Abstract
Vegetation restoration is critical for improving soil quality and microbial community dynamics in degraded mining areas. This study explored the effects of different vegetation types (grassland, shrubland, and mixed grass–shrub areas) on soil physicochemical properties, organic carbon fractions, and abundant versus scarce microbial taxa assemblies in a Loess Plateau coal mining area. Soil samples from four depths (0–100 cm) were analyzed using high-throughput sequencing for nutrient content; carbon components, soil organic carbon (SOC), particulate organic carbon (POC), mineral-associated organic carbon (MAOC), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), microbial biomass organic carbon (MBC), and readily oxidizable organic carbon (ROC); microbial diversity. Shrubland soils exhibited significantly higher total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and organic carbon components (SOC, MAOC, and POC) than other vegetation types (p < 0.05), with the greatest carbon accumulation noted in the surface layer depths (0–20 cm). Microbial communities displayed vegetation-specific patterns: abundant taxa (e.g., Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria) dominated nutrient cycling and exhibited resilience to environmental gradients, while rare taxa (e.g., Methylomirabilota, Olpidiomycota) correlated strongly with labile carbon fractions (DOC and POC) and demonstrated metabolic flexibility. Mantel tests identified soil pH, TN, and organic carbon components as key drivers of microbial community divergence (p < 0.01). Shrubland vegetation enhanced soil nutrient retention and carbon stabilization, whereas the mixed grass–shrub systems promoted niche partitioning among rare taxa. These findings highlight the roles of vegetation-mediated carbon inputs and environmental filtering in shaping microbial assembly, providing a scientific framework for optimizing restoration strategies in mining ecosystems.
1. Introduction
Owing to the acceleration of industrialization, the exploitation of mineral resources has had a profound impact on the ecology and environment. Mining activities have severely damaged soils, leading to soil degradation, species loss, and diminished ecological functionality and ecosystem services [1,2]. Vegetation restoration plays a crucial role in improving the ecological environment in mining areas, serving not only to stabilize soil structure and enhance fertility, but also as a vital indicator of ecosystem recovery [3,4,5]. However, vegetation growth is dependent on, and limited by, the functional recovery of reclaimed soil in mining areas, especially in the relatively fragile ecological environment of the Loess Plateau coal mining area. Soil is heavily degraded in this area, with scattered soil structure, poor fertility, and low organic carbon content, all of which severely limit the nutrient supply for vegetation recovery [6,7]. As an integral part of the ecosystem, soil microbial communities play an important role in plant growth, nutrient cycling, soil health, and carbon and nitrogen cycling. Therefore, the development of reclaimed soil microbiota directly affects soil function and traits, and, thus, vegetation growth [4,8]. Root secretion and apoplastic inputs from different vegetation types can significantly alter the soil microenvironment, thereby affecting the composition, abundance, distribution, and metabolic functions of the soil microbial communities [9,10,11,12]. Therefore, clarifying soil–plant–microbe interactions can help to stimulate the self-recovery potential of an ecosystem, which is crucial for ecological restoration of the Loess Plateau coal mining area.
Soil microbes are diverse and functionally complex, with differentially abundant taxa playing various roles in biogeochemical cycles [4,13,14]. Microorganisms typically exhibit skewed species abundance distributions in different habitats, with a few relatively high-abundance species (abundant taxa, defined as taxa with a relative abundance ≥ 1%) and most relatively low-abundance species (rare taxa, defined as taxa with a relative abundance < 1%) [15]. Traditionally, abundant taxa were considered primary contributors to ecosystem functions due to their broad ecological niches and biomass dominance [16]. Recent studies have revealed that these abundant taxa play disproportionate roles in carbon cycling and ecosystem stability, particularly under environmental stress [17,18], and are resistant to environmental disturbances, which enhances the overall resistance of soil communities [19]. In addition, rare taxa exhibit high metabolic diversity and serve as microbial “seed banks”, enabling rapid adaptation to environmental fluctuations [20,21]. Given the different roles of abundant and rare microbial taxa in soil functions and ecosystem services, and our limited knowledge of scarce microorganisms, it is necessary to study how abundant and rare taxa regulate the functions of reclaimed soils and vegetation–soil interactions under different vegetation restoration modes during the ecological restoration of mining areas. There are obvious environmental differences between surface soil and deep soil in terrestrial ecosystems; deep soil is a huge carbon reservoir, with >50% of soil organic carbon (SOC) stored there, and microbial-derived carbon plays an important role in the deep soil carbon pool [22]. Therefore, it is also important to probe different soil depths to determine the richness and rarity of microbial taxa. These insights underscore the need to reevaluate how vegetation-mediated changes in soil properties differentially shape the dynamics of abundant versus rare microbial communities during ecological restoration.
In the context of the fragile ecosystems on the Loess Plateau, different vegetation restoration strategies (e.g., grassland, shrubland, and mixed grass–shrub) may exert distinct impacts on soil microbiota through variations in root exudation patterns and litter composition [23]. However, the mechanisms through which these vegetation types regulate the diversity and composition of abundant and rare microbial communities, as well as their environmental driving mechanisms, particularly across soil depth gradients, remain poorly understood. Addressing this knowledge gap is critical for optimizing restoration practices to enhance soil functionality and ecosystem resilience.
