Abstract
Late-season foliar nitrogen (N) application is widely employed to improve wheat grain yield and protein concentration, particularly during later growth stages when root activity declines and N uptake becomes less efficient. However, the reported effects of foliar N application on grain yield and the quality of wheat remain inconsistent. This meta-analysis, based on 51 field trials encompassing 1498 observations, quantitatively evaluates the impact of late-season foliar N application on wheat yield and protein concentration. The results demonstrate that late-season foliar N application significantly enhances both grain yield (+4.1%) and protein concentration (+5.9%) compared to control treatments. Notably, split foliar N application primarily increased protein concentration (+6.3%), whereas late-season N supplementation enhanced both yield (+3.4%) and protein concentration (+6.0%). Subgroup analyses reveal that the effectiveness of foliar N application is influenced by N management practices. Split foliar N application significantly increased both yield and protein concentration at N rates of 101–200 kg N/ha, whereas late-season N supplementation was beneficial only at higher N rates (≥200 kg N/ha). Moreover, the timing of foliar N application played a crucial role: application at anthesis resulted in the greatest increases in both yield (+5.3%) and protein concentration (+5.8%), while applications at booting or post-anthesis stages primarily increased protein concentration with minimal yield effects. Additionally, late-season foliar N application mitigated the conventional negative correlation between wheat yield and protein concentration, particularly when applied as a split N strategy, allowing for improved grain quality without reducing yield potential. This study highlights the importance of optimizing foliar N timing, the method, and N rate to maximize both wheat yield and quality while improving N use efficiency.
1. Introduction
Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is one of the most essential staple crops globally, with an annual production exceeding 770 million tons, providing over 20% of the calories and protein for the world’s population [1]. Due to the unique viscoelastic properties of wheat dough, it is widely utilized in various food products, such as bread, noodles, and biscuits, making it a crucial component of the global food industry [2]. With the continuous rise in global population and food demand, enhancing both wheat yield and quality has become a major objective in modern agricultural production [3].
Nitrogen (N) is a critical nutrient for wheat growth, directly influencing grain yield and processing quality [4,5,6]. It plays a vital role in protein synthesis, particularly in the formation of gluten proteins, which determine the processing quality of wheat grains. However, the relationship between N fertilization and wheat yield is complex. While early-stage N application primarily enhances vegetative growth and yield potential, later-stage N application is more effective in supporting grain protein accumulation [7,8]. Notably, N application after the flag leaf stage (GS 37) has been shown to improve grain protein concentration and processing quality by promoting protein synthesis during the reproductive phase [9,10].
Despite its benefits, late-season N management presents significant challenges. During the later stages, particularly from anthesis to maturity, root senescence reduces the ability of wheat to absorb N from the soil, resulting in low N use efficiency and insufficient nutrient supply [11]. Additionally, soil-based N applications at these stages are often inefficient, particularly in large-scale farming systems, due to logistical constraints and potential environmental losses. In contrast, foliar N application provides a more efficient and convenient alternative, allowing for direct nutrient absorption through the leaves and improving N use efficiency [12]. Consequently, foliar N application has emerged as a promising strategy to optimize wheat N management while simultaneously improving yield and grain quality.
While extensive research has explored the effects of late-season foliar N application, the reported outcomes vary considerably depending on application timing, N rate, and management practices [13,14,15,16,17]. For instance, Rekowski et al. [17] reported that foliar N application at the heading stage significantly enhanced both wheat yield and protein concentration. In contrast, Rossmann et al. [14] found that foliar N application at anthesis improved wheat processing quality but had minimal impact on yield. Other studies have suggested that the optimal timing for foliar N application ranges from anthesis to mid-grain filling [18,19]. However, long delays in foliar N application may reduce its effectiveness in promoting grain protein synthesis, ultimately limiting its benefits [20].
The inconsistent findings in the literature suggest that the efficacy of late-season foliar N application may depend on two key strategies: split foliar N application (where part of the total N is applied during the late growth stages without increasing the total N input) and late-season N supplementation (where additional N is supplied during the late growth stages to increase total N input). However, the specific effects of these strategies on wheat grain yield and quality remain unclear, particularly under different fertilization regimes and environmental conditions.
Compared to conventional soil-based N fertilization, foliar N application offers distinct advantages [21]. Studies have shown that foliar N uptake occurs more rapidly than root absorption, with peak nutrient absorption achieved within hours, whereas soil-based N uptake typically requires at least 72 h [22]. Furthermore, foliar-applied N can be directly transported to the grains, bypassing nitrate assimilation in the leaves and improving N translocation efficiency [23,24]. Previous research has identified the booting stage as a critical period for optimizing wheat yield and quality through split soil N applications [25]. Given the rapid absorption and direct translocation of foliar N, it is hypothesized that foliar N application during anthesis or grain filling stages could similarly enhance both wheat yield and quality. However, this hypothesis remains largely unexplored in the existing literature.
