Humic Acids Properties of Luvisol of 40-Year Fertilizer Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Design
2.2. Methods
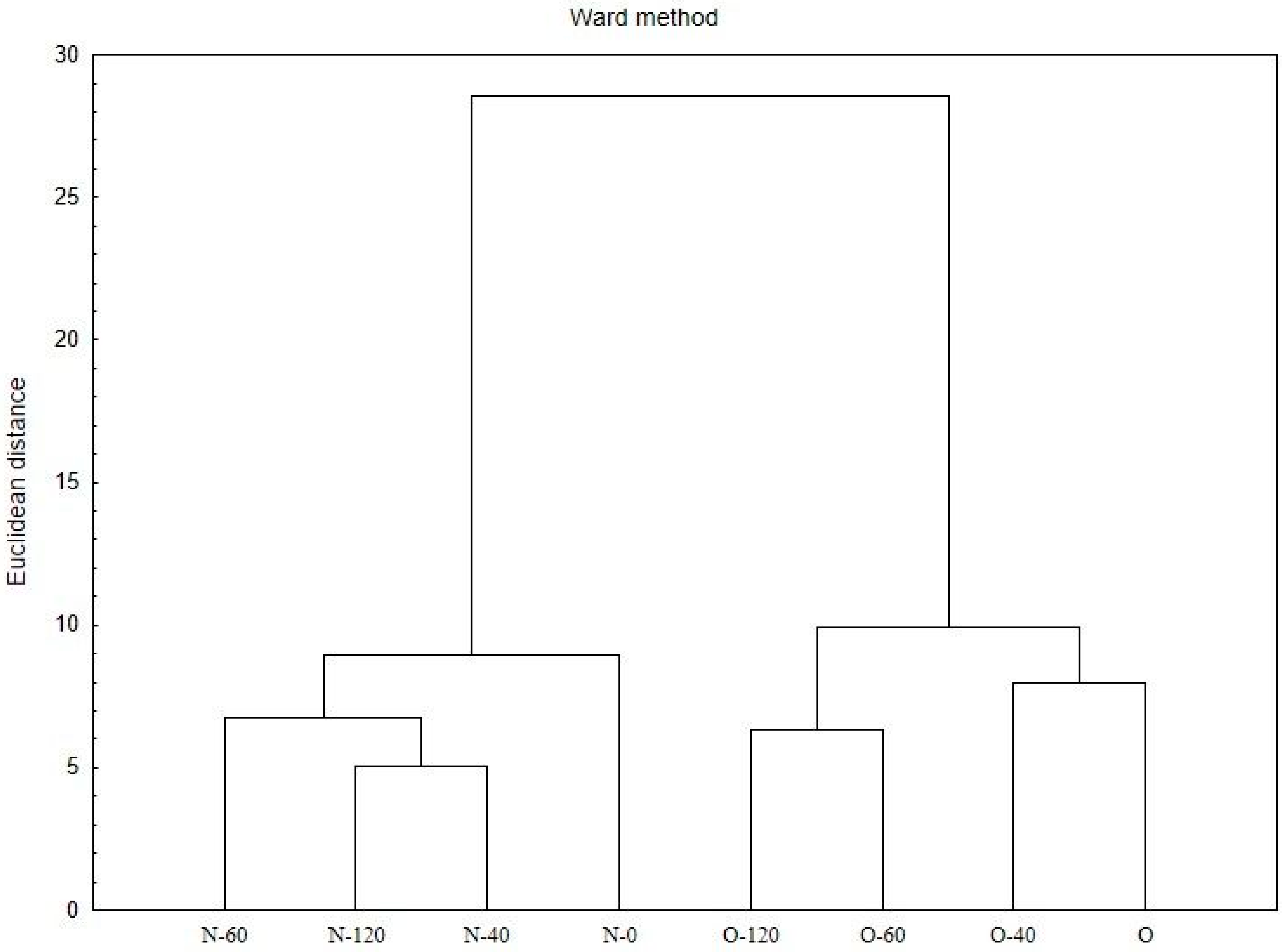
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Elemental Analysis
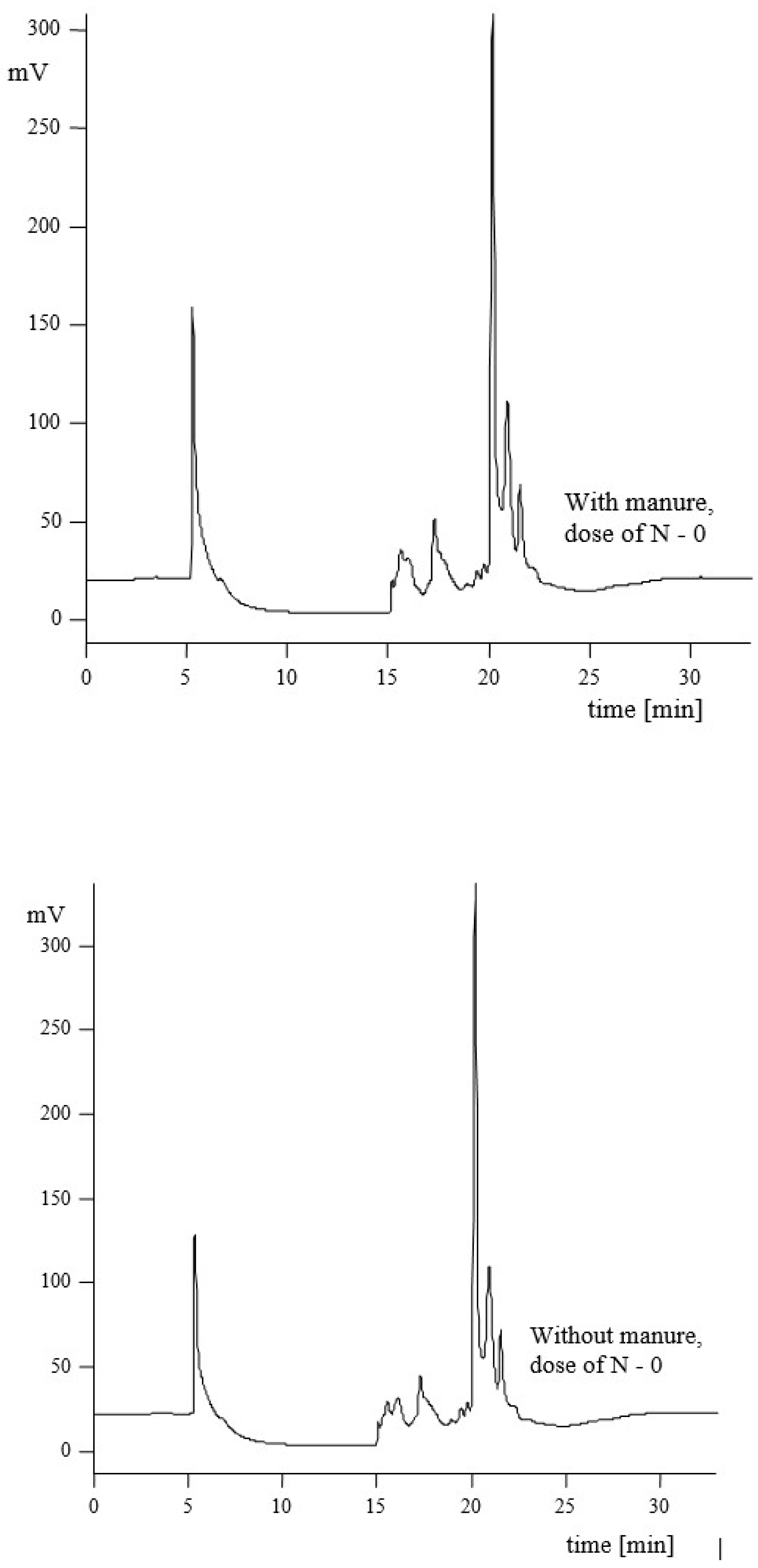
3.2. Hydrophilic–Hydrophobic Properties of Humic Acids
3.3. Spectrometric Properties of HAs
3.4. FT-IR Spectra
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cao, Z.Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.J.; He, N.P. Soil organic carbon contents, aggregate stability, and humic acid composition in different alpine grasslands in Qinghai-Tibet plateau. J. Mt. Sci. 2016, 13, 2015–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Hou, R.; Gong, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of 11 years of conservation tillage on soil organic matter fractions in wheat monoculture in Loess Plateau of China. Soil Till. Res. 2009, 106, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, F.; Zhai, C.; Zhong, R.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Q. Long-term effects of cattle manure application on the soil aggregate stability of salt-affected soil on the Songnen Plain of North-Eastern China. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezuglova, O.; Komarov, A.; Komarov, A. Identification of humic substances on the transformation of an organic substrate. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2022, 11, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, D.S. Humus Acids of Soils, 1st ed.; Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, J.; Chen, Y.; Jamroz, E.; Miano, T. Preface: Humic substances in the environment. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 2665–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debska, B.; Dlugosz, J.; Piotrowska-Dlugosz, A.; Banach-Szott, M. The impact of bio-fertilizer on the soil organic matter status and carbon sequestration-results from a fiel-scale study. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 2335–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwiatkowska-Malina, J. The comparison of the structure of humic acids from soil amended with different sources of organic matter. Pol. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 48, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, F.V.; Mercer, E.J.; Rice, J.A. Chemical characteristics of glomalin-related soil protein (GRSP) extracted from soils of varying organic matter content. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olk, D.C.; Bloom, P.R.; De Nobili, M.; Chen, Y.; McKnight, D.M.; Wells, M.J.M.; Weber, J. Using humic fractions to understand natural organic matter processes in soil and water: Selected studies and applications. J. Environ. Qual. 2019, 48, 1633–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debska, B.; Banach-Szott, M.; Dziamski, A.; Gonet, S.S. Chromatographic characteristics (HPLC, HPSEC) of humic acids of soil fertilized with various organic fertilizers. Chem. Ecol. 2010, 26, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debska, B.; Drąg, M.; Tobiasova, E. Effect of post-harvest residue of maize, rapeseed, and sunflower on humic acids properties in various soils. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 603–613. [Google Scholar]
- Enev, V.; Pospisilova, L.; Klucakova, M.; Liptaj, T.; Doskocil, L. Spectral characterization of selected humic substances. Soil Water Res. 2014, 9, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, F.P.; Vidal-Torrado, P.; Otero, X.L.; Buurman, P.; Martin-Neto, L.; Boluda, R.; Macias, F. Chemical and spectroscopic characteristics of humic acids in marshes from the Iberian Peninsula. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.H.B.; Swift, R.S. An appreciation of the contribution of Frank Stevenson to the advancement of studies of soil organic matter and humic substances. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 1212–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, F.J.; Schlenger, P.; García-Valverde, M. Monitoring changes in the structure and properties of humic substances following ozonation using UV-Vis, FTIR and H NMR techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 626–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinoco, P.; Almendros, G.; Francisco, J.; Gonzalez-Vila, F.J.; Sanz, J.; Gonzalez-Perez, J.A. Revisiting molecular characteristics responsive for the aromaticity of soil humic acids. J. Soils Sediments 2015, 15, 781–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubetskaya, O.; Trubetskoj, O.; Richard, C. Hydrophobicity of electrophoretic fractions of different soil humic acids. J. Soils Sediments 2014, 14, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, K. Chemistry of Soil Organic Matter, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Senesi, N. Binding mechanisms of pesticides to soil humic substances. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 123–124, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, F.J. Reactive functional groups of humic substances. In Humus Chemistry; Genesis, Composition, Reactions; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1982; pp. 221–243. [Google Scholar]
- Dou, S.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, K. Effect of organic matter applications 13C-NMR spectra of humic acids of soil. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 2008, 59, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Liu, J.; Jin, S.; He, X.; Liu, S.; Kong, X.; Dong, F. Differences of C sequestration in functional groups of soil humic acid under long term application of manure and chemical fertilizers in North China. Soil Till. Res. 2018, 176, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; An, T.; Wei, D.; Chi, F.; Zhou, B. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil humic acid composition and structure in Black Soil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; An, T.; Chi, F.; Wei, D.; Zhou, B.; Hao, X.; Jin, L.; Wang, J. Evolution over years of structural characteristics of humic acids in Black Soil as a function of various fertilization treatments. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, I.; Kodaolu, B.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y.; Audette, Y.; Longstaffe, J. Analysis of molecular structure changes in humic acids from manure-amended soils over 17-years using elemental analysis and Solid-State 13C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy. Soil Syst. 2023, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavyalova, N.E. Elemental composition of humic acids of Sod-Podzolic Clay Loam Soil of Cisuralia during long-term use of fertilizer systems. Russ. Agric. Sci. 2011, 37, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach-Szott, M.; Jaskulska, I.; Debska, B.; Jaskulski, D. Effect of the tillage system on the properties of humic acids of soil of the Kujawy Region in Poland. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 12, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banach-Szott, M.; Debska, B.; Tobiasova, E. Properties of humic acids depending on the land use in different parts of Slovakia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 58068–58080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonet, S.S.; Debska, B. Properties of humic acids developed during humification process of post-harvest plant residues. Environ. Int. 1998, 24, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonet, S.S.; Debska, B. Properties of humic acids produced during decomposition of plant residues in soil. Rostl. Vyrob. 1999, 45, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeya, K.; Sleighter, R.L.; Hatcher, P.G.; Watanabe, A. Characterization of the chemical composition of soil humic acids using Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2015, 153, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dou, S.; Ma, R.; Zhang, D.; Ndzelu, B.S.; Zhou, J.; Yang, H. Effects of returning corn straw incorporated with fungi, and fermented corn straw on soil humic acid structural characteristics. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 2048–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.H. Hierarchical grouping to optimise an objective function. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1963, 58, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drag, M.; Debska, B.; Dziamski, A. Properties of humic substances of forest and meadow soil in the area of the Wierzchlas Reserve. Humic Subst. Ecosys. 2007, 7, 141–151. [Google Scholar]
- Kobierski, M.; Banach-Szott, M. Organic matter in Riverbank Sediments and Fluvisols from the flood zones of Lower Vistula River. Agronomy 2022, 12, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, J.; Gopinath, A.; Vareed, R.A. Spectroscopic characterization of humic substances isolated from tropical mangrove sediments. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorado, J.; Zancada, M.-C.; Almendros, G.; Lopez-Fando, C. Changes in soil properties and humic substances after long-term amendments with manure and crop residues in dryland farming systems. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2003, 166, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, S.; Maie, N.; Kitamura, S.; Watanabe, A. Effect of organic amendment on amount and chemical characteristics of humic acids in upland field soils. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Olk, D.C.; Fang, X.; He, Z.; Schmidt-Rohr, K. Influence of animal manure application on the chemical structures of soil organic matter as investigated by advanced solid-state NMR and FT-IR spectroscopy. Geoderma 2008, 146, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debska, B.; Kotwica, K.; Banach-Szott, M.; Spychaj-Fabisiak, E.; Tobiasova, E. Soil fertility improvement and carbon sequestration through exogenous organic matter and biostimulant application. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakumov, E.; Yaneva, R.; Polyakov, V.; Zhiyanski, M. Characterization of humic acids isolated from selected soils of Livingston Island by CP/MAS 13CNMR and ESR Spectroscopy. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2022, 7540077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, K. Elementary composition and absorption spectra of humic and fulvic acids. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 1985, 31, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dose N (kg ha−1) | C | H | N | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Manure (30 t ha−1)—Factor I | ||||
| 0 | 52.31 ± 0.26 Ab * | 5.01 ± 0.15 Bb | 4.46 ± 0.16 Bb | 38.23 ± 0.17 Aa |
| 40 | 55.09 ± 0.28 Aa | 5.36 ± 0.18 Aa | 4.97 ± 0.15 Aa | 34.58 ± 0.24 Bc |
| 60 | 52.81 ± 0.35 Ab | 5.22 ± 0.21 Aa | 4.87 ± 0.15 Aa | 37.09 ± 0.28 Bb |
| 120 | 51.63 ± 0.36 Ac | 4.94 ± 0.35 Ab | 4.58 ± 0.25 Ab | 38.84 ± 0.26 Aa |
| Mean | 52.96 a ** | 5.13 a | 4.72 a | 37.19 b |
| Without manure—Factor I | ||||
| 0 | 52.71 ± 0.27 Aab | 5.40 ± 0.17 Aa | 4.88 ± 0.04 Aa | 37.01 ± 0.22 Bc |
| 40 | 51.29 ± 0.29 Bb | 5.01 ± 0.14 Bb | 4.68 ± 0.04 Ac | 39.01 ± 0.26 Aa |
| 60 | 52.89 ± 0.25 Aa | 4.69 ± 0.17 Bc | 4.77 ± 0.17 Ab | 37.66 ± 0.22 Ab |
| 120 | 51.29 ± 0.31 Ab | 4.78 ± 0.23 Ac | 4.69 ± 0.18 Ac | 39.24 ± 0.28 Aa |
| Mean | 52.04 b | 4.97 b | 4.76 a | 38.23 a |
| Average values for different nitrogen doses—Factor II | ||||
| 0 | 52.51 b | 5.21 a | 4.67 b | 37.62 b |
| 40 | 53.19 a | 5.19 a | 4.83 a | 36.80 c |
| 60 | 52.85 ab | 4.96 b | 4.82 a | 37.38 b |
| 120 | 51.46 c | 4.86 b | 4.64 b | 39.04 a |
| Dose N (kg ha−1) | C | H | N | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Manure (30 t ha−1)—Factor I | ||||
