Changes in Microbial Necromass Carbon in Soil Profiles of Grasslands with Different Stages of Restoration in a Karst Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Sampling
2.2. Laboratory Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
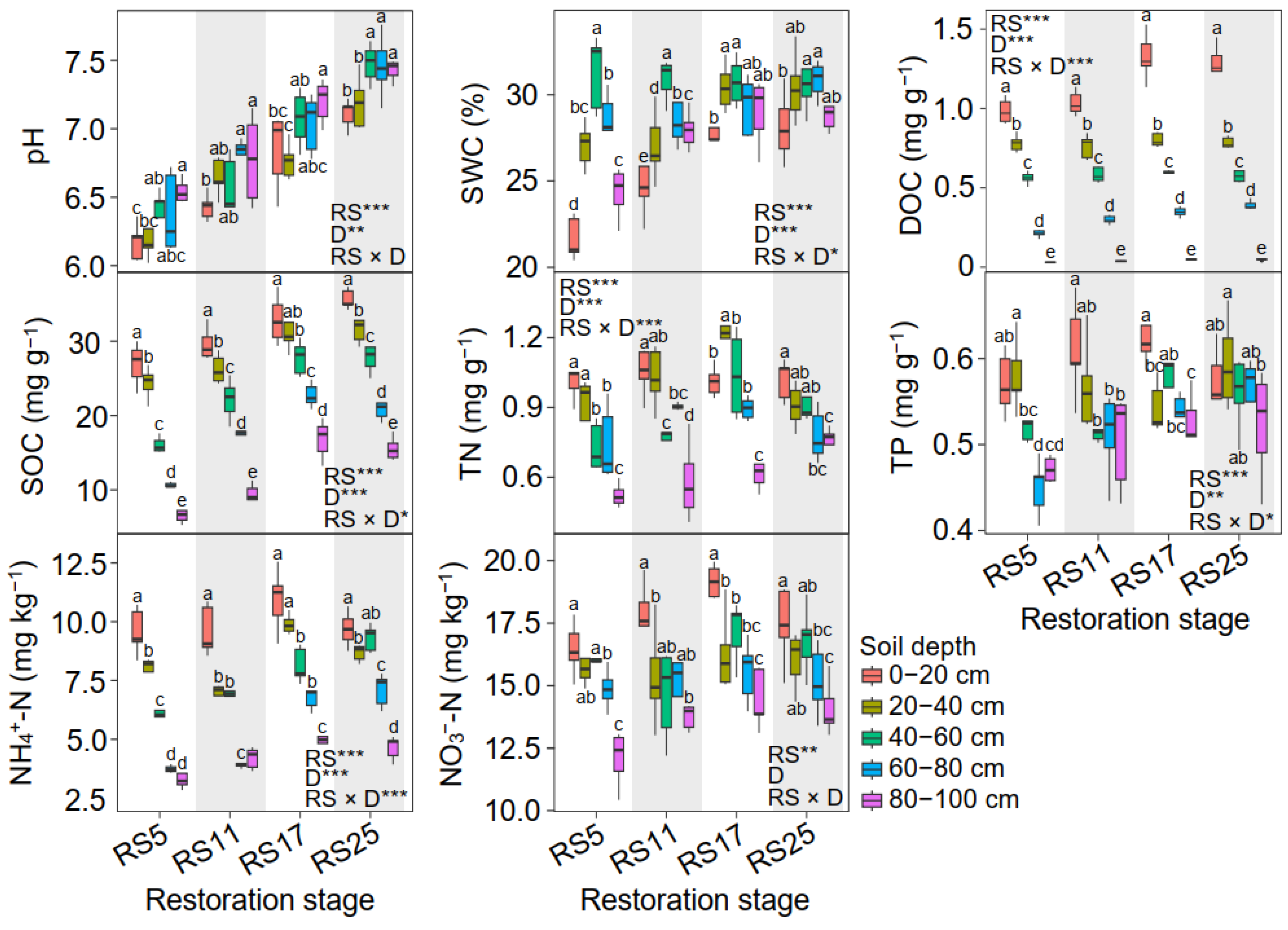
3.1. Soil Properties Among Different Soil Depths and Grassland Restoration Stages
3.2. Microbial Necromass Carbon C Among Different Soil Depths and Grassland Restoration Stages
3.3. Soil Enzyme Activities Among Different Soil Depths and Grassland Restoration Stages
3.4. Effects of Soil Properties and Enzyme Activities on MNC and the Contribution to SOC
4. Discussion
4.1. Variations in Soil Properties Among Soil Depths and Grassland Restoration Stages
4.2. Variations in Soil Enzyme Activities Among Soil Depths and Grassland Restoration Stages
4.3. Variations in Microbial Necromass C Among Soil Depths and Grassland Restoration Stages
4.4. Driving Factors of Microbial Necromass C
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| C | Carbon |
| SOC | Soil organic carbon |
| BNC | Bacterial necromass carbon |
| FNC | Fungal necromass carbon |
| MNC | Microbial necromass carbon |
| RS | Restoration stage |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| MurA | Muramic acid |
| GlcN | Glucosamine |
| GalN | Galactosamine |
| RDA | Redundancy analysis |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
| NH4+-N | Ammonium nitrogen |
| NO3−-N | Nitrate nitrogen |
| SWC | Soil water content |
| BG | Glucosidase |
| CB | Cellobiohydrolase |
| PPO | Polyphenol oxidase |
References
- Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Piao, S.; Liu, M.; Han, G.; Li, J.; Liang, E.; Lee, T.M.; Liu, G.; Wilkes, A.; et al. Toward a sustainable grassland ecosystem worldwide. Innovation 2022, 3, 4100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardgett, R.D.; Bullock, J.M.; Lavorel, S.; Manning, P.; Schaffner, U.; Ostle, N.; Chomel, M.; Durigan, G.; Fry, L.; Johnson, D.; et al. Combatting global grassland degradation. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 720–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Soil carbon sequestration impacts on global climate change and food security. Science 2004, 304, 1623–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, B.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Knapp, A.K.; Smith, M.D.; Reed, S.; Osborne, B.; Carrillo, Y.; Maestre, F.T.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, A.; et al. Aridity drives the response of soil total and particulate organic carbon to drought in temperate grasslands and shrublands. Sci. Adv. 2024, 10, eadq2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Anderson, I.C.; Singh, B.K. Microbial modulators of soil carbon storage: Integrating genomic and metabolic knowledge for global prediction. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhu, X. The soil microbial carbon pump as a new concept for terrestrial carbon sequestration. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, L.C.; Lajtha, K.; Rousk, J. Nutrient limitation may induce microbial mining for resources from persistent soil organic matter. Ecology 2021, 102, e03328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Wang, R.; Chang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, T.; Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Shi, X.; Lu, J.; Luo, D.; et al. The contribution of microbial necromass to soil organic carbon and influencing factors along a variation of habitats in alpine ecosystems. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Fang, K.; Chen, L.; Feng, X.; Qin, S.; Kou, D.; He, H.; Liang, C.; Yang, Y. Depth-dependent drivers of soil microbial necromass carbon across Tibetan alpine grasslands. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; An, S.; Liang, C.; Liu, Y.; Kuzyakov, Y. Microbial necromass as the source of soil organic carbon in global ecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 162, 108422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Wang, L.; Qi, X.; Wang, K. Vegetation restoration in South China’s karst region under geological background constraint: Forest or non-forest. Trans. Earth Environ. Sustain. 