Maize Seed Variety Classification Based on Hyperspectral Imaging and a CNN-LSTM Learning Framework
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Material Preparation
2.2. Hyperspectral Imaging Acquisition
2.3. Spectral Data Preprocessing
2.4. Characteristic Variable Selection
2.5. Model Building
2.6. Model Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spectral Analysis
3.2. Results of Characteristic Variable Extraction
3.3. Classification Results of Maize Varieties Based on PLS-DA
3.4. Classification Results of Maize Varieties Based on SVM
3.5. Classification Results of Maize Varieties Based on ELM
3.6. Classification Results of Maize Varieties Based on CNN-LSTM
3.7. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, F.; Wang, M.; Zhang, F.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Ali, S.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, S. Hyperspectral imaging combined with GA-SVM for maize variety identification. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 3177–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherakhane, M.; Parashivamurthy; Lohithaswa, H.C.; Sinchana Kashyap, G.S.; Gowda, B.; Siddaraju, R.; Keshavareddy, G. Genetic purity assessment of maize hybrid (Zea mays L.) and its parental lines employing SSR markers. J. Adv. Biol. Biotechnol. 2025, 28, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Kang, K.; Luo, B. Data fusion-driven hyperspectral imaging for non-destructive detection of single maize seed vigor. Measurement 2025, 253, 117416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Tang, W.; Yang, T.; Zhou, M.; Guo, C.; Cheng, T.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, X. Grain protein content phenotyping in rice via hyperspectral imaging technology and a genome-wide association study. Plant Phenomics 2024, 6, 0200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, S.; Xu, M.; Yao, K.; Cao, Y.; Tang, N. Identification of maize seed varieties based on stacked sparse autoencoder and near-infrared hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Wang, J.; Men, S.; Yan, L.; Xiao, J. Hyperspectral imaging coupled with multivariate methods for seed vitality estimation and forecast for Quercus variabilis. Spectroc. Acta Part A-Molec. Biomolec. Spectr. 