Effect of Hydropriming on Seedling Growth of Different Bambara Groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.) Landraces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. Seed Priming and Sowing
2.3. Experimental Design and Greenhouse Conditions
2.4. Emergence Assessment
2.5. Water Imbibition
2.6. Seedling Growth and Morphological Measurements
2.7. Root and Shoot Biomass Allocation
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Imbibition Responses of BGN Genotypes
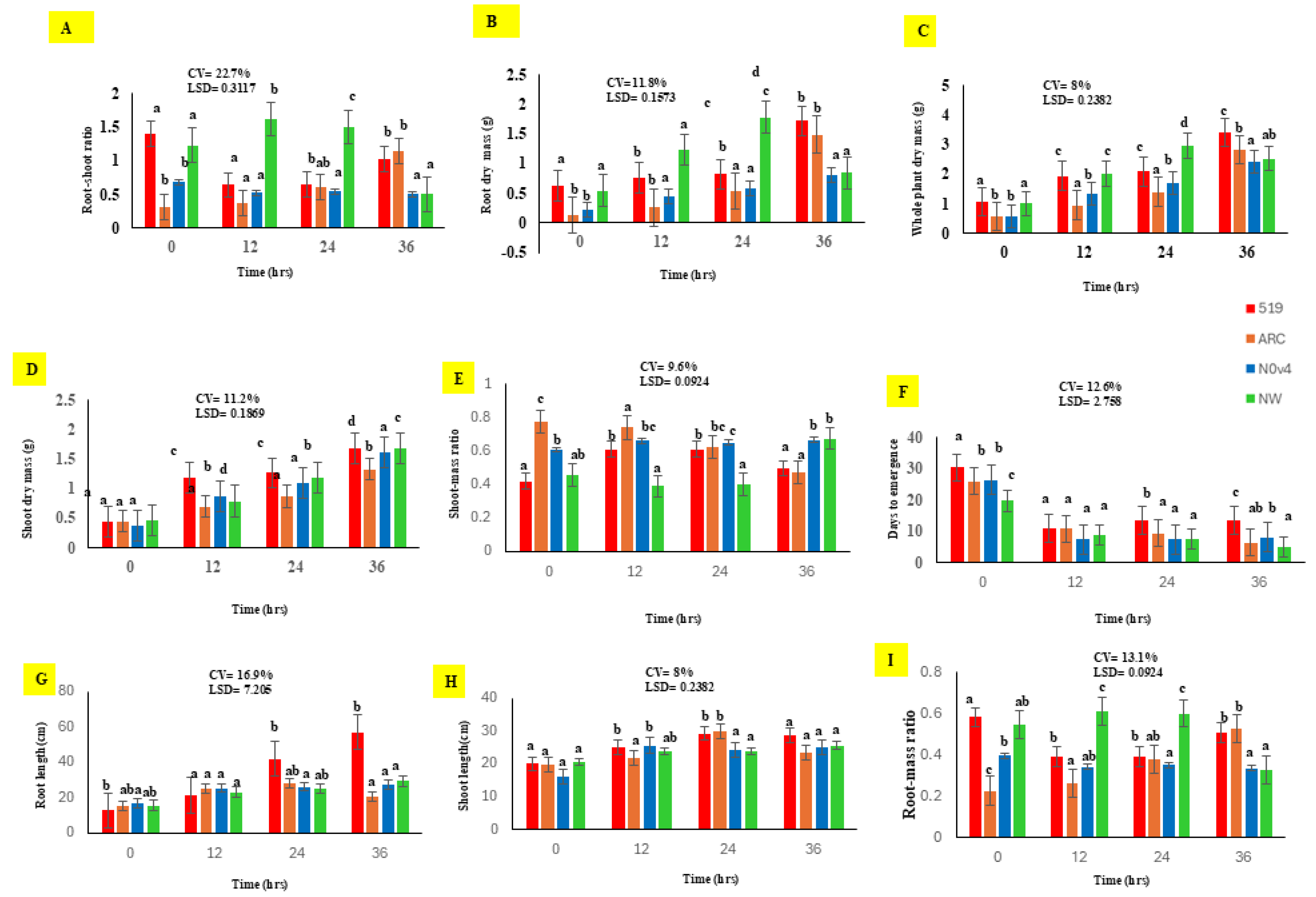
3.2. Effects of Priming Duration on Seedling Growth of BGN Genotypes
3.3. Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.4. Pearson Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mayes, S.; Ho, W.K.; Chai, H.H.; Gao, X.; Kundy, A.C.; Mateva, K.I.; Zahrulakmal, M.; Hahiree, M.K.I.M.; Kendabie, P.; Licea, L.C. Bambara groundnut: An exemplar underutilised legume for resilience under climate change. Planta 2019, 250, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubaiwa, J.; Fogliano, V.; Chidewe, C.; Bakker, E.J.; Linnemann, A.R. Utilization of bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.) for sustainable food and nutrition security in semi-arid regions of Zimbabwe. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.L.; Azam-Ali, S.; Goh, E.V.; Mustafa, M.; Chai, H.H.; Ho, W.K.; Mayes, S.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Azam-Ali, S.; Massawe, F. Bambara groundnut: An underutilized leguminous crop for global food security and nutrition. Front. Nutr. 2020, 7, 601496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT (FAOSTAT—Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations). Statistical Databases; FAOSTAT—Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Majola, N.G.; Gerrano, A.S.; Shimelis, H. Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea [L.] Verdc.) production, utilisation and genetic improvement in Sub-Saharan Africa. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumare, A.; Diedhiou, A.G.; Kane, A. Bambara groundnut: A neglected and underutilized climate-resilient crop with great potential to alleviate food insecurity in sub-Saharan Africa. J. Crop Improv. 2022, 36, 747–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanrewaju, O.S.; Oyatomi, O.; Babalola, O.O.; Abberton, M. Breeding potentials of Bambara groundnut for food and nutrition security in the face of climate change. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 798993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulu, N.; Modi, A. A preliminary study to determine water stress tolerance in wild melon (Citrullus lanatus L.). S. Afr. J. Plant Soil 2010, 27, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Khan, M.M.H.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ramlee, S.I.; Jusoh, M.; Al-Mamun, M. Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea L. Verdc.): A crop for the new millennium, its genetic diversity, and improvements to mitigate future food and nutritional challenges. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Korres, N.E.; Khan, M.D.; Nizami, A.-S.; Deeba, F.; Ali, I.; Hussain, H. Advances in the concept and methods of seed priming. In Priming and Pretreatment of Seeds and Seedlings: Implication in Plant Stress Tolerance and Enhancing Productivity in Crop Plants; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 11–41. [Google Scholar]
- Marthandan, V.; Geetha, R.; Kumutha, K.; Renganathan, V.G.; Karthikeyan, A.; Ramalingam, J. Seed priming: A feasible strategy to enhance drought tolerance in crop plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obura, M.; Oballim, G.; Ochuodho, J.; Maina, F.; Anjichi, V. Effect of Phosphorus Fertilizer Rates and Seed Priming Treatments on Seed Quality of Bambara Groundnut. Agric. Food Sci. J. Ghana 2021, 14, 1337–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Johnson, R.; Puthur, J.T. Seed priming: A cost-effective strategy to impart abiotic stress tolerance. In Plant Performance Under Environmental Stress: Hormones, Biostimulants and Sustainable Plant Growth Management; Springer: Singapore, 2021; pp. 459–480. [Google Scholar]
- Samota, M.K.; Sasi, M.; Awana, M.; Yadav, O.P.; Amitha Mithra, S.; Tyagi, A.; Kumar, S.; Singh, A. Elicitor-induced biochemical and molecular manifestations to improve drought tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.) through seed-priming. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarrar, H.; El-Keblawy, A.; Ghenai, C.; Abhilash, P.; Bundela, A.K.; Abideen, Z.; Sheteiwy, M.S. Seed enhancement technologies for sustainable dryland restoration: Coating and scarification. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabassum, T.; Farooq, M.; Ahmad, R.; Zohaib, A.; Wahid, A.; Shahid, M. Terminal drought and seed priming improves drought tolerance in wheat. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2018, 24, 845–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, I.; Javed, T.; Amirkhani, M.; Taylor, A.G. Modern seed technology: Seed coating delivery systems for enhancing seed and crop performance. Agriculture 2020, 10, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, B.