Deep Fertilization Is More Beneficial than Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizer on Crop Productivity and Environmental Cost: Evidence from a Global Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search and Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Data Analysis
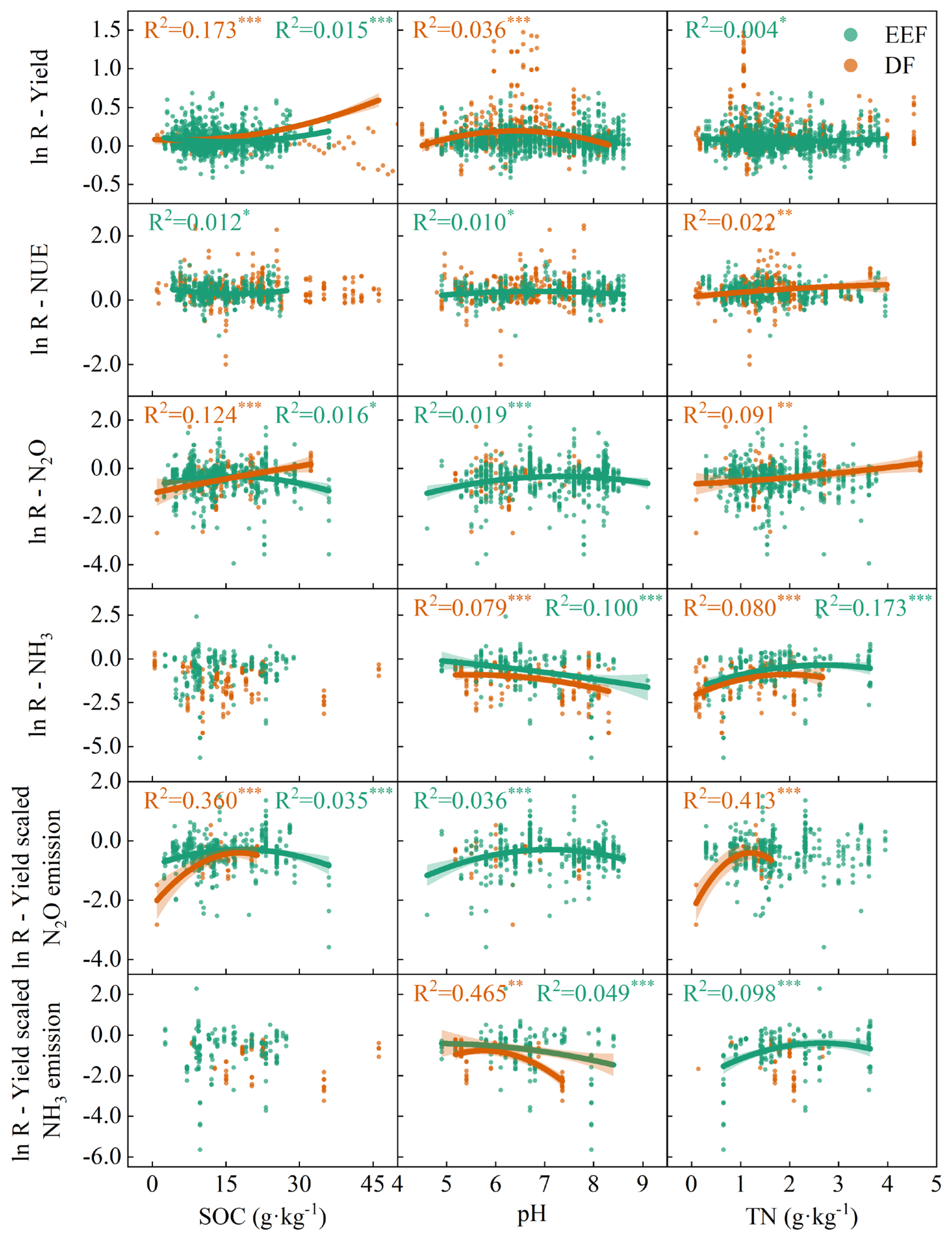
3. Results
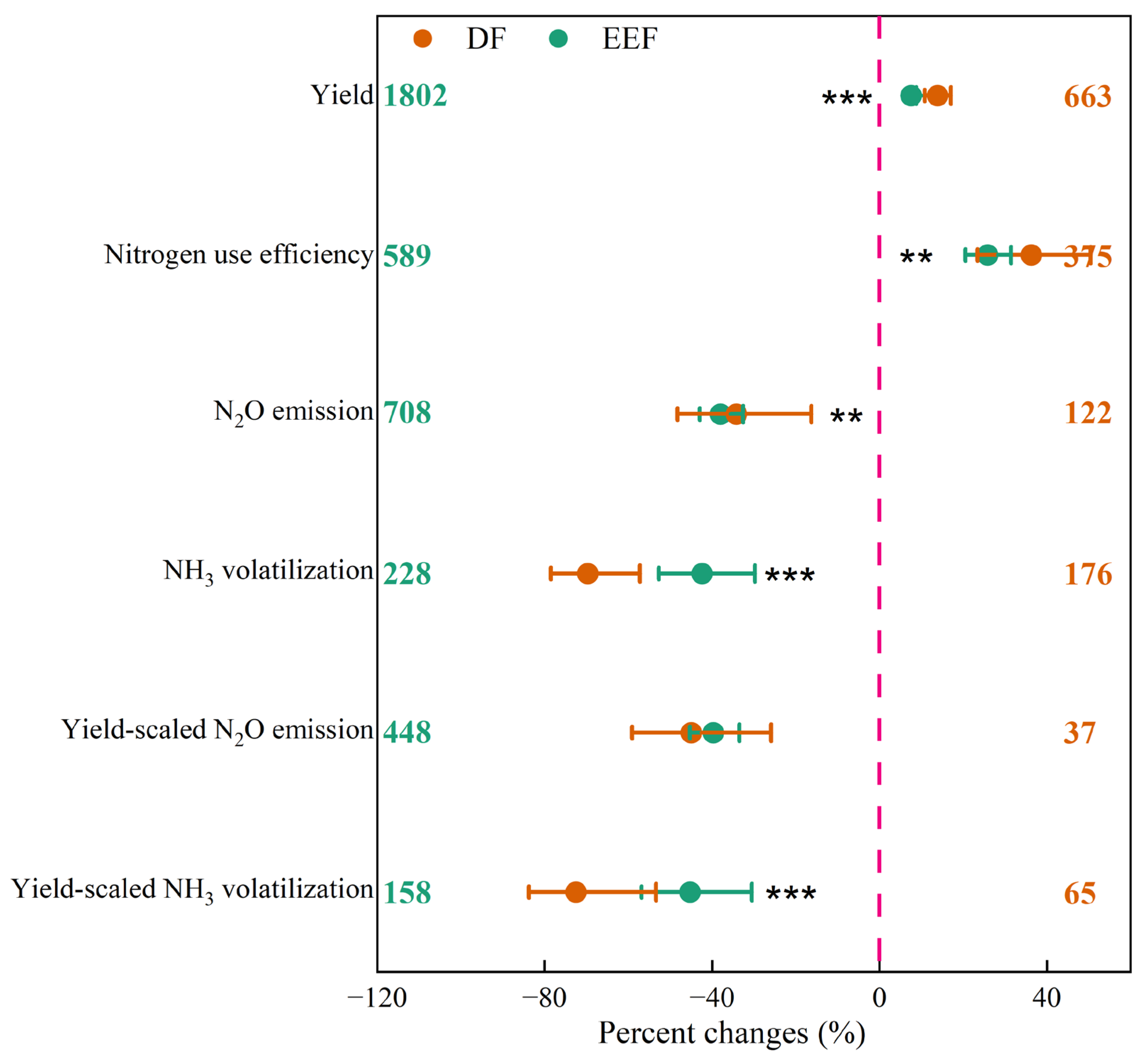
3.1. Overall Effect
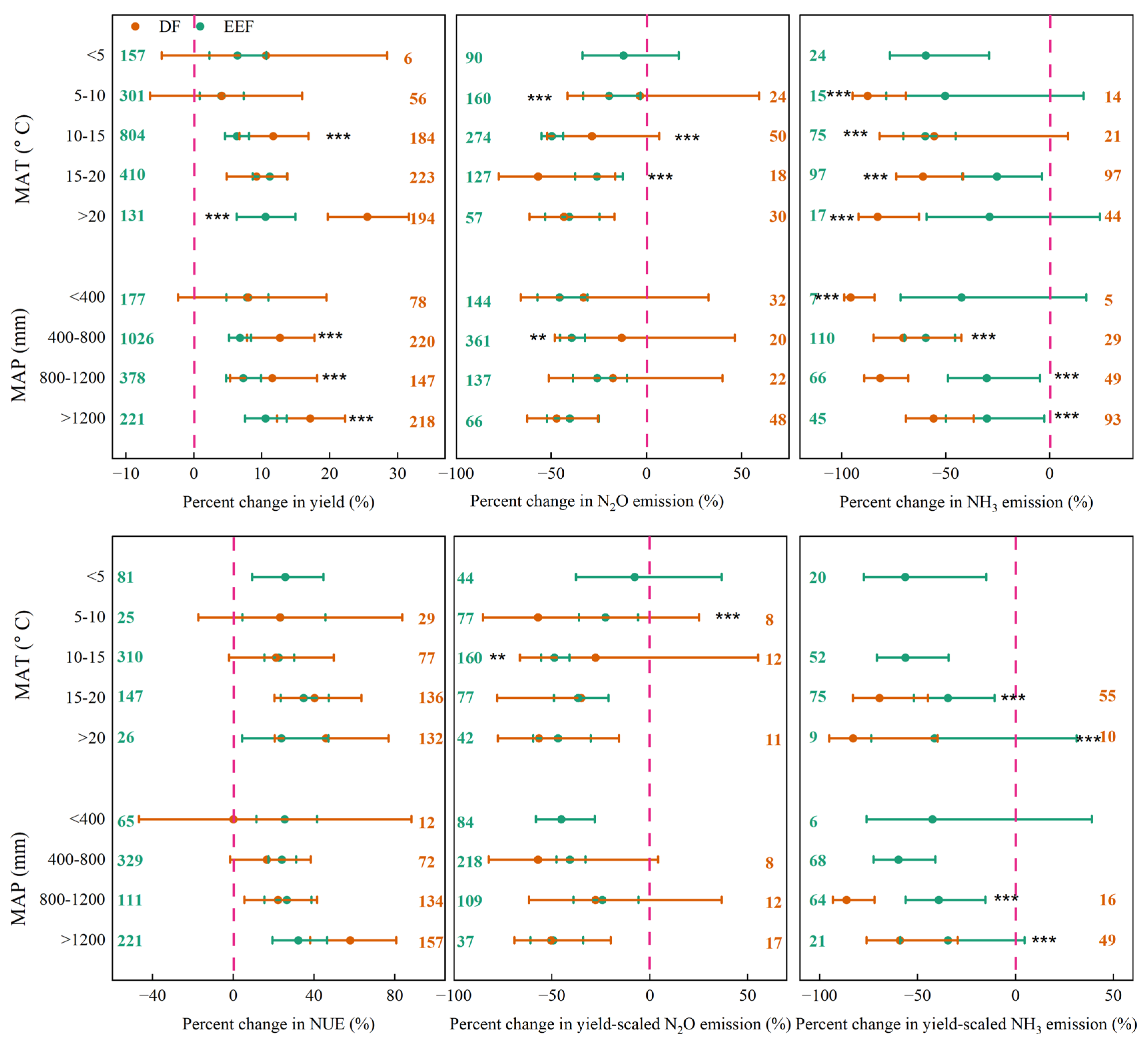
3.2. Effects of Climate Characteristics
3.3. Effects of Soil Properties
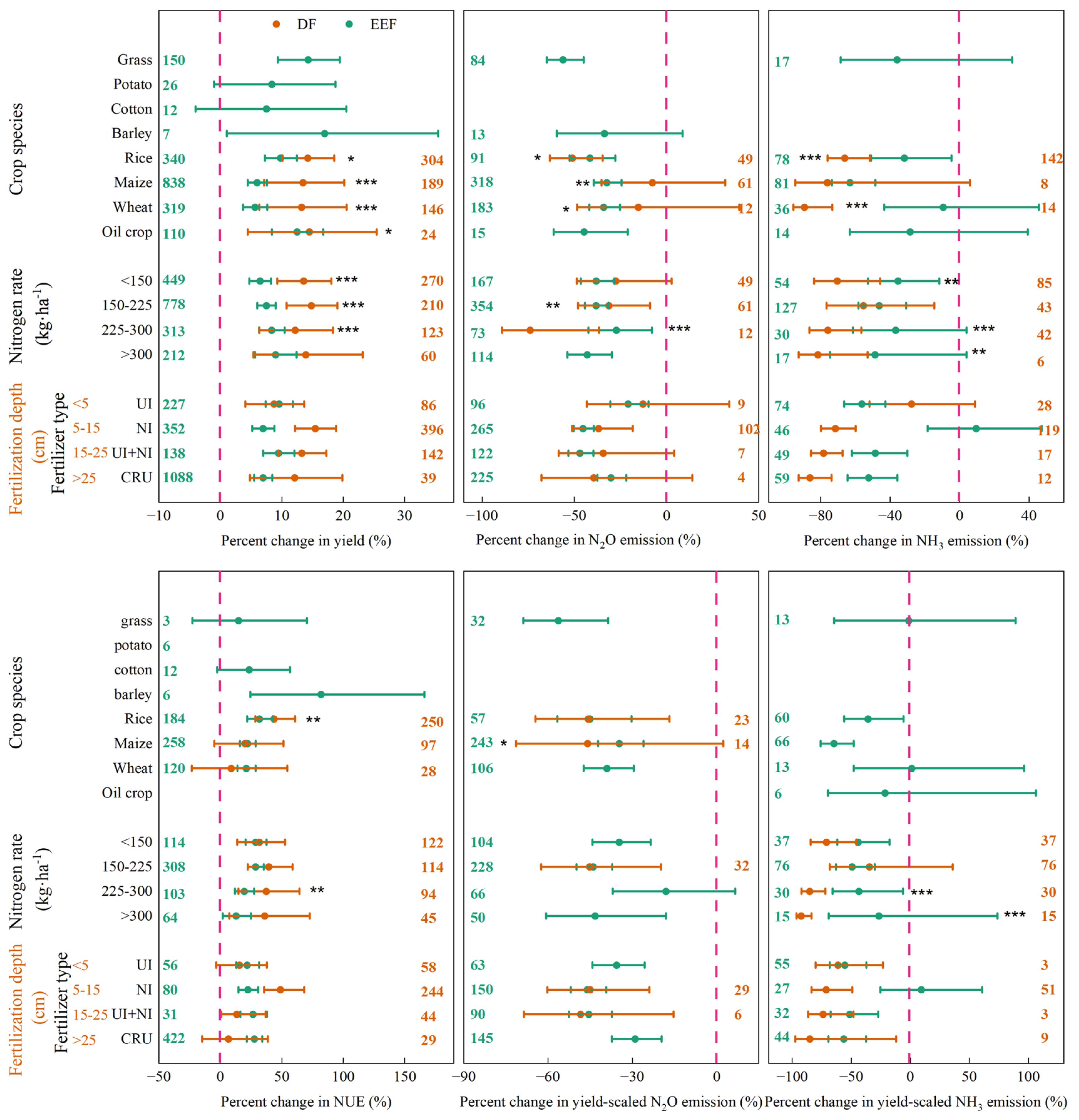
3.4. Effects of Field Management Practices
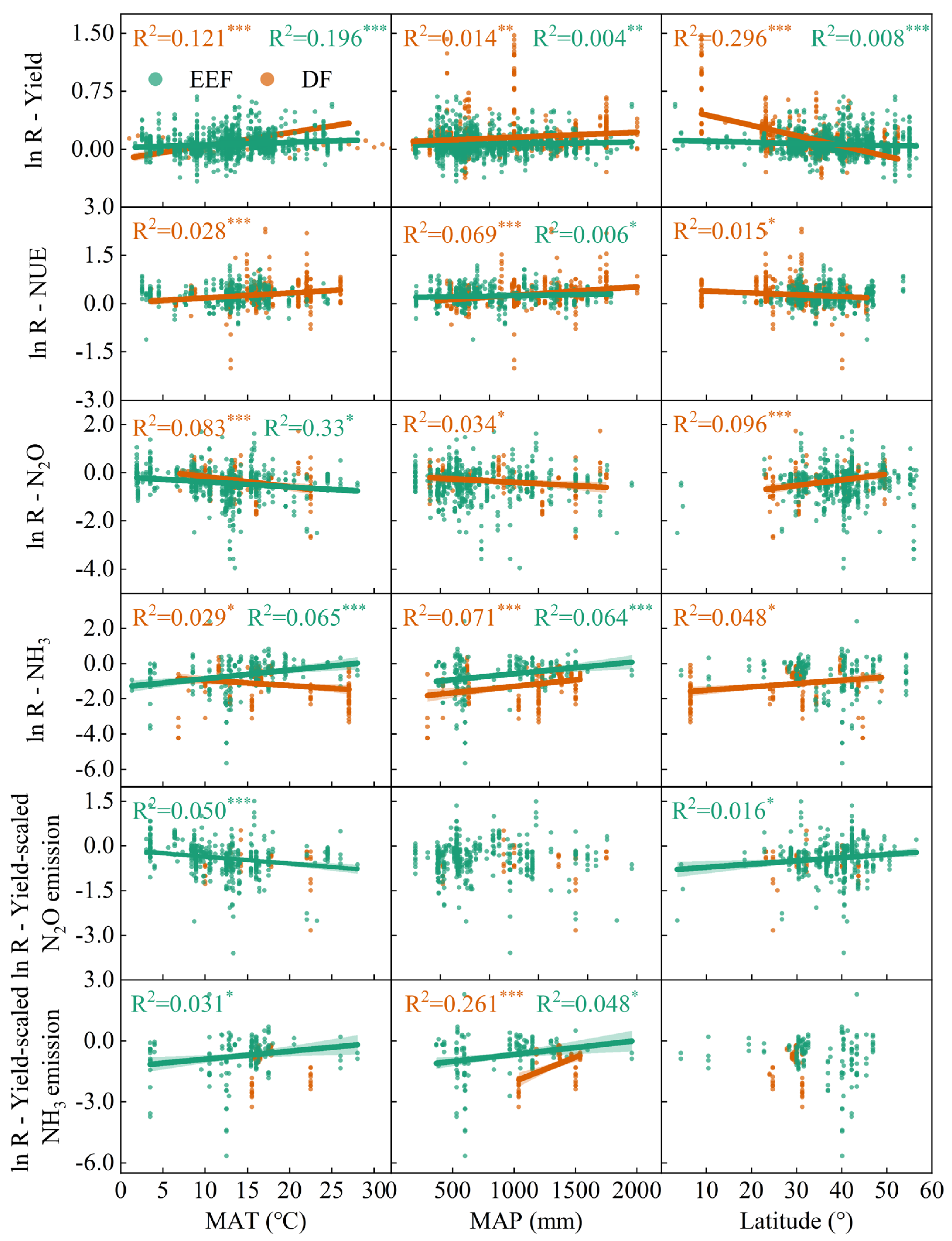
3.5. Correlation Between Climate Characteristics, Soil Properties, Field Management Practices, Crop Productivity, and Gaseous Nitrogen Losses
3.6. Important Predictors
4. Discussion
4.1. General Effects of DF and EEF on Crop Productivity
4.2. General Effects of DF and EEF on the Reduction of Gaseous Nitrogen
4.3. Conditions in Which the DF Strategy More Beneficial than the EEF Strategy
4.4. Limitations and Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, F.; Harindintwali, J.D.; Wei, K.; Shan, Y.; Mi, Z.; Costello, M.J.; Grunwald, S.; Feng, Z.; Wang, F.; Guo, Y.; et al. Climate change: Strategies for mitigation and adaptation. Innov. Geosci. 2023, 1, 100015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Yan, X. Maximizing Earth’s feeding capacity. Nat. Food 2023, 4, 353–354. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reay, D.S.; Davidson, E.A.; Smith, K.A.; Smith, P.; Melillo, J.M.; Dentener, F.; Crutzen, P.J. Global agriculture and nitrous oxide emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 410–416. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, H.; Xu, R.; Canadell, J.G.; Thompson, R.L.; Winiwarter, W.; Suntharalingam, P.; Davidson, E.A.; Ciais, P.; Jackson, R.B.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; et al. A comprehensive quantification of global nitrous oxide sources and sinks. Nature 2020, 586, 248–256. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Wen, Z.; Chang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, X.; Sha, Z.; Li, Z.; Kang, J.; et al. Increasing importance of ammonia emission abatement in PM(2.5) pollution control. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 1745–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Yuan, L.; Cai, Z.; Fu, J.; Wu, G. Emission inventory and distribution characteristics of NH3 from agricultural fertilizers in Hunan, China, from 2012 to 2021. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2025, 16, 102479. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Tan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, P.; Mu, Y. Effect of fertilizer deep placement and nitrification inhibitor on N2O, NO, HONO, and NH3 emissions from a maize field in the North China Plain. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 334, 120684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Tang, Q.; Yan, X. Can knowledge-based N management produce more staple grain with lower greenhouse gas emission and reactive nitrogen pollution? A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2017, 23, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, K.; Gao, K.; Guan, S.; Zhao, J.; Yang, L.; Liu, M.; Su, J. The impact of the combined application of biochar and organic fertilizer on the growth and nutrient distribution in wheat under reduced chemical fertilizer conditions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; He, W.; Wei, Z.; Chen, Y.; Gao, W. Integrating green manure and fertilizer reduction strategies to enhance soil carbon sequestration and crop yield: Evidence from a two-season pot experiment. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2025, 8, 1514409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Zeleke, K.; Yi, R.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Liang, Y. Effects of irrigation and nitrogen topdressing on water and nitrogen use efficiency for winter wheat with micro-sprinkling hose irrigation in North China. Agric. Agric. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 302, 109005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pan, Y.; Wang, W.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, Z.; Cao, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; et al. Potential benefits of variable rate nitrogen topdressing strategy coupled with zoning technique: A case study in a town-scale rice production system. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 155, 127132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, S.; Zhao, X.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. Optimal nitrogen rate strategy for sustainable rice production in China. Nature 2023, 615, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Chen, X.; Ren, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Ren, B.; Liu, P. Deep nitrogen fertilizer placement improves the yield of summer maize (Zea mays L.) by enhancing its photosynthetic performance after silking. BMC Plant Biol. 2025, 25, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakeel, A.; Qadeer, A.; Bano, Z.; Shahid, M.R.; Rizwan, M.; Kiran, A.; Sanaullah, M.; Aziz, T.; Rees, R.M.; Bhatia, A.; et al. Managing Fertilizer Rates and Tillage Depth to Improve Nitrogen Use Efficiency and Soil Health. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Yin, P.; Zhang, N.; Lin, Z.; Ma, Q.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; et al. Blending of Slow-Release N Fertilizer and Urea Improve Rainfed Maize Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency While Reducing Apparent N Losses. Agronomy 2025, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.K.; Wille, U.; Hu, H.-W.; Caruso, F.; Mumford, K.; Liang, X.; Pan, B.; Malcolm, B.; Roessner, U.; Suter, H.; et al. Next-generation enhanced-efficiency fertilizers for sustained food security. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenkel, M.E. Slow-and Controlled-Release and Stabilized Fertilizers: An Option for Enhancing Nutrient Use Effiiency in Agriculture; International Fertilizer Industry Association (IFA): Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.-W.; Chen, D.; He, J.-Z. Microbial regulation of terrestrial nitrous oxide formation: Understanding the biological pathways for prediction of emission rates. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 39, 729–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantarella, H.; Otto, R.; Soares, J.R.; de Brito Silva, A.G. Agronomic efficiency of NBPT as a urease inhibitor: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 13, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Song, S.; Du, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, Z.; Zhou, C.; Li, P. Nutrient controlled release performance of bio-based coated fertilizer enhanced by synergistic effects of liquefied starch and siloxane. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 236, 123994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, D.; Bol, R.; Shi, Y.; Guo, Y.; Meng, F.; Wu, W. Nitrification inhibitor’s effect on mitigating N2O emissions was weakened by urease inhibitor in calcareous soils. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Xing, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Reducing environmental risk by improving N management in intensive Chinese agricultural systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Rees, R.M.; Ju, X. Using nitrification inhibitors and deep placement to tackle the trade-offs between NH3 and N2O emissions in global croplands. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 4409–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Yue, G.; Mo, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, S. Controlled-release urea derived from various coating materials on the impacts of maize production: A meta-analysis. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 225, 120485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; He, P.; Fan, D.; Jiang, R.; Zou, G.; Song, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; He, W. Trade-offs between agronomic and environmental benefits: A comparison of inhibitors with controlled release fertilizers in global maize systems. Field Crops Res. 2025, 323, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LÜ, H.; Wang, X.; Pan, Z.; Zhao, S. Assessment of the crucial factors influencing the responses of ammonia and nitrous oxide emissions to controlled release nitrogen fertilizer: A meta-analysis. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 3549–3559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Pang, S.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, R.; Lin, X.; Wang, D. Nitrogen losses trade-offs through layered fertilization to improve nitrogen nutrition status and net economic benefit in wheat-maize rotation system. Field Crops Res. 2024, 312, 109406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liu, F.; Chen, G.; Wang, J.; Huang, F.; Cai, T.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. Can deep fertilizer application enhance maize productivity by delaying leaf senescence and decreasing nitrate residue levels? Field Crops Res. 2022, 277, 108417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, M.; Zeng, K.; Yin, B. Urea deep placement for minimizing NH3 loss in an intensive rice cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Nie, L.; Ashraf, U.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, T.; Tian, H.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Tang, X.; et al. Deep placement of nitrogen fertilizer increases rice yield and energy production efficiency under different mechanical rice production systems. Field Crops Res. 2022, 276, 108359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi, S.; Shi, S.; Obaid, H.; Dong, X.; He, X. Differential Effects of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilization Rates and Fertilizer Placement Methods on P Accumulations in Maize. Plants 2024, 13, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Wu, Q.; Huang, H.; Xie, L.; An, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, F.; Gao, Z.; Zhang, R.; Bangura, K.; et al. Global meta-analysis and three-year field experiment shows that deep placement of fertilizer can enhance crop productivity and decrease gaseous nitrogen losses. Field Crops Res. 2024, 307, 109263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, T.M.; Sapkota, T.B.; Eagle, A.J.; Kantar, M.B.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Majumdar, K. Meta-analysis of yield and nitrous oxide outcomes for nitrogen management in agriculture. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2343–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, J.L.; Anderson, J.G. The Analysis of Response in Crop and Livestock Production; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, P.; Liu, F.; Li, H.; Cai, T.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. Suitable fertilizer application depth can increase nitrogen use efficiency and maize yield by reducing gaseous nitrogen losses. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Huang, Z.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J. Urea ammonium nitrate solution combined with urease and nitrification inhibitors jointly mitigate NH3 and N2O emissions and improves nitrogen efficiency of summer maize under fertigation. Field Crops Res. 2023, 296, 108909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, P.; Sheng, X.; Chen, Z.; Ning, Q.; Zhang, H.; Lu, H.; Zhang, H. Optimizing One-Time Nitrogen Fertilization for Rice Production Using Controlled-Release Urea and Urease Inhibitors. Agronomy 2024, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; He, X.; Wang, Q.; Deng, O.; Zhou, W.; Luo, L.; Chen, G.; Zeng, J.; Yuan, S.; Zeng, M.; et al. Synergistic effects of biological nitrification inhibitor, urease inhibitor, and biochar on NH3 volatilization, N leaching, and nitrogen use efficiency in a calcareous soil–wheat system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 174, 104412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, K.; Vietinghoff, M.; Pacholski, A. Targeting yield and reducing nitrous oxide emission by use of single and double inhibitor treated urea during winter wheat season in Northern Germany. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 347, 108391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Sun, H.; Kronzucker, H.J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, W. Comprehensive assessment of the effects of nitrification inhibitor application on reactive nitrogen loss in intensive vegetable production systems. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 307, 107227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, L.; Petersen, S.O. Efficacy of three nitrification inhibitors to reduce nitrous oxide emissions from pig slurry and mineral fertilizers applied to spring barley and winter wheat in Denmark. Geoderma Reg. 2023, 32, e00597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-H.; Cheng, G.-G.; Lu, W.-P.; Lu, D.-L. Differences of yield and nitrogen use efficiency under different applications of slow-release fertilizer in spring maize. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 554–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorup-Kristensen, K.; Dresbøll, D.B.; Kristensen, H.L. Crop yield, root growth, and nutrient dynamics in a conventional and three organic cropping systems with different levels of external inputs and N re-cycling through fertility building crops. Eur. J. Agron. 2012, 37, 66–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, H.; Rengel, Z.; Whalley, W.R.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Shen, J.; Jin, K. Localized nutrient supply can facilitate root proliferation and increase nitrogen-use efficiency in compacted soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, J.; Ren, B.; Li, Z.; Wang, Z. Root physiological adaptations that enhance the grain yield and nutrient use efficiency of maize (Zea mays L) and their dependency on phosphorus placement depth. Field Crops Res. 2022, 276, 108378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, P.; Dong, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B.; Ren, B. Nitrogen placement at sowing affects root growth, grain yield formation, N use efficiency in maize. Plant Soil 2020, 457, 355–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Wu, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ren, L.; Cai, T.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. How do different fertilization depths affect the growth, yield, and nitrogen use efficiency in rain-fed summer maize? Field Crops Res. 2023, 290, 108759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Cai, T.; Jia, Z. Sustainable nitrogen placement depth under different rainfall levels can enhance crop productivity and maintain the nitrogen balance in winter wheat fields. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 233, 105817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Liu, T.; Sheng, F.; Li, S.; Cao, C.; Li, C. Nitrogen deep placement mitigates methane emissions by regulating methanogens and methanotrophs in no-tillage paddy fields. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 711–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, G.; Chen, F.; Wu, Q.; Lai, N.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, F. Ideotype root architecture for efficient nitrogen acquisition by maize in intensive cropping systems. Sci. China Life Sci. 2010, 53, 1369–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Zeng, H.; Fan, J.; Lai, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, F.; Wang, H.; Cheng, M.; Guo, J.; Li, Z.; et al. Effects of plant density, nitrogen rate and supplemental irrigation on photosynthesis, root growth, seed yield and water-nitrogen use efficiency of soybean under ridge-furrow plastic mulching. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 268, 107688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Chen, G.; Liu, F.; Cai, T.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. How does deep-band fertilizer placement reduce N2O emissions and increase maize yields? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, P.; Cai, T.; Jia, Z. Optimizing urea deep placement to rainfall can maximize crop water-nitrogen productivity and decrease nitrate leaching in winter wheat. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 274, 107971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Yan, S.; Zheng, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, X.; et al. Blending urea and slow-release nitrogen fertilizer increases dryland maize yield and nitrogen use efficiency while mitigating ammonia volatilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148058. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Cai, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ren, L.; Wu, P.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. Suitable Fertilizer Application Depth Enhances the Efficient Utilization of Key Resources and Improves Crop Productivity in Rainfed Farmland on the Loess Plateau, China. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 900352. [Google Scholar]
- Netzer, F.; Pozzi, L.; Dubbert, D.; Herschbach, C. Improved photosynthesis and growth of poplar during nitrogen fertilization is accompanied by phosphorus depletion that indicates phosphorus remobilization from older stem tissues. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 162, 421–432. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, S.; Li, Y. Reduction of photosynthesis under P deficiency is mainly caused by the decreased CO2 diffusional capacities in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 198, 107680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Elrys, A.S.; Wang, J.; Xu, C.; Ni, K.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S.; Cai, Z.; Pacholski, A. Application of enhanced-efficiency nitrogen fertilizers reduces mineral nitrogen usage and emissions of both N2O and NH3 while sustaining yields in a wheat-rice rotation system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 324, 107720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunling, Y.; Shahzad, A.; Wang, M.; Xi, Y.; Shaik, M.R.; Khan, M. Urease and nitrification inhibitors with drip fertigation strategies to mitigate global warming potential and improve water-nitrogen efficiency of maize under semi-arid regions. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 295, 108750. [Google Scholar]