2021, 245, 118888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Nirere, A.; Dusabe, K.D.; Zhong, Y.; Adrien, G. Rapid and nondestructive watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) seed viability detection based on visible near-infrared hyperspectral imaging technology and machine learning algorithms. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 4403–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Fu, L.; Xu, M.; Tang, N.; Cao, Y.; Yao, K.; Jing, J. Identification of red jujube varieties based on hyperspectral imaging technology combined with CARS-IRIV and SSA-SVM. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e14137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, G.; Mireei, S.A.; Jafari, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Karimmojeni, H.; Nazeri, M. Spatial analysis of hyperspectral images for detecting adulteration levels in bon-sorkh (Allium jesdianum L.) seeds: Application of voting classifiers. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 10, 100810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, R.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Fast detection of the early decay in oranges using visible-LED structured- illumination imaging combined with spiral phase transform and feature-based classification model. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2024, 17, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Yang, S.; Huang, M.; Zhu, Q.; Guo, Y.; Qin, J. Maize seed classification using hyperspectral image coupled with multi-linear discriminant analysis. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 103, 103077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Huang, W.; Fan, S.; Zhao, F.; Liang, D.; Tian, X. Non-destructive discrimination of the variety of sweet maize seeds based on hyperspectral image coupled with wavelength selection algorithm. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 109, 103418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Bu, Y.; Han, L.; Tian, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Huang, D.; Luo, H. Rapid nondestructive detecting of wheat varieties and mixing ratio by combining hyperspectral imaging and ensemble learning. Food Control 2023, 150, 109740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Song, S. Detection of sweet corn seed viability based on hyperspectral imaging combined with firefly algorithm optimized deep learning. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1361309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Jayan, H.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Alzamora, S.M.; Gomez, P.L.; Zou, X. Detection model transfer of apple soluble solids content based on NIR spectroscopy and deep learning. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 212, 108127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donmez, E. Enhancing classification capacity of CNN models with deep feature selection and fusion: A case study on maize seed classification. Data Knowl. Eng. 2022, 141, 102075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.; Garg, N.M.; Iyengar, S.R.S. Nondestructive identification of barley seeds variety using near-infrared hyperspectral imaging coupled with convolutional neural network. J. Food Process Eng. 2021, 44, e13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, H.; Zhao, X.; Sun, X.; Zhu, Q.; Huang, M. Identification of wheat kernel varieties based on hyperspectral imaging technology and grouped convolutional neural network with feature intervals. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2023, 131, 104653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maginga, T.J.; Masabo, E.; Bakunzibake, P.; Kim, K.S.; Nsenga, J. Using wavelet transform and hybrid CNN–LSTM models on VOC & ultrasound IoT sensor data for non-visual maize disease detection. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Hang, R.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, X. Hyperspectral image classification using spectral-spatial LSTMs. Neurocomputing 2019, 328, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Wang, F.; Fan, S.; Zhu, B.; Yan, L.; Chen, Y.; Wei, Y.; Chen, W. Evaluation and process monitoring of jujube hot air drying using hyperspectral imaging technology and deep learning for quality parameters. Food Chem. 2025, 467, 141999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, S.; An, T.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Huang, W. Detection of insect-damaged maize seed using hyperspectral imaging and hybrid 1D-CNN-BiLSTM model. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2024, 137, 105208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Wei, Y.; Liu, J.; An, D.; Wu, J. Open set maize seed variety classification using hyperspectral imaging coupled with a dual deep SVDD-based incremental learning framework. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 234, 121043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Wang, F.; Zhu, B.; Yan, L.; Wei, Y.; Chen, Y. Detection of dried jujube from fresh jujube with different variety and maturity after hot air drying based on hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 133, 106378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, S.; Wu, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, F.; Yang, X.; Li, J. Application of long-wave near infrared hyperspectral imaging for determination of moisture content of single maize seed. Spectrochim. Acta. A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 254, 119666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wu, P.; Li, J.; Xia, Y.; Fan, S. Rapid prediction and visualization of moisture content in single cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seed using hyperspectral imaging technology. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2019, 102, 103034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, Y.; Tian, X.; Long, Y.; Huang, W.; Chen, L. Development of a rapid detection method for maize seed purity using a modular high-throughput near-infrared non-destructive testing system. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2025, 148, 105836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, E.; Liu, Z.; Yue, J. Maize quality detection based on MConv-SwinT high-precision model. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0312363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, X.; Li, H. A CARS-SPA-GA feature wavelength selection method based on hyperspectral imaging with potato leaf disease classification. Sensors 2024, 24, 6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.; Adels, K.; Gaponova, A.; Panchuk, V.; Kirsanov, D.; Monakhova, Y. Fast spectroscopic and multisensor methods for analysis of glucosamine and hyaluronic acid in dietary supplements. Microchem. J. 2024, 207, 112116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Jiao, T.; Adade, S.Y.S.S.; Wang, Z.