Biofertilizers Enhance Soil Fertility and Crop Yields Through Microbial Community Modulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design and Soil Sampling
2.2. Analysis of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR, and High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Microbial Network Analysis
2.5. Structural Equation Modeling Construction
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Different Fertilization Regimes on Soil Physicochemical Properties and Crop Yield
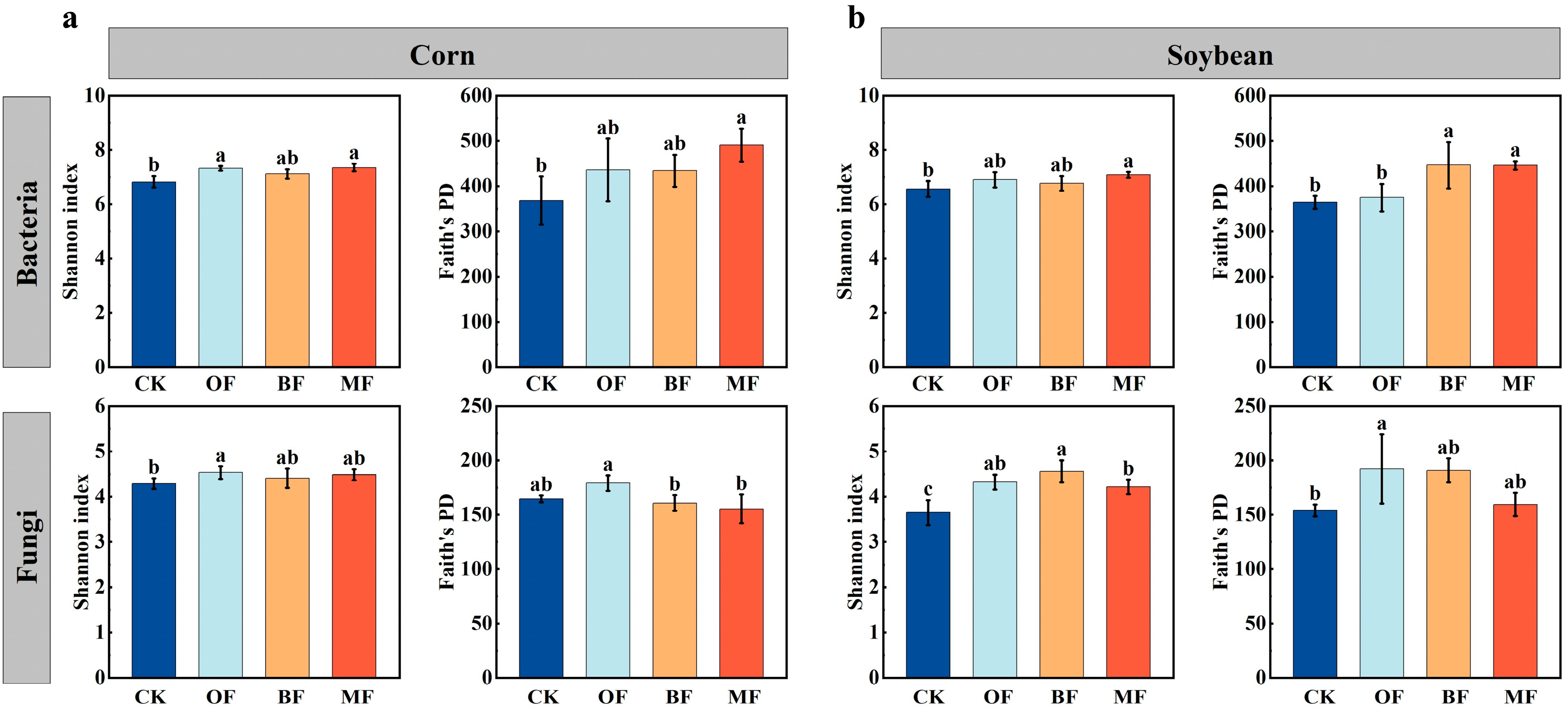
3.2. Effect of Different Fertilization Regimes on the Diversity of Microbial Communities
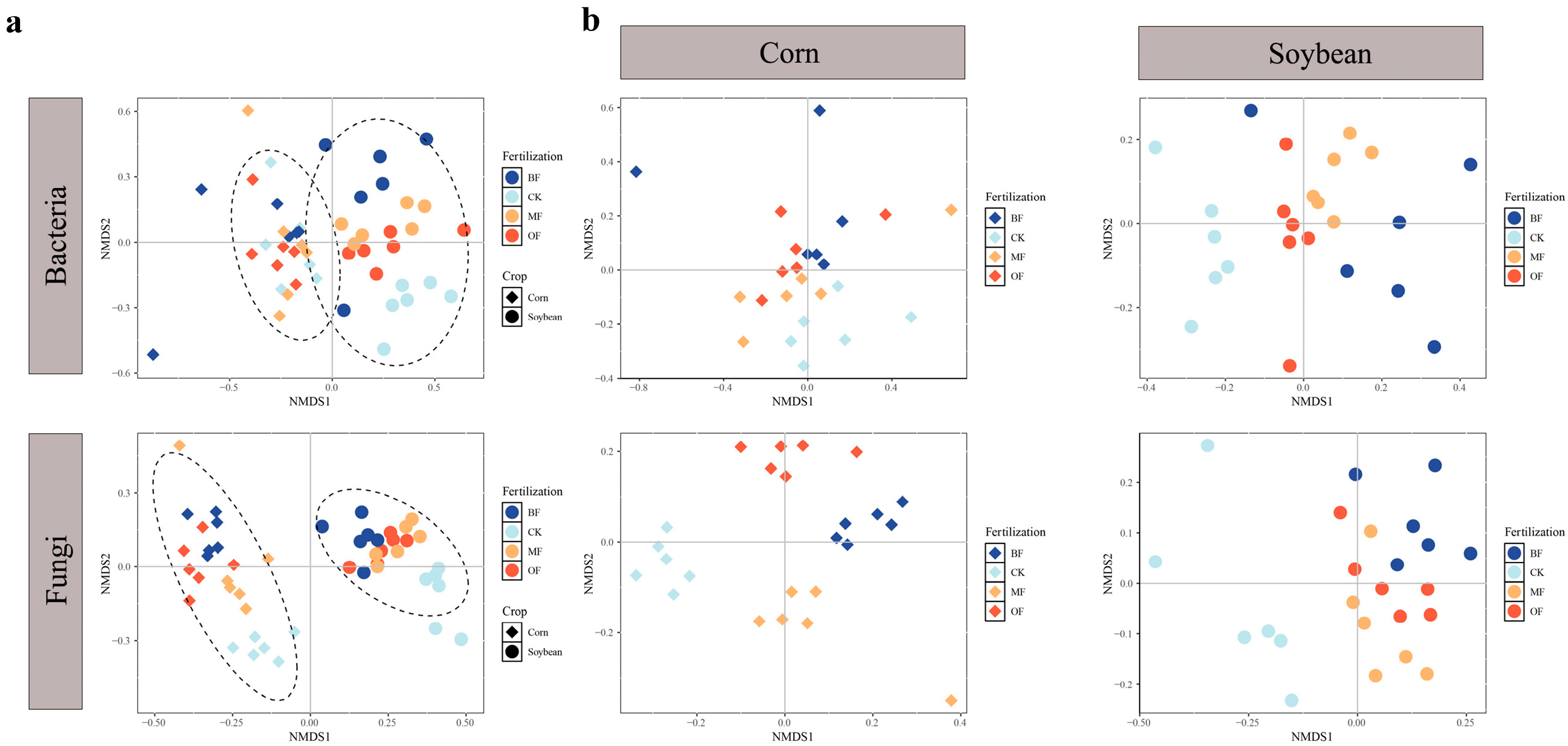
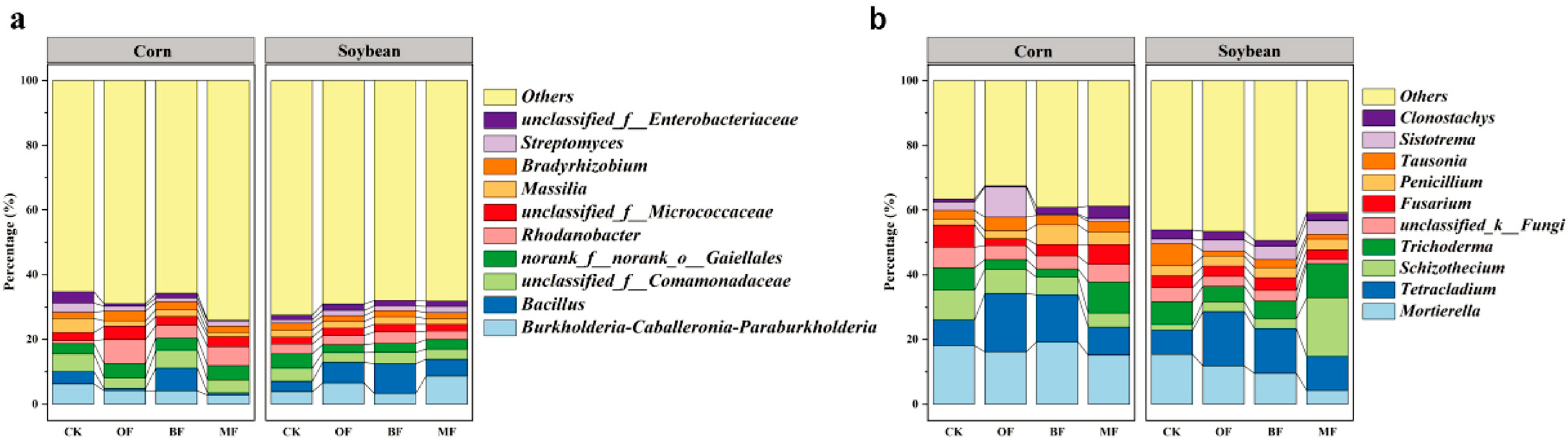
3.3. Effect of Different Fertilization Regimes on Microbial Community Composition
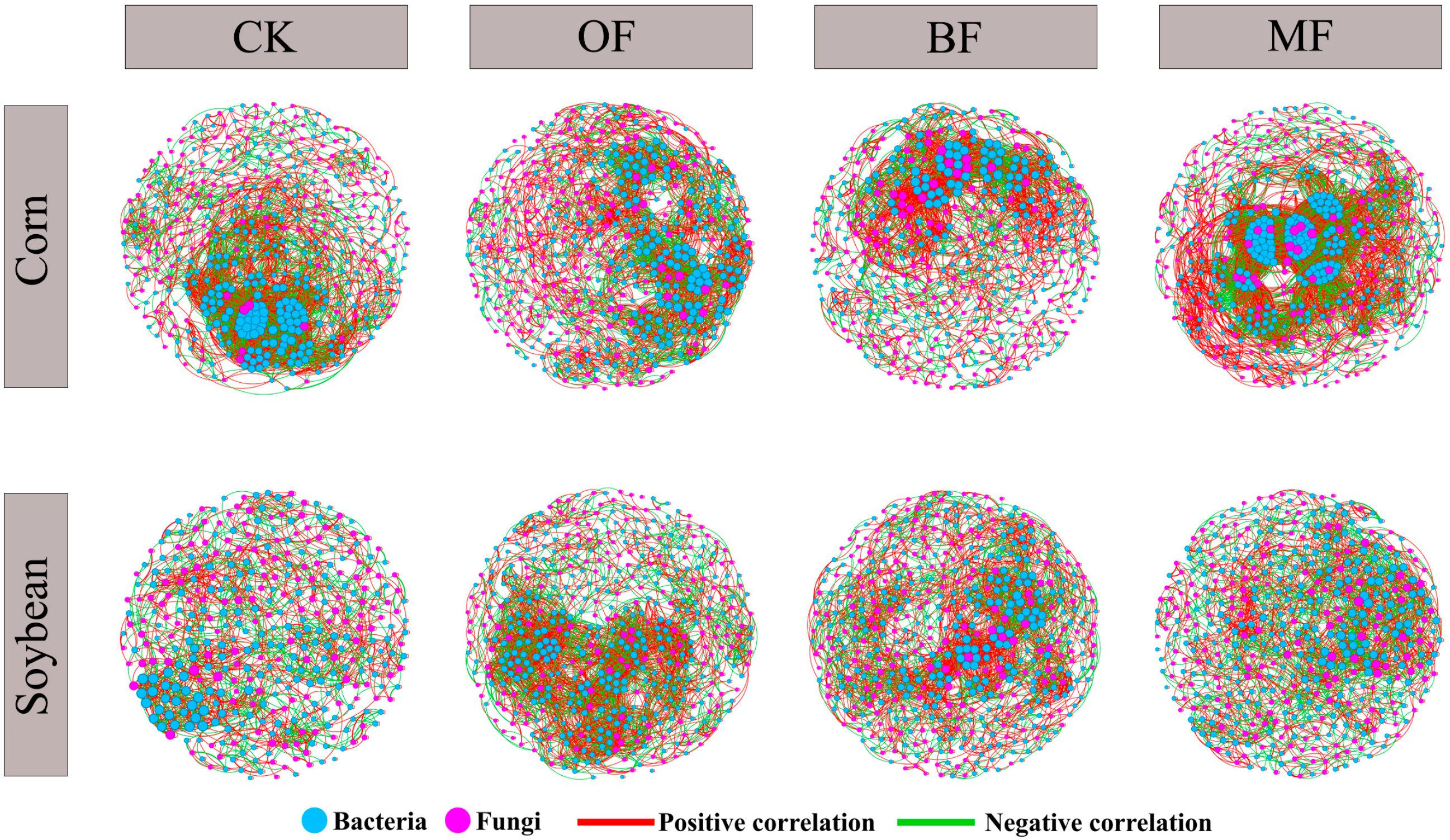
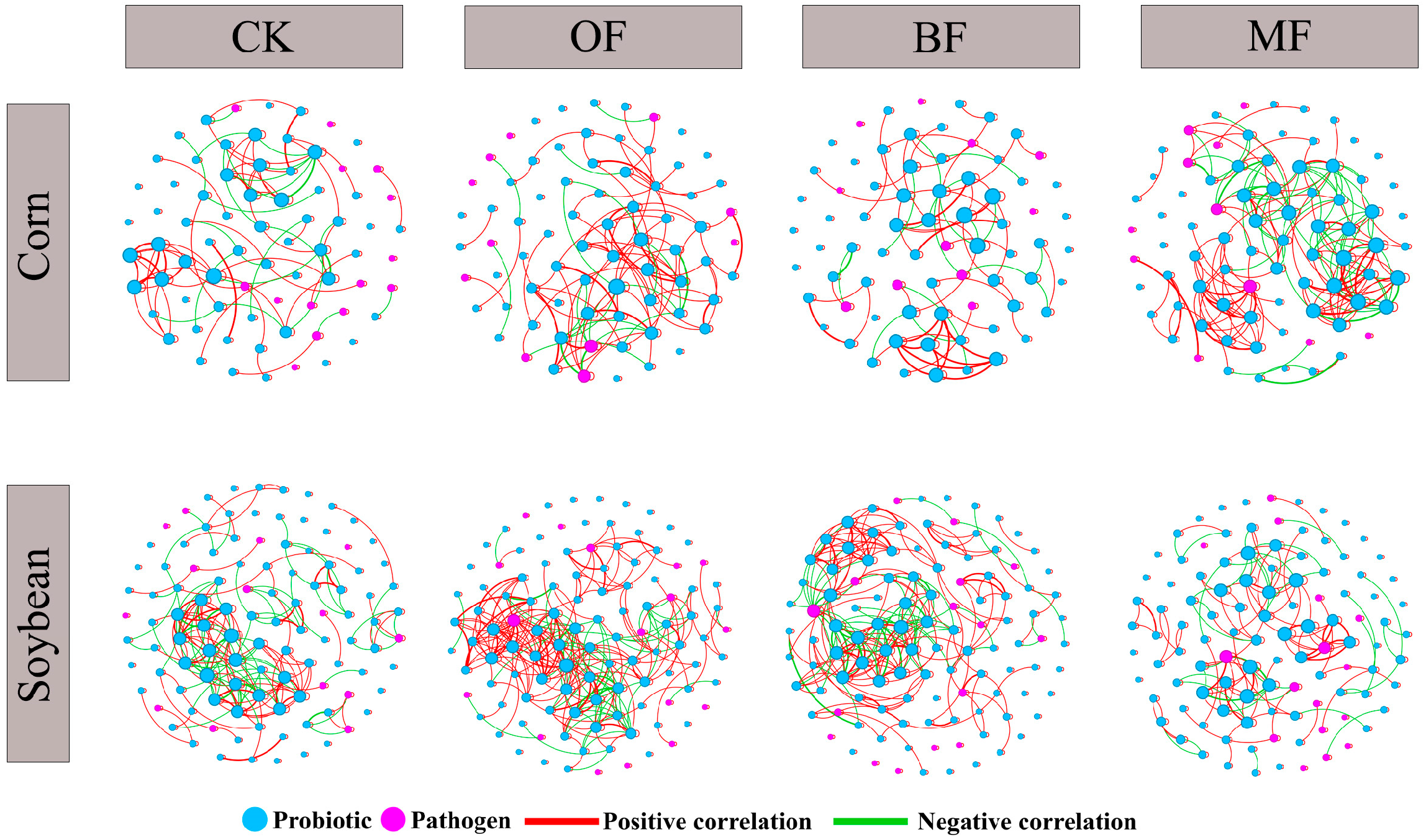
3.4. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis of Microbial Communities in Soils Under Different Fertilization Regimes
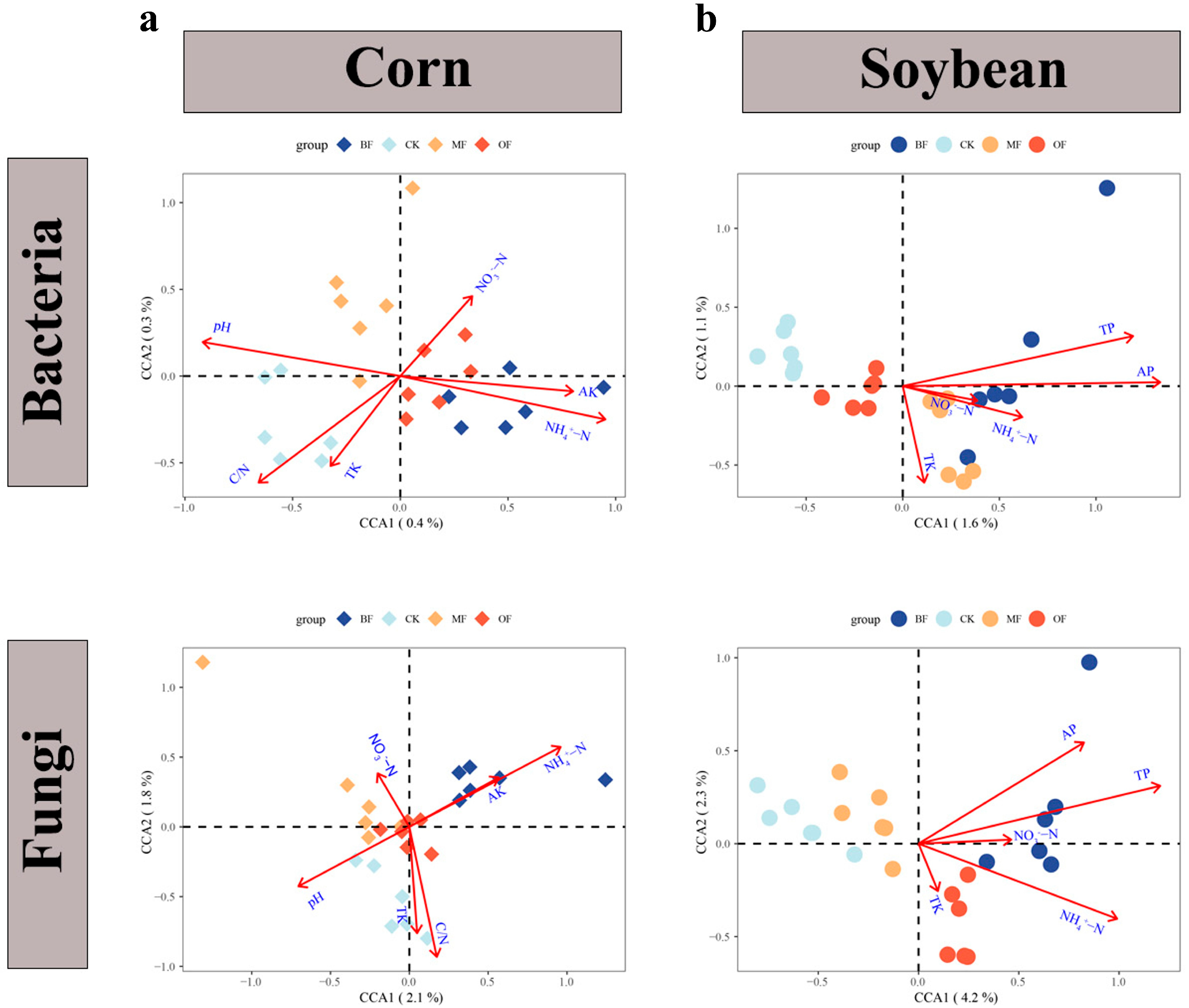
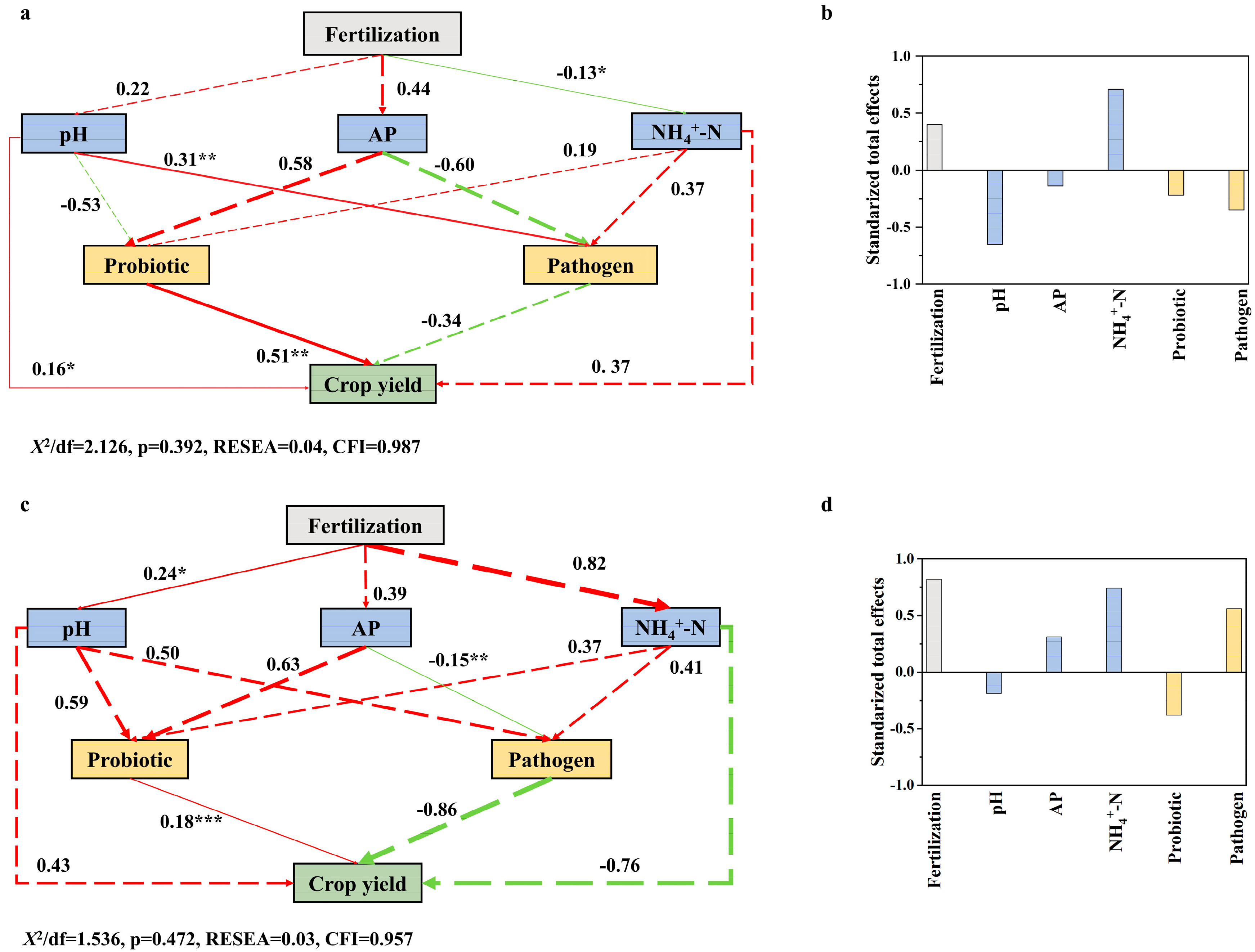
3.5. Abiotic and Biotic Factors Influencing Crop Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. Response of Soil Properties and Crop Yield to Different Fertilizer Treatments
4.2. Effects of Different Fertilizer Treatments on Soil Microbial Communities
4.3. Relationship Between Soil Quality Index, Soil Microbial Communities, and Crop Yield
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kang, Y.L.; Ma, Y.W.; An, X.R.; Kan, L.P.; Xie, C.Y.; Mei, X.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Xu, Y.C.; Dong, C.X. Effects on the Root Morphology and Mircostructure of Young Pear (Pyrus pyrifolia) Tree by Split-Root Supply of Bioorganic and Chemical Fertilizer. Rhizosphere 2022, 22, 100504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.Z.; Zhou, T.; Crowley, D.; Li, L.Q.; Liu, D.W.; Zheng, J.W.; Yu, X.Y.; Pan, G.X.; Hussain, Q.; Zhang, X.H.; et al. Decline in Topsoil Microbial Quotient, Fungal Abundance and C Utilization Efficiency of Rice Paddies under Heavy Metal Pollution across South China. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, J.H.; Song, J.; Kim, B.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Joa, J.H.; Weon, H.Y. Characterization of the Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in Rice Field Soils Subjected to Long-Term Fertilization Practices. J. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 754–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.S.; Zhang, S.B.; Hui, D.F.; Vancov, T.; Fang, Y.Y.; Tang, C.X.; Jiang, Z.H.; Ge, T.D.; Cai, Y.J.; Yu, B.; et al. Pyrogenic Organic Matter Decreases While Fresh Organic Matter Increases Soil Heterotrophic Respiration Through Modifying Microbial Activity in a Subtropical Forest. Biol. Fert. Soils. 2024, 60, 509–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Z.; Hu, Z.R.; Tan, G.; Fan, J.Q.; Chen, Y.Q.; Xiao, Y.S.; Wu, S.L.; Zhi, Q.Q.; Liu, T.B.; Yin, H.Q.; et al. Enhancing Plant Growth in Biofertilizer-Amended Soil Through Nitrogen-Transforming Microbial Communities. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1259853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.T.; Yang, D.; Wu, Y.H.; Zhou, F.; Yu, J.X.; Chi, R.; Xiao, C.Q. Preparation of Biofertilizer with Phosphogypsum and Straw: Microbial Community Changes and Plant Growth Effects. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2024, 24, 3873–3888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.F.; He, X.H.; Chen, S.G.; Li, Y.J.; Huang, Q.W.; Xue, C.; Shen, Q.R. Long-Term Organic–Inorganic Fertilization Regimes Alter Bacterial and Fungal Communities and Rice Yields in Paddy Soil. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 890712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, S.J.; Wolinska, K.W.; Hacquard, S. Microbiota-Root-Shoot-Environment Axis and Stress Tolerance in Plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2021, 62, 102028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Zhao, M.L.; Yuan, J.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; Shen, Q.R. Root Exudates Mediate Plant Defense Against Foliar Pathogens by Recruiting Beneficial Microbes. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2021, 3, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, A.S.F.; Pereira, A.P.d.A.; da Costa, D.P.; de Medeiros, E.V.; Araujo, F.F.; Sharma, S.; Mendes, L.W. Enhancing Plant Resilience to Pathogens Through Strategic Breeding: Harnessing Beneficial Bacteria from the Rhizosphere for Progeny Protection. Rhizosphere 2024, 30, 100890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo, G. How Plants Recruit their Microbiome? New Insights into Beneficial Interactions. J. Adv. Res. 2022, 40, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, Y.P.; Fei, J.C.; Rong, X.M.; Peng, J.W.; Luo, G.W. Crop Rotation-Driven Changes in Rhizosphere Metabolite Profiles Regulate Soil Microbial Diversity and Functional Capacity. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 358, 108716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.K.; Yan, C.R.; Mei, X.R.; He, W.Q.; Bing, S.H.; Ding, L.P.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Fan, T.L. Long-Term Effect of Chemical Fertilizer, Straw, and Manure on Soil Chemical and Biological Properties in Northwest China. Geoderma 2010, 158, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.Q.; Groenigen, V.K.J.; Hungate, B.A.; Cao, J.J.; Zhou, X.H.; Wang, R.W. A Keystone Microbial Enzyme for Nitrogen Control of Soil Carbon Storage. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomiero, T.; David, P.; Paoletti, M.G. Environmental Impact of Different Agricultural Management Practices: Conventional vs. Organic Agriculture. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2011, 30, 95–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, D.; Rana, K.L.; Yadav, A.N.; Yadav, N.; Kumar, M.; Kumar, V.; Vyas, P.; Dhaliwal, H.S.; Saxena, A.K. Microbial Biofertilizers: Bioresources and Eco-friendly Technologies for Agricultural and Environmental Sustainability. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 23, 101487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahanty, T.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Goswami, M.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Das, B.; Ghosh, A.; Tribedi, P. Biofertilizers: A Potential Approach for Sustainable Agriculture Development. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 3315–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assainar, S.K.; Abbott, L.K.; Mickan, B.S.; Whiteley, A.S.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Solaiman, Z.M. Response of Wheat to a Multiple Species Microbial Inoculant Compared to Fertilizer Application. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzola, M.; Freilich, S. Prospects for Biological Soilborne Disease Control: Application of Indigenous Versus Synthetic Microbiomes. Phytopathology 2016, 107, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Wang, W.X.; Yuan, Z.B.; Sederoff, R.R.; Sederoff, H.; Chiang, V.L.; Borriss, R. Microbial Interactions Within Multiple-Strain Biological Control Agents Impact Soil-Borne Plant Disease. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 585404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugtenberg, B.; Kamilova, F. Plant-Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2009, 63, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vejan, P.; Abdullah, R.; Khadiran, T.; Ismail, S.; Boyce, A.N. Role of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria in Agricultural Sustainability—A Review. Molecules 2016, 21, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamkhi, I.; Cheto, S.; Geistlinger, J.; Zeroual, Y.; Kouisni, L.; Bargaz, A.; Ghoulam, C. Legume-Based Intercropping Systems Promote Beneficial Rhizobacterial Community and Crop Yield Under Stressing Conditions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 183, 114958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varghese, E.M.; Kour, B.; Ramya, S.; Krishna, P.D.; Nazla, K.A.; Sudheer, K.; Anith, K.N.; Jisha, M.S.; Ramakrishnan, B. Rice in Acid Sulphate Soils: Role of Microbial Interactions in Crop and Soil Health Management. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 196, 105309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Li, D.C.; Jing, H.; Ahmed, W.; Abbas, M.; Qaswar, M.; Anthonio, C.K.; Lu, Z.; Wang, B.; Xu, Y.M.; et al. Soil Microbial Biomass and Extracellular Enzymes Regulate Nitrogen Mineralization in a Wheat-Maize Cropping System After Three Decades of Fertilization in a Chinese Ferrosol. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, P.Y.; Dou, T.; Song, X.H.; Li, L.Y. Control of Coptis Root Rot by Combination of Bacillus cereus isolate Y9 and Other Antagonistic Microorganisms. J. Plant Pathol. 2024, 106, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, L.; Singh, I. Microbe-Mediated Biotic Stress Signaling and Resistance Mechanisms in Plants. In Plant Stress Biology: Strategies and Trends; Giri, B., Sharma, M.P., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 297–334. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, M.Y.; Narayanan, M.; Shi, X.J.; Chen, X.P.; Li, Z.L.; Ma, Y. Optimistic Contributions of Plant Growth-Promoting Bacteria for Sustainable Agriculture and Climate Stress Alleviation. Environ. Res. 2023, 217, 114924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rodriguez, M.M.; Piccoli, P.; Anzuay, M.S.; Baraldi, R.; Neri, L.; Taurian, T.; Lobato Ureche, M.A.; Segura, D.M.; Cohen, A.C. Native Bacteria Isolated from Roots and Rhizosphere of Solanum lycopersicum L. Increase Tomato Seedling Growth Under a Reduced Fertilization Regime. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pešaković, M.; Karaklajić-Stajić, Ž.; Milenković, S.; Mitrović, O. Biofertilizer Affecting Yield Related Characteristics of Strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa Duch.) and Soil Micro-organisms. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 150, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhuang, M.H.; Shan, N.; Zhao, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, L.G. Substituting Organic Manure for Compound Fertilizer Increases Yield and Decreases NH3 and N2O Emissions in an Intensive Vegetable Production Systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 1184–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.Y.; Ran, W.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Shen, Q.R.R.; Shen, S.; Xu, Y.C. Biocontrol of Fusarium Wilt Disease in Muskmelon with Bacillus subtilis Y-IVI. BioControl 2013, 58, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Gu, L.K.; Bao, L.J.; Zhang, S.W.; Wei, Y.X.; Bai, Z.H.; Zhuang, G.Q.; Zhuang, X.L. Application of Biofertilizer Containing Bacillus subtilis Reduced the Nitrogen Loss in Agricultural Soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.Y.; Li, J.W.; Liu, F.H.; Liu, Z.C.; Luo, S.L.; Wu, Y.; Lyu, J.; Yu, J.H. Reduced Chemical Fertilizer Combined with Bio-Organic Fertilizer Affects the Soil Microbial Community and Yield and Quality of Lettuce. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 863325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Sowinski, S.; Herschkovitz, Y.; Okon, Y.; Jurkevitch, E. Effects of Inoculation with Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria on Resident Rhizosphere Microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2007, 276, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viterbo, A.; Landau, U.; Kim, S.; Chernin, L.; Chet, I. Characterization of ACC Deaminase from the Biocontrol and Plant Growth-Promoting Agent Trichoderma asperellum T203. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2010, 305, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Guo, S.; Jousset, A.; Zhao, Q.Y.; Wu, H.S.; Li, R.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; Shen, Q.R. Bio-fertilizer Application Induces Soil Suppressiveness Against Fusarium Wilt Disease by Reshaping the Soil Microbiome. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 114, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.Y.; Li, R.; Xiong, W.; Shen, Z.Z.; Liu, S.S.; Wang, B.B.; Ruan, Y.Z.; Geisen, S.; Shen, Q.R.; Kowalchuk, G.A. Bio-organic Fertilizers Stimulate Indigenous Soil Pseudomonas Populations to Enhance Plant Disease Suppression. Microbiome 2020, 8, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subiramani, S.; Ramalingam, S.; Muthu, T.; Nile, S.H.; Venkidasamy, B. Development of Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crops by Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria (PGPR). In Phyto-Microbiome in Stress Regulation; Kumar, M., Kumar, V., Prasad, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 125–145. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Ling, N.; Yuan, Y.J.; Zheng, X.Y.; Shen, B.; Shen, Q.R. Bacillus subtilis SQR 9 Can Control Fusarium Wilt in Cucumber by Colonizing Plant Roots. Biol. Fert. Soils 2011, 47, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.M.; Meng, X.H.; Li, T.; Raza, W.; Liu, D.Y.; Shen, Q.R. The Growth Promotion of Peppers (Capsicum annuum L.) by Trichoderma guizhouense NJAU4742-Based Biological Organic Fertilizer: Possible Role of Increasing Nutrient Availabilities. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.S.; Raza, W.; Yang, X.M.; Hu, J.; Huang, Q.W.; Xu, Y.C.; Liu, X.H.; Ran, W.; Shen, Q.R. Control of Fusarium Wilt Disease of Cucumber Plants with the Application of a Bioorganic Fertilizer. Biol. Fert. Soils 2008, 44, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Xiong, W.; Hang, X.N.; Gao, Z.L.; Jiao, Z.X.; Liu, H.J.; Mo, Y.N.; Zhang, N.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; Li, R.; et al. Protists as Main Indicators and Determinants of Plant Performance. Microbiome 2021, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Pang, G.; Cai, F.; Zhang, J.; Shen, Z.Z.; Li, R.; Shen, Q.R. Two-Step Genomic Sequence Comparison Strategy to Design Trichoderma Strain-Specific Primers for Quantitative PCR. AMB Express 2019, 9, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allende-Montalbán, R.; San-Juan-Heras, R.; Martín-Lammerding, D.; Delgado, M.d.M.; Albarrán, M.d.M.; Gabriel, J.L. The Soil Sample Conservation Method and Its Potential Impact on Ammonium, Nitrate and Total Mineral Nitrogen Measurements. Geoderma 2024, 448, 116963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, A.P.; Grimshaw, H.M. A Wet Oxidation Procedure Suitable for Total Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 1985, 16, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.K.R.; John, B.; Wingwafi, R.W. Comparison of Three Digestion Methods for Total Soil Potassium Estimation in Soils of Papua New Guinea Derived from Varying Parent Materials. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2011, 42, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.H.; Vaz, J.E.; Benzo, Z.; Mejias, C. A Comparison of Extraction and Suspension Methods for Determining Exchangeable Potassium in Soils. Appl. Clay Sci. 1999, 14, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoch, C.L.; Seifert, K.A.; Huhndorf, S.; Robert, V.; Spouge, J.L.; Levesque, C.A.; Chen, W.; Bolchcova, E.; Voigt, K.; Crous, P.W.; et al. Nuclear Ribosomal Internal Transcribed Spacer (ITS) Region as A Universal DNA Barcode Marker for Fungi. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6241–6246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Maruyama, F.; Kato, H.; Toyoda, A.; Dozono, A.; Ohtsubo, Y.; Nagata, Y.; Fujiyama, A.; Tsuda, M.; Kurokawa, K. Design and Experimental Application of a Novel Non-Degenerate Universal Primer Set that Amplifies Prokaryotic 16S rRNA Genes with a Low Possibility to Amplify Eukaryotic rRNA Genes. DNA Res. 2013, 21, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolyen, E.; Rideout, J.R.; Dillon, M.R.; Bokulich, N.A.; Abnet, C.C.; Al-Ghalith, G.A.; Alexander, H.; Alm, E.J.; Arumugam, M.; Asnicar, F.; et al. Reproducible, Interactive, Scalable and Extensible Microbiome Data Science Using QIIME 2. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kõljalg, U.; Nilsson, R.H.; Abarenkov, K.; Tedersoo, L.; Taylor, A.F.S.; Bahram, M.; Bates, S.T.; Bruns, T.D.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Callaghan, T.M.; et al. Towards a Unified Paradigm for Sequence-Based Identification of Fungi. Mol. Ecol. 2013, 22, 5271–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.J.; Liu, J.J.; Liang, A.Z.; Li, L.J.; Yao, Q.; Yu, Z.H.; Li, Y.S.