Heavy Metal Immobilization by Phosphate-Solubilizing Fungus and Phosphogypsum Under the Co-Existence of Pb(II) and Cd(II)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PG Preparation and A. niger Activation
2.2. A. niger Incubation
2.3. Chemical Properties and Spectral Analysis
2.4. Instrumentation
3. Results
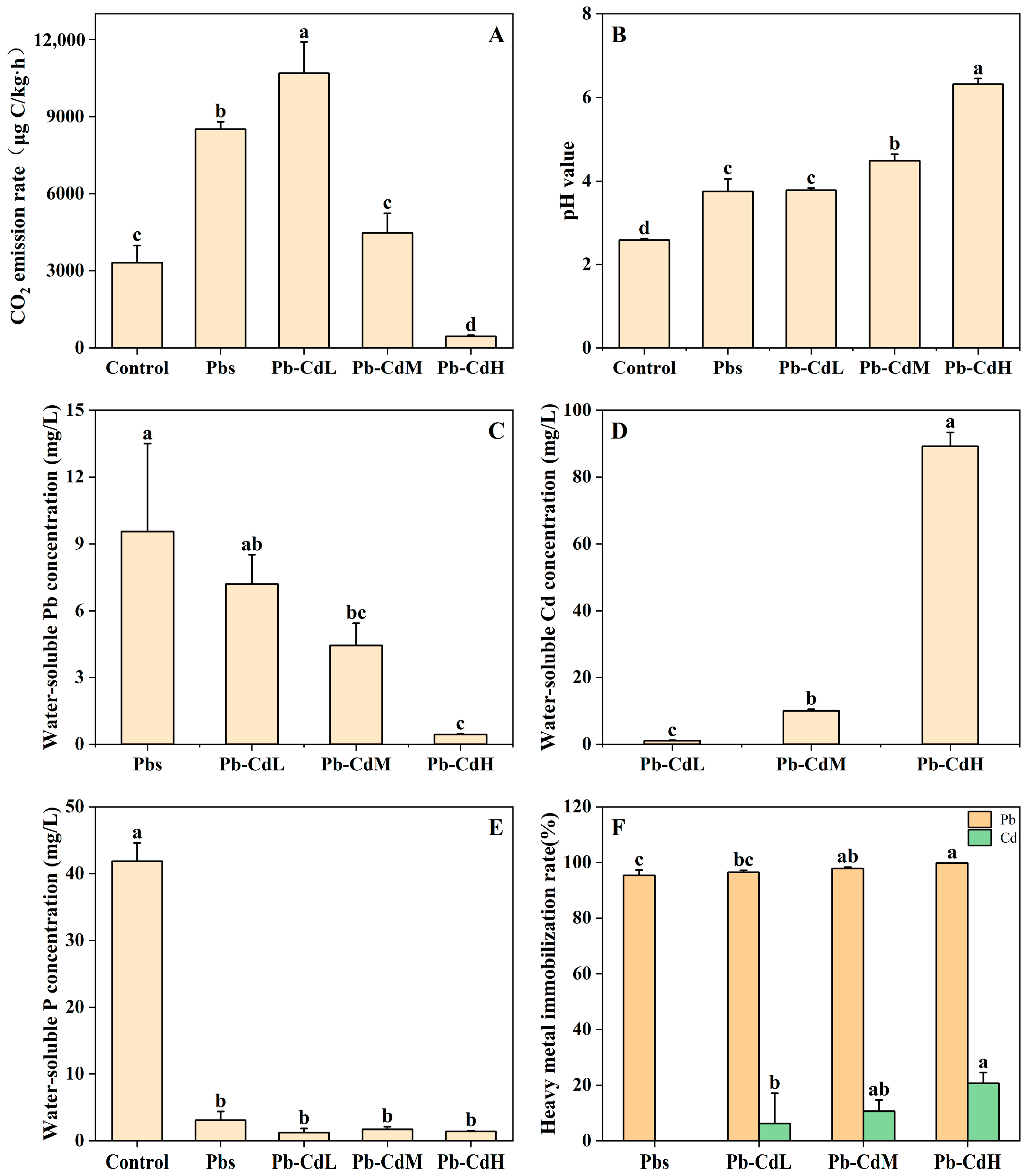
3.1. CO2 Emission Rate and pH Value
3.2. Pb, Cd, and P Concentrations
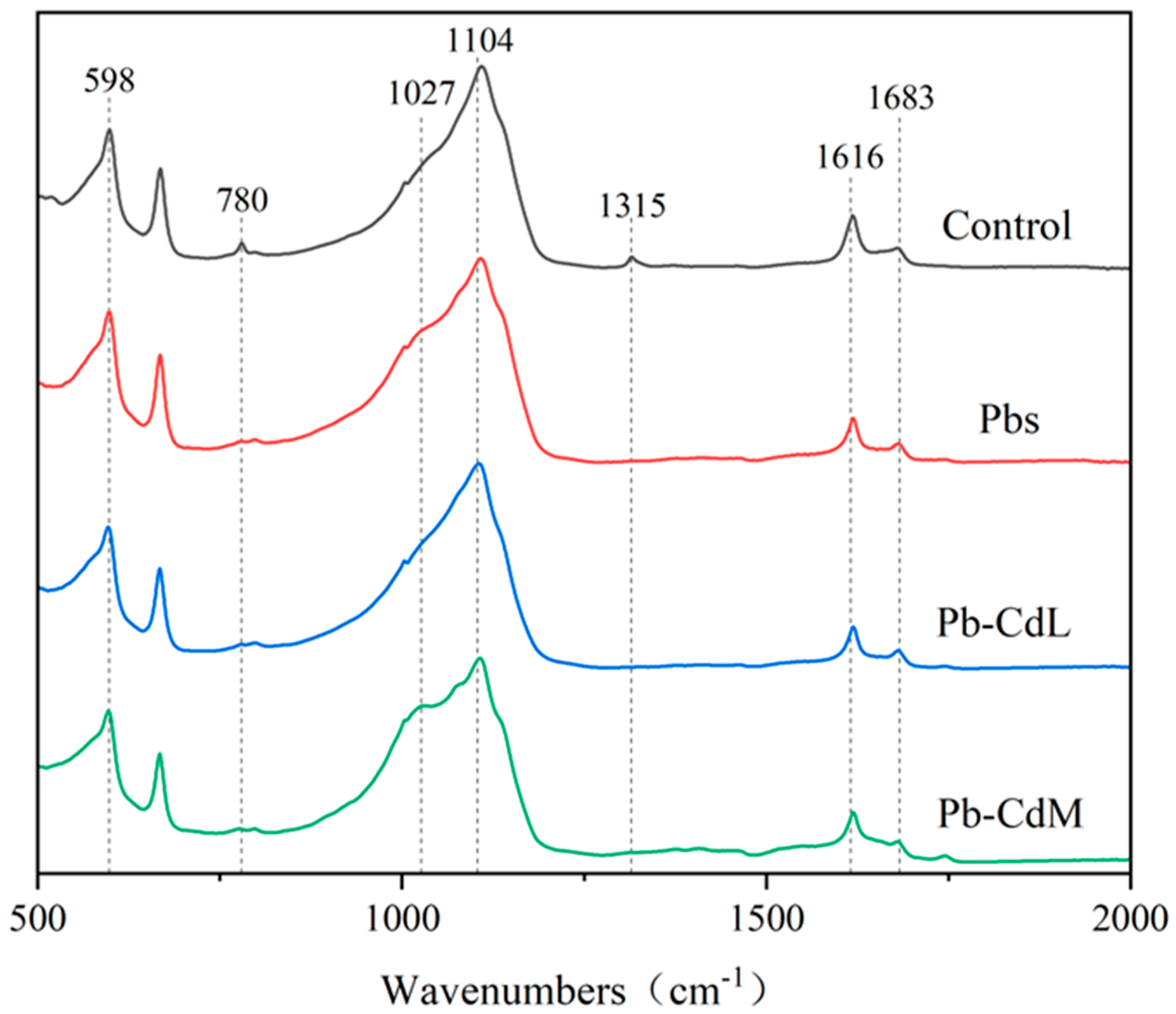
3.3. ATR-IR Analysis
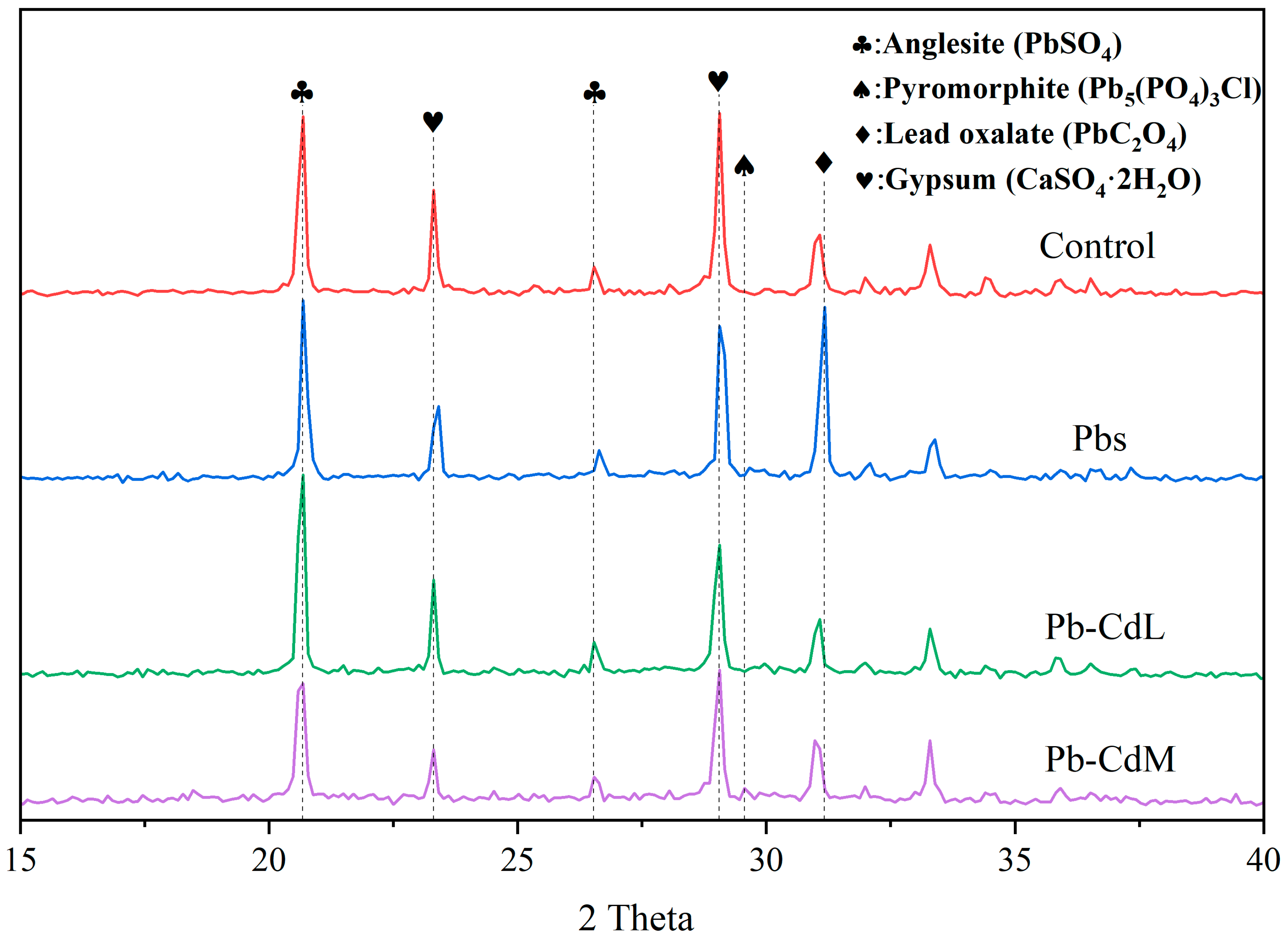
3.4. XRD Analysis
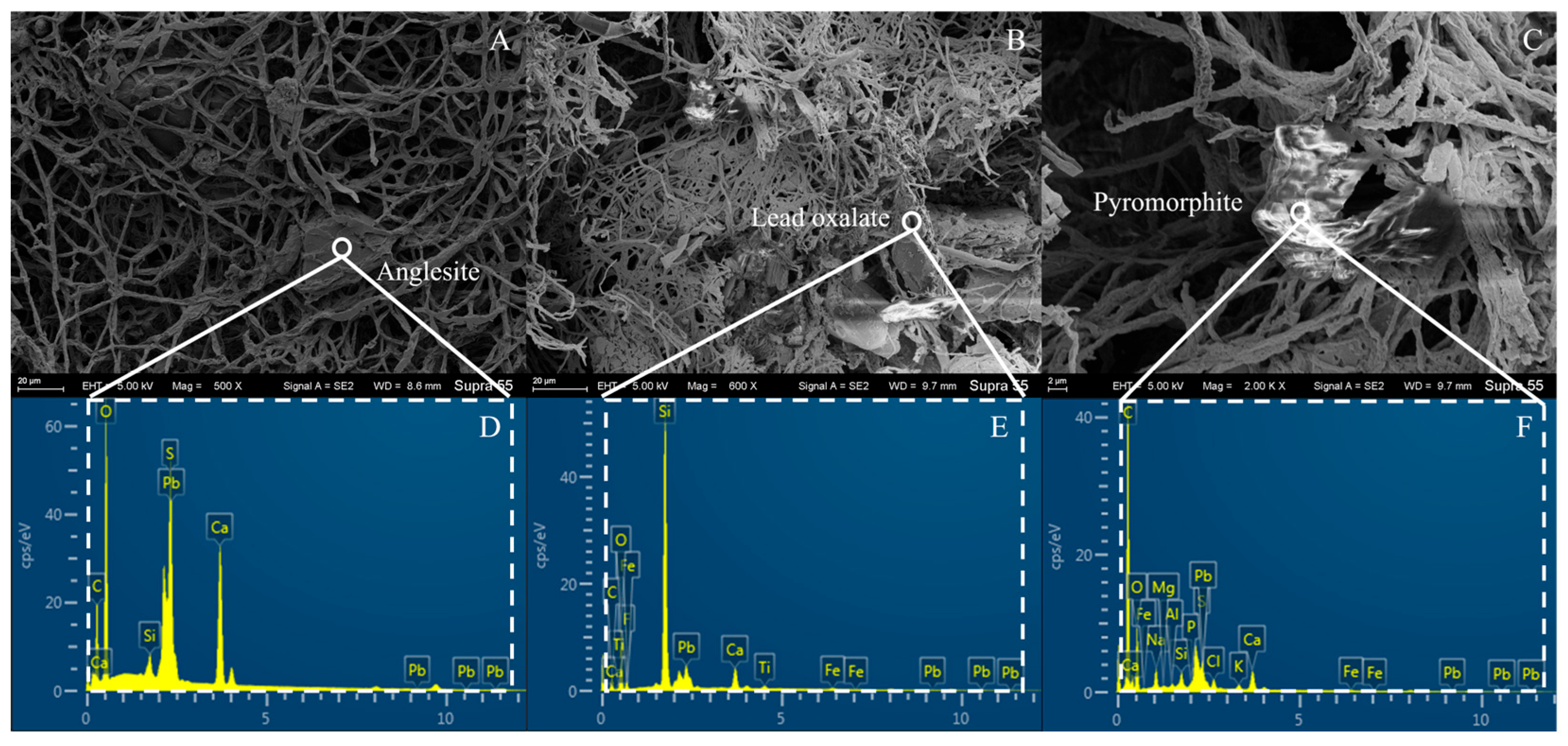
3.5. SEM-EDS Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rassaei, F. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm Modeling of Lead in Calcareous Soils: Insights into Thermodynamics, Desorption, and Soil Properties. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2023, 54, 2059–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Song, Q.; Tang, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Brookes, P.C. Human health risk assessment of heavy metals in soil-vegetable system: A multi-medium analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fewtrell, L.J.; Prüss-Üstün, A.; Landrigan, P.; Ayuso-Mateos, J.L. Estimating the global burden of disease of mild mental retardation and cardiovascular diseases from environmental lead exposure. Environ. Res. 2004, 94, 120–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newby, P.J.; Gadd, G.M. Synnema induction in penicillium-funiculosum by tributyltin compounds. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 1987, 89, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Cao, L.; Huang, H.; Jiang, X.; Wang, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, R. Characterization of Cd- and Pb-resistant fungal endophyte Mucor sp. CBRF59 isolated from rapes (Brassica chinensis) in a metal-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 185, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zare, M.-R.; Amin, M.-M.; Nikaeen, M.; Bina, B.; Rahmani, A.; Hemmati-Borji, S.; Rahmani, H. Acute toxicity of Hg, Cd, and Pb towards dominant bacterial strains of sequencing batch reactor (SBR). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genchi, G.