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q. Digital twin for predicting and controlling food fermentation: A case study of kombucha fermentation. J. Food Eng. 2025, 393, 112467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, H.; Jayan, H.; Majeed, U.; Ashiagbor, K.; Jiang, S.; Zou, X. Multi-sensor fusion and deep learning for batch monitoring and real-time warning of apple spoilage. Food Control 2025, 172, 111174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wu, X.; Jayan, H.; Yin, L.; Xue, S.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X. Recent developments and applications of surface enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy in safety detection of fruits and vegetables. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Hao, Y.; Wu, W.; Tu, K.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Mao, Y.; Sun, Q. Rapid detection of turtle cracks in corn seed based on reflected and transmitted images combined with deep learning method. Microchem. J. 2024, 201, 110698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongchaisuwat, P.; Chakranon, P.; Yinpin, A.; Onwimol, D.; Wonggasem, K. Rapid maize seed vigor classification using deep learning and hyperspectral imaging techniques. Smart Agric. Technol. 2025, 10, 100820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, K.; Jha, G.K.; Jaiswal, R.; Kumar, R.R. A genetic algorithm optimized hybrid model for agricultural price forecasting based on VMD and LSTM network. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonic, M.; Ficko, M.; Klancnik, S. Predicting corn moisture content in continuous drying systems using LSTM neural networks. Foods 2025, 14, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Liu, Q.; Fan, S.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, F.; Cao, X.; Yan, L. Development of a predictive model for assessing quality of winter jujube during storage utilizing hyperspectral imaging technology. J. Food Process Eng. 2024, 47, e14688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Fan, S.; Zuo, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, Q.; Kong, J. Discrimination of new and aged seeds based on on-line near-infrared spectroscopy technology combined with machine learning. Foods 2024, 13, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Q.; Chen, Q.; Ahmad, W.; Pan, J.; Zhao, S.; Xia, Y.; Ouyang, Q.; Chen, Q. Quantitative analysis and visualization of chemical