2023, 1, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Yue, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, M.; Qi, X.; Fu, Z. Karst landscapes of China: Patterns, ecosystem processes and services. Landscape Ecol. 2019, 34, 2743–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiong, K.; Liu, Z.; Li, K.; Luo, D. Distribution and influencing factors of soil organic carbon in a typical karst catchment undergoing natural restoration. Catena 2022, 212, 106078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhao, X.; Li, H.; Nie, L.; Li, W. Carbon storage patterns in typical subalpine meadows with varying vegetation cover in Southwestern China. Curr. Res. Environ. Sus. 2025, 9, 100290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Yang, X.; Ren, F.; Zhou, H.; Zhu, B.; He, J.S. Neutral effect of nitrogen addition and negative effect of phosphorus addition on topsoil extracellular enzymatic activities in an alpine grassland ecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.D.; Amelung, W. Gas chromatographic determination of muramic acid, glucosamine, mannosamine, and galactosamine in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1996, 28, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joergensen, R.G. Amino sugars as specific indices for fungal and bacterial residues in soil. Biol Fertil. Soils. 2018, 54, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Franzluebbers, A.J.; Stuedemann, J.A. Soil-profile organic carbon and total nitrogen during 12 years of pasture management in the Southern Piedmont USA. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. The vertical distribution of soil organic carbon and its relation to climate and vegetation. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 423–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Qiu, J.; Xu, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Li, B.; Lu, Y. Responses of soil aggregate stability to organic C and total N as controlled by land-use type in a region of south China affected by sheet erosion. Catena 2022, 218, 106543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tückmantel, T.; Leuschner, C.; Preusser, S.; Kandeler, E.; Angst, G.; Mueller, C.W.; Meier, I.C. Root exudation patterns in a beech forest: Dependence on soil depth, root morphology, and environment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 107, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, J.M.B.; Vermeiren, C.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; Darch, T.; Granger, S.J.; Dunham, S.J.; Hernandez-Allica, J.; Smolders, E.; McGrath, S. The effect of soil organic matter on long-term availability of phosphorus in soil: Evaluation in a biological P mining experiment. Geoderma 2022, 423, 115965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condron, L.; Stark, C.; O’callaghan, M.; Clinton, P.; Huang, Z. The Role of Microbial Communities in the Formation and Decomposition of Soil Organic Matter; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 81–118. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.P.; Zhang, J.; Pang, X.P.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W.N.; Wang, J.; Guo, Z.G. Responses of plant productivity and soil nutrient concentrations to different alpine grassland degradation levels. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, S.G.; Kitchen, D.J.; Blair, J.M.; Rice, C.W. Changes in ecosystem structure and function along a chronosequence of restored grasslands. Ecol. Appl. 2002, 12, 1688–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, P.N.J.; Noske, P.J.; Sheridan, G.J. Phosphorus enrichment from point to catchment scale following fire in eucalypt forests. Catena 2011, 87, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Gao, Z.; Lin, Z.; Luo, J.; Fan, X. Vegetation influence on the soil hydrological regime in permafrost regions of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, China. Geoderma 2019, 354, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, K.S.; Sehgal, V.K.; Singh, S.K.; Ray, S.S. Soil moisture estimation using triangular method at higher resolution from MODIS