Optimizing Sulfur Fertilization for Yield and Aroma Enhancement in Fragrant Rice Under Varying Soil Sulfur Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Field Experiment and Soil Analysis
2.2. Data Collection and Chemical Analysis
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
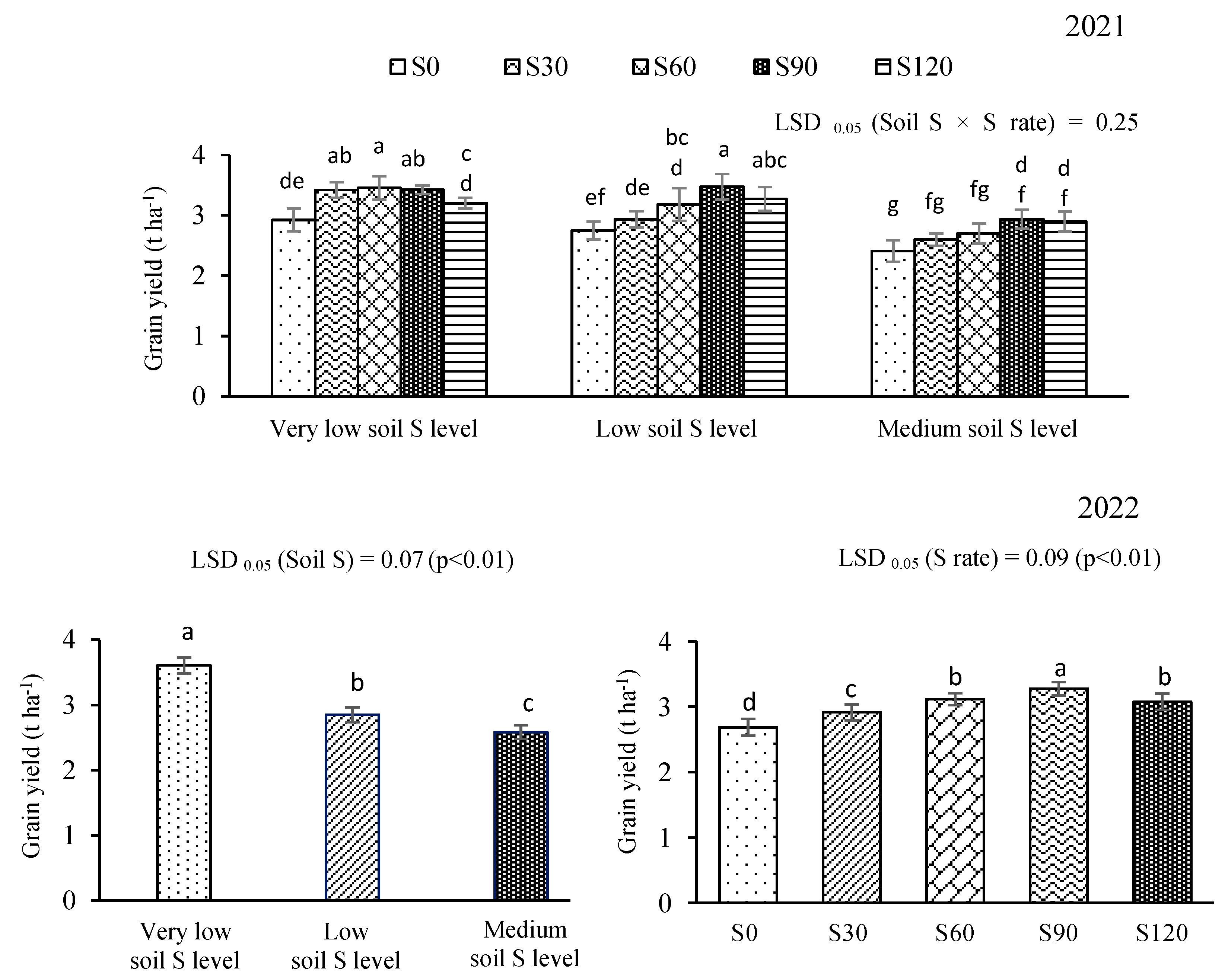
3.1. Grain Yield and Yield Component
3.2. Grain 2AP and S Concentration
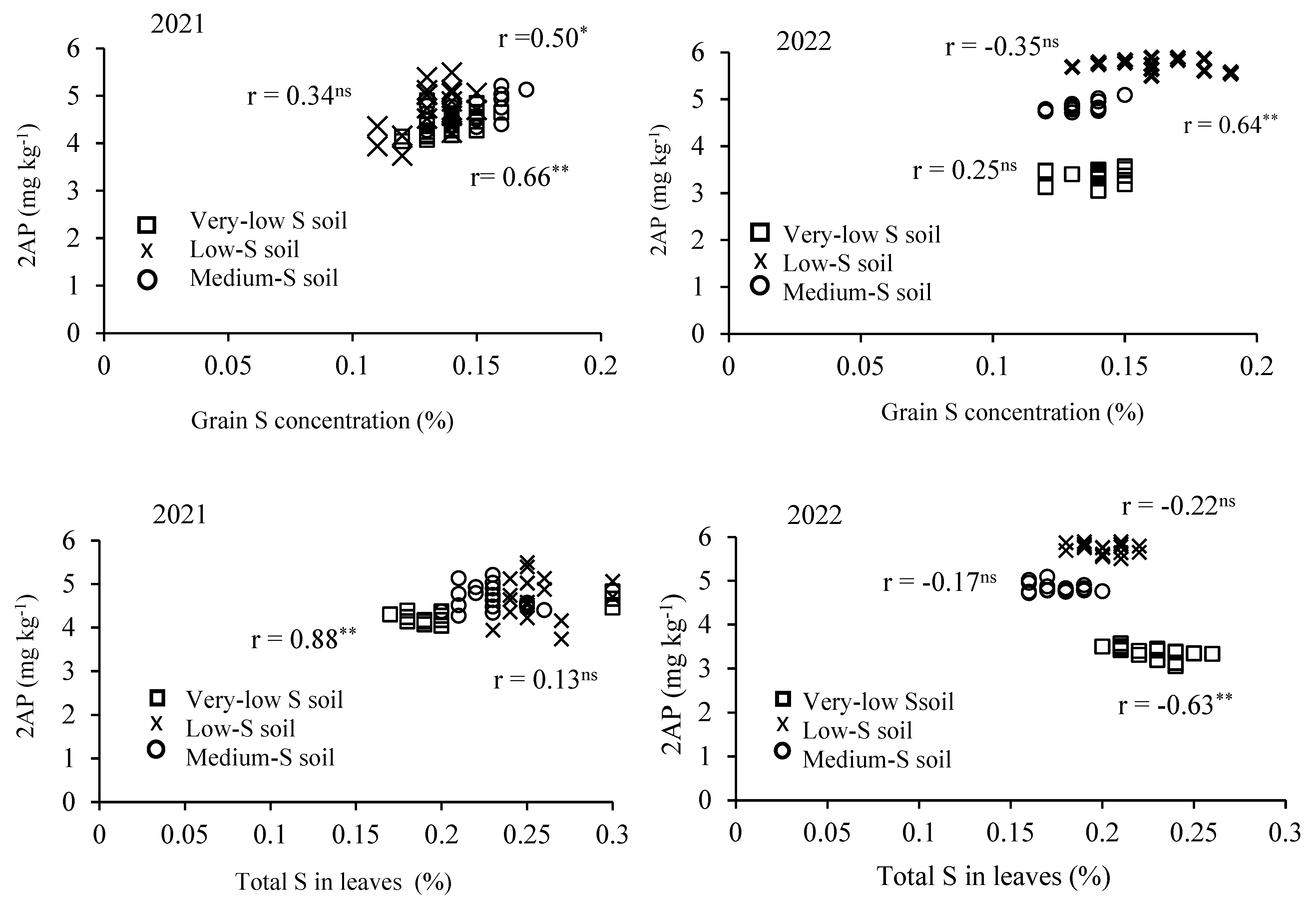
3.3. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Ge, Y.; Haim, P.G.; Mey-Tal, S.; Magen, H.; Huang, C. Sulfur fertilization contributes to China’s food security: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenda, T.; Liu, S.; Dong, A.; Duan, H. Revisiting sulphur-the once neglected nutrient: It’s roles in plant growth, metabolism, stress tolerance and crop production. Agriculture 2021, 11, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; He, C.; Hou, W.; Mou, H.; Chen, W.; Zhou, X. Quantitative study on reducing arsenic concentration in rice by sulfur fertilizer based on meta-analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Deng, H.; Song, Z.; Wu, S.; Liang, B.; Luo, J.; Xiao, T. Excess supply of sulfur mitigates thallium toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa L.) growth in hydroponic experiment. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renuka, N.; Barvkar, V.T.; Ansari, Z.; Zhao, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Nadaf, A.B. Co-functioning of 2AP precursor amino acids enhances 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline under salt stress in aromatic rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 3911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrawat, K.L. Short-term incubation method for mineralizable nitrogen. Arid. Land Res. Manag. 1998, 12, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, R.H.; Kurtz, L.T. Determination of total organic and available forms of phosphorus in soils. J. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analytik Jena, A.G. Multi EA 4000 Elementary Analyzer C, S and Cl Solids Analysis: TS Analysis. Documentation Number: 11–889.729 Version 01.16. 2016. Available online: http://www.analytik-jena.com (accessed on 15 August 2023).
