Coupling of Biochar and Manure Improves Soil Carbon Pool Stability, Pore Structure, and Microbial Diversity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Field Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Determination
2.4. Soil Microstructural Porosity
2.5. Soil DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, NovaSeq
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
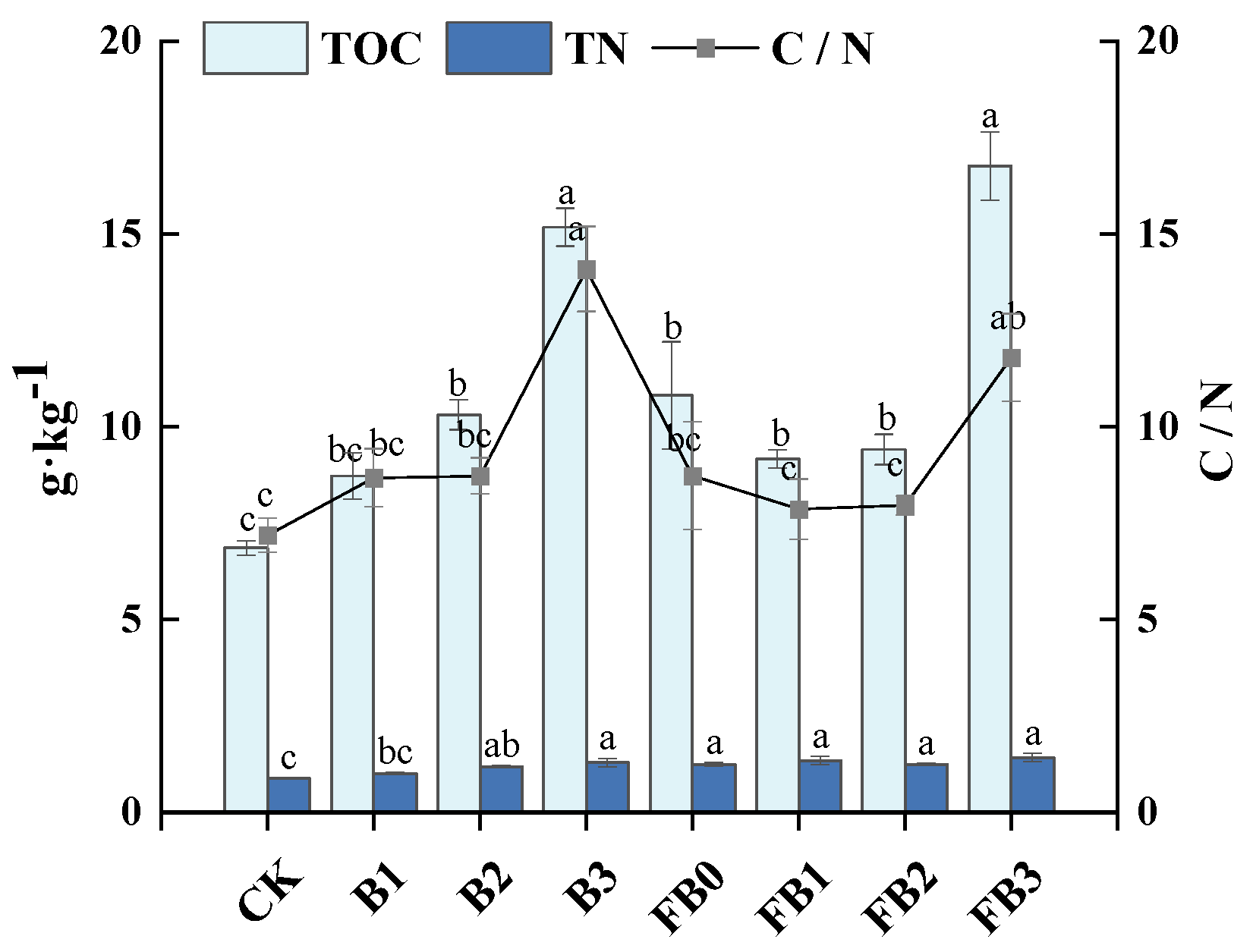
3.1. Soil Organic Carbon Content and Fractions
3.2. Soil pH and Pore Characteristics
3.3. Soil Microorganism Diversity and Enzyme Activity
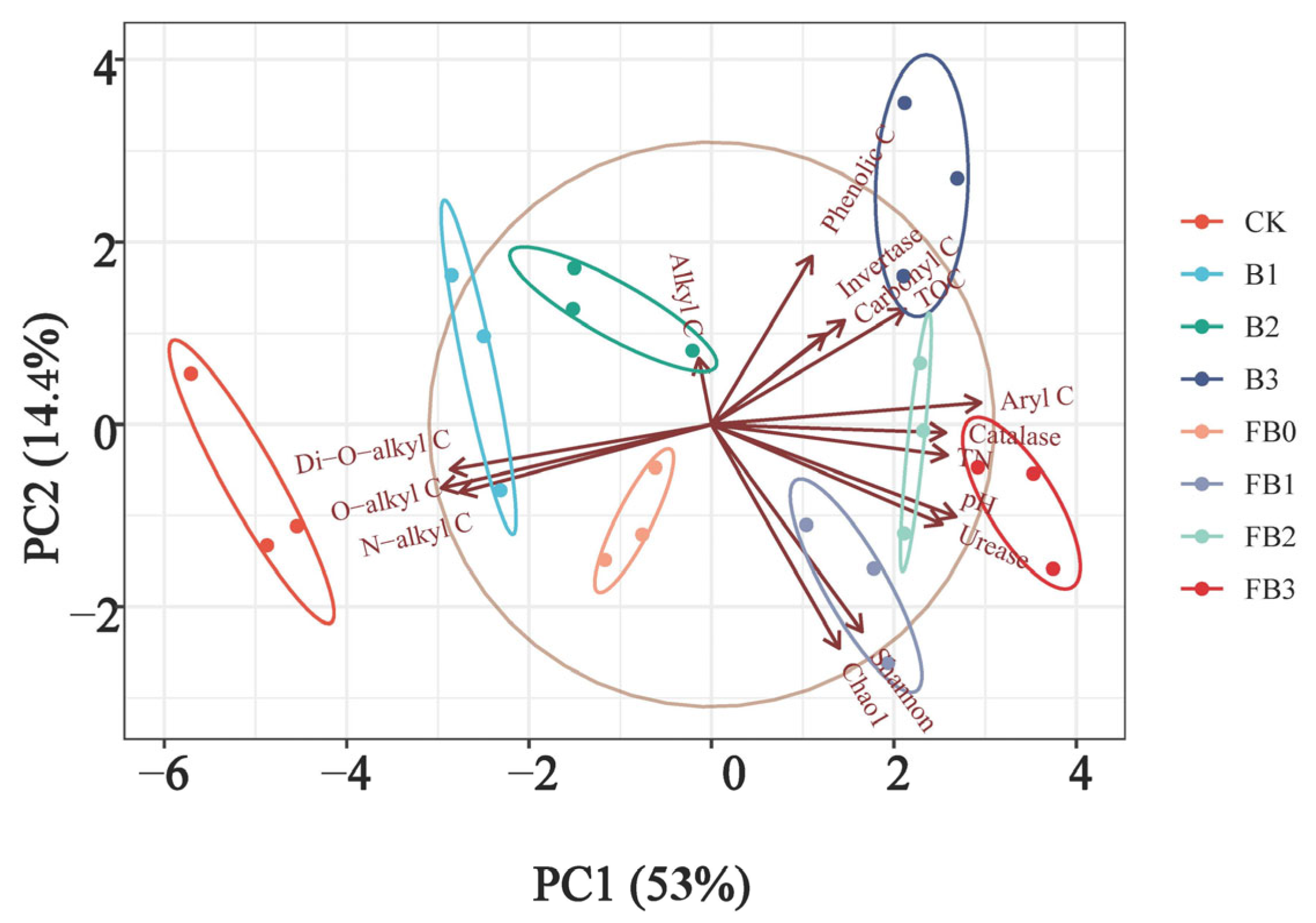
3.4. PCA
4. Discussion
4.1. Coupling Application Increases Soil Carbon Accumulation and Stability
4.2. Coupling Application Improves Soil Porosity
4.3. Coupling Application Benefits Soil Functional Microorganisms and Enhances Its Diversity
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X. Effects of Biochar Soil Amendments on Physical and Chemical Properties and Microstructure of Albic Soils. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ji, J.; Hao, X.; Liu, S.; Sun, N. Effect of Different Fertilization on Soil Fertility, Biological Activity, and Maize Yield in the Albic Soil Area of China. Plants 2025, 14, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, S.; Pandey, B.K.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Griffiths, S.; Bennett, M.J.; Mooney, S.J. Future crop breeding needs to consider future soils. Nat. Plants 2025, 29, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Xu, Q.; Chen, L.; Li, X.; Meng, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, H. The impacts of a biochar application on selected soil properties and bacterial communities in an Albic Clayic Luvisol. Soil Water Res. 2020, 15, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, S.; Shengyan, P.; Sangeeta, A.; Hui, M.; Do-Heyoung, K.; Yingchen, B.; Hou, D. Progress and future prospects in biochar composites: Application and reflection in the soil environment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 219–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Chowdhary, P.; Gnansounou, E.; Chaturvedi, P. Biochar and environmental sustainability: Emerging trends and techno-economic perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 332, 125102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoakwah, E.; Arthur, E.; Frimpong, K.A.; Lorenz, N.; Rahman, M.A.; Nziguheba, G.; Islam, K.R. Biochar amendment impacts on microbial community structures and biological and enzyme activities in a weathered tropical sandy loam. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 172, 104364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demisie, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M. Effect of biochar on carbon fractions and enzyme activity of red soil. Catena 2014, 121, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.-F.; Li, K.-J.; Zheng, B.-X.; Liu, X.-P.; Li, H.-Z.; Jin, B.-J.; Ding, K.; Yang, X.-R.; Lin, X.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-G. Partial replacement of inorganic phosphorus (P) by organic manure reshapes phosphate mobilizing bacterial community and promotes P bioavailability in a paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, D.; Liao, X.; Miao, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Z.; Ding, W. Field-aged biochar enhances soil organic carbon by increasing recalcitrant organic carbon fractions and making microbial communities more conducive to carbon sequestration. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 340, 108177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathers, N.J.; Xu, Z.; Blumfield, T.J.; Berners-Price, S.J.; Saffigna, P.G. Composition and quality of harvest residues and soil organic matter under windrow residue management in young hoop pine plantations as revealed by solid-state 13C NMR spectroscopy. For. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 175, 467–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; Peng, Y.; Xiang, P.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, B.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, C. Co-application of biochar and organic fertilizer promotes the yield and quality of red pitaya (Hylocereus polyrhizus) by improving soil properties. Chemosphere 2022, 294, 133619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Lan, Y.; Chen, W.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Ge, S.; Yang, J.; Wang, Q. Successive applications of fertilizers blended with biochar in the soil improve the availability of phosphorus and productivity of maize (Zea mays L.). Eur. J. Agron. 