Abstract
Ammonia (NH3) is a significant air pollutant with major environmental and health impacts, largely attributed to agriculture. Pig production is a major contributor, accounting for 25% of livestock NH3 emissions. This study developed a new system based on gas-permeable membranes (GPM) technology for NH3 recovery from the atmosphere obtaining a solution of ammonium sulfate as the resulting fertilizer product. Various experimental configurations were evaluated in the novel system using a synthetic NH3-emitting solution. The optimal arrangement was a GPM system with recirculation of the generated NH3 and without recirculation of the acidic trapping solution, yielding a nitrogen (N) recovery rate of up to 237 g m−2 d−1. Subsequent tests using pig manure (PM) at varying durations achieved rates of up to 73 g m−2 d−1, representing a four-fold increase in N capture efficiency compared to previous research. The influence of manure temperature on NH3 emission and capture were analyzed, simulating the possible differences between seasons (summer and winter), and revealing higher N recovery rates at elevated temperatures. At 21.5 °C, the recovery rate was 7.7 g m−2 d−1, while increased temperatures of 38.8 °C and 49.3 °C yielded rates of 15.9 and 27.2 g m−2 d−1, respectively.
1. Introduction
Among air pollutants, NH3 is one of the greatest gases of concern in terms of air quality, environmental impact, and nutrient loss from manure. In addition, NH3 contributes significantly to soil acidification, water eutrophication, loss of biodiversity, and deterioration of human health [1]. By 2030, NH3 emissions to the atmosphere from livestock (e.g., beef, dairy, swine, and poultry) are projected to reach 2.67 million metric tons per year−1 [2]. Consequently, the livestock sector faces a difficult situation, as it must ensure both a high level of production and a reduction of its environmental impact.
About 94% of all anthropogenic NH3 emissions in the European Union (EU) are attributable to agriculture, and animal production produces 75% of these emissions. Pigs are the second largest producer of NH3 emissions of all livestock categories when it comes to the complete manure handling cycle (housing, storage, application), accounting for 25% of the emissions of the entire livestock sector [3].
NH3 emissions pose a persistent challenge in the EU, with 33% of Member States struggling to achieve significant reductions. Since 2005, NH3 emissions have shown minimal decrease across many EU countries [3]. This trend underscores the urgent need for more robust policies targeting the agricultural sector, which is the primary source of NH3 emissions. According to the Directive (EU) 2016/2284 [4], nine Member States must further reduce their NH3 output to meet the 2020–2029 national emission reduction commitments, while a substantial 66% of Member States need to implement additional measures to achieve their 2030 targets. The impact of NH3 emissions extends beyond air quality, affecting biodiversity and contributing to the formation of secondary PM2.5, recognized as the principal air pollutant responsible for premature deaths in the EU. Addressing NH3 emissions is not only crucial for air quality but also aligns with the Zero Pollution Action Plan 2021 [5], which aims to reduce by 25% the number of ecosystems threatened by air pollution-induced biodiversity loss. This multifaceted challenge requires a coordinated approach, combining agricultural innovation, policy reform, and cross-sector collaboration to effectively mitigate NH3 emissions and their far-reaching consequences.
In this way, livestock farmers are forced to adopt the best available techniques (BAT) to reduce NH3 emissions. Therefore, there is a lot of interest in the application of control technologies to decrease NH3 emissions through Nitrogen (N) capture and recovery, which would help to partially offset the costs of their implementation and maintenance through the sales of the fertilizer product [6,7]. Air-stripping towers and acidic absorption [8], filtration methods such as biotrickling or biofilters [9], adsorption with zeolites [10], precipitation by struvite, ultrafiltration/reverse osmosis, or gas-permeable membrane (GPM) technology are some technologies for N recovery from NH3 emitted in livestock buildings [11,12]. GPM technology offers significant advantages for recovering N from the air if compared to other technologies. More specifically, GPM technology does not require pretreatments or the use of chemical additives, while air-stripping towers and adsorption with zeolites need pretreatment, and precipitation by struvite requires the use of chemicals. Ultrafiltration/reverse osmosis requires high pressure in the process [13], while GPM technology works at atmospheric pressure. Additionally, the GPM technology boasts low energy requirements, making it a more sustainable option in comparison to energy-intensive alternatives [14,15]. Therefore, the utilization of GPM technology results in lower economic costs compared to alternative technologies, as the N recovery per animal is less than in the others [16].
GPM technology relies on the diffusion of NH3 through a hydrophobic microporous membrane, followed by its capture and concentration in an extraction solution on the opposite side of the membrane. Primarily, it provides an expansive surface area for gas transfer, enhancing the efficiency of ammonia capture. At the same time, the N captured is retained in the extraction solution (i.e., acidic trapping solution), obtaining a valuable and sustainable fertilizer product [14].