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Lauria, G.; Carocci, A.; Catalano, A. The Effects of Cadmium Toxicity. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadd, G.M. Interactions of fungi with toxic metals. New Phytol. 1993, 124, 25–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Hu, Y.; Gong, Y.; Wu, X.; Ju, T.; Hou, H.; Zhao, L. Status of lead accumulation in agricultural soils across China (1979–2016). Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.S.; De Sherbinin, A.; Ye, C.; Shi, G.Q. China’s Soil Pollution: Farms on the Frontline. Science 2014, 344, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xiao, Q.; Li, B.; Zhou, T.; Cen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y. Insights into remediation of cadmium and lead contaminated-soil by Fe-Mn modified biochar. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, D.; Li, X. The Status and Research Progress of Cadmium Pollution in Rice- (Oryza sativa L.) and Wheat- (Triticum aestivum L.) Cropping Systems in China: A Critical Review. Toxics 2022, 10, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Yang, X.; Dai, X.; Zhang, Q.; Malik, A.; Sadeghpour, A. Heavy metal pollution risk assessments and their transportation in sediment and overlay water for the typical Chinese reservoirs. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 112, 106166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, B.; Lin, Q.; Hamid, Y.; Sanaullah, M.; Di, L.; Hashmi, M.L.U.R.; Khan, M.B.; He, Z.; Yang, X. Foliage application of selenium and silicon nanoparticles alleviates Cd and Pb toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Su, M.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; Hu, S. A new insight into lead (II) tolerance of environmental fungi based on a study of Aspergillus niger and Penicillium oxalicum. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cui, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Cui, Z. Combined toxicity and detoxification of lead, cadmium and arsenic in Solanum nigrum L. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Lombi, E.; McGrath, S.P. Assessing the potential for zinc and cadmium phytoremediation with the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Soil 2003, 249, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, J.A.; Kazi, T.G.; Shah, A.Q.; Arain, M.B.; Afridi, H.I.; Khan, S.; Kandhro, G.A.; Soomro, A.S. Evaluating the accumulation of arsenic in maize (Zea mays L.) plants from its growing media by cloud point extraction. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 48, 3051–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komjarova, I.; Blust, R. Multimetal interactions between Cd, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn uptake from water in the zebrafish Danio rerio. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 7225–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Fowler, B.A. Roles of biomarkers in evaluating interactions among mixtures of lead, cadmium and arsenic. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 233, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y.; Li, D.; Li, M. Combined toxicity of cadmium and lead on the earthworm Eisenia fetida (Annelida, Oligochaeta). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 81, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothilf, Y.; Coon, S.L.; Toyama, R.; Chitnis, A.; Namboodiri, M.A.A.; Klein, D.C. Zebrafish serotonin N-acetyltransferase-2: Marker for development of pineal photoreceptors and circadian clock function. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 4895–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, G.; Su, P. Research Progress on Physical and Chemical Remediation Methods for the Removal of Cadmium from Soil. Separations 2024, 11, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, K.T.; Shukor, M.Y.; Wasoh, H. Physical, Chemical, and Biological Methods for the Removal of Arsenic Compounds. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 503784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, F.; Giotta, L.; Lambreva, M.D. Perspectives on nanomaterial-empowered bioremediation of heavy metals by photosynthetic microorganisms. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 216, 109090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, J.; Liu, S.; Li, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Zeng, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Remediation of heavy metal-contaminated estuarine sediments by strengthening microbial in-situ mineralization. Appl. Geochem. 