Meta-analysis is a statistical method for quantitatively synthesizing research results. It allows for the integration and analysis of findings from multiple independent studies. Specifically, meta-analysis combines the results of studies with similar research objectives in a quantitative manner, enabling the identification of patterns in study differences and providing a comprehensive evaluation of the overall research outcomes. Given the variability in research findings, meta-analysis provides a powerful approach to synthesizing the results from multiple studies, identifying overarching trends, and elucidating the key factors influencing the effectiveness of late-season foliar N application [26,27]. Previous meta-analyses on wheat N management have primarily focused on the impact of N application rates, N fertilizer types, and N splitting strategies [28,29,30,31]. However, comprehensive assessments of foliar N application on wheat yield and grain quality remain limited. To address these gaps, this study conducts a meta-analysis of 51 global field trials and 1498 comparative data points to (i) quantitatively evaluate the effects of split foliar N application and late-season foliar N supplementation on wheat yield and grain protein concentration, (ii) determine the applicability of these strategies under different N management conditions (N fertilization rate, application timing, and top-dressing ratio), and (iii) investigate how split foliar N and late-season N supplementation influence the relationship between wheat grain yield and protein concentration. By providing a quantitative synthesis of the effects of late-season foliar N application, this study offers new insights into optimizing wheat N management strategies, balancing high yield with improved grain quality and advancing sustainable agricultural practices.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Selection Criteria
This meta-analysis was conducted based on published field studies that investigated the effects of late-season foliar N application on wheat grain yield and protein concentration. Data were retrieved from major academic databases, including ISI-Web of Science (http://www.webofknowledge.com/ (accessed on 20 February 2024)), Google Scholar (https://scholar.google.com/ (accessed on 20 February 2024)), and the China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI, http://www.cnki.net/ (accessed on 20 February 2024)). The literature search covered publications from January 1, 1985, to January 31, 2024, using the keywords: (“wheat” OR “Triticum aestivum”) AND (“foliar”) AND (“N fertilizer” or “N application”) AND (“protein”), to establish a foliar N application regulation database.
In this meta-analysis, we categorized late-season foliar N application into two distinct treatment strategies based on the timing and amount of N applied during the late growth stages of wheat. (i) Split N application: this refers to a fertilization strategy in which a portion of the total seasonal N input is applied during the late stages of wheat development (e.g., booting, anthesis, or post-anthesis). Under this strategy, the total amount of N applied throughout the growing season remains the same as the control treatment, but a part of it is delayed to be applied at the late stage. (ii) Late N supplementation: this strategy involves applying additional N during the late growth stages, thereby increasing the total N input compared to the control treatment.
Following the data integration requirements of the meta-analysis methodology and the objectives of this study, the following selection criteria were applied: (i) the study must report field experiments comparing late-season foliar N application with a control treatment (no late-season foliar N application); (ii) the study must include or allow for the estimation of mean values and sample sizes for at least one response variable (e.g., wheat yield, grain protein concentration). In addition to the grain yield and grain protein concentration, we also extracted wheat type, total N rate, late-season foliar N application timing, and late-stage foliar N application ratios (the proportion of late-stage foliar N application to total N application). (iii) Late-season N application must be applied exclusively through foliar spraying, without additional soil-based topdressing during the later growth stages. (iv) The study must not combine N treatments with plant growth regulators, nitrification inhibitors, or other agrochemicals that could confound the results. (v) The study must apply conventional foliar N fertilizers and not include nanofertilizers. If data were presented in graphical format, the GetData Graph Digitizer (version 2.25, Russian Federation) was used for data extraction. In total, 51 studies comprising 1498 paired observations were included in the final dataset for statistical analysis.
2.2. Effect Size Calculation
To quantify the impact of late-season foliar N application, effect sizes were calculated using the log response ratio (lnR), which standardizes treatment effects across studies [26]. The log response ratio was computed as follows:
where XA and XB represent the mean values of the response variables (yield or quality concentration) in the foliar N treatment and control treatment, respectively. The response ratio (R) was subsequently transformed into a percentage change (Z) using the following:
Since many of the included studies did not report standard deviations or standard errors, sample sizes were used to determine the weight of each response ratio with the following formula [32]:
where Na and Nb are the sample sizes (replications) for the foliar N treatment and the control treatment, respectively.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
A mixed-effects model was employed to account for variations among studies while estimating the overall effect of late-season foliar N application on wheat yield and quality. Statistical analyses were conducted using the nlme package in R statistical software (version 4.3.3). Effect sizes and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were computed for each subgroup.
The N application rates used in the subgroup analyses refer to the total N input of each treatment rather than the amount applied solely via foliar spraying. To assess the in-fluence of key moderating factors, subgroup analyses were performed based on (i) total N application rate, categorized into ≤100 kg N/ha (low N level), 101–150 kg N/ha (global average level), 151–200 kg N/ha (recommended N level), ≥200 kg N/ha (traditional farmer application rate), and 251–300 kg N/ha (high N level) [33]; (ii) timing of late-season foliar N application, classified as booting, anthesis, and post-anthesis stages [34]; (iii) ratio of late-season foliar N application to total N input, categorized into <0.15, 0.15–0.3, and >0.3; and (iv) wheat type, categorized as winter wheat or spring wheat based on descriptions provided in the original studies. When not explicitly mentioned, wheat type was inferred from the geographic location and local cropping systems following the established agronomic practices reported in the literature.
Publication bias was evaluated using funnel plots, a common diagnostic tool in me-ta-analysis [35]. The symmetry of the funnel plots was visually inspected for wheat yield and grain quality parameters to determine potential bias [36]. To further validate the robustness of the findings, we plotted the relationship between wheat grain yield, grain protein concentration, and sample size across all studies [37,38]. The funnel plots for wheat yield and quality parameters were symmetric, suggesting no publication bias.
2.4. Data Visualization
To facilitate interpretation, data distributions and effect size estimates were visualized using forest plots, which illustrate the magnitude and direction of treatment effects along with confidence intervals. These visual representations were generated using the ggplot2 package in R.
2.5. Model Assumptions and Sensitivity Analysis
To confirm the reliability of the meta-analysis, a heterogeneity test was conducted using Cochran’s Q statistic and I2 values, where I2 < 25% indicates low heterogeneity, 25% ≤ I2 < 50% suggests moderate heterogeneity, and I2 ≥ 50% denotes high heterogeneity.
Additionally, leave-one-out sensitivity analysis was performed to assess whether the exclusion of any single study significantly altered the overall effect size.