Several experimental tests utilizing GPM technology for atmospheric N capture have been conducted, yielding promising results. Laboratory-scale experiments have demonstrated recovery rates of up to 25 g m−2 d−1 [13], while pilot plant-scale tests have achieved rates as high as 28.6 g m−2 d−1 [17]. However, it is crucial to note that N recovery is influenced by a multitude of factors, so more research is needed to elucidate the influence of different factors on N recovery using GPM technology. For instance, temperature has been highlighted as a crucial parameter for N recovery from the atmosphere. According with Tichý et al. (2023) [18], significant variations in N capture rates between winter and summer seasons were observed. This seasonal variation is primarily attributed to the temperature-dependent volatilization of ammonia from the soil, with emissions reaching their highest levels during the summer months (563 Gg) and declining to their lowest during the winter season (286 Gg).
The Life Green Ammonia project is developing a novel system for the recovery of NH3 from the livestock sector; therefore, the aim of this study—which is part of this project—is to evaluate how to mitigate NH3 emissions with the use of a novel technology based on gas-permeable membranes. In order to select the most advantageous conditions for GPM technology implementation on an industrial scale (TRL 8–9), this study is firstly aimed at developing an NH3 capture system based on GPM technology for NH3 recovery in the atmosphere of livestock buildings. Different system configurations were studied to maximize N recovery rate. Then, the effect of NH3 contact time with the gas-permeable membrane system and the effect of PM temperature on N recovery were investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Origin and Composition of the Substrates
Pig manure (PM) was obtained from a pig farm in Segovia, Spain. The manure had been subjected to solid–liquid separation on-farm through a separator with a filter size of 0.5 mm mesh. The liquid fraction of PM was used. The characterization of the PM is shown in Table 1. The PM used was the same in the three experiments; however, due to the non-simultaneous nature of the experiments, initial parameters were measured independently for each. This approach was necessary to account for potential variations in TAN concentration, pH levels, and electrical conductivity that may occur over time in stored PM.

Table 1.
Characterization of PM. Standard deviation between duplicate analyses is shown in parenthesis.
A synthetic NH3 solution was used in some experiments. It was prepared with concentrated ammonia (Panreac Química S.L.U, Barcelona, Spain) and diluted to the concentration required for each test. The synthetic NH3 solution had an initial total ammonia nitrogen (TAN) of 663.47 mg N L−1, an initial conductivity of 738 mS cm−1, and an initial pH of 11.65.
2.2. Ammonia Capture System
2.2.1. Description of the Novel Configuration for N Recovery
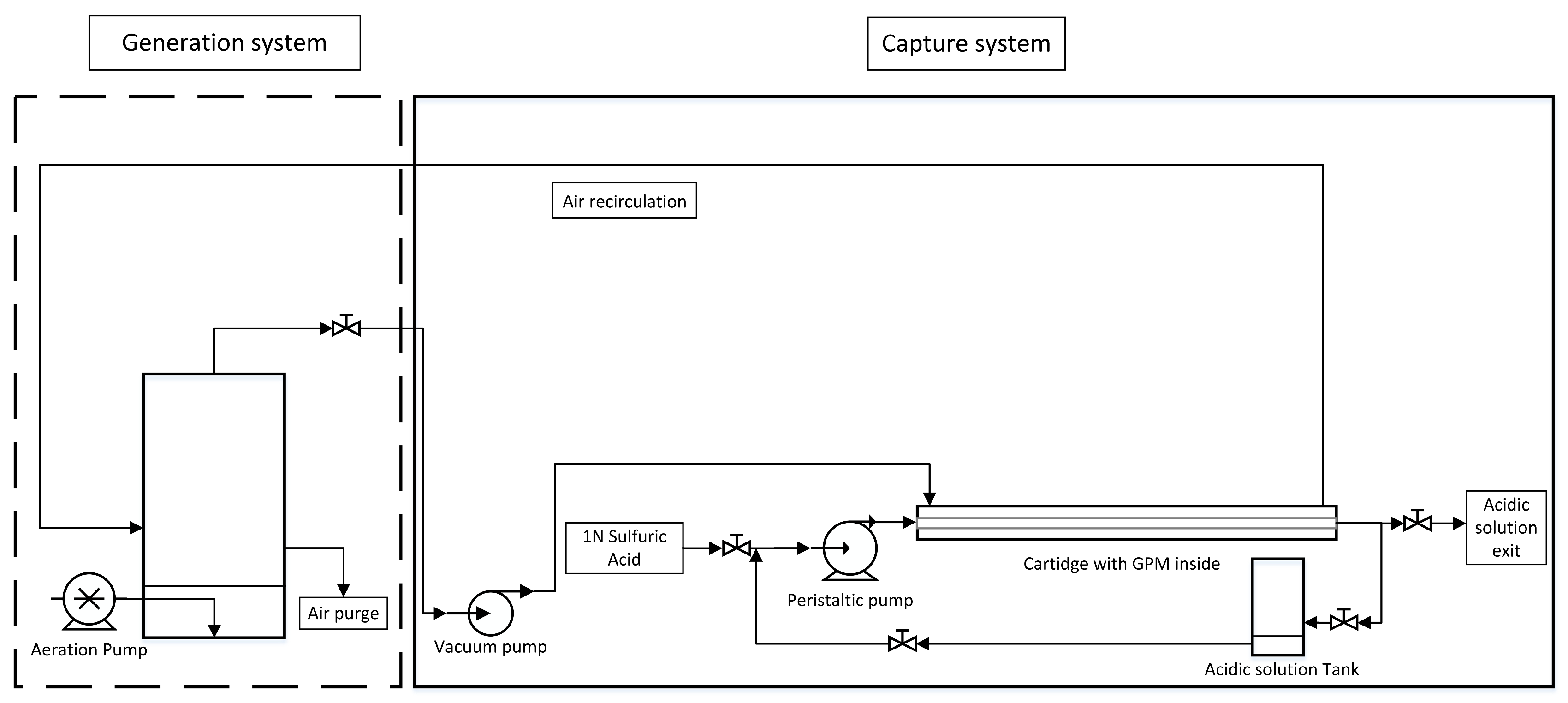
A two-part system was designed to capture NH3 from the air. A first part was named “Generation system”, in which the NH3 was generated in gaseous form to simulate the atmosphere of a farm, and a second part was named “Capture system”, in which the gas was introduced into a cartridge, where the GPM system was located and the NH3 was captured. The membrane was placed longitudinally inside the cartridge, in parallel with the cartridge walls, and fixed centrally (Figure 1). The membrane was made of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (e-PTFE) (Zeus Industrial Products Inc., Orangeburg, SC, USA) with an outside diameter of 5.2 mm, a wall thickness of 0.64 mm, a polymer density of 0.95 g cm−3, an average pore size of 2.5 µm, and a bumble point of 207 kPa. The membrane had a length of 1 m. The membrane’s surface area was 163.36 m2. This system is shown in Figure 1. In the generation system, a variable volume of synthetic solution or PM was added and