Improvement of Morkhor 60-3 Upland Rice Variety for Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance Using Marker–Assisted Backcross Selection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
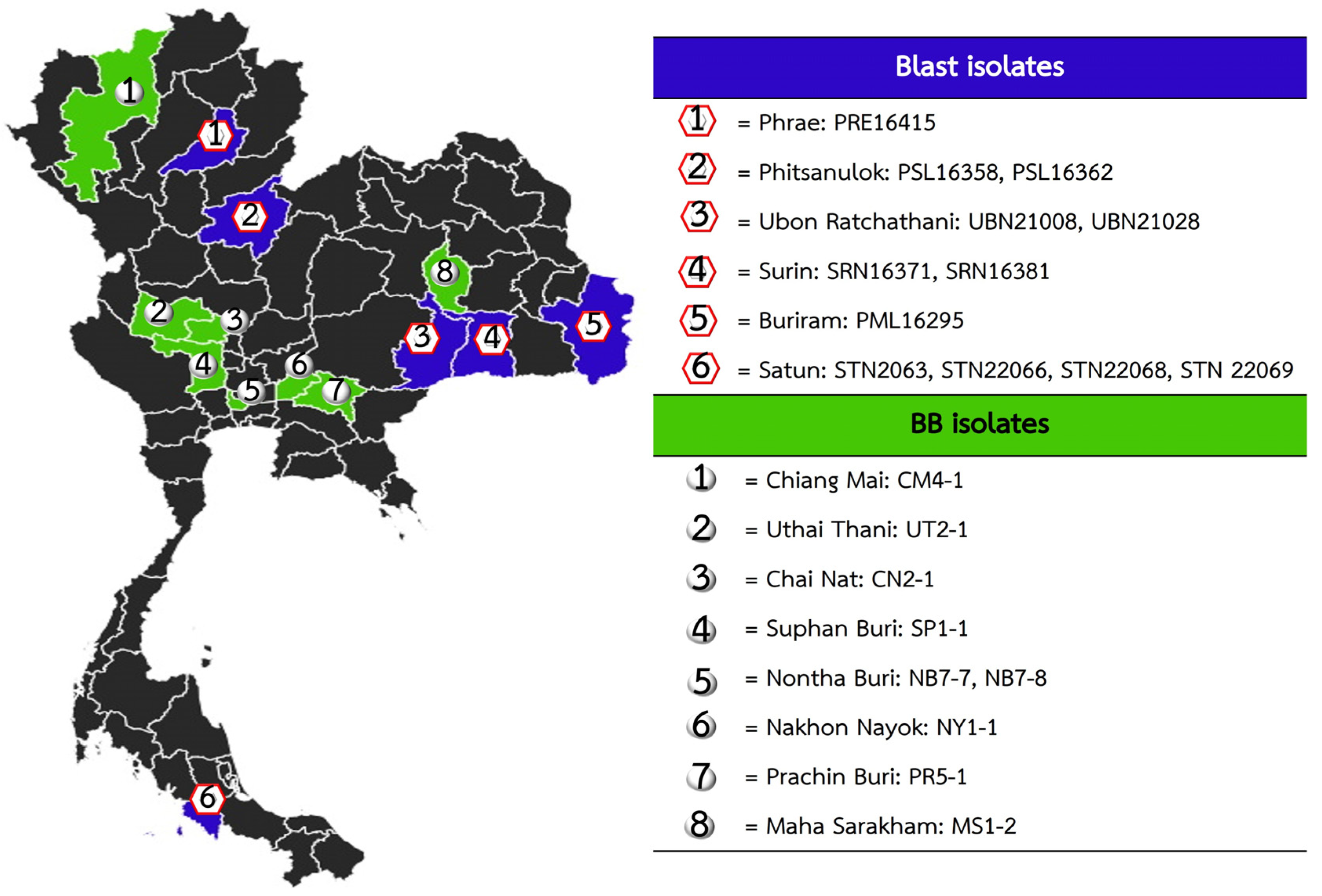
2.1. Population Development Using Marker-Assisted Selection
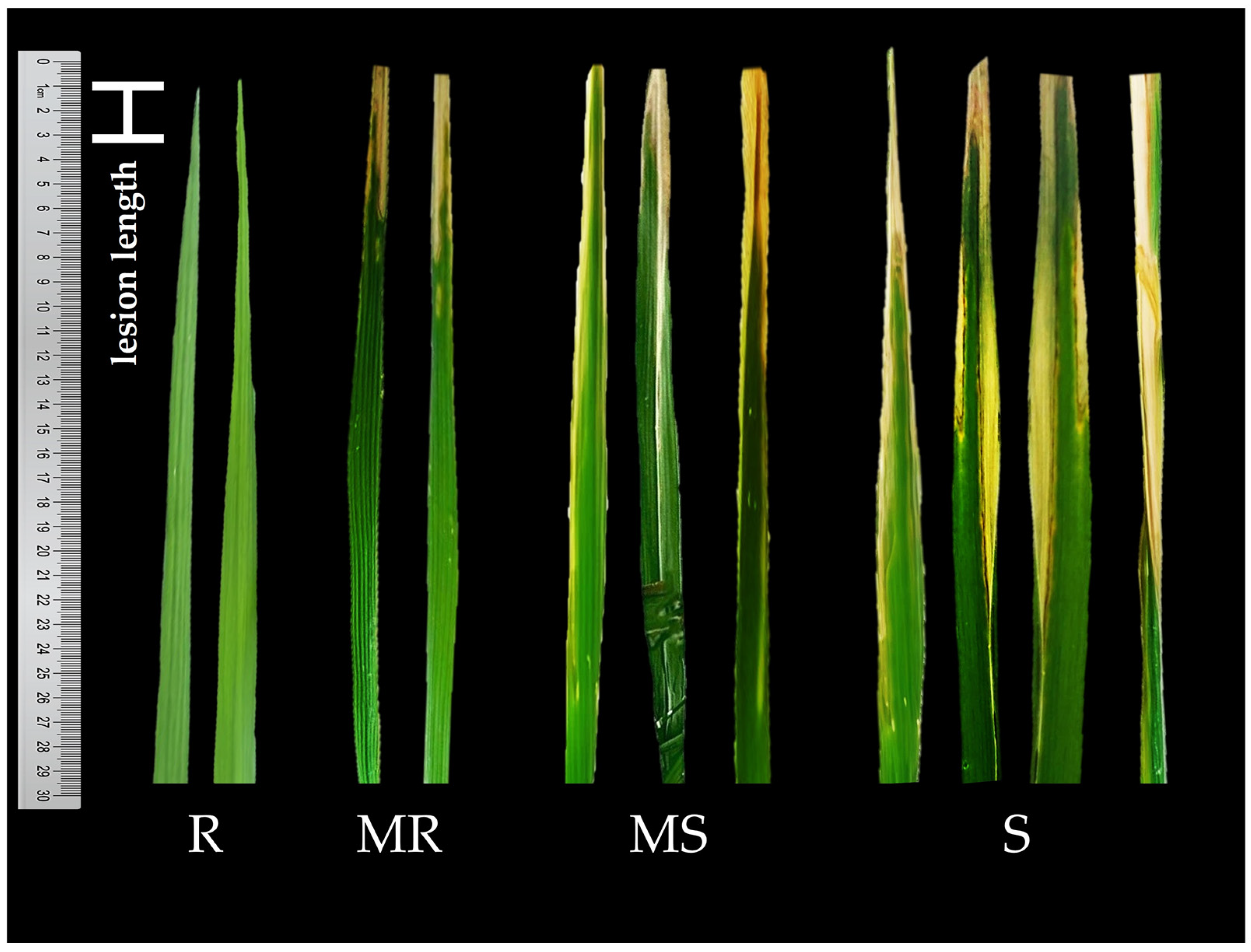
2.2. Evaluation of Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance
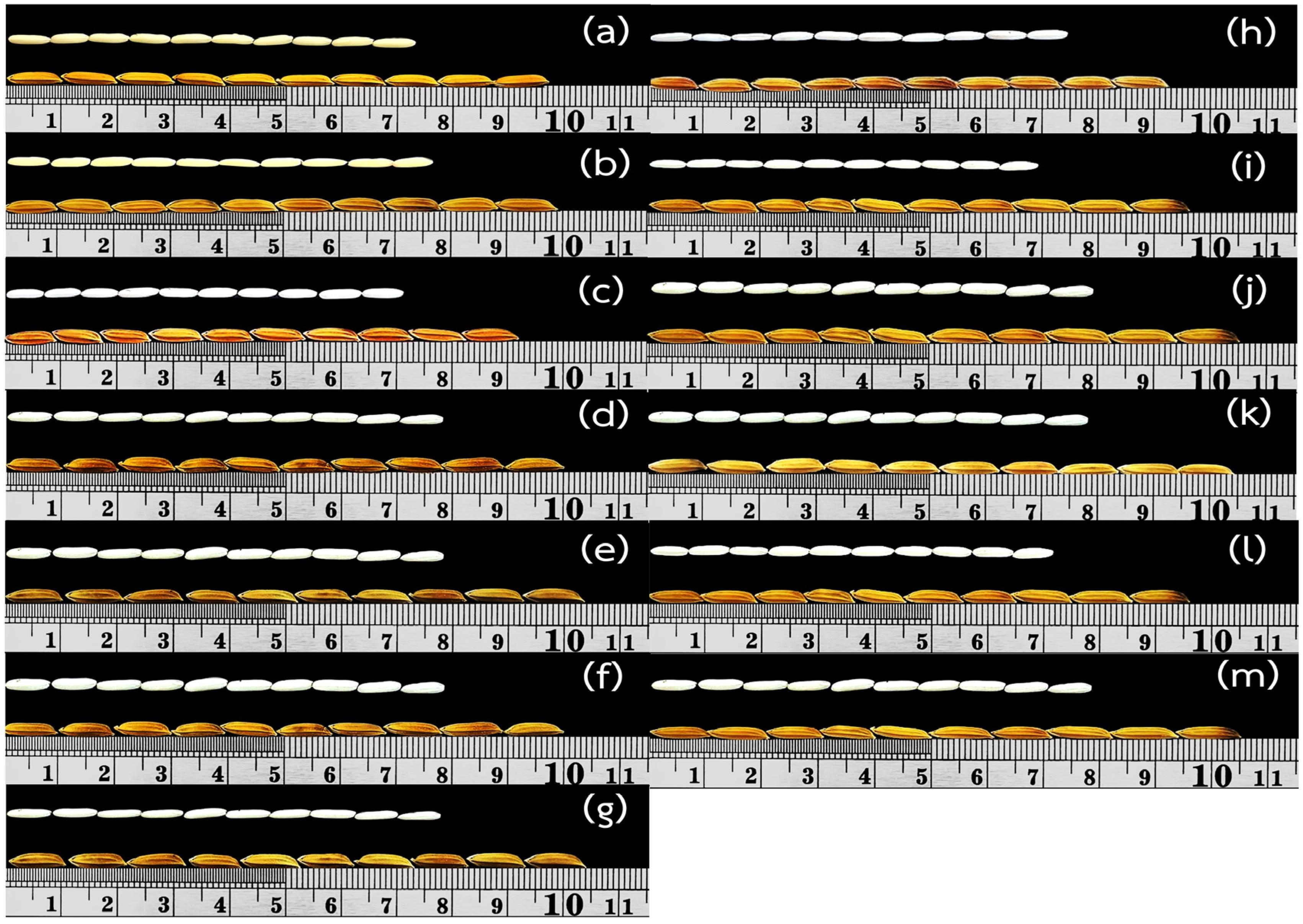
2.3. Evaluation of Agronomic Traits, Yield Components, and Seed Quality
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Development of Introgression Lines Using Marker-Assisted Selection
3.2. Validation of Bacterial Blight Resistance
3.3. Validation of Blast Resistance
3.4. Agronomic Traits and Yield Components
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The Rice Department. Rice Knowledge Bank: Rice Varieties. 2016. Available online: http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/step-by-step-production/pre-planting/rice-varieties (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Ou, S.H. Rice Diseases, 2nd ed.; Commonwealth Mycological Institute: Kew, UK, 1980; p. 380. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=1958442 (accessed on 18 January 2021).
