Biodegradation Potential of Glyphosate by Bacteria: A Systematic Review on Metabolic Mechanisms and Application Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
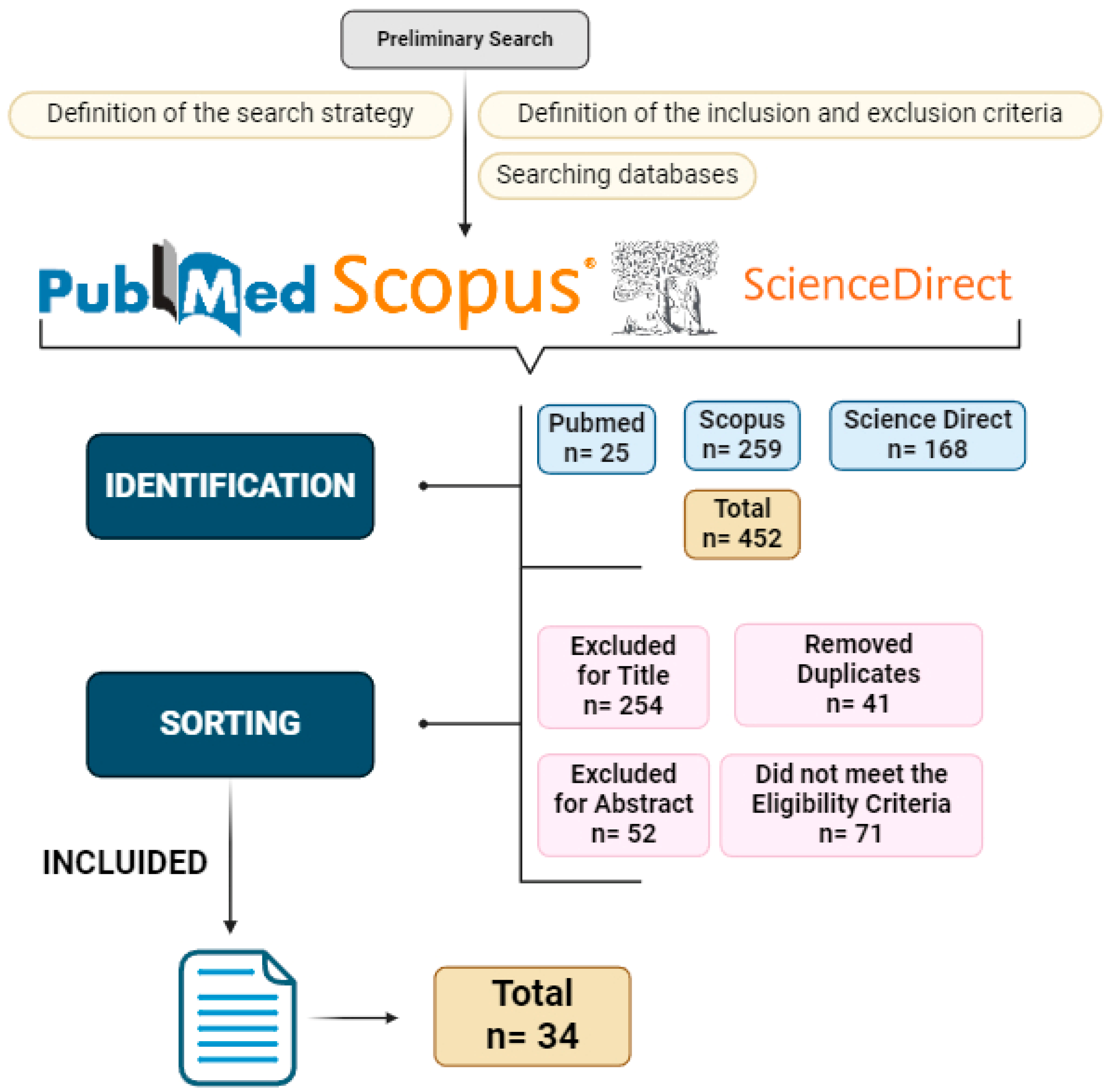
2. Methodology
Protocol
3. Eligibility Criteria
4. Information Sources and Search
5. Article Selection
6. Data Collection Process
7. Risk of Bias
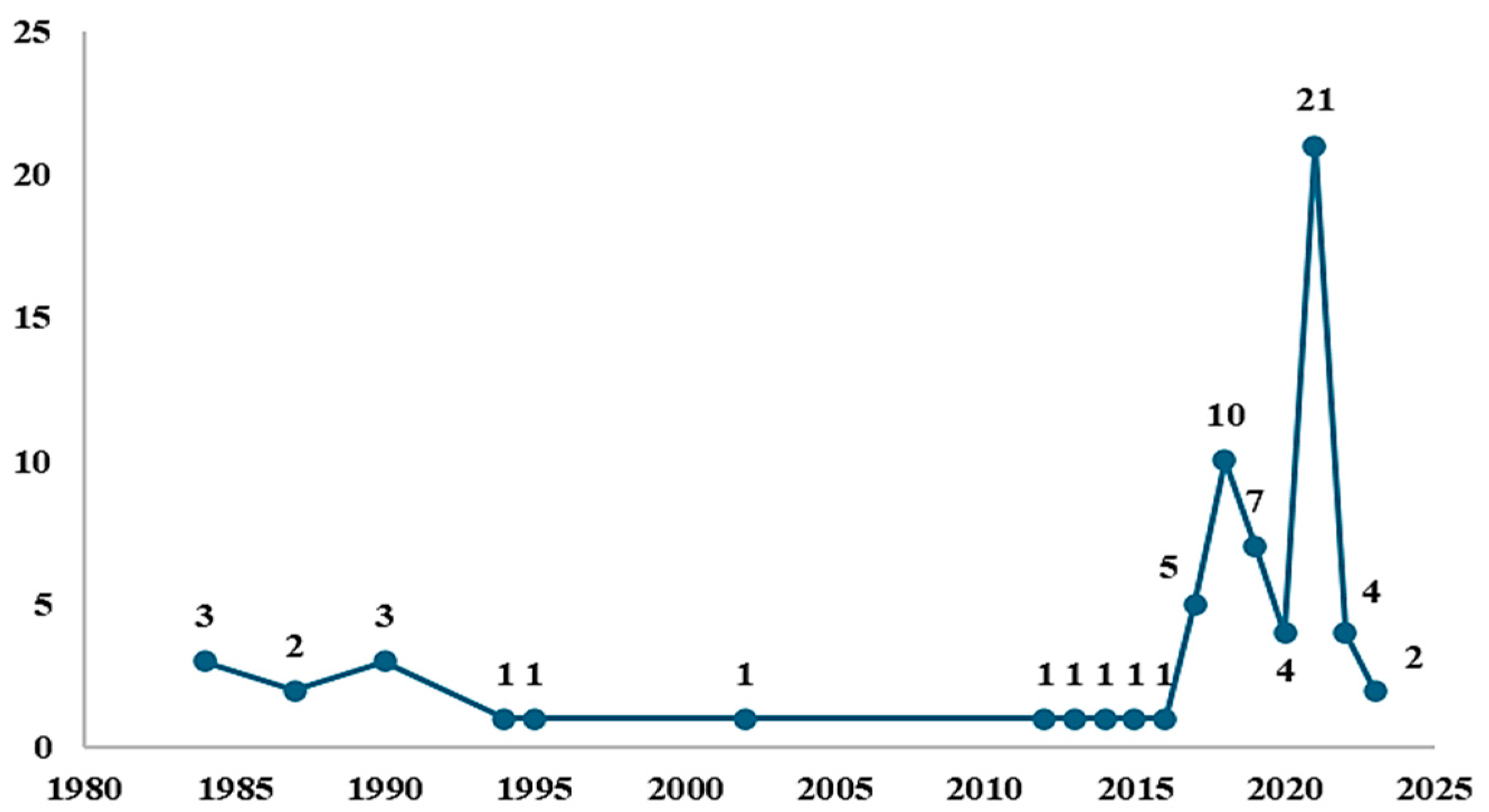
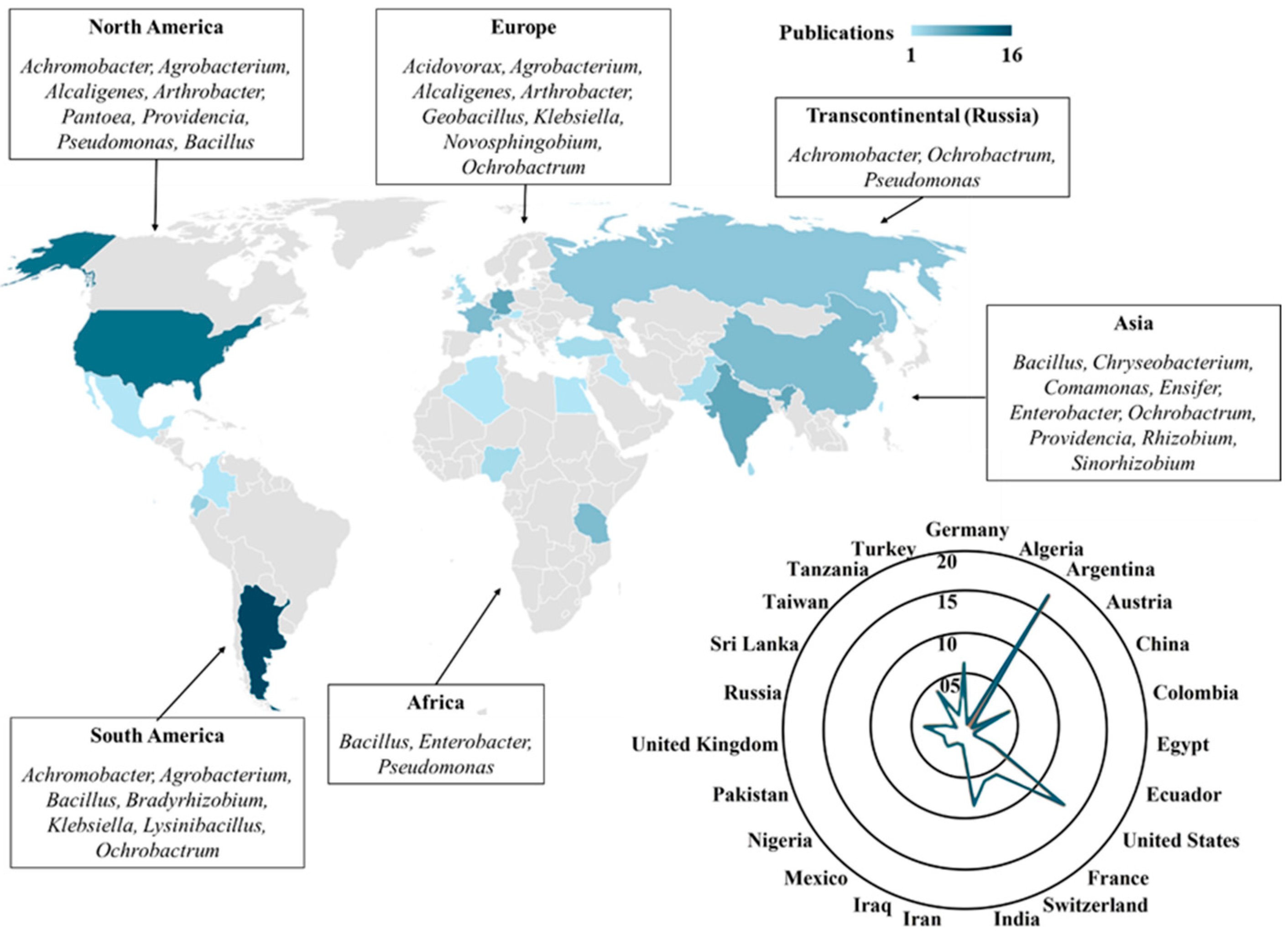
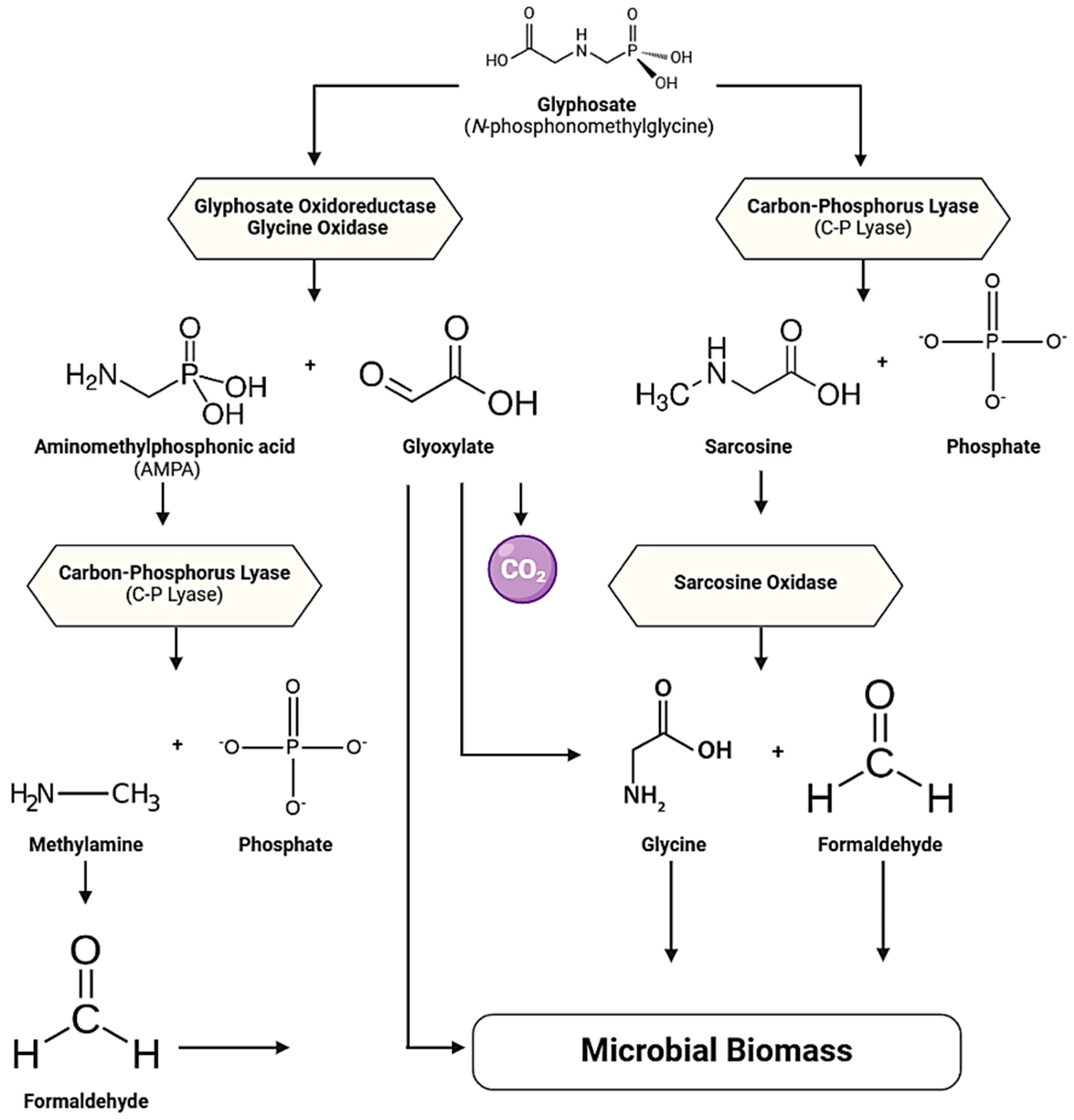
8. Results
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mohy-Ud-Din, W.A.Q.A.S.; Akhtar, M.J.; Bashir, S.A.F.D.A.R.; Asghar, H.N.; Nawaz, M.F.; Chen, F.E.N.G. Isolated bacterial strains efficiently degrade glyphosate under different environmental conditions. Pak. J. Bot 2024, 56, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohy-Ud-Din, W.; Chen, F.; Bashir, S.; Akhtar, M.J.; Asghar, H.N.; Farooqi, Z.U.R.; Zulfiqar, U.; Haider, F.U.; Afzal, A.; Alqahtani, M.D. Unlocking the potential of glyphosate-resistant bacterial strains in biodegradation and maize growth. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1285566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojelade, B.S.; Durowoju, O.S.; Adesoye, P.O.; Gibb, S.W.; Ekosse, G.I. Review of glyphosate-based herbicide and aminomethylphosphonic acid (AMPA): Environmental and health impacts. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, N.E.; Sevakumaran, V.; Ariffin, F. Preliminary study on glyphosate-degrading bacteria isolated from agricultural soil. Environ. Adv. 2023, 12, 100368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esikova, T.Z.; Anokhina, T.O.; Suzina, N.E.; Shushkova, T.V.; Wu, Y.; Solyanikova, I.P. Characterization of a New Pseudomonas putida Strain Ch2, a Degrader of Toxic Anthropogenic Compounds Epsilon-Caprolactam and Glyphosate. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, M.A.; Dubey, A.; Kumar, A.; Yadav, S.; Kumari, S. Modeling and optimization of chlorpyrifos and glyphosate biodegradation using RSM and ANN: Elucidating their degradation pathways by GC-MS based metabolomics. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 252, 114628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Christina, E. Indigenous microorganisms as an effective tool for in situ bioremediation. Relatsh. Between Microbes Environ. Sustain. Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 2, 273–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Arslan, M.; Nowak, K.M. Microbial activity, community composition and degraders in the glyphosate-spiked soil are driven by glycine formation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 168206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Carles, L.; Donnadieu, F.; Batisson, I.; Artigas, J. Glyphosate-degrading behavior of five bacterial strains isolated from stream biofilms. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, R.L.; Whaley, P.; Thayer, K.A.; Schünemann, H.J. Identifying the PECO: A framework for formulating good questions to explore the association of environmental and other exposures with health outcomes. Environ. Int. 2018, 121, 1027. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lockwood, C.; Porrit, K.; Munn, Z.; Rittenmeyer, L.; Salmond, S.; Bjerrum, M.; Loveday, H.; Carrier, J.; Stannard, D. Systematic reviews of qualitative evidence. In Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer’s Manual; The Joanna Briggs Institute: Adelaide, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masotti, F.; Garavaglia, B.S.; Piazza, A.; Burdisso, P.; Altabe, S.; Gottig, N.; Ottado, J. Bacterial isolates from Argentine Pampas and their ability to degrade glyphosate. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuliffe, K.S.; Hallas, L.E.; Kulpa, C.F. Glyphosate degradation by Agrobacterium radiobacter isolated from activated sludge. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1990, 6, 219–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermakova, I.T.; Shushkova, T.V.; Sviridov, A.V.; Zelenkova, N.F.; Vinokurova, N.G.; Baskunov, B.P.; Leontievsky, A.A. Organophosphonates utilization by soil strains of Ochrobactrum anthropi and Achromobacter sp. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 665–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbot, H.W.; Johnson, L.M.; Munnecke, D.M. Glyphosate utilization by Pseudomonas sp. and Alcaligenes sp. isolated from environmental sources. Curr. Microbiol. 1984, 10, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerbs, W.; Stock, M.; Parthier, B. Physiological aspects of glyphosate degradation in Alcaligenes spec. strain GL. Arch. Microbiol. 1990, 153, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipke, R.; Amrhein, N.; Jacob, G.S.; Schaefer, J.; Kishore, G.M. Metabolism of glyphosate in an Arthrobacter sp. GLP-1. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 165, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijekoon, N.; Yapa, N. Assessment of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) on potential biodegradation of glyphosate in contaminated soil and aquifers. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 7, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elarabi, N.I.; Abdelhadi, A.A.; Ahmed, R.H.; Saleh, I.; Arif, I.A.; Osman, G.; Ahmed, D.S. Bacillus aryabhattai FACU: A promising bacterial strain capable of manipulate the glyphosate herbicide residues. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 2207–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezaka, E.; Akintokun, A.K.; Akintokun, P.O.; Taiwo, L.B.; Uthman, A.C.O.; Oyedele, O.A.; Aluko, O.I. Glyphosate degradation by two plant growth promoting bacteria (PGPB) isolated from rhizosphere of maize. Microb. Resea. J. Inter. 2018, 26, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yang, G.; Zhao, H.; Shi, G.; Geng, Y.; Hou, T.; Tao, K. Isolation, identification and characterization of a glyphosate-degrading bacterium, Bacillus cereus CB4, from soil. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés, A.G.; Martinez-Ledezma, C.; López-Chuken, U.J.; Kaushik, G.; Nimesh, S.; Villarreal-Chiu, J.F. Polyphosphate recovery by a native Bacillus cereus strain as a direct effect of glyphosate uptake. ISME J. 2019, 13, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, N.; Ali, A.; Hussein, M. Bacillus megaterium biodegradation glycophate. Iraqi J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 50, 1674–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Singh, J. Kinetic study of the biodegradation of glyphosate by indigenous soil bacterial isolates in presence of humic acid, Fe (III) and Cu (II) ions. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.M.; Yu, T.; Yin, G.H.; Dong, Q.L.; An, M.; Wang, H.R.; Ai, C.X. Glyphosate biodegradation and potential soil bioremediation by Bacillus subtilis strain Bs-15. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015, 14, 14717–14730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guijarro, K.; De Gerónimo, E.; Erijman, L. Glyphosate biodegradation potential in soil based on glycine oxidase gene (thiO) from Bradyrhizobium. Curr. Microbiol. 2021, 78, 1991–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, W.J.; Chen, S.F.; Lei, Q.; Li, J.; Bhatt, P.; Mishra, S.; Chen, S. Cellular response and molecular mechanism of glyphosate degradation by Chryseobacterium sp. Y16C. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 6650–6661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Characterization of a novel glyphosate-degrading bacterial species, Chryseobacterium sp. Y16C, and evaluation of its effects on microbial communities in glyphosate-contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firdous, S.; Iqbal, S.; Anwar, S. Optimization and modeling of glyphosate biodegradation by a novel Comamonas odontotermitis P2 through response surface methodology. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, M.P.; Singh, N.K.; Chaudhary, A.K.; Shalini, R. Characterization of rhizobium isolates from Sesbania rhizosphere and their role in bioremediation of glyphosate and Monocrotophos. Int. J. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2017, 6, 11–22. [Google Scholar]
- Benslama, O.; Boulahrouf, A. High-quality draft genome sequence of Enterobacter sp. Bisph2, a glyphosate-degrading bacterium isolated from a sandy soil of Biskra, Algeria. Genom. Data 2016, 8, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obojska, A.; Ternan, N.G.; Lejczak, B.; Kafarski, P.; McMullan, G. Organophosphonate utilization by the thermophile Geobacillus caldoxylosilyticus T20. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2081–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtoğlu, C.; Ceylan, F.; Cömertpay, S.; Akyol, İ. Determination of herbicide degradation potentials of bacteria isolated from glyphosate applied soil. Biol. Divers. Conserv. 2020, 13, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alomia, F.; Ballesteros, I.; Castillejo, P. Bioremediation potential of glyphosate-degrading microorganisms in eutrophicated Ecuadorian water bodies. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, M.; Melo, C.; Jiménez, E.; Dussán, J. Glyphosate bioremediation through the sarcosine oxidase pathway mediated by Lysinibacillus sphaericus in soils cultivated with potatoes. Agriculture 2019, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, F.; Mousavi, A.; Noghabi, K.A.; Tabar, H.G.; Salmanian, A.H. New bacterial strain of the genus Ochrobactrum with glyphosate-degrading activity. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2013, 48, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrl, B.N.; Mogusu, E.O.; Kim, K.; Hofstetter, H.; Pedersen, J.A.; Elsner, M. High permeation rates in liposome systems explain rapid glyphosate biodegradation associated with strong isotope fractionation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 7259–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Sun, Q.J.; Lan, J.C.W.; Chen, W.M.; Hsueh, C.C.; Chen, B.Y. Exploring the glyphosate-degrading characteristics of a newly isolated, highly adapted indigenous bacterial strain, Providencia rettgeri GDB 1. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2019, 128, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, R.E.; Quinn, J.P. Control of glyphosate uptake and metabolism in Pseudomonas sp. 4ASW. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1995, 134, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, G.M.; Jacob, G.S. Degradation of glyphosate by Pseudomonas sp. PG2982 via a sarcosine intermediate. J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 12164–12168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvapandiyan, A.; Bhatnagar, R.K. Isolation of a glyphosate-metabolising Pseudomonas: Detection, partial purification and localisation of carbon-phosphorus lyase. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1994, 40, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Gill, J.P.K.; Datta, S.; Singh, S.; Dhaka, V.; Kapoor, D.; Wani, A.B.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Kumar, M.; et al. Herbicide glyphosate: Toxicity and microbial degradation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabaloy, M.C.; Allegrini, M.; Hernandez Guijarro, K.; Behrends Kraemer, F.; Morrás, H.; Erijman, L. Microbiomes and glyphosate biodegradation in edaphic and aquatic environments: Recent issues and trends. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 38, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidoli, P.; Baran, N.; Angulo-Jaramillo, R. Glyphosate and AMPA adsorption in soils: Laboratory experiments and pedotransfer rules. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5733–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artigas, J.; Batisson, I.; Carles, L. Dissolved organic matter does not promote glyphosate degradation in auto-heterotrophic aquatic microbial communities. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, H.; Feng, Y.; Fan, X.; Chen, S. Recent advances in glyphosate biodegradation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5033–5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, J.T.; Selim, H.M. Time-Dependent Sorption and Desorption of Glyphosate in Soils: Multi-reaction Modeling. Vadose Zone J. 2019, 18, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, W.J.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhong, J.; Zhang, W.; Zou, Y.; Mishra, S.; Bhatt, P.; Chen, S. Insights into the microbial degradation and resistance mechanisms of glyphosate. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lescano, M.R.; Pizzul, L.; Castillo, M.D.P.; Zalazar, C.S. Glyphosate and aminomethylphosphonic acid degradation in biomixtures based on alfalfa straw, wheat stubble and river waste. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 228, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpenter, J.K.; Monks, J.M.; Nelson, N. The effect of two glyphosate formulations on a small, diurnal lizard (Oligosoma polychroma). Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugowska, K. The effects of Roundup on gametes and early development of common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 44, 1109–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dovidauskas, S.; Okada, I.A.; Dos Santos, F.R. Validation of a simple ion chromatography method for simultaneous determination of glyphosate, aminomethylphosphonic acid and ions of Public Health concern in water intended for human consumption. J. Chromatogr. A 2020, 1632, 461603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, V.; Yildirim, N.; Erguven, G.O.; Durmus, B.; Nuhoglu, Y. The bioremediation of glyphosate in soil media by some newly isolated bacteria: The COD, TOC removal efficiency and mortality assessment for Daphnia magna. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Banerjee, M.; Mondal, S. Policies and Issues in Environmental Biotechnology Research. In Emerging Trends in Environmental Biotechnology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 177–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggi, F.; la Cecilia, D.; Tang, F.H.; McBratney, A. The global environmental hazard of glyphosate use. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingelhöfer, D.; Braun, M.; Brüggmann, D.; Groneberg, D.A. Glyphosate: How do ongoing controversies, market characteristics, and funding influence the global research landscape? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 765, 144271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kang, J.; Kim, K. Global collaboration research strategies for sustainability in the post COVID-19 era: Analyzing virology-related national-funded projects. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Kim, K.; Kogler, D.F. Scientific collaboration, research funding, and novelty in scientific knowledge. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0271678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, I.; Mushtaq, A. Water pollution from agricultural activities: A critical global review. Int. J. Chem. Biochem. Sci. 2023, 23, 164–176. [Google Scholar]
- Masic, I.; Jankovic, S.M. Meta-analysing methodological quality of published research: Importance and effectiveness. Stud. Health Technol. Inf. 2020, 272, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Genus | Species | Source | Biodegradation Analysis | Metabolites | Enzymes | Journal | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Achromobacter | Achromobacter sp. | Soil | Spectrophotometry and NMR * | AMPA * | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Science of the Total Environment | [13] |
| Activated Sludge | HPLC * | C-P Lyases | Journal of Industrial Microbiology | [14] | |||
| Soil | Inorganic Phosphate | Applied and Environmental Microbiology | [15] | ||||
