Water Levels More than Earthworms Impact Rice Growth and Productivity: A Greenhouse Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Properties and Earthworm Model
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Earthworm Development and Bioturbation Activity
2.4. Rice Development and Yield
2.5. Soil Analyses
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Development of Earthworms and Bioturbation
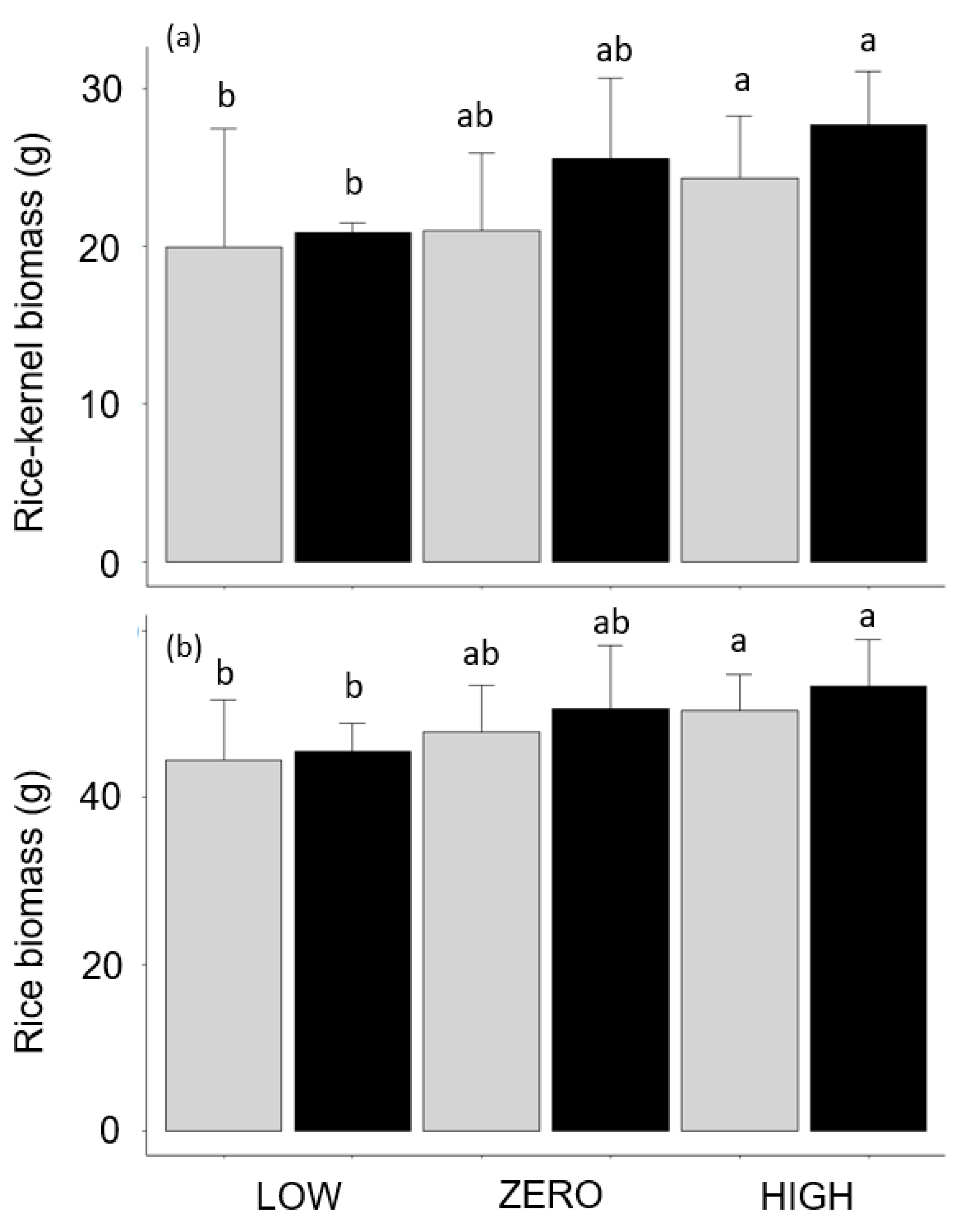
3.2. Effect of Water Level and Earthworms on Rice Development and Productivity
3.3. Effect on Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Water Level on Earthworm Activity
4.2. Effect of Glyphidrilus sp. on Soil Properties and Rice Growth
4.3. Concluding Remarks
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pingali, P. Agricultural mechanization: Adoption patterns and economic impact. Handb. Agric. Econ. 2007, 3, 2779–2805. [Google Scholar]
- FAO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020; 320p, Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/ca9692en (accessed on 1 December 2024).