- The Rice Department. Rice Knowledge Bank: Blast Disease and Bacterial Blight Disease. 2021. Available online: http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/training/fact-sheets/pest-management/diseases (accessed on 30 May 2021).
- Shahriar, S.A.; Imtiaz, A.A.; Hossain, B.; Husna, A.; Eaty, N.K. Rice Blast Disease. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2020, 1, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djatmiko, H.A.; Prakoso, B.; Prihatiningsih, N. Penentuan Patotipe Dan Keragman Genetik Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae Pada Tanaman Padidi Wilayah Karesidenan Banyumas. J. Hama Dan Penyakit Tumbuh. Tropika 2011, 11, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.L. Molecular Markers and Marker-Assisted Breeding in Plants. In Plant Breeding from Laboratories to Fields; Andersen, S.B., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2013; pp. 45–83. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/40178 (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Akhtar, S.; Bhat, M.A.; Wani, S.A.; Bhat, K.A.; Chalkoo, S.; Mir, M.R.; Wani, S.A. Marker-assisted selection in rice. Phytology 2010, 10, 66–81. [Google Scholar]
- Pedrozo, R.; Osakina, A.; Huang, Y.; Nicolli, C.P.; Wang, L.; Jia, Y. Status on Genetic Resistance to Rice Blast Disease in the Post-Genomic Era. Plant 2025, 14, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, S.; Rathour, R. Current status on mapping of genes for resistance to leaf- and neck-blast disease in rice. Biotechnology 2019, 9, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wu, L.; Guo, L.; Song, F.; Zheng, Z.; Cheng, Z. Genetic analysis and molecular mapping of Pitb with broad-spectrum resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice. Euphytica 2016, 209, 547–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utami, M.D.; Moeljopawiro, S.; Aswidinnoor, H.; Setiawan, A.; Hanarida, I. Blast resistance genes in wild rice Oryza rufipogon and rice cultivar IR64. SABRAO J. Breed. Genetics 2008, 1, 71–76. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Wang, L.; Pan, Q. A New Recessive Gene Conferring Resistance Against Rice Blast. Rice 2016, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, T.R.; Rai, A.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Singh, N.K. Broad-spectrum Blast Resistance Gene Pi-k h Cloned from Rice Line Tetep Designated as Pi54. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 19, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Zhai, C.; Wang, W.; Zeng, X.; Xu, X.; Hu, H.; Lin, F.; Wang, L.; Pan, Q. The Pik-p resistance to Magnaporthe oryzae in rice is mediated by a pair of closely linked CC-NBS-LRR genes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011, 122, 1017–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Naeem, M.; Iqbal, M. Breeding approaches for bacterial leaf blight resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Current status and future directions. Plant Pathol. 2014, 139, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Suh, J.; Qin, Y.; Noh, T.; Reinke, R.F.; Jena, K.K. Identification and fine-mapping of a new resistance gene, Xa40, conferring resistance to races in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chukwu, S.C.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ramleeb, I.S.; Ismailc, S.I.; Oladosue, Y.; Okporied, E.; Onyishie, G.; Utobod, E.; Ekwud, L.; Swaraya, S.; et al. Marker-assisted selection and gene pyramiding for resistance to bacterial leaf blight disease of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Biotechnol. Equip. 2019, 33, 1314–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noenplab, A.; Vanavichit, A.; Toojinda, T.; Sirithunya, P.; Tragoonrung, S.; Sriprakhon, S.; Vongsaprom, C. QTL mapping for leaf and neck blast resistance in Khao Dawk Mali105 and Jao Hom Nin recombinant inbred lines. Sci. Asia 2006, 33, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silprakhon, S. Identification and mapping genes controlling leaf blast resistance in double haploid lines IR64 × Azucena population. In Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on Rice for Future, Bangkok, Thailand, 31 August–3 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Pattawatang, P. Mapping of Quantitative Trait Loci Controlling Bacterial Blight Resistance in Rice. Master’s Thesis, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand, 2005. Available online: https://kukr.lib.ku.ac.th/kukr_es/kukr/search_detail/dowload_digital_file/155271/28166 (accessed on 4 April 2022).