| Acidovorax | Acidovorax sp. | Water | HPLC * | AMPA *, Sarcosine, Formaldehyde e Glycine | C-P Lyases, Glycine Oxidoreductase | Journal of Hazardous Materials | [9] |
| Agrobacterium | Agrobacterium tumefaciens | Soil | Spectrophotometry and NMR * | AMPA * | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Science of the Total Environment | [13] |
| Water | HPLC * | AMPA *, Sarcosine, Formaldehyde e Glycine | C-P Lyases, Glycine Oxidoreductase | Journal of Hazardous Materials | [9] | ||
| Agrobacterium radiobacter | Activated Sludge | AMPA * | C-P Lyases | Journal of Industrial Microbiology | [14] | ||
| Alcaligenes | Alcaligenes sp. | Water e Soil | HPLC * | AMPA | C-P Lyases | Current Microbiology | [16] |
| Laboratory Culture | TLC * | AMPA *, Sarcosine, Glycine | Archives of Microbiology | [17] | |||
| Arthrobacter | Arthrobacter sp. | Soil | TLC * | Glycine, Sarcosine, Formaldehyde, Methionine, Histidine, Serine, Cysteine | C-P Lyases, Sarcosine Dehydrogenase Sarcosine and Oxidase | European Journal of Biochemistry | [18] |
| Bacillus | Bacillus sp. | Soil | Spectrophotometry | AMPA *, Sarcosine | C-P Lyases | Groundwater for Sustainable Development | [19] |
| Bacillus aryabhattai | Spectrophotometry UV–Vis | AMPA *, Sarcosine | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase, Sarcosine and Oxidase | Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences | [20] | ||
| Spectrophotometry and NMR * | AMPA * | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Science of the Total Environment | [13] | |||
| Bacillus cereus | GC-MS * | AMPA * | C-P Lyases Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Microbiology Research Journal International | [21] | ||
| HPLC * | AMPA *, Sarcosine, Formaldehyde, Glyoxylate e Glycine | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase, C-P Lyases | Journal of General and Applied Microbiology | [22] | |||
| Inorganic Phosphate, Polyphosphate | C-P Lyases | The ISME Journal | [23] | ||||
| Bacillus megaterium | AMPA *, Sarcosine, Formaldehyde, Glyoxylate e Glycine | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase, C-P Lyases | Iraqi Journal of Agricultural Sciences | [24] | |||
| Bacillus subtilis | ESI-MS *, HPLC * | AMPA *, Sarcosine, Glyoxylate, Metaphosphoric Acid, Phosphate | C-P Lyase, Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering | [25] | ||
| Spectrophotometry UV–Vis | - | - | Genetics and Molecular Research | [26] | |||
| Bradyrhizobium | Bradyrhizobium sp. | Soil | UPLC-ESI-MS * | AMPA * | Oxidase of Glycine, C-P Lyases | Current Microbiology | [27] |
| Bradyrhizobium japonicum | |||||||
| Bradyrhizobium diazoefficiens | |||||||
| Bradyrhizobium ottawaense | |||||||
| Bradyrhizobium lablabi | |||||||
| Bradyrhizobium erythrophlei | |||||||
| Bradyrhizobium jicamae | |||||||
| Bradyrhizobium elkanii | |||||||
| Bradyrhizobium canariense | |||||||
| Bradyrhizobium lupini | |||||||
| Bradyrhizobium icense | |||||||
| Chryseobacterium | Chryseobacterium sp. | Activated Sludge | HPLC *, LC-MS * | AMPA *, Glycolic Acid, Hydrogen Peroxide | Oxidase of Glycine | Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry | [28] |