| 0 | 36.10 ± 0.17 Ab * | 41.48 ± 0.27 Ac | 2.64 ± 0.01 Bc | 19.79 ± 0.02 Ab |
| 40 | 36.82 ± 0.19 Aa | 42.99 ± 0.28 Aa | 2.85 ± 0.01 Aa | 17.34 ± 0.04 Bd |
| 60 | 35.82 ± 0.14 Bc | 42.48 ± 0.30 Ab | 2.83 ± 0.02 Ba | 18.87 ± 0.06 Bc |
| 120 | 35.87 ± 0.15 Abc | 41.16 ± 0.25 Ac | 2.73 ± 0.01 Bb | 20.24 ± 0.13 Ba |
| Mean | 36.04 a ** | 41.29 a | 2.82 a | 19.86 a |
| Without manure—Factor I | ||||
| 0 | 35.27 ± 0.16 Bc | 43.36 ± 0.24 Aa | 2.80 ± 0.02 Ab | 18.57 ± 0.02 Bc |
| 40 | 35.43 ± 0.18 Bc | 41.58 ± 0.24 Bb | 2.77 ± 0.04 Bc | 20.21 ± 0.11 Ab |
| 60 | 37.36 ± 0.12 Aa | 39.80 ± 0.27 Bd | 2.89 ± 0.06 Aa | 19.96 ± 0.15 Ab |
| 120 | 36.10 ± 0.20 Ab | 40.43 ± 0.23 Bc | 2.83 ± 0.13 Ab | 20.71 ± 0.05 Aa |
| Mean | 36.15 a | 40.03 b | 2.76 b | 19.06 b |
| Average values for different nitrogen doses—Factor II | ||||
| 0 | 35.68 c | 42.42 a | 2.72 c | 19.18 b |
| 40 | 36.13 b | 42.29 a | 2.81 ab | 18.78 c |
| 60 | 36.59 a | 41.14 b | 2.86 a | 19.41 b |
| 120 | 36.00 b | 40.79 c | 2.78 bc | 20.48 a |
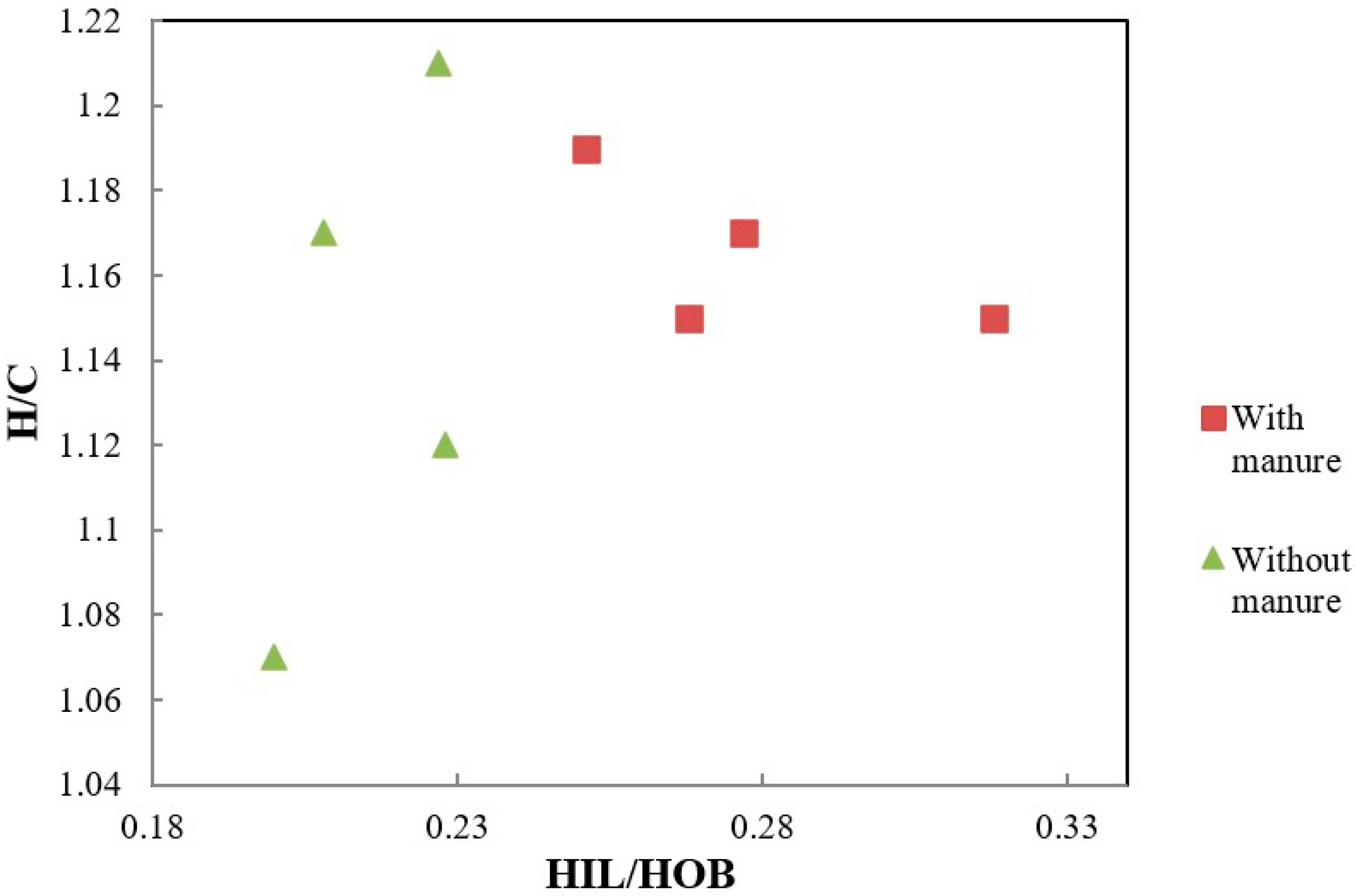
| Dose N (kg ha−1) | H/C | N/C | O/C | O/H | ω |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Manure (30 t ha−1)—Factor I | |||||
| 0 | 1.15 Ba * | 0.073 Aa | 0.55 Aab | 0.48 Aa | 0.166 Ab |
| 40 | 1.17 Aa | 0.077 Aa | 0.47 Bc | 0.40 Bc | 0.006 Bd |
| 60 | 1.19 Aa | 0.079 Aa | 0.52 Ab | 0.44 Bb | 0.105 Bc |
| 120 | 1.15 Aa | 0.076 Aa | 0.56 Aa | 0.49 Aa | 0.209 Ba |
| Mean | 1.16 a ** | 0.076 a | 0.55 a | 0.45 a | 0.122 b |
| Without manure—Factor I | |||||
| 0 | 1.21 Aa | 0.080 Aa | 0.53 Ab | 0.43 Bb | 0.062 Bc |
| 40 | 1.17 Aa | 0.078 Aa | 0.57 Aa | 0.49 Aa | 0.202 Ab |
| 60 | 1.07 Bc | 0.077 Aa | 0.53 Ab | 0.50 Aa | 0.235 Aa |
| 120 | 1.12 Ab | 0.078 Aa | 0.57 Aa | 0.51 Aa | 0.264 Aa |
| Mean | 1.14 a | 0.078 a | 0.53 a | 0.48 a | 0.191 a |
| Average values for different nitrogen doses—Factor II | |||||
| 0 | 1.18 a | 0.076 a | 0.54 ab | 0.46 b | 0.114 c |
| 40 | 1.17 a | 0.078 a | 0.52 b | 0.44 bc | 0.104 c |
| 60 | 1.13 b | 0.078 a | 0.53 b | 0.47 b | 0.170 b |
| 120 | 1.13 b | 0.077 a | 0.57 a | 0.50 a | 0.237 a |
| Dose N (kg ha−1) | HIL | HOB-1 | HOB-2 | HOB-3 | ΣHOB | HIL/ΣHOB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Manure (30 t ha−1)—Factor I | ||||||