- Koide, Y.; Kobayashi, N.; Xu, D.; Fukuta, Y. Resistance gene and selection DNA marker for blast disease in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Jpn. Agric. Res. Q. 2009, 43, 255–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, T.; Haileselassie, T.; Tesfaye, K. Identification, Mapping and Pyramiding of Genes/Quantitative Trait Loci (QTLs) for Durable Resistance of Crops to Biotic Stresses. J. Plant Pathol. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, J.; Raveendra, C.; Savitha, P.; Vidya, V.; Chaithra, T.L.; Velprabakaran, S.; Saraswathi, R.; Ramanathan, A.; Pillai, M.P.A.; Arumugachamy, S.; et al. Gene Pyramiding for Achieving Enhanced Resistance to Bacterial Blight, Blast, and Sheath Blight Diseases in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 591457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannual, T.; Chankaew, S.; Monkham, T.; Saksirirat, W.; Sanitchon, J. Pyramiding four blast resistance QTLs into Thai rice cultivar RD6 through marker-assisted selection. Plant Breed 2017, 53, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsaprom, C.; Sirithunya, P.; Vanavichit, A.; Pantuwan, G.; Jongdee, B.; Sidhiwong, N.; Lanceras-Siangliw, J.; Toojinda, T. Two introgressed quantitative trait loci confer a broad-spectrum resistance to blast disease in the genetic background of the cultivar RD6, a Thai. glutinous jasmine rice. Field Crops Res. 2010, 119, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srichan, N.; Chankaew, S.; Monkham, T.; Thammbenjapone, P.; Sanichon, J. Development of Sakon Nakhon Rice Variety for Blast Resistance through Marker-Assisted Backcross Breeding. Agronomy 2019, 9, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinta, W.; Toojinda, T.; Thummabenjapone, P.; Sanitchon, J. Pyramiding of blast and bacterial leaf blight resistance genes into rice cultivar RD6 using marker-assisted selection. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2013, 28, 4433–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A Rapid DNA Isolation Procedure for Small Quantities of Fresh Leaf Tissue. Phytochem. Bull. 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sallaud, C.; Lorieux, M.; Roumen, E.; Tharreau, D.; Berruyer, R.; Svestasrani, P.; Garsmeur, O.; Ghesquiere, A.; Notteghem, J.L. Identification of five new blast resistance genes in the highly blast-resistant rice variety IR64 using a QTL mapping strategy. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 106, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veillet, S.; Filippi, C.M.; Gallais, A. Combined genetic analysis of partial blast resistance in an upland rice population and recurrent selection for line and hybrid values. Trends Plant Sci. 1996, 92, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackill, D.J.; Bonman, J.M. Inheritance of blast resistance in near-isogenic rice lines. Phytopathology 1992, 82, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Rice Research Institute. Standard Evaluation System for Rice (SES); International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 2013; Available online: https://ricepedia.blogspot.com/2018/04/2013-irri-ses-standard-evaluation.html (accessed on 14 May 2025).
- Sirithanya, P. Mapping Gene Controlling Blast Resistance in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Ph.D. Thesis, Kasetsart University, Bangkok, Thailand, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sribunrueang, A.; Chankaew, S.; Thummabenjapone, P.; Sanitchon, J. Stability of Four New Sources of Bacterial Leaf Blight Resistance in Thailand Obtained from Indigenous Rice Varieties. Agrivita J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 39, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kauffman, H.E.; Reddy, A.P.K. Seed transmission studies of Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. Phytopathology 1974, 65, 663–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Rice Research Institute. Standard Evaluation System for Rice (SES); International Rice Research Institute: Manila, Philippines, 2002; Available online: http://www.knowledgebank.irri.org/images/docs/rice-standard-evaluation-system.pdf (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Weber, D.J.; Rochelle, R.; Singh, U.S. Chemistry and Biochemistry of Aroma in Scented Rice. In Aromatic Rices; Singh, R.K., Singh, U.S., Khush, G.S., Eds.; Oxford and IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2000; pp. 135–151. Available online: https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/77895?Z3CBO6wi5apfvXx=Nu7xqnUtX (accessed on 9 September 2022).
- Sriseadka, I.; Mahatheeranont, S.; Kitsawatpaiboon, P. Rapid method for quantitative analysis of the aroma impact compound, 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, in fragrant rice using automated headspace gas chromatography. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 8183–8189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.W. International collaboration on breeding for resistance to rice blast. In Rice Blast Disease; Zeigler, R.S., Leong, S.A., Teng, P.S., Eds.; Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International (CABI): Wallingford, UK, 1994; pp. 137–153. Available online: https://www.scirp.org/reference/referencespapers?referenceid=1561907 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Gomez, K.A.; Gomez, A.A. Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1984; p. 680. Available online: https://www.wiley.com/en-us/Statistical+Procedures+for+Agricultural+Research%2C+2nd+Edition-p-9780471870920 (accessed on 1 September 2022).