The objectives of this study were to investigate the Hongliulin mining area on the Loess Plateau to (1) explore the effects of different vegetation types on soil physicochemical properties and carbon fractions; (2) assess the influence of different vegetation types on abundant and rare soil microbial communities; (3) delineate interactions among abundant and rare soil microbial communities, vegetation, and environmental factors. The subsequent results revealed key environmental factors that drive the differences in the characteristics of abundant and rare soil microbial communities. Through these analyses, this study highlighted the succession patterns of soil microbial communities during vegetation restoration and their potential roles in the ecological restoration of mining areas. These findings provide a theoretical basis and practical guidance for the ecological restoration of mining areas.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site and Soil Sampling
This study selected the Hongliulin Coal Mine in Shenmu City, Shaanxi Province (38°53′13″ to 38°57′30″ N, 110°10′21″ to 110°24′15″ E) as the research area, located in the transitional zone between the Loess Plateau and the Mu Us Sandy Land. The region is characterized by a warm temperate to mid-temperate semi-arid continental monsoon climate. This area also experiences drought conditions with low rainfall and high evaporation. The average annual precipitation is 436.7 mm, with extremely uneven distribution throughout the year. Rainfall is primarily concentrated in the summer and autumn months, with 70% occurring in July, August, and September. Annual evaporation ranges from 1907.2 to 2122.7 mm, 4–5 times higher than precipitation [23]. According to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) soil classification system, Arenosols are the predominant soil type, accounting for 70–80% of the mining region. The area suffers from severe soil erosion and features sparse vegetation with low coverage. However, long-term vegetation restoration projects have led to the coexistence of multiple vegetation types in the region [24].
We selected the experimentation grasslands based on field investigations and standard local practices in July 2023: (G, dominated by Stipa bungeana and Artemisia desertorum), shrub (S, dominated by Salix cheilophila and Caragana korshinskii), and mixed grass–shrub (GS) as the vegetation restoration types in the area. For each vegetation type, five 10 m × 10 m sampling plots with similar slope aspects and relatively homogeneous vegetation were established, spaced 10 m apart. Within each plot, soil samples were collected from depths of 0–20 cm, 20–40 cm, 40–60 cm, and 60–100 cm at five sampling points arranged in an S-shaped pattern. After removing stones and organic debris, soil samples from the same layer were thoroughly mixed. Each soil sample was partitioned into three fractions. One fraction was promptly preserved by freezing in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C for DNA extraction. The second fraction was refrigerated at 4 °C to measure ammonium nitrogen (NH4+–N), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−–N), dissolved organic carbon (DOC), and microbial biomass carbon (MBC). The third fraction was air-dried and passed through a 2 mm sieve to analyze the physicochemical properties of the soil.
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Properties
Total nitrogen (TN) content was determined using the Kjeldahl method, while soil NO3−–N and NH4+–N were extracted with KCl and measured using an Analytical AutoAnalyzer 3 (AA3) continuous flow analyzer (Hamburg, Germany). Total phosphorus (TP) was determined using the potassium dichromate volumetric and molybdenum–antimony resistance colorimetric method. Soil available phosphorus (SAP) was determined by NaHCO3 extraction and the molybdenum–antimony resistance colorimetric method [25]. Soil pH was measured using a PHS-3C pH meter (Shanghai, China) at a 2.5:1 water/soil ratio after the suspension was formed [26].
The SOC was determined using the K2Cr2O7 oxidation-outer heating method [25]. A wet sieve assembly was used to separate particulate organic carbon (POC; ≥53 μm) and mineral-associated organic carbon (MAOC; <53 μm) after dispersing soil particles in a sodium hexametaphosphate solution [27]. The MBC was determined via chloroform fumigation and K2SO4 solution extraction [28]. The DOC was determined through deionized water extraction [29]. Readily oxidizable organic carbon (ROC) was measured using the KMnO4 oxidation method [30].
2.3. Soil DNA Analysis
Soil DNA was assessed using a NanoDrop One (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) after extraction using a PowerSoil DNA Isolation kit (MO BIO Laboratories, Carlsbad, CA, USA). PCR amplification was performed using an S1000 instrument (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Primers used to amplify bacterial 16S rRNA genes were 341F (5′-CCTAYGGGRBGCASCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACNNGGGTATCTAAT-3′). For amplification of fungal ITS2 genes, the primers were ITS2F (5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′) and ITS2R (5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCGATGC-3′). For each sample, triplicate PCR products of the 16S rDNA and ITS regions were pooled separately to minimize stochastic PCR bias. These amplicons were then purified using the Agarose Gel DNA Purification kit (TaKaRa), following the manufacturer’s protocol. The purified 16S and ITS amplicons were sequenced independently to avoid cross-region interference. Purified PCR products were combined into a single tube at equimolar ratios, and high-throughput sequencing analysis was performed using an Illumina Nova 6000 platform (Guangdong Magigene Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Guangzhou, China). Sequencing results were quality-controlled using fastp (v0.14.1), and paired-end reads were merged using USEARCH fastq-mergepairs (v10). Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered using Uparse and annotated against the Silva 16S rRNA (v132) database [31]. Abundant and rare microbial taxa were analyzed based on the relative abundance as determined in previous studies [32,33]. At the phylum level, taxa with a relative abundance ≥ 1% were defined as abundant taxa, while those with a relative abundance ≤ 1% were classified as rare taxa.