| Soil | UPLC-MS * | AMPA *, Glyoxylate, Sarcosine, Glycine | C-N Lyases | Journal of Hazardous Materials | [29] | ||
| Comamonas | Comamonas odontotermitis | Soil | HPLC * | AMPA *, Sarcosine, Glycine | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase C-P Lyases | Pedosphere | [30] |
| Ensifer | Ensifer sp. | Soil | HPLC * | AMPA *, CO2 *, Phosphate and Water | Phosphatase, Phosphotriesterase | International Journal of Applied and Natural Sciences | [31] |
| Enterobacter | Enterobacter sp. | Soil | HPLC * | AMPA * | C-P Lyases | Genomics Data | [32] |
| Geobacillus | Geobacillus caldoxylosilyticus | Water | HPLC *, NMR * | AMPA *, Glyoxylate | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Applied and Environmental Microbiology | [33] |
| Klebsiella | Klebsiella variicola | Soil | Spectrophotometry | AMPA * | - | Biological Diversity and Conservation | [34] |
| Spectrophotometry and NMR * | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Science of the Total Environment | [35] | ||||
| Water | Spectrophotometry UV-Vis | C-P Lyases | Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences | [34] | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae | Soil | Spectrophotometry | - | Biological Diversity and Conservation | [34] | ||
| Spectrophotometry and NMR * | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Science of the Total Environment | [13] | ||||
| Lysinibacillus | Lysinibacillus sphaericus | Soil | UHPLC-MS * | AMPA *, Sarcosine | Sarcosine Oxidase | Agriculture | [36] |
| Novosphingobium | Novosphingobium sp. | Water | HPLC * | AMPA *, Sarcosine, Formaldehyde e Glycine | C-P Lyases, Glycine Oxidoreductase | Journal of Hazardous Materials | [9] |
| Ochrobactrum | Ochrobactrum sp. | Soil | Spectrophotometry and NMR * | AMPA * | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Science of the Total Environment | [13] |
| HPLC * | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Journal of Environmental Science and Health | [37] | ||||
| Ochrobactrum anthropi | NMR *, LC-IRMS * | - | - | Environmental Science & Technology | [38] | ||
| HPLC * | Inorganic Phosphate | C-P Lyases | Applied and Environmental Microbiology | [15] | |||
| Ochrobactrum rhizosphaerae | NMR *, LC-IRMS * | - | - | Environmental Science & Technology | [38] | ||
| Ochrobactrum intermedium | |||||||
| TLC, HPLC | Sarcosine and Glycine | C-P Lyases | Pest Management Science | [30] | |||
| Ochrobactrum hematophilum | NMR *, LC-IRMS * | - | - | Environmental Science & Technology | [38] | ||
| Ochrobactrum pituitosum | |||||||
| Water | HPLC * | AMPA *, Sarcosine, Formaldehyde and Glycine | C-P Lyases, Glycine Oxidoreductase | Journal of Hazardous Materials | [9] | ||
| Pantoea | Pantoea stewartii | Water | Spectrophotometry UV-Vis | AMPA * | C-P Lyase | Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences | [35] |
| Providencia | Providencia rettgeri | Soil | HPLC * | AMPA * | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase, C-P Lyase | Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering | [39] |
| Pseudomonas | Pseudomonas sp. | Soil | Spectrophotometry | AMPA *, Sarcosine | C-P Lyases | Groundwater for Sustainable Development | [19] |