2.6. Research Framework
A flowchart (Figure 1) summarizes the workflow for data collection, processing, and analysis, ensuring transparency and reproducibility. The initial literature search yielded 366 records from ISI Web of Science, 401 from Google Scholar, and 103 from CNKI. After applying the predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, a total of 51 studies were retained for quantitative synthesis.
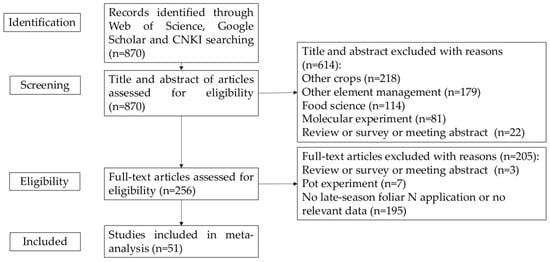
Figure 1.
Flowchart of the process of building the database and conducting the meta-analysis.
3. Results
3.1. Overall Effect of Late-Season Foliar N Application on Wheat Yield and Quality
Based on 1498 paired observations from 51 field studies, the results demonstrate that late-season foliar N application significantly enhances both wheat yield and quality. Compared to the control (no late-season foliar N application), late-season foliar N application led to a 4.1% increase in grain yield and a 5.9% increase in protein concentration (Figure 2a). However, the effect varied depending on the specific N application strategy.
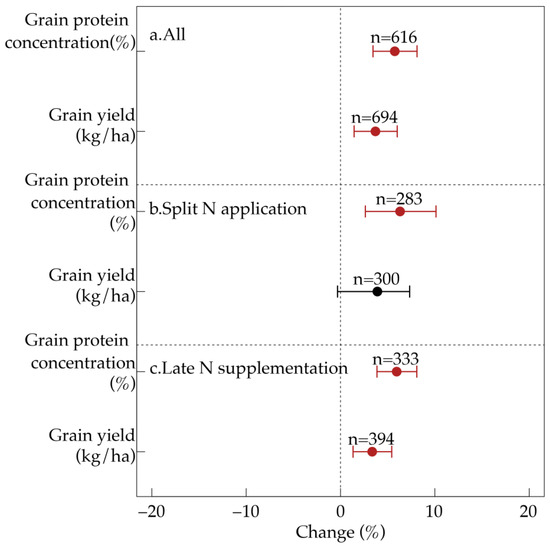
Figure 2.
Comprehensive effects of late-season foliar N application on grain yield and quality for all (a), split N application (b), and late N supplementation (c) datasets. Data points represent treatment means, and horizontal bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. Numbers denote the number of observations used for statistical analysis. Red points indicate statistically significant effects, while black points indicate non-significant effects.
Split foliar N application primarily improved protein concentration, resulting in a 6.3% increase, but it had no significant effect on yield (Figure 2b). In contrast, late-season N supplementation significantly increased grain yield (+3.4%) and protein concentration (+6.0%) (Figure 2c).
Further subgroup analysis revealed that the effectiveness of late-season foliar N application varied between winter and spring wheat. For winter wheat, foliar N application significantly increased grain yield by 4.5–5.9% and protein concentration by 4.7–6.7%. However, for spring wheat, while foliar N application significantly increased protein concentration by 3.9–5.0%, it had no significant effect on grain yield (Figure 3). These findings suggest that late-season foliar N application is a viable strategy for improving both wheat grain yield and processing quality, with its effectiveness largely dependent on the application method and wheat type.
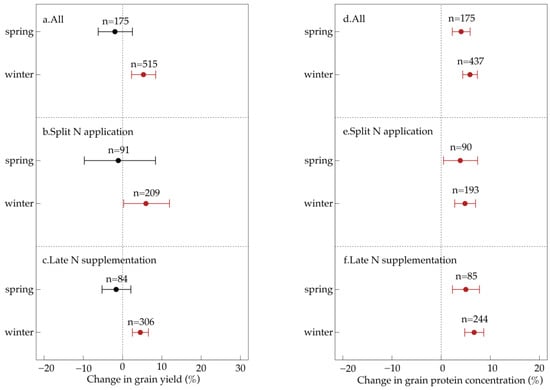
Figure 3.
Comprehensive effects of late-season foliar N application on grain yield (a–c) and quality (d–f) of winter and spring wheat. Data points represent treatment means, and horizontal bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. Numbers denote the number of observations used for statistical analysis. Red points indicate statistically significant effects, while black points indicate non-significant effects.
3.2. Effects of Late-Season Foliar N Application on Wheat Yield and Quality Under Different N Rates
The effectiveness of late-season foliar N on wheat yield and quality was significantly influenced by total N application levels. When the total N application rate was ≥200 kg N/ha, late-season foliar N application led to a notable increase in grain yield (+8.0%) and protein concentration (+8.6%) (Figure 4a–d). However, at N application rates below 200 kg N/ha, foliar N application significantly improved protein concentration (+3.5% to +4.1%) but had no significant effect on grain yield (Figure 4a–d).
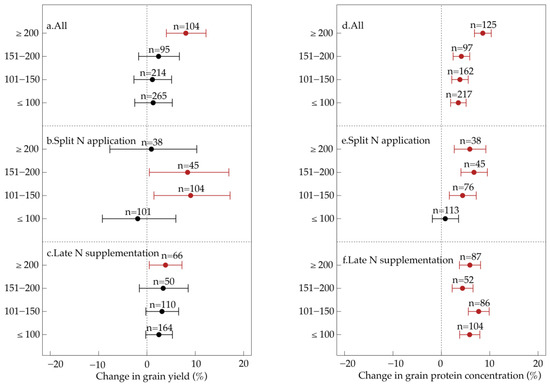
Figure 4.