- Cobb, J.N.; Juma, R.U.; Biswas, P.S.; Arbelaez, J.D.; Rutkoski, J.; Hagen, G.A.T.; Quinn, M.; Ng, E.H. Enhancing the rate of genetic gain in public-sector plant breeding programs: Lessons from the breeder’s equation. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 627–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamichhane, S.; Thapa, S. Advances from Conventional to Modern Plant Breeding Methodologies. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, A. Molecular cytogenetics of introgressive hybridization in plants. Methods Cell Sci. 2001, 23, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benchimol-Reis, L.L. Molecular Marker in Plant Breeding. J. Agric. Sci. 2023, 15, 58–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha1, S.; Subedi, S.; Shrestha, J. Marker-assisted selection: A smart biotechnological strategy for modern plant breeding Selección asistida por marcadores: Una estrategia biotecnológica inteligente para el fitomejoramiento moderno. Peruv. J. Agron. 2020, 4, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, S.; Dinglasan, E.; Leung, M.K.; Riaz, A.; Derbal, N.; Voss-Fels, P.K.; Able, A.J.; Bassi, M.F.; Christopher, J.; Lee, T. Hickey Speed breeding for multiple quantitative traits in durum wheat. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaszmann, J.C. Isozymes and classification of Asian rice varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1987, 42, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, T.; Yamamoto, T.; Taura, S.; Endo, N.; Kaku, H.; Ikeda, R.; Khush, G.S.; Mew, T.W. Research on resistance to bacterial blight in rice. In Blessings from Nature and Science for the Future; IRRI Limited Proceedings No. 10; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 2004; pp. 3–16. Available online: http://books.irri.org/LP10_content.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Iyer-Pascuzzi, A.S.; Jiang, H.; Huang, L.; McCouch, S.R. Genetic and functional characterization of the rice bacterial blight disease resistance gene xa5. Phytopathology 2007, 98, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ancheta, J.; Toojind, T.; Reanwarakorn, K.; Patarapuwadol, S. Geographic distribution of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae pathotype in central region of Thailand. Khon Kaen Agric. J. 2021, 50, 204–215. [Google Scholar]
- Mackill, D.J.; Bonman, J.M. New host of Pyricularia oryzae. Plant Dis. 1986, 70, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, N.; Chu, Z.; Wang, S. Three types of defense-responsive genes are involved in resistance to bacterial blight and fungal blast diseases in rice. Genom. Genet. 2003, 269, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosack, K.E.; Jones, J.D.G. Plant disease resistance genes. Plant Mol. Biol. 1997, 48, 575–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nica, C.A.; Dermitzakis, E.T. Expression quantitative trait loci: Present and future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korinsak, S. Identification of Blast Resistance QTLs in Two Rice RIL Populations and Marker-Assisted Selection for Pyramiding of Four QTLs in RD 6 Rice Variety; Kasetsart University: Bangkok, Thailand, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| SOV | Blast | BB | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | MS | df | MS | |
| Isolate (I) | 11 | 2091.8 ** | 8 | 45.92 ** |
| Genotype (G) | 17 | 16276.8 ** | 16 | 328 ** |
| G × I | 187 | 413.0 ** | 128 | 9.36 ** |
| Error | 430 | 260.9 | 304 | 4.25 |
| C.V. (%) | 92.76 | 29.68 | ||
| Lines, Varieties | QTLs Located on Chromosome | Lesion Length (cm) and Reaction to Rice Bacterial Blight Disease | BSR | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SP 1-1 | NB 7-7 | NY 1-1 | CN 2-1 | CM 4-1 | UT 2-1 | NB 7-8 | MS 1-2 | PR 5-1 | |||
| BC1F3 22-7-60 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 4.2 d (R) | 9.0 b (MR) | 5.9 b–e (MR) | 6.5 de (MR) | 5.3 cd (MR) | 4.5 de (R) | 6.3 c–e (MR) | 9.0 bc (MR) | 5.3 d–f (MR) | 0.61 |
| BC1F3 22-7-128 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 4.6 d (R) | 5.3 c–f (MR) | 7.2 b–d (MR) | 7.9 cd (MR) | 6.7 b–d (MR) | 7.7 a–d (MR) | 6.8 c–e (MR) | 8.4 c (MR) | 3.5 e–f (R) | 0.61 |
| BC1F3 22-7-140 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 6.0 cd (MR) | 7.7 bc (MR) | 7.3 b–d (MR) | 3.5 e–g (R) | 4.5 c–f (R) | 6.4 b–d (MR) | 8.7 cd (MR) | 6.8 cd (MR) | 7.3 cd (MR) | 0.61 |
