Separately Collected Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste Compost as a Sustainable Improver of Soil Characteristics in the Open Field and a Promising Selective Booster for Nursery Production
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SC-OFMSWC Characterization
2.2. SC-OFMSWC Evaluation for Nursery Production
2.2.1. Germination Rate and Index in Liquid Culture
2.2.2. In-Pot Germination Rate and Growth Tests
2.2.3. Evaluation of Epigeal Biomass Production
2.2.4. Evaluation of Total Leaf Area
2.2.5. Determination of Photosynthetic Pigments Content
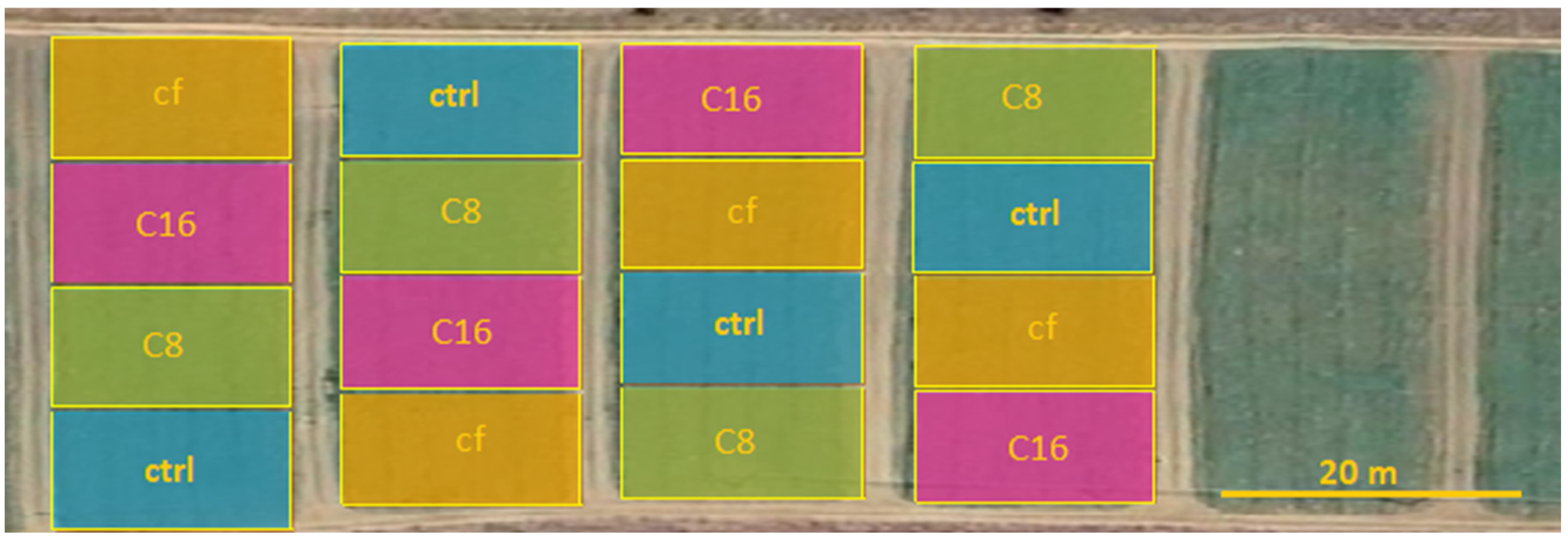
2.3. In-Field SC-OFMSWC Evaluation
2.3.1. Soil Chemo-Physical Properties
2.3.2. Biochemical Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. SC-OFMSWC Characterization
3.2. SC-OFMSWC Evaluation for Nursery Production
3.2.1. Germination Rate and Index in Liquid Culture
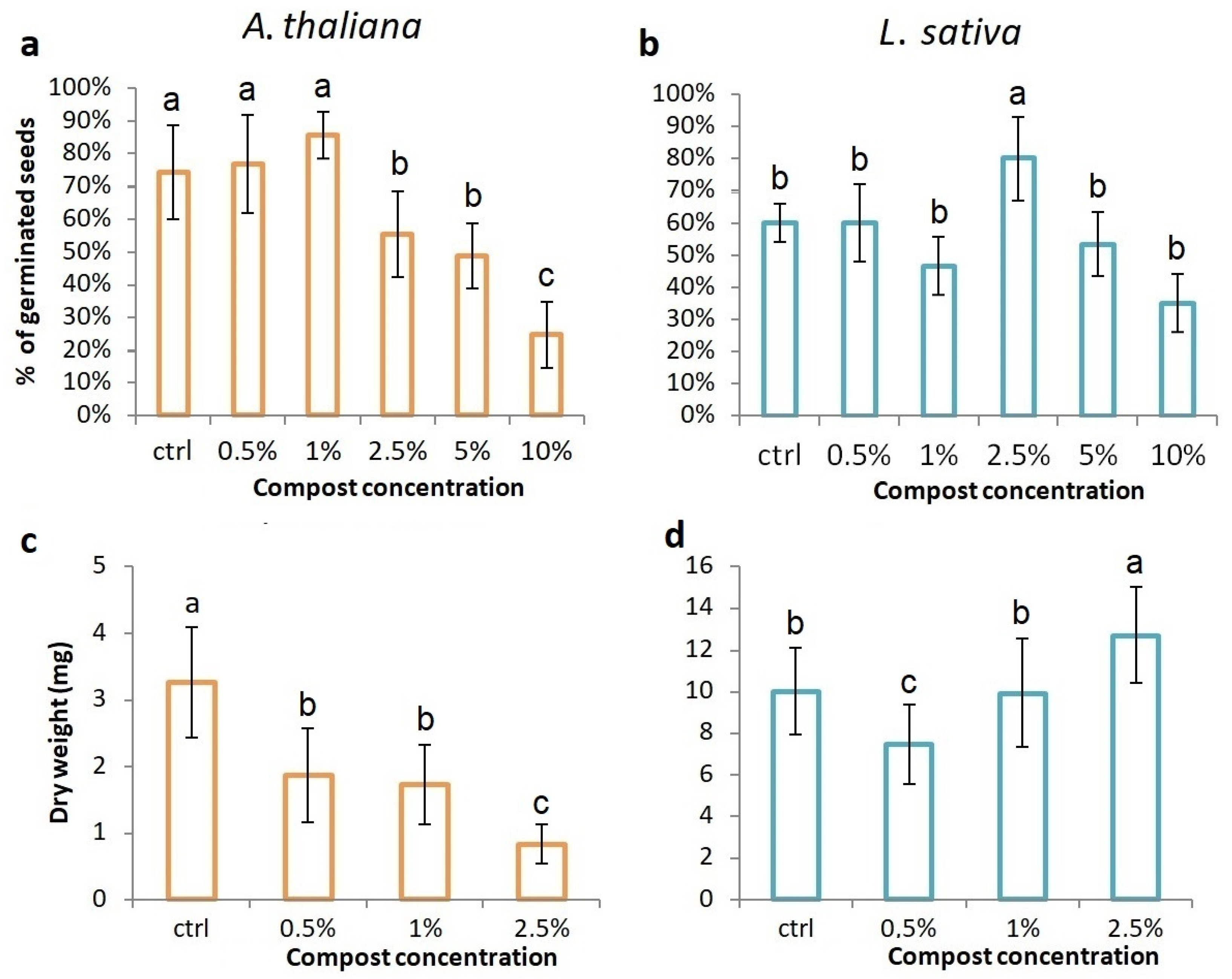
3.2.2. In-Pot Germination Rate, Growth Tests, and Evaluation of Epigeal Biomass Production
3.2.3. Total Leaf Area
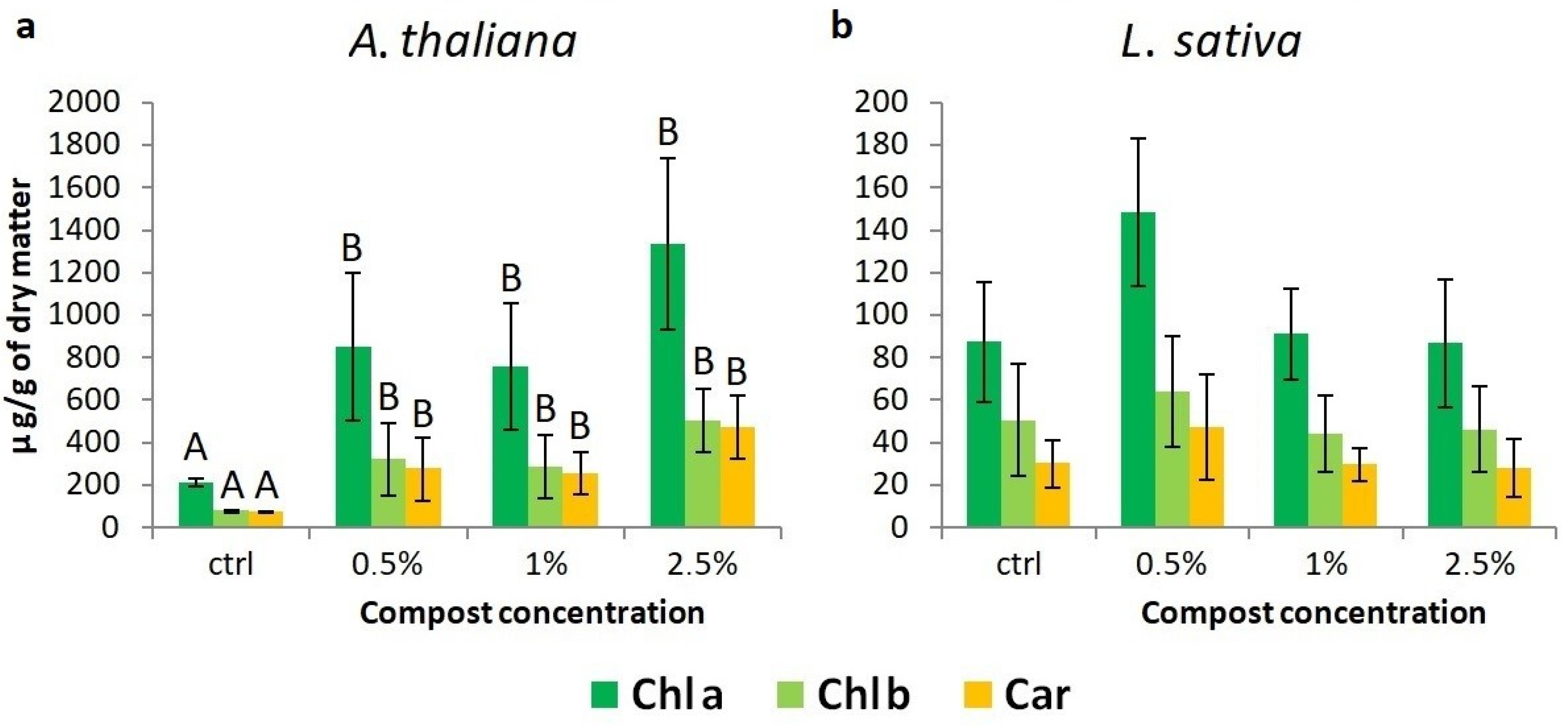
