Transcriptome Insights into Carbohydrate Metabolism and Frying Quality Traits in Waxy and Mealy Potatoes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Frying-Quality-Related Phenotype Assessment
2.2. RNA Sequencing
2.3. Read Processing, Mapping, and Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) Analysis
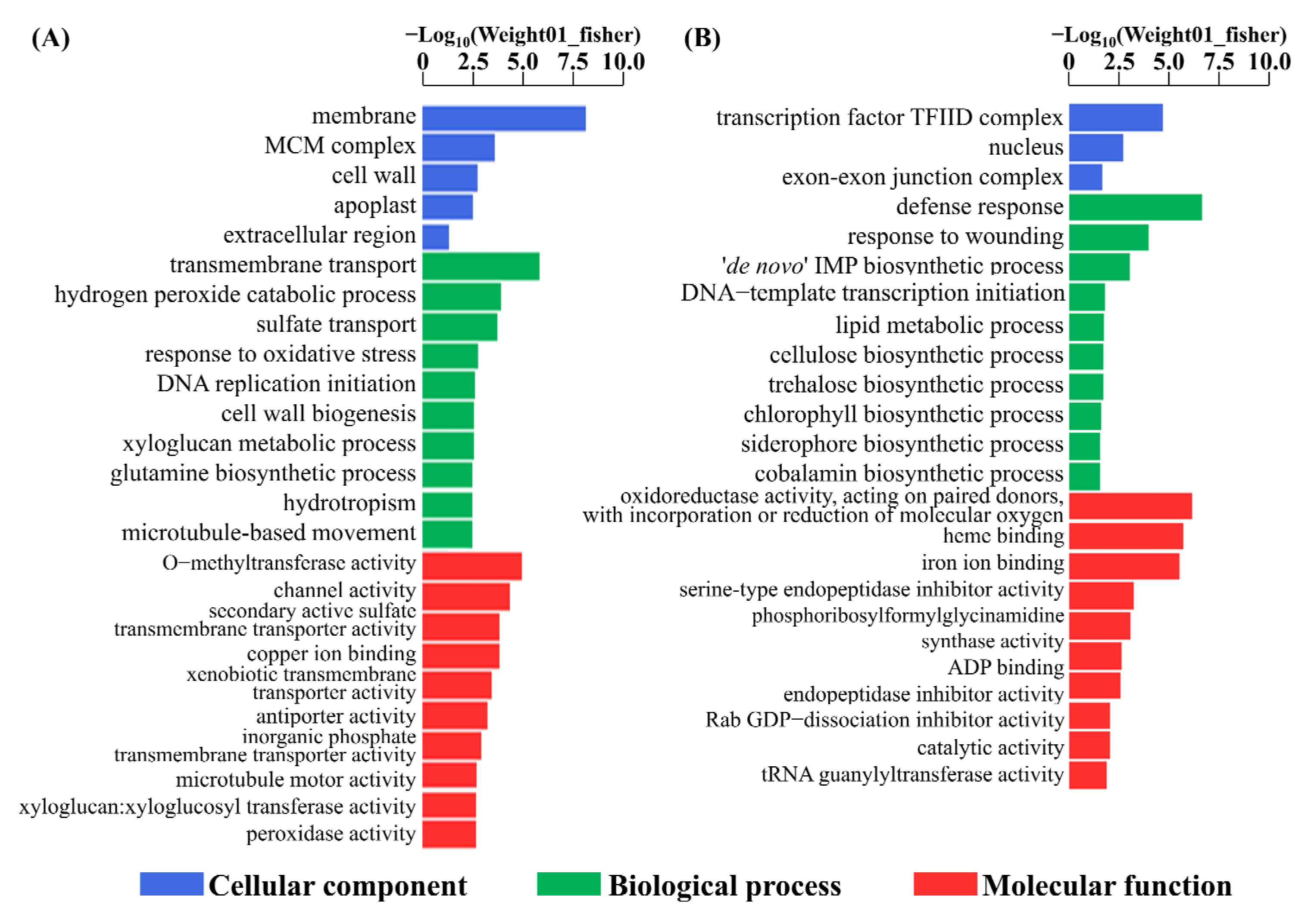
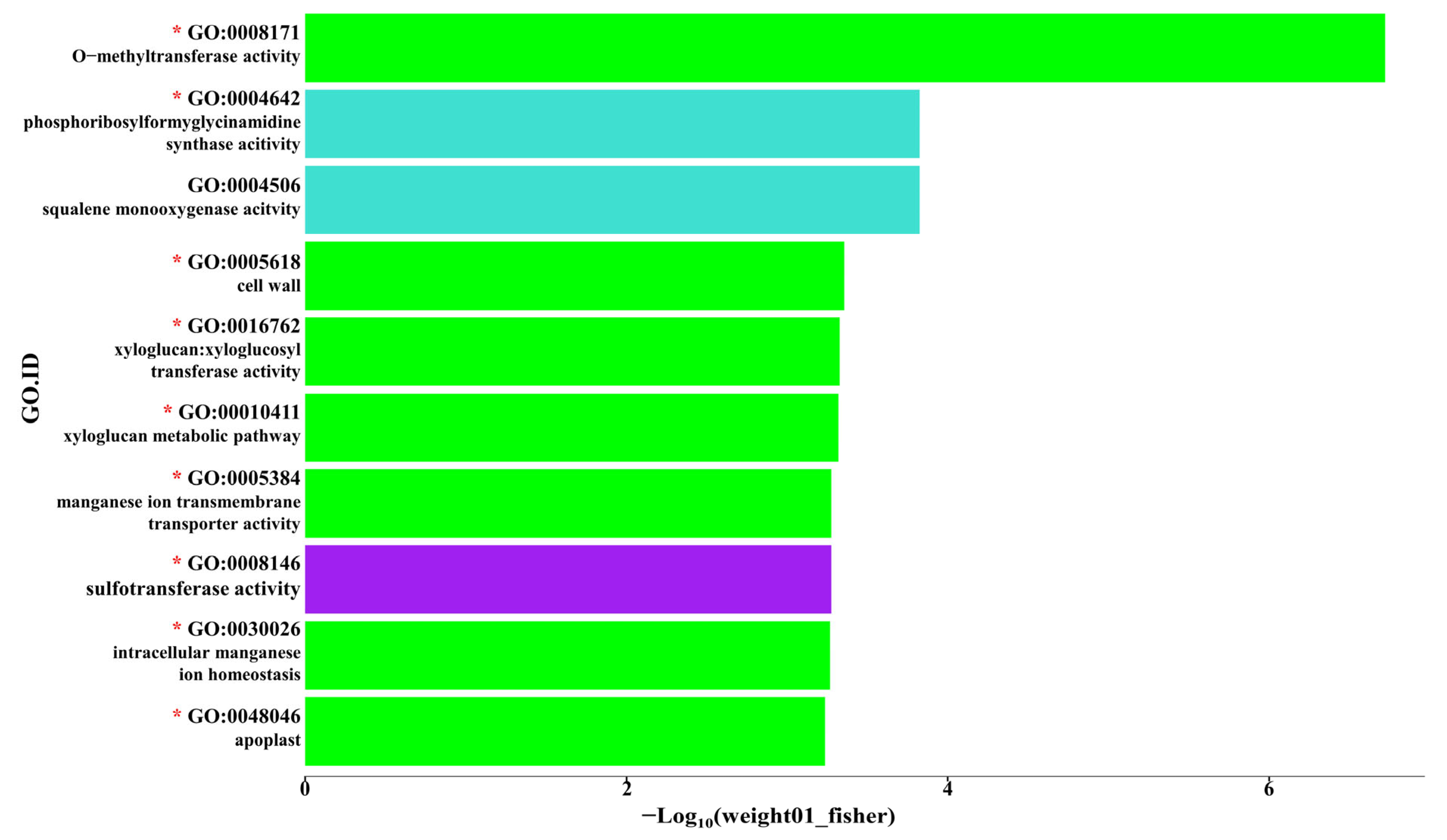
2.4. Gene Ontology (GO) Analysis
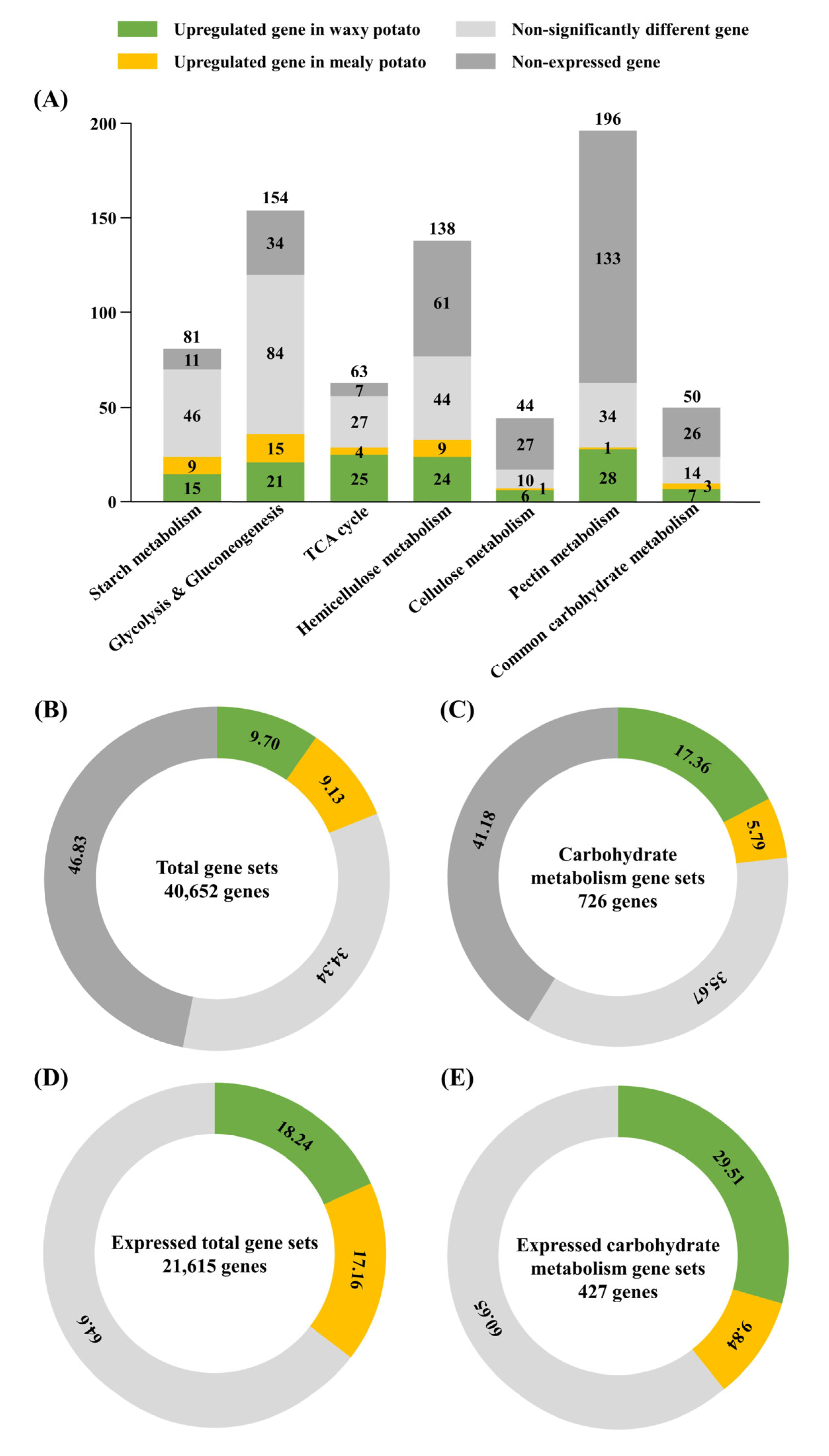
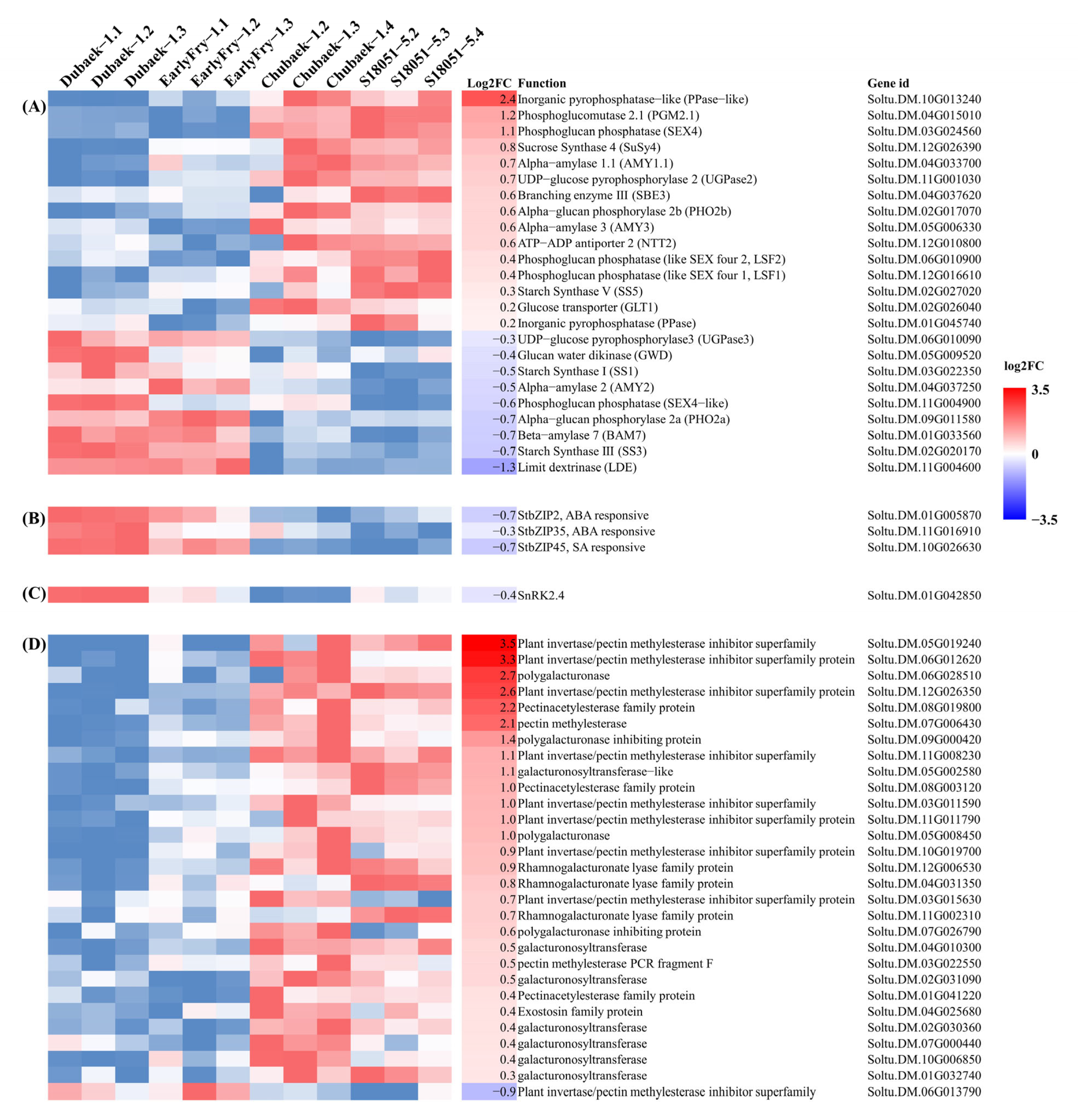
2.5. Carbohydrate Metabolic Gene Expression Analysis
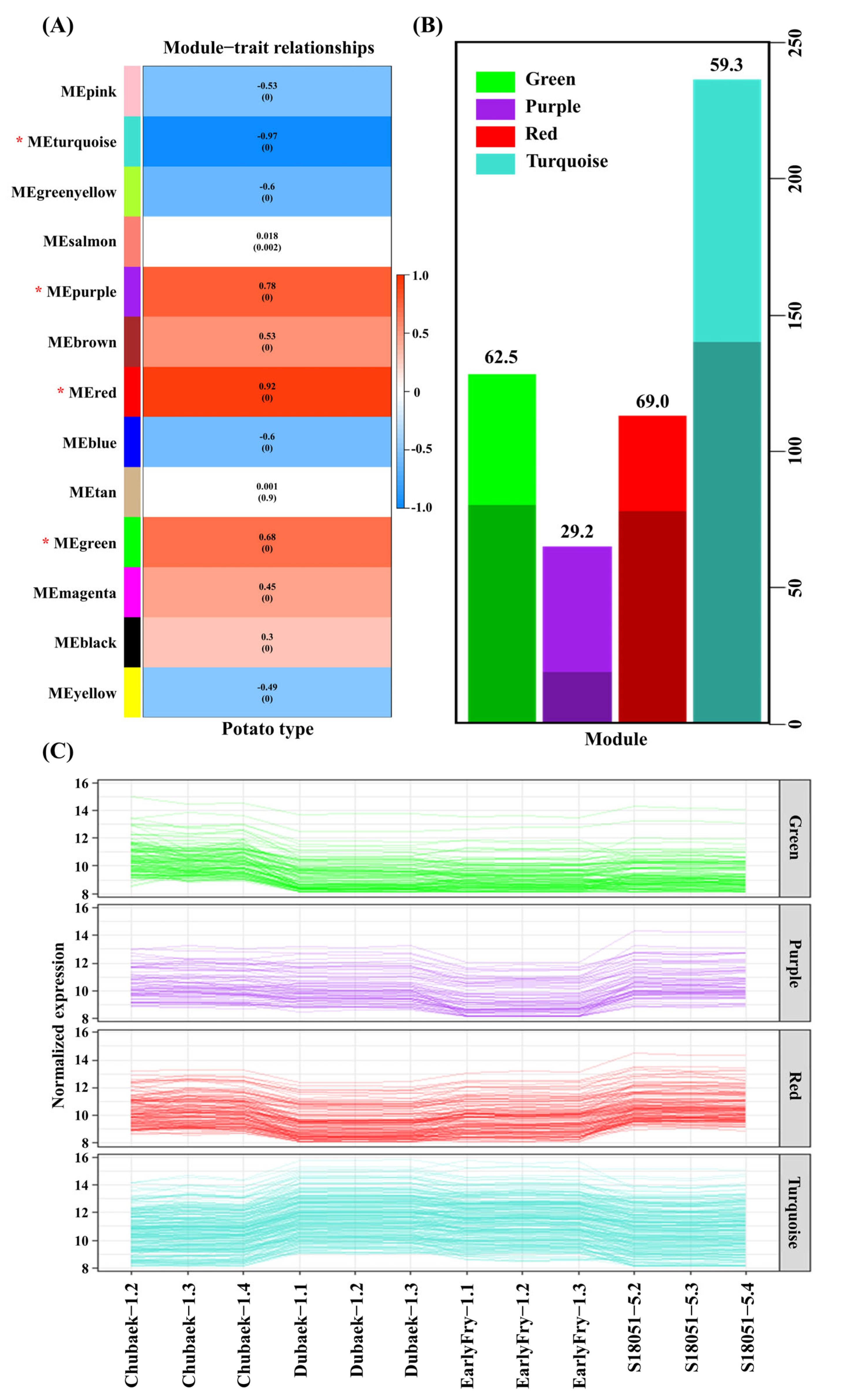
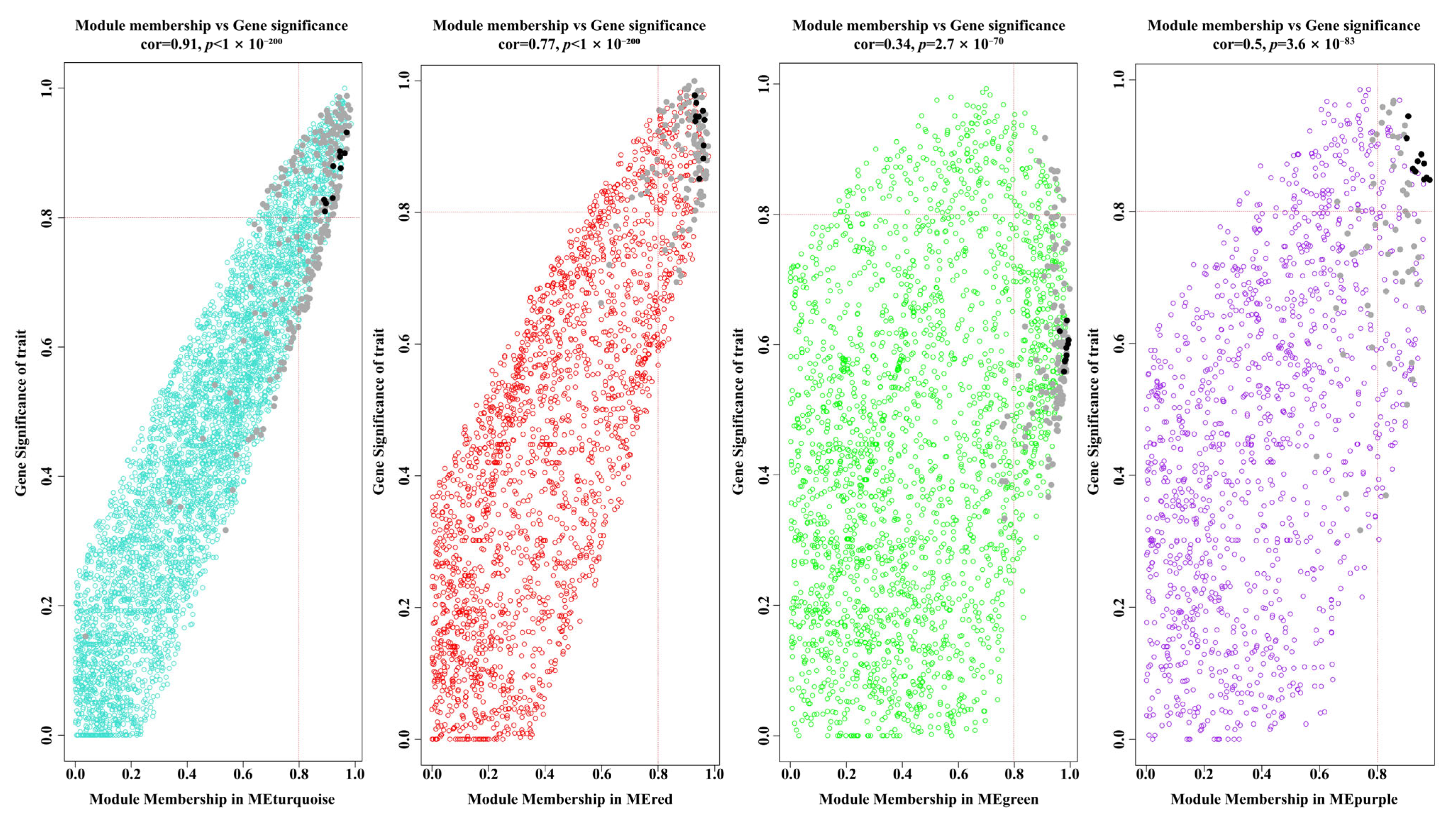
2.6. Coexpression Analysis with Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Analysis (WGCNA)
2.7. Transcription Factor Coexpression Analysis
3. Results
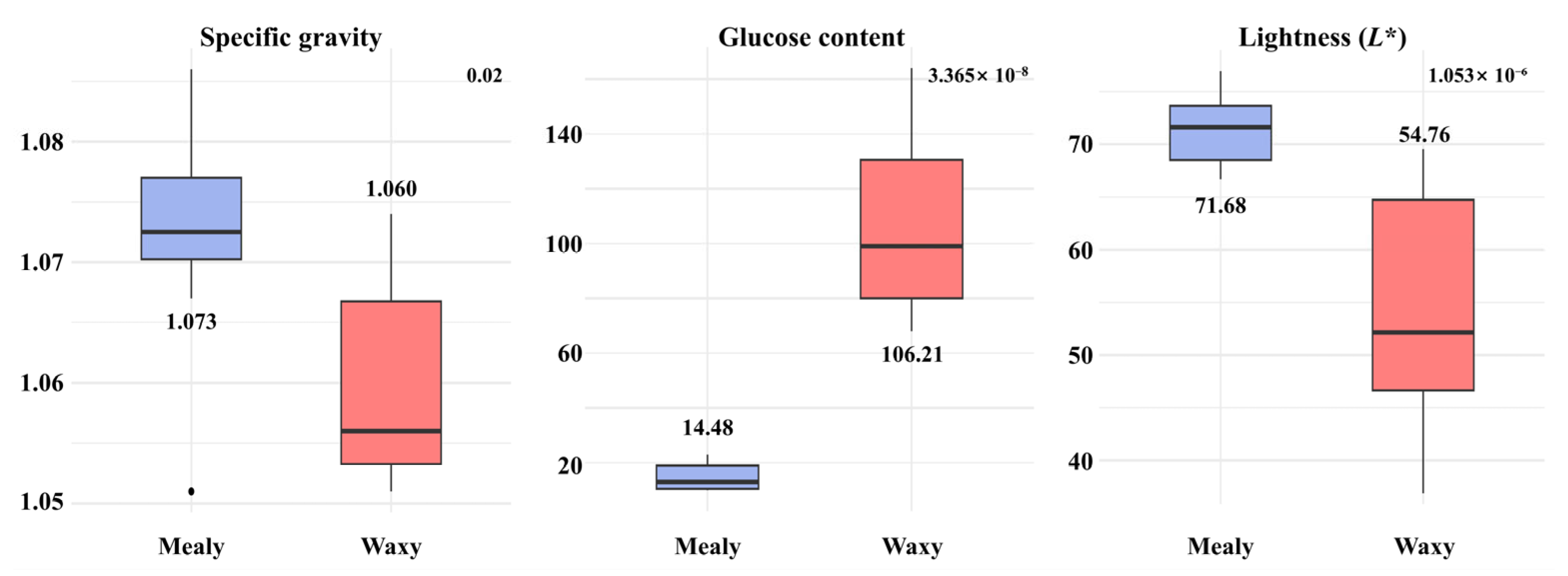
3.1. Phenotypes Related to Frying Quality
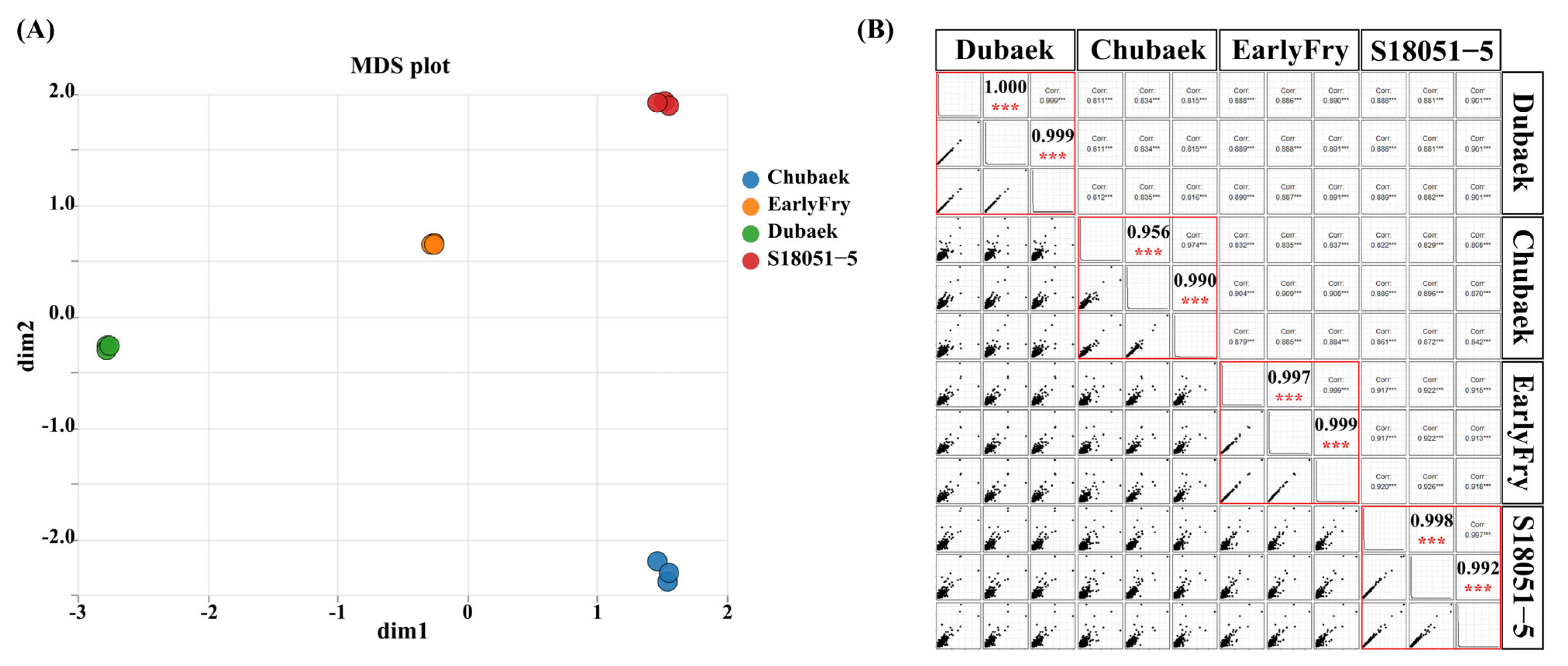
3.2. Transcriptome Sequencing and Mapping
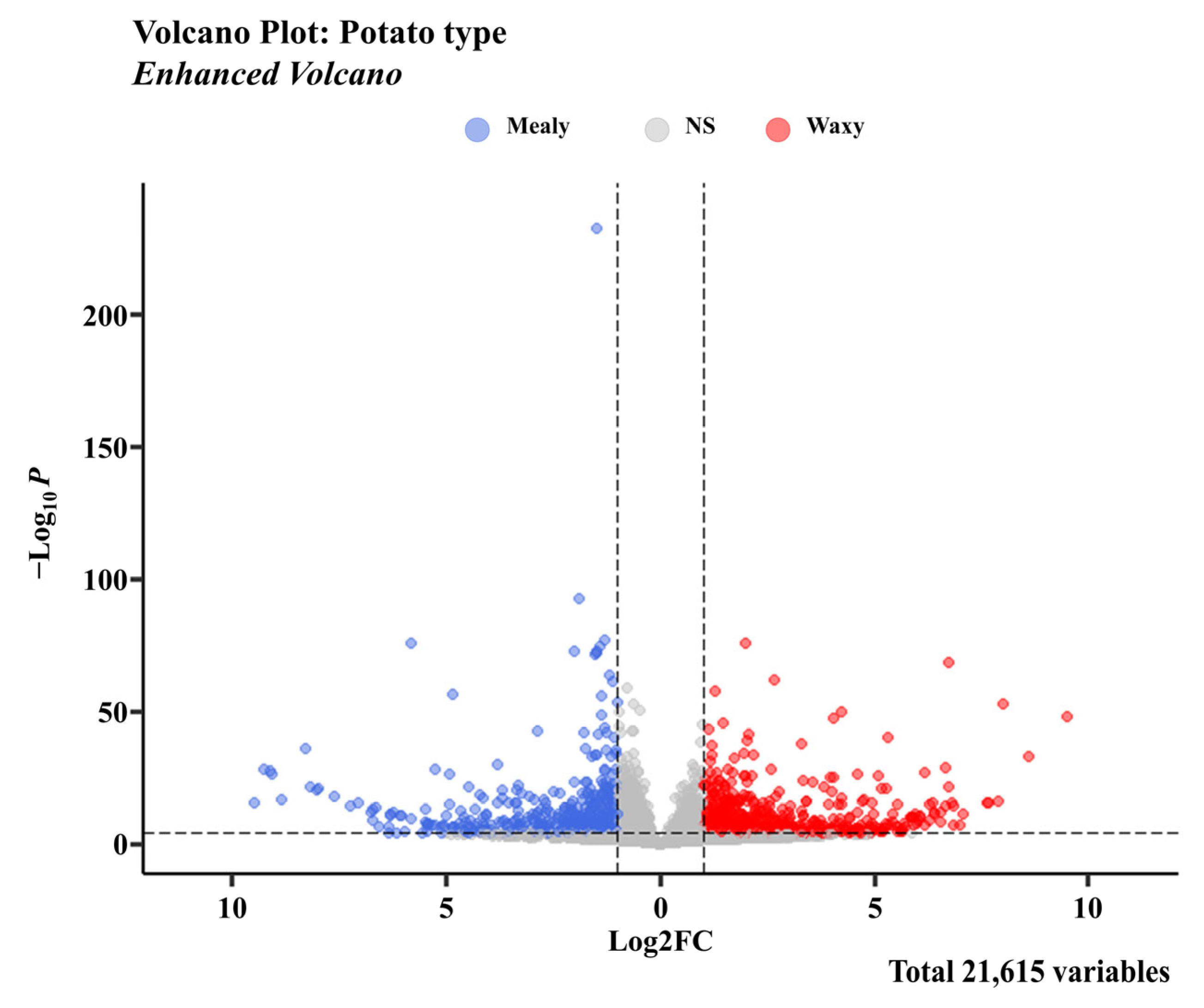
3.3. Gene Expression Patterns in Two Types of Potato
3.4. Functional Classification of DEGs
3.5. Carbohydrate Metabolic Gene Expression Analysis
3.6. Gene Coexpression Analysis
3.7. Transcription Factor Coexpression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lutaladio, N.; Castaldi, L. Potato: The hidden treasure. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2009, 22, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J. Global distribution of the potato crop. Am. J. Potato Res. 2001, 78, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haverkort, A.; Struik, P. Yield levels of potato crops: Recent achievements and future prospects. Field Crops Res. 2015, 182, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierer, W.; Rüscher, D.; Sonnewald, U.; Sonnewald, S. Tuber and tuberous root development. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2021, 72, 551–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernie, A.R.; Willmitzer, L. Molecular and biochemical triggers of potato tuber development. Plant Physiol. 2001, 127, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, J.C.; Love, S.L.; Knowles, N.R. Tuber quality. In Potato Production Systems; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 479–497. [Google Scholar]
- Mccomber, D.R.; Osman, E.M.; Lohnes, R.A. Factors related to potato mealiness. J. Food Sci. 1988, 53, 1423–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlista, A.D. Potato types: Their characteristics & uses. Am. Biol. Teach. 1997, 59, 26–29. [Google Scholar]
- Jaggan, M.; Mu, T.; Sun, H. The effect of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) cultivars on the sensory, nutritional, functional, and safety properties of French fries. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 44, e14912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lusas, E.W.; Rooney, L.W. Snack Foods Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkman, M.A. Global markets for processed potato products. In Potato Biology and Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 27–44. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.M.; Naznin, S.; Naznin, A.; Uddin, M.N.; Amin, M.N.; Rahman, M.M.; Tipu, M.M.H.; Alsuhaibani, A.M.; Gaber, A.; Ahmed, S. Dry matter, starch content, reducing sugar, color and crispiness are key parameters of potatoes required for chip processing. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, J.E. Potato-breeding strategy. In Potato Biology and Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 157–177. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, A.T.; Cogan, N.O.; Hayes, B.J.; Schultz, L.; Dale, M.F.B.; Bryan, G.J.; Forster, J.W. Improving breeding efficiency in potato using molecular and quantitative genetics. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 2279–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de Arcaute, R.; Carrasco, A.; Ortega, F.; Rodriguez-Quijano, M.; Carrillo, J.M. Evaluation of Genetic Resources in a Potato Breeding Program for Chip Quality. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaswal, A. Non-starch polysaccharides and the texture of French fried potato. Am. Potato J. 1970, 47, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, H.A.; Wright, K.M.; McDougall, G.J.; Roberts, A.G.; Chapman, S.N.; Morris, W.L.; Hancock, R.D.; Stewart, D.; Tucker, G.A.; James, E.K. Potato tuber pectin structure is influenced by pectin methyl esterase activity and impacts on cooked potato texture. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Sman, R.; Schenk, E. Causal factors concerning the texture of French fries manufactured at industrial scale. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajner-Czopek, A.; Figiel, A. Effect of the content of potato non-starch polysaccharides (NSP) and lignin on the mechanical properties of French fries. Pol. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2003, 53, 136–140. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, S.; Singh, S.; Marwaha, R.; Pattanayak, D. Indian potato processing varieties: Their impact and future priorities. Potato J. 2009, 36, 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, W. The sugar balance in some British potato varieties during storage. II. The effects of tuber age, previous storage temperature, and intermittent refrigeration upon low-temperature sweetening. Potato Res. 1969, 12, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, M.A.; Faulks, R.M.; Belsten, J.L. Role of reducing sugars and amino acids in fry colour of chips from potatoes grown under different nitrogen regimes. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1990, 52, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Paulo, M.-J.; Strahwald, J.; Lübeck, J.; Hofferbert, H.-R.; Tacke, E.; Junghans, H.; Wunder, J.; Draffehn, A.; van Eeuwijk, F. Natural DNA variation at candidate loci is associated with potato chip color, tuber starch content, yield and starch yield. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 116, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pandey, J.; Scheuring, D.C.; Koym, J.W.; Endelman, J.B.; Vales, M.I. Genomic selection and genome-wide association studies in tetraploid chipping potatoes. Plant Genome 2023, 16, e20297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rak, K.; Bethke, P.C.; Palta, J.P. QTL mapping of potato chip color and tuber traits within an autotetraploid family. Mol. Breed. 2017, 37, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, S.; Meade, F.; Mesiti, F.; Griffin, D.; Kennedy, C.; Milbourne, D. Genome-wide association and genomic prediction for fry color in potato. Agronomy 2020, 10, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, K.R.; Choi, J.-G.; Kwon, D.-H.; Park, Y.-E.; Kim, S.-J. Revealing genetic variations associated with chip-processing properties in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Agronomy 2023, 13, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, H.V.; Ulvskov, P. Hemicelluloses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 263–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauly, M.; Gille, S.; Liu, L.; Mansoori, N.; de Souza, A.; Schultink, A.; Xiong, G. Hemicellulose biosynthesis. Planta 2013, 238, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohnen, D. Pectin structure and biosynthesis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2008, 11, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinze, T. Cellulose: Structure and properties. In Cellulose Chemistry and Properties: Fibers, Nanocelluloses and Advanced Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; pp. 1–52. [Google Scholar]
