Mitigating Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Agricultural Soils with Biochar: A Scientometric and Visual Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
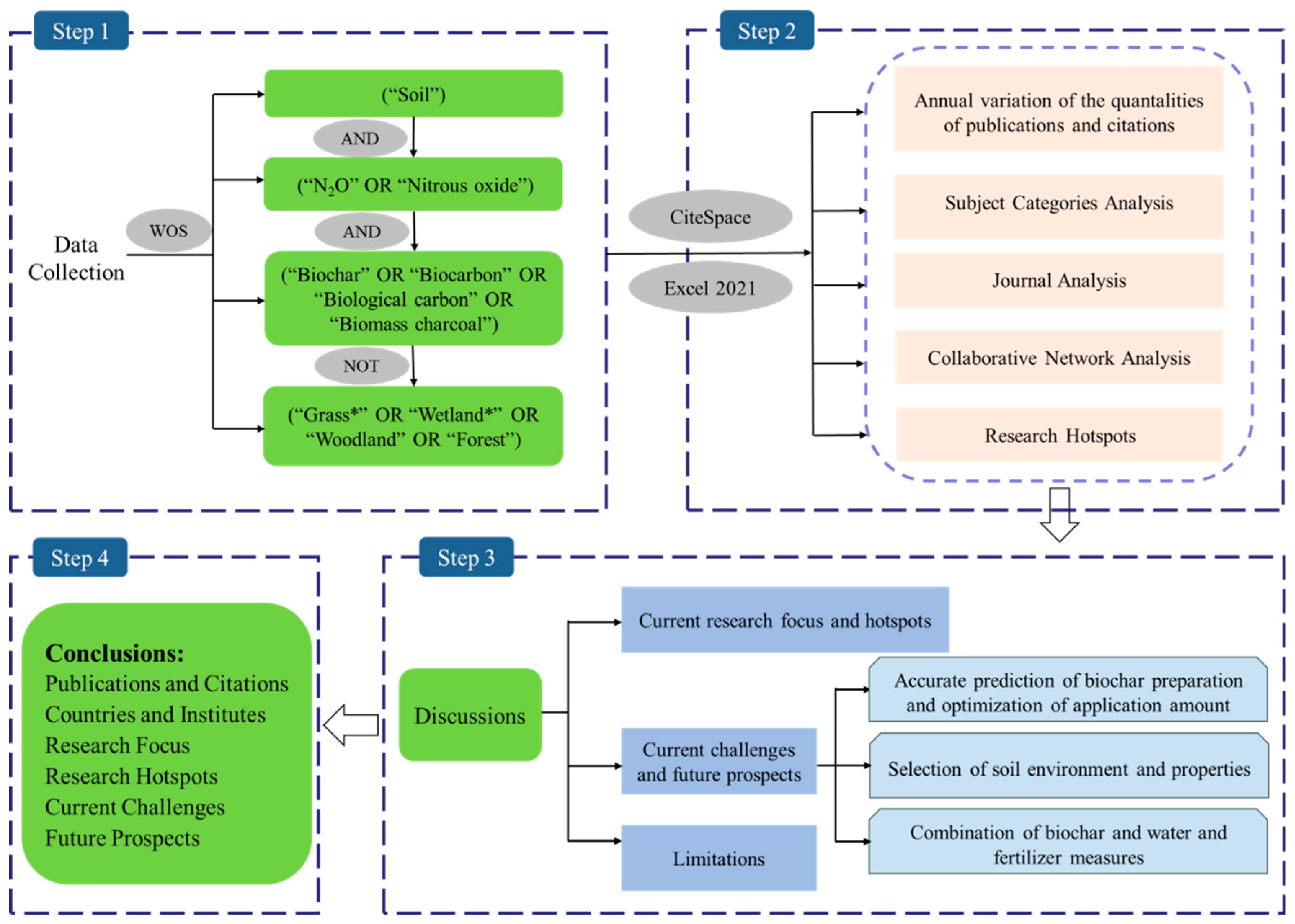
2. Materials and Methodology
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Basic Characteristics
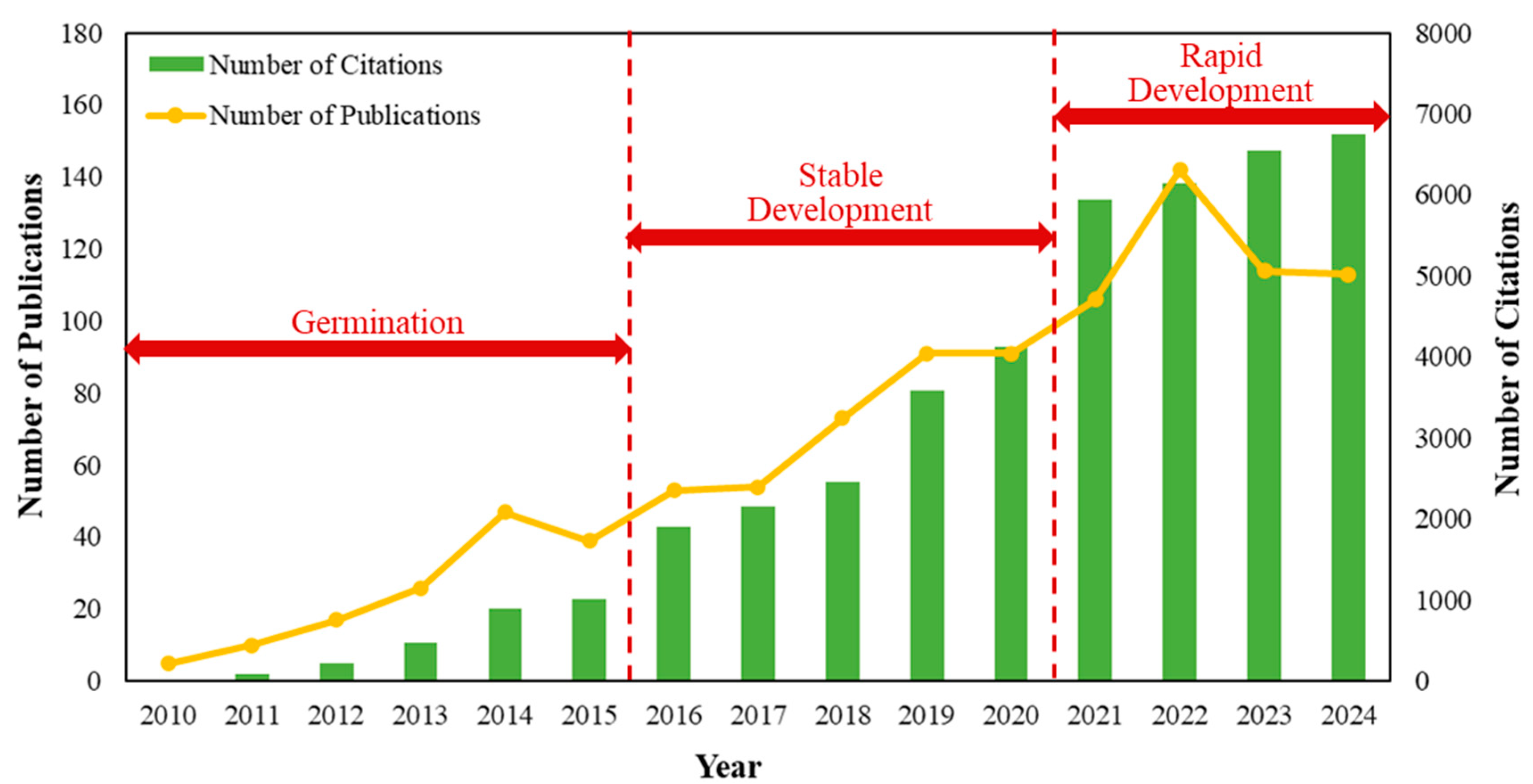
3.1.1. Annual Variation of the Quantities of Publications and Citations
3.1.2. Subject Categories Analysis
3.1.3. Journal Analysis
- (1)
- Issuing journal analysis
- (2)
- Cited journal analysis
3.2. Collaborative Network Analysis
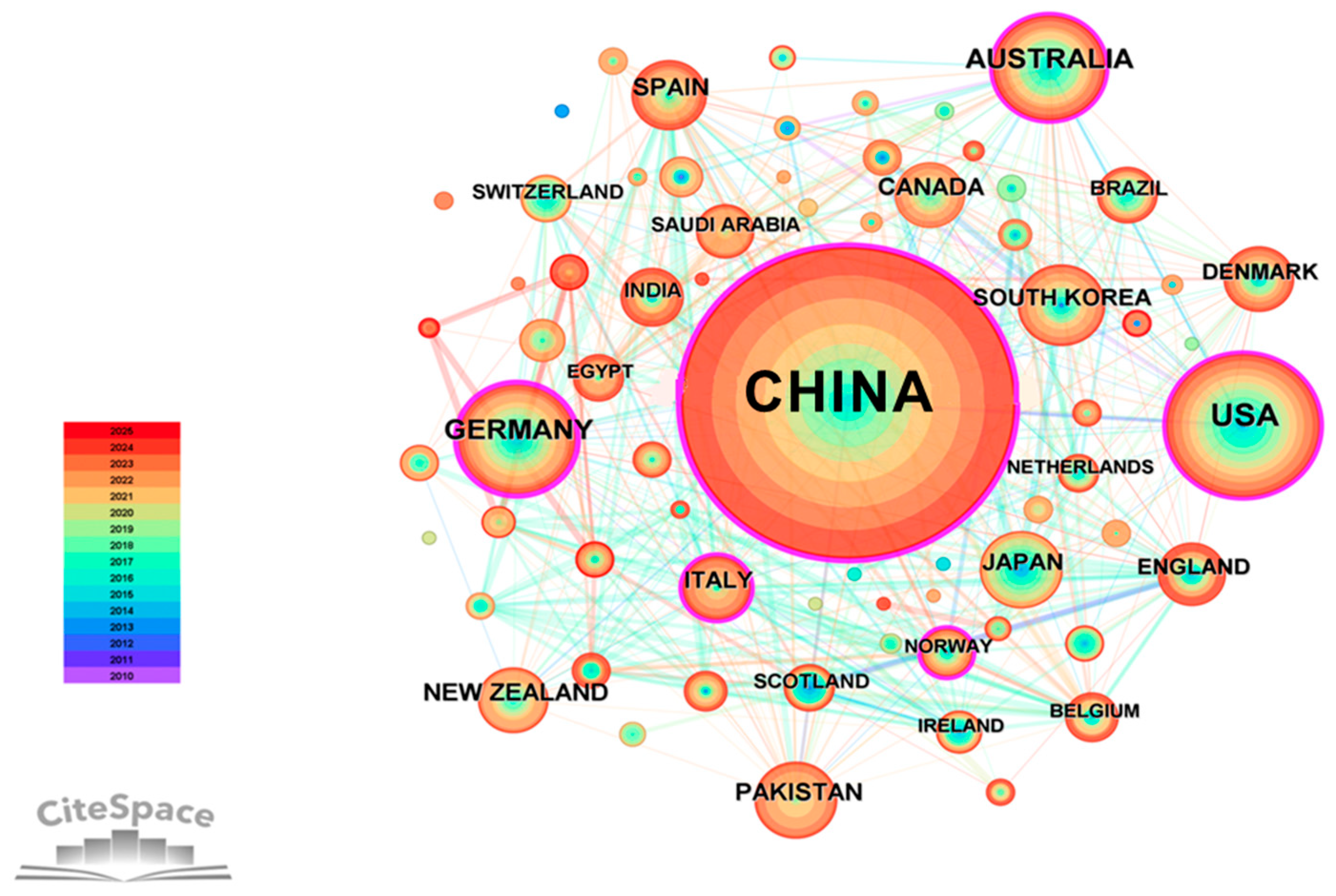
3.2.1. Country Analysis
- (1)
- Co-operation network analysis
- (2)
- High-volume countries analysis
3.2.2. Institution Analysis
- (1)
- Collaborative network analysis
- (2)
- High-volume institution analysis
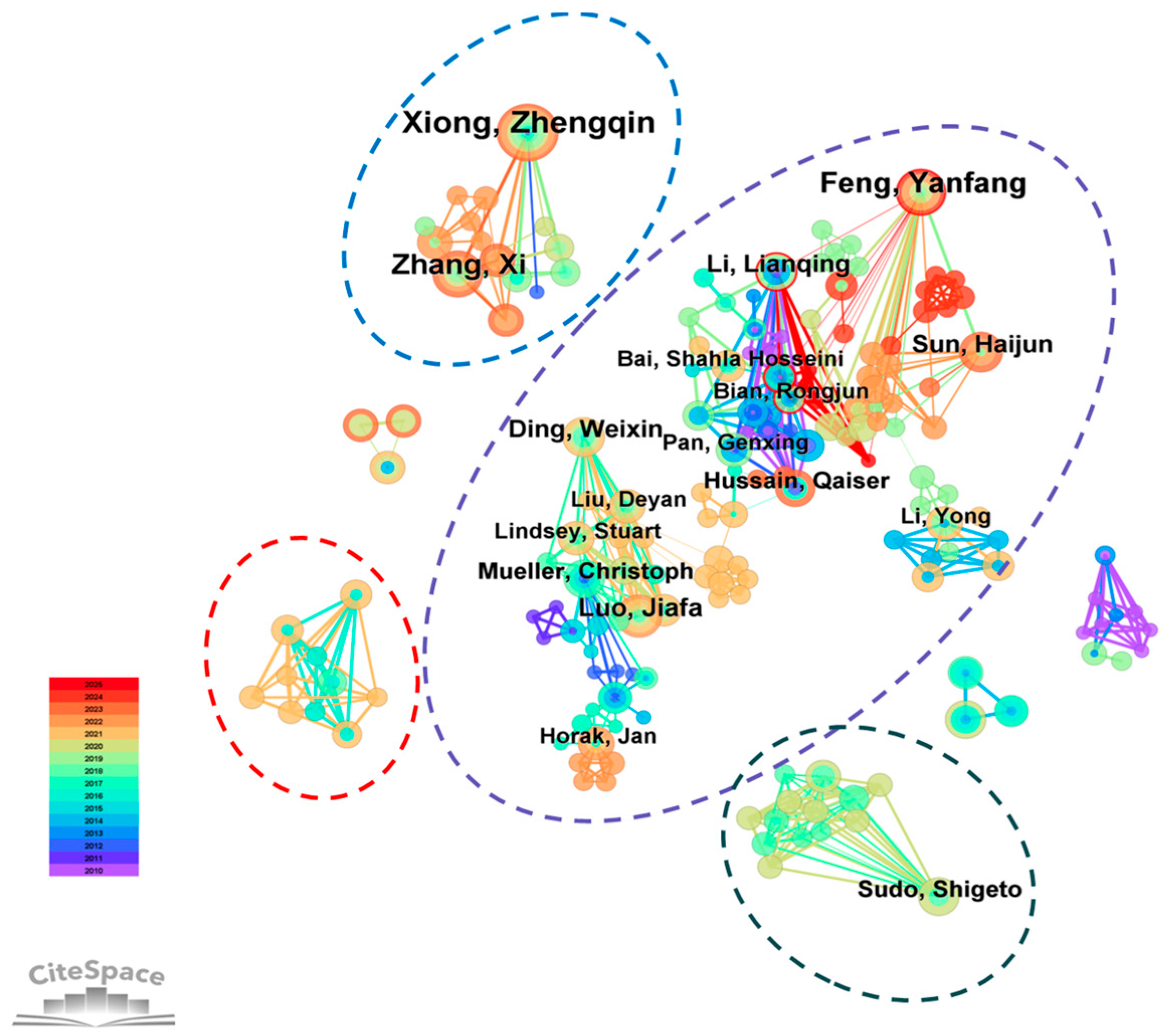
3.2.3. Author Analysis
- (1)
- Author collaboration network
- (2)
- Highly published scholars’ analysis
- (3)
- Highly Cited Scholars’ Analysis
3.3. Research Hotspots
3.3.1. Keyword Co-Occurrence
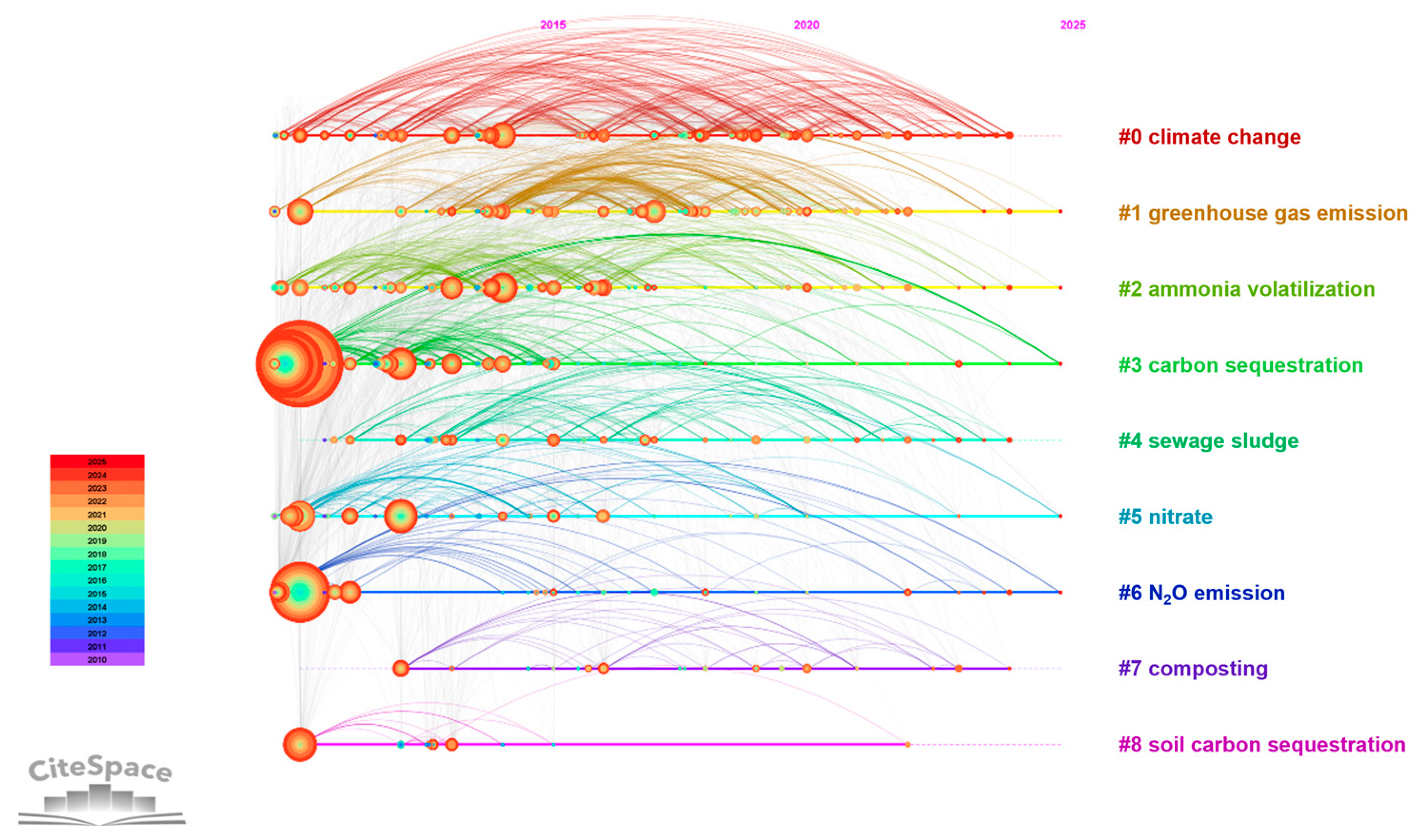
3.3.2. Cluster Analysis of Keyword
3.3.3. Keyword Bursts Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Current Research Focus and Hotspots
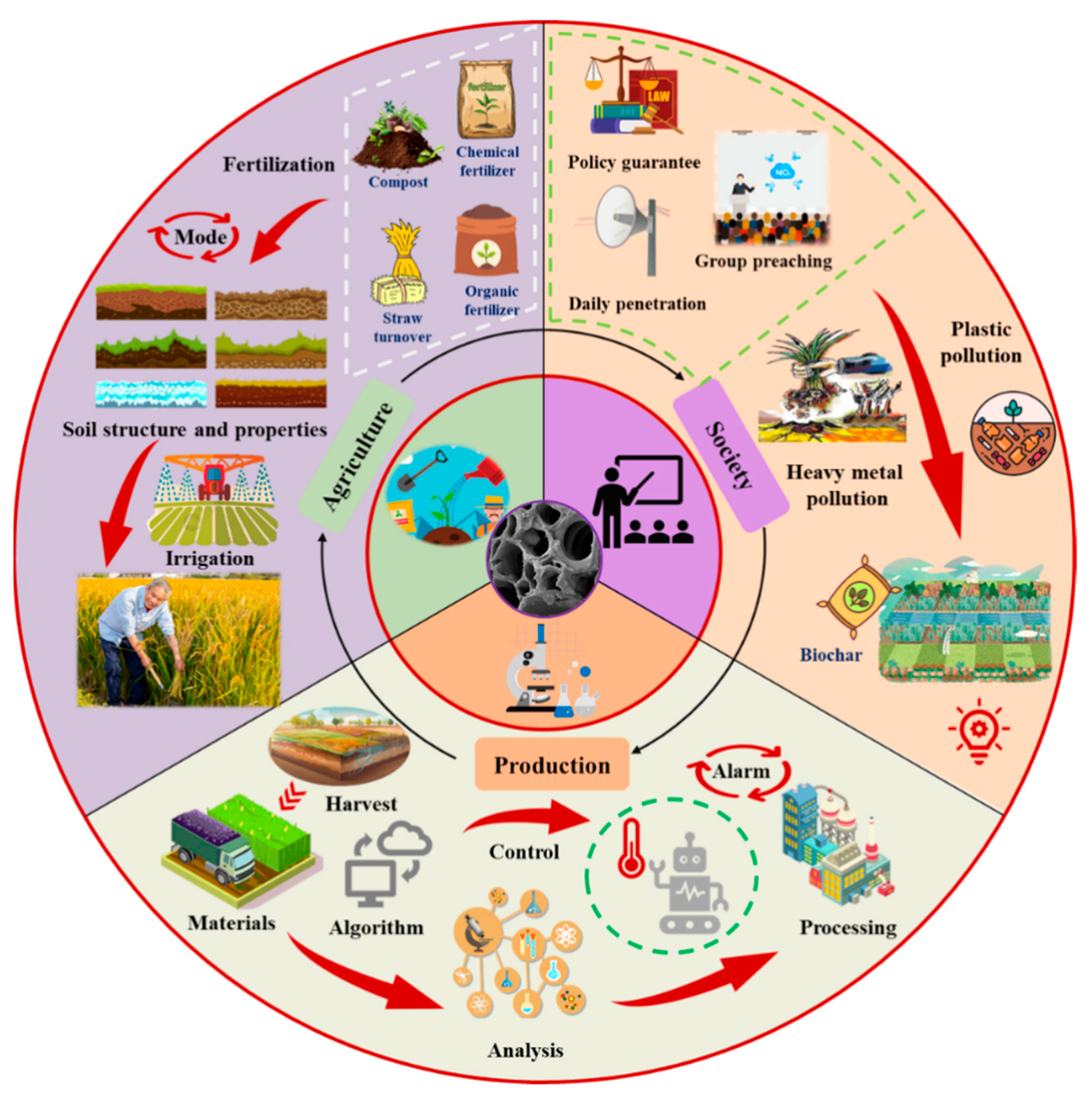
4.2. Current Challenges and Future Prospects
4.2.1. Accurate Prediction of Biochar Preparation and Optimization of Application Rates
4.2.2. Selection of Soil Environment and Properties
4.2.3. Combination of Biochar and Water Fertilization Measures
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harter, J.; Krause, H.-M.; Schuettler, S.; Ruser, R.; Fromme, M.; Scholten, T.; Kappler, A.; Behrens, S. Linking N2O emissions from biochar-amended soil to the structure and function of the N-cycling microbial community. ISME J. 2014, 8, 660–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Change, I. The Earth’s Energy Budget, Climate Feedbacks and Climate Sensitivity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2023; pp. 923–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, Z.; Wei, Y.; Liu, C.; Zheng, X.; Xie, B. Organically fertilized tea plantation stimulates N2O emissions and lowers NO fluxes in subtropical China. Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 5915–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, T.M.; Sapkota, T.B.; Eagle, A.J.; Kantar, M.B.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Majumdar, K. Meta-analysis of yield and nitrous oxide outcomes for nitrogen management in agriculture. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2343–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Yang, J.; Xu, R.; Lu, C.; Canadell, J.; Davidson, E.; Jackson, R.; Arneth, A.; Chang, J.; Ciais, P.; et al. Global soil nitrous oxide emissions since the preindustrial era estimated by an ensemble of terrestrial biosphere models: Magnitude, attribution, and uncertainty. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 640–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J. A handful of carbon. Nature 2007, 447, 143–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J. Bio-energy in the black. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2007, 5, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Liang, Z. Adsorption Mechanisms of Cadmium (II)on Biochars Derived from Corn Straw. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2012, 31, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar]
- Gabetto, F.P.; Tenelli, S.; Netto-Ferreira, J.B.; Tenelli, S.; Gonzaga, L.C.; Isidório, M.A.S.; Carvalho, J.L.N. Exploring the potential of sugarcane straw biochar: Insights into N2O emissions and microbial functional genes. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 182, 107070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.-P.; Kammann, C.; Hagemann, N.; Leifeld, J.; Bucheli, T.D.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.; Cayuela, M.L. Biochar in agriculture–A systematic review of 26 global meta-analyses. GCB Bioenergy 2021, 13, 1708–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Cowie, A.; Masiello, C.A.; Kammann, C.; Woolf, D.; Amonette, J.E.; Cayuela, M.L.; Arbestain, M.C.; Whitman, T. Biochar in climate change mitigation. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Kieffer, C.; Ren, W.; Hui, D. How much is soil nitrous oxide emission reduced with biochar application? An evaluation of meta-analyses. GCB Bioenergy 2023, 15, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Ahmad, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Tang, J. A review of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs) adsorption by biochar and modified biochar in water. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xu, P.; Han, Z.; Wu, J.; Bo, X.; Wang, J.; Zou, J. Effect of biochar and DMPP application alone or in combination on nitrous oxide emissions differed by soil types. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2023, 59, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Rong, X.; Zhou, X.; Fei, J.; Peng, J.; Luo, G. Biochar and organic fertilizer applications enhance soil functional microbial abundance and agroecosystem multifunctionality. Biochar 2024, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; He, H.; Zhou, G.; He, Q.; Yang, S. Rice Yield and Greenhouse Gas Emissions Due to Biochar and Straw Application under Optimal Reduced N Fertilizers in a Double Season Rice Cropping System. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umair Hassan, M.; Huang, G.; Munir, R.; Khan, T.; Noor, M. Biochar Co-Compost: A Promising Soil Amendment to Restrain Greenhouse Gases and Improve Rice Productivity and Soil Fertility. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Jeyakumar, P.; Yin, C.; Sun, H. Effects of biochar in combination with varied N inputs on grain yield, N uptake, NH3 volatilization, and N2O emission in paddy soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1174805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.; Dong, Y.; Xiong, Z. N2O and NO production and functional microbes responding to biochar aging process in an intensified vegetable soil. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 307, 119491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, B.; Xu, X.; Dong, Y.; Xiong, Z. Biochar amendments and climate warming affected nitrification associated N2O and NO production in a vegetable field. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 330, 117178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Yuan, H.; He, X.; Hu, H.; Qin, S.; Clough, T.; Wrage-Mönnig, N.; Luo, J.; He, X.; Chen, M.; et al. Identification and verification of key functional groups of biochar influencing soil N2O emission. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, D.; Yuan, J.; Jia, Z.; Wu, P.; Hu, C.; Clough, T.J.; Cheng, H.; Qin, S. Hydrochar Surpasses Pyrochar in Mitigating Soil N2O Emissions from Denitrification Due to Its Improved Electron Shuttle Function and Low Levels of Persistent Free Radicals. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2024, 11, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastorelli, R.; Casagli, A.; Rocchi, F.; Tampio, E.; Laaksonen, I.; Becagli, C.; Lagomarsino, A. Effects of Anaerobic Digestates and Biochar Amendments on Soil Health, Greenhouse Gas Emissions, and Microbial Communities: A Mesocosm Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Wei, Q.; Xu, J.Z.; Liu, Y.Z.; Wang, D.; Chen, S.Y.; Qian, W.H.; He, M.; Chen, P.; Zhou, X.Y.; et al. Nitrogen losses from soil as affected by water and fertilizer management under drip irrigation: Development, hotspots and future perspectives. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 296, 108791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jiang, H.; Gao, J.; Wan, X.; Yan, B.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, G.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W. Effects of biochar application methods on greenhouse gas emission and nitrogen use efficiency in paddy fields. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 915, 169809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, B.P.; Gao, S.; Thao, T.; Gonzales, M.L.; Williams, K.L.; Scott, N.; Hale, L.; Ghezzehei, T.; Diaz, G.; Ryals, R.A. Methane and nitrous oxide emissions during biochar-composting are driven by biochar application rate and aggregate formation. GCB Bioenergy 2024, 16, e13121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Dong, F.; Chen, L.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, L.; Sun, S.Y.; Wang, Z.; Lai, J.L.; Fang, L.C. Biochar-mediated remediation of uranium-contaminated soils: Evidence, mechanisms, and perspectives. Biochar 2024, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Wang, H.; Lazcano, C.; Voroney, P.; Elrys, A.; Gou, G.L.; Li, H.F.; Zhu, Q.L.; Chen, Y.Z.; Wu, Y.Z.; et al. Biochar amendments to tropical paddy soil increase rice yields and decrease N2O emissions by modifying the genes involved in nitrogen cycling. