Deficit Irrigation Provides a Trade-Off Between Water Use and Alfalfa Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Materials
2.3. Experimental Design and Field Management
2.4. Measurements
2.5. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Alfalfa Quality Content and Hay Yield
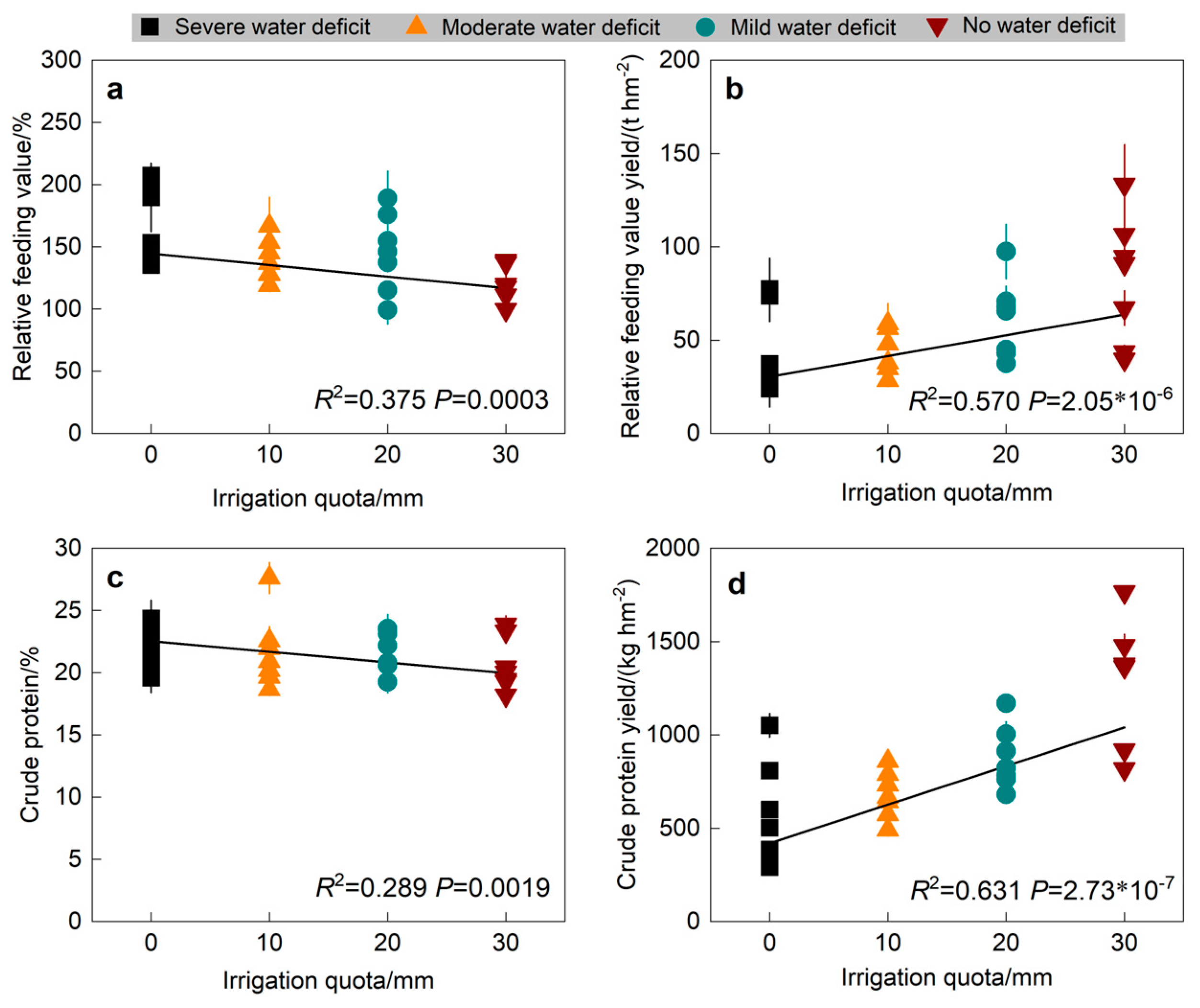
3.2. Relationship Between Alfalfa Quality and Quality Yield with Irrigation Quota
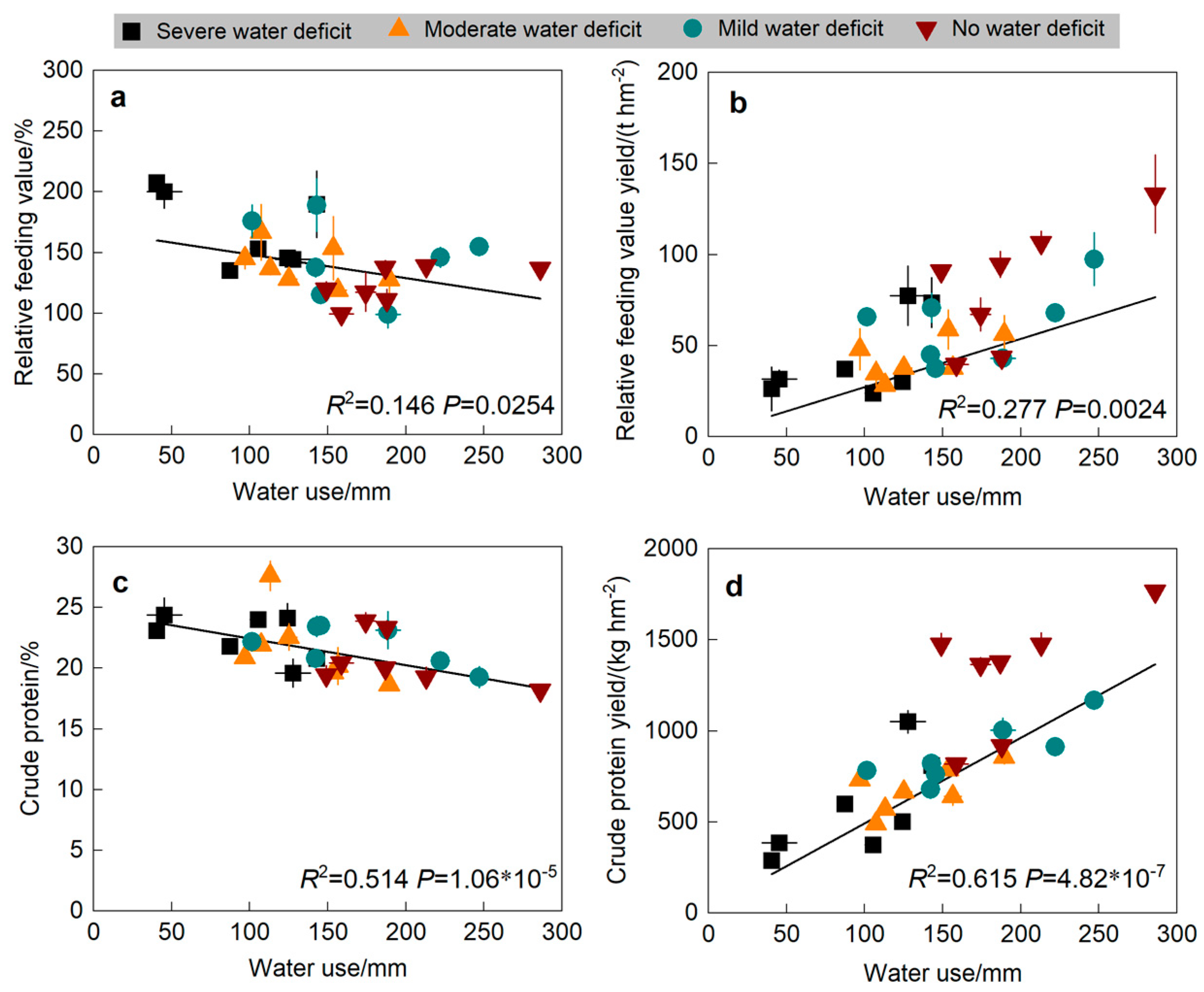
3.3. Relationship Between Alfalfa Quality and Water Use
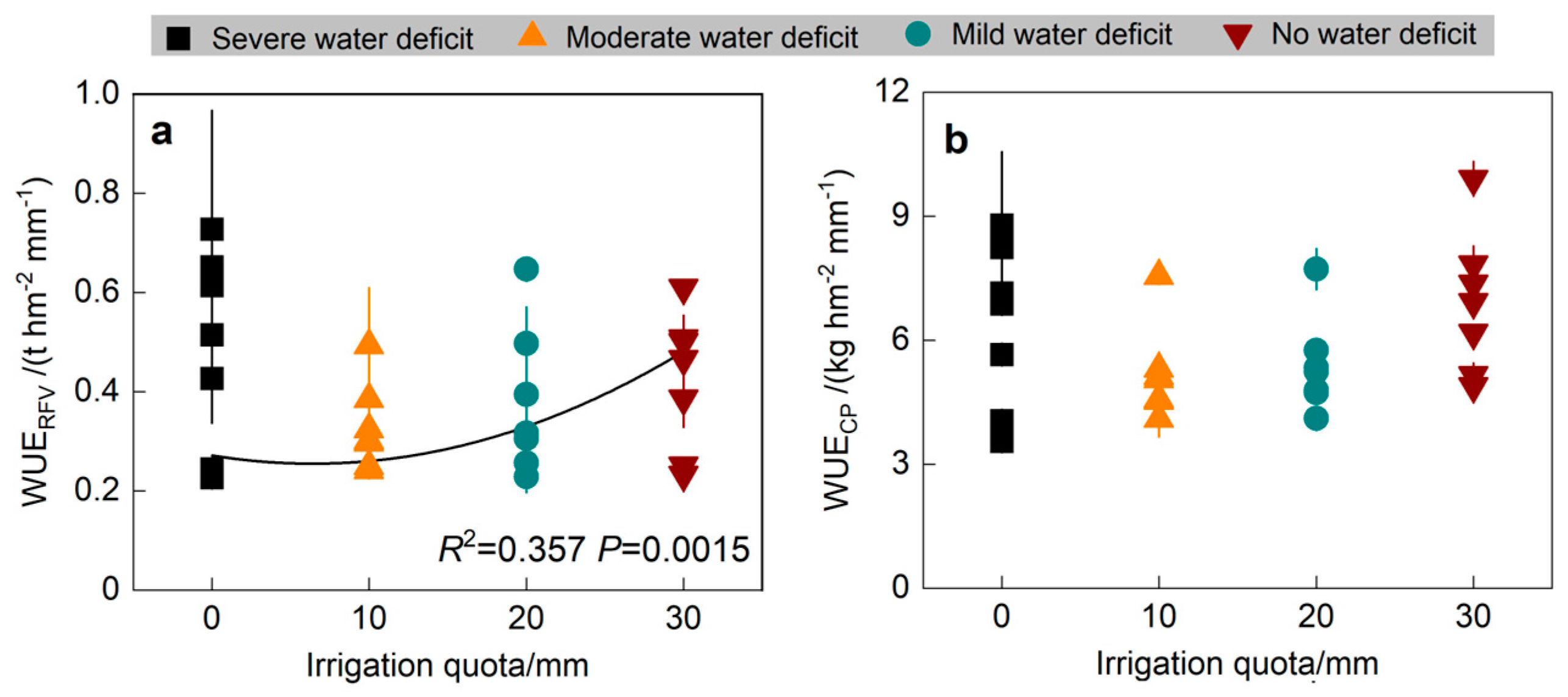
3.4. Alfalfa QWUE and the Relationship with Irrigation Quota
4. Discussion
4.1. The Relationship Between Alfalfa Quality and Water Use
4.2. Effects of Different Water Deficits on Alfalfa QWUE and the Relationship with Irrigation Quota
4.3. Limitations and Prospects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miguez-Macho, G.; Fan, Y. Spatiotemporal Origin of Soil Water Taken Up by Vegetation. Nature 2021, 598, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, N.D.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Ray, D.K.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Closing Yield Gaps through Nutrient and Water Management. Nature 2012, 490, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orduña Alegría, M.E.; Zipper, S.; Shin, H.C.; Deines, J.M.; Hendricks, N.P.; Allen, J.J.; Bohling, G.C.; Golden, B.; Griggs, B.W.; Lauer, S.; et al. Unlocking Aquifer Sustainability through Irrigator-driven Groundwater Conservation. Nat. Sustain. 2024, 7, 1574–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Sharretts, T.; Ali, T.; Ao, Y.Z.; Chiarelli, D.D.; Demeke, B.; Marston, L.; Mehta, P.; Mekonnen, M.; Rulli, M.C.; et al. Deepening Water Scarcity in Breadbasket Nations. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, L.; Chiarelli, D.D.; Rulli, M.C.; Dell Angelo, J.; Odorico, P.D. Global Agricultural Economic Water Scarcity. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaaz6031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Angadi, S.; Begna, S.; VanLeeuwen, D.; Idowu, O.J.; Singh, P.; Trostle, C.; Gowda, P.; Brewer, C. Deficit Irrigation Strategy to Sustain Available Water Resources using Guar. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 211, 118272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patanè, C.; Tringali, S.; Sortino, O. Effects of Deficit Irrigation on Biomass, Yield, Water Productivity and Fruit Quality of Processing Tomato under Semi-arid Mediterranean Climate Conditions. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.J.S.; Hansen, S.; Styczen, M.E.; Holbak, M.; Jensen, S.M.; Petersen, C.T. Yield and Development of Winter Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and Spring Barley (Hordeum vulgare) in Field Experiments with Variable Weather and Drainage Conditions. Eur. J. Agron. 2021, 122, 126075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, G.; Yan, G.; Liu, H.; Turner, N.C. Morphological Features and Biomass Partitioning of Lucerne Plants (Medicago sativa L.) Subjected to Water Stress. Agronomy 2020, 10, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, C.; Sun, H.; Ren, W.; Wang, X. Maximizing the Water Productivity and Economic Returns of Alfalfa by Deficit Irrigation in China: A Meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 287, 108454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, A.; Porcheron, B.; Kodjovi, G.C.; Moumen, B.; Vriet, C.; Maurousset, L.; Lemoine, R.; Pourtau, N.; Doidy, J. Genome-wide Transcriptional Responses to Water Deficit during Seed Development in Pisum sativum, Focusing on Sugar Transport and Metabolism. Physiol. Plant. 2023, 175, e14062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araniti, F.; Prinsi, B.; Cocetta, G.; Negrini, N.; Nocito, F.F.; Espen, L. Impact of Cyclic-mild-drought Stress on the Metabolism of Mentha spicata L.: A Strategy to Improve Quality Traits. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 210, 118129. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Coulter, J.A.; Shen, Y. Replacing Summer Fallow with Annual Forage Improves Crude Protein Productivity and Water Use Efficiency of the Summer Fallow-winter Wheat Cropping System. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 230, 105980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, J.; Yang, X.; Ma, L. Impact of Precipitation Variation on Summer Forage Crop Productivity and Precipitation Use Efficiency in a Semi-arid Environment. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 141, 126616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, P.R.; Sheaffer, C.C.; Hall, M.H. Drought Effects on Perennial Forage Legume Yield and Quality. Agron. J. 1992, 84, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annicchiarico, P.; Pecetti, L.; Tava, A. Physiological and Morphological Traits Associated with Adaptation of Lucerne (Medicago sativa) to Severely Drought-stressed and to Irrigated Environments. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2013, 162, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavero, J.; Faci, J.M.; Medina, E.T.; Martínez-Cob, A. Alfalfa Forage Production under Solid-set Sprinkler Irrigation in a Semiarid Climate. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 191, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Medina, C.A.; Boge, B.; Hu, J.; Fransen, S.; Norberg, S.; Yu, L. Identification of Genetic Loci Associated with Forage Quality in Response to Water Deficit in Autotetraploid Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Cui, P.; Su, D. Effects of Partial Root-zone Drying on Alfalfa Growth, Yield and Quality under Subsurface Drip Irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, C.; Gu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; He, J.; Li, X.; Han, L.; Su, D. Partial Root-zone Drying Subsurface Drip Irrigation Increased the Alfalfa Quality Yield but Decreased the Alfalfa Quality Content. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1297468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Liu, L.; Gao, J.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Irrigation Methods and Fertilization Strategies for Alfalfa: A Meta-analysis. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2023, 209, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, R.A.; Buxton, D.R.; Hattendorf, M.J.; Carlson, R.E. Crop Water Stress Index and Forage Quality Relationships in Alfalfa. Agron. J. 1990, 82, 906–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Yan, Z.; Jia, Q.; Chang, S.; Ahmad, I.; Ghani, M.U.; Hou, F. Irrigation and Nitrogen Fertilization Influence on Alfalfa Yield, Nutritive Value, and Resource Use Efficiency in an Arid Environment. Field Crops Res. 2022, 284, 108587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, G.; Gresta, F.; Cosentino, S.L. Dry Matter and Qualitative Characteristics of Alfalfa as Affected by Harvest Times and Soil Water Content. Eur. J. Agron. 2011, 34, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, M.E.; Lawson, A.R.; Chandra, S.; Kelly, K.B. Limited Application of Irrigation Water Does Not Affect the Nutritive Characteristics of Lucerne. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2014, 54, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, B.A.; Prospero, J.M.; Mackie, D.; Gaiero, D.; Hesse, P.P.; Balkanski, Y. Global Connections between Aeolian Dust, Climate and Ocean Biogeochemistry at the Present Day and at the Last Glacial Maximum. Earth-Sci Rev. 2010, 99, 61–97. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Bell, L.W.; Shen, Y.; Whish, J.P.M. Indices of Forage Nutritional Yield and Water Use Efficiency Amongst Spring-sown Annual Forage Crops in North-west China. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohweder, D.A.; Barnes, R.F.; Jorgensen, N. Proposed Hay Grading Standards Based on Laboratory Analysis for Evaluating Quality. J. Anim. Sci. 1978, 47, 747–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, J.; Min, D.; Klocke, N.; Kisekka, I.; Currie, R. Effects of Irrigation Amount and Timing on Alfalfa Nutritive Value. T. ASABE 2016, 59, 849–860. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, S.; Peng, X.; Ge, X.; Wen, B.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B. Alternating Partial Root-Zone Subsurface Drip Irrigation Enhances the Productivity and Water Use Efficiency of Alfalfa by Improving Root Characteristics. Agronomy 2024, 14, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitterson, J.M.; Andales, A.A.; Mooney, D.F.; Capurro, M.C.; Brummer, J.E. Developing a Crop Water Production Function for Alfalfa under Deficit Irrigation: A Case Study in Eastern Colorado. Agriculture 2023, 13, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabeiro, C.; de Santa Olalla, F.M.; de Juan, J.A. Production of Muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.) under Controlled Deficit Irrigation in a Semi-arid Climate. Agric. Water Manag. 2002, 54, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensoya, S.; Ertekb, A.; Gedikc, I.; Kucukyumukc, C. Irrigation frequency and amount affect yield and quality of field-grown melon (Cucumis melo L). Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 88, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kang, S.; Du, T.; Guo, P.; Qiu, R.; Chen, R.; Gu, F. Modeling Relations of Tomato Yield and Fruit Quality with Water Deficit at Different Growth Stages under Greenhouse Condition. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 146, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staniak, M.; Harasim, E. Changes in Nutritive Value of Alfalfa (Medicago × varia T. Martyn) and Festulolium (Festulolium braunii (K. Richt) A. Camus) under Drought Stress. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2018, 204, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wim, V.; Shukla, M.K.; Du, T. Drip Irrigation Provides a Trade-off between Yield and Nutritional Quality of Tomato in the Solar Greenhouse. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 249, 106777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.M.A.; Oliveira, M.D.R.G. Tomato Root Distribution, Yield and Fruit Quality under Different Subsurface Drip Irrigation Regimes and Depths. Irrig. Sci. 2005, 24, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katuwal, K.B.; Cho, Y.; Singh, S.; Angadi, S.V.; Begna, S.; Stamm, M. Soil Water Extraction Pattern and Water Use Efficiency of Spring Canola under Growth-stage-based Irrigation Management. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandelous, M.M.; Kamai, T.; Vrugt, J.A.; Šimůnek, J.; Hanson, B.; Hopmans, J.W. Evaluation of Subsurface Drip Irrigation Design and Management Parameters for Alfalfa. Agric. Water Manag. 2012, 109, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Pang, X.P.; Xu, H.P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.N.; Guo, Z.G. Effect of Partial Root-zone Drying Irrigation (PRDI) on the Biomass, Water Productivity and Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Allocations in Different Organs of Alfalfa. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 243, 106525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.M.; Bahn, M. Drought Legacies and Ecosystem Responses to Subsequent Drought. Global Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5086–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Génard, M.; Kang, S. An Integrated Irrigation Strategy for Water-saving and Quality-improving of Cash Crops: Theory and Practice in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 241, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Year | Harvest | Treatment | Rainfall/mm | Irrigation Frequency/No. | Irrigation Quota/mm | Irrigation Time /(Day Month) | Annual Irrigation/mm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 1st harvest | Severe water deficit | 12.4 | 5 | 0 | 17 June a, 24 June, 1 July, 8 July, 15 July | 0 |
| Moderate water deficit | 12.4 | 5 | 10 | 50 | |||
| Mild water deficit | 12.4 | 5 | 20 | 100 | |||
| No water deficit | 12.4 | 5 | 30 | 150 | |||
| 2nd harvest | Severe water deficit | 73.6 | 3 | 0 | 22 July, 5 August, 12 August | 0 | |
| Moderate water deficit | 73.6 | 3 | 10 | 40 | |||
| Mild water deficit | 73.6 | 3 | 20 | 80 | |||
| No water deficit | 73.6 | 3 | 30 | 120 | |||
| 3rd harvest | Severe water deficit | 23.4 | 5 | 0 | 27 August, 3 September, 10 September, 16 September, 23 September | 0 | |
| Moderate water deficit | 23.4 | 5 | 10 | 50 | |||
| Mild water deficit | 23.4 | 5 | 20 | 100 | |||
| No water deficit | 23.4 | 5 | 30 | 150 | |||