3.2.4. Determination of Photosynthetic Pigment Content
3.3. In-Field SC-OFMSWC Evaluation
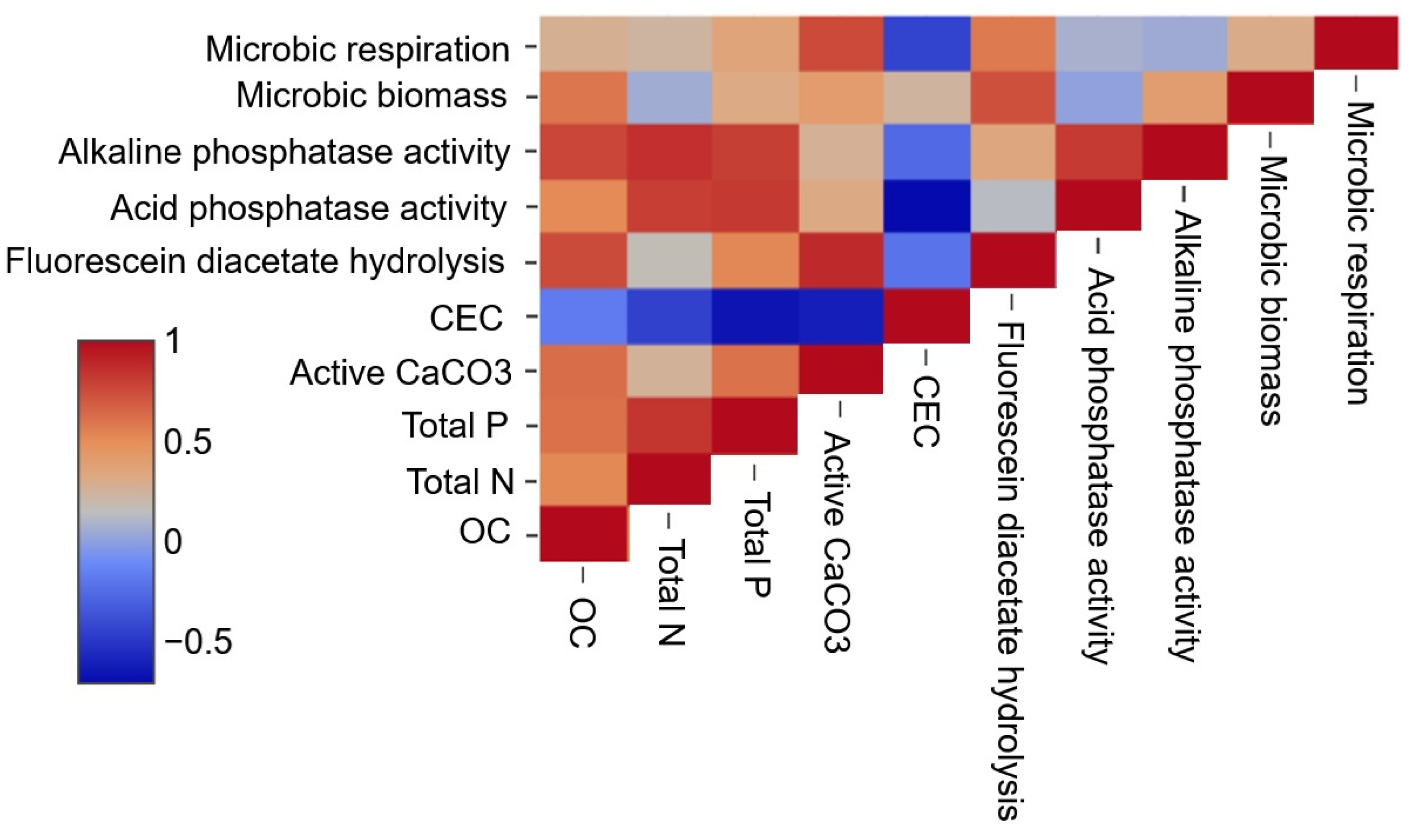
3.3.1. Soil Chemo-Physical Properties
3.3.2. Biochemical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UNCCD. Global Land Outlook. United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD); Secretariat of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification: Bonn, Germany, 2017; ISBN 9789295110489. Available online: https://www.unccd.int/resources/publications/global-land-outlook-1st-edition (accessed on 24 February 2025).
