Diversified Cropping Modulates Microbial Communities and Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Enhancing Soil Nutrients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Research Methodology and Data Sources
2.2. Analytical Tools
3. Results
3.1. Continuous Cropping Disorder
3.2. Species Diversity
3.2.1. Effect of Plant Mixtures on Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.2.2. Effect of Plant Mixtures on Soil Microbial Diversity
3.2.3. Effect of Plant Mixtures on Greenhouse Gas Emissions (CO2, N2O, or CH4)
3.2.4. Effect of Plant Mixtures on Crop Yield and Economic Benefit
4. Discussion
4.1. Development of Diversified Cropping Research
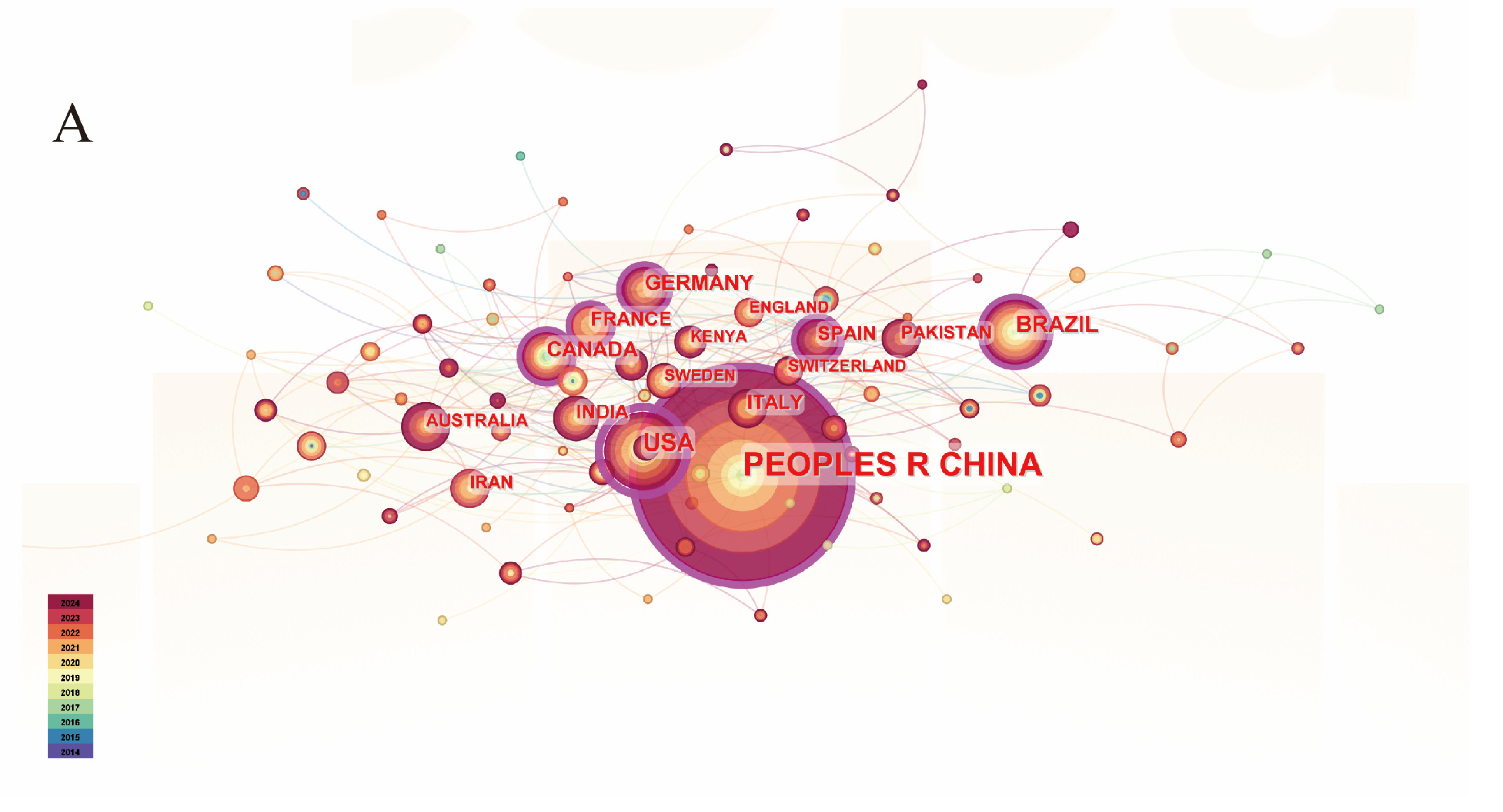
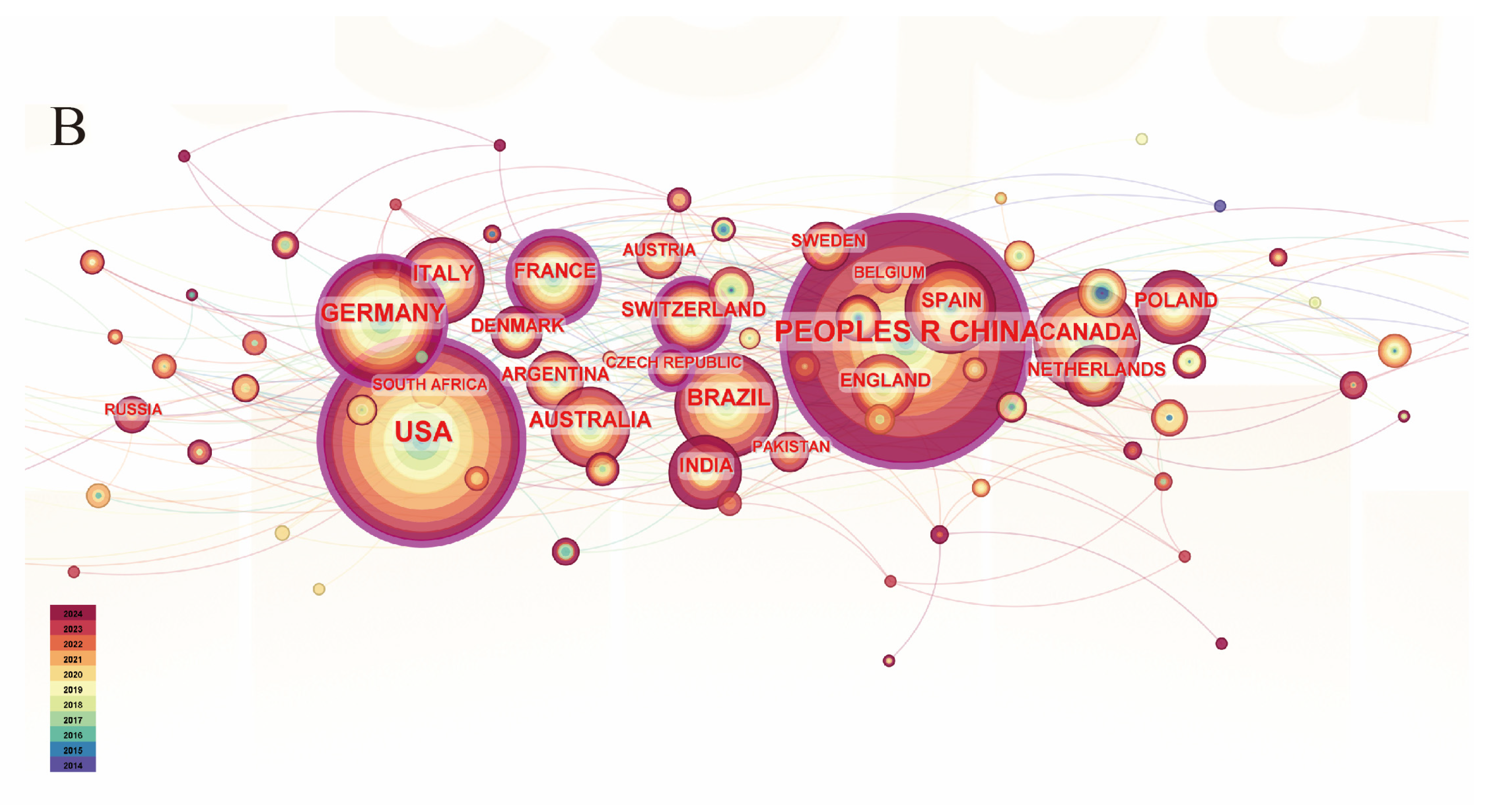
4.1.1. Trends in Intercropping Research
4.1.2. Trends in Crop Rotation Research
4.2. Mechanisms of Continuous Cropping Disorder
4.3. The Impacts of Intercropping and Crop Rotation on Soil–Plant–Atmosphere Systems
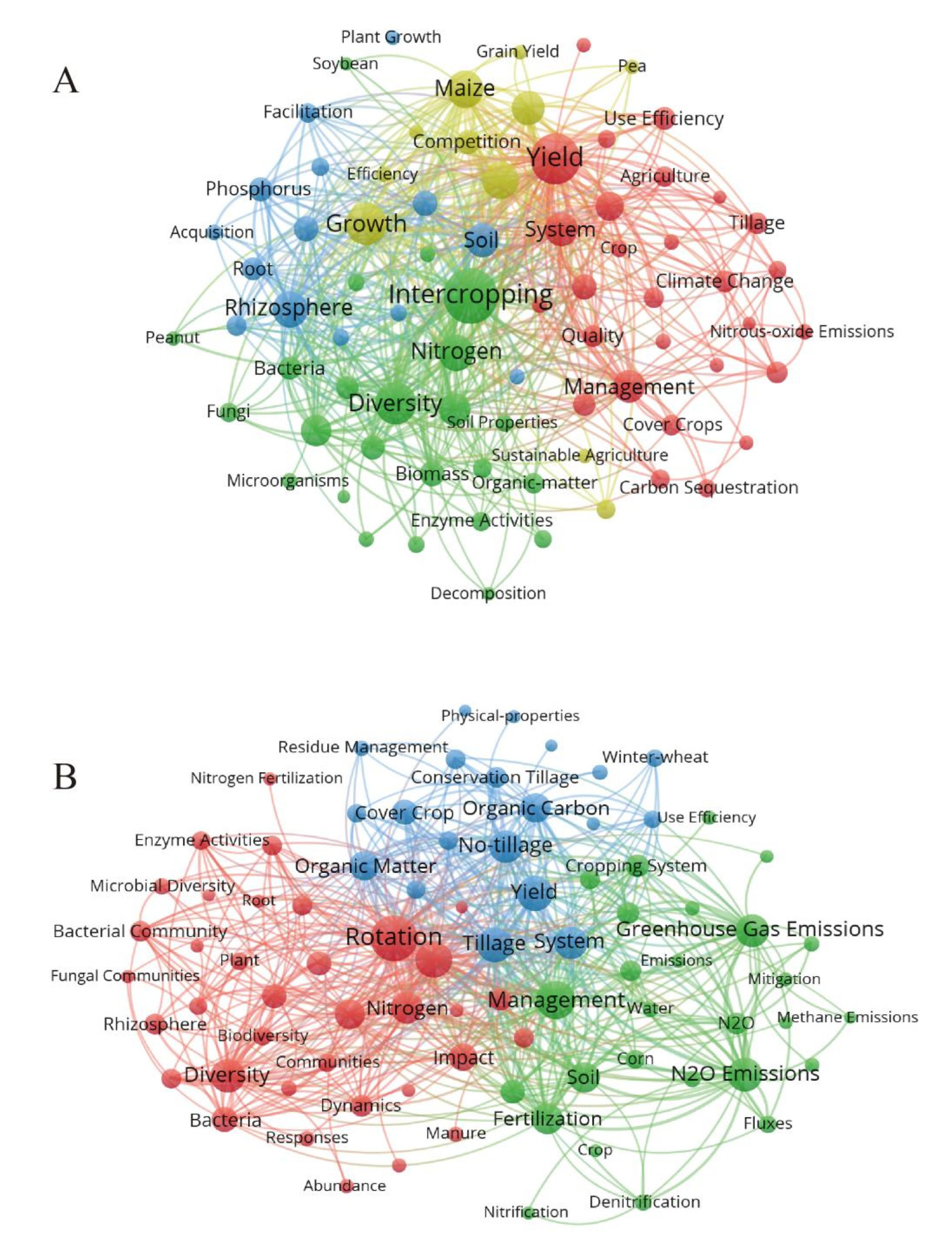
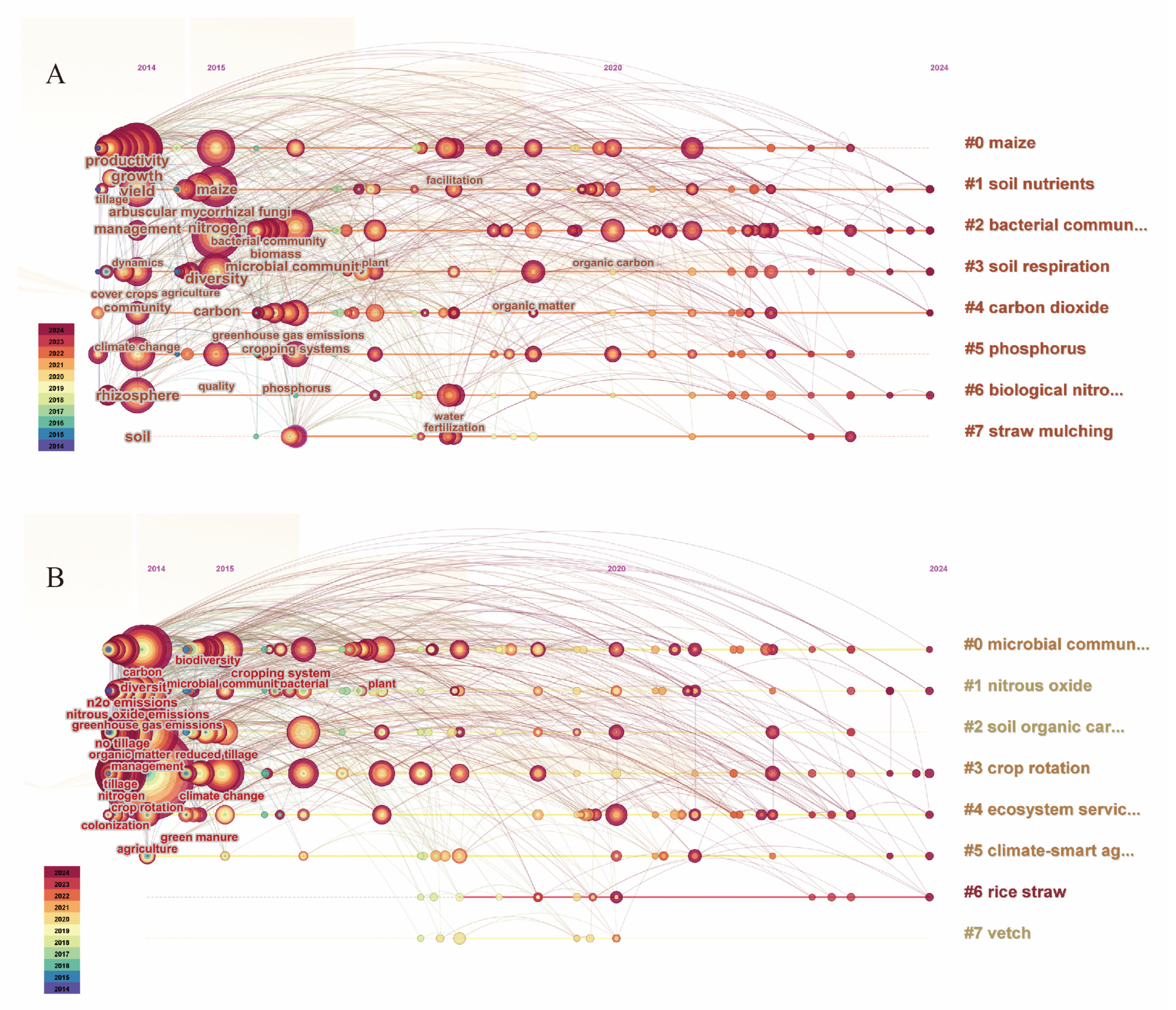
4.4. Hotspots and Future Outlook
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muller, A.; Schader, C.; El-Hage Scialabba, N.; Brüggemann, J.; Isensee, A.; Erb, K.H.; Smith, P.; Klocke, P.; Leiber, F.; Stolze, M.; et al. Strategies for feeding the world more sustainably with organic agriculture. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, A.J.; Bending, G.D.; Chandler, D.; Hilton, S.; Mills, P. Meeting the demand for crop production: The challenge of yield decline in crops grown in short rotations. Biol. Rev. 2012, 87, 52–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, C.K.; Bjorkman, A.D.; Dempewolf, H.; Ramirez-Villegas, J.; Guarino, L.; Jarvis, A.; Rieseberg, L.H.; Struik, P.C. Increasing homogeneity in global food supplies and the implications for food security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4001–4006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dempewolf, H.; Bordoni, P.; Rieseberg, L.H.; Engels, J.M. Food security: Crop species diversity. Science 2010, 328, 169–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, M.; Pixley, K.; Zinyengere, N.; Meng, S.; Tufan, H.; Cichy, K.; Bizikova, L.; Isaacs, K.; Ghezzi-Kopel, K.; Porciello, J. A scoping review of adoption of climate-resilient crops by small-scale producers in low-and middle-income countries. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfray, H.C.J.; Beddington, J.R.; Crute, I.R.; Haddad, L.; Lawrence, D.; Muir, J.F.; Pretty, J.; Robinson, S.; Thomas, S.M.; Toulmin, C. Food security: The challenge of feeding 9 billion people. Science 2010, 327, 812–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Balzer, C.; Hill, J.; Befort, B.L. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20260–20264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raseduzzaman, M.D.; Jensen, E.S. Does intercropping enhance yield stability in arable crop production? A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 91, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, P.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Loreau, M.; Duffy, J.E.; Li, X.E.; Wen, S.Y.; Han, X.Q.; Liao, L.C.; Huang, T.T.; et al. Plant diversity decreases greenhouse gas emissions by increasing soil and plant carbon storage in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol. Lett. 2024, 27, e14469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, M.Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, S.G.; Tao, H.Y.; Khan, A.; Uzamurera, A.G.; Wang, B.Z.; Jin, J.M.; Ma, Y.; et al. Effects of interspecific interactions on soil carbon emission and efficiency in the semiarid intercropping systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 234, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Guo, Y.; Hu, F.; Fan, Z.; Feng, F.; Zhao, C.; Yu, A.; Yu, A.; Chai, Q. Wheat-maize intercropping with reduced tillage and straw retention: A step towards enhancing economic and environmental benefits in arid areas. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, E.S.; Bedoussac, L.; Carlsson, G.; Journet, E.P.; Justes, E.; Hauggaard-Nielsen, H. Enhanced yields in organic arable crop production by eco-functional intensification using intercropping. Sustain. Agric. Res. 2015, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Tan, X.; Lou, H.; Wang, X.; Shao, D.; Ning, N.; Kuai, J.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z.; et al. Developing diversified forage cropping systems for synergistically enhancing yield, economic benefits, and soil quality in the Yangtze River Basin. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 365, 108929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.L.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Chen, C.; Ma, Z.L.; Searle, E.B.; Yu, Z.P.; Huang, Z.Q. Effects of plant diversity on soil carbon in diverse ecosystems: A global meta-analysis. Biol. Rev. 2020, 95, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breza, L.C.; Mooshammer, M.; Bowles, T.M.; Jin, V.L.; Schmer, M.R.; Thompson, B.; Grandy, A.S. Complex crop rotations improve organic nitrogen cycling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 177, 108911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, H.Y.H. Plant mixture balances terrestrial ecosystem C:N:P stoichiometry. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Hou, X.; Fang, X.; Razavi, B.; Zang, H.; Zeng, Z.; Yang, Y. Short-term continuous monocropping reduces peanut yield mainly via altering soil enzyme activity and fungal community. Environ. Res. 2024, 245, 117977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xiong, W.; Xing, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lin, X.; Dong, Y. Long-Term Coffee Monoculture Alters Soil Chemical Properties and Microbial Communities. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flower, K.C.; Hüberli, D.; Collins, S.J.; Thomas, G.; Ward, P.R.; Cordingley, N. Progression of plant-parasitic nematodes and foliar and root diseases under no-tillage with different crop rotations. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.C.; Li, B.X.; Xu, C.Y.; Raza, M.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.Z.; Fu, Y.N.; Hu, J.Y.; Imoulan, A.; Hussain, M.; et al. Intercropping Walnut and Tea: Effects on Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activity, and Microbial Communities. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 852342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Hao, C.; Zhang, R.; Jiao, N.; Tian, J.; Lambers, H.; Liang, C.; Cong, W.; Zhang, F. Intercropping increases soil macroaggregate carbon through root traits induced microbial necromass accumulation. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 185, 109146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Sun, C.; Dai, B.; He, Y.; Zhong, J. Intercropping system modulated soil–microbe interactions that enhanced the growth and quality of flue-cured tobacco by improving rhizospheric soil nutrients, microbial structure, and enzymatic activities. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1233464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera-Huertas, J.; Parras-Alcántara, L.; González-Rosado, M.; Lozano-García, B. Intercropping in rainfed Mediterranean olive groves contributes to improving soil quality and soil organic carbon storage. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 361, 108826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcos-Pérez, M.; Sánchez-Navarro, V.; Martinez-Martinez, S.; Martínez-Mena, M.; García, E.; Zornoza, R. Intercropping organic melon and cowpea combined with return of crop residues increases yields and soil fertility. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 43, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Ruan, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; et al. Metagenomes reveal the effect of crop rotation systems on phosphorus cycling functional genes and soil phosphorus avail-ability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 364, 108886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Xiong, J.; Du, T.; Ju, X.; Gan, Y.; Li, S.; Xia, L.; Shen, Y.; Pacenka, S.; Steenhuis, T.S.; et al. Diversifying crop rotation increases food production, reduces net greenhouse gas emissions and improves soil health. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, L.; Chu, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, J.; Zang, H.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, Z. Improving soil quality and wheat yield through diversified crop rotations in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xia, L.; Sun, Y.; Gao, S. Soil nutrients and enzyme activities based on millet continuous cropping obstacles. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fei, J.; Rong, X.; Peng, J.; Yin, L.C.; Luo, G.W. Intercropping enhances maize growth and nutrient uptake by driving the link between rhizosphere metabolites and microbiomes. New Phytol. 