-u.; Ali, A.; Akram, M.; Mahmood, I.; Arshadullah, M.; Tabassam, T. Sunflower seed-priming with phosphate salts and seedling growth under salt stress. Asian Res. J. Agric. 2017, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjan, A.S.; Dhanelappagol, M.; Jolli, R. Seed quality enhancement through seed priming in pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.]. Legume Res.-Int. J. 2017, 40, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumeera, B.; Swapnil, M.; Chaurasia, A.; Ramteke, P. Effect of seed priming with inorganics on growth, yield and physiological parameters of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) under drought. Pharma Innov. J. 2018, 7, 411–414. [Google Scholar]
- Perera, D.; Devkota, L.; Garnier, G.; Panozzo, J.; Dhital, S. Hard-to-cook phenomenon in common legumes: Chemistry, mechanisms and utilisation. Food Chem. 2023, 415, 135743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, J.D.; Bradford, K.J.; Hilhorst, H.W.; Nonogaki, H.; Bewley, J.D.; Bradford, K.J.; Hilhorst, H.W.; Nonogaki, H. Environmental regulation of dormancy and germination. In Seeds: Physiology of Development, Germination and Dormancy, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 299–339. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulkareem, Y.; Muhammad, A.; Alaba, N.; Shuaib, M.; Musa, A. Effect of seed priming using potassium dihydrogen phosphate on seedlings emergence, growth and yield of Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L) Verdc.). J. Agric. Environ. 2024, 20, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchie, J.; Adu-Dapaah, H.; Sarkodie-Addo, J.; Asare, E.; Agyemang, A.; Addy, S.; Donkoh, J. Effect of seed priming on seedling emergence and establishment of four bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea L. Verdc.) Landraces. J. Agron. 2010, 9, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bradford, K.J. Water relations in seed germination. In Seed Development and Germination; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 351–396. [Google Scholar]
- Louf, J.-F.; Zheng, Y.; Kumar, A.; Bohr, T.; Gundlach, C.; Harholt, J.; Poulsen, H.F.; Jensen, K.H. Imbibition in plant seeds. Phys. Rev. E 2018, 98, 042403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upretee, P.; Bandara, M.S.; Tanino, K.K. The Role of Seed Characteristics on Water Uptake Preceding Germination. Seeds 2024, 3, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandizvo, T.; Odindo, A. Seed coat structural and imbibitional characteristics of dark and light coloured Bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea L.) landraces. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, P.A.; Mir, R.; Zargar, S.M.; Rani, S.; Fatima, S.; Shafi, S.; Zaffar, A. What makes the beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) soft: Insights into the delayed cooking and hard to cook trait. Proc. Indian Natl. Sci. Acad. 2022, 88, 142–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.K.; Singh, R.; Tripathi, S.; Devi, R.S.; Srivastava, P.; Singh, P.; Kumar, A.; Bhadouria, R. Seed priming: State of the art and new perspectives in the era of climate change. In Climate Change and Soil Interactions; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 143–170. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, L.; Zeng, P.; He, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Identification of genes involved in rice seed priming in the early imbibition stage. Plant Biol. 2017, 19, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostoláni, D.; Ndiffo Yemeli, G.B.; Švubová, R.; Kyzek, S.; Machala, Z. Physiological responses of young pea and barley seedlings to plasma-activated water. Plants 2021, 10, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.S.; Elozeiri, A.A. Metabolic processes during seed germination. Adv. Seed Biol. 2017, 2017, 141–166. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, C.G.; de Castro, R.D.; Neto, V.G.; Marques, A.C.; Takahashi, D.; Fernandez, L.G.; Cruz, C.R.; Toorop, P.; Aflitos, S.A.; Hilhorst, H.W. Osmopriming-associated genes in Poincianella pyramidalis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2021, 183, 104345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghassemi-Golezani, K. Effects of Hydropriming Duration and Limited Irrigation on Field Performance of Chickpea K. Ghassemi-Golezani, P. Sheikhzadeh-Mosaddegh and M. Valizadeh Faculty of Agriculture, University of Tabriz, Tabriz, Iran. Res. J. Seed Sci. 2008, 1, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bester, A.U.; Shimoia, E.P.; Da-Silva, C.J.; Posso, D.A.; Carvalho, I.R.; Corrêa, F.M.; de Oliveira, A.C.; do Amarante, L. Enhancing stress resilience in soybeans (Glycine max): Assessing the efficacy of priming and cross-priming for mitigating water deficit and waterlogging effects. Funct. Plant Biol. 2024, 51, FP24064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Mayes, S.; Sparkes, D.L. Preanthesis biomass accumulation of plant and plant organs defines yield components in wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 81, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmick, M.; Duary, B.; Biswas, P.; Rakshit, A.; Adhikari, B. Seed priming, row spacing and foliar nutrition in relation to growth and yield of chickpea under rainfed condition. SATSA Mukhapatra-Annu. Tech. Issue 2013, 17, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Shariatmadari, M.H.; Parsa, M.; Nezami, A.; Kafi, M. The effects of hormonal priming on emergence, growth and yield of chickpea under drought stress in glasshouse and field. Biosci. Res. 2017, 14, 34–41. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Q.; Tian, T.; Han, X.; Xu, J.; Chai, Y.; Mo, J.; Lei, M.; Wang, L.; Yue, M. The relationships between biomass allocation and plant functional trait. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 102, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monson, R.K.; Trowbridge, A.M.; Lindroth, R.L.; Lerdau, M.T. Coordinated resource allocation to plant growth–defense tradeoffs. New Phytol. 2022, 233, 1051–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
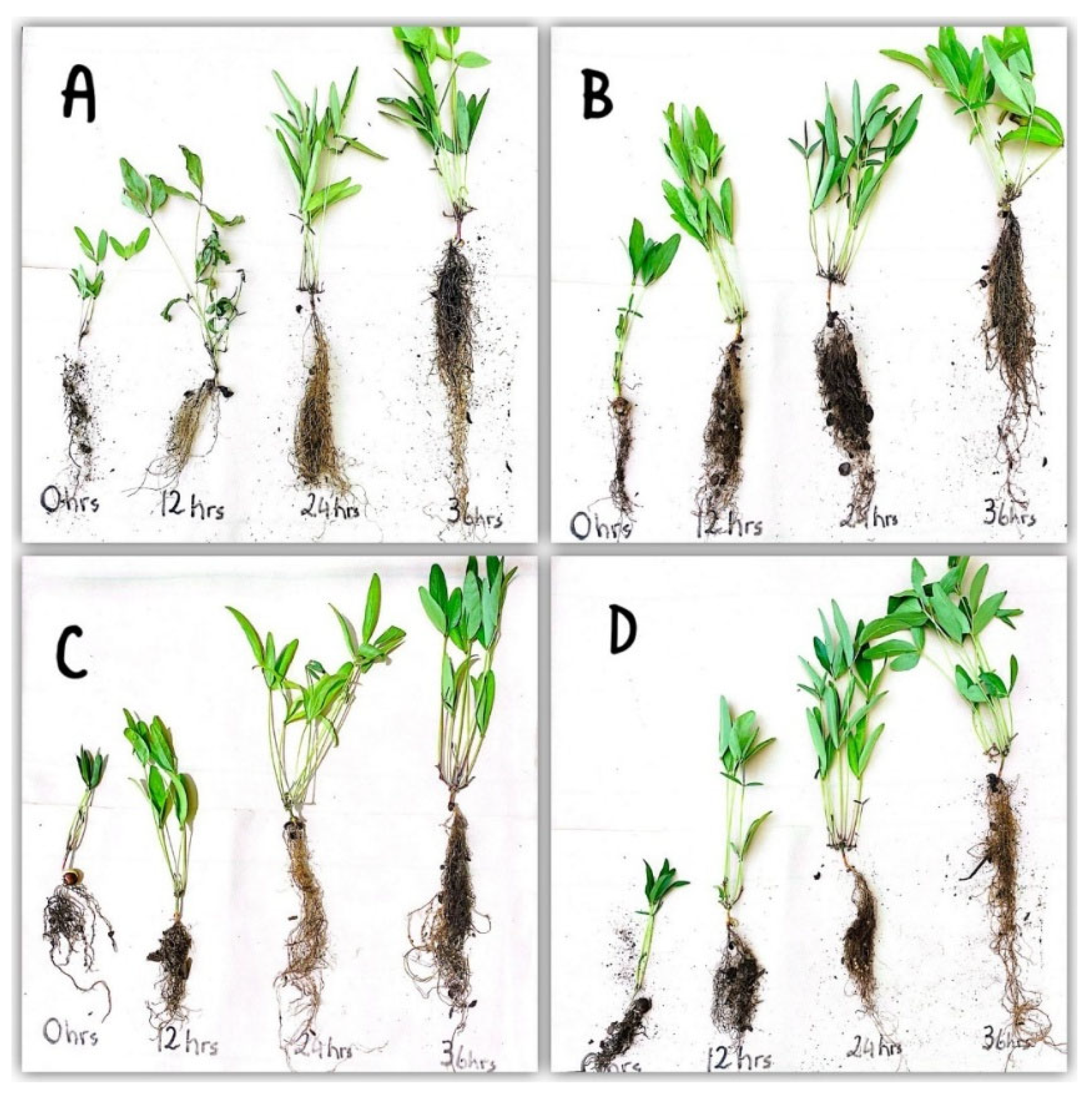





| Genotype | 0 | 12 | 24 | 36 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARC | 10.5 | 10.7 | 11.5 | 13.5 |
| B | 8.7 | 11.6 | 14.5 | 17.3 |
| NW | 10.1 | 11.2 | 11.8 | 13.5 |
| Nov4 | 4.9 | 5.9 | 6.6 | 11.1 |
| Source of Variation | df | DE | SL | RL | LL | RFM | SFM | WPFM | RDM | SDM | WPDM | RSR | SMR | RMR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype (G) | 3 | 98.139 ** | 19.833 * | 315.50 ** | 3.951 ** | 1.970 ** | 15.419 ** | 18.072 ** | 0.957 ** | 0.195 ** | 1.728 ** | 1.108 ** | 0.086 ** | 0.086 ** |
| Time (T) | 3 | 831.694 ** | 141.722 ** | 807.93 ** | 13.076 ** | 8.802 ** | 18.757 ** | 52.598 ** | 1.523 ** | 2.739 ** | 8.322 ** | 0.035 * | 0.003 NS | 0.003 NS |
| G × T | 9 | 11.083 * | 16.037 * | 221.37 ** | 1.001 * | 0.679 ** | 1.394 ** | 1.593 ** | 0.463 ** | 0.039 * | 0.408 ** | 0.518 ** | 0.044 ** | 0.044 ** |
| Residual | 32 | 2.750 NS | 6.963 NS | 18.77 NS | 0.322 NS | 0.012 NS | 0.062 NS | 0.067 NS | 0.009 NS | 0.013 NS | 0.021 NS | 0.035 NS | 0.003 NS | 0.003 NS |
| 0 h | 12 h | 24 h | 36 h | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 | PC1 | PC2 | PC3 |
| WPDM | 0.328 | −0.170 | −0.035 | 0.318 | −0.193 | 0.107 | 0.372 | 0.073 | 0.118 | 0.372 | 0.073 | 0.118 |
| RSR | 0.285 | −0.269 | −0.167 | 0.300 | −0.032 | −0.313 | 0.324 | −0.244 | 0.023 | 0.324 | −0.244 | 0.023 |
| RDM | 0.310 | −0.219 | −0.110 | 0.331 | −0.098 | −0.134 | 0.369 | −0.101 | 0.091 | 0.369 | −0.101 | 0.091 |