- Aziz, I.; Mahmood, T.; Islam, K.R. Effect of Long Term No-till and Conventional Tillage Practices on Soil Quality. Soil Tillage Res. 2013, 131, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Caspari, T.; Gonzalez, M.R.; Batjes, N.H.; Mäder, P.; Bünemann, E.K.; de Goede, R.; Brussaard, L.; Xu, M.; Ferreira, C.S.S.; et al. Effects of Agricultural Management Practices on Soil Quality: A Review of Long-Term Experiments for Europe and China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, L.; Palese, A.M.; Grasso, F.; Duffy, D.H.; Briccoli Bati, C.; Xiloyannis, C. Mechanical Tillage Diversely Affects Glomalin Content, Water Stable Aggregates and AM Fungal Community in the Soil Profiles of Two Differently Managed Olive Orchards. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksandrowicz, L.; Green, R.; Joy, E.J.M.; Smith, P.; Haines, A. The Impacts of Dietary Change on Greenhouse Gas Emissions, Land Use, Water Use, and Health: A Systematic Review. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAO. The State of the World’s Land and Water Resources for Food and Agriculture—Systems at Breaking Point; Main Report; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhin, M.; Coyne, M.S.; Sistani, K.R. How Much Margin Is Left for Degrading Agricultural Soils? The Coming Soil Crises. Soil Syst. 2022, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO Food and Agriculture Organization. FAO SoiLEXportal. Available online: https://www.fao.org/soils-portal/soilex/soil-keywords/soil-restoration/en/ (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Ho, T.T.K.; Tra, V.T.; Le, T.H.; Nguyen, N.-K.-Q.; Tran, C.-S.; Nguyen, P.-T.; Vo, T.-D.-H.; Thai, V.-N.; Bui, X.-T. Compost to Improve Sustainable Soil Cultivation and Crop Productivity. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajura, R. Composting Municipal Solid Waste and Animal Manure in Response to the Current Fertilizer Crisis—A Recent Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Policastro, G.; Cesaro, A. Composting of Organic Solid Waste of Municipal Origin: The Role of Research in Enhancing Its Sustainability. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 20, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; Soliva, M.; Martínez-Farré, F.X.; Fernández, M.; Huerta-Pujol, O. Evaluation of MSW Organic Fraction for Composting: Separate Collection or Mechanical Sorting. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, M.; Jones, D.L. Critical Evaluation of Municipal Solid Waste Composting and Potential Compost Markets. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 4301–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANPA. Il Recupero Di Sostanza Organica Dai Rifiuti per La Produzione Di Ammendanti Di Qualità; Unità Normativa Tecnica; Agenzia Nazionale per la Protezione dell’Ambiente: Rome, Italy, 2012; pp. 1–214. ISBN 88-448-0052-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sæbo, A.; Ferrini, F. The Use of Compost in Urban Green Areas—A Review for Practical Application. Urban For. Urban Green. 2006, 4, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Pera, A.; Sellaro, M.; Bencivenni, E.; D’Amico, F. Environmental Sustainability of an Integrate Anaerobic Digestion-Composting Treatment of Food Waste: Analysis of an Italian Plant in the Circular Bioeconomy Strategy. Waste Manag. 2022, 139, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, J.H.; Romero, S.; Ramasco, J.J.; Estrada, E. The World-Wide Waste Web. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECN. Compost and Digestate for a Circular Bioeconomy; European Compost Network ECN e.V.: Bochum, Germany, 2022; ISBN 978-3-9820825-1-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves, J.C.; Adl, M.S.; Warman, P.R. A Review of the Use of Composted Municipal Solid Waste in Agriculture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 123, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emino, E.R.; Warman, P.R. Biological Assay for Compost Quality. Compost Sci. Util. 2004, 12, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H.; Chu, L.M.; Chan, W.C. The Effects of Heavy Metals and Ammonia in Sewage Sludge and Animal Manure on the Growth of Chlorella Pyrenoidosa. Environ. Pollut. Ser. A Ecol. Biol. 1984, 34, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, M.H. Phytotoxicity of Refuse Compost during the Process of Maturation. Environ. Pollut. Ser. A Ecol. Biol. 1985, 37, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, D.; Kammann, C.; Grünhage, L.; Müller, C. Simple Biotoxicity Tests for Evaluation of Carbonaceous Soil Additives: Establishment and Reproducibility of Four Test Procedures. J. Environ. Qual. 2012, 41, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Gu, J.; Wu, H.; Rauf, A.; Emran, T.B.; Khan, Z.; Mitra, S.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Alhumaydhi, F.A.; Al-Awthan, Y.S.; et al. Phytochemicals, Nutrition, Metabolism, Bioavailability, and Health Benefits in Lettuce—A Comprehensive Review. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-H.; Huang, M.-Y.; Huang, W.-D.; Hsu, M.-H.; Yang, Z.-W.; Yang, C.-M. The Effects of Red, Blue, and White Light-Emitting Diodes on the Growth, Development, and Edible Quality of Hydroponically Grown Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. Var. Capitata). Sci. Hortic. 