and Advisory Approaches: A Case Study from Shaanxi Province, Northwest China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 209, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Ma, D.; Kang, G. Determining the Optimal N Input to Improve Grain Yield and Quality in Winter Wheat with Reduced Apparent N Loss in the North China Plain. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, A.; Liu, H.; Zhai, L.; Lei, B.; Ren, T. An Optimal Regional Nitrogen Application Threshold for Wheat in the North China Plain Considering Yield and Environmental Effects. Field Crops Res. 2017, 207, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Shi, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Zheng, W.; Li, Z.; Zhai, B. 15N Labelling of Cattle Manure Reveals the Distribution of Organic Fertiliser Nitrogen in a Winter Wheat System. Field Crops Res. 2022, 283, 108529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dordas, C. Variation in Dry Matter and Nitrogen Accumulation and Remobilization in Barley as Affected by Fertilization, Cultivar, and Source–Sink Relations. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 37, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, C.; Yu, H.; Cao, B.; Tian, S.; Liao, Y.; Siddique, K.H.M. Wheat Yield Improvements in China: Past Trends and Future Directions. Field Crops Res. 2015, 177, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadras, V.O.; Lawson, C. Genetic Gain in Yield and Associated Changes in Phenotype, Trait Plasticity and Competitive Ability of South Australian Wheat Varieties Released between 1958 and 2007. Crop Pasture Sci. 2011, 62, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.G.; Qian, Z.G.; Wu, K.; Liu, J.J.; Xia, X.C.; Ji, W.Q.; He, Z.H. Genetic Gains in Grain Yield and Physiological Traits of Winter Wheat in Shandong Province, China, from 1969 to 2006. Crop Sci. 2012, 52, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeaud, G.; Karatoğma, H.; Özturk, I.; Roumet, P.; Ecarnot, M.; Crossa, J.; Özer, E.; Özdemir, F.; Lopes, M.S. Predicting Wheat Maturity and Stay–Green Parameters by Modeling Spectral Reflectance Measurements and Their Contribution to Grain Yield under Rainfed Conditions. Field Crops Res. 2016, 196, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadras, V.O.; Mahadevan, M.; Zwer, P.K. Stay-Green Associates with Low Water Soluble Carbohydrates at Flowering in Oat. Field Crops Res. 2019, 230, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manschadi, A.M.; Soltani, A. Variation in Traits Contributing to Improved Use of Nitrogen in Wheat: Implications for Genotype by Environment Interaction. Field Crops Res. 2021, 270, 108211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Zhu, Y.-H.; Chai, N.; Zhang, X.-T.; Du, Y.-L.; Turner, N.C.; Du, P.; Li, F.-M. Increased Grain Yield in Modern Genotypes of Spring Wheat for Dryland Cultivation in Northwest China Is Associated with the Decreased Allocation of Carbon to Roots. Field Crops Res. 2023, 303, 109114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-H.; Weiner, J.; Jin, Y.; Yu, M.-X.; Li, F.-M. Biomass Allocation Responses to Root Interactions in Wheat Cultivars Support Predictions of Crop Evolutionary Ecology Theory. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 858636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindtler, N.L.; Sheikh, S.; Richardy, J.; Krogh, E.; Maccario, L.; Vestergård, M.; Da Fonseca, R.R.; Ekelund, F.; Laursen, K.H. Fertilizer Regime and Cultivar Affect Barley Growth and Rhizobiome Composition. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 198, 105384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fageria, N.K. Nitrogen Harvest Index and Its Association with Crop Yields. J. Plant Nutr. 2014, 37, 795–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, S.; Tian, H.; Wang, Z. Variations of winter wheat nitrogen harvest index in field wheat population. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2021, 54, 583–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afreh, D.; Zhang, J.; Guan, D.; Liu, K.; Song, Z.; Zheng, C.; Deng, A.; Feng, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; et al. Long-Term Fertilization on Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Greenhouse Gas Emissions in a Double Maize Cropping System in Subtropical China. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 180, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.M.; Messina, C.D.; Vyn, T.J. Simultaneous Gains in Grain Yield and Nitrogen Efficiency over 70 Years of Maize Genetic Improvement. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, M.; Gao, S.; Yang, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, B. Nitrogen Use Efficiency in a Wheat–Corn Cropping System from 15 Years of Manure and Fertilizer Applications. Field Crops Res. 2014, 157, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Sun, Y.; Zou, H.; Li, D.; Lu, C.; Duan, Y.; Zhang, W. Effect of Replacing Synthetic Nitrogen Fertilizer with Animal Manure on Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency in China: A Meta-analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1153235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Pandey, P.C.; Nanda, G.; Gupta, S. Long-Term Effects of Inorganic Fertilizer and Farmyard Manure Application on Productivity, Sustainability and Profitability of Rice-Wheat System in Mollisols. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaduvanshi, N.P.S. Substitution of Inorganic Fertilizers by Organic Manures and the Effect on Soil Fertility in a Rice–Wheat Rotation on Reclaimed Sodic Soil in India. J. Agric. Sci. 2003, 140, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caviglia, O.P.; Melchiori, R.J.M.; Sadras, V.O. Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency in Maize as Affected by Hybrid and N Rate in Late-Sown Crops. Field Crops Res. 2014, 168, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muurinen, S.; Slafer, G.A.; Peltonen-Sainio, P. Breeding Effects on Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Spring Cereals under Northern Conditions. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira Silva, A.; Ciampitti, I.A.; Slafer, G.A.; Lollato, R.P. Nitrogen Utilization Efficiency in Wheat: A Global Perspective. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 114, 126008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, D.J. Land Required for Legumes Restricts the Contribution of Organic Agriculture to Global Food Security. Outlook Agric. 2018, 47, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, D.J. Analysis of Farming Systems Establishes the Low Productivity of Organic Agriculture and Inadequacy as a Global Option for Food Supply. Npj Sustain. Agric. 2024, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Season (S) | Fertilization (F) | Variety (V) | S × F | S × V | F × V | S × F × V | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (kg ha−1) | 0.1759 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.3937 | 0.0055 | 0.0034 | 0.0014 |
| Biomass (kg ha−1) | 0.2055 | <0.0001 | 0.0022 | 0.0052 | 0.2719 | 0.0372 | 0.0022 |
| Harvest index | 0.0076 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0454 | 0.3827 | 0.0578 | 0.3596 |
| Grain number (m−2) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0558 | 0.0394 | 0.0185 |
| Grain weight (g) | <0.0001 | 0.0005 | <0.0001 | 0.5500 | 0.0013 | 0.2983 | 0.4438 |
| WSC at anthesis (kg ha−1) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0804 | 0.0395 | 0.0084 | 0.4044 | 0.8819 |
| WSC at maturity (kg ha−1) | 0.6449 | 0.0142 | 0.0035 | 0.4998 | 0.7589 | 0.4471 | 0.8342 |
| WSC translocation amount (kg ha−1) | <0.0001 | 0.0016 | 0.5283 | 0.1532 | 0.0236 | 0.4554 | 0.9090 |
| WSC translocation ratio (%) | <0.0001 | 0.4389 | 0.0635 | 0.6218 | 0.6336 | 0.5312 | 0.7508 |
| SPADmin | 0.5392 | 0.1068 | 0.7462 | 0.0012 | 0.6045 | 0.5205 | 0.8948 |
| SPADmax | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.1115 | 0.0755 | 0.5278 | 0.0707 |
| x50 (°Cd) | 0.4665 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0140 | 0.0950 | 0.0334 | 0.0159 |
| Rate (°Cd) | 0.7072 | 0.0184 | 0.5110 | 0.0163 | 0.2996 | 0.1928 | 0.7482 |