2024, 169, 106051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Chao, Y.Q.; Li, Y.Y.; Lin, Q.Q.; Bai, J.; Tang, L.; Wang, S.Z.; Ying, R.R.; Qiu, R.L. Survival Strategies of the Plant-Associated Bacterium Enterobacter sp. Strain EG16 under Cadmium Stress. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.B.; Shi, J.J.; Wang, C.H.; Chang, J.S. Biosorption of lead, copper and cadmium by an indigenous isolate Enterobacter sp. J1 possessing high heavy-metal resistance. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 134, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Yu, C. Nitrogen-cycling processes under long-term compound heavy metal(loids) pressure around a gold mine: Stimulation of nitrite reduction. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 147, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Song, X.; Li, S.; Zhu, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z. Experimental and modeling studies of competitive Pb (II) and Cd (II) bioaccumulation by Aspergillus niger. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 6477–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Meng, L.; Su, M.; Wang, Z.; Nong, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, Z. Weakened Cd toxicity to fungi under coexistence of Pb in solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 127984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, R.K.; Khatri, V.N.; Panwar, V. Strength characteristics of fly ash stabilized with lime and modified with phosphogypsum. J. Build. Eng. 2017, 14, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajam, L.; Hassen, A.B.; Reguigui, N. Phosphogypsum utilization in fired bricks: Radioactivity assessment and durability. J. Build. Eng. 2019, 26, 100928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, I.A.; Sert, Y. Utilization of weathered phosphogypsum as set retarder in Portland cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Song, H.; Han, Y.; Dong, F.; Zhou, L. Rapid removal of uranium (VI) by phosphogypsum immobilized sulfate-reducing bacteria microspheres. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Ding, K.