2.4. Statistical Analyses
Data for different treatments were compared by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) based on Fisher’s least significant difference test (p < 0.05) using SPSS 25.0 for Windows (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA). Origin 2024 (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA) was used to generate the figures. Microbial community composition among different vegetation types and soil depths was visualized by principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) using the Bray–Curtis distance matrix in the ‘vegan’ R package. Mantel tests were conducted to determine the associations between microbial community structure and each environmental variable using R (v3.6).
3. Results
3.1. Variations in Soil Physicochemical Properties and Carbon Fractions Across Vegetation Types
The TN and TP levels in grassland, shrubland, and mixed grass–shrub vegetation soils ranged from 0.08 to 0.40 g/kg across vegetation types and soil depths (Figure 1). Shrubland soils consistently exhibited the highest TN and TP content across all four soil layers (0–20 cm, 20–40 cm, 40–60 cm, and 60–100 cm), with statistical significance (p < 0.05). A decreasing trend in TN and TP content was observed with increasing soil depth under identical vegetation conditions. Soil NH4+–N and NO3−–N concentrations ranged from 0.50 to 2.91 mg/kg and 0.62 to 11.10 mg/kg, respectively. The mean NH4+–N content was ordered shrubland > mixed grass–shrub > grassland vegetation, whereas NO3−–N content was ordered shrubland > grassland > mixed grass–shrub. Vertically, NH4+–N exhibited an initial increase followed by a subsequent reduction with soil depth within the same vegetation type, while NO3−–N displayed a monotonic decreasing pattern. Soil available phosphorus (AP) concentrations ranged from 0.70 to 2.43 mg/kg, with mixed grass–shrub soils showing the highest AP levels across all four soil layers. A consistent decline in AP content was observed with increasing soil depth for all vegetation types. Soil pH values exceeded 7.0 across all vegetation types and depths, indicating alkaline soil conditions in the study area. Notably, elevated pH levels were recorded in deeper soil strata compared to surface layers. These results emphasize the stratification of soil nutrient dynamics and alkalinity gradients governed by vegetation-mediated biogeochemical processes and pedogenic development.
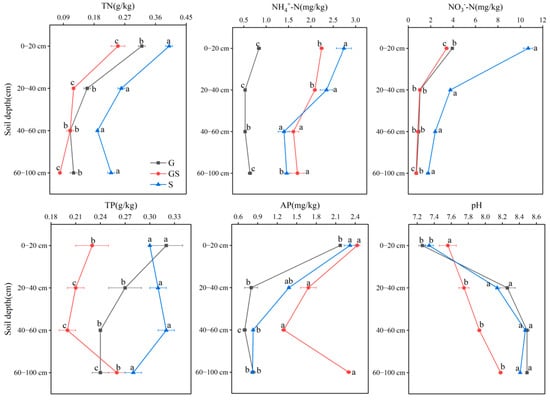
Figure 1.
Variations in soil physicochemical properties across vegetation types and soil depths. Different letters denote significant differences assessed by the Fisher LSD test (p ≤ 0.05).
Both vegetation type and soil depth exerted significant influences on SOC composition (Figure 2). Shrubland soils displayed significantly higher SOC levels than grassland and mixed grass–shrub systems (p < 0.05). Within the same vegetation type, surface soils (0–20 cm) exhibited markedly greater SOC concentrations than deeper soil strata (p < 0.05). Soil MAOC and POC contents ranged from 0.34 to 2.84 g/kg. MBC, dissolved DOC, and ROC concentrations spanned 30.01–101.34 mg/kg, 12.95–58.24 mg/kg, and 0.11–0.95 g/kg, respectively. All carbon fractions displayed significantly elevated levels in shrubland soils relative to grassland and mixed grass–shrub systems (p < 0.05), with peak values consistently observed in the 0–20 cm surface layer. Organic carbon fractions across vegetation types were ordered shrubland > grassland > mixed grass–shrub. These patterns highlight the critical role of vegetation-specific litter input, microbial activity, and stabilization mechanisms in regulating vertical carbon distribution and compositional dynamics within soil profiles.
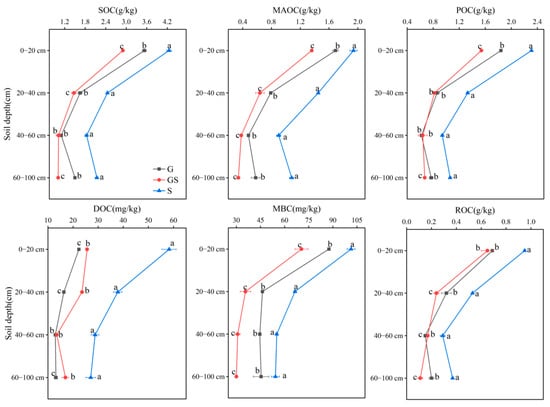
Figure 2.
Variations in soil organic carbon fractions across vegetation types and soil depths. Different letters denote significant differences assessed by the Fisher LSD test (p ≤ 0.05).