- Friedl, J.; Scheer, C.; Rowlings, D.W.; Deltedesco, E.; Gorfer, M.; De Rosa, D.; Grace, P.R.; Müller, C.; Keiblinger, K.M. Effect of the nitrification inhibitor 3,4-dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) on N-turnover, the N2O reductase-gene nosZ and N2O:N2 partitioning from agricultural soils. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irigoyen, I.; Muro, J.; Azpilikueta, M.; Aparicio-Tejo, P.; Lamsfus, C. Ammonium oxidation kinetics in the presence of nitrification inhibitors DCD and DMPP at various temperatures. Soil Res. 2003, 41, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, T.; Huang, Y.; Song, X.; Deng, O.; Zhou, W.; Luo, L.; Tang, X.; Zeng, J.; Chen, G.; Gao, X. Biological nitrification inhibitor co-application with urease inhibitor or biochar yield different synergistic interaction effects on NH3 volatilization, N leaching, and N use efficiency in a calcareous soil under rice cropping. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 293, 118499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batov, D.V.; Ivanov, E.V.; Smirnova, N.L.; Kustov, A.V. Temperature-dependent enthalpy parameters of the molecular interaction for urea and tetramethylurea as solutes in formamide, ethylene glycol and water. J. Mol. Liq. 2023, 370, 121026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liang, H.; Xing, L.; Ding, W.; Geng, Z.; Xu, C. Cellulose-based slow-release nitrogen fertilizers: Synthesis, properties, and effects on pakchoi growth. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Yusa, S.-i.; Nakamura, Y. Stimuli-Responsive Liquid Marbles: Controlling Structure, Shape, Stability, and Motion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 7206–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Luo, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, P.; Yu, C.; Liu, Z.; Peng, X.-L. Fate of fertilizer nitrogen and residual nitrogen in paddy soil in Northeast China. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 3535–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Yu, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Huang, H.; Wu, Q.; Ren, L.; Zhang, G.; Liu, E.; Bangura, K.; et al. Deep placement of controlled-release and common urea achieves the win–win of enhancing maize productivity and decreasing environmental pollution. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Z.; Khalil, M.; Xing, G.; Shearer, M.J.; Butenhoff, C. Isotopic signatures and concentration profiles of nitrous oxide in a rice-based ecosystem during the drained crop-growing season. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2009, 114, 1573659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, W.; Yue, S.; Li, S.; Huang, H.; Shen, Y. Characteristics of N2O production and transport within soil profiles subjected to different nitrogen application rates in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Gao, X.; Tenuta, M.; Gui, D.; Zeng, F. Relationship between soil profile accumulation and surface emission of N2O: Effects of soil moisture and fertilizer nitrogen. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Huang, W.; Elsgaard, L.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Yang, H.; Lu, Y. Optimal biochar amendment rate reduced the yield-scaled N2O emissions from Ultisols in an intensive vegetable field in South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zou, T.; Lassaletta, L.; Mueller, N.D.; Tubiello, F.N.; Lisk, M.D.; Lu, C.; Conant, R.T.; Dorich, C.D.; Gerber, J.; et al. Quantification of global and national nitrogen budgets for crop production. Nat. Food 2021, 2, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.