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 235, 105917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.M.; Chen, C.R.; Rashti, M.R.; Yang, H.; Zhang, D.K. Stoichiometric ratio of dissolved organic carbon to nitrate regulates nitrous oxide emission from the biochar-amended soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelissen, V.; Saha, B.K.; Ruysschaert, G.; Boeckx, P. Effect of different biochar and fertilizer types on N2O and NO emissions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 70, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, M.V.; Tesfai, M.; Borrell, A.; Nagothu, U.S.; Bui, T.P.L.; Quynh, V.D.; Thanh, L.Q. Effect of organic, inorganic and slow-release urea fertilisers on CH4 and N2O emissions from rice paddy fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2017, 15, 317–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Bai, J.; Bi, C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Cui, B.S. Global greenhouse gas emissions from aquaculture: A bibliometric analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 348, 108405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donthu, N.; Kumar, S.; Mukherjee, D.; Pandey, N.; Lim, W.M. How to conduct a bibliometric analysis: An overview and guidelines. J. Bus. Res. 2021, 133, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuciterna, R.; Ruggeri, G.; Corsi, S.; Facchi, A.; Gharsallah, O. A bibliometric analysis of scientific literature on alternate wetting and drying (AWD). Paddy Water Environ. 2024, 22, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Yuan, X.; Siemann, E.; Wang, S.L.; Fang, H.F.; Wang, B.H.; Gao, Y.; Shad, N.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, W.Y.; et al. Feedstock particle size and pyrolysis temperature regulate effects of biochar on soil nitrous oxide and carbon dioxide emissions. Waste Manag. 2021, 120, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaomei, C.; Zhigang, H.; Shengbo, L.; Hung, T. Emerging trends in regenerative medicine: A scientometric analysis in CiteSpace. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2012, 12, 593–608. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, K.; Ashworth, P. The development of Carbon Capture Utilization and Storage (CCUS) research in China: A bibliometric perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 138, 110521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalus, K.; Koziel, J.A.; Opaliński, S. A Review of Biochar Properties and Their Utilization in Crop Agriculture and Livestock Production. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Yan, M.; Niu, Y.R.; Liu, X.Y.; van Zwieten, L.; Chen, D.; Bian, R.J.; Cheng, K.; Li, L.Q.; Joseph, S.; et al. Is current biochar research addressing global soil constraints for sustainable agriculture? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 226, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cayuela, M.L.; van Zwieten, L.; Singh, B.P.; Jeffery, S.; Roig, A.; Sanchez-Monedero, M.A. Biochar’s role in mitigating soil nitrous oxide emissions: A review and meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 191, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christodoulou, E.; Agapiou, A.; Anastopoulos, I.; Omirou, M.; Ioannides, I.M. The effects of different soil nutrient management schemes in nitrogen cycling. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 243, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ma, E.; Qu, H. Knowledge mapping of hospitality research−A visual analysis using CiteSpace. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 2017, 60, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.W.; Tang, S.R.; He, Z.L.; Cheng, H.G.; Twagirayezu, G.; Zhao, J.S.; Xiang, R.B.; Hu, R.G.; Lin, S. Biochar addition under straw return reduces carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide emissions in acidic tea field soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, Z.; Liu, P.; Pan, G. Effects of biochar addition on N2O and CO2 emissions from two paddy soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Zwieten, L.; Kimber, S.W.L.; Morris, S.G.; Singh, B.P.; Grace, P.R.; Scheer, C.; Downie, A.E.; Cowie, A.L. Pyrolysing poultry litter reduces N2O and CO2 fluxes. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Song, L.; Jin, Y.; Liu, S.; Shen, Q.; Zou, J. Linking N2O emission from biochar-amended composting process to the abundance of denitrify (nirK and nosZ) bacteria community. AMB Express 2016, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Ding, W.; Liu, D.; He, T.H.; Yoo, G.; Yuan, J.J.; Chen, Z.W.; Fan, J.L. Wheat straw-derived biochar amendment stimulated N2O emissions from rice paddy soils by regulating the amoA genes of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Xie, M.; Clough, T.J.; Yuan, D.; Wu, S.H.; He, X.D.; Hu, C.S.; Zhou, S.G.; Qin, S.P. Biochar-derived persistent free radicals and reactive oxygen species reduce the potential of biochar to mitigate soil N2O emissions by inhibiting nosZ. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2023, 178, 108970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Xiong, X.; Chen, Y.; Shaaban, M.; Hu, R.G. Optimizing biochar addition for vermicomposting: A comprehensive evaluation of earthworms’ activity, N2O emissions and compost quality. Biochar 2023, 5, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Xu, J.; Yu, L.; Cai, H. Deficit irrigation interacting with biochar mitigates N2O emissions from farmland in a wheat–maize rotation system. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 297, 108843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Li, Y.; Zheng, N.; Liu, C.; Ren, H.; Yao, H. Interactive effects of microplastics, biochar, and earthworms on CO2 and N2O emissions and microbial functional genes in vegetable-growing soil. Environ. Res. 2022, 213, 113728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Song, L.; Xu, L.; Fan, Y.; Wang, T.; Tian, W.; Ju, J.; Xu, H. Knowledge Domain and Emerging Trends in Ferroptosis Research: A Bibliometric and Knowledge-Map Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 686726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C. CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Technol. 2006, 57, 359–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, L.; Tu, S. Land Use Transitions: Progress, challenges and prospects. Land 2021, 10, 903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, M.; Zhuang, D. Wastewater treatment and emerging contaminants: Bibliometric analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 297, 133932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, L.; Lu, C.; Shen, R.; Liu, T.; Ma, B.; Hua, Y. Knowledge Mapping of Drug-Induced Liver Injury: A Scientometric Investigation (2010–2019). Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; She, R.; Hu, L.; Yu, Y.; Yao, H. Effects of biochar addition on nitrous oxide emission during soil freeze–thaw cycles. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1033210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffar, M.T.; Ahmed, M.; Shi, R.; Jiang, S.H.; Kong, Z.R.; Gorkin, N.; Zhang, J.G.; Huo, H.X. Unraveling mechanisms of N₂O emissions and nitrogen cycling: The role of biochar C:N ratios in loamy and sandy soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 207, 105950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shen, G.; Sun, M.; Cao, X.; Shang, G.; Chen, p. Effect of biochar on nitrous oxide emission and its potential mechanisms. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, R.; Yao, L.; Yan, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, G.; Bahn, M.; Mo, F.; Han, J. Extreme climate weakens the effect of biochar in increasing yield and reducing N2O emissions. Field Crops Res. 2025, 322, 109765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, G.; Dong, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, X. Inhibitory Effects of Biochar on N2O Emissions through Soil Denitrification in Huanghuaihai Plain of China and Estimation of Influence Time. Sustainability 2024, 16, 5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.A.; Hoque, M.A.; Kim, P.J. Mitigating Global Warming Potentials of Methane and Nitrous Oxide Gases from Rice Paddies under different irrigation regimes. AMBIO 2013, 42, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, M.; Ni, Y.; Shen, G. Mitigation strategies for NH₃ and N₂O emissions in greenhouse agriculture: Insights into fertilizer management and nitrogen emission mechanisms. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 103995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Bhogal, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Agarwal, S.; Kumar, A.; Pathania, D.; Mola, G.; Stadler, F. Algal biochar reinforced trimetallic nanocomposite as adsorptional/photocatalyst for remediation of malachite green from aqueous medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 275, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Yun, F.; Liu, T.; Jin, J.; Yang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Wang, J. Differentiated mechanisms of biochar- and straw-induced greenhouse gas emissions in tobacco fields. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 166, 103996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, C. Long-term effects of biochar addition and straw return on N2O fluxes and the related functional gene abundances under wheat-maize rotation system in the North China Plain. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Peng, Q.; Liu, X.; Xun, C. The Effect of Biochar and Straw Return on N2O Emissions and Crop Yield: A Three-Year Field Experiment. Agriculture 2023, 13, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Meriggi, L.; Steer, M.; Fan, W.; Bulashevich, K.; Thayne, I.; Macgregor, C.; Ironside, C.; Sorel, M. Design, Simulations, and Optimizations of Mid-infrared Multiple Quantum Well LEDs. Procedia Eng. 2016, 140, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Xu, W.; Dong, J.; Ting, Y.; Zichen, S.; Jing, Q.; Xin, L.; Tan, X. The effects of biochar and its applications in the microbial remediation of contaminated soil: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, J.; Zhu, L.; Nielsen, S.; Graber, E.; Mitchell, D.; Horvat, J.; Mohammed, M.; Liu, M.; van Zwieten, L.; Donne, S.; et al. Biochar-based fertilizer: Supercharging root membrane potential and biomass yield of rice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 136431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Westholm, L.; Carvalho, L.; Thorin, E.; Yu, Z.; Yu, X.; Skreiberg, O. A critical review on production, modification and utilization of biochar. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 161, 105405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, S.; Rasse, D.P.; Budai, A.; Tomic, O.; Dörsch, P. The effect of a biochar temperature series on denitrification: Which biochar properties matter? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Yang, S.; Pang, Q.; Abdalla, M.; Qi, S.; Hu, J.; Qin, H.; Smith, P. Optimizing biochar application rate and predicting of climate change impacts on net greenhouse gas emissions in paddy systems using DNDC-BC model. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2025, 364, 110461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Shan, Y.; Wu, P.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, F.; Zhu, T. Mitigating the global warming potential of rice paddy fields by straw and straw-derived biochar amendments. Geoderma 2021, 396, 115081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Sheng, Y.; Cai, F.; Wang, W.; Zhu, L. Separated pathways for biochar to affect soil N2O emission under different moisture contents. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, S.S.; Andersen, M.N.; Liu, F. Biochar Mitigates Salinity Stress in Potato. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2015, 201, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Naggar, A.; Lee, S.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Farooq, M.; Song, H.; Sarmah, A.; Zimmerman, A.; Ahmad, M.; Shaheen, S.; Ok, Y. Biochar application to low fertility soils: A review of current status, and future prospects. Geoderma 2019, 337, 536–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Xiong, X.; Zhu, H.; Xu, H.; Leng, P.; Li, J.; Tang, C.; Xu, J. Association of biochar properties with changes in soil bacterial, fungal and fauna communities and nutrient cycling processes. Biochar 2021, 3, 239–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Gao, B.; Peng, Y.; Gao, X.; Fan, B.; Chen, Q. A meta-analysis of heavy metal bioavailability response to biochar aging: Importance of soil and biochar properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Yu, Q.; Chen, R.; Wang, J.; Liu, X. Biochar-microplastics interaction modulates soil nitrous oxide emissions and microbial communities. Biochar 2025, 7, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-M.; Park, D.-G.; Kang, S.-S.; Choi, E.-J.; Gwon, H.-S.; Lee, H.-S.; Lee, S.-I. Short-Term Effect of Biochar on Soil Organic Carbon Improvement and Nitrous Oxide Emission Reduction According to Different Soil Characteristics in Agricultural Land: A Laboratory Experiment. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Liu, L.; Ling, Q.; Cai, Y.; Yu, S.; Wang, S.; Fu, D.; Hu, B.; Wang, X. Biochar for the removal of contaminants from soil and water: A review. Biochar 2022, 4, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramlow, M.; Cotrufo, M.F. Woody biochar’s greenhouse gas mitigation potential across fertilized and unfertilized agricultural soils and soil moisture regimes. GCB Bioenergy 2018, 10, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Dai, W.; Niu, J.; Wang, J.; Yin, W.; Yan, X.; Jiang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Straw and Biochar Amendments Over a Decade Differently Modulates Denitrification Gas Products. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agegnehu, G.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bird, M.I. The role of biochar and biochar-compost in improving soil quality and crop performance: A review. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2017, 119, 156–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntacyabukura, T.; Uwiringiyimana, E.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhu, B.; Harerimana, B.; Nambajimana, J.; Nsabimana, G.; Nsengumuremyi, P. Effect of Biochar and Straw Application on Nitrous Oxide and Methane Emissions from Eutric Regosols with Different pH in Sichuan Basin: A Mesocosm Study. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd–Elrahman, S.H.; Saudy, H.S.; El–Fattah, D.A.A.; Hashem, F.A.E. Effect of Irrigation Water and Organic Fertilizer on Reducing Nitrate Accumulation and Boosting Lettuce Productivity. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Awasthi, M.K.; Pan, J.; Jiang, S.L.; Wan, F.C.; Lin, X.; Yan, B.H.; Zhang, J.C.; Zhang, L.H.; Huang, H.L.; et al. Effects of biochar and biogas residue amendments on N2O emission, enzyme activities and functional genes related with nitrification and denitrification during rice straw composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 357, 127359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Subject Category | 2010–2015 | 2016–2020 | 2021–2025 | 2010–2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Sciences | 57 | 191 | 252 | 500 |
| Soil Science | 50 | 96 | 107 | 253 |
| Agronomy | 19 | 52 | 85 | 156 |
| Plant Sciences | 12 | 28 | 57 | 97 |
| Engineering Environmental | 9 | 18 | 44 | 71 |
| Ecology | 21 | 13 | 28 | 62 |
| Agriculture Multidisciplinary | 19 | 16 | 25 | 60 |
| Energy Fuels | 10 | 21 | 27 | 59 |
| Biotechnology Applied Microbiology | 9 | 19 | 27 | 55 |
| Green Sustainable Science Technology | 4 | 15 | 33 | 52 |
| Journals | PC | TCb | TC/PC | h-Indexd | IFa | Initial Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Science of the Total Environment | 120 | 5543 | 46.19 | 45 | 8.2 | 2011 |
| Agriculture Ecosystems Environment | 44 | 4494 | 102.14 | 27 | 6.0 | 2010 |
| Journal of Environmental Management | 36 | 952 | 26.44 | 16 | 8.0 | 2014 |
| Agronomy Basel | 33 | 190 | 5.76 | 9 | 3.3 | 2018 |
| Soil Biology and Biochemistry | 30 | 2932 | 97.73 | 26 | 9.8 | 2011 |
| Global Change Biology Bioenergy | 26 | 1783 | 68.58 | 19 | 5.9 | 2012 |
| Applied Soil Ecology | 24 | 681 | 28.38 | 15 | 4.8 | 2014 |
| Geoderma | 22 | 1000 | 45.45 | 17 | 5.6 | 2013 |
| Journal of Environmental Quality | 22 | 1854 | 84.27 | 17 | 2.2 | 2010 |
| Biology and Fertility of Soils | 22 | 1040 | 47.27 | 17 | 5.1 | 2011 |
| Scientific Reports | 21 | 1821 | 86.71 | 16 | 3.8 | 2013 |
| Journal of Cleaner Production | 20 | 465 | 23.13 | 13 | 9.8 | 2015 |
| Environmental Pollution | 20 | 1030 | 51.50 | 14 | 7.6 | 2013 |
| TC | Initial Year | Cited Journal |
|---|---|---|
| 907 | 2010 | Soil Biology and Biochemistry |
| 823 | 2010 | Agriculture Ecosystems Environment |
| 778 | 2010 | Science of The Total Environment |
| 734 | 2010 | Plant and Soil |
| 663 | 2011 | Geoderma |
| 658 | 2010 | Biology and Fertility of Soils |
| 585 | 2010 | Chemosphere |
| 563 | 2010 | Journal of Environment Quality |
| 543 | 2010 | Soil Science Social of America Journal |
| 534 | 2010 | Environmental Science Technology |
| Rank | Country | Count | TC | TC/P | h-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 570 | 19,933 | 34.67 | 71 |
| 2 | USA | 148 | 9250 | 62.08 | 49 |
| 3 | Australia | 84 | 7969 | 94.87 | 39 |
| 4 | Germany | 82 | 4853 | 59.18 | 37 |
| 5 | Pakistan | 48 | 2254 | 46.96 | 23 |
| 6 | New Zealand | 44 | 3194 | 70.98 | 27 |
| 7 | Spain | 44 | 2560 | 58.18 | 21 |
| 8 | Canada | 41 | 1677 | 39.93 | 22 |
| 9 | Italy | 39 | 2071 | 53.1 | 20 |
| 10 | South Korea | 36 | 941 | 26.14 | 15 |
| Rank | Institution | Ps | TC | TC/P | h-Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | 148 | 5660 | 37.99 | 45 |
| 2 | Nanjing Agricultural University | 69 | 4685 | 67.90 | 35 |
| 3 | Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs | 69 | 1637 | 22.92 | 27 |
| 4 | University of Chinese Academy of Sciences | 66 | 2938 | 43.85 | 30 |
| 5 | Nanjing Institute of Soil Science | 57 | 2364 | 41.47 | 27 |