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huo, H.; Yu, D.; Tian, D.; Li, Z. Application of phosphogypsum and phosphate-solubilizing fungi to Pb remediation: From simulation to in vivo incubation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 933, 173171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, V.; Labrincha, J.; Dias-Ferreira, C. Extraction of phosphorus and struvite production from the anaerobically digested organic fraction of municipal solid waste. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2837–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Dai, M.; Lu, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. Risk assessment and driving factors for artificial topography on element heterogeneity: Case study at Jiangsu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 246–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Su, M.; Duan, X.; Tian, D.; Yang, M.; Guo, J.; Wang, S.; Hu, S. Induced biotransformation of lead (II) by Enterobacter sp. in SO4-PO4-Cl solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2018, 357, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourkoumelis, N.; Lani, A.; Tzaphlidou, M. Infrared spectroscopic assessment of the inflammation-mediated osteoporosis (IMO) model applied to rabbit bone. J. Biol. Phys. 2012, 38, 623–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garip, S.; Severcan, F. Determination of simvastatin-induced changes in bone composition and structure by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy in rat animal model. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 52, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeasmin, S.; Singh, B.; Kookana, R.S.; Farrell, M.; Sparks, D.L.; Johnston, C.T. Influence of mineral characteristics on the retention of low molecular weight organic compounds: A batch sorption-desorption and ATR-FTIR study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 432, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yi, H.; Jia, F.; Song, S. Design of MoS2/MMT bi-layered aerogels integrated with phase change materials for sustained and efficient solar desalination. Desalination 2022, 541, 116028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preeda, P.; Ganapathi Raman, R.; Sakthivel, P. Structural, FTIR, FT-Raman, optical and nonlinear optical properties of organic nonlinear optical crystal –3,5-diisopropyl-2-hydroxybenzoic acid. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 146, 110120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Chen, J.; He, X.; Su, Y.; Jin, Z.; Fan, J.; Qi, H.; Wang, B. Comparative analysis of colloid-mechanical microenvironments on the efficient purification of phosphogypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 132037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naimo, T.J. A review of the effects of heavy-metals on fresh-water mussels. Ecotoxicology 1995, 4, 341–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.D.; Gao, X.Y.; Zhang, S.W.; Fu, X.H.; Le, Y.Q.; Wang, L. Cadmium stimulated cooperation between bacterial endophytes and plant intrinsic detoxification mechanism in Lonicera japonica thunb. Chemosphere 2023, 325, 138411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, C.; Ma, L. Concentration, pH, and surface charge effects on cadmium and lead sorption in three tropical soils. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmykova, Y.; Strömvall, A.M.; Steenari, B.M. Adsorption of cd, cu, ni, pb and zn on Sphagnum peat from solutions with low metal concentrations. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 152, 885–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, W.; Xiong, L.; Xu, N.; Ni, J.R. Influence of pH, ionic strength and humic acid on competitive adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II) and Cr(III) onto titanate nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 215, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.H.; Xue, N.D.; Han, Z.G. A meta-analysis of heavy metals pollution in farmland and urban soils in China over the past 20 years. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.D.; Ma, L.Q.; Singh, S.P.; Zhou, Q.X. Phosphate-induced lead immobilization from different lead minerals in soils under varying pH conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miretzky, P.; Fernandez-Cirelli, A. Phosphates for Pb immobilization in soils: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2008, 6, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, C. Chitosan-based biosorbents: Modification and application for biosorption of heavy metals and radionuclides. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 160, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, G.