- Mutert, E.; Fairhurst, T.H. Developments in rice production in Southeast Asia. Better Crops Int. 2002, 15, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Gianessi, L.P. Importance of pesticides for growing rice in South and South East Asia. Int. Pestic. Benefit Case Study 2014, 108, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Chun, J.A.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Lee, W.S.; Lee, E.J.; Horstmann, N.; Park, H.; Veasna, T.; Vanndy, L.; Pros, K.; et al. Assessing rice productivity and adaptation strategies for Southeast Asia under climate change through multi-scale crop modeling. Agric. Syst. 2016, 143, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Nizam, S.N.; Haji Baharudin, N.S.; Ahmad, H. Application of pesticide in paddy fields: A Southeast Asia case study review. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 5557–5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, A.G.; Huggins, D.R.; Reganold, J.P. Linking soil health and ecological resilience to achieve agricultural sustainability. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2023, 21, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavelle, P.; Bignell, D.; Lepage, M. Soil function in a changing world: The role of invertebrate ecosystem engineers. Eur. J. Biol. 1997, 33, 159–193. [Google Scholar]
- Jouquet, P.; Dauber, J.; Lagerlöf, J.; Lavelle, P.; Lepage, M. Soil invertebrates as ecosystem engineers: Intended and accidental effects on soil and feedback loops. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2006, 32, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheu, S. Effects of earthworms on plant growth: Patterns and perspectives: The 7th international symposium on earthworm ecology Cardiff Wales 2002. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhauer, N.; Milcu, A.; Nitschke, N.; Sabais, A.; Scherber, C.; Scheu, S. Earthworm and belowground competition effects on plant productivity in a plant diversity gradient. Oecologia 2009, 161, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laossi, K.R.; Decaëns, T.; Jouquet, P.; Barot, S. Can we predict how earthworm effects on plant growth vary with soil properties? Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2010, 1, 784342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.K.; Tomar, S.; Chakraborty, D. Role of earthworm in improving soil structure and functioning. Curr. Sci. 2017, 113, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, J.P.; Schmidt, O. The feeding ecology of earthworms—A review. Pedobiologia 2007, 50, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choosai, C.; Jouquet, P.; Hanboonsong, Y.; Hartmann, C. Effects of earthworms on soil properties and rice production in the rainfed paddy fields of Northeast Thailand. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2010, 45, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owa, S.O.; Oyenusi, A.A.; Joda, A.O.; Morafa, S.O.A.; Yeye, J.A. Effect of earthworm casting on growth parameters of rice. Afr. Zool. 2003, 38, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Dhar, S.; Chaudhuri, P. Effect of earthworm, Glyphidrilus sp. on soil physico-chemical properties, growth and yield of paddy—An ‘in-situ’ pot culture experiment. World J. Agric. Sci. 2019, 15, 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Dhar, S.; Chaudhuri, P. Earthworm communities in paddy (Oryza sativa) fields of West Tripura (India). Proc. Zool. Soc. 2020, 73, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Atopkin, D.; Wang, L.; Wu, D. Description of a new earthworm species of the genus Drawida (Oligochaeta: Moniligastridae) from Northeast China and Far East Russia. J. Asia-Pac. Biodivers. 