The PCoA of bacterial and fungal communities at the amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) level, calculated using Bray–Curtis dissimilarity, revealed distinct clustering patterns for both abundant and rare taxa (Figure 3). Beta-diversity exhibited significant inter-group separation and tight intra-group clustering across vegetation restoration treatments, indicating pronounced differences in microbial community composition among treatments (PERMANOVA: p < 0.01). For bacterial communities, mixed grass–shrub vegetation displayed marked separation along the PCoA y-axis compared with other vegetation types (p < 0.01), suggesting fundamentally divergent community structures. By contrast, the grassland and shrubland vegetation groups showed overlapping clustering patterns, reflecting insignificant differences (p > 0.05) and closer phylogenetic relationships between their bacterial assemblages. Fungal communities demonstrated analogous yet distinct patterns; grassland vegetation exhibited significant separation along the y-axis relative to other vegetation types (p < 0.01), while grassland and shrubland vegetation groups maintained overlapping distributions, implying phylogenetic proximity in fungal community composition. These results underscore the vegetation-specific filtering effects on microbial assembly processes, with mixed grass–shrub systems driving unique niche partitioning in bacteria, whereas grassland dominance primarily shaped fungal community divergence.
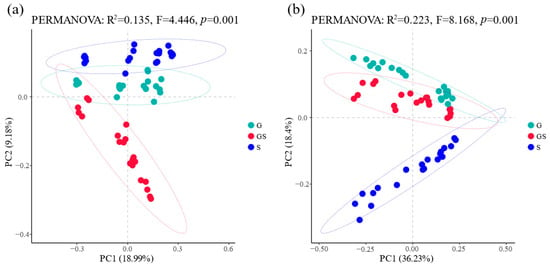
Figure 3.
Variations in beta-diversity of soil bacteria and fungi across vegetation types. (a) Beta-diversity of soil bacteria; (b) beta-diversity of soil fungi.
3.2. Composition of Abundant and Rare Bacterial/Fungal Communities in Soils Across Vegetation Types
The vegetation type exhibited no significant effects (p > 0.05) on the relative abundances of dominant bacterial phyla (relative abundance > 1%), including Acidobacteriota, Actinobacteriota, Bacteroidota, Chloroflexi, Gemmatimonadota, Myxococcota, and Proteobacteria; meanwhile, Firmicutes demonstrated depth-dependent variations with increased abundance across soil layers (Figure 4). By contrast, rare bacterial taxa (relative abundance < 1%) showed vegetation-specific responses: mixed grass–shrub vegetation significantly enhanced Planctomycetota and Verrucomicrobiota in surface soils (0–40 cm) and elevated Patescibacteria in deeper layers (40–80 cm; p < 0.05). Depth gradients drove distinct patterns: Latescibacterota and Methylomirabilota increased linearly with depth (p < 0.01), RCP2-54 and Dadabacteria displayed unimodal distributions peaking at intermediate depths (20–60 cm); in contrast, Entotheonellaeota decreased progressively with depth (p < 0.01).
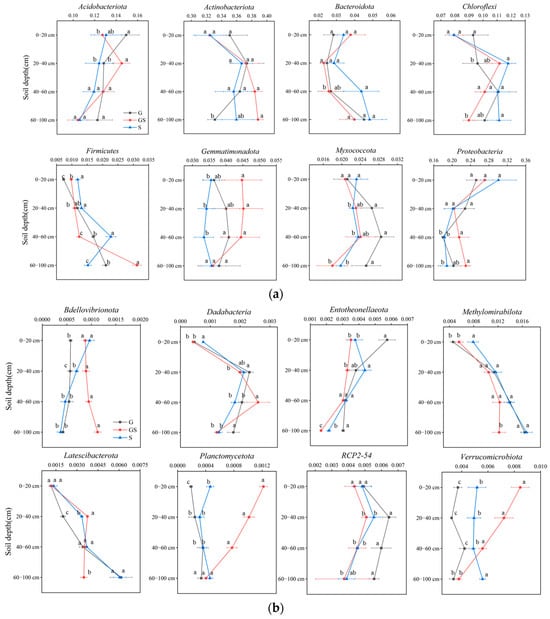
Figure 4.
Variations in soil bacterial communities across vegetation types. (a) Variations in soil abundant bacterial communities; (b) variations in soil rare bacterial communities. Different letters denote significant differences assessed by the Fisher LSD test (p ≤ 0.05).
Among abundant fungal communities, Ascomycota remained stable across vegetation types and depths (p > 0.05), whereas Mucoromycota were increased significantly in grassland soils at 20–40 cm, and Basidiomycota species were elevated in shrubland soils at 0–20 cm and 40–60 cm (p < 0.05; Figure 5). Rare fungal taxa exhibited minimal vegetation- and depth-related trends for Chytridiomycota (p > 0.05), but Olpidiomycota displayed significant fluctuations in relative abundance across vegetation types with increasing soil depth (p < 0.05). These findings underscore the resilience of dominant microbial clades to vegetation shifts and niche-specific sensitivity of rare taxa to interactive vegetation-depth gradients, governed by differential substrate accessibility and environmental filtering mechanisms.
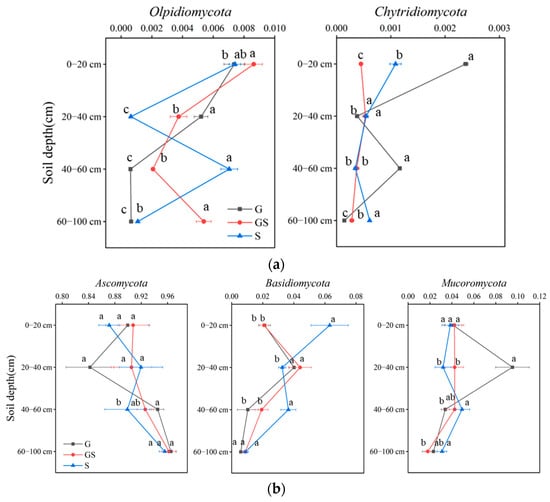
Figure 5.