- Pham, G.M.; Hamilton, J.P.; Wood, J.C.; Burke, J.T.; Zhao, H.; Vaillancourt, B.; Ou, S.; Jiang, J.; Buell, C.R. Construction of a chromosome-scale long-read reference genome assembly for potato. Gigascience 2020, 9, giaa100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönhals, E.; Ortega, F.; Barandalla, L.; Aragones, A.; Ruiz de Galarreta, J.; Liao, J.-C.; Sanetomo, R.; Walkemeier, B.; Tacke, E.; Ritter, E. Identification and reproducibility of diagnostic DNA markers for tuber starch and yield optimization in a novel association mapping population of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2016, 129, 767–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, C.; Urbany, C.; Stich, B. Dissection of potato complex traits by linkage and association genetics as basis for developing molecular diagnostics in breeding programs. In Genomics of Plant Genetic Resources: Crop productivity, food security and nutritional quality; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 47–85. [Google Scholar]
- Neilson, J.; Lagüe, M.; Thomson, S.; Aurousseau, F.; Murphy, A.; Bizimungu, B.; Deveaux, V.; Bègue, Y.; Jacobs, J.; Tai, H. Gene expression profiles predictive of cold-induced sweetening in potato. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2017, 17, 459–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Paggi, J.M.; Park, C.; Bennett, C.; Salzberg, S.L. Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 907–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Handsaker, B.; Wysoker, A.; Fennell, T.; Ruan, J.; Homer, N.; Marth, G.; Abecasis, G.; Durbin, R.; Subgroup, G.P.D.P. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2078–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Law, C.W.; Ah-Cann, C.; Asselin-Labat, M.-L.; Blewitt, M.E.; Ritchie, M.E. Glimma: Interactive graphics for gene expression analysis. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2050–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexa, A.; Rahnenführer, J. Gene set enrichment analysis with topGO. Bioconduct. Improv 2009, 27, 776. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Brouwer, M.; Pup, E.D.; van Lieshout, N.; Finkers, R.; Bachem, C.W.; Visser, R.G. Allelic variation in the autotetraploid potato: Genes involved in starch and steroidal glycoalkaloid metabolism as a case study. BMC Genom. 2024, 25, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, O.; Granot, D. An overview of sucrose synthases in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; White, P. Structure and properties of amylose, amylopectin. Cereal Chem 1994, 71, 263–268. [Google Scholar]
- Nazarian-Firouzabadi, F.; Visser, R.G. Potato starch synthases: Functions and relationships. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 10, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.; Shah, A.N.; Shah, A.A.; Nadeem, M.A.; Alsaleh, A.; Javed, T.; Alotaibi, S.S.; Abdelsalam, N.R. Genome-wide analysis of invertase gene family, and expression profiling under abiotic stress conditions in potato. Biology 2022, 11, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roldán, I.; Wattebled, F.; Mercedes Lucas, M.; Delvallé, D.; Planchot, V.; Jiménez, S.; Pérez, R.; Ball, S.; d’Hulst, C.; Mérida, Á. The phenotype of soluble starch synthase IV defective mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana suggests a novel function of elongation enzymes in the control of starch granule formation. Plant J. 2007, 49, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, V.; Verchot, J. Insight into the bZIP gene family in Solanum tuberosum: Genome and transcriptome analysis to understand the roles of gene diversification in spatiotemporal gene expression and function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yi, Q.; Cao, Y.; Wei, B.; Zheng, L.; Xiao, Q.; Xie, Y.; Gu, Y.; Li, Y.; Huang, H. ZmbZIP91 regulates expression of starch synthesis-related genes by binding to ACTCAT elements in their promoters. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-C.; Xu, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.-Q.; Cai, X.-L. OsbZIP58, a basic leucine zipper transcription factor, regulates starch biosynthesis in rice endosperm. J. Exp. Bot. 2013, 64, 3453–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; van Lammeren, A.A.; Vermeer, E.; Vreugdenhil, D. The role of gibberellin, abscisic acid, and sucrose in the regulation of potato tuber formation in vitro. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, F.; Feng, H.; Wang, X.; Cai, C. Advances in the Modulation of Potato Tuber Dormancy and Sprouting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Jin, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, F.; Zhou, W.; Qiu, B.; Qiu, L.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, G. The effect of H2O2 and abscisic acid (ABA) interaction on β-amylase activity under osmotic stress during grain development in barley. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 47, 778–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Pritchard, J.; Mieog, J.; Byrne, K.; Colgrave, M.L.; Wang, J.R.; Ral, J.P.F. Overexpression of a wheat α-amylase type 2 impact on starch metabolism and abscisic acid sensitivity during grain germination. Plant J. 2021, 108, 378–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Yang, R.; Bartels, D.; Dong, T.; Duan, H. Roles of abscisic acid and gibberellins in stem/root tuber development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, P.; Xiao, X.; Duan, L.; Guo, Y.; Qi, J.; Liao, D.; Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Li, X. Dynamic transcriptional profiling provides insights into tuberous root development in Rehmannia glutinosa. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.-L.; Jia, X.-L.; Xu, Z.-S.; Wang, F.; Xiong, A.-S. Sequencing, assembly, annotation, and gene expression: Novel insights into the hormonal control of carrot root development revealed by a high-throughput transcriptome. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2015, 290, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-G.; Jiang, W.; Tao, Z.-M.; Pan, X.-J.; Yu, W.-H.; Huang, H.-L. Morphological and stage-specific transcriptome analyses reveal distinct regulatory programs underlying yam (Dioscorea alata L.) bulbil growth. J. Exp. Bot. 2020, 71, 1899–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, S.; Noriega, X.; Pérez, F.J. ABA promotes starch synthesis and storage metabolism in dormant grapevine buds. J. Plant Physiol. 2019, 234, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, T.; Umezawa, T. The PP2C–SnRK2 complex: The central regulator of an abscisic acid signaling pathway. Plant Signal. Behav. 2010, 5, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, L.; Xie, S. Initiation and amplification of SnRK2 activation in abscisic acid signaling. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Mao, J.; Yang, H.; Khan, A.; Fan, A.; Liu, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, D.; Gao, H.; Zhang, J. Sucrose non-ferment 1 related protein kinase 2 (SnRK 2) genes could mediate the stress responses in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). BMC Genet. 2017, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hou, J.; Liu, J.; Xie, C.; Song, B. Amylase analysis in potato starch degradation during cold storage and sprouting. Potato Res. 2014, 57, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComber, D.R.; Horner, H.T.; Chamberlin, M.A.; Cox, D.F. Potato cultivar differences associated with mealiness. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1994, 42, 2433–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalk, I.; Zeng, K.; Wu, S.-K.; Stura, E.A.; Matteson, J.; Huang, M.; Tandon, A.; Wilson, I.A.; Balch, W.E. Structure and mutational analysis of Rab GDP-dissociation inhibitor. Nature 1996, 381, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lycett, G. The role of Rab GTPases in cell wall metabolism. J. Exp. Bot. 2008, 59, 4061–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ID | Sample Name | Type | Planted Year | Group | Status | Market Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chubaek | Waxy | 2022 | A | Cultivar | Fresh Potato |
| 2 | S18051-5 | Waxy | 2022 | A | Advanced breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 3 | Dubaek | Mealy | 2022 | A | Cultivar | Chip |
| 4 | EarlyFry | Mealy | 2022 | A | Cultivar | French fries |
| 5 | B4 | Waxy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 6 | B10 | Mealy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 7 | B14 | Waxy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 8 | B23 | Waxy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 9 | B25 | Mealy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 10 | B42 | Waxy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 11 | B44 | Waxy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 12 | B47 | Mealy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 13 | B50 | Waxy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 14 | B51 | Mealy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 15 | B56 | Mealy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| 16 | B57 | Mealy | 2023 | B | Breeding line | Non-evaluated |
| Sample Name | Group | Type | Trait | Value | Sample Name | Group | Type | Trait | Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chubaek | A | Waxy | SG | 1.06 | Dubaek | A | Mealy | SG | 1.07 |
| Glu | 80 | Glu | Low | ||||||
| L* | 50.77 | L* | 71.0 | ||||||
| LW | 1.06 | LW | 1.22 | ||||||
| S18051-5 | A | Waxy | SG | 1.06 | EarlyFry | A | Mealy | SG | 1.07 |
| Glu | 100 | Glu | 19 | ||||||
| L* | 45.36 | L* | 72.12 | ||||||
| LW | 1.62 | LW | 1.53 | ||||||
| B4 | A | Waxy | SG | 1.07 82 | B10 | B | Mealy | SG Glu | 1.08 Low |
| Glu | |||||||||
| B14 | A | Waxy | SG | 1.06 158 | B25 | B | Mealy | SG Glu | 1.09 12 |
| Glu | |||||||||
| B23 | A | Waxy | SG | 1.07 98 | B47 | B | Mealy | SG Glu | 1.07 13 |
| Glu | |||||||||
| B42 | A | Waxy | SG | 1.05 105 | B51 | B | Mealy | SG Glu | 1.07 16 |
| Glu | |||||||||
| B44 | A | Waxy | SG | 1.05 142 | B56 | B | Mealy | SG Glu | 1.07 16 |
| Glu | |||||||||
| B50 | A | Waxy | SG | 1.07 70 | B57 | B | Mealy | SG Glu | 1.05 21 |
| Glu |
| Sample ID | Total Reads | Paired in Sequencing | Paired Mapped Reads | Paired Mapping Rate (%) | Mapped Reads | Mapping Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chubaek-1.2 | 47,477,453 | 37,309,546 | 31,205,854 | 83.64% | 43,425,979 | 91.47% |
| Chubaek-1.3 | 38,755,816 | 32,985,454 | 28,015,594 | 84.93% | 35,205,754 | 90.84% |
