Enhancing Soil Phosphorus and Potassium Availability in Tea Plantation: The Role of Biochar, PGPR, and Phosphorus- and Potassium-Bearing Minerals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Plant and Soil Sample Collection
2.4. Plant Analysis
2.5. Soil Chemical Properties Analysis
2.6. Microbial DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing Analysis
2.7. Functional Gene Analysis of Pyrroloquinoline Quinone Biosynthesis Protein C (PqqC)
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
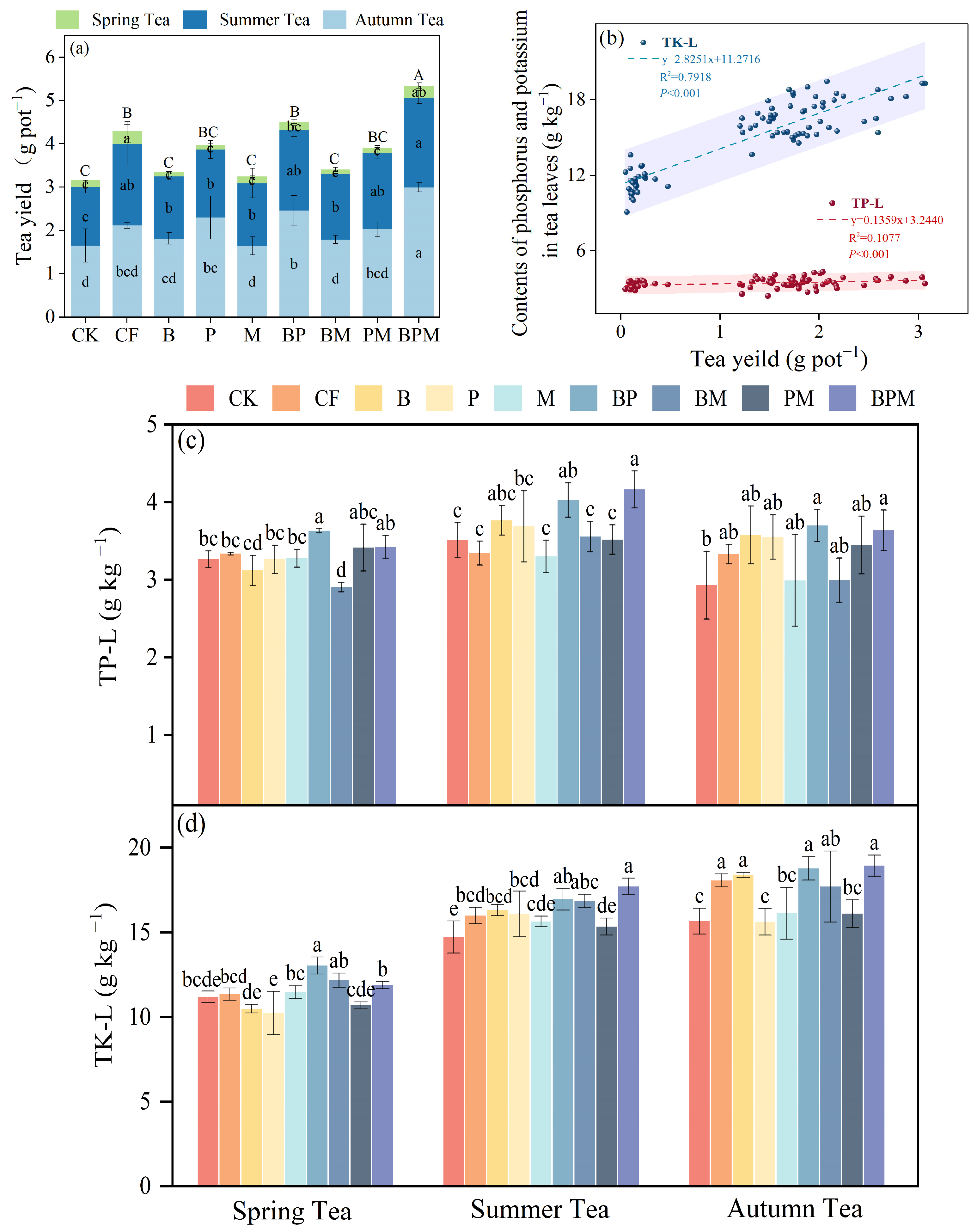
3.1. Tea Yield and Phosphorus and Potassium Content
3.2. Soil Phosphorus and Potassium Availability
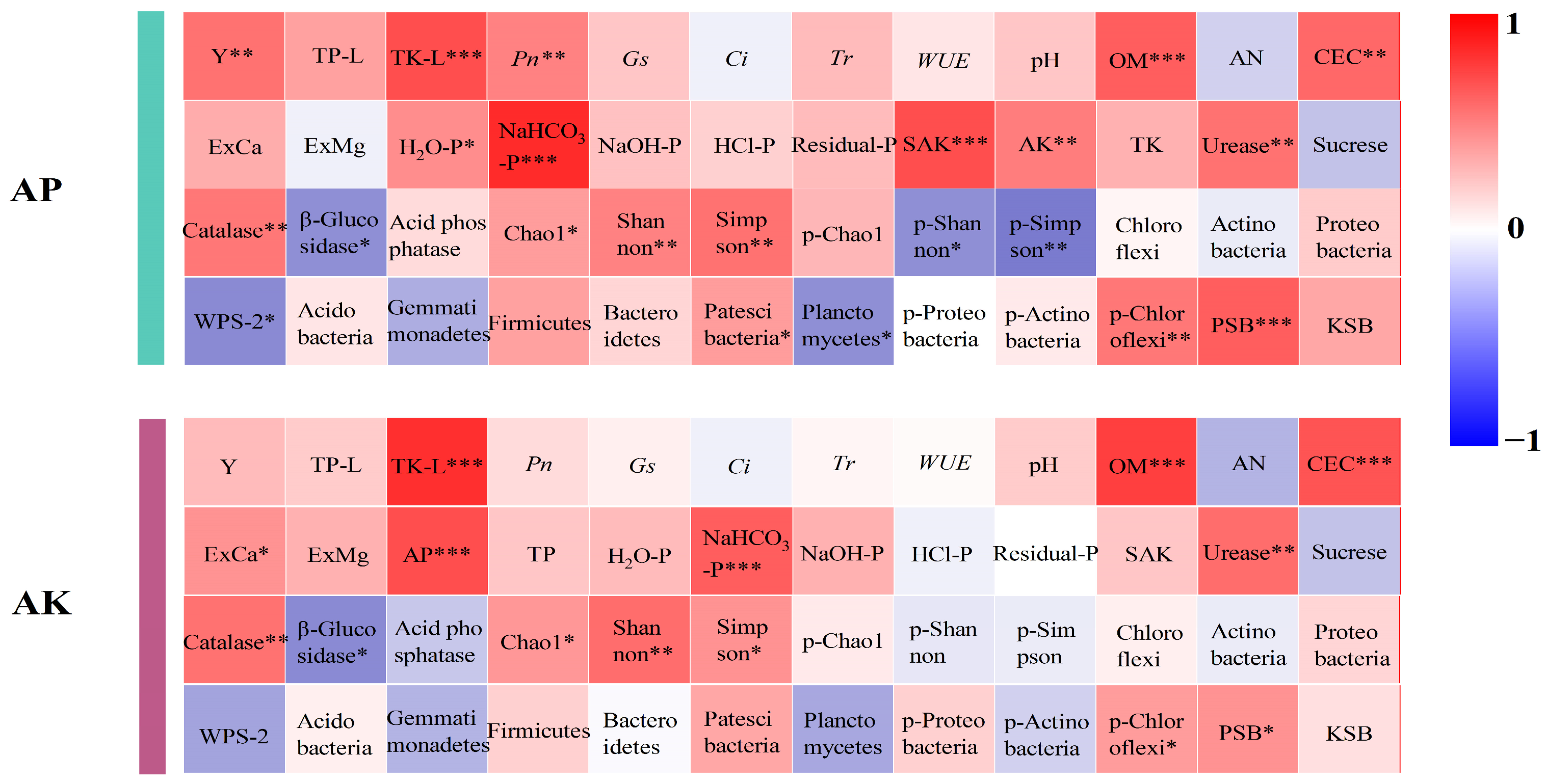
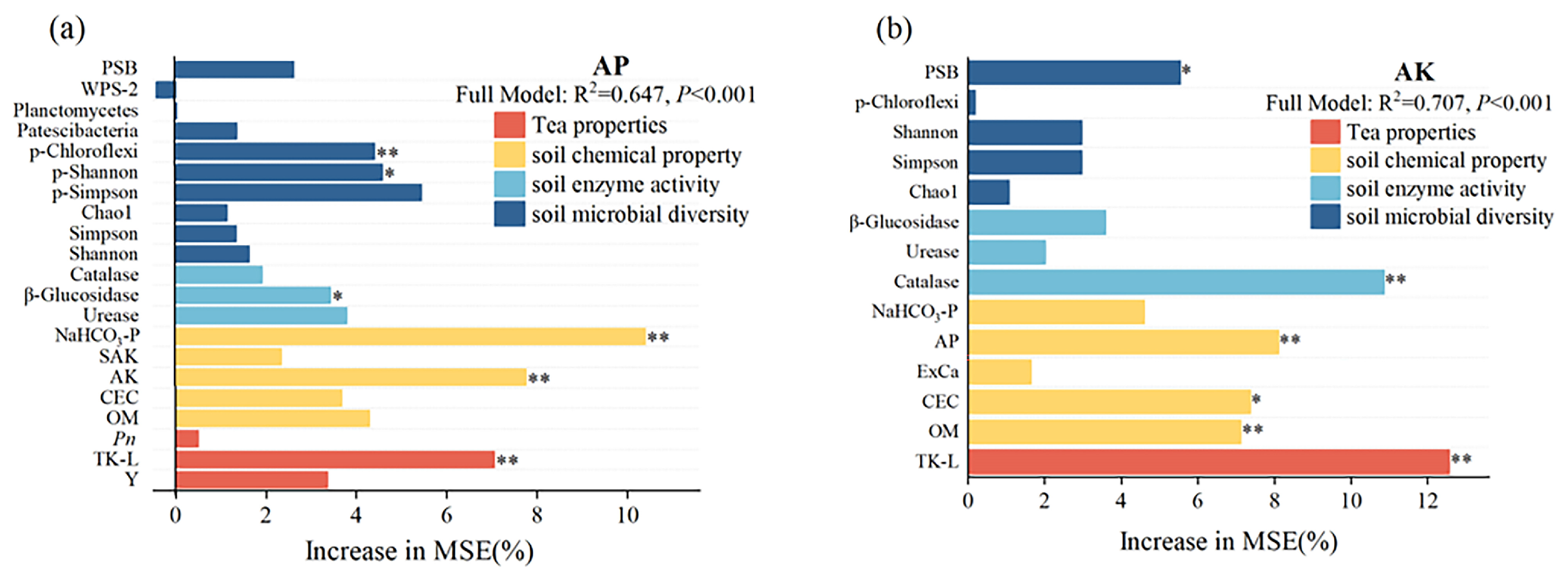
3.3. Effect of Soil Properties on the Availability of Soil Phosphorus and Potassium
4. Discussion
4.1. Co-Application of Biochar, PGPR, and Minerals Improved Tea Yield
4.2. Co-Application of Biochar, PGPR, and Minerals Improves Phosphorus and Potassium Availability in Soil
4.3. Key Factors Driving the Availability of Phosphorus and Potassium in Tea Plantations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, F.; Deng, X.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Li, C.; Song, Q.; He, Y.; Niu, S. Integrated transcriptome and metabolome provide insights into flavonoid biosynthesis in ‘P113’, a new purple tea of Camellia tachangensis. Beverage Plant Res. 2023, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, J.; Aryal, J.; Guidry, L.; Adhikari, A.; Chen, Y.; Sriwattana, S.; Prinyawiwatkul, W. Tea Quality: An Overview of the Analytical Methods and Sensory Analyses Used in the Most Recent Studies. Foods 2024, 13, 3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Geng, Y.; Liang, T. Optimization of reduced chemical fertilizer use in tea gardens based on the assessment of related environmental and economic benefits. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, L.; Li, X.; Song, Y.H.; Li, J.W.; Palansooriya, K.N. Effects of Tea Plant Varieties with High- and Low-Nutrient Efficiency on Nutrients in Degraded Soil. Plants 2023, 12, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Pan, W.K.; Tang, R.; Ma, Q.X.; Zhou, J.J.; Zheng, N.; Wang, J.; Sun, T.; Wu, L.H. Effects of balanced and unbalanced fertilisation on tea quality, yield, and soil bacterial community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 175, 104442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishanth, D.; Biswas, D.R. Kinetics of phosphorus and potassium release from rock phosphate and waste mica enriched compost and their effect on yield and nutrient uptake by wheat (Triticum aestivum). Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 3342–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, B.B.; Sarkar, B.; Maity, A.; Chari, M.S.; Banerjee, A.; Biswas, D.R. Low-grade silicate minerals as value-added natural potash fertilizer in deeply weathered tropical soil. Geoderma 2023, 433, 116433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Long, C.M.; Xu, Y.; Han, L.Z. Molecular mechanism of Tsukamurella tyrosinosolvens strain P9 in response to root exudates of peanut. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.W.; Liu, X.R.; Shi, Z.W.; Liu, L.; Fatima, M.; Wang, Z.G.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.Y. Enhancement of the utilization of coal gangue as mineral fertilizers by the thermophilic bacterium. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Z.Y.; Liu, H.G. Modification of Rhizosphere Microbial Communities: A Possible Mechanism of Plant Growth Promoting Rhizobacteria Enhancing Plant Growth and Fitness. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 920813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.B.; Tang, Y.X.; Ma, J.W.; Zhang, W.L.; Liao, S.Y.; Cui, S.Y.; Ye, Z.Q.; Liu, D. Effects of biochar and inorganic amendments on soil fertility, tea yield, and quality in both Pb-Cd-contaminated and acidified tea plantations. J. Soil. Sediment 2023, 23, 3275–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.X.; Liu, X.L.; Yan, Q.X.; Liang, G.Y.; Wang, D.P. Research on heavy metal enrichment and transportation in tea plant-soil systems of different varieties. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Riaz, M.; Tang, X.F.; Yan, L.; El-Desouki, Z.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, X.L.; Cuncang, J. Insight into mechanisms of biochar-fertilizer induced of microbial community and microbiology of nitrogen cycle in acidic soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 336, 117602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodi, L.A.; Klaic, R.; Bortoletto-Santos, R.; Ribeiro, C.; Farinas, C.S. Unveiling the Solubilization of Potassium Mineral Rocks in Organic Acids for Application as K-Fertilizer. Appl. Biochem. Biotech. 2022, 194, 2431–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhu, C.; Kong, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ning, Y.; Tian, W.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; et al. Biochar Application Alleviated Rice Salt Stress via Modifying Soil Properties and Regulating Soil Bacterial Abundance and Community Structure. Agronomy 2022, 12, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.P.; Lai, C.; Zeng, G.M.; Liang, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, J.J.; Dai, J.; Li, X.D.; Liu, J.F.; Chen, M.; et al. The interactions of composting and biochar and their implications for soil amendment and pollution remediation: A review. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 754–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Yang, H.; Shen, Z.Z.; Ye, J.R. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Potassium-Solubilizing Mechanism of Bacillus aryabhattai SK1-7. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 722379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, S.; Baloch, A.; Qasim, M.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, X.L.; Li, Y.X.; Khalid, S.; Jiang, C.C. Unearthing the soil-bacteria nexus to enhance potassium bioavailability for global sustainable agriculture: A mechanistic preview. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 288, 127885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Mao, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Tao, B.; Qi, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Co-application of biochar and microbial inoculants increases soil phosphorus and potassium fertility and improves soil health and tomato growth. J. Soil Sediment 2023, 23, 947–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.J.; Li, T.; Li, L.L.; Miao, L.; Wei, W.; Wang, Z.A. Effects of Potassium-Solubilizing Bacteria Loaded Biochar on Soil Enzyme Activity and Microbial Community Structure. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2023, 60, 1531–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.Q.; Chi, S.Q.; Lin, C.Q.; Cai, C.; Yang, L.H.; Peng, K.M.; Huang, X.F.; Liu, J. Combination of biochar and AMF promotes phosphorus utilization by stimulating rhizosphere microbial co-occurrence networks and lipid metabolites of Phragmites. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 845, 157339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.R.; Jin, W.; Li, T.; Wei, W.; Li, C.J.; Miao, L.; Li, L.L. Screening of affinity phosphate-solubilizing bacteria from typical purple soil and its growth promoting effect. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 44, 21–26. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, W.; Li, T.; Zhang, T.R.; Jin, W.; Miao, L.; Li, C.J. Effect of Biochar lmmobilized Raoultella Ornithinolytica on the Availability of Phosphorus and Potassium in Purplish Soil. Chin. J. Soil. Sci. 2021, 52, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, P.; Shen, C.; Zou, Z.H.; Fu, J.Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.P.; Zhang, L.; Han, W.Y.; Fan, L.C. Biochar stimulates tea growth by improving nutrients in acidic soil. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 283, 110078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Hu, J.; He, Y.; Wang, H.; Deng, Q.; Mi, B.; Wu, F. Microwave-assisted pyrolysis of waste lignin to prepare biochar for Cu2+ highly-efficient adsorption: Performance, kinetics and mechanism resolution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 342, 127070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.T.; Peng, J.Y.; Huang, Y.; He, B.; Wang, X.L.; Gu, M.H. Effects of Soil Amendments on Soil Zn and Pb Bioavailability and Their Accumulation in Maize. SW Chin. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 28, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.D.; Wu, L.F.; Wang, X.K.; Zhang, S.H.; Cheng, M.H.; Feng, H.; Fan, J.L.; Zhang, F.C.; Xiang, Y.Z. Optimization of water and fertilizer management improves yield, water, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium uptake and use efficiency of cotton under drip fertigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R. Methods of Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.; Chen, Y.T.; Sun, W.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Diao, M.M.; Sun, J. Extreme soil salinity reduces N and P metabolism and related microbial network complexity and community immigration rate. Environ. Res. 2025, 264, 120361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil. Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sial, T.A.; Shaheen, S.M.; Lan, Z.; Korai, P.K.; Ghani, M.I.; Khan, M.N.; Syed, A.-u.-A.; Hussain Asghar Ali, M.N.; Rajpar, I.; Memon, M.; et al. Addition of walnut shells biochar to alkaline arable soil caused contradictory effects on CO2 and N2O emissions, nutrients availability, and enzymes activity. Chemosphere 2022, 293, 133476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhou, J.J.; Pan, W.K.; Sun, T.; Liu, M.J.; Tang, R.; Li, Z.J.; Ma, Q.X.; Wu, L.H. Effects of combined application of nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers on tea (Camellia sinensis) growth and fungal community. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 181, 104661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, A.M.; Bird, M.I.; Kay, G.; Muirhead, B. Soil properties, greenhouse gas emissions and crop yield under compost, biochar and co-composted biochar in two tropical agronomic systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 550, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Riaz, M.; Liu, B.; Xia, H.; El-desouki, Z.; Jiang, C.C. Two-year study of biochar: Achieving excellent capability of potassium supply via alter clay mineral composition and potassium-dissolving bacteria activity. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajeng, A.A.; Abdullah, R.; Ling, T.C.; Ismail, S. Adhesion of Bacillus salmalaya and Bacillus amyloliquefaciens oil palm kernel shell biochar: A physicochemical approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.N.; Wang, J.H. Removal of chlortetracycline from water by Bacillus cereus immobilized on Chinese medicine residues biochar. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 101930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Miao, J.B.; Saleem, M.; Zhang, H.N.