| BC1F3 22-7-322 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 5.5 cd (MR) | 6.7 b–e (MR) | 5.1 c–e (MR) | 3.7 e–g (R) | 6.5 b–d (MR) | 5.0 de (R) | 4.0 e (R) | 8.5 c (MR) | 9.5 c (MR) | 0.66 |
| BC1F3 22-11-187 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 6.0 cd (MR) | 8.2 bc (MR) | 6.8 b–d (MR) | 4.4 e–g (R) | 4.7 c–e (R) | 4.8 de (R) | 6.0 de (MR) | 6.1 cd (MR) | 7.6 cd (MR) | 0.66 |
| BC1F3 22-11-312 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 5.8 cd (MR) | 4.1 e–g (R) | 3.2 e–g (R) | 2.8 fg (R) | 4.2 d–f (R) | 4.7 de (R) | 7.4 c–e (MR) | 9.1 bc (MR) | 9.8 c (MR) | 0.77 |
| BC1F3 22-11-131 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 5.0 d (R) | 8.9 b (MR) | 1.7 fg (R) | 3.0 fg (R) | 4.3 d–f (R) | 5.8 d (MR) | 6.3 c–e (MR) | 6.1 cd (MR) | 5.5 d–f (MR) | 0.72 |
| BC1F3 22-15-311 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 7.8 bc (MR) | 4.3 d–g (R) | 5.3 b–e (MR) | 5.5 d–g (MR) | 7.3 bc (MR) | 6.1 cd (MR) | 7.8 c–e (MR) | 6.9 cd (MR) | 6.4 c–e (MR) | 0.55 |
| BC1F3 22-15-258 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 6.7 cd (MR) | 7.6 b–d (MR) | 7.9 bc (MR) | 4.3 e–g (R) | 6.3 cd (MR) | 7.3 a–d (MR) | 6.7 c–e (MR) | 8.6 c (MR) | 7.2 cd (MR) | 0.55 |
| BC1F3 22-15-298 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 4.9 d (R) | 4.4 d–g (R) | 4.4 d–f (R) | 6.2 d–f (MR) | 6.0 ce (MR) | 5.3 d (MR) | 5.0 de (R) | 8.5 c (MR) | 4.6 d–f (R) | 0.77 |
| SKN Standard check | - | 11.4 a (MS) | 8.9 b (MR) | 15.1 a (S) | 15.4 a (S) | 15.8 a (S) | 10.2 ab (MS) | 15.3 a (S) | 12.7 a (MS) | 17.7 a (S) | 0.05 |
| Morkhor 60-3 recurrent parent | qBl11,12 | 5.5 cd (MR) | 5.0 c–f (R) | 8.3 b (MR) | 5.1 d–g (MR) | 9.4 b (MR) | 9.8 a–c (MR) | 10.6 bc (MS) | 12.3 ab (MS) | 14.4 ab (MS) | 0.38 |
| Morkhor 60-1 donor parent | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 4.8 d (R) | 2.8 f–h (R) | 3.6 e–f (R) | 3.7 f–g (R) | 3.2 e–g (R) | 1.4 ef (R) | 5.5 de (MR) | 6.8 cd (MR) | 4.9 d–f (R) | 0.88 |
| IRBB5 resistance check | xa5 | 0.1 e (R) | 0.7 h (R) | 0.9 g (R) | 2.5 g (R) | 1.6 fg (R) | 0.0 f (R) | 4.4 de (R) | 0.9 e (R) | 2.5 f (R) | 1.00 |
| IR62266 resistance check | xa5 | 0.6 e (R) | 1.4 gh (R) | 0.5 g (R) | 5.7 d–g (MR) | 1.0 g (R) | 0.3 f (R) | 5.1 de (MR) | 4.7 d (R) | 3.0 ef (R) | 0.88 |
| KDML105 susceptibility check | - | 11.6 a (MS) | 15.8 a (S) | 14.2 a (MS) | 14.3 ad (MS) | 14.6 a (MS) | 10.1 ab (MS) | 14.5 ab (MS) | 13.2 a (MS) | 13.7 b (MS) | 0.00 |
| RD6 susceptibility check | - | 9.5 ab (MR) | 12.9 a (MS) | 16.1 a (S) | 10.9 bc (MS) | 12.4 a (MS) | 10.9 a (MS) | 13.5 ab (MS) | 13.4 a (MS) | 15.3 ab (S) | 0.05 |
| Mean | 5.87 | 6.68 | 6.67 | 6.19 | 6.82 | 5.89 | 7.86 | 8.35 | 8.12 | ||
| F-test | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| C.V. % | 27.26 | 29.9 | 28.43 | 33.26 | 25.75 | 39.28 | 33.74 | 25.48 | 27.25 | ||
| Lines, Varieties | QTLs Located on Chromosome | SI and Reaction to Rice Blast Disease | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STN 22063 | SRN 16371 | SRN 16381 | PSL 16358 | PRE 16415 | PSL 16362 | STN 22069 | PML 16295 | UBN 21008 | STN 22068 | STN 22066 | UBN 21028 | BSR | ||
| BC1F3 22-7-60 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 28.13 c–f (MR) | 0 d (HR) | 0.82 ef (R) | 15.67 c–g (R) | 9.72 bc (R) | 12.98 d–f (R) | 0.37 e (R) | 0 d (HR) | 1.39 c (R) | 0 c (HR) | 15.56 de (R) | 0 c (HR) | 0.95 |
| BC1F3 22-7-128 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 18.15 d–g (R) | 0 d (HR) | 0.93 ef (R) | 9.88 e–g (R) | 4.6 c (R) | 18.78 d–f (R) | 0 e (HR) | 0 d (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0.74 e (R) | 0 c (HR) | 1.00 |
| BC1F3 22-7-140 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 16.83 d–g (R) | 0 d (HR) | 0.74 ef (R) | 5.88 g (R) | 5.71 c (R) | 9.84 ef (R) | 0 e (HR) | 0 d (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0 e (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 1.00 |
| BC1F3 22-7-322 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 14.07 e–g (R) | 0 d (HR) | 1.48 ef (R) | 11.71 d–g (R) | 2.91 c (R) | 6.61 f (R) | 0 e (HR) | 0 d (HR) | 1.11 c (R) | 0 c (HR) | 0 e (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 1.00 |
| BC1F3 22-11-187 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 21.48 d–g (MR) | 0 d (HR) | 0 f (HR) | 20.95 c–f (MR) | 8.4 bc (R) | 26.77 c–f (MR) | 0.62 e (R) | 0 d (HR) | 2.47 c (R) | 0 c (HR) | 0 e (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0.66 |