2024, 243, 1506–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, S.; Long, J.; Mao, H.; Dong, Y.; Hou, Y. Differences in microbial community structure and metabolic activity among tea plantation soils under different management strategies. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1219491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Han, L.; Chen, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, A. Intercropping enhances microbial community diversity and ecosystem functioning in maize fields. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1084452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wang, T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, M.; Lu, Q.; Wang, K.; Dou, Z.; Chi, Z.; Qiu, W.; Dai, J.; et al. Microbiome convergence enables siderophore-secreting-rhizobacteria to improve iron nutrition and yield of peanut intercropped with maize. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bao, X.; Zhang, J.; Lu, B.; Sun, N.; Wang, Y.; Yang, N.; Xing, Y.; Callaway, R.M.; Li, L. Facilitation between intercropped species increases micronutrient acquisition and controls rust disease on maize. Field Crops Res. 2024, 307, 109241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Dai, C.; Zhang, T.; Carrión, V.J.; Wei, Z.; Cao, F.; et al. Crop rotation and native microbiome inoculation restore soil capacity to suppress a root disease. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 8126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerecetto, V.; Leoni, C.; Jurburg, S.D.; Kampouris, I.D.; Smalla, K.; Babin, D. Pasture-crop rotations modulate the soil and rhizosphere microbiota and preserve soil structure supporting oat cultivation in the Pampa biome. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 195, 109451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Sui, P. Changes in soil microbial biomass, diversity, and activity with crop rotation in cropping systems: A global synthesis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 186, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinale, B.J.; Duffy, J.E.; Gonzalez, A.; Hooper, D.U.; Perrings, C.; Venail, P.; Narwani, A.; Mace, G.M.; Tilman, D.; Wardle, D.A.; et al. Biodiversity loss and its impact on humanity. Nature 2012, 486, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.E.; Godwin, C.M.; Cardinale, B.J. Biodiversity