| Chubaek-1.4 | 37,878,172 | 32,582,410 | 27,885,734 | 85.59% | 34,643,826 | 91.46% |
| S18051-5.2 | 47,575,974 | 34,113,026 | 29,186,768 | 85.56% | 44,218,019 | 92.94% |
| S18051-5.3 | 37,094,590 | 29,920,944 | 25,329,932 | 84.66% | 33,953,348 | 91.53% |
| S18051-5.4 | 50,175,130 | 37,455,716 | 31,903,142 | 85.18% | 46,526,073 | 92.73% |
| Dubaek-1.1 | 42,361,506 | 32,870,906 | 28,076,470 | 85.41% | 38,921,226 | 91.88% |
| Dubaek-1.2 | 51,182,439 | 37,619,866 | 32,427,094 | 86.20% | 47,527,388 | 92.86% |
| Dubaek-1.3 | 49,844,233 | 35,786,138 | 30,156,040 | 84.27% | 46,137,738 | 92.56% |
| EarlyFry-1.1 | 51,064,517 | 34,809,288 | 29,764,534 | 85.51% | 47,694,581 | 93.40% |
| EarlyFry-1.2 | 34,771,853 | 26,879,036 | 22,906,932 | 85.22% | 32,162,334 | 92.50% |
| EarlyFry-1.3 | 51,932,348 | 38,512,332 | 32,875,808 | 85.36% | 48,156,475 | 92.73% |
| Total | 540,114,031 | 410,844,662 | 349,733,902 | 85.13% | 498,572,741 | 92.24% |
| Module | Chubaek-1.2 | Chubaek-1.3 | Chubaek-1.4 | Dubaek-1.1 | Dubaek-1.2 | Dubaek-1.3 | Early-1.1 | Early-1.2 | Early-1.3 | S18051-5-1 | S18051-5-2 | S18051-5-3 | Adj. p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red * | 0.139 | 0.177 | 0.159 | −0.379 | −0.377 | −0.378 | −0.149 | −0.162 | −0.158 | 0.383 | 0.384 | 0.358 | 0.000 |
| Turquoise * | −0.344 | −0.297 | −0.324 | 0.371 | 0.374 | 0.376 | 0.171 | 0.199 | 0.183 | −0.245 | −0.252 | −0.211 | 0.007 |
| Purple * | 0.171 | 0.172 | 0.125 | 0.024 | 0.020 | 0.013 | −0.477 | −0.468 | −0.466 | 0.304 | 0.284 | 0.298 | 0.007 |
| Green * | 0.558 | 0.426 | 0.494 | −0.199 | −0.198 | −0.195 | −0.193 | −0.201 | −0.197 | −0.096 | −0.086 | −0.112 | 0.007 |
| Blue | −0.555 | −0.441 | −0.492 | 0.136 | 0.141 | 0.145 | 0.193 | 0.216 | 0.203 | 0.138 | 0.133 | 0.183 | 0.068 |
| Magenta | 0.364 | 0.322 | 0.411 | −0.416 | −0.407 | −0.396 | 0.171 | 0.124 | 0.145 | −0.114 | −0.090 | −0.116 | 0.292 |
| Pink | −0.036 | −0.061 | −0.078 | 0.494 | 0.489 | 0.474 | −0.183 | −0.184 | −0.175 | −0.250 | −0.253 | −0.237 | 0.292 |
| Green/yellow | 0.141 | 0.117 | 0.132 | 0.060 | 0.060 | 0.060 | 0.294 | 0.280 | 0.293 | −0.494 | −0.459 | −0.483 | 0.292 |
| Brown | −0.225 | −0.163 | −0.180 | −0.214 | −0.204 | −0.199 | −0.095 | −0.106 | −0.099 | 0.503 | 0.499 | 0.482 | 0.569 |
| Tan | −0.313 | −0.276 | −0.309 | 0.278 | 0.271 | 0.280 | −0.277 | −0.282 | −0.272 | 0.298 | 0.289 | 0.314 | 1.000 |
| Salmon | 0.438 | 0.253 | 0.304 | 0.236 | 0.234 | 0.231 | −0.238 | −0.247 | −0.247 | −0.325 | −0.305 | −0.333 | 1.000 |
| Black | −0.114 | −0.026 | −0.049 | −0.445 | −0.447 | −0.443 | 0.280 | 0.263 | 0.272 | 0.232 | 0.253 | 0.223 | 1.000 |
| Yellow | −0.200 | −0.140 | −0.140 | −0.217 | −0.211 | −0.210 | 0.500 | 0.494 | 0.494 | −0.135 | −0.108 | −0.127 | 1.000 |
| Method | Gene | Module | Function | Method | Gene | Module | Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KME | Soltu.DM.05G009940 * | Green | Hypothetical protein | KME | Soltu.DM.02G008410 * | Red | Cytochrome P450, family 76, subfamily C, polypeptide |
| KME | Soltu.DM.01G045370 * | Green | Protein kinase superfamily protein | KME | Soltu.DM.07G003160 | Red | Sucrose phosphate synthase 1F |
| KME | Soltu.DM.12G007160 * | Green | Sulfate transporter 1;2 | KME | Soltu.DM.07G026660 * | Red | Microtubule-associated proteins 65-1 |
| KME | Soltu.DM.08G015680 * | Green | Alpha/beta-Hydrolases superfamily protein | KME | Soltu.DM.04G001460 * | Red | Disease resistance protein (CC-NBS-LRR class) family |
| KME | Soltu.DM.07G003630 * | Green | Nucleoside transporter family protein | KME | Soltu.DM.01G023300 | Red | Multidrug-resistance-associated protein |