- Mahatheeranont, S.; Keawsa-Ard, S.; Dumri, K. Quantification of the rice aroma compound, 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, in uncooked Khao Dawk Mali 105 brown rice. J. Agri. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, F.; Zhang, X.; Fu, Q.; Hu, H.; Islam, S.; Fang, L.; Zhu, J. Sulfur enhances iron plaque formation and stress resistance to reduce the transfer of Cd and As in the soil-rice system. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 927, 171689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, J.; Gerwing, J.; Gelderman, R. Fertilizer Recommendations Guide. 2024. Available online: https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/sites/default/files/2023-06/EC750_2023.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2024).
- Shah, S.H.; Islam, S.; Mohammad, F. Sulphur as a dynamic mineral element for plants: A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutri. 2022, 22, 2118–2143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aula, L.; Dhillon, J.S.; Omara, P.; Wehmeyer, G.B.; Freeman, K.W.; Raun, W.R. World Sulfur Use Efficiency for Cereal Crops. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2485–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diakite, S.; Saquee, F.S.; Kavhiza, N.J.; Pakina, E.N.; Norman, P.E.; Chudinova, E.M.; Tsindeliani, A.A.; Pototskaya, I.V. Plant growth and development responses to sulfur nutrition and disease attack under climate change: Role of sulfur and management strategies for wheat and barley. Pedosphere 2024, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, M.A.; Razi, K.; Benjamin, L.K.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, T.H.; Muneer, S. Ethylene regulates sulfur acquisition by regulating the expression of sulfate transporter genes in oilseed rape. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 171, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Khare, K.N.; Gupta, P. Sulfur and phosphorus transporters in plants: Integrating mechanisms for optimized nutrient supply. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 224, 109918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Location | S Level | pH | OM | NH4+-N | Available | Exchangeable | Soil Texture | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | S | K | ||||||
| (%) | (mg kg−1) | (mg kg−1) | (mg kg−1) | |||||
| 2021 | ||||||||
| 1 | Very low | 4.9 | 1.3 | 6.6 | 10.1 | 1.4 | 57.6 | Sandy Loam |
| 2 | Low | 4.7 | 1.2 | 10.2 | 18.0 | 10.6 | 38.5 | Sandy Loam |
| 3 | Medium | 5.7 | 1.6 | 25.2 | 4.3 | 21.1 | 45.3 | Sandy Loam |
| 2022 | ||||||||
| 1 | Very low | 4.4 | 0.9 | 22.3 | 2.9 | 9.0 | 14.5 | Sandy Loam |
| 2 | Low | 4.7 | 1.3 | 40.8 | 8.8 | 11.7 | 20.1 | Sandy Loam |
| 3 | Medium | 5.4 | 1.0 | 35.0 | 2.8 | 27.1 | 23.5 | Sandy Loam |
| Parameter/Soil S Level | Sulfur Application Rate (kg ha−1) | Mean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 | ||
| (a) | ||||||
| No. of tillers hill−1 | ||||||
| Very low S | 14.2 cd | 14.6 bc | 13.5 cd | 14.5 c | 13.5 cd | 14.0 |
| Low S | 13.1 cd | 12.9 d | 16.4 a | 17.3 a | 16.1 ab | 15.2 |
| Medium S | 6.6 e | 7.6 e | 7.4 e | 7.3 e | 6.8 e | 7.1 |
| Mean | 11.3 | 11.7 | 12.4 | 13.0 | 12.1 | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ** | Soil S × S rate ** | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 0.72 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | 0.93 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | 1.61 | |||||
| No. of panicles hill−1 | ||||||
| Very low S | 9.8 bc | 10.5 ab | 9.5 bcd | 9.8 bc | 10 bc | 9.9 |
| Low S | 8.5 d | 9.0 cd | 10 bc | 10.5 ab | 11.3 a | 9.4 |
| Medium S | 6.6 e | 6.6 e | 6.2 e | 6.1 e | 6.4 e | 6.4 |
| Mean | 8.2 | 8.7 | 8.5 | 8.8 | 9.2 | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ns | Soil S × S rate ** | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 0.53 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | - | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | 1.19 | |||||
| Filled grain (%) | ||||||
| Very low S | 90.2 | 89.2 | 91.0 | 89.6 | 90.0 | 90.0 a |