2013, 150, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gariglio, N.F.; Buyatti, M.A.; Pilatti, R.A.; Russia, D.E.G.; Acosta, M.R. Use of a Germination Bioassay to Test Compost Maturity of Willow (Salix sp.) Sawdust. New Zeal. J. Crop Hortic. Sci. 2002, 30, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 Years of Image Analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellburn, A.R. The Spectral Determination of Chlorophylls a and b, as Well as Total Carotenoids, Using Various Solvents with Spectrophotometers of Different Resolution. J. Plant Physiol. 1994, 144, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicatelli, A.; Baldantoni, D.; Iovieno, P.; Carotenuto, M.; Alfani, A.; De Feis, I.; Castiglione, S. Genetically Biodiverse Potato Cultivars Grown on a Suitable Agricultural Soil under Compost Amendment or Mineral Fertilization: Yield, Quality, Genetic and Epigenetic Variations, Soil Properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministero per le Politiche Agricole e Forestali Approvazione Dei. Metodi Ufficiali Di Analisi Chimica Del Suolo; GU Serie Generale n.248 del 21-10-1999—Suppl. Ordinario n. 185; Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana: Rome, Italy, 1999; pp. 1–222. [Google Scholar]
- Springer, U.; Klee, J. Prüfun g Der Leistungsfähigkeit von Einigen Wichtigeren Verfahren Zur Bestimmung Des Kohlenstoffs Mittels Chromschwefelsäure Sowie Vorschlag Einer Neuen Schnellmethode. Z. Für Pflanzenernährung Düngung Bodenkd. 1954, 64, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldahl, J. Neue Methode Zur Bestimmung Des Stickstoffs in Organischen Körpern. Fresenius’ Z. Für Anal. Chem. 1883, 22, 366–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate. In Climate Change 2013—The Physical Science Basis; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1954; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Drouineau, G. Dosage Rapide Du Calcaire Actif Du Sol: Nouvelles Données Sur La Separation et La Nature Des Fractions Calcaires. Ann. Agron. 1942, 12, 441–450. [Google Scholar]
- Ministero per le Politiche Agricole e Forestali Approvazione Dei. Metodi Ufficiali Di Analisi Biochimica Del Suolo; GU Serie Generale n.61 del 13-03-2004—Suppl. Ordinario n. 42; Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana: Rome, Italy, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Macías, F.A.; Castellano, D.; Molinillo, J.M.G. Search for a Standard Phytotoxic Bioassay for Allelochemicals. Selection of Standard Target Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettiol, C.; De Vettori, S.; Minervini, G.; Zuccon, E.; Marchetto, D.; Ghirardini, A.V.; Argese, E. Assessment of Phenolic Herbicide Toxicity and Mode of Action by Different Assays. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7398–7408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, J. Characterization of Urban Wastes According to Fertility and Phytotoxicity Parameters. Waste Manag. Res. 1997, 15, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barral, M.T.; Paradelo, R. A Review on the Use of Phytotoxicity as a Compost Quality Indicator. Environ. Sci. Agric. Food Sci. 2011, 5, 36–44. [Google Scholar]
- Tiquia, S. Evaluating Phytotoxicity of Pig Manure from the Pig-on-Litter System. In Proceedings of the ICS99: The 13th ACM International Conference on Supercomputing, Rhodes, Greece, 20–25 June 1999; CBA Press Inc.: Truro, NS, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucconi, F.; Forte, M.; Monaco, A.; De Beritodi, M. Biological Evaluation of Compost Maturity. Biocycle 1981, 22, 27–29. [Google Scholar]
- .Zucconi, F.; Monaco, A.; Forte, M.; De Bertoldi, M. Phytotoxins during the Stabilization of Organic Matter. In Composting of Agricultural and Other Wastes; Gasser, J.K.R., Ed.; Elsevier Applied Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1985; pp. 73–86. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, M.; Wong, J.W.C. Co-Composting of Sewage Sludge and Coal Fly Ash: Nutrient Transformations. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 67, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasaridi, K.E.; Stentiford, E.I. A Simple Respirometric Technique for Assessing Compost Stability. Water Res. 1998, 32, 3717–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleszczuk, P. The Toxicity of Composts from Sewage Sludges Evaluated by the Direct Contact Tests Phytotoxkit and Ostracodtoxkit. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 1645–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, A.; Migliore, L.; Cerioli, N. Ormesi: La Rivoluzione Dose-Risposta; APAT Agenzia per la Protezione dell’Ambiente e per i Servizi Tecnici: Rome, Italy, 2006; ISBN 88-448-194-9. [Google Scholar]