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.; Weng, X.; Lin, S.; Huang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, H.; Tse, L.A.; et al. Joint toxicity of lead and cadmium on the behavior of zebrafish larvae: An antagonism. Aquat. Toxicol. 2021, 238, 105912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angumeenal, A.R.; Venkappayya, D. Growth kinetics of heavy metal adapted Aspergillus niger during citric acid biosynthesis. J. Sci. Ind. Res. 2004, 63, 610–613. [Google Scholar]
- Guha, S.; Debnath, S.; Gayen, S. Comparative Analysis of Hexavalent Chromium Biosorption Efficiency Using Dead and Live Aspergillus nomius Biomass. J. Trop. For. Environ. 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernysh, Y.; Yakhnenko, O.; Chubur, V.; Roubík, H. Phosphogypsum Recycling: A Review of Environmental Issues, Current Trends, and Prospects. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, X.; Jiang, Y.; Ding, C.; Liu, J.; Zhu, C. Synergistic remediation of lead pollution by biochar combined with phosphate solubilizing bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Chao, Z.; Li, H.; Ji, J.; Sun, X.; Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Yao, J.; et al. Heavy Metal Immobilization by Phosphate-Solubilizing Fungus and Phosphogypsum Under the Co-Existence of Pb(II) and Cd(II). Agronomy 2025, 15, 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071632
Li X, Chao Z, Li H, Ji J, Sun X, Chen Y, Li Z, Li Z, Li C, Yao J, et al. Heavy Metal Immobilization by Phosphate-Solubilizing Fungus and Phosphogypsum Under the Co-Existence of Pb(II) and Cd(II). Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071632
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xu, Zhenyu Chao, Haoxuan Li, Jiakai Ji, Xin Sun, Yingxi Chen, Zhengda Li, Zhen Li, Chuanhao Li, Jun Yao, and et al. 2025. "Heavy Metal Immobilization by Phosphate-Solubilizing Fungus and Phosphogypsum Under the Co-Existence of Pb(II) and Cd(II)" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071632
APA StyleLi, X., Chao, Z., Li, H., Ji, J., Sun, X., Chen, Y., Li, Z., Li, Z., Li, C., Yao, J., & Xiang, L. (2025). Heavy Metal Immobilization by Phosphate-Solubilizing Fungus and Phosphogypsum Under the Co-Existence of Pb(II) and Cd(II). Agronomy, 15(7), 1632. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071632