aerated to generate NH3 gas. The aeration was carried out with an aquarium pump (Marina 60, model 1110, Hagen Inc. Montréal, QC, Canada) with a continuous air flow connected to porous stones giving an aeration flow rate of 50 L h−1. Then, NH3 was allowed to enter the capture system, where the GPM was located. A solution of sulphuric acid 1N was used as an acidic trapping solution to recover N from the air. The acidic trapping solution was contained in an acidic solution tank and introduced into the membrane with the aid of a peristaltic pump (Heidolph, Peristaltic Pump, Hei-FLOW Value 01 EU, Schwabach, Germany).
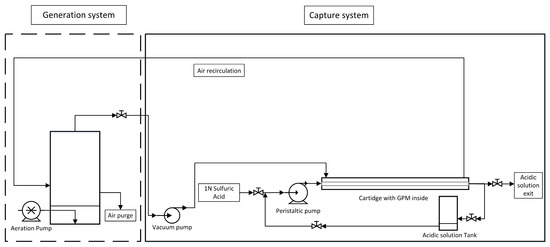
Figure 1.
System of capture of ammonia with two parts: generation system and capture system.
2.2.2. Experimental Tests to Design the Two-Parts N Recovery System
Three different experiments were carried out, namely experiment 1, 2 and 3, respectively. Experiment 1 was aimed at elucidating the best GPM system configuration. For that, five tests were carried out under different experimental conditions: (E1.1) without recirculation of the NH3 generated neither the acidic trapping solution, (E1.2) with recirculation of the NH3 generated and no recirculation of the acidic trapping solution, (E1.3) without recirculation of NH3 generated and with recirculation of the acidic trapping solution, and (E1.4) with recirculation of NH3 and the acidic trapping solution. For each test, four triplicated assays were carried out at different times of 60, 90, 120, and 180 min. For tests E1.1 to E1.4, a synthetic NH3 solution was used as an emitting solution. The fifth test (E1.5) was performed using PM as an NH3 emitting solution and the best configuration was selected among E1.1 to E1.4. For this experiment, duplicated tests were carried out at different times of 60 and 90 min.
The sampling procedure was the same for all the tests in experiment 1. An initial and final sample of the synthetic solution/PM and the acidic trapping solution were taken to measure pH, conductivity, and TAN. Then, the mass balance and the TAN recovery rate, as grams on recovered N per membrane surface and day, were calculated.
2.2.3. Experimental Tests to Study the Effect of NH3 Contact Time with the Gas-Permeable Membrane System and the Effect of PM Temperature on N Recovery
For experiment 2, the two-part system (Figure 1) was modified to capture NH3 from the atmosphere using PM as an NH3 emitting solution. Due to the generation of foams during the aeration of the PM, a second flask was placed next to the aeration flask where the foams were collected. The “Capture system” remained as shown in Figure 1. In the “Generation system”, a volume of 500 mL of PM was introduced, where aeration was carried out with a vacuum pump giving an aeration flow rate of 6.5 L min−1 (390 L h−1). In this manner, the aeration rate was increased almost eight times if compared to experiment 1. This was done to promote NH3 emission form manure [19]. Aeration was maintained during the experimental time in order to increase the pH and thus improve NH3 generation. During this time, the valve that gave access to the capture system remained open and the generated gas was introduced in the cartridge, being recirculated back to the generation and part of the system using a vacuum pump. In this way, the test was carried out in a closed cycle, reintroducing the air from the cartridge outlet into the generation system. The acidic trapping solution was introduced into the membrane with the aid of a peristaltic pump (Heidolph, Peristaltic Pump, Hei-FLOW Value 01 EU, Schwabach, Germany) and remained static until the end of the test. Duplicate tests were carried out with different test times (60, 120, and 240 min). An initial and final sample of the PM and the acidic solution was taken to calculate the mass balance. In the PM, pH, conductivity and TAN were measured at the beginning and end of each test. In the acidic solution, pH, volume, and TAN (mg L−1) were measured in all tests.