- An, M. Mathematical Modelling of Dose-Response Relationship (Hormesis) in Allelopathy and Its Application. Nonlinearity Biol. Toxicol. Med. 2005, 3, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, L.; Mencherini, T.; Mancini, E.; Aquino, R.P.; De Almeida, L.F.R.; De Feo, V. In Vitro Phytotoxicity and Antioxidant Activity of Selected Flavonoids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 5406–5419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, K.; Mondal, S.; Gorai, S.; Singh, A.P.; Kumari, A.; Ghosh, T.; Roy, A.; Hembram, S.; Gaikwad, D.J.; Mondal, S.; et al. Impacts of Salinity Stress on Crop Plants: Improving Salt Tolerance through Genetic and Molecular Dissection. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1241736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weraduwage, S.M.; Chen, J.; Anozie, F.C.; Morales, A.; Weise, S.E.; Sharkey, T.D. The Relationship between Leaf Area Growth and Biomass Accumulation in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobb, G.P.; Sands, K.; Waters, M.; Wixson, B.G.; Dorward-King, E. Accumulation of Heavy Metals by Vegetables Grown in Mine Wastes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2000, 19, 600–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Monte, J.; Vilaça, N.; Fonseca, J.; Trindade, H.; Cortez, I.; Goufo, P. Evaluation of the Potential of Agro-Industrial Waste-Based Composts to Control Botrytis Gray Mold and Soilborne Fungal Diseases in Lettuce. Processes 2021, 9, 2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofo, A.; Bochicchio, R.; Amato, M.; Rendina, N.; Vitti, A.; Nuzzaci, M.; Altamura, M.M.; Falasca, G.; Rovere, F.D.; Scopa, A. Plant Architecture, Auxin Homeostasis and Phenol Content in Arabidopsis Thaliana Grown in Cadmium- and Zinc-Enriched Media. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 216, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.-A.; Han, T.; Ahn, S.-K.; Kang, H.; Cho, M.R.; Lee, S.-C.; Im, K.-H. Effects of Heavy Metals on Plant Growths and Pigment Contents in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Plant Pathol. J. 2012, 28, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, B.; Park, H.; Kang, S. Quantitative Estimation of Synergistic Toxicity of Cu and Zn on Growth of Arabidopsis Thaliana by Isobolographic Method. Toxics 2022, 10, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbey, L.; Ijenyo, M.; Spence, B.; Asunni, A.O.; Ofoe, R.; Amo-Larbi, V. Bioaccumulation of Chemical Elements in Vegetables as Influenced by Application Frequency of Municipal Solid Waste Compost. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2021, 101, 967–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzortzakis, N.; Gouma, S.; Paterakis, C.; Manios, T. Deployment of Municipal Solid Wastes as a Substitute Growing Medium Component in Marigold and Basil Seedlings Production. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 285874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzortzakis, N.; Gouma, S.; Dagianta, E.; Saridakis, C.; Papamichalaki, M.; Goumas, D.; Manios, T. Use of Fertigation and Municipal Solid Waste Compost for Greenhouse Pepper Cultivation. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 973193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannoufa, A.; Hossain, Z. Regulation of Carotenoid Accumulation in Plants. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2012, 1, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai Kachout, S.; Ben Mansoura, A.; Jaffel, K.; Leclerc, J.C.; Rejeb, M.N.; Ouerghi, Z. The Effect of Salinity on the Growth of the Halophyte Atriplex Hortensis (Chenopodiaceae). Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2010, 7, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palta, J.P. Leaf Chlorophyll Content. Remote Sens. Rev. 1990, 5, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-H.; Wang, L.-J.; Li, S.-H.; Duan, W.; Loescher, W.; Liang, Z.-C. The Effects of UV-B Radiation on Photosynthesis in Relation to Photosystem II Photochemistry, Thermal Dissipation and Antioxidant Defenses in Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Seedlings at Different Growth Temperatures. Funct. Plant Biol. 2007, 34, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhabela, M.S.; Warman, P.R. The Influence of Municipal Solid Waste Compost on Yield, Soil Phosphorus Availability and Uptake by Two Vegetable Crops Grown in a Pugwash Sandy Loam Soil in Nova Scotia. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2005, 106, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Mardomingo, I.; Jiménez-Hernández, M.E.; Moreno, L.; de la Losa, A.; de la Cruz, M.T.; Casermeiro, M.Á. Application of High Doses of Organic Amendments in a Mediterranean Agricultural Soil: An Approach for Assessing the Risk of Groundwater Contamination. CATENA 2015, 131, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plošek, L.; Elbl, J.; Lošák, T.; Kužel, S.; Kintl, A.; Juřička, D.; Kynický, J.; Martensson, A.; Brtnický, M. Leaching of Mineral Nitrogen in the Soil Influenced by Addition of Compost and N-Mineral Fertilizer. Acta Agric. Scand. Sect. B—Soil Plant Sci. 2017, 67, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holub, P.; Klem, K.; Tůma, I.; Vavříková, J.; Surá, K.; Veselá, B.; Urban, O.; Záhora, J. Application of Organic Carbon Affects Mineral Nitrogen Uptake by Winter Wheat and Leaching in Subsoil: Proximal Sensing as a Tool for Agronomic Practice. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traoré, O.; Sinaj, S.; Frossard, E.; Van De Kerkhove, J.M. Effect of Composting Time on Phosphate Exchangeability. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 1999, 55, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turrión, M.