Monocropping Degrades Soil Quality Index and Soil Multifunctionality Compared to Natural Grasslands and Restored Shrubland in China’s Qilian Mountains (Based on Single-Year Sampling)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sample Collection and Determination
2.3.1. Sample Collection
2.3.2. Soil Property Determination
2.4. Calculation of the SQI
2.4.1. Constructing the MDS
2.4.2. Indicator Normalization and Affiliation Calculation
2.4.3. Comprehensive Calculation
2.5. Quantification of SMF
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties Under Different NG Utilization Patterns
3.2. Soil Biological Characteristics Under Different NG Utilization Patterns
3.3. Impact of NG Utilization Patterns Transformation on the SQI
3.3.1. Construction of the MDS
3.3.2. SQ Evaluation Based on the MDS
3.3.3. MDS Suitability Validation
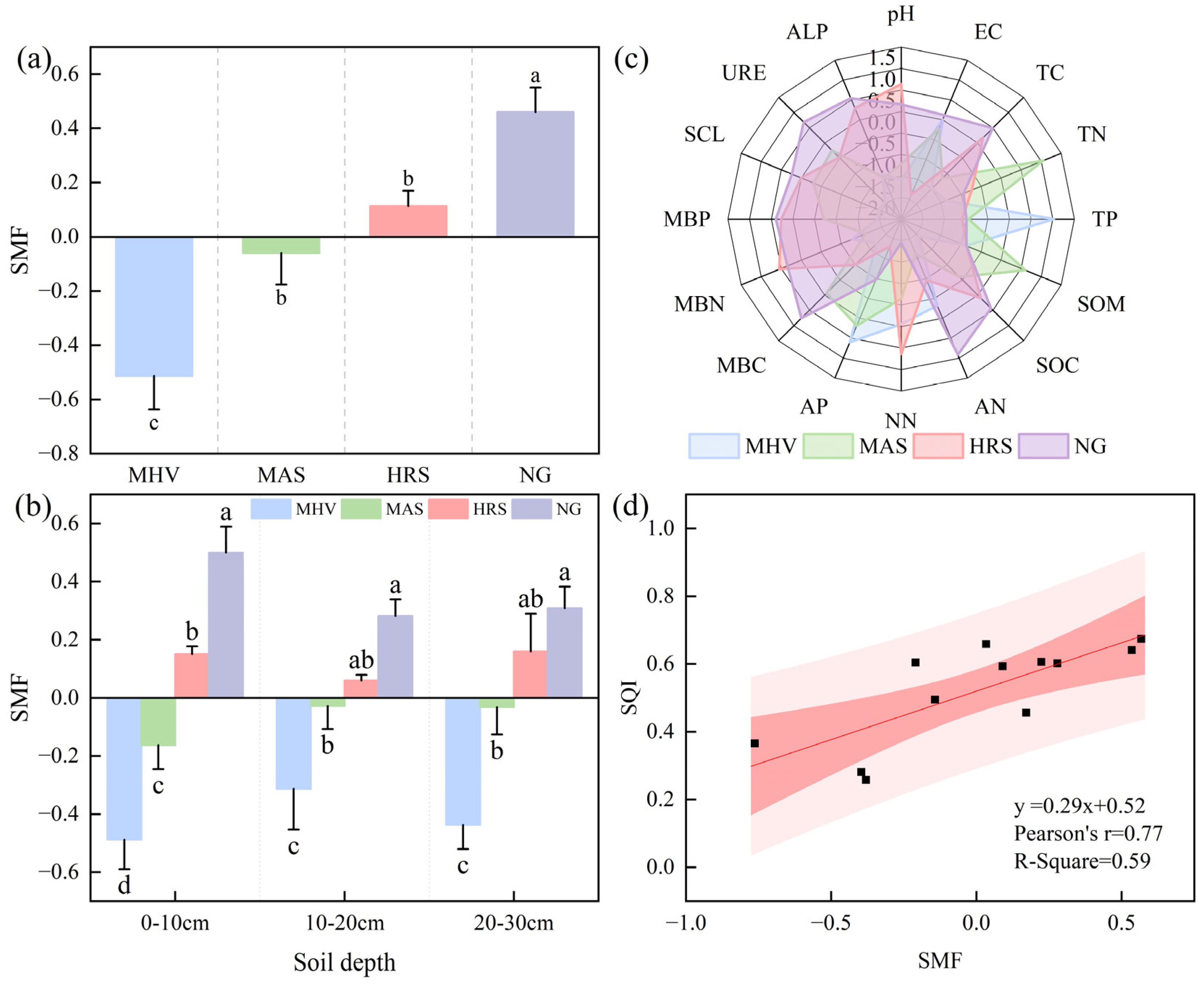
3.4. Characteristics of SMF Under Different NG Utilization Patterns
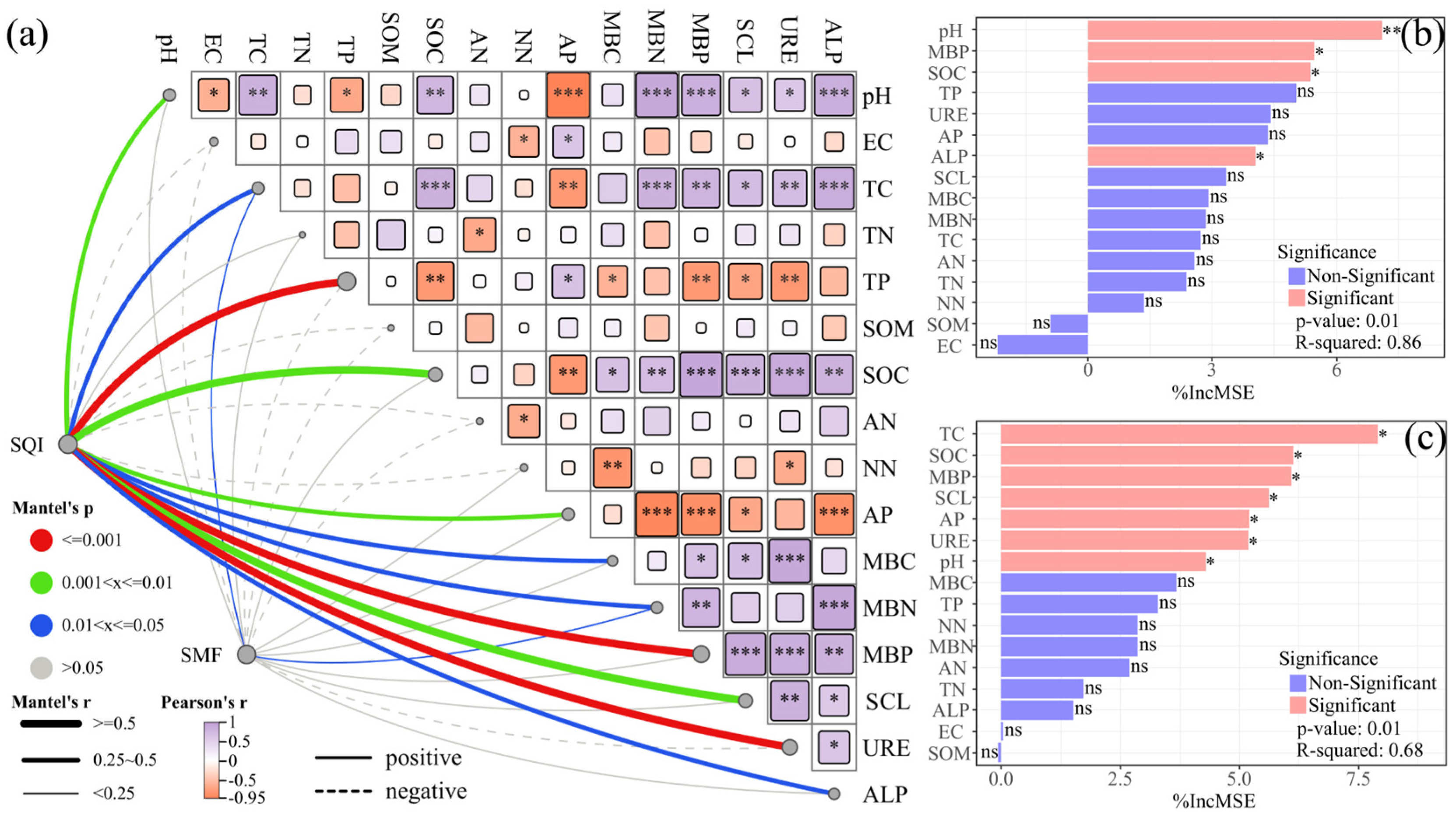
3.5. Mantel Tests and Random Forest Model Predictions
4. Discussion
4.1. Impacts of NG Utilization Patterns Transformation on Soil Chemical Characteristics
4.2. Impacts of the Transformation of NG Utilization Patterns on Soil Biological Characteristics
4.3. Impacts of NG Utilization Pattern Transformation on SQI
4.4. Impacts of NG Utilization Pattern Transformation on SMF
4.5. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MHV | Monocropping Hordeum vulgare |
| MAS | Monocropping Avena sativa |
| HRS | Hippophae rhamnoides shrubland |
| NG | Natural grassland |
| SQ | Soil quality |
| SQI | Soil quality index |
| EMF | Ecosystem multifunctionality |
| SMF | Soil ecosystem multifunctionality |
| TDS | Total data set |
| MDS | Minimum data set |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| TC | Total carbon |
| TC | Total nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| SOC | Soil organic carbon |
| AN | Ammonium nitrogen |
| NN | Nitrate nitrogen |
| AP | Available phosphorus |
| MBC | Microbial biomass carbon |
| MBN | Microbial biomass nitrogen |
| MBP | Microbial biomass phosphorus |
| SCL | Cellulase |
| URE | Urease |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
Appendix A
| Soil Indicators | pH | EC | TC | TN | TP | SOM | SOC | AN | NN | AP | MBC | MBN | MBP | SCL | URE | ALP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||
| EC 1 | −0.604 * | 1 | ||||||||||||||
| TC 1 | 0.819 ** | −0.147 | 1 | |||||||||||||
| TN 1 | −0.243 | 0.042 | −0.216 | 1 | ||||||||||||
| TP 1 | −0.670 * | 0.395 | −0.496 | −0.454 | 1 | |||||||||||
| SOM 1 | −0.298 | 0.330 | −0.089 | 0.541 | 0.016 | 1 | ||||||||||
| SOC 1 | 0.767 ** | −0.129 | 0.829 ** | 0.152 | −0.789 ** | 0.085 | 1 | |||||||||
| AN 1 | 0.295 | 0.286 | 0.454 | −0.659 * | 0.087 | −0.522 | 0.201 | 1 | ||||||||
| NN 1 | −0.009 | −0.584 * | −0.227 | −0.08 | 0.213 | −0.012 | −0.320 | −0.637 * | 1 | |||||||
| AP 1 | −0.958 ** | 0.610 * | −0.789 ** | 0.173 | 0.652* | 0.274 | −0.793 ** | −0.167 | −0.115 | 1 | ||||||
| MBC 1 | 0.342 | 0.257 | 0.541 | 0.370 | −0.588 * | 0.206 | 0.673 * | 0.375 | −0.815 ** | −0.248 | 1 | |||||
| MBN 1 | 0.929 ** | −0.446 | 0.827 ** | −0.466 | −0.468 | −0.438 | 0.719 ** | 0.502 | −0.053 | −0.926 ** | 0.260 | 1 | ||||
| MBP 1 | 0.848 ** | −0.315 | 0.800 ** | 0.113 | −0.786 ** | −0.031 | 0.939 ** | 0.235 | −0.288 | −0.864 ** | 0.661 * | 0.798 ** | 1 | |||
| SCL 1 | 0.674 * | −0.130 | 0.729 ** | 0.299 | −0.701 * | 0.254 | 0.840 ** | 0.058 | −0.317 | −0.670 * | 0.710 ** | 0.546 | 0.875 ** | 1 | ||