effects in the wild are common and as strong as key drivers of productivity. Nature 2017, 549, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, D.U.; Adair, E.C.; Cardinale, B.J.; Byrnes, J.E.; Hungate, B.A.; Matulich, K.L.; Gonzalez, A.; Duffy, J.E.; Gamfeldt, L.; O’Connor, M.I. A global synthesis reveals biodiversity loss as a major driver of ecosystem change. Nature 2012, 486, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loreau, M.; Jarne, P.; Martiny, J.B.H. Opportunities to advance the synthesis of ecology and evolution. Ecol. Lett. 2023, 26, S11–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, W.F.; Hoffland, E.; Li, L.; Six, J.; Sun, J.H.; Bao, X.G.; Zhang, F.S.; Werf, W.V.D. Intercropping enhances soil carbon and nitrogen. Glob. Change Biol. 2015, 21, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isbell, F.; Adler, P.R.; Eisenhauer, N.; Fornara, D.; Kimmel, K.; Kremen, C.; Letourneau, D.K.; Liebman, M.; Polley, H.W.; Quijas, S.; et al. Benefits of increasing plant diversity in sustainable agroecosystems. J. Ecol. 2017, 105, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Chen, H.Y.H. Plant diversity loss reduces soil respiration across terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furey, G.N.; Tilman, D. Plant biodiversity and the regeneration of soil fertility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2111321118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raseduzzaman, M.; Dong, W.; Gaudel, G.; Aluoch, S.O.; Timilsina, A.; Li, X.; Hu, C. Maize-soybean intercropping reduces greenhouse gas emissions from the fertilized soil in the North China Plain. J. Soils Sediments 2024, 24, 3115–3131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Jia, R.; Zhou, J.; Zamanian, K.; Yang, Y.; Mganga, K.Z.; Zeng, Z.; Zang, H. Soybean inclusion reduces soil organic matter mineralization despite increasing its temperature sensitivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 922, 171334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, M.; Manevski, K.; Liang, Z.; Abalos, D.; Jabloun, M.; Lærke, P.E.; Jørgensen, U. Diversifying maize rotation with other industrial crops improves biomass yield and nitrogen uptake while showing variable effects on nitrate leaching. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 371, 109091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; van Es, H.M.; Amsili, J.P.; Shi, Q.; Sun, J.; Chen, Y.; Sui, P. Lowering soil greenhouse gas emissions without sacrificing yields by increasing crop rotation diversity in the North China Plain. Field Crops Res. 2022, 276, 108366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Stomph, T.J.; Makowski, D.; Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; van der Werf, W. The productive performance of intercropping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2023, 120, e2201886120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Jiao, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, W.; Xu, S.; Guo, F. Effects of intercropping on rhizosphere soil bacterial communities in Amorphophallus konjac. Open J. Soil Sci. 2018, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Tan, X.; Gao, G.; El-Badri, A.M.; Batool, M.; Li, Z.; Ai, X.; Kuai, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Diversified spatial configuration of rapeseed-vetch intercropping benefits soil quality, radiation utilization, and forage production in the Yangtze River Basin. Field Crops Res. 2024, 318, 109587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernooy, R. Does crop diversification lead to climate-related resilience? Improving the theory through insights on practice. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 46, 877–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Wang, Z.G.; Bao, X.G.; Sun, J.H.; Yang, S.C.; Wang, P.; Wang, C.B.; Wu, J.P.; Liu, X.R.; Tian, X.L.; et al. Long-term increased grain yield and soil fertility from intercropping. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 943–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Feng, X.; Xu, Y.; Kumar, A.; Yan, Z.; Zhou, J.; Yang, Y.; Peixoto, L.; Zeng, Z.; Zang, H. Legume-based rotation enhances subsequent wheat yield and maintains soil carbon storage. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 43, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, N. Why Our Food Is So Dependent on Oil. 2005. Available online: https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=44a69b3e3745cb7fbb51239262028e456c924084 (accessed on 12 October 2024).