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.B.; Wang, G.H. Conventional and Conservation Tillage Practices Affect Soil Microbial Co-occurrence Patterns and Are Associated with Crop Yields. Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 2021, 319, 107534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.L.; Liu, J.J.; Liu, Z.X.; Hu, X.J.; Yu, Z.H.; Li, Y.S.; Chen, X.L.; Li, L.J.; Jin, J.; Wang, G.H. Chitin Amendments Eliminate the Negative Impacts of Continuous Cropping Obstacles on Soil Properties and Microbial Assemblage. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1067618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, D.; Coughlan, J.; Mullen, M. Structural Equation Modelling: Guidelines for Determining Model Fit. Electron. J. Bus. Res. Methods. 2008, 6, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.L.; Yan, Y.; Cao, J.; Christie, P.; Zhang, F.S.; Fan, M.S. Effects of Combined Application of Organic Amendments and Fertilizers on Crop Yield and Soil Organic Matter: An Integrated Analysis of Long-Term Experiments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 225, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, X.P.; Liu, H.B.; Zhai, L.M.; Tan, G.C.; Liu, J.; Ren, T.Z.; Wang, H.Y. Vegetable Yields and Soil Biochemical Properties as Influenced by Fertilization in Southern China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.A.; Gao, W.; Huang, S.; Tang, J.W.; Li, M.Y.; Zhang, H.Z.; Chen, X.P.; Masiliūnas, D. Substitution of Manure for Chemical Fertilizer Affects Soil Microbial Community Diversity, Structure and Function in Greenhouse Vegetable Production Systems. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0214041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Hu, G.Q.; Wang, H.; Bai, E.; Lou, Y.H.; Zhang, A.J.; Zhuge, Y.P. 35 years of Manure and Chemical Fertilizer Application Alters Soil Microbial Community Composition in a Fluvo-Aquic Soil in Northern China. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2017, 82, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, J.L.; Zhang, H.L.; Girma, K.; Raun, W.R.; Penn, C.J.; Payton, M.E. Soil Acidification from Long-Term Use of Nitrogen Fertilizers on Winter Wheat. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 957–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Cho, M.; Sadowsky, M.J.; Jang, J. Dissimilatory Nitrate Reductions in Soil Neobacillus and Bacillus strains Under Aerobic Condition. J. Microbiol. 2025, 63, e2411019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mpanga, I.K.; Ludewig, U.; Dapaah, H.K.; Neumann, G. Acquisition of Rock Phosphate by Combined Application of Ammonium Fertilizers and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 in Maize as Affected by Soil pH. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, W.H.; Sun, Y.; Xia, S.Q.; Zhao, H.T.; Mi, W.T.; Brookes, P.C.; Liu, Y.L.; Wu, L.H. Effect of Inorganic Fertilizers with Organic Amendments on Soil Chemical Properties and Rice Yield in a Low-Productivity Paddy Soil. Geoderma 2018, 320, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.K.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Guo, X.S.; Wang, D.Z.; Zhu, Y.G.; Chu, H.Y. Biodiversity of Key-Stone Phylotypes Determines Crop Production in A 4-Decade Fertilization Experiment. ISME J. 2021, 15, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masunga, R.H.; Uzokwe, V.N.; Mlay, P.D.; Odeh, I.; Singh, A.; Buchan, D.; De Neve, S. Nitrogen Mineralization Dynamics of Different Valuable Organic Amendments Commonly Used in Agriculture. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 101, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.X.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Zhang, Q.F.; Zhou, J.C.; Yue, K.; Chen, Y.M.; Yang, Y.S.; Fan, Y.X. Keystone Bacterial Functional Module Activates P-Mineralizing Genes to Enhance Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Organic P in a Subtropical Forest Soil with 5-year N Addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Das, S.; Shankhdhar, D.; Shankhdhar, S.C. Phosphate-Solubilizing Microorganisms: Mechanism and Their Role in Phosphate Solubilization and Uptake. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeder, P.; Fliessbach, A.; Dubois, D.; Gunst, L.; Fried, P.; Niggli, U. Soil Fertility and Biodiversity in Organic Farming. Science 2002, 296, 1694–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.B.; Dsouza, M.; Gilbert, J.A.; Guo, X.S.; Wang, D.Z.; Guo, Z.B.; Ni, Y.Y.; Chu, H.Y. Fungal Community Composition in Soils Subjected to Long-Term Chemical Fertilization Is Most Influenced by the Type of Organic Matter. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 5137–5150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shu, A.P.; Song, W.F.; Shi, W.C.; Li, M.C.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, Z.Z.; Liu, G.R.; Yuan, F.S.; Zhang, S.X.; et al. Long-Term Organic Fertilizer Substitution Increases Rice Yield by Improving Soil Properties and Regulating Soil Bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, N.W.; Slessarev, E.; Marschmann, G.L.; Nicolas, A.; Blazewicz, S.J.; Brodie, E.L.; Firestone, M.K.; Foley, M.M.; Hestrin, R.; Hungate, B.A.; et al. Life and Death in the Soil Microbiome: How Ecological Processes Influence Biogeochemistry. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.L.; Han, C.; Zhang, J.B.; Huang, Q.R.; Deng, H.; Deng, Y.C.; Zhong, W.H. Long-Term Fertilization Effects on Active Ammonia Oxidizers in An Acidic Upland Soil in China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 84, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, S.; Tamm, A.; Wu, D.; Caesar, J.; Grube, M.; Weber, B. Photoautotrophic Organisms Control Microbial Abundance, Diversity, And Physiology in Different Types of Biological Soil Crusts. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1032–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Jiao, Z.X.; Yan, Z.G.; Yan, X.Y.; Deng, X.H.; Xiong, W.; Tao, C.Y.; Liu, H.J.; Li, R.; Shen, Q.R.; et al. Predatory Protists Reduce Bacteria Wilt Disease Incidence in Tomato Plants. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.W.; Zuohereguli, K.; Zhang, L.S.; Kang, Y.L.; Shi, L.W.; Xu, H.; Ruan, Y.; Wen, T.; Mei, X.L.; Dong, C.X.; et al. Soil Microbial Mechanisms to Improve Pear Seedling Growth by Applying Bacillus and Trichoderma-Amended Biofertilizers. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 48, 3968–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Singh, J. Biofilms Forming Microbes: Diversity and Potential Application in Plant–Microbe Interaction and Plant Growth. In Plant Microbiomes for Sustainable Agriculture; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 173–197. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Wang, X.Q.; Friman, V.P.; Huang, J.F.; Wang, X.F.; Mei, X.L.; Xu, Y.C.; Shen, Q.R.; Jousset, A. Pathogen Invasion Indirectly Changes the Composition of Soil Microbiome Via Shifts in Root Exudation Profile. Biol. Fert. Soils 2016, 52, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.Q.; Li, D.; Ding, J.X.; Xiao, X.; Liang, Y.T. Microbial Coexistence in the Rhizosphere and the Promotion of Plant Stress Resistance: A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 222, 115298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Mendoza-Mendoza, A.; Zeilinger, S.; Horwitz, B.A. Mycoparasitism as a Mechanism of Trichoderma-Mediated Suppression of Plant Diseases. Fungal Biol. Rev. 2022, 39, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.Y.; Zhao, Q.Q.; Li, W.; Gao, L.W.; Liu, G.D. Strain Improvement of Trichoderma harzianum for Enhanced Biocontrol Capacity: Strategies and Prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1146210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrios, E. Soil Biota, Ecosystem Services and Land Productivity. Ecol. Econ. 2007, 64, 269–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Penton, C.R.; Ruan, Y.Z.; Shen, Z.X.; Xue, C.; Li, R.; Shen, Q.R. Inducing the Rhizosphere Microbiome by Biofertilizer Application to Suppress Banana Fusarium Wilt Disease. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.L.; Xu, Z.H.; Xie, J.Y.; Hesselberg-Thomsen, V.; Tan, T.M.; Zheng, D.Y.; Strube, M.L.; Dragoš, A.; Shen, Q.R.; Zhang, R.F.; et al. Bacillus velezensis Stimulates Resident Rhizosphere Pseudomonas stutzeri for Plant Health Through Metabolic Interactions. ISME J. 2022, 16, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, X.B.; Xiao, S.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, Y.H.; Yang, H.; Zhang, L.X. Comparative Analysis of Rhizosphere Soil Physiochemical Characteristics and Microbial Communities Between Rusty and Healthy Ginseng Root. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayat, R.; Ali, S.; Amara, U.; Khalid, R.; Ahmd, I. Soil Beneficial Bacteria and Their Role in Plant Growth Promotion: A Review. Ann. Microbiol. 2020, 60, 579–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madhaiyan, M.; Selvakumar, G.; Alex, T.H. Plant Growth Promoting Abilities of Novel Burkholderia-Related Genera and Their Interactions with Some Economically Important Tree Species. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 618305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, H.F.; Luo, S.Y.; Ye, L.B.; Wang, C.J.; Wang, X.N.; Tian, C.J.; Sun, Y. Analysis and Functional Prediction of Core Bacteria in the Arabidopsis Rhizosphere Microbiome under Drought Stress. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, B.X.; Bi, Q.F.; Zhou, G.W.; Yang, X.R. Massilia phosphatilytica sp. nov., A Phosphate Solubilizing Bacteria Isolated from a Long-term Fertilized Soil. Int. J. Syst Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 2514–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Guo, X.J.; Huang, X.; Guo, R.J.; Lu, X.H.; Li, S.D.; Zhang, H. The Co-Association of Enterobacteriaceae and Pseudomonas with Specific Resistant Cucumber against Fusarium Wilt Disease. Biology 2023, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, R.A.; Balsanelli, E.; Wassem, R.; Marin, A.M.; Brusamarello-Santos, L.C.C.; Schmidt, M.A.; Tadra-Sfeir, M.Z.; Pankievicz, V.C.S.; Cruz, L.M.; Chubatsu, L.S.; et al. Herbaspirillum-plant Interactions: Microscopical, Histological and Molecular Aspects. Plant Soil. 2012, 356, 175–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.L.; Yang, W.L.; Fang, W.W.; Zhao, Y.X.; Guo, L.; Dai, Y.J. The Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacterium Variovorax boronicumulans CGMCC 4969 Regulates the Level of Indole-3-Acetic Acid Synthesized from Indole-3-Acetonitrile. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxton, A.; Masih, S.A. Variovorax Soil Mediated Growth Amelioration and Abiotic Stress Alleviation in Capsicum Annuum. Res. J. Biotech. 