Impact of late-season foliar N application on wheat grain yield (a–c) and quality (d–f) at different N application rates. Data points represent treatment means, and horizontal bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. Numbers denote the number of observations used for statistical analysis. Red points indicate statistically significant effects, while black points indicate non-significant effects.
Further analysis showed that split foliar N application was particularly effective within the 101–200 kg N/ha range, significantly enhancing grain yield (+8.4% to +9.0%) and protein concentration (+4.4% to +6.7%) compared to the control (Figure 4b–e). At 101–150 kg N/ha, split foliar N application significantly increased protein concentration (+4.4%) but did not affect yield. At N rates below 100 kg N/ha, foliar N application showed no significant impact on either grain yield or protein concentration (Figure 4b–e).
In contrast, late-season N supplementation significantly increased both grain yield (+3.8%) and protein concentration (+5.9%), but only at N rates ≥ 200 kg N/ha (Figure 4c–f). At lower N levels, late-season N supplementation increased protein concentration (+4.4% to +7.7%) but had no significant effect on yield.
These results suggest that split foliar N application is most effective in moderately fertilized systems (101–200 kg N/ha), while late-season N supplementation benefits high-N systems (≥200 kg N/ha). In contrast, under lower N rates (≤100 kg N/ha), foliar N application alone is insufficient to improve grain yield, although it may still contribute to an increase in grain protein concentration.
3.3. Effects of Late-Season Foliar N Application on Wheat Yield and Quality Under Different N Application Timings
The timing of late-season foliar N application significantly influenced its effects on wheat grain yield and quality (Figure 5). Overall, foliar N application at anthesis resulted in the greatest improvements, leading to a 5.3% increase in grain yield and a 5.8% increase in protein concentration. In contrast, applications at booting or post-anthesis significantly increased protein concentration by 4.4–5.4% but had no significant effect on grain yield (Figure 5a–d).
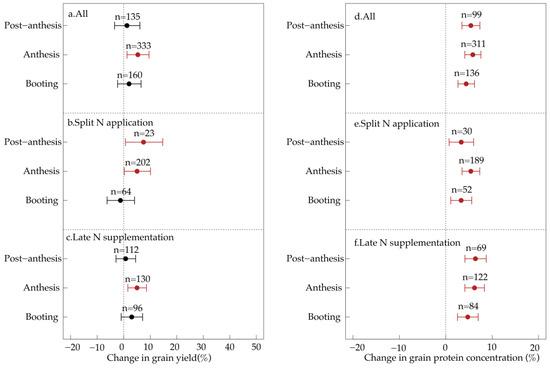
Figure 5.
Effects of late-season foliar N application on wheat grain yield (a–c) and quality (d–f) at different application timings. Data points represent treatment means, and horizontal bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. Numbers denote the number of observations used for statistical analysis. Red points indicate statistically significant effects, while black points indicate non-significant effects.
Further analysis revealed that split foliar N application at both anthesis and post-anthesis stages was effective in enhancing both grain yield and protein concentration. Specifically, foliar N application at anthesis increased grain yield by 5.0% and protein concentration by 5.4%, whereas post-anthesis application resulted in a greater yield increase (+7.5%) but a lower protein gain (+3.3%) (Figure 5b–e). In contrast, no significant improvements were observed when foliar N was applied during the booting stage.
Regarding late-season N supplementation, significant increases in both grain yield (+5.0%) and protein concentration (+6.2%) were observed only when applied at anthesis. At other stages, late-season N supplementation had no impact on yield, though it significantly enhanced protein concentration by 4.7–6.4% (Figure 5c–f).
These findings highlight that anthesis is the optimal timing for foliar N application, as it provides the most substantial benefits for both grain yield and protein accumulation. Post-anthesis applications can still enhance yield but are less effective in improving protein concentration. Conversely, applying foliar N at the booting stage yields limited benefits.
3.4. Effects of Late-Season Foliar N Application on Wheat Yield and Quality Under Different Late-Stage N Application Ratios
The proportion of N applied during the late growth stage relative to the total N application (N application ratio) significantly affected the effectiveness of the late-season foliar N application (Figure 6). When the N application ratio was below 0.15, late-season foliar N application significantly increased both grain yield (+5.9%) and protein concentration (+4.3%) (Figure 6a–d). However, at N application ratios between 0.15 and 0.3 and above 0.3, no significant yield improvements were observed, although the protein concentration increased by 5.2% and 6.8%, respectively (Figure 6a–d).
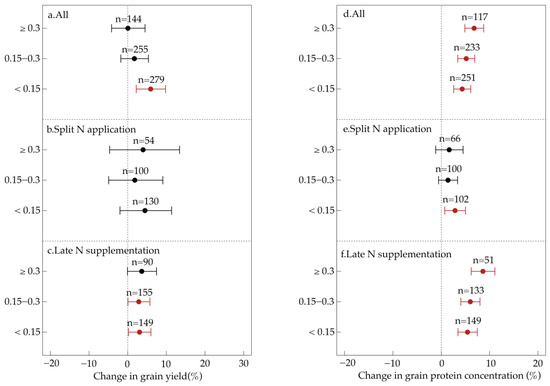
Figure 6.
Effects of late-season foliar N application on wheat grain yield (a–c) and quality (d–f) at different late-stage N application ratios. Data points represent treatment means, and horizontal bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. Numbers denote the number of observations used for statistical analysis. Red points indicate statistically significant effects, while black points indicate non-significant effects.