-B.; Bueis, T.; Lafuente, F.; López, O.; San José, E.; Eleftheriadis, A.; Mulas, R. Effects on Soil Phosphorus Dynamics of Municipal Solid Waste Compost Addition to a Burnt and Unburnt Forest Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiralipour, A.; McConnell, D.B.; Smith, W.H. Physical and Chemical Properties of Soils as Affected by Municipal Solid Waste Compost Application. Biomass Bioenergy 1992, 3, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rady, M.M.; Semida, W.M.; Hemida, K.A.; Abdelhamid, M.T. The Effect of Compost on Growth and Yield of Phaseolus Vulgaris Plants Grown under Saline Soil. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2016, 5, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, M.; Paradelo Núñez, R.; Piñeiro, J.; Barral, M.T. Physicochemical and Biochemical Properties of an Acid Soil under Potato Culture Amended with Municipal Solid Waste Compost. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2019, 8, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, G.; Porceddu, A.; Sanna, M.; Silvetti, M.; Castaldi, P. Municipal Solid Wastes as a Resource for Environmental Recovery: Impact of Water Treatment Residuals and Compost on the Microbial and Biochemical Features of As and Trace Metal-Polluted Soils. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 174, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporale, A.G.; Porfido, C.; Roggero, P.P.; Di Palma, A.; Adamo, P.; Pinna, M.V.; Garau, G.; Spagnuolo, M.; Castaldi, P.; Diquattro, S. Long-Term Effect of Municipal Solid Waste Compost on the Recovery of a Potentially Toxic Element (PTE)-Contaminated Soil: PTE Mobility, Distribution and Bioaccessibility. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 122858–122874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajaie, M.; Tavakoly, A.R. Effects of Municipal Waste Compost and Nitrogen Fertilizer on Growth and Mineral Composition of Tomato. Int. J. Recycl. Org. Waste Agric. 2016, 5, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, V.; de Araujo, A.S.F.; Vaish, B.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.; Singh, P.; Singh, R.P. Biological Response of Using Municipal Solid Waste Compost in Agriculture as Fertilizer Supplement. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio/Technol. 2016, 15, 677–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbarki, S.; Labidi, N.; Mahmoudi, H.; Jedidi, N.; Abdelly, C. Contrasting Effects of Municipal Compost on Alfalfa Growth in Clay and in Sandy Soils: N, P, K, Content and Heavy Metal Toxicity. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 6745–6750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldantoni, D.; Leone, A.; Iovieno, P.; Morra, L.; Zaccardelli, M.; Alfani, A. Total and Available Soil Trace Element Concentrations in Two Mediterranean Agricultural Systems Treated with Municipal Waste Compost or Conventional Mineral Fertilizers. Chemosphere 2010, 80, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuksel, O. Influence of Municipal Solid Waste Compost Application on Heavy Metal Content in Soil. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Chakrabarti, K.; Chakraborty, A. Effect of MSW Compost on Microbiological and Biochemical Soil Quality Indicators. Compost Sci. Util. 2003, 11, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucci, P. Effect of the Addition of Municipal Solid-Waste Compost on Microbial Biomass and Enzyme Activities in Soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1990, 10, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Businelli, D.; Giusquiani, P.L.; Gigliotti, G. Long-Term Effects of Heavy Metals from Composted Municipal Waste on Some Enzyme Activities in a Cultivated Soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1994, 17, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crecchio, C.; Curci, M.; Pizzigallo, M.D.R.; Ricciuti, P.; Ruggiero, P. Effects of Municipal Solid Waste Compost Amendments on Soil Enzyme Activities and Bacterial Genetic Diversity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gil, J.; Plaza, C.; Soler-Rovira, P.; Polo, A. Long-Term Effects of Municipal Solid Waste Compost Application on Soil Enzyme Activities and Microbial Biomass. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1907–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorge-Mardomingo, I.; Soler-Rovira, P.; Casermeiro, M.Á.; de la Cruz, M.T.; Polo, A. Seasonal Changes in Microbial Activity in a Semiarid Soil after Application of a High Dose of Different Organic Amendments. Geoderma 2013, 206, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, S.; Minervino, M.; Muto, A.; Talarico, E.; Muzzalupo, I.; Araniti, F.; Chiappetta, A.; Bruno, L. Impact of Municipal Solid Waste Compost Amendment and Mineral Fertilization on Soil Properties and Cucumis melo L. Subsp. Melo Var. Cantalupensis Crop Quality. Agrochimica 2022, 66, 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Paredes, A.; Valdés, G.; Araneda, N.; Valdebenito, E.; Hansen, F.; Nuti, M. Microbial Community in the Composting Process and Its Positive Impact on the Soil Biota in Sustainable Agriculture. Agronomy 2023, 13, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Xie, B.; Yang, S.; Hou, A.; Chen, M.; Han, G. Effects of Five Years’ Nitrogen Deposition on Soil Properties and Plant Growth in a Salinized Reed Wetland of the Yellow River Delta. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 136, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spohn, M.; Kuzyakov, Y. Phosphorus Mineralization Can Be Driven by Microbial Need for Carbon. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 61, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almási, C.; Orosz, V.; Tóth, T.; Mansour, M.M.; Demeter, I.; Henzsel, I.; Bogdányi, Z.; Szegi, T.A.; Makádi, M. Effects of Sewage Sludge Compost on Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur Ratios and Soil Enzyme Activities in a Long-Term Experiment. Agronomy 2025, 15, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Xie, T.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Xiong, W.; Xu, L.; Wu, Y.; He, Z.; Li, X. Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Mediates Soil Organic Phosphorus Mineralization in a Subalpine Forest Ecosystem. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.; Mondini, C.; Cayuela, M.L.; Roig, A.; Contin, M.; De Nobili, M. Fluorescein Diacetate Hydrolysis, Respiration and Microbial Biomass in Freshly Amended Soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2008, 44, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaghi, F.; Arthur, E.; Moosavi, A.A. Evaluating Models to Estimate Cation Exchange Capacity of Calcareous Soils. Geoderma 2021, 400, 115221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaudour, E.; Cerovic, Z.; Ebengo, D.; Latouche, G. Predicting Key Agronomic Soil Properties with UV-Vis Fluorescence Measurements Combined with Vis-NIR-SWIR Reflectance Spectroscopy: A Farm-Scale Study in a Mediterranean Viticultural Agroecosystem. Sensors 2018, 18, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Humidity | pH | OC | Humic and Fulvic C | Total N | Organic N | C/N Ratio * | P2O5 | K2O | Aggregate Content ** | Inert Lithoids | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (%) | (%) * | (%) * | (%) * | (% total N) | (%) * | (%) * | (%) * | (%) * | |||
| 18.32 | 7.88 | 25.15 | 11.63 | 1.94 | 98.75 | 12.94 | 1.4 | 2.0 | 0.31 | 0.93 | |
| ±1.11 † | ±0.21 † | ±1.78 † | ±2.41 † | ±0.33 † | ±8.44 † | ±2.27 † | ±0.13 † | ±0.10 † | ±0.02 † | ±0.09 † | |
| EC1:2 | Salmonella | Escherichia coli | Salinity | Cd | Cr6+ | Hg | Ni | Pb | Cu | Zn | Na |
| (dS/m) | (in 25 g) | (CFU/g) | (meq/100 g) | (mg/kg) * | (mg/kg) * | (mg/kg) * | (mg/kg) * | (mg/kg) * | (mg/kg) * | (mg/kg) * | (mg/kg) * |
| 4.81 | Absent ‣ | <25 ‣ | 73.66 | <0.5 | <0.50 | 0.26 | 10.8 | 33.6 | 71.02 | 179.80 | 4385 |
| ±0.81 † | ±5.04 † | ±0.10 † | ±1.13 † | ±4.09 † | ±11.46 † | ±28.88 † | ±347 † | ||||
| Species | RSG (%) | RRG (%) | GI (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| L. sativum | 99.9 ± 2.3 | 80.1 ± 7.2 | 80.0 ± 9.0 |
| L. sativa | 45.2 ± 6.8 | 30.7 ± 3.4 | 13.9 ± 3.6 |
| A. thaliana | 84.3 ± 3.3 | 47.9 ± 6.7 | 40.4 ± 5.8 |
| Treatment | OC (%) * | Total N (%) * | Total P (mg/kg) | Active CaCO3 (%) * | CEC (cmol(+)/kg) | pH | EC1:2 (dS/m) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ctrl | 0.41 ± 0.03 bcd | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 17.15 ± 4.27 | 5.05 ± 1.03 d | 11.89 ± 3.33 | 8.07 ± 0.23 | 0.28 ± 0.04 bc |
| cf | 0.26 ± 0.05 e | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 18.29 ± 3.61 | 8.21 ± 2.32 bcd | 10.40 ± 0.76 | 7.50 ± 0.37 | 0.34 ± 0.06 bc |
| cf2 | 0.32 ± 0.04 de | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 18.63 ± 5.22 | 7.77 ± 2.52 cd | 8.93 ± 0.97 | 7.63 ± 0.30 | 0.21 ± 0.04 c |
| C8 | 0.43 ± 0.03 bc | 0.08 ± 0.02 | 17.69 ± 4.55 | 11.67 ± 3.11 abc | 10.42 ± 1.04 | 7.87 ± 0.21 | 0.44 ± 0.02 ab |
| C8+8 | 0.51 ± 0.04 ab | 0.10 ± 0.01 | 19.91 ± 5.03 | 10.14 ± 2.91 bcd | 10.35 ± 0.86 | 7.78 ± 0.18 | 0.45 ± 0.03 ab |
| C16 | 0.46 ± 0.04 bc | 0.08 ± 0.01 | 18.99 ± 4.83 | 16.46 ± 3.03 a | 9.47 ± 1.11 | 7.73 ± 0.22 | 0.36 ± 0.03 abc |
| C16+16 | 0.60 ± 0.08 a | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 20.11 ± 2.34 | 15.19 ± 2.24 ab | 9.15 ± 0.98 | 7.93 ± 0.31 | 0.56 ± 0.04 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rizzo, S.; Le Pera, A.; Sellaro, M.; Lombardo, L.; Bruno, L. Separately Collected Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste Compost as a Sustainable Improver of Soil Characteristics in the Open Field and a Promising Selective Booster for Nursery Production. Agronomy 2025, 15, 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040958
Rizzo S, Le Pera A, Sellaro M, Lombardo L, Bruno L. Separately Collected Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste Compost as a Sustainable Improver of Soil Characteristics in the Open Field and a Promising Selective Booster for Nursery Production. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):958. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040958
Chicago/Turabian StyleRizzo, Santina, Adolfo Le Pera, Miriam Sellaro, Luca Lombardo, and Leonardo Bruno. 2025. "Separately Collected Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste Compost as a Sustainable Improver of Soil Characteristics in the Open Field and a Promising Selective Booster for Nursery Production" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040958
APA StyleRizzo, S., Le Pera, A., Sellaro, M., Lombardo, L., & Bruno, L. (2025). Separately Collected Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste Compost as a Sustainable Improver of Soil Characteristics in the Open Field and a Promising Selective Booster for Nursery Production. Agronomy, 15(4), 958. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040958