| 6 | Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences | 55 | 1390 | 25.27 | 21 |
| 7 | Northwest A&F University—China | 51 | 1694 | 30.80 | 24 |
| 8 | Nanjing Forestry University | 30 | 573 | 18.48 | 14 |
| 9 | Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences | 29 | 945 | 28.64 | 18 |
| 10 | China Agricultural University | 27 | 678 | 25.11 | 12 |
| Author | Freq. | Institution | Country |
|---|---|---|---|
| Xiong Zhengqin | 23 | Nanjing Agricultural University | China |
| Feng Yanfang | 17 | Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs | China |
| Pan Genxing | 16 | Nanjing Agricultural University | China |
| Lukas Van Zwieten | 15 | NSW Department of Primary Industries | Australia |
| Hussain Qaiser | 14 | Pir Mehr Ali Shah Arid Agriculture University | Pakistan |
| Li lianqing | 14 | Nanjing Agricultural University | China |
| Sun Haijun | 13 | Nanjing Forestry University | China |
| Ding Weixin | 13 | Chinese Academy of Sciences | China |
| Zou Jianwen | 13 | Nanjing Agricultural University | China |
| Maria Luz Cayuela | 13 | Consejo Superior de Investigaciones Científicas (CSIC) | Spain |
| TC | Initial Year | Author | Author Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 508 | 2010 | Johannes Lehmann | Cornell University, USA |
| 434 | 2011 | Maria Luz Cayuela | CSIC—Centro de Edafología y Biología Aplicada del Segura (CEBAS), Spain |
| 347 | 2010 | Lukas Van Zwieten | NSW Department of Primary Industries, Australia |
| 317 | 2011 | Zhang Afeng | Northwest A&F University, China |
| 317 | 2011 | Kurt A Spokas | USDA-ARS, Soil and Water Management Unit, St.Paul, MN, USA. |
| 291 | 2010 | Thomas J. Clough | Imperial College London, UK |
| 247 | 2013 | Sean D.C. Case | University of Copenhagen, Denmark. |
| 244 | 2010 | Bhupinder Pal Singh | Murdoch University, Australia |
| 230 | 2012 | Wang Jinyang | Nanjing Agricultural University, China |
| 221 | 2013 | Simon Jeffery | Harper Adams University, UK |
| 2010–2015 | 2016–2020 | 2021–2025 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Keyword | Freq. | Cen. | Keyword | Freq. | Cen. | Keyword | Freq. | Cen. |
| N2O emissions | 110 | 0.02 | N2O emissions | 285 | 0.02 | N2O emissions | 338 | 0.05 |
| biochar | 82 | 0.01 | greenhouse gas emissions | 150 | 0.03 | greenhouse gas emissions | 246 | 0.05 |
| CO2 | 61 | 0.15 | CO2 | 147 | 0.02 | soil | 162 | 0.07 |
| greenhouse gas emissions | 56 | 0.10 | soil | 126 | 0.00 | CO2 | 150 | 0.03 |
| soil | 51 | 0.05 | biochar | 109 | 0.00 | biochar | 130 | 0.01 |
| denitrification | 29 | 0.06 | impact | 66 | 0.04 | CH4 | 97 | 0.03 |
| impact | 24 | 0.02 | denitrification | 55 | 0.01 | amendment | 67 | 0.01 |
| manure | 21 | 0.16 | CH4 | 48 | 0.14 | impact | 60 | 0.03 |
| fertilizer | 20 | 0.04 | nitrification | 48 | 0.02 | organic carbon | 53 | 0.01 |
| CH4 | 18 | 0.19 | amendment | 46 | 0.00 | nitrification | 53 | 0.02 |
| Cluster ID | Size | Silhouette | Top Term (LSI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 97 | 0.482 | nitrous oxide; nitrogen dynamics; sodium ferrate; greenhouse gases; straw incorporation; greenhouse gas emissions; carbon footprint; carbon budget; rice paddies; rainfed winter wheat |
| 1 | 84 | 0.583 | nitrous oxide; intensive vegetable production; yield-scaled N2O emissions; biochar rate; wheat yield; N2O emissions; gene abundance; water regimes; yield-scaled N2O emissions; intensive vegetable production |
| 2 | 75 | 0.536 | greenhouse gas emissions; microbial community; cropping rice system; greenhouse gases; wheat productivity; soil fertility; organic matter; soil mesofauna; mediterranean climate; cropping rice system |
| 3 | 74 | 0.722 | nitrous oxide; greenhouse gas emissions; soil carbon; exchangeable cations; fumigation; carbon sequestration; greenhouse gas; carbon neutrality; agricultural soil management; release |
| 4 | 46 | 0.648 | nitrous oxide; first-principles calculation; sodium ferrate; nitrification; manure; greenhouse gases; soil amendment; cropping systems; soil porosity; banana peels |
| 5 | 43 | 0.675 | nitrous oxide; nitrification inhibitors; biochar application; nitrogen mineralization; camellia oleifera; N2O emissions; fertilizer; impact; sorption; nitrification |
| 6 | 41 | 0.674 | nitrous oxide; soil moisture; temporal variation; available n; labile carbon; N2O emission; clayey loam soil; bulk density; water retention capacity; field-aged biochar |
| 7 | 24 | 0.781 | N2O emissions; soil moisture; fertilizer; nutrient; drainage ditches; greenhouse gases; sewage sludge; bacterial agents; microbial functional genes; pyrolysis atmosphere |