For split foliar N application, a low N application ratio (<0.15) did not significantly affect grain yield but resulted in a 2.9% increase in protein concentration (Figure 6b–e). In contrast, late-season N supplementation had a more pronounced effect, significantly enhancing both grain yield and protein concentration when the N application ratio was below 0.3. Specifically, at ratios below 0.15, grain yield increased by 3.1%, and protein concentration by 5.4%, while at ratios between 0.15 and 0.3, grain yield increased by 2.9% and protein concentration by 6.0% (Figure 6c–f). When the N application ratio exceeded 0.3, late-season N supplementation had no significant impact on grain yield but led to a notable increase in protein concentration (+8.6%) (Figure 6c–f).
These results indicate that a lower late-stage N application ratio (<0.15) is optimal for balancing wheat yield and quality. While late-season N supplementation at moderate application ratios (0.15–0.3) can still improve both parameters, excessively high ratios (>0.3) primarily benefit protein accumulation without contributing to yield enhancement.
3.5. Correlations Between Wheat Grain Yield and Protein Concentration Under Various N Management Strategies
The relationship between grain yield and protein concentration was analyzed using data extracted from the literature (Figure 7). The results confirmed a significant negative correlation (p < 0.001) between grain yield and protein concentration under both the control treatment (no late-season foliar N) and late-season foliar N application (Figure 7a,b).
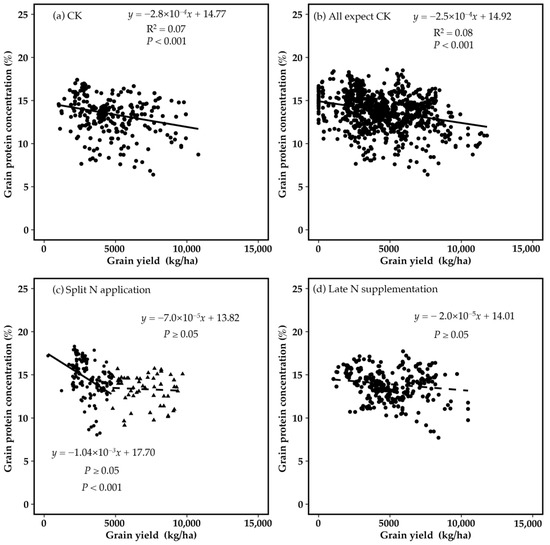
Figure 7.
Correlations between wheat grain yield and protein concentration under the N management strategies of the control treatment (CK) with no late-season foliar N (a), all late-season foliar N application (b), split foliar N application (c), and late-season N supplementation (d).
Further analysis revealed that under split foliar N application, the yield–protein trade-off was dependent on yield levels. When grain yield was below 4950 kg/ha, a significant negative correlation between yield and protein concentration persisted (p < 0.001). However, when grain yield exceeded 4950 kg/ha, this negative correlation became non-significant (p ≥ 0.05) (Figure 7c).
In contrast, under late-season N supplementation, no significant negative correlation between grain yield and protein concentration was observed at any yield level (p ≥ 0.05) (Figure 7d).
These findings suggest that split foliar N application can, to some extent, mitigate the conventional yield–protein trade-off, allowing for simultaneous improvements in grain yield and protein accumulation. Moreover, late-season N supplementation appears to better overcome this trade-off, indicating that increasing total N availability at later growth stages can effectively balance yield and quality.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Different Late-Season Foliar N Management Strategies on Wheat Grain Yield and Quality
4.1.1. Impacts of N Management Strategies on Yield and Quality Formation
This study confirms that late-stage foliar N application has a positive effect on wheat grain yield and protein concentration, though the extent of improvement varies depending on the management strategy (Figure 2). Compared with conventional N fertilization, split foliar N application led to a notable increase in grain protein concentration (+6.3%), while its impact on grain yield was negligible (Figure 2b). In contrast, late-season N supplementation resulted in simultaneous increases in both grain yield (+3.4%) and protein concentration (+6.0%) (Figure 2c). These differences are likely attributed to variations in grain N uptake efficiency and allocation, which influence whether N is primarily utilized for yield formation or protein accumulation.
During the vegetative growth stage of wheat, N application primarily supports biomass accumulation and yield formation [39]. The N applied between the tillering and jointing stages promotes tiller and spike development, which are crucial determinants of final grain yield [40]. Additionally, N application at the flag leaf stage predominantly increases grain number per spike and thousand-grain weight [41]. Conversely, late-season N application contributes more significantly to grain protein accumulation rather than starch synthesis [7,8]. The findings of this study align with this view, demonstrating that late-season foliar N application optimizes the balance between protein synthesis and starch accumulation by adjusting the timing of N supply, ultimately enhancing wheat grain quality.
4.1.2. Effects of Application Levels, Timing, and Proportions on Grain Yield and Quality
The effects of late-season foliar N application on wheat grain yield and quality are influenced by N application levels, split N proportions, and application timing (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5, Figure 6 and Figure 7). Subgroup analysis revealed that split foliar N application was most effective within the 101–200 kg N/ha range, significantly enhancing both grain yield and protein concentration. However, late-season N supplementation significantly increased both grain yield and protein concentration only at rates ≥ 200 kg N/ha (Figure 2a and Figure 3a). A possible explanation is that early-season N application already ensures sufficient biomass accumulation, providing an adequate sink for grain formation under both strategies. Late-season N supply extends leaf lifespan [42,43], delays N re-mobilization, shifts N translocation to the grain filling stage [8,44], and enhances N uptake in grains, thereby supporting grain protein synthesis and accumulation [10,45,46,47].