2021, 14, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanabun, R.; Bantaowong, U.; Sutcharit, C.; Tongkerd, P.; Inkavilay, K.; James, S.W.; Pantha, S. A new species of semi-aquatic freshwater earthworm of the genus Glyphidrilus Horst, 1889 from Laos (Oligochaeta: Almidae). Trop. Nat. Hist. 2011, 11, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanabun, R.; Bantaowong, U.; Sutcharit, C.; Tongkerd, P.; James, S.W.; Panha, S. A new species of semi-aquatic freshwater earthworm of the genus Glyphidrilus Horst, 1889 from the Mekong River (Oligochaeta: Almidae). Raffles Bull. Zool. 2012, 60, 265–277. [Google Scholar]
- Chanabun, R.; Lin, A.; Jirapatrasilp, P.; Bantaowong, U. The semi-aquatic freshwater earthworm genus Glyphidrilus Horst, 1889 from Myanmar (Oligochaeta: Almidae) with description of a new species. Trop. Nat. Hist. 2020, 20, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, K.; Janz, B.; Kiese, R.; Wassmann, R.; Zaitsev, A.S.; Wolters, V. Earthworms offset straw-induced increase of greenhouse gas emission in upland rice production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrion, A.T.; Litsinger, J.A. Dichogaster nr. curgensis Michaelsen (Annelida: Octochaetidae): An earthworm pest of terraced rice in the Philippine Cordilleras. Crop Prot. 1997, 16, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.M.; Warren, G.N. Laboratory studies on the influence of the earthworm Eukarria saltensis (Beddard) (Oligochaeta: Ocnerodrilidae) on overlying quality and rice plant establishment. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2000, 46, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, M.M. Improving Bloodworm, Earthworm and Snail Control in Rice; RIRDC: Wagga Wagga, Australia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhana, S.; Nair, N.B. On the breeding biology of Glyphidrilus annandalei Michaelson (Haplotaxida: Glossoscolecidae) and its relation to the various physical and chemical factors. Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 1986, 71, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Duc, K.N.; Ancev, T.; Randall, A. Evidence of climatic change in Vietnam: Some implications for agricultural production. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 524–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.T.; Nguyen, A.T.; Kieu, H.T.; Pham, Q.V.; Tran, T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.; Dinh, V.M.; Nguyen, M.N. Earthworms can mobilize soil arsenic through their casts. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 893, 164891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouquet, P.; Van Pham, Q.; Bottinelli, N.; Nguyen, M.N.; Quan, D.T.; Meunier, J.-D. Earthworms impact the availability of Si to plants in northern Vietnamese paddy fields. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2024, 121, 103615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.N.; Dultz, S.; Kasbohm, J.; Le, D. Clay dispersion and its relation to surface charge in a paddy soil of the Red River Delta, Vietnam. J. Plant Nut. Soil Sci. 2009, 172, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelsen, W. Oligochaeten. Ergebnisse einer zoologishen Forschungsreise in den Molukken und in Borneo, im Auftrage der Senckenbergischen naturforschenden Gesellschaft ausgeführt von Dr. Willy Kükenthal. Abh. Senckenberg. Naturforschenden Ges. 1896, 23, 193–243. [Google Scholar]