| 0 | 24.09 ± 1.33 *** | 11.40 ± 0.54 Aa * | 13.30 ± 0.26 | 51.19 ± 2.12 Bb | 75.91 ± 1.33 | 0.318 |
| 40 | 21.66 ± 1.39 | 10.52 ± 0.34 Aab | 13.02 ± 0.19 | 54.80 ± 1.56 Ba | 78.34 ± 1.39 | 0.277 |
| 60 | 20.10 ± 0.66 | 10.00 ± 0.45 Ab | 13.40 ± 0.22 | 56.50 ± 0.84 Aa | 79.90 ± 0.66 | 0.251 |
| 120 | 21.11 ± 0.50 | 10.70 ± 0.21 Aab | 12.75 ± 0.38 | 55.43 ± 0.35 Aa | 78.89 ± 0.50 | 0.268 |
| Mean | 21.74 a ** | 10.65 a | 13.13 a | 54.48 b | 78.26 b | 0.278 a |
| Without manure—Factor I | ||||||
| 0 | 18.47 ± 0.36 | 9.67 ± 0.46 Ba | 13.63 ± 0.34 | 57.93 ± 0.43 Aa | 81.53 ± 0.36 | 0.227 |
| 40 | 17.21 ± 0.24 | 10.07 ± 0.03 Aa | 13.20 ± 0.07 | 59.52 ± 0.28 Aa | 82.79 ± 0.24 | 0.208 |
| 60 | 16.65 ± 0.43 | 10.17 ± 0.4 Aa | 13.45 ± 0.31 | 59.73 ± 0.39 Aa | 83.35 ± 0.44 | 0.200 |
| 120 | 18.54 ± 0.98 | 10.43 ± 0.34 Aa | 13.14 ± 0.21 | 57.88 ± 0.99 Aa | 81.46 ± 0.98 | 0.228 |
| Mean | 17.72 b | 10.16 a | 13.36 a | 58.77 a | 82.28 a | 0.216 b |
| Average values for different nitrogen doses—Factor II | ||||||
| 0 | 21.28 a | 10.68 a | 13.48 a | 54.56 b | 78.72 b | 0.272 a |
| 40 | 19.43 b | 10.30 a | 13.11 a | 57.16 a | 80.57 a | 0.242 b |
| 60 | 18.37 b | 10.08 a | 13.43 a | 58.12 a | 81.62 a | 0.226 b |
| 120 | 19.83 ab | 10.57 a | 12.95 a | 56.66 a | 80.17 a | 0.248 b |
| Dose N (kg ha−1) | A280 | A400 | A465 | A600 | A665 | Au465 | Au665 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Manure (30 t ha−1)—Factor I | |||||||
| 0 | 4.32 Ba * | 1.35 Bb | 0.740 Ba | 0.252 Ba | 0.138 a | 0.352 Ba | 0.066 Ba |
| 40 | 3.52 Bc | 1.09 Bd | 0.582 Bc | 0.194 Bb | 0.106 c | 0.272 Bc | 0.052 Bb |
| 60 | 4.27 Ba | 1.57 Aa | 0.678 Bb | 0.220 Ac | 0.118 b | 0.294 Bb | 0.054 Bb |
| 120 | 3.85 Bb | 1.20 Bc | 0.654 Bb | 0.220 Ac | 0.122 b | 0.296 Bb | 0.054 Bb |
| Mean | 3.99 b ** | 1.30 b | 0.664 b | 0.222 b | 0.121 b | 0.304 b | 0.057 b |
| Without manure—Factor I | |||||||
| 0 | 4.46 Ab | 1.43 A | 0.828 Ab | 0.294 Ac | 0.164 c | 0.388 Ac | 0.074 Ac |
| 40 | 4.19 Ac | 1.40 A | 0.764 Ac | 0.270 Ad | 0.150 d | 0.392 Ac | 0.076 Ac |
| 60 | 4.94 Aa | 1.60 A | 0.964 Aa | 0.354 Ba | 0.200 a | 0.484 Aa | 0.092 Aa |
| 120 | 4.50 Ab | 1.44 A | 0.848 Ab | 0.310 Bb | 0.176 b | 0.448 Ab | 0.084 Ab |
| Mean | 4.52 a | 1.47 a | 0.851 a | 0.307 a | 0.173 a | 0.428 a | 0.082 a |
| Average values for different nitrogen doses—Factor II | |||||||