The distinct effects of split foliar N application and late-season N supplementation suggest different underlying mechanisms. Split foliar N application enhances N uptake efficiency, facilitating better N allocation to grain protein. Under moderate to low N conditions, grain N accumulation is primarily sink-regulated [48], meaning that early-season N establishes yield potential, while split foliar N further supports grain N translocation. This optimizes synchronization between crop N demand and supply throughout the growing season [28,49,50,51]. Conversely, late-season N supplementation achieves higher yield and protein concentration by increasing total N availability, ensuring that both sink and source limitations are minimized. These findings suggest that split foliar N application, even without increasing total N input, can achieve effects similar to late-season foliar N supplementation by improving N use efficiency. This presents a potential optimization strategy for improving wheat grain yield and quality, though further targeted studies are needed to clarify the precise physiological mechanisms.
Previous studies have identified the booting stage as a critical timing for optimizing grain yield and processing quality through split N application in soil-based fertilization systems [25]. However, foliar N uptake occurs much faster than root uptake, with peak absorption occurring within hours, compared to at least 72 h for soil-applied N [22]. This suggests that the growth stages after the booting stage (e.g., anthesis or even post-anthesis stages) may be the most effective timing for foliar N application. The findings of this study confirm this hypothesis, demonstrating that anthesis-stage foliar N application resulted in the greatest improvements in both wheat grain yield and protein concentration (Figure 4a and Figure 5a). At this stage, wheat exhibits high N demand, and late-season N translocation becomes more efficient, supporting grain development and protein accumulation [52,53].
The proportion of N applied at different growth stages also plays a crucial role in determining yield and quality outcomes [54]. This study found that when late-season foliar N application accounts for less than 0.15 of the total N amount, both grain yield and protein concentration improvements were maximized (Figure 6a and Figure 7a). In contrast, higher late-season N proportions (>0.3) increased protein accumulation without yield benefits. These findings underscore the importance of optimized N distribution across growth stages to enhance efficiency and minimize unnecessary resource competition, promoting both high productivity and environmental sustainability [55].
4.2. Correlation Between Wheat Grain Yield and Protein Concentration Under Different Late-Season Foliar N Management Strategies
The relationship between wheat grain yield and protein concentration was significantly influenced by late-season foliar N management. Under conventional N fertilization, a negative correlation between grain yield and protein concentration is often observed (Figure 7a), consistent with previous studies [6,56]. This phenomenon is primarily driven by carbohydrate dilution effects (higher starch accumulation reducing protein concentration) and competition between carbon and N for energy allocation [57,58,59].
However, this study demonstrates that different late-season foliar N strategies can mitigate the conventional yield–protein trade-off to varying degrees (Figure 7c,d). Specifically, under split foliar N application, a significant negative correlation (p < 0.001) between grain yield and protein concentration was observed when yield was below 4950 kg/ha. However, at higher yield levels (>4950 kg/ha), this correlation was no longer significant (p ≥ 0.05) (Figure 7c).
In contrast, under late-season N supplementation, no significant negative correlation between grain yield and protein concentration was observed at any yield level (p ≥ 0.05) (Figure 7d). This suggests that late-season N supplementation provides sufficient N to meet the metabolic demands of both yield formation and protein synthesis, avoiding the trade-offs typically associated with N limitations [10,46,53]. Meanwhile, split foliar N application improves N utilization efficiency, allowing for simultaneous yield enhancement and protein accumulation without additional N input. This reduces competition between protein and starch biosynthesis, offering a potential solution to the yield–protein trade-off. Although the R² values associated with these regressions are relatively low—potentially limiting the explanatory power of simple linear models—this outcome is not unexpected given the global scope of the dataset. The analysis integrates data from a wide range of agroecological zones, wheat cultivars, and nitrogen management practices, all of which contribute to considerable heterogeneity. This inherent variability can reduce the strength of the observed associations. Nevertheless, the consistent statistical significance observed (p < 0.001 in several cases) indicates the existence of meaningful underlying relationships. These findings highlight the strength of meta-analytical approaches in revealing overarching trends across diverse conditions while also emphasizing the importance of adopting more sophisticated modeling strategies in future research to better account for between-study variability.
In summary, this study highlights the critical role played by late-season foliar N application in regulating the balance between wheat grain yield and quality. Different N management strategies not only improve grain yield and protein concentration but also alleviate or eliminate the conventional negative correlation between these two traits. These findings provide scientific evidence supporting the optimization of N fertilization strategies, contributing to the broader goal of achieving high-yield, high-quality, and high-efficiency wheat production.
5. Conclusions
This study systematically assessed the effects of late-season foliar N application on wheat grain yield and protein concentration through a comprehensive meta-analysis. The results demonstrate that late-season foliar N application significantly increases both wheat grain yield and protein concentration, particularly when applied at anthesis and post-anthesis stages, which are critical periods for determining grain filling and protein accumulation.
Moreover, without increasing the total N input, split foliar N application at moderate N levels (101–200 kg N/ha) and low late-season application ratios (<0.15) effectively enhances protein concentration while maintaining yield stability, thereby mitigating the traditional yield–protein trade-off. This approach helps alleviate the traditional trade-off between yield and protein content, offering a promising strategy for improving grain quality without compromising productivity. In contrast, under high N input conditions (≥200 kg N/ha), late-season N supplementation achieves simultaneous improvements in yield and protein concentration, likely due to enhanced N availability during the grain filling period.
These findings underscore the importance of optimizing both the timing and method of late-season foliar N application, particularly during the critical reproductive growth stages of wheat. By aligning N supply with crop demand, late-season foliar N application not only enhances wheat grain yield and grain quality but also improves N use efficiency, supporting the development of efficient, high-yield, high-quality, and environmentally sustainable fertilization practices.