| KME | Soltu.DM.04G001450 * | Green | Disease resistance protein (CC-NBS-LRR class) family | KME | Soltu.DM.12G012700 * | Red | Porphyromonas-type peptidyl-arginine deiminase family protein |
| KME | Soltu.DM.02G007350 * | Green | M-type MADS-box transcription factor | KME | Soltu.DM.09G017000 | Red | Rotamase FKBP |
| KME | Soltu.DM.09G001240 * | Green | Adenine nucleotide alpha hydrolases-like superfamily protein | KME | Soltu.DM.12G020050 | Red | Replication factor-A protein 1-related |
| KME | Soltu.DM.02G003450 * | Green | Phloem protein 2-A10 | KME | Soltu.DM.12G014910 * | Red | Nuclear factor Y, subunit C9 |
| KME | Soltu.DM.12G010700 * | Green | Sulfate transporter 3;4 | KME, GS | Soltu.DM.08G025210 * | Red | Bifunctional inhibitor/lipid-transfer protein/seed storage 2S albumin superfamily protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.01G020280 * | Green | NAD(P)-linked oxidoreductase superfamily protein | GS | Soltu.DM.01G002970 * | Red | Damaged DNA binding;DNA-directed DNA polymerases |
| GS | Soltu.DM.01G030060 * | Green | Cyclin/Brf1-like TBP-binding protein | GS | Soltu.DM.12G029530 * | Red | FAD/NAD(P)-binding oxidoreductase family protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.03G025470 * | Green | Cytochrome P450, family 71, subfamily A, polypeptide | GS | Soltu.DM.04G015010 * | Red | Phosphoglucomutase/phosphomannomutase family protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.12G017990 * | Green | Rhodanese/Cell cycle control phosphatase superfamily | GS | Soltu.DM.12G014430 * | Red | Hypothetical protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.12G024860 * | Green | Protein of unknown function, DUF538 | GS | Soltu.DM.12G021480 * | Red | BNR/Asp-box repeat family protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.06G025180 | Green | CCAAT-displacement protein alternatively spliced pro | GS | Soltu.DM.06G005790 * | Red | Hypothetical protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.10G026800 * | Green | Translation protein SH3-like family protein | GS | Soltu.DM.12G026350 * | Red | Plant invertase/pectin methylesterase inhibitor superfamily protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.12G017970 * | Green | Rhodanese/Cell cycle control phosphatase superfamily | GS | Soltu.DM.10G022330 * | Red | NB-ARC domain-containing disease resistance protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.11G018210 | Green | ADP/ATP carrier | GS | Soltu.DM.12G009230 * | Red | Translocase of inner mitochondrial membrane |
| GS | Soltu.DM.06G023440 * | Green | Gibberellin 3-oxidase | KME | Soltu.DM.08G030240 * | Turquoise | Polyketide cyclase/dehydrase and lipid transport superfamily protein |
| KME | Soltu.DM.08G008810 | Purple | Beta-fructofuranosidase | KME | Soltu.DM.08G027980 * | Turquoise | Hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein family protein |
| KME | Soltu.DM.11G005660 | Purple | UDP-Glycosyltransferase superfamily protein | KME | Soltu.DM.06G025450 | Turquoise | Histone-lysine N-methyltransferases |
| KME | Soltu.DM.02G016440 | Purple | Alpha/beta-Hydrolases superfamily protein | KME | Soltu.DM.05G001020 * | Turquoise | Reversibly glycosylated polypeptide |
| KME | Soltu.DM.01G048270 | Purple | Hypothetical protein | KME | Soltu.DM.03G030890 * | Turquoise | Phox (PX)-domain-containing protein |
| KME | Soltu.DM.01G049750 | Purple | RING/U-box superfamily protein | KME | Soltu.DM.06G021390 * | Turquoise | tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR)-containing protein |
| KME | Soltu.DM.03G032030 * | Purple | Non-intrinsic ABC protein | KME | Soltu.DM.05G002470 * | Turquoise | Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit A |