Variations in soil fungal communities across vegetation types. (a) Variations in soil abundant fungal communities; (b) variations in soil rare fungal communities. Different letters denote significant differences assessed by the Fisher LSD test (p ≤ 0.05).
3.3. Correlations Between Environmental Factors and Soil Microbial Communities (Abundant vs. Rare Taxa) Across Vegetation Types
Mantel tests between soil microbial communities (rare/abundant bacteria and fungi) and soil physicochemical/carbon fraction indices revealed vegetation-specific modulation of microbial–environment interactions (p < 0.05; Figure 6). In grassland vegetation, rare bacterial communities exhibited extreme sensitivity to all measured indices (p < 0.01); meanwhile, abundant bacteria were strongly influenced by TN, MAOC, DOC, and ROC (p < 0.01), with TP and POC showing secondary effects (p < 0.05). Rare fungal communities correlated significantly with TN, TP, pH, SOC, MAOC, POC, DOC, and ROC (p < 0.01), whereas abundant fungi responded primarily to ROC and MAOC (p < 0.05).
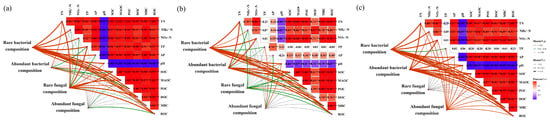
Figure 6.
Environmental factors and community diversity of abundant and rare bacteria and fungi correlated with different vegetation types. (a) Environmental factors and community diversity of abundant and rare bacteria and fungi associated with the grassland. (b) Environmental factors and community diversity of abundant and rare bacteria and fungi correlated with mixed grass–shrub. (c) Environmental factors and community diversity of abundant and rare bacteria and fungi correlated with the shrubland. Correlation coefficients marked with “*”, “**” and “***” are significant at p < 0.05, p < 0.01 and p < 0.001, respectively.
In the mixed grass–shrub vegetation, rare bacterial communities were strongly correlated with nitrogen-related metrics and carbon fractions (p < 0.01), alongside a moderate association with TP (p < 0.05). Abundant bacterial communities were predominantly influenced by carbon fractions (excluding DOC), TN, NO3−–N, and pH (p < 0.01), while DOC, NH4+–N, and TP exerted secondary effects (p < 0.05). Rare fungal communities showed significant associations with TN, NH4+–N, pH, SOC, MAOC, POC, MBC, and ROC (p < 0.05), while DOC displayed stronger correlations (p < 0.01). Abundant fungal taxa were predominantly shaped by TP, pH (p < 0.01), and AP (p < 0.05).
In the shrubland vegetation, TP moderately influenced rare bacterial communities (p < 0.05), whereas all other physicochemical and carbon metrics exerted a significant influence on both bacterial groups (p < 0.01). Abundant bacterial and fungal communities displayed universal sensitivity to all soil properties (p < 0.01), highlighting intensified environmental filtering in shrubland vegetation.
4. Discussion
Rare microbial taxa, characterized by high diversity and functional redundancy, serve as a critical ecological insurance within microbial communities, which ensures functional stability under environmental fluctuations. In contrast, abundant taxa are associated with broader adaptive capacities to environmental perturbations, supporting superior resilience to ecosystem disturbance [34]. Thus, investigating the dynamics of abundant and rare microbial groups across vegetation types in mining areas is essential for ecological restoration, particularly in understanding how these taxa regulate soil functionality and mediate plant–soil interactions.
This study revealed significant differences in the effects of vegetation restoration types on soil properties and carbon fractions (Figure 1 and Figure 2). Variations in root exudates and physiological metabolism among vegetation types are known to be critical drivers of soil physicochemical and carbon fraction modifications [35].
Shrubland soils exhibited significantly higher levels of TN, NH4+–N, NO3−–N, TP, and SOC fractions than grassland and mixed grass–shrub systems. This disparity is likely attributed to differences in litter quality and root exudation capacity, with shrubland vegetation demonstrating superior nutrient and organic carbon input capabilities relative to grassland plants [36]. A marked decline in TN, NH4+–N, NO3−–N, TP, and SOC fractions was observed with increasing soil depth, primarily due to the accumulation of plant litter in surface layers, which provides continuous organic carbon inputs, coupled with the shallow distribution of root systems [37].
Soil microbial communities are closely linked to aboveground vegetation types through direct mechanisms (e.g., variations in litter biomass, decomposition rates, and root exudates) and indirect pathways (e.g., vegetation-mediated alterations in soil physicochemical properties). These interactions selectively enrich specific microbial taxa, driving structural shifts in soil communities [38]. Notably, abundant and rare microbial taxa exhibit divergent responses in both diversity and composition following environmental changes, leading to vegetation-specific abundance patterns.
The dominant bacterial phyla across all vegetation types included Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Gemmatimonadota (Figure 4), likely due to their broad environmental adaptability and ecological niche specialization. Actinobacteria, key decomposers of recalcitrant polymers such as cellulose and lignin, thrive even in nutrient-poor soils [39]. Proteobacteria, known for their nitrogen-fixing capabilities and alkaline tolerance, dominate in nitrogen-limited environments, while Gemmatimonadota species exhibit exceptional ecological resilience [40,41]. Their prevalence aligns with findings in arid and semi-arid mining soils, where Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria consistently dominate [42,43,44], suggesting minimal vegetation dependency and robust adaptability to harsh conditions.