| URE 1 | 0.612 * | 0.026 | 0.714 ** | 0.305 | −0.797 ** | 0.142 | 0.882 ** | 0.308 | −0.635 * | −0.556 | 0.911 ** | 0.511 | 0.855 ** | 0.827 ** | 1 | |
| ALP 1 | 0.854 ** | −0.256 | 0.870 ** | −0.335 | −0.522 | −0.409 | 0.813 ** | 0.543 | −0.220 | −0.856 ** | 0.437 | 0.933 ** | 0.822 ** | 0.590 * | 0.621 * | 1 |
References
- Enjavinezhad, S.M.; Naghibi, S.J.; Shirazi, M.P.; Baghernejad, M.; Fernandez-Raga, M.; Rodrigo-Comino, J. From fields to cities: Innovating assessment of soil quality in Southern Iran’s Urban areas. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0321312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drobnik, T.; Greiner, L.; Keller, A.; Gret-Regamey, A. Soil quality indicators—From soil functions to ecosystem services. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 94, 151–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olson, C.; Sztein, A.E.; Sparks, D.L. Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 2015, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montanarella, L.; Pennock, D.J.; McKenzie, N.; Badraoui, M.; Chude, V.; Baptista, I.; Mamo, T.; Yemefack, M.; Aulakh, M.S.; Yagi, K.; et al. World’s soils are under threat. Soil 2016, 2, 79–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laudicina, V.A.; Ruisi, P.; Badalucco, L. Soil Quality and Crop Nutrition. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghche-Maryam, M.Z.; Sheklabadi, M.; Ayoubi, S. Covariate selection approaches in spatial prediction of soil quality indices using machine learning models at the watershed scale, west of Iran. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 252, 106571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, P.; Singh, A.K.; Zakari, S.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Liu, W. Soil quality assessment of different Hevea brasiliensis plantations in tropical China. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 285, 112147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.; Hazra, G.C.; Purakayastha, T.J.; Saha, N.; Mitran, T.; Roy, S.S.; Basak, N.; Mandal, B. Establishment of critical limits of indicators and indices of soil quality in rice-rice cropping systems under different soil orders. Geoderma 2017, 292, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timilsina, B.; Kharel, M.; Shrestha, R.; Saqr, A.M.; Pant, R.R. Assessment of soil quality along the elevation gradient of the Seti River watershed in Pokhara Metropolitan City, Nepal. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkaj, E.S.; Sepehry, A.; Barani, H.; Motamedi, J.; Shahbazi, F. Establishing a Suitable Soil Quality Index for Semi-arid Rangeland Ecosystems in Northwest of Iran. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2019, 19, 648–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahsay, A.; Haile, M.; Gebresamuel, G.; Mohammed, M. Developing soil quality indices to investigate degradation impacts of different land use types in Northern Ethiopia. Heliyon 2025, 11, e41185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Ai, X.; Sheng, M.; Ai, S.; Miao, N.; Ai, Y. Using a soil quality index to evaluate the artificial soil quality response to rehabilitation time. Ecol. Eng. 2024, 202, 107234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, J.E.K.; Gamfeldt, L.; Isbell, F.; Lefcheck, J.S.; Griffin, J.N.; Hector, A.; Cardinale, B.J.; Hooper, D.U.; Dee, L.E.; Duffy, J.E. Investigating the relationship between biodiversity and ecosystem multifunctionality: Challenges and solutions. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2014, 5, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, P.; van der Plas, F.; Soliveres, S.; Allan, E.; Maestre, F.T.; Mace, G.; Whittingham, M.J.; Fischer, M. Redefining ecosystem multifunctionality. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creamer, R.E.; Barel, J.M.; Bongiorno, G.; Zwetsloot, M.J. The life of soils: Integrating the who and how of multifunctionality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 166, 108561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.Y.; Eldridge, D.J. Climate and plants regulate the spatial variation in soil multifunctionality across a climatic gradient. Catena 2021, 201, 105233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, R.P.O.; Creamer, R.E.; Donnellan, T.; Farrelly, N.; Fealy, R.; O’Donoghue, C.; O’HUallachain, D. Functional land management: A framework for managing soil-based ecosystem services for the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Environ. Sci. Policy 2014, 38, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Ran, J.; Dong, L.; Du, Q.; Ji, M.; Yao, S.; Sun, Y.; Gong, C.; Hou, Q.; Gong, H.; et al. Aridity-driven shift in biodiversity-soil multifunctionality relationships. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schils, R.L.M.; Bufe, C.; Rhymer, C.M.; Francksen, R.M.; Klaus, V.H.; Abdalla, M.; Milazzo, F.; Lellei-Kovacs, E.; ten Berge, H.; Bertora, C.; et al. Permanent grasslands in Europe: Land use change and intensification decrease their multifunctionality. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 330, 107891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Yue, P.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Zuo, X. Progress in research on soil multifunctionality and influence mechanisms in grassland ecosystems. Chin. Desert 2023, 43, 151–165. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Jia, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, H.; Zhu, G. Spatiotemporal Differentiation of Soil Organic Carbon of Grassland and Its Relationship with Soil Physicochemical Properties on the Northern Slope of Qilian Mountains, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dignam, B.E.A.; O’Callaghan, M.; Condron, L.M.; Raaijmakers, J.M.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; Wakelin, S.A. Challenges and opportunities in harnessing soil disease suppressiveness for sustainable pasture production. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 95, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassen, E.E.; Assen, M. Land use/cover dynamics and its drivers in Gelda catchment, Lake Tana watershed, Ethiopia. Environ. Syst. Res. 2017, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; XIao, Q. Compendium of Administrative Divisions of the People’s Republic of China: Gansu Province Volume; China Social Press: Beijing, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- China Soil Science Database. Available online: http://vdb3.soil.csdb.cn/ (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2022. Available online: https://www.fao.org/soils-portal (accessed on 29 March 2025).
- NY/T 1377-2007; Determination of Soil pH. 2007. Institute of Agricultural Quality Standards and Testing Technology: Beijing, China, 2007.
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 39228-2020; Determination of Soil Microbial Biomass—Fumigation Extraction Method. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2020.