Experiment 3 was aimed at evaluating the effect of PM temperature on NH3 emission and, consequently, N capture. The same experimental set-up than in experiment 2 was used. To modify the temperature of the PM used as an emitting solution, a water bath with different operating temperatures was used to heat the flask containing the PM. The temperature of the bath was monitored throughout the test, and the final temperature of the PM was measured at the end of the test. The bath temperatures selected to carry out the experiment 3 were atmospheric temperature (21.5 (0.5) °C), 38.8 (1.3) °C, and 49.9 (0.7) °C). In the PM, pH, conductivity, and TAN were measured at the beginning and end of each test. In the acidic solution, pH, volume, and TAN were measured in all tests.
2.3. Analytical Methods and Yield
A Crison Basic 20 pH meter (Crison Instrumentos S.A., Barcelona, Spain) was used to measure pH. Electrical Conductivity was monitored using a pH/Cond 340i/SET (WTW Wissenschaftlich-Technische Werkstätten, Weilheim, Germany). A Kjeltec TM 8100 nitrogen distillation equipment from Foss Iberia S.A. in Barcelona, Spain, was used to perform TAN analysis, which was carried out by distillation, absorption of the distillate in borate buffer, and subsequent titration with 0.4 M HCl. Analyses of TAN were measured according to APHA standard methods (2005) [20]. To calculate the N emitted, it is necessary to know the initial and final TAN in the PM with which the test has been carried out and multiply by the volume with which the test is carried out. As the volume was measured at the end of the tests, the volume loss was corrected in all the calculations.
Initial TAN (mg) was calculated following Equation (1):
where initial is total ammonia nitrogen initial in mg or mg L−1 and is the initial volume of PM in L.
Final TAN (mg) was calculated following Equation (2):
where final is total ammonia nitrogen final in mg or mg L−1 and is the final volume of PM in L.
Emitted N (mg) was calculated following Equation (3):
Emitted (%) was calculated following Equation (4):
N recovery (%) was calculated following Equation (5):
N recovery rate (g m−2 d−1) was calculated following Equation (6):
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design and Optimization of a Novel System Based on GPM Technology for NH3 Capture in the Air—Experiment 1
The results obtained in experiment 1 are shown in Table 2. The different configurations were as follows: (E1.1) without recirculating the NH3 generated neither the acidic trapping solution, (E1.2) with recirculation of NH3 generated and no recirculation of the acidic trapping solution, (E1.3) without recirculation of NH3 generated and with recirculation of the acidic trapping solution, and (E1.4) with recirculation of both the NH3 and the acidic trapping solution.

Table 2.
Results obtained in experiment 1. N.d. stands for not determined. Standard deviation between triplicate (E1.1–E1.4) and duplicated (E1.5) tests is shown in parenthesis.
The best results were obtained with the configuration tested in test E1.2, where NH3 was recirculated through cartridge and the acidic trapping solution remained static inside the gas-permeable membrane. N recoveries in the acidic solution of up to 89% of the emitted N were reached for the experimental time of 180 min (Table 2). The best N recovery rates were also obtained with the configuration tested in E1.2, being in the range of 164 to 237 g m−2 d−1, depending on the experimental time. The following best result was obtained with the configuration tested in E1.4, with recirculation of the NH3 and the acidic solution, with N recovery percentages in the acidic solution in the range of 37–39% of the emitted N, and N recovery rates of up to 205 g m−2 d−1. However, E1.2 was chosen as the best configuration since it presented a higher capture ratio in less time and the non-recirculation of the acidic trapping solution would result in lower operational costs.
When analyzing the experimental times versus N recovery rate, it was observed that an increase in experimental time resulted in a reduction in N recovery rate, so that the configuration used in E1.2 and experimental times of 60 and 90 min were selected for test E1.5 (Table 2).
Test E1.5 was carried out using PM as an NH3 emitting solution. It can be observed that the N emitted in PM (E1.5), 167 mg and 223 mg for 60 and 90 min, respectively, represented 37% and 45% of the N emitted, which was much lower than those obtained in E1.2 tests, where a synthetic solution was used as an emitting solution. This was because the PM has a buffer capacity which can influence NH3 emissions, as a stable pH environment can affect the equilibrium between ammonium (NH4⁺) and ammonia (NH3), thereby impacting volatilization rates, and making the emission slower [21]. The N recovery results obtained in E1.5 were 8.3% and 6.7% for the 60- and 90-min tests, respectively, with N recovery rates of 20.4 and 14.6 m−2 d−1, respectively.