2024, 19, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogra, T.; Priyadarshini, A.; Kanika; Kumar, A.; Singh, N.K. Identification of Genes Involved in Salt Tolerance and Symbiotic Nitrogen Fixation in Chickpea Rhizobium Mesorhizobium ciceri Ca181. Symbiosis 2013, 61, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liswadiratanakul, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Matsutani, M.; Wattanadasaree, V.; Kihara, S.; Shiwa, Y.; Shiwachi, H. Replacement of Water yam (Dioscorea alata L.) Indigenous Root Endophytes and Rhizosphere Bacterial Communities via Inoculation with a Synthetic Bacterial Community of Dominant Nitrogen-fixing Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1060239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.Y.; Hammed, A.; Huang, H.; Young, C.C. Allorhizobium terrae sp. nov., Isolated from Paddy Soil, and Reclassification of Rhizobium oryziradici. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, I.; Narayan, S.; Shukla, J.; Shirke, P.A.; Kumar, M. Endofungal Rhizobium Species Enhance Arsenic Tolerance in Colonized Host Plant under Arsenic Stress. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Kang, Y.; Wang, Z.B.; Du, C.Y.; Tan, J.; Zhao, X.Y.; Qi, G.F. Ralstonia solanacearum Infection Induces Tobacco Root to Secrete Chemoattractants to Recruit Antagonistic Bacteria and Defensive Compounds to Inhibit Pathogen. Pest Manag. Sci. 2025, 81, 1817–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagide, C. Identification of Plant Compounds Involved in the Microbe-Plant Communication During the Coinoculation of Soybean with Bradyrhizobium elkanii and Delftia sp. strain JD2. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2018, 31, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.G.; Sun, L.; Dong, X.Z.; Cai, Z.Q.; Sun, X.L.; Yang, H.L.; Wang, Y.S.; Song, W. Characterization of a Novel Plant Growth-promoting Bacteria Strain Delftia tsuruhatensis HR4 Both as a Diazotroph and a Potential Biocontrol Agent Against Various Plant Pathogens. Syst Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 28, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.H.; Ji, C.C.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, C.C.; Cai, H.M. Zinc Application Promotes Nitrogen Transformation in Rice Rhizosphere Soil by Modifying Microbial Communities and Gene Expression Levels. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 849, 157858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.H.; Anand, S.; Singh, B.; Bohra, A.; Joshi, R. WRKY Transcription Factors and Plant Defense Responses: Latest Discoveries and Future Prospects. Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 1071–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luca, D.G.; Barkat, M.; Verméglio, A.; Archouak, W.; Heulin, T. The Bacterial Genus Ramlibacter: Betaproteobacteria Capable of Surviving in Oligotrophic Environments Thanks to Several Shared Genetic Adaptation Traits. Environ. Microbiol. 2025, 27, 70059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timofeeva, A.M.; Galyamova, M.R.; Sedykh, S.E. Plant Growth-Promoting Soil Bacteria: Nitrogen Fixation, Phosphate Solubilization, Siderophore Production, and Other Biological Activities. Plants 2023, 12, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borah, P.; Asd, S.A.; Rabha, A.J.; Arooq, M. An Insight into Plant Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria-Mediated Mitigation of Stresses in Plant. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 3229–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laslo, É.; György, É.; Mara, G.; Tamás, É.; Ábrahám, B.; Lányi, S. Screening of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria as Potential Microbial Inoculants. Crop Protect. 2012, 40, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.L.; Waqas, M.; Kang, S.M.; Al-Harrasi, A.A.; Hussain, J.; Al-Rawahi, A.A.; Al-Khiziri, S.; Ullah, I.; Ali, L.; Jung, H.Y.; et al. Bacterial Endophyte Sphingomonas sp. LK11 Produces Gibberellins and IAA and Promotes Tomato Plant Growth. J. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wei, Y.L.; Yin, T.Z.; Wang, C.C.; Chao, Y.H.; Jia, M.Y.; An, L.Z.; Sheng, H.M. Sphingomonas sp. Hbc-6 Alters Physiological Metabolism and Recruits Beneficial Rhizosphere Bacteria to Improve Plant Growth and Drought Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1002772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Mohanta, T.K.; Asaf, S.; Rehman, N.; Al-Housni, S.; Al-Harrasi, A.; Khan, A.L.K.; Al-Rawahi, A. Biotransformation of Benzoin by Sphingomonas sp. LK11 and Ameliorative Effects on Growth of Cucumis sativus. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadamgahi, F.; Tarighi, S.; Taheri, P.; Saripella, G.V.; Anzalone, A.; Kalyandurg, P.B.; Catara, V.; Ortiz, R.; Vetukuri, R.R. Plant Growth-Promoting Activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa FG106 and Its Ability to Act as a Biocontrol Agent against Potato, Tomato and Taro Pathogens. Biology 2022, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessy, A.; Fillion, M. Phenazines in Plant-beneficial Pseudomonas spp.: Biosynthesis, Regulation, Function and Genomics. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 3905–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.Y.; Liu, T.B.; Fan, J.Q.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wu, S.L.; Li, J.J.; Liu, Z.H.; Yang, Z.D.; Li, L.Z.; Liu, S.N.; et al. Biocontrol Agents Modulate Phyllosphere Microbiota Interactions against Pathogen Pseudomonas syringae. Environ. Sci. Ecotech. 2024, 21, 100431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macey, M.C.; Pratscher, J.; Crombie, A.T.; Murrell, J.C. Impact of Plants on the Diversity and Activity of Methylotrophs in Soil. Microbiome 2020, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.Y.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, J.S.; Shin, D.; Ku, B.; Son, K.; Park, H. Identification and Characterization of a Novel, Cold-Adapted d-Xylobiose- and d-Xylose-Releasing Endo-β-1,4-xylanase from an Antarctic Soil Bacterium, Duganella sp. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haack, F.S.; Poehlein, A.; Kröger, C.; Voigt, C.A.; Piepenbring, M.; Bode, H.B.; Daiel, R.; Schäfer, W.; Streit, W.R. Molecular Keys to the Janthinobacterium and Duganella spp. Interaction with the Plant Pathogen Fusarium graminearum. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Liu, Y.Y.; Mao, F.F.; Liu, Y.R.; Wei, X.L. Purification, Characterization, and Biological Cytotoxic Activity of the Extracellular Cholesterol Oxidase Produced by Castellaniella sp. COX. J. Basic Microbiol. 2020, 60, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, A.; Ramakumar, A.; Bartels, D.; Battistoni, F.; Bekel, T.; Boch, J.; Böhm, M.; Friedrich, F.; Hurek, T.; Krause, L.; et al. Complete Genome of the Mutualistic, N2-fixing Grass Endophyte Azoarcus sp. strain BH72. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 1385–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandham, R.; Indiragandhi, P.; Madhaiyan, M.; Ru, K.Y.; Jee, H.J.; Sa, T.M. Chemolithoautotrophic Oxidation of Thiosulfate and Phylogenetic Distribution of Sulfur Oxidation Gene (soxB) in Rhizobacteria Isolated from Crop Plants. Res. Microbiol. 2008, 159, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.H. The Photosynthetic Bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris Strain PS3 Exerts Plant Growth-Promoting Effects by Stimulating Nitrogen Uptake and Elevating Auxin Levels in Expanding Leaves. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 573634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, P.; Tan, X.Q.; Li, C.G.; Zhang, D.Y.; Cheng, J.E.; Zhang, S.B.; Zhou, X.G.; Yan, Q.P.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Photosynthetic Bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris GJ-22 Induces Systemic Resistance against Viruses. Microb. Biotechnol. 2017, 10, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, G.C.; Videira, S.S.; Urquiaga, S.; Reis, V.M. Differential Plant Growth Promotion and Nitrogen Fixation in Two Genotypes of Maize by several Herbaspirillum inoculants. Plant Soil. 2015, 387, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, G.T. Infection, Colonization and Growth-promoting Effects of Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis L.) by the Endophytic Bacterium Herbaspirillum sp. WT00C. Afr. J. Agr. Res. 2016, 11, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusamarello-Stantos, L.C.C.; Alnerton, D.; Valdament, G.; Camilios-Neto, D.; Covre, R.; Lpes, K.d.P.; Tadra-Sfeir, M.Z.; Faoro, H.; Monteiro, R.; Barbosa-Silva, A.; et al. Modulation of Defence and Iron Homeostasis Genes in Rice Roots by the Diazotrophic Endophyte Herbaspirillum seropedicae. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramandi, A.; Jaghargh, M.B.; Nourashrafeddin, S.M.; Seifi, A. Cupriavidus metallidurans: A Species-non-specific and Multifaceted Plant Growth-promoting Bacteria. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.; Kalam, S.; Sharm, N.K.; Podile, A.R. Phosphate Solubilization and Plant Growth Promotion by Two Pantoea strains Isolated from the Flowers of Hedychium coronarium L. Front. Agron. 2022, 4, 990869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, F.X.; Hernandez, A.G.; Glick, B.R.; Rossi, M.J. The Extreme Plant-growth-promoting Properties of Pantoea phytobeneficialis MSR2 Revealed by Functional and Genomic Analysis. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1341–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallucchini, M.; Franchini, M.; El-Ballat, E.M.; Naraidoo, N.; Pointer-GLeadhill, B.P.; Palframan, M.J.; Hayes, C.J.; Dent, D.; Cocking, E.C.; Perazzolli, M.; et al. Gluconacetobacter diazotrophicus AZ0019 Requires Functional nifD Gene for Optimal Plant Growth Promotion in Tomato plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1469676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.W. Potentiality of Beneficial Microbe Bacillus siamensis GP-P8 for the Suppression of Anthracnose Pathogens and Pepper Plant Growth Promotion. Plant Patho. J. 2024, 40, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharwad, K.; Rajkumar, S. Modulation of PQQ-dependent Glucose Dehydrogenase (mGDH and sGDH) Activity by Succinate in Phosphate Solubilizing Plant Growth Promoting Acinetobacter sp. SK2. 3 Biotech. 2019, 10, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.; Gajjar, H.; Joshi, B.; Krishnamurthy, R.; Amaresan, N. Inoculation of Salt-Tolerant Acinetobacter sp. (RSC9) Improves the Sugarcane (Saccharum sp. Hybrids) Growth Under Salinity Stress Condition. Sugar Tech. 2022, 24, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.P.; Liao, W.M.; Zhang, P.Y.; Li, J.; Nai, M.; Wang, S.Q.; Cai, Y.J.; Li, F. Fe1-xS/Biochar Combined with Thiobacillus Enhancing Lead Phytoavailability in Contaminated Soil: Preparation of Biochar, Enrichment of Thiobacillus and Their Function on Soil Lead. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 267, 115447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, C.; Christensen, M.N.; Kovács, Á. Molecular Aspects of Plant Growth Promotion and Protection by Bacillus subtilis. Mol. Plant Micro. Interact. 2020, 34, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Jin, X.; Wen, J.T.; Zhang, Y.F.; Yang, X.; Wei, G.Y.; Wang, Y.K.; Qin, M. Biocontrol and Growth Promotion Potential of Bacillus subtilis CTXW 7-6-2 against Rhizoctonia solani that Causes Tobacco Target Spot Disease. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2024, 73, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Pool, J.A.; Calderón-Pérez, B.; Ruiz-Medrano, R.; Ortiz-Castro, R.; Xoconostle-Cazares, B. Bacillus Strains as Effective Biocontrol Agents Against Phytopathogenic Bacteria and Promoters of Plant Growth. Microbo. Ecol. 2024, 87, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjort, K.; Bergström, M.; Adesina, M.F.; Jansson, J.K.; Smalla, K.; Sjöling, S. Chitinase Genes Revealed and Compared in Bacterial Isolates, DNA Extracts and A Metagenomic Library from a Phytopathogen-suppressive Soil. Fems. Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 71, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, Q.; Wang, X.K.; Haider, F.U.; Kučerik, J.; Mumtaz, M.Z.; Holatko, J.; Naseem, M.; Kintl, A.; Ejza, M.; Naveed, M.; et al. Rhizosphere Bacteria in Plant Growth Promotion, Biocontrol, and Bioremediation of Contaminated Sites: A Comprehensive Review of Effects and Mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, M.; Ali, Q.; Zhao, W.; Chi, Y.K.; Ali, F.; Rashid, K.A.; Cao, S.; He, Y.Q.; Bukero, A.A.; Huang, W.K.; et al. Exploring Plant Growth Promoting Traits and Biocontrol Potential of New Isolated Bacillus subtilis BS-2301 Strain in Suppressing Sclerotinia sclerotiorum through Various Mechanisms. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1444328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, F.; Arshad, H.; Ahad, M.; Jamal, A.; Smith, D. In Vitro Assessment of Bacillus subtilis FJ3 Affirms its Biocontrol and Plant Growth Promoting Potential. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1205894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, A.F.; Gu, C.Y.; Zang, H.Y.; Chen, Y. First Report of Clonostachys rhizophaga as a Pathogen of Water Chestnut (Eleocharis dulcis) in Anhui Province of China. Plant Dis. 2018, 103, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Ali, Q.; Yan, W.W.; Zhang, G.G.; Li, H.; Zhou, L.T.; Yao, H.M.; Chong, J.J.; Gu, Q.; Wu, H.J.; et al. Role of Iturin from Bacillus velezensis DMW1 in Suppressing Growth and Pathogenicity of Plectosphaerella cucumerina in Tomato by Reshaping the Rhizosphere Microbial Communities. Microbio. Res. 2025, 296, 128150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Q.; Wang, W.X.; Li, Y.P.; Guo, Y.L.; Zhang, D.F.; Ma, X.N.; Song, W.; Zhao, J.R.; Xu, M.L. A transposon-directed Epigenetic Change in ZmCCT Underlies Quantitative Resistance to Gibberella Stalk Rot in Maize. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 1503–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, K.; Chu, T.R.; Shi, Y.X.; Xie, X.W.; Li, L.; Fan, T.F.; Sun, B.X.; Li, B.J.; Chai, A. First Report of Gibellulopsis nigrescens Causing Yellow Wilt on Chinese Cabbage in China. Plant Dis. 2024, 108, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlström, A.; Papp-Rupar, M.; Passey, T.A.J.; Deakin, G.; Xu, X.M. Quantitative Trait Loci Associated with Apple Endophytes During Pathogen Infection. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1054914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timilsina, S.; Potnis, N.; Newberry, E.A.; Liyanapatiranage, P.; Iruegas-Bocardo, F.; White, F.F.; Goss, E.M.; Jones, J.B. Xanthomonas Diversity, Virulence and Plant-pathogen Interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 18, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.H.; Park, G.C.; Kim, K.S. Antagonistic Evaluation of Chromobacterium sp. JH7 for Biological Control of Ginseng Root Rot Caused by Cylindrocarpon destructans. Mycobiology 2017, 45, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrión, V.J.; Perez-Jaramillo, J.; Cordovex, V.; Tracanna, V.; Hollander, M.d.; Ruiz-Buck, D.; Mendes, L.W.; Ijcken, W.F.J.v.; Gomez-Exposito, R.; Elsayed, S.S.; et al. Pathogen-induced Activation of Disease-suppressive Functions in the Endophytic Root Microbiome. Science 2019, 366, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piewngam, P.; Zheng, Y.; Nguyen, T.H.; Dickey, S.W.; Joo, H.S.; Villaruz, A.E.; Glose, K.A.; Fisher, E.L.; Hunt, R.L.; Li, B.; et al. Pathogen Elimination by Probiotic Bacillus via Signalling Interference. Nature 2018, 562, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitkowski, N.; Chaves, A. Identification of Waitea circinata as a Pathogen of the Moss Bryum argenteum var. argenteum on a Golf Course Fairway. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Shen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Gu, H.; Hu, X.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; et al. Biofertilizers Enhance Soil Fertility and Crop Yields Through Microbial Community Modulation. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071572
Zhang X, Zhang L, Liu J, Shen Z, Liu Z, Gu H, Hu X, Yu Z, Li Y, Jin J, et al. Biofertilizers Enhance Soil Fertility and Crop Yields Through Microbial Community Modulation. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071572
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xu, Lei Zhang, Junjie Liu, Zongzuan Shen, Zhuxiu Liu, Haidong Gu, Xiaojing Hu, Zhenhua Yu, Yansheng Li, Jian Jin, and et al. 2025. "Biofertilizers Enhance Soil Fertility and Crop Yields Through Microbial Community Modulation" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071572
APA StyleZhang, X., Zhang, L., Liu, J., Shen, Z., Liu, Z., Gu, H., Hu, X., Yu, Z., Li, Y., Jin, J., & Wang, G. (2025). Biofertilizers Enhance Soil Fertility and Crop Yields Through Microbial Community Modulation. Agronomy, 15(7), 1572. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071572