- Guan, S. Soil Enzymes and Their Research Methods; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Damiba, W.A.F.; Gathenya, J.M.; Raude, J.M.; Home, P.G. Soil quality index (SQI) for evaluating the sustainability status of Kakia-Esamburmbur catchment under three different land use types in Narok County, Kenya. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbajal, C.; Moya-Ambrosio, F.; Barja, A.; Ottos-Diaz, E.; Aguilar-Tito, C.; Advíncula-Zeballos, O.; Cruz-Luis, J.; Solórzano-Acosta, R. Soil quality variation associated with land cover in the Peruvian jungle of the Junín region. Soil Secur. 2025, 19, 100188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasu, D.; Tiwary, P.; Chandran, P. A novel and comprehensive soil quality index integrating soil morphological, physical, chemical, and biological properties. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, X.; Wang, J. Soil quality evaluation of different land use modes in small watersheds in the hilly region of southern Jiangsu. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Bai, J. Evaluation of soil quality of four land-use modes on the southern Tibetan Plateau. Grass Sci. 2024, 41, 1614–1623. [Google Scholar]
- Yazhuan, S.; Yang, Y.; Cai, L.D.; Yufeng, A.; Fujiang, H. Effects of grazing on soil quality of alpine typical grassland in Qilian Mountains. Ecol. Lett. 2023, 43, 6364–6377. [Google Scholar]
- Ebadati, E.; Switalska, E.; Lombi, E.; Warren-Smith, S.C.; Evans, D. Challenges of polymer-based pH sensing in soil. J. Polym. Sci. 2024, 62, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartemink, A.E.; Barrow, N.J. Soil pH-nutrient relationships: The diagram. Plant Soil 2023, 486, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili, A.; Ramesh, A.; Sharma, M.P. Soil Rhizosphere pH, Enzymatic and Microbial Activities Under Different Nitrogen and Sulfur Fertilization of Soybean (Glycine max L.). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 3986–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavvadias, V.; Ioannou, Z.; Vavoulidou, E.; Paschalidis, C. Short Term Effects of Chemical Fertilizer, Compost and Zeolite on Yield of Lettuce, Nutrient Composition and Soil Properties. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.L.B.; Antonangelo, J.A.; Zhang, H.; Reed, V.; Finch, B.; Arnall, B. Impact of long-term fertilization in no-till on the stratification of soil acidity and related parameters. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 228, 105624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naveed, M.; Brown, L.K.; Raffan, A.C.; George, T.S.; Bengough, A.G.; Roose, T.; Sinclair, I.; Koebernick, N.; Cooper, L.; Hackett, C.A.; et al. Plant exudates may stabilize or weaken soil depending on species, origin and time. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2017, 68, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Yang, T.; Li, L.; Zhao, B.; Liu, J. Response of oat morphologies, root exudates, and rhizosphere fungal communities to amendments in a saline-alkaline environment. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Miao, N.; Wang, P.; Ju, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Dramatic loss of inorganic carbon by nitrogen-induced soil acidification in Chinese croplands. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 3738–3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, L.; Yuan, S.; Chen, D.; Kang, Y.; Shaghaleh, H.; Okla, M.K.; AbdElgawad, H.; Alhaj Hamoud, Y. Changes in salinity and vegetation growth under different land use types during the reclamation in coastal saline soil. Chemosphere 2024, 366, 143427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baridón, J.E.; Casas, R.R. Salinity Dynamics in Subsoiled Soils of the Northwest of the Argentine Pampean Plain. Int. J. Plant Soil Sci. 2021, 33, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Mao, L.; Yan, X.; Liu, C.; Song, X.; Sun, X. Long-term cotton stubble return and subsoiling increases cotton yield through improving root growth and properties of coastal saline soil. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 177, 114472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anning, D.K.; Ghanney, P.; Qiu, H.; Abalori, T.A.; Zhang, C.; Luo, C. Stimulation of soil organic matter fractions by maize straw return and nitrogen fertilization in the Loess Plateau of Northwest China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 191, 105061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S. Effect of Monospecific and Mixed SeaBuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides) Plantations on the Structure and Activity of Soil Microbial Communities. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angers, D.; Arrouays, D.; Cardinael, R.; Chenu, C.; Corbeels, M.; Demenois, J.; Farrell, M.; Martin, M.; Minasny, B.; Recous, S.; et al. A well-established fact: Rapid mineralization of organic inputs is an important factor for soil carbon sequestration. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2022, 73, e13242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiegel, H.; Sanden, T.; Sanden, H.; Goetzinger, S.; Miloczki, J.; Kandeler, E. Changes in Biological and Chemical Soil Properties in an Austrian Long-Term Tillage Experiment. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2025, 76, e70037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Q.; Li, S.; Yu, Y.; Ma, J.; Zheng, C.; Cui, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, H. The Relative Contribution of Root Morphology and Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Colonization on Phosphorus Uptake in Rice/Soybean Intercropping Under Dry Cultivation. Plants 2025, 14, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Crous, K.Y.; Carrillo, Y.; Macdonald, C.A.; Anderson, I.C.; Boer, M.M.; Farrell, M.; Gherlenda, A.N.; Castaneda-Gomez, L.; Hasegawa, S.; et al. Microbial competition for phosphorus limits the CO2 response of a mature forest. Nature 2024, 630, 660–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.; Bai, H.; Liu, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, G.; Chai, G.; He, Y.; Shi, J.; Duan, Y. Response of ecological stoichiometry and homeostasis characteristic to nitrogen addition in Hippophae rhamnoides L. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, D.; Ponder, F., Jr.; Hubbard, V.C. Effects of soil compaction, forest leaf litter and nitrogen fertilizer on two oak species and microbial activity. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2003, 23, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Chang, S.X.; Kabzems, R. Soil compaction and forest floor removal reduced microbial biomass and enzyme activities in a boreal aspen forest soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 44, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Tong, C.; Hu, K.; Zhou, B.; Xing, S.; Mao, Y. Biochar-fertilizer interaction modifies N-sorption, enzyme activities and microbial functional abundance regulating nitrogen retention in rhizosphere soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 140065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinsonneault, A.J.; Moore, T.R.; Roulet, N.T. Effects of long-term fertilization on peat stoichiometry and associated microbial enzyme activity in an ombrotrophic bog. Biogeochemistry 2016, 129, 149–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Cordeiro, C.F.; Echer, F.R.; Araujo, F.F. Cover Crops Impact Crops Yields by Improving Microbiological Activity and Fertility in Sandy Soil. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawaraya, K. Response of mycorrhizal symbiosis to phosphorus and its application for sustainable crop production and remediation of environment. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 68, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Fan, B.; Zhou, G. Soil microbial network complexity predicts soil multifunctionality better than soil microbial diversity during grassland-farmland-shrubland conversion on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 379, 109356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Sui, X.; Li, M. Effects of Forest Age on Soil Fungal Community in a Northern Temperate Ecosystem. Indian J. Microbiol. 2016, 56, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannikos, N.; Leinweber, P.; Helgason, B.L.; Baum, C.; Walley, F.L.; Van Rees, K.C.J. Impact of Populus trees on the composition of organic matter and the soil microbial community in Orthic Gray Luvisols in Saskatchewan (Canada). Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirima, D.D.; Totland, O.; Moe, S.R. The relative importance of vertical soil nutrient heterogeneity, and mean and depth-specific soil nutrient availabilities for tree species richness in tropical forests and woodlands. Oecologia 2016, 182, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, H.; Xu, J.; Yang, H.; Song, J.; Yu, X. Reduced Soil Quality but Increased Microbial Diversity in Cultivated Land Compared to Other Land-Use Types in the Longzhong Loess Plateau. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Zamanian, K. Reviews and syntheses: Agropedogenesis—Humankind as the sixth soil-forming factor and attractors of agricultural soil degradation. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 4783–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, P.; Deb, S.; Deb, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Santra, P.; Dutta, P.; Hoque, A.; Choudhury, A. Soil quality under different land uses in eastern India: Evaluation by using soil indicators and quality index. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Han, J.; Yin, H.; Xue, J.; Jia, L.; Zhen, X.; Chang, J.; Wang, S.; Yu, B. Assessing the effects of different long-term ecological engineering enclosures on soil quality in an alpine desert grassland area. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jia, L.; Yang, L.; Guo, Z.; Sang, W.; Lu, L.; Xiao, C. Assessment of the Effects of Fencing Enclosure on Soil Quality Based on Minimum Data Set in Biru County of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopezosa, P.; Soliveres, S.; Serra, L.; Constan-Nava, S.; Berdugo, M. Land use determines Mediterranean ecosystems’ multifunctionality more than plant richness or habitat composition. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 61, 476–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.; Wu, S.; Zeng, W.; Deng, Y.; Luo, G.; Li, P.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hu, Q.; Tan, L. High-elevation-induced decrease in soil pH weakens ecosystem multifunctionality by influencing soil microbiomes. Environ. Res. 2024, 257, 119330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garba, I.I.; Bell, L.W.; Chauhan, B.S.; Williams, A. Optimizing ecosystem function multifunctionality with cover crops for improved agronomic and environmental outcomes in dryland cropping systems. Agric. Syst. 2024, 214, 103821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, J.; Ding, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, W. Afforestation promotes ecosystem multifunctionality in a hilly area of the Loess Plateau. Catena 2023, 223, 106905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, Y.; He, W.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Bol, R.; Chen, H.; Fan, M. Soil quality and ecosystem multifunctionality after 13-year of organic and nitrogen fertilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 931, 172789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Zhou, J.; Chu, J.; Shahbaz, M.; Yang, Y.; Jones, D.L.; Zang, H.; Razavi, B.S.; Zeng, Z. Insights into the associations between soil quality and ecosystem multifunctionality driven by fertilization management: A case study from the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 362, 132265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres-Abellan, M.; Wic-Baena, C.; Lopez-Serrano, F.R.; Garcia-Morote, F.A.; Martinez-Garcia, E.; Picazo, M.I.; Rubio, E.; Moreno-Ortego, J.L.; Bastida-Lopez, F.; Garcia-Izquierdo, C. A soil-quality index for soil from Mediterranean forests. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2019, 70, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
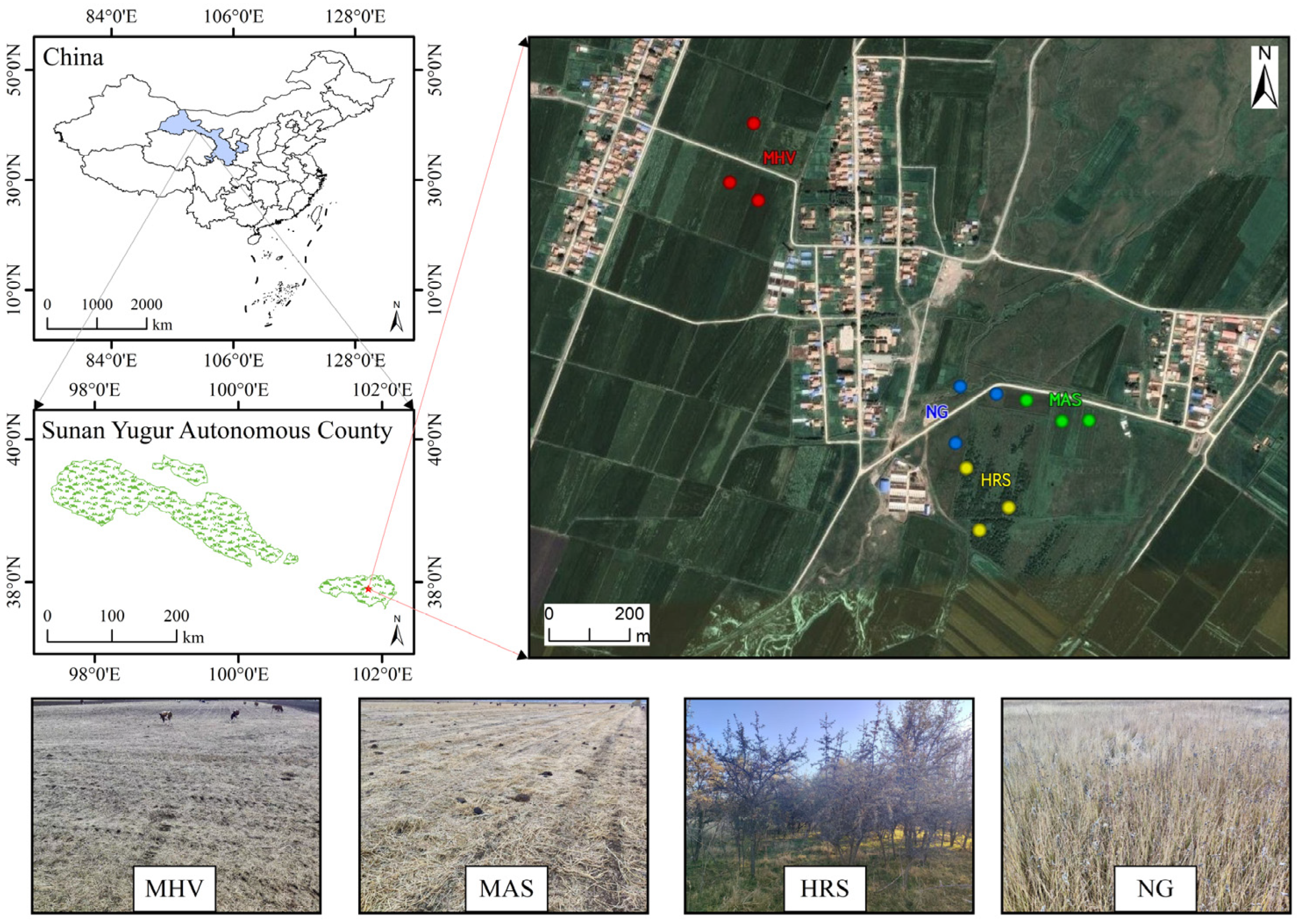
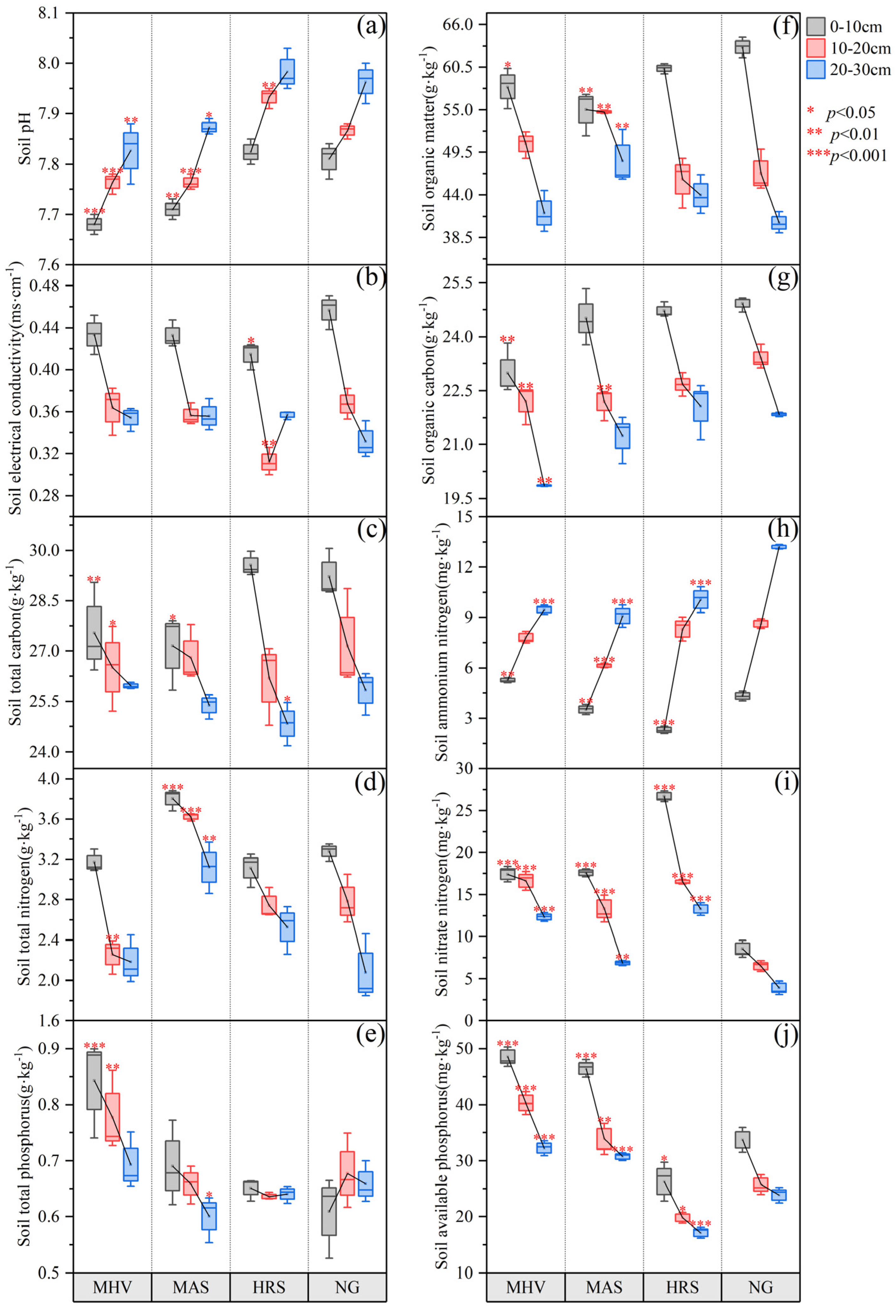
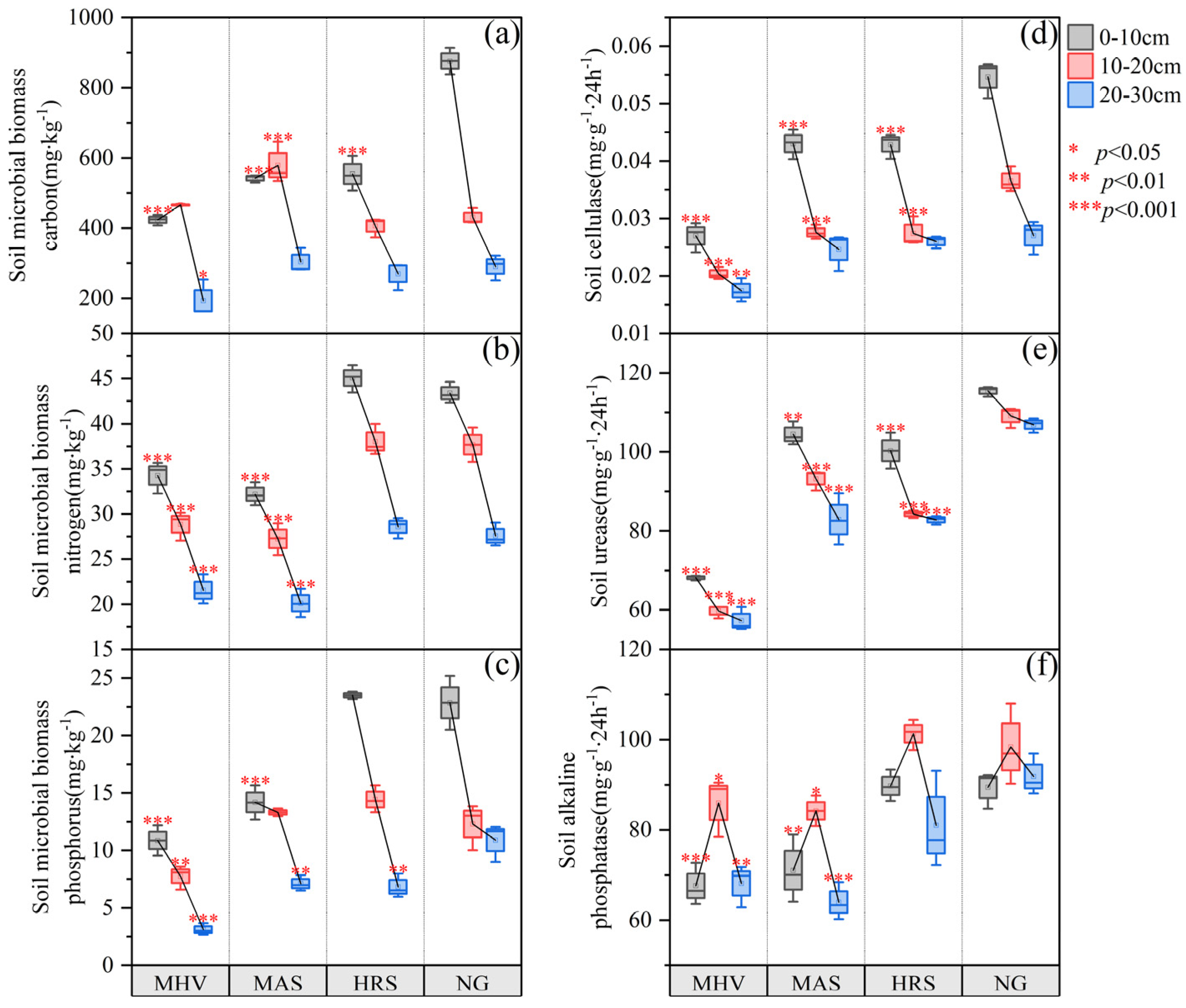
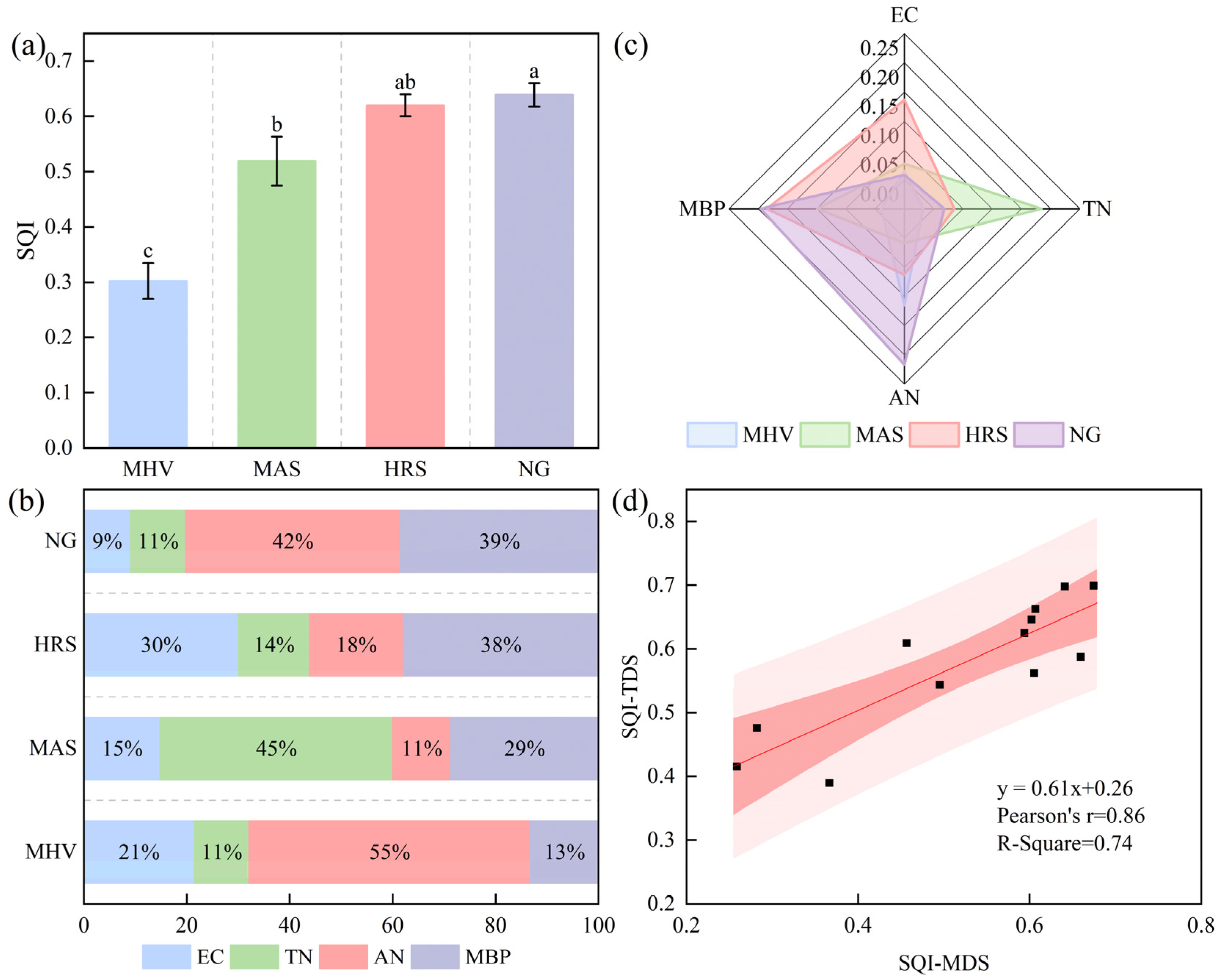
| Related Information | MHV 1 | MAS 2 | HRS 3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conversion time | 2012 | 2012 | 2000 | |
| Species | Oat | Barley | Sea buckthorn | |
| Crop cycles | April-October | June-September | Perennial | |
| Machinery used | Tractor-drawn share plows, disc harrows, and harvesters | Tractor-drawn share plows, disc harrows, harvesters, and balers | None | |
| Irrigation | Mode | Flood irrigation | Flood irrigation | None |
| Times | 2 | 2 | None | |
| Agrochemical | Brand name | Benzenesulfuron, tebuconazole | Benzenesulfuron, tebuconazole | None |
| Frequency | 2 | 2 | None | |
| Function Type | Evaluation Indicators | Membership Functions | Membership Parameters | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | b1 | b2 | a2 | Unit | |||
| S-type | TC 1 | 25.86 | 27.60 | g kg−1 | |||
| TN 1 | 2.50 | 3.56 | g kg−1 | ||||
| TP 1 | 0.60 | 0.79 | g kg−1 | ||||
| SOM 1 | 47.72 | 54.51 | g kg−1 | ||||
| SOC 1 | 21.31 | 23.46 | g kg−1 | ||||
| AN 1 | 5.87 | 8.74 | mg kg−1 | ||||
| NN 1 | 5.73 | 19.24 | mg kg−1 | ||||
| AP 1 | 20.10 | 41.13 | mg kg−1 | ||||
| MBC 1 | 346.93 | 556.60 | mg kg−1 | ||||