-G.; Giltrap, D.; Sapkota, T.B. Understanding response of yield-scaled N2O emissions to nitrogen input: Data synthesis and introducing new concepts of background yield-scaled N2O emissions and N2O emission-yield curve. Field Crops Res. 2023, 290, 108737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Wang, T.; Ma, Z.; Zhao, C.; Siddique, K.H.; Ju, X. Enhanced efficiency nitrogen fertilizers maintain yields and mitigate global warming potential in an intensified spring wheat system. Field Crops Res. 2019, 244, 107624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Wang, T.; Song, X.; Zhao, C.; Rees, R.M.; Liu, Z.; Xiaotang, J.; Siddique, K.H. Reducing N2O emissions with enhanced efficiency nitrogen fertilizers (EENFs) in a high-yielding spring maize system. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 273, 116422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Qian, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cao, Y.; Tao, R.; Zhu, M.; Ding, J.; Li, C.; Guo, W.; Zhu, X. Controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer application mitigated N losses and modified microbial community while improving wheat yield and N use efficiency. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 349, 108445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia, G.; Abalos, D.; Mateo-Marín, N.; Nair, D.; Petersen, S.O. Using DMPP with cattle manure can mitigate yield-scaled global warming potential under low rainfall conditions. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 316, 120679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Yan, H.; Xu, S.; Lin, X.; Wang, W.; Wang, D. Moderately deep banding of phosphorus enhanced winter wheat yield by improving phosphorus availability, root spatial distribution, and growth. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 220, 105388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Huang, F.; Ahmad, S.; Zhang, P.; et al. Suitable fertilization depth can improve the water productivity and maize yield by regulating development of the root system. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 271, 107784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yan, H.; Wang, W.; Han, R.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Wang, D. Layered application of phosphate fertilizer increased winter wheat yield by promoting root proliferation and phosphorus accumulation. Soil Tillage Res. 2023, 225, 105546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, P.; Cai, T.; Jia, Z. Adopting nitrogen deep placement based on different simulated precipitation year types enhance wheat yield and resource utilization by promoting photosynthesis capacity. Field Crops Res. 2023, 294, 108862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, A.M.; Forrestal, P.; Ikoyi, I.; Brennan, F. Assessing the long-term impact of urease and nitrification inhibitor use on microbial community composition, diversity and function in grassland soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 170, 108709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; He, W.; Smith, W.N.; Drury, C.F.; Jiang, R.; Grant, B.B.; Shi, Y.; Song, D.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; et al. Global evaluation of inhibitor impacts on ammonia and nitrous oxide emissions from agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5121–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpi, I.; Laville, P.; Bonari, E.; o di Nasso, N.N.; Bosco, S. Improving the management of mineral fertilizers for nitrous oxide mitigation: The effect of nitrogen fertilizer type, urease and nitrification inhibitors in two different textured soils. Geoderma 2017, 307, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Yang, Z.; Yang, S.; Chen, L.; Xin, J.; Xu, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, B.