2021, 130, 126344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xiangmin, R.; Fei, J.; Peng, J.; Luo, G. Coupling amendment of biochar and organic fertilizers increases maize yield and phosphorus uptake by regulating soil phosphatase activity and phosphorus-acquiring microbiota. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 355, 108582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Choudhury, B.U.; Hazarika, S.; Mishra, V.K.; Laha, R. Long-term effect of organic fertilizer and biochar on soil carbon fractions and sequestration in maize-black gram system. Biomass Convers. Biorefinery 2024, 14, 23425–23438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Zhao, F.; Kang, D.; Yang, G.; Han, X.; Tong, X.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G. Linkages of C:N:P stoichiometry and bacterial community in soil following afforestation of former farmland. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 376, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.Z.; Ren, C.J.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.H.; Yang, G.H.; Wang, J. Changes in soil microbial community are linked to soil carbon fractions after afforestation. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.T.; Zhong, X.L.; Wang, F.; Zhao, Q.G. Effect of poultry litter and livestock manure on soil physical and biological indicators in a rice-wheat rotation system. Plant Soil Environ. 2011, 57, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, P.; Lin, H.; Ren, S.; He, X. Effects of Sodic Soil Reclamation using Flue Gas Desulphurization Gypsum on Soil Pore Characteristics, Bulk Density, and Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 1201–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagliai, M.; Vignozzi, N.; Pellegrini, S. Soil structure and the effect of management practices. Soil Tillage Res. 2004, 79, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, L.; Lu, Z.; Ma, H.; Jin, S. Effect of biochar on carbon dioxide release, organic carbon accumulation, and aggregation of soil. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2014, 33, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Tian, C.; Luo, S. Biochar application enhances microbial interactions in mega-aggregates of farmland black soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.; Lee, D.; Shim, C.; Nam, J.; Park, S.; Hong, S.; Song, J.