- Horrigan, L.; Lawrence, R.S.; Walker, P. How sustainable agriculture can address the environmental and human health harms of industrial agriculture. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.K.; Modi, B.; Pandey, H.P.; Subedi, A.; Aryal, G.; Pandey, M.; Shrestha, J. Diversified crop rotation: An approach for sustainable agriculture production. Adv. Agric. 2021, 2021, 8924087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Luo, Z.; Wang, E.; Zhang, W. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions while maintaining yield in the croplands of Huang-Huai-Hai Plain, China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 260, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, T.E.; Carton, W.; Olsson, L. Is the future of agriculture perennial? Imperatives and opportunities to reinvent agriculture by shifting from annual monocultures to perennial polycultures. Glob. Sustain. 2018, 1, e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Wu, S.; Li, X. Breeding with dominant genic male-sterility genes to boost crop grain yield in the post-heterosis utilization era. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 531–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Q.; Li, G.; Lin, Q.; Zhu, S. Untargeted metabolomics reveal rhizosphere metabolites mechanisms on continuous ramie cropping. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1217956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, J.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, W.; Deng, L.; Gao, Q.; Mi, Q.; Li, X.; et al. Autotoxins in continuous tobacco cropping soils and their management. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1106033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, R.L.; Pieterse, C.M.; Bakker, P.A. The rhizosphere microbiome and plant health. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- She, S.; Niu, J.; Zhang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, W.; Dai, L.; Liu, X.; Yin, H. Significant relationship between soil bacterial community structure and incidence of bacterial wilt disease under continuous cropping system. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Castro-Izaguirre, N.; Baruffol, M.; Brezzi, M.; Lang, A.; Li, Y.; Härdtle, W.; von Oheimb, G.; Yang, X.; et al. Impacts of species richness on productivity in a large-scale subtropical forest experiment. Science 2018, 362, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilman, D.; Wedin, D.; Knops, J. Productivity and sustainability influenced by biodiversity in grassland ecosystems. Nature 1996, 379, 718–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchene, O.; Vian, J.F.; Celette, F. Intercropping with legume for agroecological cropping systems: Complementarity and facilitation processes and the importance of soil microorganisms: A review. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 240, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fei, J.; Rong, X.; Peng, J.; Wei, X.; Luo, G. Intercropping regulates plant-and microbe-derived carbon accumulation by influencing soil physicochemical and microbial physiological properties. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 364, 108880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ruijven, J.; Berendse, F. Diversity-productivity relationships: Initial effects, long-term patterns, and underlying mechanisms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Huang, W.; Xiao, W.; Hu, D.; Shao, J.; Yao, B. Comparison of soil enzyme activity and microbial community structure between rapeseed-rice and rice-rice plantings. Int. J. Agric. Biol 2018, 20, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar]
- Veryard, R.; Wu, J.; O’Brien, M.J.; Anthony, R.; Both, S.; Burslem, D.F.R.P.; Chen, B.; Cagigal, E.F.M.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Godoong, E.; et al. Positive effects of tree diversity on tropical forest restoration in a field-scale experiment. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadf0938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.Y.H.; Chen, X.; Huang, Z. Meta-analysis shows positive effects of plant diversity on microbial biomass and respiration. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Luo, G.; Luo, B.; Yu, C.; Wang, H.; Chang, J.; Ge, Y. Effects of plant diversity on greenhouse gas emissions in microcosms simulating vertical constructed wetlands with high ammonium loading. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 77, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, R.; Yu, X.; Grün, C. Climate change, risk and grain yields in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2013, 12, 1279–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Xuan, H.; Liu, B.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, T.; Liu, Y.; Dai, L.; Xie, Y.; Shang, X.; Zhang, L.; et al. Diversified Cropping Modulates Microbial Communities and Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Enhancing Soil Nutrients. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061472
Wang Z, Xuan H, Liu B, Zhang H, Zheng T, Liu Y, Dai L, Xie Y, Shang X, Zhang L, et al. Diversified Cropping Modulates Microbial Communities and Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Enhancing Soil Nutrients. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061472
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhongyan, Huaqiang Xuan, Bei Liu, Hongfeng Zhang, Tongyan Zheng, Yunxia Liu, Luping Dai, Yi Xie, Xianchao Shang, Li Zhang, and et al. 2025. "Diversified Cropping Modulates Microbial Communities and Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Enhancing Soil Nutrients" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061472
APA StyleWang, Z., Xuan, H., Liu, B., Zhang, H., Zheng, T., Liu, Y., Dai, L., Xie, Y., Shang, X., Zhang, L., Yang, L., Pattanaik, S., Yuan, L., & Hou, X. (2025). Diversified Cropping Modulates Microbial Communities and Greenhouse Gas Emissions by Enhancing Soil Nutrients. Agronomy, 15(6), 1472. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061472