| Area (°Cd) | 0.2426 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.1871 | 0.0034 | 0.0072 | 0.0152 |
| Total N uptake at anthesis (kg ha−1) | 0.2955 | <0.0001 | 0.4150 | 0.2251 | 0.4977 | 0.0230 | 0.8531 |
| Total N uptake at maturity (kg ha−1) | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.3960 | 0.3057 | 0.2906 | 0.0533 | 0.0126 |
| N translocation (kg ha−1) | 0.4982 | <0.0001 | 0.2174 | 0.3309 | 0.3519 | 0.0189 | 0.9100 |
| N translocation efficiency (%) | 0.3069 | 0.8314 | 0.0061 | 0.5222 | 0.0959 | 0.2176 | 0.9726 |
| N harvest index | <0.0001 | 0.1712 | 0.0005 | 0.4213 | 0.0451 | 0.9086 | 0.3196 |
| N utilization efficiency (kg kg−1) | <0.0001 | 0.0004 | 0.0019 | 0.4276 | 0.0005 | 0.9503 | 0.8259 |
| Partial factor productivity (kg kg−1) | 0.3255 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.7248 | 0.0012 | <0.0001 | 0.0012 |
| GY | TGW | GN/m2 | DM ant | DM mat | HI | SPADmax | Rate | x50 | SPAD min | Area | WSC ant | WSC mat | WSC Amount | WSC Ratio | Nup ant | Nup mat | NHI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −0.25 | TGW | |||||||||||||||||
| 0.29 | 0.05 | GN/m2 | ||||||||||||||||
| 0.69 | −0.17 | 0.33 | DM ant | |||||||||||||||
| 0.86 | −0.19 | 0.34 | 0.95 | DM mat | ||||||||||||||
| 0.70 | −0.19 | 0.05 | 0.00 | 0.25 | HI | |||||||||||||
| 0.76 | −0.20 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.52 | 0.75 | SPADmax | ||||||||||||
| 0.26 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.42 | 0.39 | −0.08 | 0.14 | rate | |||||||||||
| 0.60 | −0.57 | 0.31 | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.55 | 0.43 | −0.23 | x50 | ||||||||||
| 0.20 | -0.10 | 0.12 | 0.18 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.35 | −0.07 | SPADmin | |||||||||
| 0.80 | −0.47 | 0.29 | 0.38 | 0.57 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 0.02 | 0.85 | 0.30 | area | ||||||||
| 0.20 | −0.34 | −0.80 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 0.21 | 0.30 | 0.07 | -0.01 | 0.05 | 0.10 | WSC ant | |||||||
| -0.03 | 0.07 | −0.22 | 0.43 | 0.28 | −0.43 | −0.37 | 0.28 | −0.31 | −0.21 | −0.41 | 0.28 | WSC mat | ||||||
| 0.20 | −0.36 | −0.79 | 0.07 | 0.11 | 0.26 | 0.35 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.14 | 0.99 | 0.18 | WSC amount | |||||
| 0.22 | −0.36 | −0.58 | −0.15 | -0.02 | 0.49 | 0.55 | −0.20 | 0.20 | 0.22 | 0.38 | 0.74 | −0.39 | 0.81 | WSC ratio | ||||
| 0.85 | −0.19 | 0.42 | 0.71 | 0.81 | 0.48 | 0.70 | 0.27 | 0.53 | 0.37 | 0.77 | 0.04 | −0.13 | 0.05 | 0.11 | Nup ant | |||
| 0.89 | −0.30 | 0.01 | 0.60 | 0.76 | 0.64 | 0.83 | 0.29 | 0.49 | 0.19 | 0.74 | 0.41 | −0.01 | 0.42 | 0.39 | 0.80 | Nup mat | ||
| 0.00 | 0.13 | −0.66 | −0.34 | −0.25 | 0.37 | 0.15 | −0.11 | −0.15 | −0.17 | −0.12 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 0.58 | 0.51 | −0.23 | 0.07 | NHI | |
| −0.15 | 0.22 | 0.49 | −0.10 | −0.14 | −0.12 | −0.43 | −0.18 | 0.06 | −0.12 | −0.15 | −0.56 | −0.08 | −0.57 | −0.45 | −0.22 | −0.57 | −0.13 | NutE |
 .
.Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herlinawati, E.; Lei, X.; Yang, M.; Hu, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S. Variety-Dependent Yield and Physiological Responses to Combined Inorganic and Organic Sources of Nitrogen in Wheat. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071679
Herlinawati E, Lei X, Yang M, Hu C, Yang X, Zhang S. Variety-Dependent Yield and Physiological Responses to Combined Inorganic and Organic Sources of Nitrogen in Wheat. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071679
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerlinawati, Eva, Xiaoxiao Lei, Maoling Yang, Changlu Hu, Xueyun Yang, and Shulan Zhang. 2025. "Variety-Dependent Yield and Physiological Responses to Combined Inorganic and Organic Sources of Nitrogen in Wheat" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071679
APA StyleHerlinawati, E., Lei, X., Yang, M., Hu, C., Yang, X., & Zhang, S. (2025). Variety-Dependent Yield and Physiological Responses to Combined Inorganic and Organic Sources of Nitrogen in Wheat. Agronomy, 15(7), 1679. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071679