| Low S | 89.5 | 90.5 | 91.3 | 91.1 | 90.7 | 90.6 a |
| Medium S | 91.9 | 92.2 | 91.6 | 90.5 | 91.0 | 91.4 a |
| Mean | 90.5 A | 90.6 A | 91.3 A | 90.4 A | 90.5 A | |
| F-test | Soil S ns | S rate ns | Soil S × S rate ns | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | - | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | - | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | - | |||||
| 1000-grain weight (g) | ||||||
| Very low S | 27.7 | 27.9 | 28.4 | 28.1 | 27.6 | 27.9 b |
| Low S | 29.0 | 28.8 | 28.8 | 29.5 | 28.8 | 29.0 a |
| Medium S | 27.9 | 28.1 | 27.4 | 27.8 | 27.3 | 27.7 b |
| Mean | 28.2 A | 28.3 A | 28.2 A | 28.5 A | 27.9 A | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ns | Soil S × S rate ns | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 0.48 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | - | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | - | |||||
| (b) | ||||||
| No. of tillers hill−1 | ||||||
| Very low S | 10.7 | 11.6 | 10.7 | 12.4 | 13.3 | 11.7 a |
| Low S | 7.1 | 7.7 | 7.4 | 7.1 | 9.8 | 7.8 b |
| Medium S | 8.0 | 8.1 | 8.4 | 9.4 | 8.6 | 8.5 b |
| Mean | 8.6 B | 9.1 AB | 8.8 B | 9.6 AB | 10.6 A | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ns | Soil S × S rate ns | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 1.20 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | - | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | - | |||||
| No. of panicles hill−1 | ||||||
| Very low S | 8.4 | 8.4 | 8.2 | 9.8 | 9.5 | 8.9 a |
| Low S | 5.7 | 5.9 | 6.2 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 6.0 b |
| Medium S | 5.6 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 7.0 | 6.6 | 6.4 b |
| Mean | 6.6 C | 6.9 B | 7.0 BC | 7.6 A | 7.5 AB | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ** | Soil S × S rate ns | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 0.43 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | 0.56 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | - | |||||
| Filled grain (%) | ||||||
| Very low S | 92.8 ab | 90.9 bcd | 91.7 ab | 93.1 a | 92.1 ab | 92.1 |
| Low S | 92.1 ab | 87.1 f | 91.3 abc | 88.8 def | 92.4 ab | 90.3 |
| Medium S | 89.3 cde | 92.9 ab | 88.0 ef | 89.3 cde | 93.2 a | 90.5 |
| Mean | 91.4 | 90.3 | 90.3 | 90.4 | 92.6 | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ** | Soil S × S rate ** | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 0.95 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | 1.23 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | 2.13 | |||||
| 1000-grain weight (g) | ||||||
| Very low S | 29.3 | 29.3 | 29.1 | 29.1 | 29.1 | 29.2 a |
| Low S | 26.6 | 26.7 | 26.7 | 26.6 | 26.6 | 26.7 b |
| Medium S | 26.2 | 26.3 | 26.5 | 26.5 | 26.1 | 26.3 b |
| Mean | 27.3 A | 27.4 A | 27.4 A | 27.4 A | 27.3 A | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ns | Soil S × S rate ns | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 0.38 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | - | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | - | |||||
| Parameter/Soil S Level | Sulfur Application Rate (kg ha−1) | Mean | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 30 | 60 | 90 | 120 | ||
| Grain S concentration (%) | ||||||
| 2021 | ||||||
| Very low S | 0.127 | 0.130 | 0.143 | 0.147 | 0.147 | 0.139 b |
| Low S | 0.113 | 0.133 | 0.137 | 0.147 | 0.137 | 0.133 b |
| Medium S | 0.137 | 0.143 | 0.153 | 0.163 | 0.140 | 0.147 a |
| Mean | 0.126 D | 0.136 C | 0.144 AB | 0.152 A | 0.141 BC | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ** | Soil S × S rate ns | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 0.006 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | 0.008 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | - | |||||
| 2022 | ||||||
| Very low S | 0.137 cd | 0.140 cde | 0.137 de | 0.130 e | 0.143 cde | 0.137 |
| Low S | 0.137 de | 0.170 b | 0.193 a | 0.157 bc | 0.15 cd | 0.161 |
| Medium S | 0.127 e | 0.143 cde | 0.130 e | 0.130 e | 0.127 e | 0.131 |