| MBN 1 | 26.40 | 37.40 | mg kg−1 | ||||
| MBP 1 | 6.71 | 16.02 | mg kg−1 | ||||
| SCL 1 | 0.02 | 0.03 | mg g−1 24 h−1 | ||||
| URE 1 | 60.56 | 111.92 | mg g−1 24 h−1 | ||||
| ALP 1 | 70.56 | 95.84 | mg g−1 24 h−1 | ||||
| Inverse s-type | EC 1 | 0.35 | 0.39 | ms cm−1 | |||
| Parabolic shape | pH 1 | 7.73 | 7.78 | 7.90 | 7.93 | - | |
| Soil Indicators | Principal Components | Norm | Group | MDS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC1 2 | PC2 2 | PC3 2 | ||||
| pH 1 | 0.904 | −0.347 | −0.164 | 2.732 | 1 | No |
| EC 1 | −0.293 | 0.549 | 0.659 | 1.678 | 2 | Yes |
| TC 1 | 0.891 | −0.097 | 0.124 | 2.622 | 1 | No |
| TN 1 | −0.030 | 0.781 | −0.53 | 1.643 | 2 | Yes |
| TP 1 | −0.765 | −0.265 | 0.377 | 2.368 | 1 | No |
| SOM 1 | −0.15 | 0.705 | −0.313 | 1.434 | 2 | No |
| SOC 1 | 0.937 | 0.200 | −0.087 | 2.771 | 1 | No |
| AN 1 | 0.380 | −0.241 | 0.882 | 1.844 | 3 | Yes |
| NN 1 | −0.332 | −0.555 | −0.709 | 1.795 | 3 | No |
| AP 1 | −0.880 | 0.363 | 0.277 | 2.695 | 1 | No |
| MBC 1 | 0.662 | 0.645 | 0.288 | 2.306 | 2 | No |
| MBN 1 | 0.861 | −0.485 | 0.071 | 2.671 | 1 | No |
| MBP 1 | 0.968 | 0.093 | −0.127 | 2.847 | 1 | Yes |
| SCL 1 | 0.834 | 0.353 | −0.183 | 2.540 | 1 | No |
| URE 1 | 0.861 | 0.471 | 0.090 | 2.664 | 1 | No |
| ALP 1 | 0.898 | −0.304 | 0.176 | 2.701 | 1 | No |
| Eigenvalue | 8.574 | 3.246 | 2.539 | |||
| Contribution/% | 53.587 | 20.285 | 15.870 | |||
| Cumulative contribution/% | 53.587 | 73.872 | 89.742 | |||
| Soil Indicators | TDS 2 | MDS 3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common Factor Variance | Weight | Common Factor Variance | Weight | |
| pH 1 | 0.965 | 0.067 | ||
| EC 1 | 0.822 | 0.057 | 0.822 | 0.225 |
| TC 1 | 0.819 | 0.057 | ||
| TN 1 | 0.892 | 0.062 | 0.892 | 0.244 |
| TP 1 | 0.798 | 0.056 | ||
| SOM 1 | 0.618 | 0.043 | ||
| SOC 1 | 0.926 | 0.064 | ||
| AN 1 | 0.979 | 0.068 | 0.979 | 0.268 |
| NN 1 | 0.92 | 0.064 | ||
| AP 1 | 0.983 | 0.068 | ||
| MBC 1 | 0.938 | 0.065 | ||
| MBN 1 | 0.981 | 0.068 | ||
| MBP 1 | 0.961 | 0.067 | 0.961 | 0.263 |
| SCL 1 | 0.854 | 0.059 | ||
| URE 1 | 0.972 | 0.068 | ||
| ALP 1 | 0.93 | 0.065 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Wei, S.; Xiang, H.; Yu, X. Monocropping Degrades Soil Quality Index and Soil Multifunctionality Compared to Natural Grasslands and Restored Shrubland in China’s Qilian Mountains (Based on Single-Year Sampling). Agronomy 2025, 15, 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061461
Zhang L, Wei S, Xiang H, Yu X. Monocropping Degrades Soil Quality Index and Soil Multifunctionality Compared to Natural Grasslands and Restored Shrubland in China’s Qilian Mountains (Based on Single-Year Sampling). Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061461
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Longji, Shaochong Wei, Hang Xiang, and Xiaojun Yu. 2025. "Monocropping Degrades Soil Quality Index and Soil Multifunctionality Compared to Natural Grasslands and Restored Shrubland in China’s Qilian Mountains (Based on Single-Year Sampling)" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061461
APA StyleZhang, L., Wei, S., Xiang, H., & Yu, X. (2025). Monocropping Degrades Soil Quality Index and Soil Multifunctionality Compared to Natural Grasslands and Restored Shrubland in China’s Qilian Mountains (Based on Single-Year Sampling). Agronomy, 15(6), 1461. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061461