From the results obtained in Table 2, an increase in the pH of synthetic solution and PM was observed at the end of the test, which is due to the aeration of the manure. pH is a critical factor because it affects the equilibrium between ammonium (NH4+) and free ammonia (NH3), with higher pH values favoring NH3 volatilization and its transfer across the membrane [22,23]. The pH in the acidic solution increased as NH3 concentration increased, although in this case it did not reach saturation of acidic solution. The conductivity decreased with the ammonium concentration decreasing in all experiments.
3.2. Effect of Contact Time on N Capture with GPM—Experiment 2
The modified two-part system was used for capturing NH3 using PM as an emitting solution. The volume of PM and the flow rate of aeration in PM were increased with respect to experiment 1, being the volume of PM used in experiment 2; five times higher than that of experiment 1. Results are shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
Effect of contact time on N recovery. Standard deviation between duplicate tests is shown in parenthesis.
An increase in the pH of the PM was observed at the end of the tests, due to the aeration of the manure. As expected, the longer the aeration time the greater the NH3 emission. More specifically, 93, 238, and 406 mg N were emitted in 60, 120, and 240 min, respectively. This represents 4%, 10%, and 20% of the initial N content in the PM, being proportional to the time. The pH in the acidic trapping solution increased as N concentration increased, although in this case it did not reach saturation of acidic solution. The N recovery results obtained were 17%, 42%, and 42% for 60, 120, and 240 min, respectively. Nitrogen capture rates of 22.7, 73.2, and 59.7 g m−2 d−1 were obtained for 60, 120, and 240 min, respectively.
The N recovery rate was observed to have a non-lineal relationship with time. Initially, it increased from 22.7 g m−2 d−1 (60 min) to 73.2 g m−2 d−1 (120 min) during the first two hours of the test but subsequently decreased to 59.7 g m−2 d−1 (180 min). This pattern can be attributed to the significant pH increase from 8.0 to 8.9 within the first 60 min, which caused a shift in the ammonia–ammonium equilibrium, generating the majority of N emissions. However, during this period, only 17% of the emitted N was recovered, resulting in an N recovery rate of 22.7 g m−2 d−1. By extending the test duration to 120 min, a substantial percentage of the N emitted in the first 60 min was recovered, increasing the N recovery to 42% and consequently elevating the N recovery rate to 73.2 g m−2 d−1. In the 180-min test, the rate decreased due to the PM buffer capacity. Initially, the pH increased, but then stabilized, leading to reduced N emissions. As a result, while the N recovery remained at 42%, the N recovery rate declined to 59.7 g m−2 d−1.
A revision on TAN recovery values using different configurations of GPM systems to recover N from the atmosphere has been carried out. This revision is shown in Table 4.
Regarding laboratory experiments, the different studies involved different NH3 emitting substrates, including poultry litter, PM, synthetic manure, and synthetic solutions. The results obtained from poultry litter tests demonstrated that the N recovery rate of 5.1 g m−2 d−1 achieved by Soto-Herranz (2021b) [24] was significantly higher than the N recovery rates of 1.3–1.4 g m−2 d−1 observed in other tests. While all experiments involved acidic trapping solution recirculation through the interior of the membranes, ref. [25] carried out a test circulating NH3-laden air on the exterior of the membranes, resulting in improved N capture rates. When using PM as the emitting substrate, the configuration used in this study circulating NH3-laden air yielded higher N recovery rates (11.4–73.2 g m−2 d−1) compared to static gas conditions, which produced N recovery rates of 9.5–12.7 g m−2 d−1. Notably, tests recirculating the acidic trapping solution inside the membrane at a flow rate of 2.1 L h−1 achieved N recovery rates (11.4–18.8 g m−2 d−1) lower than those maintaining a static acidic trapping solution (22.7–73.2 g m−2 d−1), as conducted in this study. These findings suggest that a design incorporating NH3 gas circulation on the exterior of the membranes while maintaining a static the acidic trapping solution enhances N capture rates.


Table 4.
Revision of studies reported in the literature attained in laboratory and pilot plant scale using to recover N from the atmosphere using GPM technology.
Table 4.
Revision of studies reported in the literature attained in laboratory and pilot plant scale using to recover N from the atmosphere using GPM technology.