| BC1F3 22-11-312 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 10.26 fg (R) | 0 d (HR) | 0 f (HR) | 14.83 d–g (R) | 3.02 c (R) | 25.57 c–f (MR) | 0 e (HR) | 0 d (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0 e (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0.95 |
| BC1F3 22-11-131 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 14.39 e–g (R) | 0 d (HR) | 0 f (HR) | 17.50 c–g (R) | 16.4 bc (R) | 32.04 b–e (MR) | 1.59 de (R) | 6.12 cd (R) | 0 c (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 36.51 c–e (MR) | 0 c (HR) | 0.87 |
| BC1F3 22-15-311 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 31.75 b–e (MR) | 0 d (HR) | 29.63 c–f (MR) | 15.82 c–g (R) | 11.64 bc (R) | 28.57 b–f (MR) | 6.42 de (R) | 0 d (HR) | 1.39 c (R) | 7.04 c (R) | 3.7 e (R) | 3.7 c (R) | 0.87 |
| BC1F3 22-15-258 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 19.05 d–g (R) | 1.11 d (R) | 0 f (HR) | 7.74 e–g (R) | 5.85 bc (R) | 18.1 d–f (R) | 0.62 e (R) | 0 d (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0 e (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 1.00 |
| BC1F3 22-15-298 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 21.88 d–g (MR) | 0 d (HR) | 0 f (HR) | 6.79 e–g (R) | 7.83 bc (R) | 18.99 d–f (R) | 2.47 de (R) | 0 d (HR) | 1.23 c (R) | 0 c (HR) | 0 e (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 0.95 |
| SKN standard check | - | 69.55 a (S) | 32.04 bc (MR) | 43.70 a–c (MS) | 41.9 ab (MS) | 73.54 a (S) | 69.14 a (S) | 74.07 b (S) | 64.76 ab (S) | 61.11 a (S) | 55.46 b (MS) | 94.81 ab (HS) | 69.63 a (S) | 0.04 |
| Morkhor 60-3 recurrent parent | qBl11,12 | 49.63 ab (MS) | 7 cd (R) | 33.46 b–f (MR) | 29.29 ab (MR) | 26.87 b (MR) | 44.76 a–c (MS) | 8.52 de (R) | 18.52 cd (MR) | 11.64 c (R) | 18.02 c (R) | 56.3 b–d (MS) | 4.44 c (R) | 0.62 |
| Morkhor 60-1 donor parent | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 35.56 b–d (MR) | 5.49 d (R) | 67.20 ab (S) | 21.05 c–e (MR) | 19.58 bc (R) | 25.71 c–f (MR) | 3.17 de (R) | 3.7 cd (R) | 0 c (HR) | 6.94 c (R) | 59.26 a–c (MS) | 3.17 c (R) | 0.66 |
| P0489 resistance check | qBl2,12 | 7.48 g (R) | 1.59 d (R) | 37.41 b–e (MR) | 6.55 fg (R) | 6.1 bc (R) | 12.98 d–f (R) | 5.35 de (R) | 0 d (HR) | 2.47 c (R) | 0 c (HR) | 0 e (HR) | 1.59 c (R) | 0.95 |
| JHN resistance check | qBl1,11 | 17.69 d–g (R) | 9.26 cd (R) | 6.17 d–f (R) | 7.6 fg (R) | 12.43 bc (R) | 7.82 ef (R) | 15.43 d (R) | 7.14 cd (R) | 0 c (HR) | 0 c (HR) | 1.48 e (R) | 0 c (HR) | 1.00 |
| IR64 resistance check | - | 14.74 e–g (R) | 0 d (HR) | 0 f (HR) | 6.39 g (R) | 7.41 bc (R) | 8.57 ef (R) | 3.7 de (R) | 2.31 d (R) | 7 c (R) | 0 c (HR) | 2.65 e (R) | 10.05 bc (R) | 1.00 |
| Azucena resistance check | - | 42.06 bc (MR) | 48.15 ab (MS) | 44.9 a–c (MS) | 7.16 e–g (R) | 9.79 bc (R) | 11.9 d–f (R) | 0 e (HR) | 38.1 bc (MR) | 2.78 c (R) | 51.85 b (MS) | 68.15 a–c (S) | 55.56 a (MS) | 0.25 |
| KDML 105 susceptibility check | - | 49.63 ab (MS) | 66.67 a (S) | 77.78 a (S) | 48.57 a (MS) | 56.61 a (MS) | 53.02 ab (MS) | 91.11 a (HS) | 80.95 a (HS) | 62.96 a (S) | 100 a (HS) | 100 a (HS) | 69.73 a (S) | 0.00 |
| RD 6 susceptibility check | - | 28.26 c–f (R) | 40.7 b (MS) | 40.41 b–d (MS) | 25.71 cd (MR) | 9.95 bc (R) | 35.24 b–d (MR) | 35.19 c (MR) | 2.78 cd (R) | 38.89 b (MR) | 49.21 b (MS) | 62.96 a–c (S) | 39.81 ab (MR) | 0.45 |
| Mean | 26.87 | 11.15 | 20.24 | 16.89 | 15.70 | 24.60 | 13.08 | 11.81 | 10.23 | 15.18 | 26.42 | 13.55 | ||
| F-test | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ||
| C.V. % | 45.22 | 137.34 | 111.22 | 51.54 | 80.84 | 61.30 | 67.20 | 181.13 | 92.33 | 107.02 | 98.60 | 139.69 | ||
| Lines, Varieties | QTLs Located on Chromosome | DF (day) | PH (cm) | NPP | PL (cm) | NGP | TGW (g.) | HI | GY (g/plant) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BC1F4 22-7-60-2 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 74 g | 136 ab | 7.25 | 35.7 a | 141 | 28.96 c–e | 0.42 | 66.88 |
| BC1F4 22-7-128-3 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 81 c–e | 146 a | 6.75 | 24.5 c | 172 | 28.77 c–e | 0.27 | 60.58 |
| BC1F422-7-140-4 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 83 b–d | 142 a | 7.25 | 37.5 a | 159 | 28.18 d | 0.28 | 74.49 |
| BC1F4 22-7-322-5 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 89 a | 146 a | 7.75 | 35.0 ab | 160 | 32.61 ab | 0.24 | 73.83 |
| BC1F4 22-11-187-6 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 80 c–f | 143 a | 6.75 | 35.2 a | 158 | 30.46 b–d | 0.27 | 56.83 |
| BC1F422-11-312-7 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 78 d–g | 145 a | 7.50 | 33.7 ab | 168 | 31.21 a–c | 0.41 | 81.57 |