- Capowiez, Y.; Sammartino, S.; Michel, E. Using X-ray tomography to quantify earthworm bioturbation non-destructively in repacked soil cores. Geoderma 2011, 162, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheik, S.; Bottinelli, N.; Minh, T.T.; Doan, T.T.; Jouquet, P. Quantification of three dimensional characteristics of macrofauna macropores and their effects on soil hydraulic conductivity in northern Vietnam. Front. Environ. Sci. 2019, 7, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, M.J.R.; Sánchez-Moreiras, A.M. Determination of transpiration using a steady-state porometer. Handb. Plant Ecophysiol. Tech. 2001, 16, 223–233, ISBN: 90-6672-044-1. [Google Scholar]
- Markwell, J.; Osterman, J.C.; Mitchell, J.L. Calibration of the Minolta SPAD-502 leaf chlorophyll meter. Photosynth. Res. 1995, 46, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolhar-Nordenkampf, H.R.; Long, S.P.; Baker, N.R.; Öquist, G.; Schreiber, U.L.E.G.; Lechner, E.G. Chlorophyll fluorescence as a probe of the photosynthetic competence of leaves in the field: A review of current instrumentation. Funct. Ecol. 1989, 3, 497–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISRIC. Procedures for Soil Analysis; ISRIC Technical Paper; ISRIC: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2002; ISSN 0923-3792. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, D.W.; Sommers, L.E. Total carbon, organic carbon, and organic matter. Methods Soil Anal. Part 3 Chem. Methods 1996, 5, 961–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Hiemstra, T.; Antelo, J.; Rahnemaie, R.; van Riemsdijk, W.H. Nanoparticles in natural systems I: The effective reactive surface area of the natural oxide fraction in field samples. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.B.; Talibudeen, O. Critical potassium potentials for crops: 2. Potentials for wheat, maize, peas, beans and sugar beet in their early growth on a sandy loam. J. Soil Sci. 1982, 33, 771–778. [Google Scholar]
- DeMaster, D.J. The supply and accumulation of silica in the marine environment. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1981, 45, 1715–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korndörfer, G.H.; Coelho, N.M.; Snyder, G.H.; Mizutani, C.T. Evaluation of soil extractants for silicon availability in upland rice. Rev. Bras. Cienc. Solo 1999, 23, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haysom, M.B.C.; Chapman, L.S. Some aspects of the calcium silicate trials at Mackay. Proc. Austr. Sugar Cane Technol. 1975, 42, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Khalid, R.A.; Silva, J.A.; Fox, R.L. Residual effects of calcium silicate in tropical soils: II. Biological extraction of residual soil silicon. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019; Available online: https://www.john-fox.ca/Companion/ (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Pinheiro, J.; Bates, D.; Debroy, S.; Sarkar, D.; R Core Team. Nlme: Nonlinear mixed-effects models. R Package 2013, 3. Available online: https://docs.w3cub.com/r/library/nlme/html/nlme (accessed on 17 May 2025).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruapukee, A.; Iwai, C.B.; Kaewjampa, N. Earthworm communities and activities in rice ecosystem under different soil salinity levels in Northeast Thailand. Int. J. Environ. Rural Dev. 2016, 7, 169–173. [Google Scholar]