-S.; Jeong, C. Nutrient release pattern and mitigation of N2O emissions under the application of activated poultry manure compost biochar with organic resources. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 356, 124250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, S.; Zhang, J.J.; Li, K. Effect of organic matter applications on 13C-NMR spectra of humic acids of soil. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2008, 59, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, G.; Wang, S. Seven years of biochar amendment has a negligible effect on soil available P and a progressive effect on organic C in paddy soils. Biochar 2022, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L. Effects of temperature on soil organic carbon fractions contents, aggregate stability and structural characteristics of humic substances in a Mollisol. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 1849–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Li, L.; Wang, R.; Xu, X.; Zhang, F.; Mao, G.; Wang, T. Effects of organic fertilizers on organic carbon accumulation in alkalized saline soil and silage maize yield. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2024, 17, 159–168. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Di, H. Effects of long-term mowing on the fractions and chemical composition of soil organic matter in a semiarid grassland. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2685–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Crowther, T.W.; Sui, Y.; Sun, B.; Liang, Y. High stability and metabolic capacity of bacterial community promote the rapid reduction of easily decomposing carbon in soil. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.L.; Patti, A.F.; Rose, M.T.; Schefe, C.R.; Wilkinson, K.; Smernik, R.J.; Cavagnaro, T.R. Does the chemical nature of soil carbon drive the structure and functioning of soil microbial communities? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, G.; Chen, Y.; Wei, T.; Guo, X.; Yu, H.; Jiang, S.; Xin, P.; Ren, K. Responses of soil microbial communities to vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau of China: A meta-analysis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 189, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Ying, H.; Lu, S. Soil pore structure changes induced by biochar affect microbial diversity and community structure in an Ultisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 224, 105505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Zhang, B.; Li, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, A. Straw-derived biochar mitigates CO2 emission through changes in soil pore structure in a wheat-rice rotation system. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Feng, G.; Tewolde, H. Biochar derived from papermill factories improves soil physical and hydraulic properties in no-till cotton fields. Biochar 2023, 5, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feeney, D.S.; Crawford, J.W.; Daniell, T.; Hallett, P.D.; Nunan, N.; Ritz, K.; Rivers, M.; Young, I.M. Three-dimensional Microorganization of the Soil–Root–Microbe System. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 52, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Ren, X.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, F.; Shi, J. Ecological effects of biochar in heavy metal-contaminated soils from multidimensional perspective: Using meta-analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2025, 432, 132695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, G. Changes of bacterial community compositions after three years of biochar application in a black soil of northeast China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 113, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, J. Biochar enhanced soil aggregation and C-related enzyme activity in post-mining land on the Loess Plateau, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Wen, J.; Mo, F.; Liu, Y. Continuous manure application strengthens the associations between soil microbial function and crop production: Evidence from a 7-year multisite field experiment on the Guanzhong Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 338, 108082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.S.; Ros, G.H.; Furtak, K.; Iqbal, H.M.N.; Parra-Saldívar, R. Soil carbon sequestration—An interplay between soil microbial community and soil organic matter dynamics. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Tang, J.; Ren, X.; Schaeffer, S.M. Effects of phosphorus modified nZVI-biochar composite on emission of greenhouse gases and changes of microbial community in soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 116483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, T.; Dong, X.; Yu, L.; Li, D.; Han, H.; Tu, S.; Wan, J. Influence of Pteris vittata-maize intercropping on plant agronomic parameters and soil arsenic remediation. Chemosphere 2024, 359, 142331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.-H.; Xu, R.-K.; Qian, W.; Wang, R.-H. Comparison of the ameliorating effects on an acidic ultisol between four crop straws and their biochars. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Y.; An, W.; Jin, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, X. Effects of biochar addition on the abundance, speciation, availability, and leaching loss of soil phosphorus. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-M.; Duan, Y.; Wang, G.-l.; Wang, A.-Q.; Shao, G.-Z.; Meng, X.-H.; Hu, H.-Y.; Zhang, D.-M. Straw alters the soil organic carbon composition and microbial community under different tillage practices in a meadow soil in Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 208, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Rong, X.; Zhou, X.; Fei, J.; Peng, J.; Luo, G. Biochar and organic fertilizer applications enhance soil functional microbial abundance and agroecosystem multifunctionality. Biochar 2024, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Gu, J.-D. Alteration of extracellular enzyme activity and microbial abundance by biochar addition: Implication for carbon sequestration in subtropical mangrove sediment. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 182, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Gao, W.; Shi, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhu, J.; He, J.-S. Effects of short- and long-term nutrient addition on microbial carbon use efficiency and carbon accumulation efficiency in the Tibetan alpine grassland. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 229, 105657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ferreiro, J.; Gascó, G.; Gutiérrez, B.; Méndez, A. Soil biochemical activities and the geometric mean of enzyme activities after application of sewage sludge and sewage sludge biochar to soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P. Processes in submerged soils—linking redox potential, soil organic matter turnover and plants to nutrient cycling. Plant Soil 2021, 464, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominchin, M.F.; Verdenelli, R.A.; Berger, M.G.; Aoki, A.; Meriles, J.M. Impact of N-fertilization and peanut shell biochar on soil microbial community structure and enzyme activities in a Typic Haplustoll under different management practices. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2021, 104, 103298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y. Impacts of farmland conversion to apple (Malus domestica) orchard on soil organic carbon stocks and enzyme activities in a semiarid loess region. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2015, 178, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, R.; Rabbi, S.M.F.; Zhang, Y.; Young, I.M.; Jones, A.R.; Dennis, P.G. Soil organic carbon is significantly associated with the pore geometry, microbial diversity and enzyme activity of the macro-aggregates under different land uses. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Han, X.; Lu, X.; Yan, J.; Chen, X.; Zou, W. Response of soil enzymatic activity to pore structure under inversion tillage with organic materials incorporation in a haplic chernozem. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, E.R.; de Jesus Franco, A.; da Silva, A.P.V.; da Silva, J.A.G.F.; Tavares, D.S.; De Souza, J.K. Organic substrate availability and enzyme activity affect microbial-controlled carbon dynamics in areas disturbed by a mining dam failure. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, A.I.; Xu, Y.; Shi, D.; Li, J.; Li, H.; El-Sappah, A.H.; Elrys, A.S.; Alharbi, S.A.; Zhou, C.; Wang, L.; et al. Nitrogen transformation genes and ammonia emission from soil under biochar and urease inhibitor application. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 223, 105491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

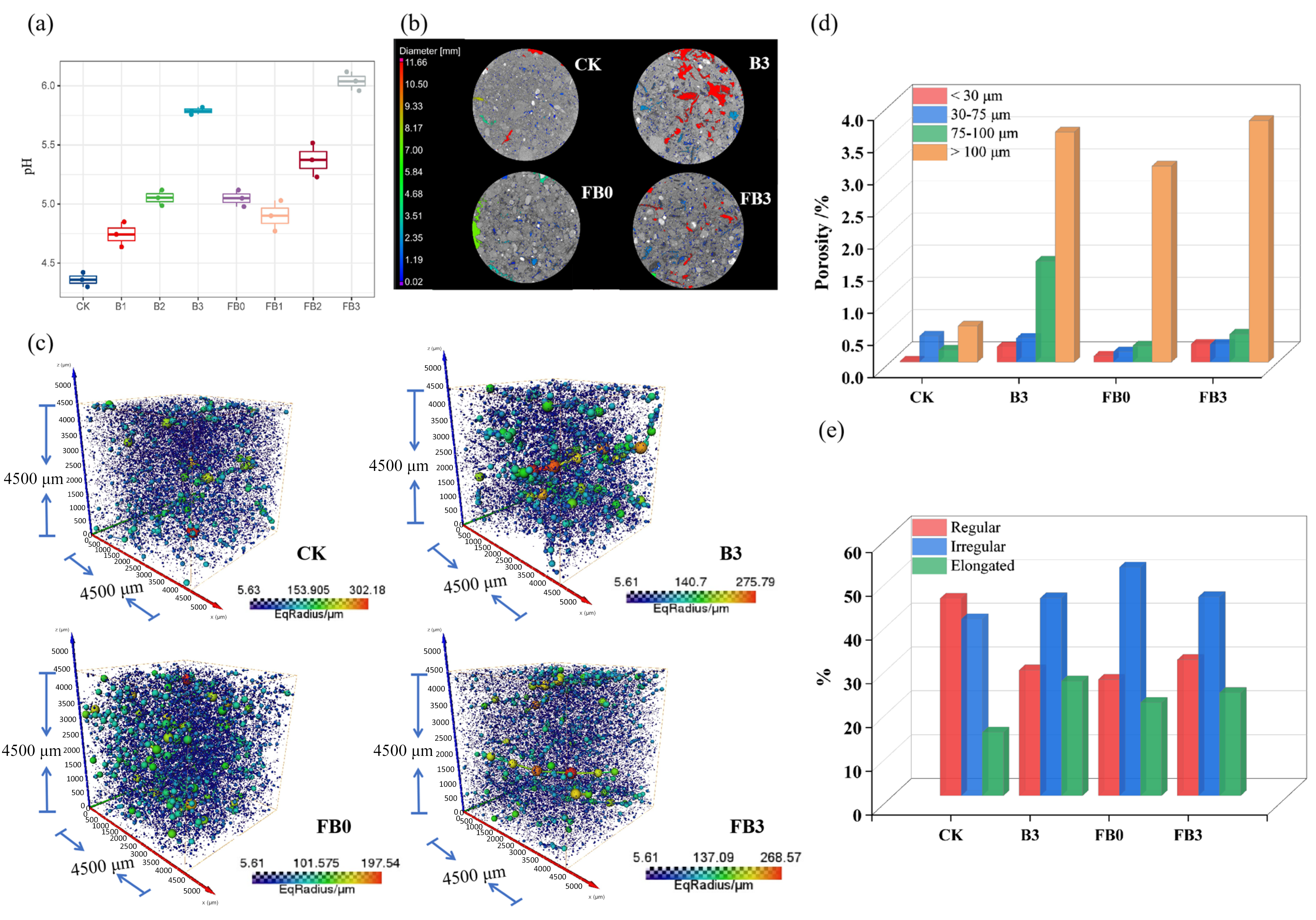

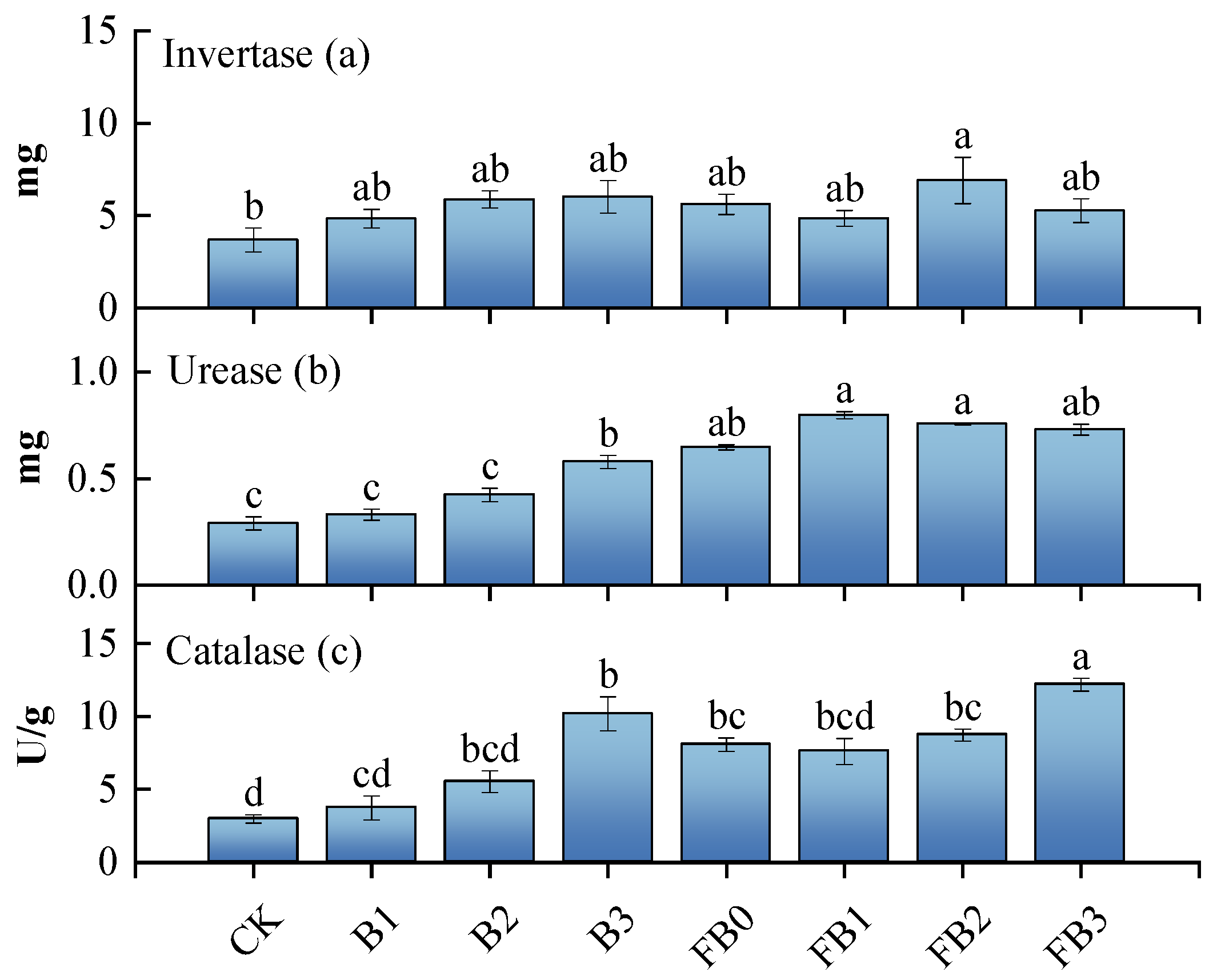
| Treatment | Porosity/% | Soil Pore Count/Million |
|---|---|---|
| CK | 3.73 ± 0.05 c | 0.53 ± 0.01 a |
| B3 | 5.53 ± 0.06 a | 0.35 ± 0.03 c |