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.M. Bacterial compatibility and immobilization with biochar improved tebuconazole degradation, soil microbiome composition and functioning. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 398, 122941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.X.; Li, F.M.; Chang, L.Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Wu, T.C.; Wu, Y.L.; Wang, Z.; Su, Y.L.; Yang, X.Y.; et al. Broad-spectrum applications of plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) across diverse crops and intricate planting systems. Microbiol. Spectr. 2025, 13, e01879-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Aharnmed, G.J.; Li, Z.X.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J.P.; Yan, P.; Zhang, L.P.; Han, W.Y. Freezing stress deteriorates tea quality of new flush by inducing photosynthetic inhibition and oxidative stress in mature leaves. Sci. Hortic. 2018, 230, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leakey, A.D.B.; Ferguson, J.N.; Pignon, C.P.; Wu, A.; Jin, Z.N.; Hammer, G.L.; Lobell, D.B. Water Use Efficiency as a Constraint and Target for Improving the Resilience and Productivity of C3 and C4 Crops. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 781–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.Z.; Bahar, M.M.; Sarkar, B.; Donne, S.W.; Ok, Y.S.; Palansooriya, K.N.; Kirkham, M.B.; Chowdhury, S.; Bolan, N. Biochar and its importance on nutrient dynamics in soil and plant. Biochar 2020, 2, 379–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilias, F.; Kalderis, D.; Richardson, C.; Barbayiannis, N.; Gasparatos, D. Biochar application as a soil potassium management strategy: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabir, E.; Kim, K.H.; Kwon, E.E. Biochar as a tool for the improvement of soil and environment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1324533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.Q.; Gu, W.Q.; Sun, Y.Y.; Wu, D.; Wang, Y.N.; Zhang, H.G.; Zhang, W.M.; Chen, W.F. The fate and supply capacity of potassium in biochar used in agriculture. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 902, 165969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, S.; Liu, B.; Lan, Y.B.; Han, L.; Hu, Y.X.; Dongye, G.; Cheng, K.; Liu, Z.Q.; Yang, F. Artificial humic acid coated ferrihydrite strengthens the adsorption of phosphate and increases soil phosphate retention. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 169870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.P.; Rong, X.M.; Zhou, X.; Fei, J.C.; Peng, J.W.; Luo, G.W. Biochar and organic fertilizer applications enhance soil functional microbial abundance and agroecosystem multifunctionality. Biochar 2024, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunito, T.; Hiruta, N.; Miyagishi, Y.; Sumi, H.; Moro, H. Changes in phosphorus fractions caused by increased microbial activity in forest soil in a short-term incubation study. Chem. Spec. Bioavailab. 