- Zorn, M.I.; Van Gestel, C.A.M.; Morrien, E.; Wagenaar, M.; Eijsackers, H. Flooding responses of three earthworm species, Allolobophora chlorotica, Aporrectodea caliginosa and Lumbricus rubellus, in a laboratory-controlled environment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2008, 40, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütz, K.; Nagel, P.; Dill, A.; Scheu, S. Structure and functioning of earthworm communities in woodland flooding systems used for drinking water production. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2008, 39, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, T.J. Redox potential as a soil health indicator–how does it compare to microbial activity and soil structure? Plant Soil 2024, 494, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, J.P. Clusters in earthworm spatial distribution: The 7th international symposium on earthworm ecology Cardiff Wales 2002. Pedobiologia 2003, 47, 490–496. [Google Scholar]
- Lavelle, P.; Spain, A.V. Soil Ecology; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Alberda, T. Growth and root development of lowland rice and its relation to oxygen supply. Plant Soil 1953, 5, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Yoshida, S.; Nishiyama, I. Nature of oxidizing power of rice roots. Plant Soil 1983, 72, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbumozhi, V.; Yamaji, E.; Tabuchi, T. Rice crop growth and yield as influenced by changes in ponding water depth, water regime and fertigation level. Agric. Water Manag. 1998, 37, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asargew, M.F.; Masutomi, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Aono, M. Water stress changes the relationship between photosynthesis and stomatal conductance. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.C. Imposing and maintaining soil water deficits in drought studies in pots. Plant Soil 2019, 439, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib-ur-Rahman, M.; Raza, A.; Ahrends, H.E.; Hüging, H.; Gaiser, T. Impact of in-field soil heterogeneity on biomass and yield of winter triticale in an intensively cropped hummocky landscape under temperate climate conditions. Precis Agric. 2022, 23, 912–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhu, R.; Li, H.; Chen, Q.; Jing, P.; Li, X. Response of rice’s hydraulic transport and photosynthetic capacity to drought-flood abrupt alternation. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 303, 109023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.Y.; Xu, H.X.; Jiang, D.A. Characteristics of gas exchange, chlorophyll fluorescence and expression of key enzymes in photosynthesis during leaf senescence in rice plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2005, 47, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, D.; Rondón, M.; Laossi, K.R.; Hoyos, V.; Lavelle, P.; de Carvalho, M.H.C.; Barot, S. Contrasted effect of biochar and earthworms on rice growth and resource allocation in different soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguera, D.; Barot, S.; Laossi, K.R.; Cardoso, J.; Lavelle, P.; De Carvalho, M.C. Biochar but not earthworms enhances rice growth through increased protein turnover. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2012, 52, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntzer, F.; Keller, C.; Meunier, J.D. Benefits of plant silicon for crops: A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2012, 32, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotzbücher, T.; Marxen, A.; Vetterlein, D.; Schneiker, J.; Türke, M.; Van Sinh, N.; Hung Manh, N.; Chien, H.V.; Marquez, L.; Villareal, S.; et al. Plant-available silicon in paddy soils as a key factor for sustainable rice production in Southeast Asia. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2015, 16, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, T.; Tubana, B.; Paye, W.; Kanke, Y.; Datnoff, L. Establishing soil silicon test procedure and critical silicon level for rice in Louisiana soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016, 47, 1578–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
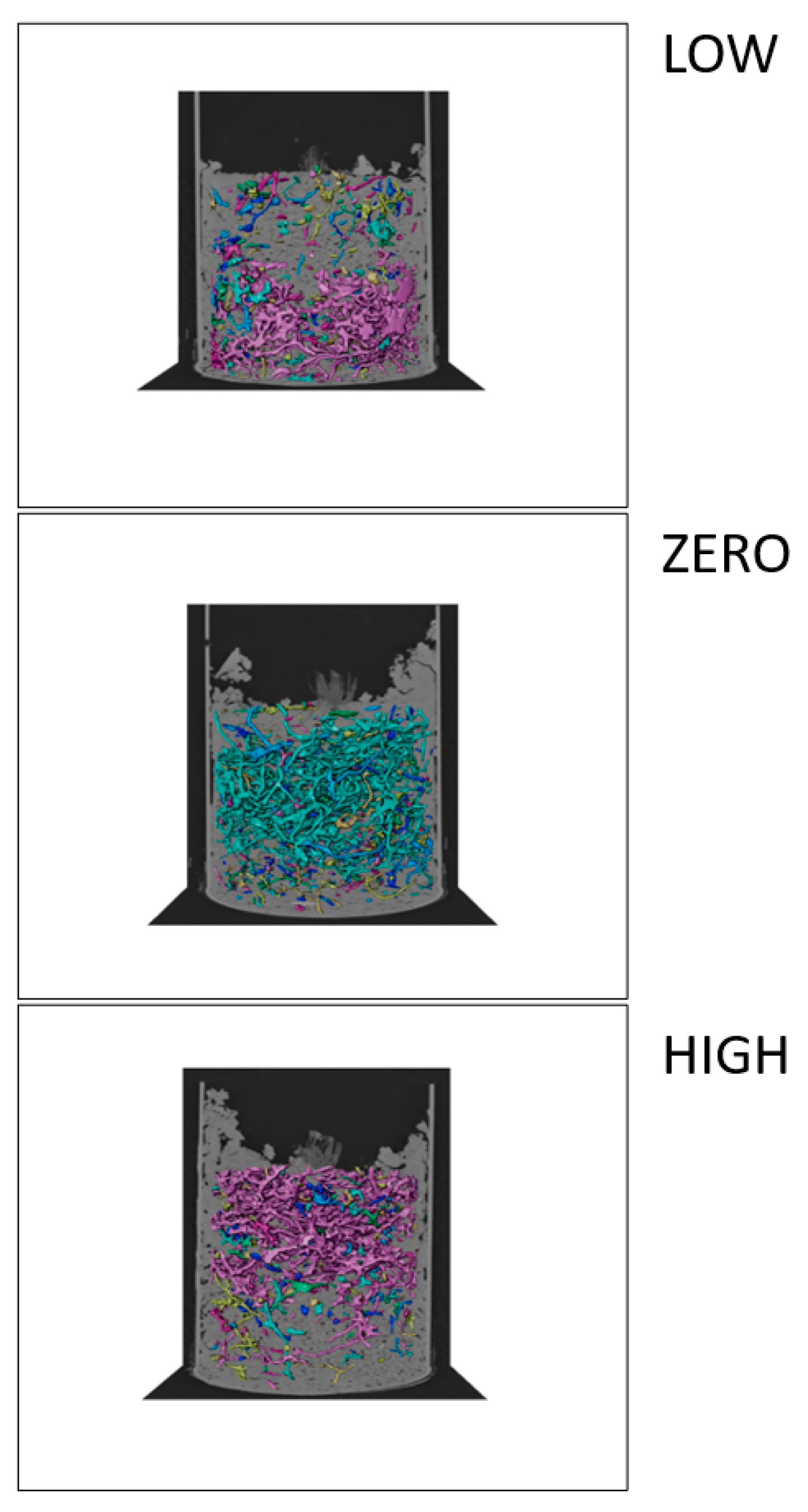
| Earthworm Number | Earthworm Biomass (g) | |
|---|---|---|
| LOW | 8.2 b (1.3) | 4.3 b (0.9) |
| ZERO | 10.0 a (0.0) | 6.1 a (0.1) |
| HIGH | 10.2 a (0.4) | 7.1 a (1.0) |
| Pores Upper Part of the Cylinder (%) | Total Porosity (%) | Surface Casts (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOW | 25.99 b (7.54) | 4.08 b (0.77) | 227.61 b (85.50) |
| ZERO | 63.94 a (18.34) | 6.09 a (0.93) | 674.31 a (134.64) |
| HIGH | 80.04 a (7.68) | 6.35 a (0.95) | 835.01 a (447.47) |
| Rice Height | Leaf Collar Height | Grain Biomass | Rice Biomass | Tiller Number | 50-Kernel Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | F2,23 = 1.48 p = 0.248 | F2,23 = 0.14 p = 0.871 | F2,24 = 3.65 p = 0.042 | F2,23 = 3.64 p = 0.042 | F2,23 = 1.65 p = 0.215 | F2,23 = 1.21 p = 0.317 |
| Earthworms | F1,23 = 1.0 p = 0.750 | F1,23 = 0.69 p = 0.416 | F1,24 = 1.25 p = 0.274 | F1,23 = 1.25 p = 0.274 | F1,23 = 0.11 p = 0.745 | F1,23 = 0.05 p = 0.821 |
| Water × Earthworms | F2,23 = 0.39 p = 0.683 | F2,23 = 0.12 p = 0.890 | F2,24 = 0.02 p = 0.980 | F3,31 = 0.02 p = 0.980 | F3,31 = 0.02 p = 0.981 | F3,31 = 0.67 p = 0.519 |
| Time | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 68 DAS | 77 DAS | 82 DAS | Source of Deviance | ||||||||
| −EW | +EW | −EW | +EW | −EW | +EW | Water | Earthworms | Water × Earthworms | Time | ||
| Stomatal conductance (mmolH20 m−2 s−1) | LOW | n.d. | n.d. | 229 (18.9) a | 306.1 (37.1) ab | 134.5 (24.2) a | 189.5 (27.6) ab | W(2) = 8.39 p = 0.015 | W(1) = 0.03 p = 0.863 | W(2) = 6.35 p = 0.042 | W(1) = 38.1 p < 0.001 |
| ZERO | n.d. | n.d. | 287.1 (41.4) ab | 287.7 (66.6) ab | 169.3 (25.5) ab | 180.6 (36.5) ab | |||||
| HIGH | n.d. | n.d. | 393.2 (58.6) b | 341.3 (50.6) ab | 236.5 (12.7) b | 167.1 (20.2) ab | |||||
| Chlorophyll content (SPAD units) | LOW | 41 (1.3) a | 40.7 (1.1) a | 38.5 (1.1) a | 38.3 (1.5) a | 35.0 (1.4) a | 36.9 (1.7) a | W(2) = 0.68 p = 0.712 | W(1) = 2.59 p = 0.107 | W(2) = 0.58 p = 0.748 | W(2) = 52.2 p < 0.001 |
| ZERO | 41.6 (2.2) a | 42.8 (0.6) a | 39.2 (1.5) a | 38.2 (0.8) a | 33.3 (1.7) a | 38.5 (1.7) a | |||||
| HIGH | 41.4 (2.1) a | 40.8 (0.7) a | 35.7 (1.5) a | 39.6 (1.1) a | 34.2 (1.6) a | 36.7 (2.1) a | |||||