| Scale | Substrate | Acidic Solution Static: Yes/No | Ammonia Gas Static: Yes/No | Ammonia Recovery Rate | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | - | g m−2 d−1 | ||||
| Laboratory | Poultry Litter | No | No | 5.1 | [24] | ||
| No | Yes | 1.4 | [26] | ||||
| No | Yes | 1.3 | [6] | ||||
| Pig Manure | No | Yes | 9.5–12.7 | [25] | |||
| No | No | 11.4–18.8 | [25] | ||||
| Yes | No | 22.7–73.2 | This study | ||||
| Synthetic Manure | 12 g L−1 TAN | No | Yes | 19–34 | [13] | ||
| 6 g L−1 TAN | No | Yes | 13–21.4 | [13] | |||
| 3 g L−1 TAN | No | Yes | 6–7 | [13] | |||
| 6 g L−1 TAN | No | Yes | 24–25 | [14] | |||
| Synthetic Solution | 0.6 g L−1 TAN | Yes | No | 163.8–237.0 | This study | ||
| Pilot | Poultry Litter | No | No | 0.41 | [24] | ||
| No | Yes | 10.4–28.6 | [17] | ||||
| No | Yes | 16.5 | [26] | ||||
| Poultry Manure Composting | No | No | 1.9–6.9 | [16] | |||
| Pig Manure | No | No | 2.3 | [24] | |||
The results obtained by Soto-Herranz in various studies [13,14] using synthetic manure reveal significant differences based on different parameters. In Soto-Herranz (2021a) [13], the N capture rate for synthetic manure was analyzed at three different N concentrations: 3, 6, and 12 g L−1. Experiments were conducted using two different membrane surface areas: 0.0164 m2 and 0.00817 m2, all carried out with an acid flow rate of 0.8 L h−1. For synthetic manure with 3 g L−1 N concentration, better N recovery rates were achieved with the 0.0164 m2 membrane length, yielding 7 g m−2 d−1 compared to 6 g m−2 d−1 with the 0.00817 m2 membrane. However, for 6 and 12 g L−1 concentrations, superior N recovery rates were obtained with the 0.0164 m2 membrane, reaching 14 g m−2 d−1 and 34 g m−2 d−1, respectively, in contrast to the results obtained with the 0.00817 m2 membrane, which were 13 g m−2 d−1 and 34 g m−2 d−1, respectively.
This study also examined the impact of acid flow rate on N capture rate, utilizing a synthetic manure solution of 6 g L−1 and a membrane surface area of 0.01225 m2. Various tests were conducted for four acid flow rates: 0.8, 1.3, 1.6, and 2.1 L h−1, resulting in N recovery rates of 13.5, 15.6, 16.0, and 21.4 g m−2 d−1, respectively. The research concluded that higher acid flow rates correspond to improved N recovery rates. A subsequent study by Soto-Herranz (2022a) [14] employed an acid rate of 2.1 L h−1, with a synthetic manure solution of 6 g L−1 N, and a membrane area of 0.0164 m2, achieving capture ratios of 24–25 g m−2 d−1. Nevertheless, a design that combines circulating gas on the exterior of the membrane while maintaining static acid conditions enhances capture ratios, as evidenced by comparing the results obtained by Soto-Herranz (2021a) [13] with those from this study using PM.
The experiments conducted in this study using a synthetic solution demonstrated a significant improvement in N recovery rates, ranging from 163.8 to 237.0 g m−2 d−1. This enhancement was attributed to the novel GPM system design and configuration, which involved circulating gas on the exterior of the membrane while maintaining a static acid trapping solution inside. The exceptionally high ratios observed were primarily due to the elevated N emission generated by the synthetic solution, which lacks the buffering capacity present in synthetic manure and PM. Although these results may not directly correspond to farm conditions, they provide valuable insight into the potential outcomes that could be achieved when NH3 emissions from PM are increased.
In the experiments carried out in pilot plants, N recovery rates of up to 28.6 g m−2 d−1 in a poultry farm and 2.3 g m−2 d−1 in a pig farm were reported (Table 4). More specifically, Soto-Herranz (2021b) [24], studied the performance of pilot plants for the recovery of NH3 from the atmosphere of a pig farm and a poultry farm, operating for 232 days and 256 days, respectively. In those studies, an acidic trapping solution was recirculated inside the membranes with a flow rate of 2.1 L h−1, and the gas with NH3 from inside the farm was introduced with a flow rate of 52.6 m3 h−1. In the experiments conducted by Rothrock (2010) [6], the recovery of NH3 from 32.5 kg of poultry litter was studied using flat membranes with recirculation of acid solution with a flow rate of 27 L d−1. N recovery rates of 10.42–28.62 g m−2 d−1 were obtained. These ratios are higher than those obtained by Soto-Herranz (2021b) [24] in pilot plants. If the results obtained in the pilot plants are compared with those obtained in this study, the results obtained with the GMP configuration system proposed in this study are much higher, obtaining N recovery rates of up to 73.15 g m−2 d−1 for PM.
The results obtained with the new system proposed in this study demonstrate significantly higher recovery ratios compared to those reported in previous studies. Specifically, recovery rates were up to four times higher when using PM in a laboratory scale, in comparison with the higher result obtained by Soto-Herranz (2022b) [25]. The use of synthetic solution significantly increased the N recovery rate showing the huge potential of this new designed system, which represents a much more efficient and innovative technology. This is attributed to the static operation of the acidic trapping solution, while NH3 gas circulates externally around the membranes.
3.3. Effect of Manure Temperature on N Capture—Experiment 3
The objective of experiment 3 was to evaluate the effect of the PM temperature on the emission of NH3 and subsequent capture with the GPM membrane system proposed. For this purpose, PM was used as the emitting solution at different temperatures using a water bath to heat the flask containing the PM. Tests were carried out for 60 min. The results obtained for the different tests are shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Effect of temperature. Standard deviation between duplicate tests is shown in parenthesis.