2018, 30, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Mackay, A.D.; Tuohy, M.P.; Betteridge, K.; Sanches, I.D.; Inoue, Y. Potential for spectral indices to remotely sense phosphorus and potassium content of legume-based pasture as a means of assessing soil phosphorus and potassium fertility status. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 103–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, F.; Wang, F. Organic management improves soil P availability via increasing inorganic P solubilization in tea plantations. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 39, 104223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.C.; Liu, C.A.; Zhao, H.L.; Wang, Y. Changes of soil physico-chemical properties and enzyme activities in relation to grassland salinization. Eur. J. Soil. Biol. 2013, 55, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, B.G.; Averill, C.; Hawkes, C.V. Differences in fungal and bacterial physiology alter soil carbon and nitrogen cycling: Insights from meta-analysis and theoretical models. Ecol. Lett. 2013, 16, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.M.; Chen, F. Evaluating Status Change of Soil Potassium from Path Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.J.; Mou, R.; Wang, L.H.; Liu, J.R.; Tang, Y.X.; Chen, J.; Hedenec, P.; Xu, Z.F.; Tan, B.; Cui, X.L.; et al. Fertilization effects on soil organic matter chemistry. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 246, 106346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Riaz, M.; Xia, H.; Li, Y.X.; Wang, X.L.; Jiang, C.C. Four-year biochar study: Positive response of acidic soil microenvironment and citrus growth to biochar under potassium deficiency conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 813, 152515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Fernández, M.; Míguez-Montero, A.; Valentine, A. Phosphorus and Nitrogen Modulate Plant Performance in Shrubby Legumes from the Iberian Peninsula. Plants 2019, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamagoos, A.A.; Alharby, H.F.; Belal, E.E.; Khalaf, A.E.A.; Abdelfattah, M.A.; Rady, M.M.; Ali, E.F.; Mersal, G.A.M. Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria as a Panacea to Alleviate Stress Effects of High Soil CaCO3 Content in Phaseolus vulgaris with Special Reference to P-Releasing Enzymes. Sustainability 2021, 13, 7063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.L.; Zhao, J.; Yang, S.M.; Zhou, H.