| Fv/Fm | LOW | 0.79 (0.01) a | 0.81 (0.01) a | 0.79 (0.01) a | 0.78 (0.01) a | 0.75 (0.03) a | 0.68 (0.08) a | W(2) = 1.92 p = 0.382 | W(1) = 0.73 p = 0.393 | W(2) = 2.18 p = 0.337 | W(2) = 30.6 p < 0.001 |
| ZERO | 0.78 (0.01) a | 0.8 (0.01) a | 0.75 (0.01) a | 0.79 (0.01) a | 0.70 (0.04) a | 0.73 (0.05) a | |||||
| HIGH | 0.81 (0) a | 0.81 (0.01) a | 0.80 (0.01) a | 0.80 (0.01) a | 0.70 (0.04) a | 0.77 (0.02) a | |||||
| LOW | HIGH | p-Values | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −EW | +EW | −EW | +EW | ||||
| Soil | Cast | Soil | Cast | ||||
| pHH20 | 6.04 ab (0.16) | 6.18 a (0.07) | 6.21a (0.34) | 5.96 b (0.07) | 5.99 ab (0.10) | 6.20 a (0.10) | 0.017 * |
| pHKCl | 5.31 bc (0.10) | 5.54 bc (0.05) | 5.49 ab (0.30) | 5.26 c (0.06) | 5.26 c (0.12) | 5.41 abc (0.08) | 0.023 * |
| Clay (%) | 24.59 (2.33) | 25.24 (1.11) | 27.00 (3.03) | 27.08 (0.47) | 25.40 (2.96) | 25.40 (1.49) | 0.123 |
| Silt (%) | 55.99 ab (1.87) | 54.17 bc (1.45) | 51.84 c (3.24) | 54.20 bc (0.95) | 54.58 ab (0.74) | 56.94 a (2.84) | 0.014 * |
| Sand (%) | 19.42 (0.58) | 20.59 (1.96) | 21.15 (2.83) | 18.72 (1.13) | 20.02 (1.74) | 19.32 (0.32) | 0.243 |
| C (g kg−1) | 15.24 (0.52) | 15.44 (1.09) | 15.62 (0.48) | 14.98 (0.52) | 15.46 (0.89) | 15.64 (0.48) | 0.681 |
| N (g kg−1) | 2.26 (0.05) | 2.36 (0.23) | 2.27 (0.07) | 2.30 (0.10) | 2.30 (0.08) | 2.28 (0.07) | 0.960 |
| Nmin (mg kg−1) | 671.2 (60.0) | 687.2 (94.5) | 658.4 (106.8) | 726.4 (158.0) | 752.0 (155.8) | 696.0 (116.9) | 0.828 |
| K (mg kg−1) | 64.4 b (9.3) | 59.2 bc (6.4) | 82.8 a (10.3) | 55.6 c (2.5) | 55.4 c (3.2) | 63.8 bc (5.4) | <0.001 *** |
| P (mg kg−1) | 126.45 (27.8) | 106.7 (17.6) | 94.5 (36.3) | 134.4 (17.5) | 89.6 (15.7) | 106.5 (34.1) | 0.080 |
| SiH2O (mg kg−1) | 59.62 ab (6.58) | 62.90 ab (6.62) | 65.76 a (5.07) | 52.09 c (2.23) | 51.11 c (3.80) | 57.05 bc (4.11) | <0.001 *** |
| SiCaCl2 (mg kg−1) | 53.99 abc (6.65) | 55.02 ab (9.41) | 59.39 a (4.54) | 46.03 d (2.11) | 46.97 cd (2.76) | 51.00 bcd (3.72) | 0.013 * |
| SiHOac (mg kg−1) | 95.93 (13.01) | 88.13 (11.31) | 88.89 (4.94) | 74.33 (6.37) | 85.76 (13.02) | 87.05 (6.04) | 0.0515 |
| Phytoliths (mg SiO2 kg−1) | 1.956 (0.255) | 2.003 (0.492) | 2.544 (0.900) | 2.159 (0.791) | 2.257 (0.394) | 2.083 (0.545) | 0.683 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sinh, S.; Pham, Q.V.; Le, L.A.T.; Puga Freitas, R.; Repellin, A.; Ann, V.; Bottinelli, N.; Jouquet, P. Water Levels More than Earthworms Impact Rice Growth and Productivity: A Greenhouse Study. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051245
Sinh S, Pham QV, Le LAT, Puga Freitas R, Repellin A, Ann V, Bottinelli N, Jouquet P. Water Levels More than Earthworms Impact Rice Growth and Productivity: A Greenhouse Study. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051245
Chicago/Turabian StyleSinh, Sreypich, Quang Van Pham, Lan Anh Thi Le, Ruben Puga Freitas, Anne Repellin, Vannak Ann, Nicolas Bottinelli, and Pascal Jouquet. 2025. "Water Levels More than Earthworms Impact Rice Growth and Productivity: A Greenhouse Study" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051245
APA StyleSinh, S., Pham, Q. V., Le, L. A. T., Puga Freitas, R., Repellin, A., Ann, V., Bottinelli, N., & Jouquet, P. (2025). Water Levels More than Earthworms Impact Rice Growth and Productivity: A Greenhouse Study. Agronomy, 15(5), 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051245