| BC1F4 22-11-131-8 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 78 d–g | 129 bc | 7.25 | 36.5 a | 124 | 28.07 de | 0.36 | 78.30 |
| BC1F4 22-15-311-9 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 88 ab | 147 a | 6.50 | 22.7 c | 147 | 28.60 de | 0.26 | 73.12 |
| BC1F4 22-15-258-10 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 75 fg | 138 ab | 8.00 | 24.7 c | 150 | 30.11 cd | 0.30 | 71.47 |
| BC1F4 22-15-298-11 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 77 e–g | 138 ab | 7.00 | 25.5 c | 153 | 29.33 c–e | 0.30 | 66.63 |
| SKN standard check | - | 87 a–c | 146 a | 7.75 | 28.0 bc | 129 | 33.53 a | 0.34 | 99.91 |
| Morkhor 60-3 recurrent parent | qBl11,12 | 84 b–d | 141 ab | 6.00 | 24.2 c | 144 | 27.16 e | 0.38 | 76.90 |
| Morkhor 60-1 donor parent | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 73 g | 122 b | 7.25 | 21.7 c | 136 | 29.06 c–e | 0.40 | 67.03 |
| Mean | 80.82 | 141.15 | 7.15 | 29.59 | 149.38 | 0.32 | 29.69 | 70.37 | |
| F-test | ** | ** | ns | ** | ns | ** | ns | ns | |
| C.V. % | 4.80 | 6.00 | 15.04 | 17.03 | 18.71 | 27.64 | 5.83 | 28.32 |
| Lines, Varieties | QTLs Located on Chromosome | 2AP (ppm) | Seed Shape | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paddy Size (mm) | Brown Rice Size (mm) | |||||||
| Length | Breadth | L/B ratio | Length | Breadth | L/B ratio | |||
| BC1F4 22-7-60-2 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 8.82 | 9.72 de | 2.58 ab | 3.77 d | 7.21 b–d | 2.14 | 3.37 |
| BC1F4 22-7-128-3 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 10.28 | 9.79 c–e | 2.27 cd | 4.31 a–d | 6.95 de | 2.02 | 3.44 |
| BC1F4 22-7-140-4 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 9.38 | 9.72 de | 2.36 bc | 4.12 a–d | 7.13 b–e | 2.19 | 3.26 |
| BC1F4 22-7-322-5 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 10.47 | 10.01 b–e | 2.60 ab | 3.86 de | 7.34 a–d | 2.26 | 3.25 |
| BC1F4 22-11-187-6 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 10.70 | 10.13 b–d | 2.36 bc | 4.29 a–d | 7.51 ab | 2.07 | 3.63 |
| BC1F4 22-11-312-7 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 10.11 | 10.72 a | 2.29 cd | 4.68 a | 7.56 ab | 1.99 | 3.80 |
| BC1F4 22-11-131-8 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 8.73 | 9.81 c–e | 2.67 a | 3.67 e | 7.14 b–e | 2.11 | 3.38 |
| BC1F4 22-15-311-9 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 10.79 | 9.76 c–e | 2.52 a–c | 3.87 de | 7.46 ab | 2.17 | 3.44 |
| BC1F4 22-15-258-10 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 7.31 | 10.27 a–c | 2.35 bc | 4.37 ab | 7.44 ab | 2.05 | 3.63 |
| BC1F4 22-15-298-11 | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 12.70 | 10.40 ab | 2.28 cd | 4.56 ab | 7.42 ab | 2.02 | 3.67 |
| SKN standard check | - | 13.26 | 10.71 a | 2.02 d | 4.47 a–d | 6.75 e | 1.69 | 4.53 |
| Mor khor 60-3 recurrent parent | qBl1,11 | 8.42 | 9.51 e | 2.40 bc | 3.96 c–e | 6.98 c–e | 2.13 | 3.28 |
| Mor khor 60-1 donor parent | qBl1,2,11,12 and xa5 | 7.33 | 9.66 de | 2.36 bc | 4.11 a | 6.75 d | 2.07 | 3.26 |
| Mean | 10.01 | 2.39 | 4.15 | 7.27 | 2.10 | 3.46 | ||
| F-test | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns | ns | ||
| C.V. % | 3.63 | 7.39 | 8.10 | 4.15 | 6.39 | 8.54 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Panmaha, S.; Netpakdee, C.; Wongsa, T.; Chankaew, S.; Monkham, T.; Sanitchon, J. Improvement of Morkhor 60-3 Upland Rice Variety for Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance Using Marker–Assisted Backcross Selection. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071600
Panmaha S, Netpakdee C, Wongsa T, Chankaew S, Monkham T, Sanitchon J. Improvement of Morkhor 60-3 Upland Rice Variety for Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance Using Marker–Assisted Backcross Selection. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071600
Chicago/Turabian StylePanmaha, Sawinee, Chaiwat Netpakdee, Tanawat Wongsa, Sompong Chankaew, Tidarat Monkham, and Jirawat Sanitchon. 2025. "Improvement of Morkhor 60-3 Upland Rice Variety for Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance Using Marker–Assisted Backcross Selection" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071600
APA StylePanmaha, S., Netpakdee, C., Wongsa, T., Chankaew, S., Monkham, T., & Sanitchon, J. (2025). Improvement of Morkhor 60-3 Upland Rice Variety for Blast and Bacterial Blight Resistance Using Marker–Assisted Backcross Selection. Agronomy, 15(7), 1600. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071600