| FB0 | 4.74 ± 0.04 b | 0.43 ± 0.02 b |
| FB3 | 5.64 ± 0.05 a | 0.36 ± 0.03 c |
| Treatment | OTU | Chao1 | Shannon | Pielou_e | Simpson | Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 1430.01 ± 161.46 b | 1333.29 ± 161.68 b | 8.20 ± 0.65 b | 0.78 ± 0.05 b | 0.97 ± 0.02 b | 0.99 ± 0.01 a |
| B1 | 1435.67 ± 164.69 b | 1438.70 ± 163.46 b | 8.23 ± 0.52 b | 0.79 ± 0.04 b | 0.98 ± 0.01 ab | 0.99 ± 0.01 a |
| B2 | 1479.33 ± 78.82 b | 1482.10 ± 79.19 b | 8.08 ± 0.27 b | 0.78 ± 0.02 b | 0.98 ± 0.01 ab | 0.99 ± 0.01 a |
| B3 | 1476.33 ± 122.13 b | 1480.79 ± 121.63 b | 8.21 ± 0.28 b | 0.79 ± 0.02 b | 0.98 ± 0.01 ab | 0.99 ± 0.01 a |
| FB0 | 1658.67 ± 93.66 ab | 1661.23 ± 93.30 ab | 8.88 ± 0.37 ab | 0.83 ± 0.03 ab | 0.99 ± 0.01 ab | 0.99 ± 0.01 a |
| FB1 | 1888.67 ± 123.41 a | 1893.01 ± 123.28 a | 9.55 ± 0.19 a | 0.88 ± 0.01 a | 1.00 ± 0.01 a | 0.99 ± 0.01 a |
| FB2 | 1913.33 ± 141.00 a | 1918.27 ± 142.11 a | 9.55 ± 0.13 a | 0.88 ± 0.01 a | 1.00 ± 0.01 a | 0.99 ± 0.01 a |
| FB3 | 1769.33 ± 141.25 a | 1772.77 ± 140.19 ab | 9.28 ± 0.20 ab | 0.86 ± 0.10 ab | 1.00 ± 0.01 a | 0.99 ± 0.01 a |
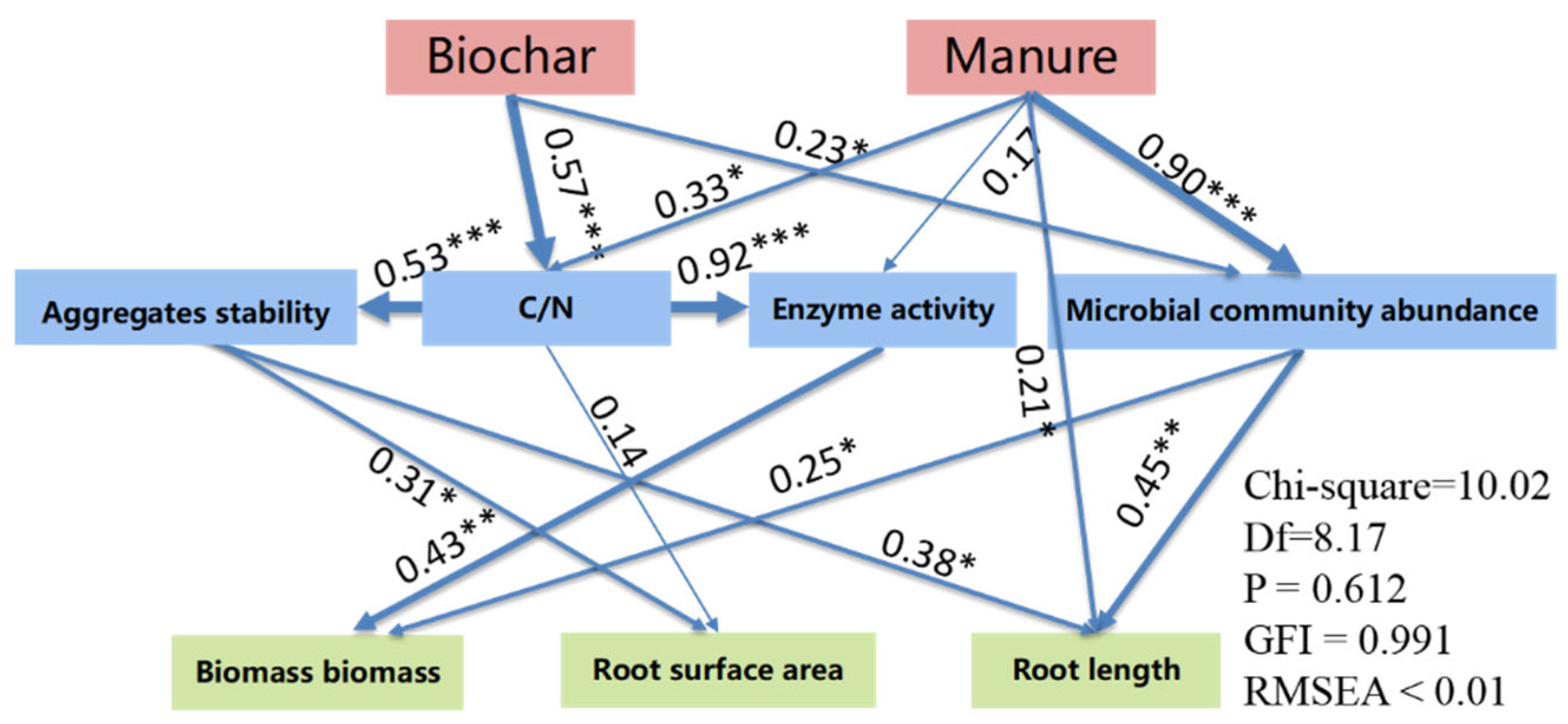
| Index | Criteria Judging | Model Fit Results |
|---|---|---|
| x2/df | 1–3 | 1.23 |
| GFI | >0.90 | 0.991 |
| CFI | >0.95 | 1.000 |
| RMSEA | <0.05 | 0.003 |
| RMR | - | 5.650 |
| SRMR | <0.08 | 0.037 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Tu, S.; Lu, X.; Li, X. Coupling of Biochar and Manure Improves Soil Carbon Pool Stability, Pore Structure, and Microbial Diversity. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061384
Sun J, Tu S, Lu X, Li X. Coupling of Biochar and Manure Improves Soil Carbon Pool Stability, Pore Structure, and Microbial Diversity. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061384
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jing, Shuxin Tu, Xinrui Lu, and Xiujun Li. 2025. "Coupling of Biochar and Manure Improves Soil Carbon Pool Stability, Pore Structure, and Microbial Diversity" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061384
APA StyleSun, J., Tu, S., Lu, X., & Li, X. (2025). Coupling of Biochar and Manure Improves Soil Carbon Pool Stability, Pore Structure, and Microbial Diversity. Agronomy, 15(6), 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061384