products. Phys. Chem. Earth 2022, 126, 103051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neemisha; Sharma, S. Soil Enzymes and Their Role in Nutrient Cycling. In Structure and Functions of Pedosphere; Giri, B., Kapoor, R., Wu, Q.S., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, L.; Shangguan, Z.P. Afforestation drives soil carbon and nitrogen changes in China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskelinen, A.; Harpole, W.S.; Jessen, M.T.; Virtanen, R.; Hautier, Y. Light competition drives herbivore and nutrient effects on plant diversity. Nature 2022, 611, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thotakuri, G.; Angidi, S.; Athelly, A. Soil carbon pool as influenced by soil microbial activity-an overview. Am. J. Clim. Change 2024, 13, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, Q.; Fang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Duan, C.; Song, X.; Tian, X. Enlarging interface reverses the dominance of fungi over bacteria in litter decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 198, 109543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Mechanisms and implications of bacterial-fungal competition for soil resources. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Guo, J.; Jin, W.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zha, L.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, Y. Responses of SOC, labile SOC fractions, and amino sugars to different organic amendments in a coastal saline-alkali soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 239, 106051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Soong, J.L.; Horton, A.J.; Campbell, E.E.; Haddix, M.L.; Wall, D.H.; Parton, W.J. Formation of soil organic matter via biochemical and physical pathways of litter mass loss. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 776–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Du, M.; Chen, J.; Tie, L.; Zhou, S.; Buckeridge, K.M.; Cornelissen, J.H.C.; Huang, C.; Kuzyakov, Y. Microbial necromass under global change and implications for soil organic matter. Glob. Change Biol. 2003, 29, 3503–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotrufo, M.F.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Boot, C.M.; Denef, K.; Paul, E. The Microbial Efficiency-Matrix Stabilization (MEMS) framework integrates plant litter decomposition with soil organic matter stabilization: Do labile plant inputs form stable soil organic matter? Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, F.; Bååth, E.; De Nicola, F. Bacterial and fungal growth on different plant litter in Mediterranean soils: Effects of C/N ratio and soil pH. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 108, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Noll, L.; Zhang, S.; Wanek, W. Direct measurement of the in situ decomposition of microbial-derived soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Cotrufo, M.F. Grassland soil carbon sequestration: Current understanding, challenges, and solutions. Science 2022, 37, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, X.; Liu, H.; Bai, X.; Lv, D.; Lv, M.; Yang, Y.; Li, W. Changes in Microbial Necromass Carbon in Soil Profiles of Grasslands with Different Stages of Restoration in a Karst Region. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061436
Wu X, Liu H, Bai X, Lv D, Lv M, Yang Y, Li W. Changes in Microbial Necromass Carbon in Soil Profiles of Grasslands with Different Stages of Restoration in a Karst Region. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061436
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Xuefeng, Heng Liu, Xiaolong Bai, Dongpeng Lv, Mingzhi Lv, Yurong Yang, and Wangjun Li. 2025. "Changes in Microbial Necromass Carbon in Soil Profiles of Grasslands with Different Stages of Restoration in a Karst Region" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061436
APA StyleWu, X., Liu, H., Bai, X., Lv, D., Lv, M., Yang, Y., & Li, W. (2025). Changes in Microbial Necromass Carbon in Soil Profiles of Grasslands with Different Stages of Restoration in a Karst Region. Agronomy, 15(6), 1436. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061436