compositions during shrimp flesh deterioration using hyperspectral imaging: A comparative study of machine learning and deep learning models. Food Chem. 2025, 481, 143997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Tang, X.; Fan, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Huang, W. Identification of mould varieties infecting maize kernels based on Raman hyperspectral imaging technique combined with multi-channel residual module convolutional neural network. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2024, 125, 105727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zareef, M.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Ouyang, Q. Monitoring chlorophyll changes during Tencha processing using portable near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2023, 412, 135505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Park, B.; Kang, R.; Chen, Q.; Ouyang, Q. Quantitative prediction and visualization of matcha color physicochemical indicators using hyperspectral microscope imaging technology. Food Chem. 2024, 163, 110531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
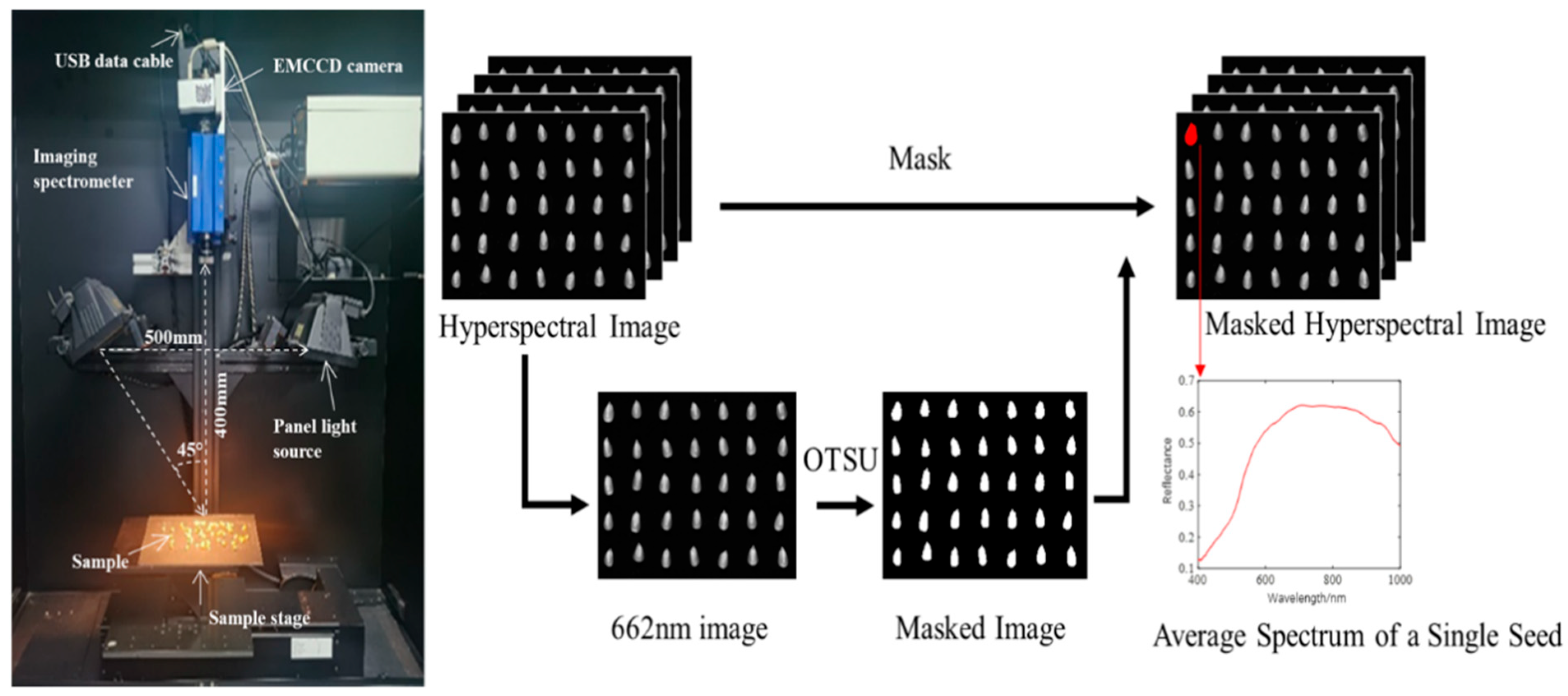
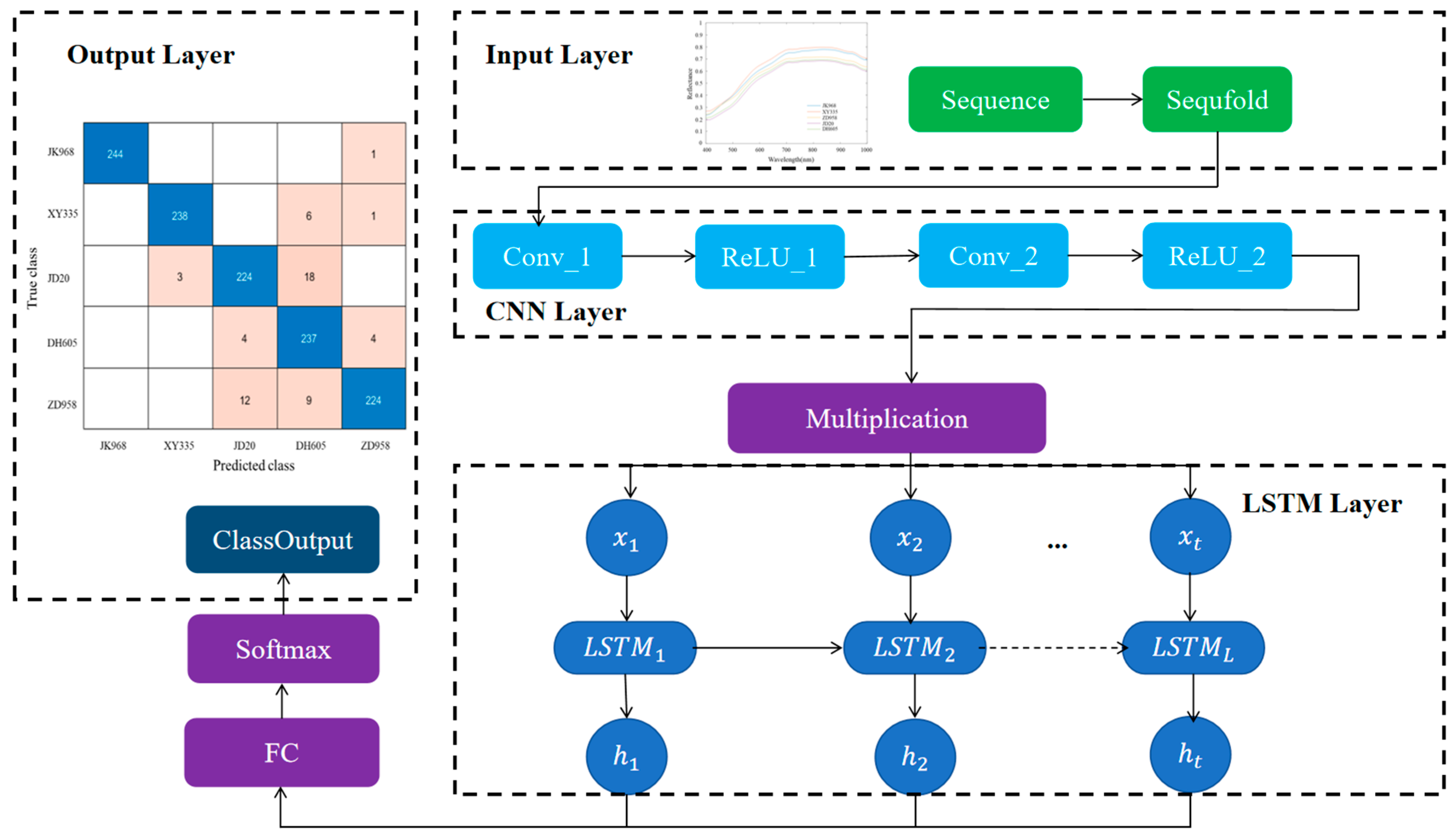

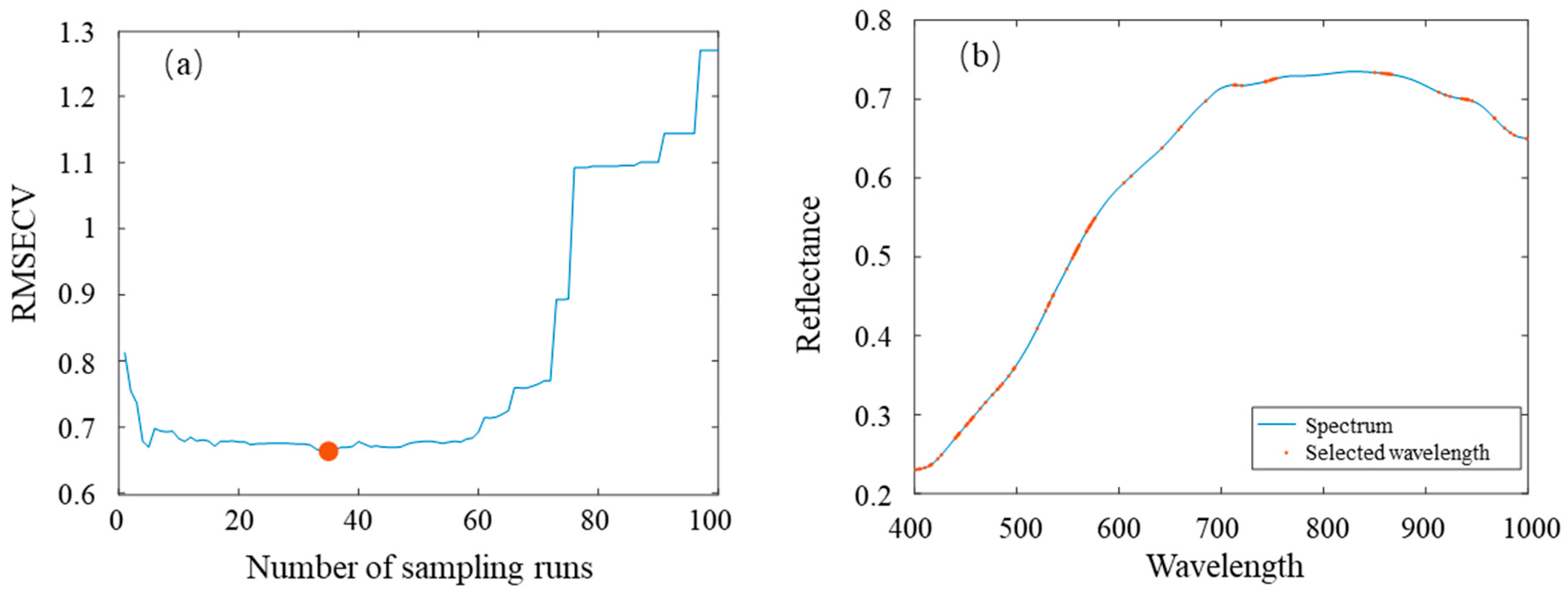


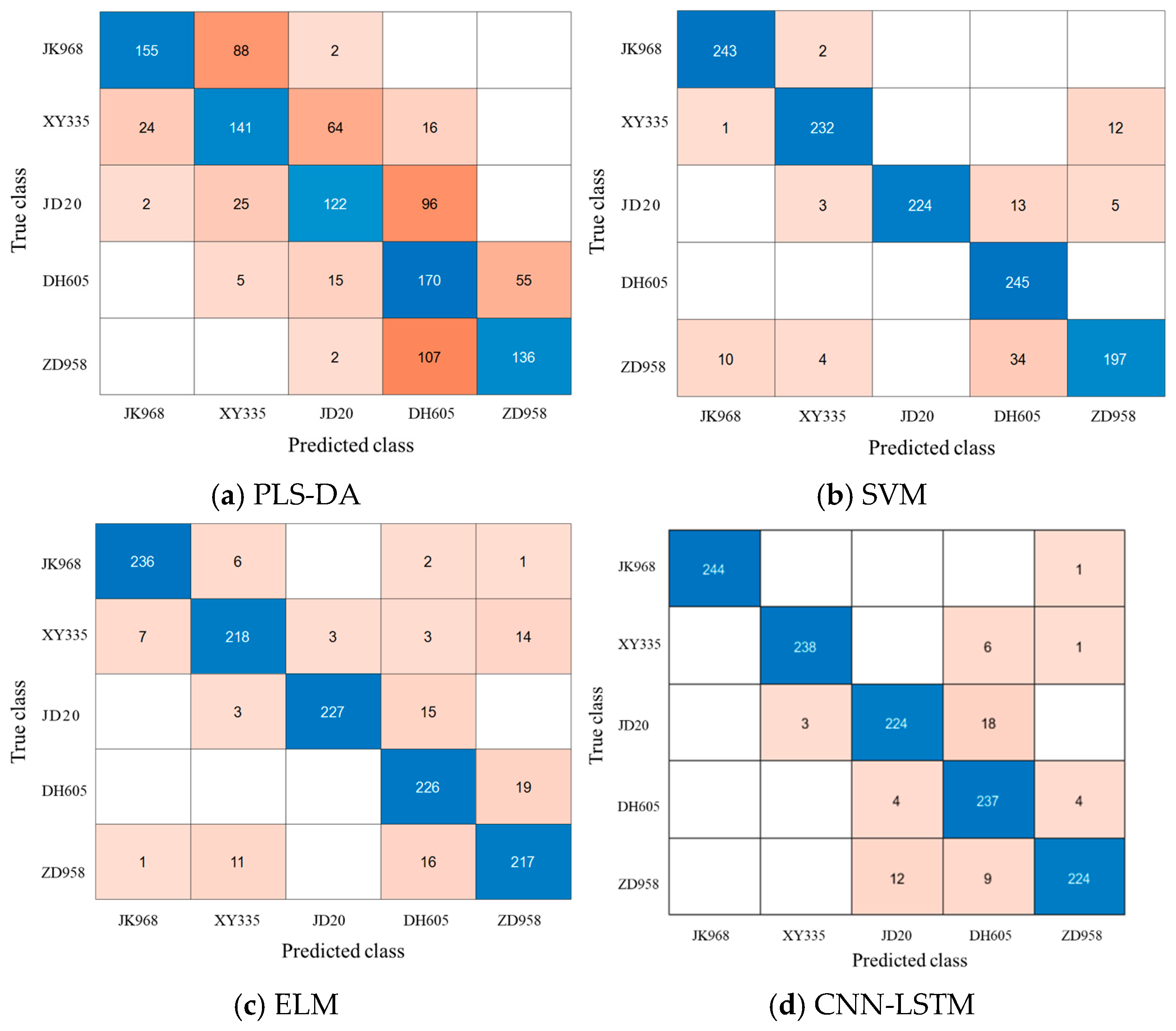
| Samples Set | JK968 | XY335 | JD20 | DH605 | ZD958 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All samples | 810 | 810 | 810 | 810 | 810 |
| Calibration set | 565 | 565 | 565 | 565 | 565 |
| Prediction set | 245 | 245 | 245 | 245 | 245 |
| Numbers | Selected Wavelength (nm) |
|---|---|
| 100 | 401.3, 404.2, 405.7, 410.1, 414.5, 416.0, 416.8, 422.7, 426.3, 439.7, 440.4, 441.9, 442.7, 443.4, 444.1, 450.1, 451.6, 452.3, 454.6, 455.3, 456.8, 457.5, 464.3, 469.5, 476.2, 480.7, 481.5, 483.7, 486.0, 492.0, 496.5, 497.3, 498.0, 520.0, 528.3, 530.6, 531.4, 532.1, 535.2, 535.9, 548.9, 554.2, 555.7, 556.5, 557.3, 558.0, 558.8, 559.6, 560.3, 561.1, 568.0, 568.8, 570.3, 571.1, 571.8, 572.6, 574.1, 575.7, 576.4, 604.9, 611.8, 642.0, 658.4, 660.7, 684.9, 712.2, 713.8, 714.6, 720.1, 742.8, 743.6, 744.4, 747.6, 748.4, 749.9, 751.5, 753.9, 850.2, 856.6, 858.9, 861.3, 862.9, 864.5, 865.3, 866.9, 912.8, 919.2, 924.0, 935.1, 937.4, 939.0, 940.6, 941.4, 945.4, 966.8, 967.6, 977.1, 982.6, 986.6, 998.5 |