Among rare bacterial taxa, Desulfobacterota and Methylomirabilota emerged as dominant phyla (Figure 4). Elevated Methylomirabilota abundance in surface soils correlates with methane seepage from coal seam fires, mirroring its prevalence in methane-rich environments [45]. Grassland and mixed systems showed higher Desulfobacterota abundance, potentially linked to root exudate-driven organic acid metabolism, which may suppress nitrogen mineralization and organic carbon accumulation [46].
Fungal communities exhibited parallel trends: Ascomycota dominated abundant taxa across vegetation types, consistent with their saprophytic versatility in alkaline soils [47,48]. Rare fungal taxa were characterized by Olpidiomycota, an endophytic group enriched in shrubland soils at a depth of 40–60 cm, likely due to deep root biomass distribution and its functional role in organic matter decomposition and carbon sequestration [49]. These findings highlight how vegetation restoration shapes microbial niche partitioning, with abundant taxa maintaining ecosystem stability and rare taxa reflecting localized nutrient dynamics.
These results demonstrate that abundant and rare microbial taxa are significantly influenced by distinct soil physicochemical properties and carbon fractions across vegetation restoration types (Figure 6). Consistent with previous findings [50,51], bacteria were more sensitive to environmental factors than fungi, with rare bacterial taxa demonstrating significantly stronger responses to these factors than their abundant counterparts. Multiple environmental factors, including TP, MAOC, and ROC, exerted a pronounced influence on the distribution of abundant communities in restored soils, consistent with previous reports on grassland ecosystems [52]. Abundant taxa displayed lower sensitivity to environmental gradients than rare taxa, likely due to their directional convergence during community succession under environmental filtering. This enables abundant taxa to dominate microbial communities through broader niche occupation and competitive resource utilization, thereby maintaining adaptive advantages in mining area environments during ecological disturbances. These observations align with previous findings, which showed that abundant bacteria are primary contributors to core functions, such as nutrient cycling and energy metabolism [53]. In contrast, rare communities exhibited significant correlations with SOC, POC, and DOC, likely attributable to their high diversity and metabolic flexibility. These traits allow rare taxa to rapidly respond to environmental shifts, facilitating niche expansion and enhanced resource competitiveness under fluctuating conditions.
5. Conclusions
Vegetation types significantly influenced both the abundance and rarity of microbial taxa in soils of a previously mined area. Shrubland vegetation significantly improved the physicochemical properties, SOC, and fractions of the soil. Specifically, shrubland vegetation was advantageous for the accumulation of soil nutrients and organic carbon, as well as its fractions. Different vegetation types significantly affected the structural composition of abundant and rare soil bacterial and fungal communities. Bacteria exhibited greater sensitivity to environmental factors than fungi, with rare bacterial taxa demonstrating significantly stronger responses to these factors than their abundant counterparts. Under different vegetation restoration types, both abundant and rare microbial taxa were significantly influenced by soil physicochemical properties and organic carbon fractions (p < 0.01), albeit to varying degrees.
We investigated the interactions between and mechanisms associated with abundant and rare soil microbial communities, vegetation, and environmental factors. These results highlight the key environmental factors driving the differences in the characteristics of abundant and rare microbial communities and establish a scientific framework for assessing how vegetation type influences soil quality in mining areas. These findings also provide a theoretical basis for vegetation restoration strategies in degraded mining ecosystems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.M., H.Z., H.L., Q.G. and J.S.; Methodology: Y.M., H.Z., H.L., Q.G. and J.S.; Software, Y.M., D.Z., P.L. and S.S.; Validation, D.Z.; Formal analysis, D.Z., P.L. and H.Z.; Investigation, Y.M., H.Z., H.L., Q.G. and J.S.; Writing—original draft and review and editing, D.Z., H.Z., P.L. and S.S.; Visualization, D.Z., H.Z. and P.L.; Project administration and funding acquisition, Y.M., H.L. and J.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Group-level scientific research project of Shenmu Hongliulin Mining Company of Shaanxi Coal Group, China area, grant number 2020SMHKJ-A-J-03-02/02.