The final pH was higher when the temperature in PM increased, reaching values between 8.5 and 8.7, compared to the ambient temperature, which resulted in a pH of 8.2. Consequently, the highest emission of 151.7 mg N was observed at the maximum temperature (Table 5). Notably, the N recovery rate showed a clear upward trend with increasing temperature in PM. More specifically, the test conducted at atmospheric temperature achieved an N recovery rate of 7.7 g m−2 d−1, while tests with increased temperature in PM resulted in N recovery rates of 15.9 and 27.2 g m−2 d−1 for test temperatures of 38.8 and 49.3 °C, respectively.
From these results it can be seen that an increase in manure temperature resulted in an increased N recovery rate. Therefore, in the case of a real farm, during the times of the year with higher temperatures (summer season), the N recovery rates using GPM technology will increase compared to those in winter. Ammonia emissions from animal manure are significantly influenced by temperature, which affects both the emission rate and the ammonium–ammonia equilibrium. NH₃ is produced through the breakdown of nitrogenous compounds in manure, and its emission is a concern due to its environmental and health impacts [27,28]. The equilibrium between ammonium (NH4+) and NH3 is highly dependent on temperature and pH. At higher temperatures, the equilibrium shifts towards the gaseous form of ammonia (NH3), increasing emissions. This is because the solubility of ammonia in water decreases with rising temperature, leading to more NH₃ being released into the atmosphere. Additionally, at higher temperatures, microbial activity in manure increases, accelerating the breakdown of urea and other nitrogenous compounds into ammonia [28]. As a result, the higher temperatures produced more ammonia gas, which led to an improvement in the transfer of ammonia through the GPM and an enhancement of the nitrogen recovery rate as the temperature rises [29,30,31].
4. Conclusions
A new system based on gas-permeable membranes (GPM) for ammonia recovery from the atmosphere was designed and evaluated. Nitrogen recovery rates of up to 237 g m−2 d−1 were achieved using the novel system with recirculation of the generated NH3 and without recirculation of the acidic trapping solution. Subsequent tests using pig manure at varying durations achieved rates of up to 73 g m−2 d−1, representing a four-fold increase in capture efficiency compared to previous studies. The effect of manure temperature on ammonia emission and capture with the novel GPM system was studied, obtaining N recovery rates of 7.7, 15.9, and 27.2 g m−2 d−1, for temperatures of 21.5, 38.8 °C, and 49.3 °C, respectively. This study reveals the high potential of GPM technology for nitrogen recovery from ammonia-rich environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.C.-d.D., M.C.G.-G., M.S.-B. and B.M.-S.; methodology, P.C.-d.D., M.C.G.-G., M.S.-B. and B.M.-S.; software, P.C.-d.D. and B.M.-S.; validation, M.C.G.-G., M.S.-B. and B.M.-S.; formal analysis, P.C.-d.D. and B.M.-S.; investigation, P.C.-d.D. and B.M.-S.; resources, B.M.-S.; data curation, P.C.-d.D.; writing—original draft preparation, P.C.-d.D. and B.M.-S.; writing—review and editing, M.C.G.-G., M.S.-B. and B.M.-S.; visualization, P.C.-d.D. and B.M.-S.; supervision, M.C.G.-G., M.S.-B. and B.M.-S.; project administration, M.S.-B. and B.M.-S.; funding acquisition, M.C.G.-G., M.S.-B. and B.M.-S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the European Union under the Project Life+ GREEN AMMONIA (LIFE20-ENV/ES/000858). B. Molinuevo- Salces thanks AEI for funding, through RYC-2020-029030-I/AEI/10.13039/501100011033.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request. The data are not publicly available due to their relevance as a part of an ongoing Ph.D. thesis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| GPM | Gas-permeable membrane |
| PM | Pig Manure |
| N | Nitrogen |
| EU | European Union |
| BAT | Best available techniques |
| TAN | Total ammonia nitrogen |
| TS | Total solids |
| VS | Volatile Solids |
| e-PTFE | Expanded polytetrafluoroethylene |
References
- Ti, C.; Xia, L.; Chang, S.X.; Yan, X. Potential for mitigating global agricultural ammonia emission: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 245, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Emission Inventory. Ammonia Emissions from Animal Husbandry. EPA 2004. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/air-emissions-inventories (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Malherbe, L.; German, R.; Couvidat, F.; Zanatta, L.; Blannin, L.; James, A.; Lètinois, L.; Schucht, S.; Berthelot, B.; Raoult, J. Emissions of Ammonia and Methane from the Agricultural Sector. Emissions from Livestock Farming (Eionet Report—ETC HE 2022/21). European Topic Centre on Human Health and the Environment. 2022. Available online: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/all-etc-reports (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- European Union. Directive (EU) 2016/2284 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 14 December 2016 on the Reduction of National Emissions of Certain Atmospheric Pollutants. Off. J. Eur. Union 2016. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2016/2284/oj/eng (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- European Commission. Zero Pollution Action Plan. COM(2021) 400 Final 2021. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/?uri=celex%3A52021DC0400 (accessed on 10 March 2025).