| Mean | 0.133 | 0.151 | 0.153 | 0.139 | 0.140 | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ** | Soil S × S rate ** | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 0.007 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | 0.009 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | 0.017 | |||||
| Leave S concentration (%) | ||||||
| 2021 | ||||||
| Very low S | 0.193 gh | 0.177 h | 0.200 fg | 0.360 a | 0.303 b | 0.247 |
| Low S | 0.247 cd | 0.243 cd | 0.253 c | 0.303 b | 0.253 c | 0.260 |
| Medium S | 0.220 e | 0.230 de | 0.247 cd | 0.220 e | 0.213 ef | 0.226 |
| Mean | 0.220 | 0.217 | 0.233 | 0.294 | 0.257 | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ** | Soil S × S rate ** | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 0.008 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | 0.011 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | 0.018 | |||||
| 2022 | ||||||
| Very low S | 0.237 b | 0.210 cd | 0.230 b | 0.210 cd | 0.250 a | 0.227 |
| Low S | 0.190 ef | 0.187 fg | 0.200 de | 0.213 c | 0.213 c | 0.201 |
| Medium S | 0.163 i | 0.170 hi | 0.180 fgh | 0.190 ef | 0.177 gh | 0.176 |
| Mean | 0.197 | 0.189 | 0.203 | 0.204 | 0.213 | |
| F-test | Soil S ** | S rate ** | Soil S × S rate ** | |||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S) | 0.006 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (S rate) | 0.007 | |||||
| LSD0.05 (Soil S × S rate) | 0.013 | |||||
| Year/Degree of S | No. of Tillers hill−1 | No. of Panicles hill−1 | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | 2AP Content (mg kg−1) | Grain S Concentration (%) | Leave S Concentration (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | ||||||
| Very low soil S | r = 0.17 | r = −0.064 | r = 0.47 | r = 0.19 | r = 0.20 | r = 0.12 |
| (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p < 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | |
| Low soil S | r = 0.69 | r = 0.55 | r = 0.43 | r = 0.45 | r = 0.51 | r = 0.52 |
| (p < 0.01) | (p < 0.05) | (p < 0.05) | (p < 0.05) | (p < 0.05) | (p < 0.05) | |
| Medium soil S | r = −0.009 | r = 0.094 | r = −0.11 | r = 0.52 | r = 0.37 | r = −0.28 |
| (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p < 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | |
| 2022 | ||||||
| Very low soil S | r = 0.12 | r = 0.42 | r = 0.22 | r = 0.74 | r = 0.18 | r = −0.21 |
| (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p < 0.01) | (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | |
| Low soil S | r = 0.064 | r = 0.28 | r = −0.034 | r = −0.37 | r = 0.47 | r = 0.54 |
| (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p < 0.05) | (p < 0.05) | |
| Medium soil S | r = 0.15 | r = 0.6 | r = 0.20 | r = 0.11 | r = 0.097 | r = 0.75 |
| (p > 0.05) | (p < 0.01) | (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p > 0.05) | (p < 0.01) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaiboontha, S.; Chanauksorn, C.; Santasup, C.; Chaiwan, F.; Prom-u-thai, C. Optimizing Sulfur Fertilization for Yield and Aroma Enhancement in Fragrant Rice Under Varying Soil Sulfur Conditions. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071569
Chaiboontha S, Chanauksorn C, Santasup C, Chaiwan F, Prom-u-thai C. Optimizing Sulfur Fertilization for Yield and Aroma Enhancement in Fragrant Rice Under Varying Soil Sulfur Conditions. Agronomy. 2025; 15(7):1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071569
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaiboontha, Sirilak, Chananath Chanauksorn, Choochad Santasup, Fapailin Chaiwan, and Chanakan Prom-u-thai. 2025. "Optimizing Sulfur Fertilization for Yield and Aroma Enhancement in Fragrant Rice Under Varying Soil Sulfur Conditions" Agronomy 15, no. 7: 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071569
APA StyleChaiboontha, S., Chanauksorn, C., Santasup, C., Chaiwan, F., & Prom-u-thai, C. (2025). Optimizing Sulfur Fertilization for Yield and Aroma Enhancement in Fragrant Rice Under Varying Soil Sulfur Conditions. Agronomy, 15(7), 1569. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15071569