| Corn Varieties | Full-Spectrum PLS-DA Model | CARS-MLR-DA Model | CARS-PLS-DA Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration Set Accuracy | Prediction Set Accuracy | Calibration Set Accuracy | Prediction Set Accuracy | Calibration Set Accuracy | Prediction Set Accuracy | |
| JK968 | 68.67% | 64.48% | 70.97% | 61.63% | 70.29% | 63.27% |
| XY335 | 74.33% | 57.95% | 64.42% | 58.37% | 61.42% | 57.55% |
| JD20 | 70.61% | 53.46% | 63.36% | 51.43% | 64.96% | 49.80% |
| DH605 | 73.45% | 65.30% | 70.97% | 71.43% | 55.75% | 69.39% |
| ZD958 | 69.73% | 66.12% | 58.05% | 57.55% | 64.28% | 55.51% |
| Total | 71.36% | 61.46% | 65.56% | 60.08% | 63.27% | 59.10% |
| Parameters | Parameters | Calibration Set Accuracy | Prediction Set Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Linear | c, gamma = 10, 0.1 | 99.11% | 93.14% |
| RBF | c, gamma = 4.6, 0.1 | 99.07% | 81.38% |
| Poly | c, gamma = 0.1, 1 | 99.20% | 86.45% |
| Corn Varieties | CNN-LSTM a | SVM (Linear Kernel) a | ELM (Number of Neurons: 290) a | PLS-DA b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JK968 | 99.59% | 99.18% | 96.33% | 63.27% |
| XY335 | 97.14% | 94.69% | 88.98% | 57.55% |
| JD20 | 91.43% | 91.43% | 92.65% | 49.80% |
| DH605 | 96.73% | 100% | 92.24% | 69.39% |
| ZD958 | 91.43% | 80.41% | 88.57% | 55.51% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Ma, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, A.; Fan, S. Maize Seed Variety Classification Based on Hyperspectral Imaging and a CNN-LSTM Learning Framework. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071585
Zhu Q, Liu Q, Ma D, Zhu Y, Zhang L, Wang A, Fan S. Maize Seed Variety Classification Based on Hyperspectral Imaging and a CNN-LSTM Learning Framework. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071585
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Qingzhen, Quancheng Liu, Didi Ma, Yanqiu Zhu, Liyuan Zhang, Aichen Wang, and Shuxiang Fan. 2025. "Maize Seed Variety Classification Based on Hyperspectral Imaging and a CNN-LSTM Learning Framework" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071585
APA StyleZhu, Q., Liu, Q., Ma, D., Zhu, Y., Zhang, L., Wang, A., & Fan, S. (2025). Maize Seed Variety Classification Based on Hyperspectral Imaging and a CNN-LSTM Learning Framework. Agronomy, 15(7), 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071585