| KME | Soltu.DM.05G014610 | Purple | LRR- and NB-ARC-domain-containing disease resistance protein | KME | Soltu.DM.01G050570 | Turquoise | ATP-dependent RNA helicase, putative |
| KME, GS | Soltu.DM.02G034330 * | Purple | Conserved hypothetical protein | KME | Soltu.DM.03G002170 | Turquoise | Proline-rich spliceosome-associated (PSP) family protein |
| KME | Soltu.DM.12G008090 | Purple | Glutathione S-transferase THETA | KME | Soltu.DM.02G006930 | Turquoise | TCP-1/cpn60 chaperonin family protein |
| KME | Soltu.DM.09G029680 * | Purple | Disease resistance protein (TIR-NBS-LRR class) family | GS | Soltu.DM.04G002760 * | Turquoise | MLP-like protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.11G023420 * | Purple | NB-ARC domain-containing disease resistance protein | GS | Soltu.DM.01G008110 * | Turquoise | Gag-polypeptide of LTR copia-type domain containing protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.06G016240 * | Purple | ACT domain repeat | GS | Soltu.DM.06G026340 * | Turquoise | Serine/threonine protein kinase |
| GS | Soltu.DM.07G009630 * | Purple | Transposase family tnp2 domain containing protein | GS | Soltu.DM.08G016860 * | Turquoise | Conserved hypothetical protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.08G024310 * | Purple | Homeobox protein | GS | Soltu.DM.04G038280 * | Turquoise | TBP-associated factor |
| GS | Soltu.DM.12G027440 * | Purple | SOS3-interacting protein | GS | Soltu.DM.04G029040 * | Turquoise | Glycosyl hydrolase family protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.08G020410 * | Purple | Transglutaminase-like superfamily domain containing protein | GS | Soltu.DM.09G024430 * | Turquoise | Papain family cysteine protease |
| GS | Soltu.DM.01G010080 | Purple | Eukaryotic elongation factor 5A-1 | GS | Soltu.DM.04G033150 * | Turquoise | F-box family protein |
| GS | Soltu.DM.08G012390 * | Purple | Mechanosensitive channel of small conductance-like | GS | Soltu.DM.03G032660 * | Turquoise | NF-X-like |
| GS | Soltu.DM.04G021610 * | Purple | NAD(P)-binding Rossmann-fold superfamily protein | GS | Soltu.DM.01G027700 * | Turquoise | Tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR)-like superfamily protein |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, J.-J.; Kwon, D.-H.; Choi, J.-G.; Lee, G.-B.; Yi, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-T.; Won, H.-S.; Park, Y.-E.; Jin, Y.-I.; Chang, D.-C.; et al. Transcriptome Insights into Carbohydrate Metabolism and Frying Quality Traits in Waxy and Mealy Potatoes. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061430
Choi J-J, Kwon D-H, Choi J-G, Lee G-B, Yi J-Y, Lee H-T, Won H-S, Park Y-E, Jin Y-I, Chang D-C, et al. Transcriptome Insights into Carbohydrate Metabolism and Frying Quality Traits in Waxy and Mealy Potatoes. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061430
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Jeong-Jin, Do-Hee Kwon, Jang-Gyu Choi, Gyu-Bin Lee, Jae-Youn Yi, Hui-Tae Lee, Hong-Sik Won, Young-Eun Park, Yong-Ik Jin, Dong-Chil Chang, and et al. 2025. "Transcriptome Insights into Carbohydrate Metabolism and Frying Quality Traits in Waxy and Mealy Potatoes" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061430
APA StyleChoi, J.-J., Kwon, D.-H., Choi, J.-G., Lee, G.-B., Yi, J.-Y., Lee, H.-T., Won, H.-S., Park, Y.-E., Jin, Y.-I., Chang, D.-C., & Cho, K.-S. (2025). Transcriptome Insights into Carbohydrate Metabolism and Frying Quality Traits in Waxy and Mealy Potatoes. Agronomy, 15(6), 1430. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061430