Data Availability Statement
All the data that support the findings of this study are available in the paper. Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
Author Hongchao Zhao and Jianxuan Shang were employed by the company Shaanxi Coal Chemical Industry Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare that this study received funding from the company Shaanxi Coal Chemical Industry Technology Research Institute Co., Ltd. The funder had the following involvement with the study: Effects of Vegetation Restoration Type on Abundant and Scarce Soil Microbial Taxa in a Loess Plateau Mining Area.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| SOC | Soil organic carbon |
| POC | Particulate organic carbon |
| MAOC | Mineral-associated organic carbon |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
| MBC | Microbial biomass carbon |
| ROC | Readily oxidizable organic carbon |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| NH4+-N | Ammonium nitrogen |
| NO3−-N | Nitrate nitrogen |
| G | Grassland |
| S | Shrubland |
| GS | Mixed grass-shrub |
References
- Hossain, M.N.; Paul, S.K.; Hasan, M.M. Environmental impacts of coal mine and thermal power plant to the surroundings of Barapukuria, Dinajpur, Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Ma, J.; Yang, Y.J.; Luo, Z.B.; Wang, Y.F.; Chen, F. Mining subsidence-induced microtopographic effects alter the interaction of soil bacteria in the sandy pasture, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 9, 656708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keesstra, S.; Joao, N.; Agata, N.; David, F.; David, A.; Zahra, K.; Artemi, C. The superior effect of nature based solutions in land management for enhancing ecosystem services. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610–611, 997–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hua, Z.Y.; Cheng, Y.J.; Zhu, Y.F.; Yang, Y.J.; Chen, F. Impacts of vegetation restoration type on abundant and rare microflora inreclaimed soil of open-pit mining area. Coal Sci. Technol. 2024, 52, 363–377. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, B. Quantitative contribution of climate change and vegetation restoration to ecosystem services in the Inner Mongolia under ecological restoration projects. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.W.; Yang, L.; Liao, Y.; Li, J.W.; Jiao, S.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Deng, L. Soil labile organic carbon fractions mediate microbial community assembly processes during long-term vegetation succession in a semiarid region. iMeta 2023, 2, e142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Xu, M.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of different vegetation types on the characteristics of soil bacterial communities in the hilly area of Central Guizhou. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2021, 37, 518–525. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.D.; Qu, H.T.; Liao, S.M.; Dai, Y.; Ji, Y.; Li, J.P.; Chao, L.M.; Liu, H.J.; Bao, Y.Y. Changes in assembly processes and differential responses of soil microbial communities during mining disturbance in mining reclamation and surrounding grassland. CATENA 2023, 231, 107332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, B.R.; Shen, J.K.; Xu, F.J.; Li, N.; Jia, P.H.; Jia, Y.J.; An, S.S.; Amoah, I.D.; Huang, Y.M. Shifts in C-degradation genes and microbial metabolic activity with vegetation types affected the surface soil organic carbon pool. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2024, 192, 109371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.Y.; Li, X.L.; Zhang, Y.X.; Sun, H.J.; Li, C.Y.; Jin, L.Q.; Yang, X.G.; Liu, K. Responses of different degradation stages of alpine wetland on soil microbial community in the Yellow River source zone. Environ. Sci. 2021, 42, 3971–3984. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Cao, J.; Lan, G.; Liang, Y.; Li, Q. The influence of land use patterns on soil bacterial community structure in the karst graben basin of Yunnan province, China. Forests 2020, 11, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Janssens, I.A.; Deng, Y.; He, X.J.; Liu, L.L.; Yi, Y.; Xiao, N.W.; Wang, X.D.; Li, C.; et al. Divergent rhizosphere and non-rhizosphere soil microbial structure and function in long-term warmed steppe due to altered root exudation. Glob. Change Biol. 2024, 30, e17111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.K.; Quince, C.; Macdonald, C.A.; Khachane, A.; Thomas, N.; Abu Al-Soud, W.; Sorensen, S.J.; He, Z.L.; White, D.; Sinclair, A.; et al. Loss of microbial diversity in soils is coincident with reductions in some specialized functions. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 2408–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, S.; Wang, J.M.; Wei, G.H.; Chen, W.M.; Lu, Y.H. Dominant role of abundant rather than rare bacterial taxa in maintaining agro-soil microbiomes under environmental disturbances. Chemosphere 2019, 235, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.Y.; Zhang, W.J.; Yang, J.; Lin, Y.S.; Yu, Z.; Lin, S.J. Biogeographic patterns of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in three subtropical bays resulting from selective and neutral processes. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jousset, A.; Bienhold, C.; Chaztzinotas, A.; Gallien, L.; Gobet, A.; Kurm, V.; Küsel, K.; Rillig, M.C.; Rivett, D.W.; Salles, J.F.; et al. Where less may be more: How the rare biosphere pulls ecosystems strings. ISME J. 2017, 11, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Nuccio, E.E.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, N.; Xue, K.; Cohan, F.M.; Zhou, J.; Sun, B.D. Differentiation strategies of soil rare and abundant microbial taxa in response to changing climatic regimes. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; Ou, J.; Li, L.; Yang, S.; He, Y.; Li, C. Community composition and ecological function analysis of endophytic fungi in the roots of Rhododendron simsii in Pinus massoniana forest in Central Guizhou. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, L.; Niu, W.Q.; Li, G.C.; Du, Y.D.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Siddique, K.H.M. Crucial role of rare taxa in preserving bacterial community stability. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 35, 1397–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Ma, S.; Tian, D.I.; Xiao, W.; Jiang, L.; Xing, A.; Zou, A.; Zhou, L.; Shen, H.; Zheng, C.; et al. Patterns and determinants of soil microbial residues from tropical to boreal forests. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 151, 108059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ye, F.; Wu, S.; Wu, J.; Yan, J.; Xu, K.; Hong, Y. Biogeographic pattern of bacterioplanktonic community and potential function in the Yangtze River: Roles of abundant and rare taxa. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 747, 141335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.G.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Liang, Y.T. Drivers of microbially and plant-derived carbon in topsoil and subsoil. Glob. Change Biol. 2023, 29, 6188–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.W.; Liu, C.Y.; Yuan, J.Q.; Li, P.F.; Guo, Q.; Wang, X.D.; Lai, H.X. Effects of different vegetation on soil microorganisms and carbon cycling genes in mining areas. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2025, 44, 1029–1045. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Mao, Z.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Han, J.; Wanag, H.; He, W. Impacts of climate change and afforestation on vegetation dynamic in the Mu Us Desert, China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 108020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Agrochemical Analysis of Soil; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Sheng, M.Y.; Xiong, K.N.; Wang, L.J.; Li, X.N.; Li, R.; Tian, X.J. Response of soil physical and chemical properties to rocky desertification succession in South China Karst. Carbonates Evaporites 2018, 33, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Paustian, K.; Elliott, E.T.; Combrink, C. Soil structure and organic matter I. distribution of aggregate-size classes and aggregate-associated carbon. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.S.; Lin, Q.M.; Huang, Q.Y. Determination of soil microbial biomass and its application. In China Meteorological; Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ghani, A.; Dexter, M.; Perrott, K.W. Hot-water extractable carbon in soils: A sensitive measurement for determining impacts of fertilization, grazing and cultivation. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 1231–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Zhou, Y.C.; Wang, S.J.; Huang, X.F. Change in SOC content in a small karst basin for the past 35 years and its influencing factors. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 64, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, S.; Chen, W.M.; Wei, G.H. Biogeography and ecological diversity patterns of rare and abundant bacteria in oil-contaminated soils. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5305–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.B.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zhang, F.G. Abundant and rare bacteria possess different diversity and function in crop monoculture and rotation systems across regional farmland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 171, 108742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chai, Y.; Xie, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Hao, S.; Gai, J.; Chen, Y. Responses of soil microbial diversity, network complexity and multifunctionality to three land-use changes. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 859, 160255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J.; Dong, W.; You, Y.; Yang, Y. Mechanism, potential and regulation of carbon sequestration and sink enhancement in ecological restoration of mining areas in the Loess Plateau. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 51, 502–513. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.L.; Paul, E.A. The significance of soil microbial biomass estimations. In Soil Biochemistry; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 357–398. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, M.; Eisenhauer, N.; Sierra, C.A.; Bessler, H.; Engels, C.; Griffiths, R.I.; Mellado-Vázquez, P.G.; Malik, A.A.; Roy, J.; Scheu, S.; et al. Plant diversity increases soil microbial activity and soil carbon storage. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Luo, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, H.; Peng, H.; Sheng, M.; Xu, F.; Xu, H. Effects of environmental factors on soil bacterial community structure and diversity in different contaminated districts of Southwest China mine tailings. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 802, 149899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Ma, J.; He, H.; Zhu, Y.; You, Y.; Chen, F. Effects of land reclamation on soil microbial community structure and function in the Huang-Huai plain mining area. Coal Sci. Technol. 2023, 51, 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Cheng, S.; Fang, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y. Responses of soil fungal taxonomic attributes and enzyme activities to copper and cadmium co-contamination in paddy soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.M.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.G.; Sun, W.M.; Wang, Y.F.; Long, S.X.; He, X.T.; Lin, Z.; Liang, Z.; et al. Rhizobacteria communities reshaped by red mud based passivators is vital for reducing soil Cd accumulation in edible amaranth. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 826, 154002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastida, F.; Hernández, T.; Albaladejo, J.; García, C. Phylogenetic and functional changes in the microbial community of long-term restored soils under semiarid climate. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2013, 65, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; He, Z.; Chen, L.; Yang, R.; Du, J. Efficiency of biochar, nitrogen addition, and microbial agent amendments in remediation of soil properties and microbial community in Qilian Mountains mine soils. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 11, 9318–9331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Hao, M.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y. Effects of vegetation restoration on soil bacterial communities, enzyme activities, and nutrients of reconstructed soil in a mining area on the Loess Plateau, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Karwautz, C.; Andrei, S.; Klingl, A.; Pernthaler, J.; Lueders, T. A novel Methylomirabilota methanotroph potentially couples methane oxidation to iodate reduction. mLife 2022, 1, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.X.; Tao, X.F.; Jia, R.; Hou, Y.R.; Li, Z.W.; Dong, Y.; Li, B.; Zhu, J. Effects of two rice-shrimp co-cultural models on soil organic nitrogen mineralization. J. South. Agric. 2022, 53, 1357–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Dou, Y.; Huang, Y.; An, S. Links between soil fungal diversity and plant and soil properties on the Loess Plateau. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.J.; Yao, H.; Liu, H.; Tian, M.R. Evolution characteristics of soil nutrients and microorganisms during alfalfa restoration of mining area in Yanshan Mountain. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 270–279. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Man, H.; Han, J.; Jia, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Shi, G. Soil Microorganism Interactions under Biological Fumigations Compared with Chemical Fumigation. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Bai, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, B. Different stochastic processes regulate bacterial and fungal community assembly in estuarine wetland soils. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2022, 167, 108586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, S.; Or, D. The chosen few—Variations in common and rare soil bacteria across biomes. ISME J. 2021, 15, 3315–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Feng, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Yu, X.; Ren, S. Rare soil bacteria are more responsive in desertification restoration than abundant bacteria. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 33323–33334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shi, J.S.; Gao, J.; Li, P.; Ren, Y.L.; Wang, L.Y. Effects of Long-Term Application of Organic Fertilizer on Rare and Abundant Bacterial Sub-Communities in Greenhouse Tomato Soil. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2023, 56, 3615–3628. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).