- Rothrock, M.J., Jr.; Szögi, A.A.; Vanotti, M.B. Recovery of ammonia from poultry litter using gas-permeable membranes. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hristov, A.N.; Hanigan, M.; Cole, A.; Todd, R.; McAllister, T.A.; Ndegwa, P.M.; Rotz, A. Ammonia emissions from dairy farms and beef feedlots. Can. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 91, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laureni, M.; Palatsi, J.; Llovera, M.; Bonmatí, A. Influence of pig slurry characteristics on ammonia stripping efficiencies and quality of the recovered ammonium-sulfate solution. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melse, R.W.; Ploegaert, J.P.; Ogink, N.W. Biotrickling filter for the treatment of exhaust air from a pig rearing building: Ammonia removal performance and its fluctuations. Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 113, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellersdorfer, M.; Pesendorfer, S.; Stocker, K. Nitrogen recovery from swine manure using a zeolite-based process. Processes 2020, 8, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.K.; Englehardt, J.D.; Dvorak, A.C. Technologies for recovering nutrients from wastewater: A critical review. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2019, 36, 511–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munasinghe-Arachchige, S.P.; Nirmalakhandan, N. Nitrogen-fertilizer recovery from the centrate of anaerobically digested sludge. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Herranz, M.; Sánchez-Báscones, M.; Antolín-Rodríguez, J.M.; Vanotti, M.B.; Martín-Ramos, P. Effect of acid flow rate, membrane surface area, and capture solution on the effectiveness of suspended gpm systems to recover ammonia. Membranes 2021, 11, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Herranz, M.; Sánchez-Báscones, M.; Antolín-Rodríguez, J.M.; Martín-Ramos, P. Evaluation of different capture solutions for ammonia recovery in suspended gas permeable membrane systems. Membranes 2022, 12, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarebska, A.; Romero Nieto, D.; Christensen, K.V.; Fjerbæk Søtoft, L.; Norddahl, B. Ammonium fertilizers production from manure: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 1469–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Herranz, M.; Sánchez-Báscones, M.; Antolín-Rodríguez, J.M.; Martín-Ramos, P. Pilot plant for the capture of ammonia from the atmosphere of pig and poultry farms using gas-permeable membrane technology. Membranes 2021, 11, 859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buabeng, F.; Hashem, F.M.; Millner, P.; Matias, B.V.; Timmons, J.; Arthur, A. Controlling poultry house ammonia emissions using gas permeable membrane systems. Br. J. Environ. Sci. 2018, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Tichý, O.; Eckhardt, S.; Balkanski, Y.; Hauglustaine, D.; Evangeliou, N. Decreasing trends of ammonia emissions over Europe seen from remote sensing and inverse modelling. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 15235–15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet, S.; Hunt, J.; Misselbrook, T.H. Low frequency aeration of pig slurry affects slurry characteristics and emissions of greenhouse gases and ammonia. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 159, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Wastewater; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, S.C.; Kim, S.H.; Jeong, C.D.; Mamuad, L.L.; Son, A.R.; Kang, S.H.; Lee, S.S. Increasing buffering capacity enhances rumen fermentation characteristics and alters rumen microbiota composition of high concentrate fed Hanwoo steers. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 20739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daguerre-Martini, S.; Vanotti, M.B.; Rodriguez-Pastor, M.; Rosal, A.; Moral, R. Nitrogen recovery from wastewater using gas-permeable membranes: Impact of inorganic carbon content and natural organic matter. Water Res. 2018, 137, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanotti, M.B.; Szogi, A. Systems and Methods for Reducing Ammonia Emissions from Liquid Effluents and for Recovering the Ammonia. U.S. Patent No. 9,708,200, 18 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Soto-Herranz, M.; Sánchez-Báscones, M.; Antolín-Rodríguez, J.M.; Martín-Ramos, P. Reduction of ammonia emissions from laying hen manure in a closed composting process using gas-permeable membrane technology. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto-Herranz, M.; Sánchez-Báscones, M.; García-González, M.C.; Martín-Ramos, P. Comparison of the Ammonia Trapping performance of different gas-permeable tubular membrane system configurations. Membranes 2022, 12, 1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothrock, M.J.; Szögi, A.A.; Vanotti, M.B. Recovery of ammonia from poultry litter using flat gas permeable membranes. Waste Manag. 2013, 33, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Manuzon, R.; Hadlocon, L.J. Ammonia Emission from Animal Feeding Operations and Its Impacts. Agric. Nat. Resour. 2014. Available online: https://ohioline.osu.edu/factsheet/AEX-723.1 (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Koenig, K.M.; McGinn, S.M. Effect of temperature on ammonia emissions from feedlot cattle manure. J. Anim. Sci. 2016, 94 (Suppl. S5), 569–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Nan, J.; Deng, K.; Antwi, P. Effect of temperature on nitrogen removal and biological mechanism in an up-flow microaerobic sludge reactor treating wastewater rich in ammonium and lack in carbon source. Chemosphere 2019, 216, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleizgys, R.; Naujokienė, V. Ammonia emissions from cattle manure under variable moisture exchange between the manure and the environment. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.; Misselbrook, T.H.; Chadwick, D.; Coutinho, J.; Trindade, H. Effects of temperature and dairy cattle excreta characteristics on potential ammonia and greenhouse gas emissions from housing—A laboratory study. Biosyst. Eng. 2012, 112, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).