| SL | 0.286 | 0.131 | 0.370 | 0.035 | −0.550 | 0.134 | 0.204 | 0.381 | 0.181 | 0.204 | 0.381 | 0.181 |
| RL | −0.306 | −0.150 | 0.274 | −0.269 | 0.022 | −0.399 | 0.263 | 0.311 | 0.232 | 0.263 | 0.311 | 0.232 |
| WPFM | 0.308 | 0.236 | −0.001 | 0.332 | 0.120 | 0.099 | 0.265 | 0.221 | −0.438 | 0.265 | 0.221 | −0.438 |
| LL | 0.293 | 0.227 | 0.219 | 0.193 | 0.437 | −0.189 | 0.005 | 0.436 | −0.294 | 0.005 | 0.436 | −0.294 |
| RFM | 0.283 | −0.251 | 0.222 | 0.308 | −0.253 | −0.001 | −0.274 | 0.229 | 0.398 | −0.274 | 0.229 | 0.398 |
| SFM | 0.191 | 0.414 | −0.128 | 0.297 | 0.262 | 0.128 | 0.271 | 0.204 | −0.445 | 0.271 | 0.204 | −0.445 |
| DE | 0.026 | 0.247 | −0.633 | 0.042 | 0.385 | 0.463 | 0.265 | 0.174 | 0.497 | 0.265 | 0.174 | 0.497 |
| SMR | −0.254 | 0.322 | 0.186 | −0.312 | 0.099 | 0.247 | −0.331 | 0.229 | −0.054 | −0.331 | 0.229 | −0.054 |
| RMR | 0.254 | −0.322 | −0.186 | 0.312 | −0.099 | −0.247 | 0.331 | −0.229 | 0.054 | 0.331 | −0.229 | 0.054 |
| SDM | 0.272 | 0.172 | 0.383 | 0.102 | −0.272 | 0.530 | −0.039 | 0.464 | 0.059 | −0.039 | 0.464 | 0.059 |
| Eigenvalue | 8.216 | 3.894 | 1.891 | 8.447 | 3.129 | 2.425 | 6.911 | 4.571 | 1.518 | 6.911 | 4.571 | 1.518 |
| Variability (%) | 58.685 | 27.811 | 13.504 | 60.332 | 22.350 | 17.318 | 53.163 | 35.162 | 11.675 | 53.163 | 35.162 | 11.675 |
| Cumulative (%) | 58.685 | 86.496 | 100 | 60.332 | 82.682 | 100 | 53.163 | 88.325 | 100 | 53.163 | 88.325 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chisa, A.L.; Mandizvo, T.; Odindo, A.; Mafongoya, P. Effect of Hydropriming on Seedling Growth of Different Bambara Groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.) Landraces. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061301
Chisa AL, Mandizvo T, Odindo A, Mafongoya P. Effect of Hydropriming on Seedling Growth of Different Bambara Groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.) Landraces. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061301
Chicago/Turabian StyleChisa, Anne Linda, Takudzwa Mandizvo, Alfred Odindo, and Paramu Mafongoya. 2025. "Effect of Hydropriming on Seedling Growth of Different Bambara Groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.) Landraces" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061301
APA StyleChisa, A. L., Mandizvo, T., Odindo, A., & Mafongoya, P. (2025). Effect of Hydropriming on Seedling Growth of Different Bambara Groundnut (Vigna subterranea (L.) Verdc.) Landraces. Agronomy, 15(6), 1301. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061301