| 0 | 4.39 b | 1.39 b | 0.784 b | 0.273 b | 0.151 b | 0.370 b | 0.070 a |
| 40 | 3.86 d | 1.24 c | 0.673 d | 0.232 c | 0.128 c | 0.332 c | 0.064 c |
| 60 | 4.61 a | 1.59 a | 0.821 a | 0.287 a | 0.159 a | 0.389 a | 0.073 a |
| 120 | 4.18 c | 1.32 b | 0.751 c | 0.265 b | 0.149 b | 0.372 b | 0.069 b |
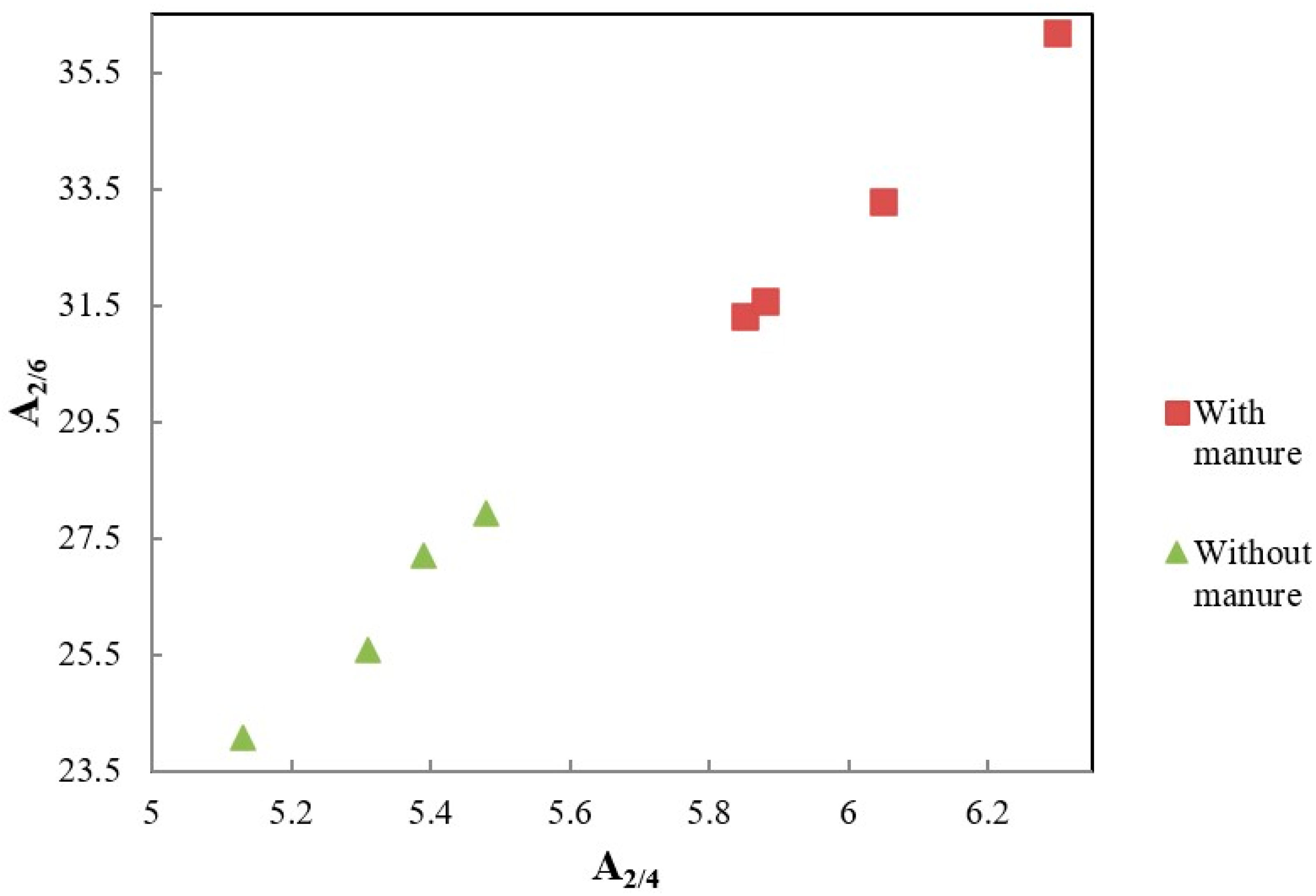
| Dose N (kg ha−1) | A2/6 | A2/4 | A4/6 | ΔlogK | ΔAu465 | ΔAu665 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| With Manure (30 t ha−1)—Factor I | ||||||
| 0 | 31.31 Ab * | 5.85 Ab | 5.37 Aa | 0.729 Ab | 52.32 Ab | 52.17 Aab |
| 40 | 33.28 Ab | 6.05 Aab | 5.50 Aa | 0.750 Ab | 53.27 Ab | 50.84 Ab |
| 60 | 36.20 Aa | 6.30 Aa | 5.75 Aa | 0.854 Aa | 56.64 Aa | 54.23 Aab |
| 120 | 31.57 Ab | 5.88 Ab | 5.36 Aa | 0.737 Ab | 54.74 Aab | 55.71 Aa |
| Mean | 33.09 a ** | 6.02 a | 5.50 a | 0.767 a | 54.24 a | 53.24 a |
| Without manure—Factor I | ||||||
| 0 | 27.19 Ba | 5.39 Ba | 5.05 Aa | 0.687 Aa | 53.14 Aa | 54.87 Aab |
| 40 | 27.94 Ba | 5.48 Ba | 5.10 Aa | 0.715 aA | 48.69 Bb | 49.32 Ab |
| 60 | 24.07 Bb | 5.13 Ba | 4.82 Aa | 0.655 Bb | 49.79 Bb | 54.00 Aa |
| 120 | 25.57 Bab | 5.31 Ba | 4.82 Aa | 0.667 Bb | 47.17 Bb | 52.27 ab |
| Mean | 26.35 b | 5.33 b | 4.95 b | 0.681 b | 49.70 b | 52.62 a |
| Average values for different nitrogen doses—Factor II | ||||||
| 0 | 29.25 b | 5.62 a | 5.21 a | 0.708 b | 52.73 a | 53.52 a |
| 40 | 30.61 a | 5.77 a | 5.30 a | 0.732 a | 50.98 a | 50.08 b |
| 60 | 30.45 a | 5.71 a | 5.28 a | 0.755 a | 53.22 a | 54.12 a |
| 120 | 28.57 b | 5.60 a | 5.09 a | 0.702 b | 50.95 b | 53.99 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dębska, B.; Banach-Szott, M. Humic Acids Properties of Luvisol of 40-Year Fertilizer Experiment. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061405
Dębska B, Banach-Szott M. Humic Acids Properties of Luvisol of 40-Year Fertilizer Experiment. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061405
Chicago/Turabian StyleDębska, Bożena, and Magdalena Banach-Szott. 2025. "Humic Acids Properties of Luvisol of 40-Year Fertilizer Experiment" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061405
APA StyleDębska, B., & Banach-Szott, M. (2025). Humic Acids Properties of Luvisol of 40-Year Fertilizer Experiment. Agronomy, 15(6), 1405. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061405