| Water | Spectrophotometry UV–Vis | AMPA * | C-P Lyases | Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences | [35] | ||
| Soil | TLC * | Sarcosine | C-P Lyases | FEMS Microbiology Letters | [40] | ||
| Sarcosine Desidrogenase | The Journal of Biological Chemistry | [41] | |||||
| Water and Soil | HPLC * | AMPA * | C-P Lyases | Current Microbiology | [16] | ||
| Soil and Sludge | Spectrophotometry | Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology | [42] | ||||
| Pseudomonas stutzeri | Water and Soil | HPLC * | Current Microbiology | [16] | |||
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Soil | GC-MS * | C-P Lyases Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Microbiology Research Journal International | [21] | ||
| Pseudomonas putida | TLC *, HPLC * | Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Microorganisms | [5] | |||
| Rhizobium | Rhizobium sp. | Soil | HPLC * | AMPA *, CO2 *, Phosphate and Water | Phosphatase, Phosphotriesterase | International Journal of Applied and Natural Sciences | [31] |
| Rhizobium leguminosarum | ESI-MS *, HPLC * | AMPA *, Sarcosine, Glyoxylate, Metaphosphoric Acid, Phosphate | C-P Lyases, Glyphosate Oxidoreductase | Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering | [25] | ||
| Sinorhizobium | Sinorhizobium saheli | Soil | HPLC * | AMPA *, CO2 *, Phosphate and Water | Phosphatase, Phosphotriesterase | International Journal of Applied and Natural Sciences | [31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Souza, K.S.; da Silva, M.R.F.; Candido, M.A.; Lins, H.T.S.; de Lima Torres, G.; da Silva Felix, K.C.; Silva, K.C.C.; Filho, R.M.N.; Bhadouria, R.; Tripathi, S.; et al. Biodegradation Potential of Glyphosate by Bacteria: A Systematic Review on Metabolic Mechanisms and Application Strategies. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051247
Souza KS, da Silva MRF, Candido MA, Lins HTS, de Lima Torres G, da Silva Felix KC, Silva KCC, Filho RMN, Bhadouria R, Tripathi S, et al. Biodegradation Potential of Glyphosate by Bacteria: A Systematic Review on Metabolic Mechanisms and Application Strategies. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051247
Chicago/Turabian StyleSouza, Karolayne Silva, Milena Roberta Freire da Silva, Manoella Almeida Candido, Hévellin Talita Sousa Lins, Gabriela de Lima Torres, Kátia Cilene da Silva Felix, Kaline Catiely Campos Silva, Ricardo Marques Nogueira Filho, Rahul Bhadouria, Sachchidanand Tripathi, and et al. 2025. "Biodegradation Potential of Glyphosate by Bacteria: A Systematic Review on Metabolic Mechanisms and Application Strategies" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051247
APA StyleSouza, K. S., da Silva, M. R. F., Candido, M. A., Lins, H. T. S., de Lima Torres, G., da Silva Felix, K. C., Silva, K. C. C., Filho, R. M. N., Bhadouria, R., Tripathi, S., Singh, R., Santos, M. D. V., Silva, I. P. S., de Barros, A. V., de Araújo, L. C. A., Motteran, F., & de Oliveira, M. B. M. (2025). Biodegradation Potential of Glyphosate by Bacteria: A Systematic Review on Metabolic Mechanisms and Application Strategies. Agronomy, 15(5), 1247. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051247