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhao, X.; Xing, G.X. Successive biochar amendment improves soil productivity and aggregate microstructure of a red soil in a five-year wheat-millet rotation pot trial. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Q.; Zhao, G.Y.; Wei, Y.H.; Dong, Y.H.; Hou, L.Y.; Jiao, R.Z. Isolation and screening of multifunctional phosphate solubilizing bacteria and its growth-promoting effect on Chinese fir seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Zhu, X.Y.; Ruan, C.J.; Wu, H.Q.; Chen, G.W.; Zhu, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, G. Micro-biophysical interactions at bacterium-mineral interfaces determine potassium dissolution. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 33, 103524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.S.; Gao, Q.; Yang, Y.F.; Hobbie, S.E.; Reich, P.B.; Zhou, J.Z. Soil enzymes as indicators of soil function: A step toward greater realism in microbial ecological modeling. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 1935–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Items | pH | Total Carbon (g kg−1) | Organic Matter (g kg−1) | Total Nitrogen (g kg−1) | Total Phosphorus (g kg−1) | Total Potassium (g kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil | 4.20 | - | 9.92 | 0.38 | 0.17 | 12.25 | 6.71 | 45.97 |
| Biochar | 7.21 | 751.46 | - | 0.73 | 1.24 | 6.26 | 169.74 | 5365.47 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, W.; Li, K.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Li, L.; Xie, J.; Li, T.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, S.; Pu, Y.; et al. Enhancing Soil Phosphorus and Potassium Availability in Tea Plantation: The Role of Biochar, PGPR, and Phosphorus- and Potassium-Bearing Minerals. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061287
Wei W, Li K, Li C, Wang S, Li L, Xie J, Li T, Zhou Z, Zhang S, Pu Y, et al. Enhancing Soil Phosphorus and Potassium Availability in Tea Plantation: The Role of Biochar, PGPR, and Phosphorus- and Potassium-Bearing Minerals. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061287
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Wen, Kunyu Li, Changjun Li, Siyu Wang, Lulu Li, Jinchuan Xie, Ting Li, Zijun Zhou, Shirong Zhang, Yulin Pu, and et al. 2025. "Enhancing Soil Phosphorus and Potassium Availability in Tea Plantation: The Role of Biochar, PGPR, and Phosphorus- and Potassium-Bearing Minerals" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061287
APA StyleWei, W., Li, K., Li, C., Wang, S., Li, L., Xie, J., Li, T., Zhou, Z., Zhang, S., Pu, Y., Jia, Y., Liu, X., Xu, X., & Wang, G. (2025). Enhancing Soil Phosphorus and Potassium Availability in Tea Plantation: The Role of Biochar, PGPR, and Phosphorus- and Potassium-Bearing Minerals. Agronomy, 15(6), 1287. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061287