Author Contributions
W.W.: Conceptualization, Investigation, Software, Methodology, Data Curation, Visualization, Writing—Original Draft. Y.W.: Methodology, Writing—Review and Editing. H.X. and M.L.: Formal Analysis, Data Curation, Software. C.X.: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing—Review and Editing, Funding Acquisition, Validation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (no. 2021YFD1901005) and the Central Guidance for Local Technology Development Fund (236Z6402G).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- FAOSTAT. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. FAOSTAT Food Balance Sheets. 2022. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FBS (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Shewry, P.R.; Halford, N.G. Cereal seed storage proteins: Structures, properties and role in grain utilization. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, T.; Halford, N.G. Food security: The challenge of increasing wheat yield and the importance of not compromising food safety. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 164, 354–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkesford, M.J. Reducing the reliance on nitrogen fertilizer for wheat production. J. Cereal Sci. 2014, 59, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandino, M.; Vaccino, P.; Reyneri, A. Late-Season Nitrogen Increases Improver Common and Durum Wheat Quality. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zörb, C.; Ludewig, U.; Hawkesford, M.J. Perspective on Wheat Yield and Quality with Re-duced Nitrogen Supply. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barneix, A.J. Physiology and biochemistry of source-regulated protein accumulation in the wheat grain. J. Plant Physiol. 2007, 164, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ercoli, L.; Masoni, A.; Pampana, S.; Mariotti, M.; Arduini, I. As durum wheat productivity is affected by nitrogen fertilisation management in Central Italy. Eur. J. Agron. 2013, 44, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandino, M.; Visioli, G.; Marando, S.; Marti, A.; Reyneri, A. Impact of late-season N ferti-lisation strategies on the gluten content and composition of high protein wheat grown under hu-mid Mediterranean conditions. J. Cereal Sci. 2020, 94, 102995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Auf’m Erley, G.S.; Rossmann, A.; Schuster, R.; Koehler, P.; Muhling, K.H. Split Ni-trogen Application Improves Wheat Baking Quality by Influencing Protein Composition Rather Than Concentration. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Ma, D.; Lu, H.; Feng, W.; Xie, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Guo, T. Effects of different irrigation and nitrogen regimes on root growth and its correlation with above-ground plant parts in high-yielding wheat under field conditions. Field Crops Res. 2014, 165, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.H.; Liu, C.; Huang, M.L.; Liu, K.Z.; Yan, D.Y. Effects of Foliar Fertilization: A Review of Current Status and Future Perspectives. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, N.; Ku, L.; Hou, Y.; Wen, X. Foliar applications of various nitrogen (N) forms to winter wheat affect grain protein accumulation and quality via N metabolism and re-mobilization. Crop J. 2022, 10, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossmann, A.; Buchner, P.; Savill, G.P.; Hawkesford, M.J.; Scherf, K.A.; Mühling, K.H. Foliar N application at anthesis alters grain protein composition and enhances baking quality in winter wheat only under a low N fertiliser regimen. Eur. J. Agron. 2019, 109, 125909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blandino, M.; Pilati, A.; Reyneri, A. Effect of foliar treatments to durum wheat on flag leaf senescence, grain yield, quality and deoxynivalenol contamination in North Italy. Field Crops Res. 2009, 114, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tea, I.; Genter, T.; Naulet, N.; Boyer, V.; Lummerzheim, M.; Kleiber, D. Effect of Foliar Sul-fur and Nitrogen Fertilization on Wheat Storage Protein Composition and Dough Mixing Proper-ties. Cereal Chem. 2004, 81, 759–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekowski, A.; Wimmer, M.A.; Henkelmann, G.; Zörb, C. Is a Change of Protein Composition after Late Application of Nitrogen Sufficient to Improve the Baking Quality of Winter Wheat? Agriculture 2019, 9, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Verma, O. Seed Quality and Storage of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) as Influenced by Basal and Foliar Application of Nitrogen. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2018, 41, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, M.J.; Davies, W.P. Foliar urea fertilization of cereals: A review. Fertil. Res. 1992, 32, 209–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Liu, W.; Li, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, C.; Lu, H.; Wang, L.; Xie, Y.; Ma, D.; Kang, G. Deter-mining the Optimal N Input to Improve Grain Yield and Quality in Winter Wheat with Reduced Apparent N Loss in the North China Plain. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilas, B.L.; Legg, J.O.; Wolf, D.C. Foliar Fertilization of Soybeans: Absorption and Translocation of 15N-Labeled Urea. Agron. J. 1980, 72, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarandón, S.J.; Gianibelli, M.C. Effect of foliar urea spraying and nitrogen application at sowing upon dry matter and nitrogen distribution in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Agronomie 1990, 10, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegeder, M.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Source and sink mechanisms of nitrogen transport and use. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, S.; Charnel, A. Foliar absorption and transport of inorganic nutrients. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1986, 4, 341–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.S.; Zörb, C.; Geilfus, C.M.; Xue, C.; Sun, Z.M.; Ma, W.Q. Booting stage is the key timing for split nitrogen application in improving grain yield and quality of wheat—A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2022, 287, 108665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Gurevitch, J.; Curtis, P.S. The Meta-Analysis of Response Ratios in Experi-mental Ecology. Ecology 1999, 80, 1150–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Coulter, J.A.; Xie, J.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, R.; Deng, X.; Li, L. Winter wheat yield and water use efficiency response to organic fertilization in northern China: A meta-analysis. Agr. Water Manag. 2020, 229, 105934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Tang, Q.; Yan, X. Can knowledge-based N manage-ment produce more staple grain with lower greenhouse gas emission and reactive nitrogen pollu-tion? A meta-analysis. Global Change Biol. 2017, 23, 1917–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Lv, W.; Bloszies, S.; Shi, Q.; Pan, X.; Zeng, Y. Effects of fertilizer management practices on yield-scaled ammonia emissions from croplands in China: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2016, 192, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkama, E.; Salo, T.; Esala, M.; Turtola, E. Nitrogen balances and yields of spring cereals as affected by nitrogen fertilization in northern conditions: A meta-analysis. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 164, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Sadras, V.O.; Lu, G.; Zhang, P.; Han, Y.; Liu, L.; Xie, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S. A global meta-analysis of split nitrogen application for improved wheat yield and grain protein content. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 213, 105111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Ma, W.; Velthof, G.L.; Hou, Y.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F. Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: A meta-analysis. Global Change Biol. 2020, 26, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, P.; Shangguan, Z. Winter wheat grain yield in response to different production practices and soil fertility in northern China. Soil. Till Res. 2018, 176, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancashire, P.D.; Bleiholder, H.; Boom, T.V.D.; LangelÜDdeke, P.; Stauss, R.; Weber, E.; Witzenberger, A. A uniform decimal code for growth stages of crops and weeds. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1991, 119, 561–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez-Lopez, A.; Alkemade, R.; Schipper, A.M.; Ingram, D.J.; Verweij, P.A.; Eikelboom, J.A.; Huijbregts, M.A. The impact of hunting on tropical mammal and bird populations. Science 2017, 356, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philibert, A.; Loyce, C.; Makowski, D. Assessment of the quality of meta-analysis in agronomy. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 148, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Stomph, T.-J.; Makowski, D.; van der Werf, W. Temporal niche differentiation in-creases the land equivalent ratio of annual intercrops: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Guay, M.O.; Paquette, A.; Dupras, J.; Rivest, D. The new Green Revolution: Sustaina-ble intensification of agriculture by intercropping. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 615, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diacono, M.; Rubino, P.; Montemurro, F. Precision nitrogen management of wheat. A Review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2013, 33, 219–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Wang, S.; Lin, X.; Gu, S.; Wang, D. Supplemental irrigation at jointing improves spike formation of wheat tillers by regulating sugar distribution in ear and stem. Agr. Water Manage. 2023, 279, 108160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Yang, M.; Cai, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Q.; Cao, W.; Dai, T.; Jiang, D. Nitrogen top-dressing timing influences the spatial distribution patterns of protein components and quality traits of flours from different pearling fractions of wheat (Triticum aestivum L. ) grains. Field Crops Res. 2018, 216, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, C.F.; Paulsen, G.M. Development of Hard Winter Wheat after Anthesis as Affected by Nitrogen Nutrition. Crop. Sci. 1985, 25, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Zhao, W.; Lv, Z.; Xu, B.; Hu, W.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, Y. Optimal rate of nitrogen fertilizer improves maize grain yield by delaying the senescence of ear leaves and thereby altering their ni-trogen remobilization. Field Crops Res. 2024, 310, 109359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedone, L.; Alhajj Ali, S.; Verdini, L.; De Mastro, G. Nitrogen management strategy for op-timizing agronomic and environmental performance of rainfed durum wheat under Mediterra-nean climate. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 2058–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, H.J.; Bly, A. Relationship of nitrogen management to winter wheat yield and grain protein in South Dakota. J. Plant Nutr. 1998, 21, 217–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Schulte auf’m Erley, G.; Rücker, S.; Koehler, P.; Obenauf, U.; Mühling, K.H. Late ni-trogen application increased protein concentration but not baking quality of wheat. J. Plant Nutr. Soil. Sci. 2016, 179, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, H.; Wu, W.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Xue, C. Elevated atmospheric CO2 delays the key timing for split N applications to improve wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) protein composition. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1186890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martre, P.; Jamieson, P.D.; Semenov, M.A.; Zyskowski, R.F.; Porter, J.R.; Triboï, E. Modelling protein content and composition in relation to crop nitrogen dynamics for wheat. Eur. J. Agron. 2006, 25, 138–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, F. Integrated nutrient management for improving crop yields and nutrient utilization efficiencies in China. J. Soil. Water Conserv. 2008, 63, 126A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lü, G.; Guo, X.; Wang, Y.; Ding, S.; Wang, D. Conservation tillage and optimized fertilization reduce winter runoff losses of nitrogen and phosphorus from farmland in the Chaohu Lake region, China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2015, 101, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Xu, M.; Feng, G.; Zhang, W.; Lu, C.a. Crop yield and soil organic matter after long-term straw return to soil in China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2015, 102, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miralles, D.; Slafer, G.A. Wheat development. In Wheat; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 13–43. [Google Scholar]
- Roychowdhury, R.; Zilberman, O.; Chandrasekhar, K.; Curzon, A.Y.; Nashef, K.; Abbo, S.; Slafer, G.A.; Bonfil, D.J.; Ben-David, R. Pre-anthesis spike growth dynamics and its association to yield components among elite bread wheat cultivars (Triticum aestivum L. spp.) under Mediter-ranean climate. Field Crops Res. 2023, 298, 108948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Yu, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of nitrogen rate and ratio of base fertilizer and topdressing on uptake, translocation of nitrogen and yield in wheat. Front. Agric. China 2007, 1, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, N.W. The relation between yield and protein in cereal grain. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2006, 67, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munier-Jolain, N.G.; Salon, C. Are the carbon costs of seed production related to the quan-titative and qualitative performance? An appraisal for legumes and other crops. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acreche, M.M.; Slafer, G.A. Variation of grain nitrogen content in relation with grain yield in old and modern Spanish wheats grown under a wide range of agronomic conditions in a Mediterranean region. J. Agric. Sci. 2009, 147, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guo, D.; Blennow, A.; Zörb, C. Mineral nutrients and crop starch quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 114, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).