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, W.; et al. Nitrogen inhibitors improve soil ecosystem multifunctionality by enhancing soil quality and alleviating microbial nitrogen limitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 880, 163238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiq, W.; Vasava, H.; Cheema, M.; Dunfield, K.; Daggupati, P.; Biswas, A. Interactive role of topography and best management practices on N2O emissions from agricultural landscape. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ma, X.; Gao, X.; Cao, H.; Liu, F.; Wang, J.; Guo, G.; Liang, T.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Innovative nitrogen management strategy reduced N2O emission while maintaining high pepper yield in subtropical condition. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 354, 108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Adeli, A.; Yan, H. Effects of application methods and urea rates on ammonia volatilization, yields and fine root biomass of alfalfa. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, Y.; Fang, H.; Chen, P. Ridge-furrow mulching combined with appropriate nitrogen rate for enhancing photosynthetic efficiency, yield and water use efficiency of summer maize in a semi-arid region of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 287, 108450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Categorical Variables | Groups | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate factor | MAT (°C) | <5 | 5–10 | 10–15 | 15–20 | >20 |
| MAP (mm) | <400 | 400–800 | 800–1200 | >1200 | ||
| Soil factor | TN (g·kg−1) | <0.7 | 0.7–1.4 | 1.4–2.1 | >2.1 | |
| pH | <6 | 6–7 | 7–8 | >8 | ||
| SOC (g·kg−1) | <10 | 10–20 | 20–30 | >30 | ||
| Soil texture | Fine | Medium | Coarse | |||
| Management practice factor | Nitrogen rate (kg·ha−1) | <150 | 150–225 | 225–300 | >300 | |
| Fertilizer type | UI | NI | UI + NI | CRU | ||
| Fertilization depth (cm) | <5 | 5–15 | 15–25 | >25 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Q.; Huang, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Pei, R.; Wen, G.; Feng, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Gao, Z.; et al. Deep Fertilization Is More Beneficial than Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizer on Crop Productivity and Environmental Cost: Evidence from a Global Meta-Analysis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051103
Wu Q, Huang H, Wang Q, Liu Z, Pei R, Wen G, Feng J, Wang H, Zhang P, Gao Z, et al. Deep Fertilization Is More Beneficial than Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizer on Crop Productivity and Environmental Cost: Evidence from a Global Meta-Analysis. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051103
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Qi, Hua Huang, Qinhe Wang, Zeyu Liu, Runzhuo Pei, Guosheng Wen, Jinghui Feng, Hao Wang, Peng Zhang, Zhiqiang Gao, and et al. 2025. "Deep Fertilization Is More Beneficial than Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizer on Crop Productivity and Environmental Cost: Evidence from a Global Meta-Analysis" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051103
APA StyleWu, Q., Huang, H., Wang, Q., Liu, Z., Pei, R., Wen, G., Feng, J., Wang, H., Zhang, P., Gao, Z., Wang, C., & Wu, P. (2025). Deep Fertilization Is More Beneficial than Enhanced Efficiency Fertilizer on Crop Productivity and Environmental Cost: Evidence from a Global Meta-Analysis. Agronomy, 15(5), 1103. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051103