| 8 | 18 | 0.864 | greenhouse gas emissions; global climate change; global cropland; biochar application; functional theory calculation; nitrous oxide; nitric oxide; nitrogen oxide; plant growth bioassay; rice–vegetable rotation |
| Keyword | Strength | Begin | End | 2010–2025 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| biochar | 13.11 | 2010 | 2015 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| chemical property | 6.58 | 2010 | 2018 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| manure | 5.16 | 2010 | 2016 | ▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| increases | 4.37 | 2010 | 2012 | ▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| microbial biomass | 3.93 | 2010 | 2012 | ▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| bioenergy | 3.54 | 2010 | 2014 | ▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| amendments | 5.05 | 2011 | 2017 | ▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| sequestration | 3.51 | 2011 | 2012 | ▂▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| mineralization | 4.07 | 2012 | 2017 | ▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| pyrolysis | 3.87 | 2012 | 2017 | ▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| organic matter | 3.45 | 2012 | 2014 | ▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| decomposition | 3.14 | 2012 | 2018 | ▂▂▃▃▃▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons | 3.53 | 2013 | 2015 | ▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| rice paddy | 3.56 | 2014 | 2016 | ▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| slow pyrolysis | 4.19 | 2015 | 2018 | ▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| cropping systems | 3.08 | 2015 | 2016 | ▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| sorption | 3.40 | 2016 | 2018 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| crop productivity | 2.85 | 2016 | 2017 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| abundance | 4.18 | 2018 | 2019 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂▂▂▂▂ |
| paddy soils | 3.02 | 2018 | 2020 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂▂ |
| reduction | 3.05 | 2019 | 2022 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▂▂▂ |
| field | 2.92 | 2019 | 2021 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂▂ |
| pathways | 2.91 | 2019 | 2022 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃▂▂▂ |
| nitric oxide | 2.87 | 2020 | 2022 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▂▂▂ |
| NH3 volatilization | 3.50 | 2021 | 2022 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂▂ |
| global warming | 3.36 | 2021 | 2022 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂▂ |
| volatilization | 3.86 | 2022 | 2023 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂ |
| heavy metals | 3.40 | 2022 | 2023 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▂▂ |
| carbon footprint | 3.27 | 2022 | 2025 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃▃ |
| global warmingpotential | 5.27 | 2023 | 2025 | ▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▂▃▃▃ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ren, J.; Wang, Y.; Luo, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Wang, J.; Chai, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; et al. Mitigating Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Agricultural Soils with Biochar: A Scientometric and Visual Analysis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051115
Ren J, Wang Y, Luo M, Zhuang Y, Wang J, Chai S, Liu J, Zhang Z, Li Y, Chen P, et al. Mitigating Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Agricultural Soils with Biochar: A Scientometric and Visual Analysis. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051115
Chicago/Turabian StyleRen, Jingyi, Yixuan Wang, Mengqi Luo, Yuxiang Zhuang, Jixiong Wang, Sen Chai, Jun Liu, Ziqi Zhang, Yakun Li, Peng Chen, and et al. 2025. "Mitigating Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Agricultural Soils with Biochar: A Scientometric and Visual Analysis" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051115
APA StyleRen, J., Wang, Y., Luo, M., Zhuang, Y., Wang, J., Chai, S., Liu, J., Zhang, Z., Li, Y., Chen, P., & Wei, Q. (2025). Mitigating Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Agricultural Soils with Biochar: A Scientometric and Visual Analysis. Agronomy, 15(5), 1115. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051115