| 2018 | 1st harvest | Severe water deficit | 31.6 | 8 | 0 | 15 April, 22 April, 29 April, 6 May, 13 May, 20 May, 27 May, 4 June | 0 |
| Moderate water deficit | 31.6 | 8 | 10 | 80 | |||
| Mild water deficit | 31.6 | 8 | 20 | 160 | |||
| No water deficit | 31.6 | 8 | 30 | 240 | |||
| 2nd harvest | Severe water deficit | 13.6 | 4 | 0 | 10 June, 17 June, 24 June, 2 July | 0 | |
| Moderate water deficit | 13.6 | 4 | 10 | 40 | |||
| Mild water deficit | 13.6 | 4 | 20 | 80 | |||
| No water deficit | 13.6 | 4 | 30 | 120 | |||
| 3rd harvest | Severe water deficit | 65.2 | 4 | 0 | 8 July, 15 July, 22 July, 29 July | 0 | |
| Moderate water deficit | 65.2 | 4 | 10 | 40 | |||
| Mild water deficit | 65.2 | 4 | 20 | 80 | |||
| No water deficit | 65.2 | 4 | 30 | 120 | |||
| 4th harvest | Severe water deficit | 81.8 | 4 | 0 | 12 August, 10 September, 17 September | 0 | |
| Moderate water deficit | 81.8 | 4 | 10 | 40 | |||
| Mild water deficit | 81.8 | 4 | 20 | 80 | |||
| No water deficit | 81.8 | 4 | 30 | 120 |
| Year | Harvest | Treatment | Relative Feeding Value/% | RFVyield/ (t hm−2) | WUERFV/ (t hm−2 mm−1) | Crude Protein/% | CPyield/ (kg hm−2) | WUECP/ (kg hm−2 mm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 1st harvest | Severe water deficit | 135.39 ± 1.30 a | 37.26 ± 0.62 b | 0.43 ± 0.01 a | 21.80 ± 0.11 ab | 600.09 ± 2.96 c | 6.87 ± 06.08 b |
| Moderate water deficit | 118.89 ± 1.25 ab | 37.75 ± 0.40 b | 0.24 ± 0.01 b | 20.19 ± 0.89 b | 641.00 ± 28.20 c | 4.10 ± 0.26 d | ||
| Mild water deficit | 99.23 ± 6.53 b | 43.07 ± 2.83 b | 0.23 ± 0.02 b | 23.13 ± 0.89 a | 1003.93 ± 38.41 b | 5.34 ± 0.33 c | ||
| No water deficit | 117.75 ± 4.57 ab | 67.18 ± 5.31 a | 0.39 ± 0.03 a | 23.86 ± 0.41 a | 1364.40 ± 23.38 a | 7.84 ± 0.26 a | ||
| 2nd harvest | Severe water deficit | 145.60 ± 0.59 a | 30.36 ± 0.12 c | 0.24 ± 0.01 b | 24.12 ± 0.70 a | 502.96 ± 14.52 c | 4.05 ± 0.13 c | |
| Moderate water deficit | 128.17 ± 2.42 b | 37.77 ± 0.71 b | 0.30 ± 0.01 a | 22.57 ± 0.65 a | 664.99 ± 19.00 b | 5.31 ± 0.13 a | ||
| Mild water deficit | 137.52 ± 4.40 a | 44.98 ± 1.44 a | 0.32 ± 0.01 a | 20.80 ± 0.30 b | 680.33 ± 9.80 b | 4.78 ± 0.07 b | ||
| No water deficit | 99.46 ± 1.62 c | 39.74 ± 1.62 b | 0.25 ± 0.01 b | 20.45 ± 0.14 b | 816.98 ± 5.47 a | 5.16 ± 0.17 ab | ||
| 3rd harvest | Severe water deficit | 153.29 ± 3.11 a | 23.86 ± 0.48 d | 0.23 ± 0.00 b | 24.01 ± 0.12 b | 373.71 ± 1.81 d | 3.56 ± 0.11 c | |
| Moderate water deficit | 136.73 ± 3.07 b | 28.34 ± 0.64 c | 0.25 ± 0.01 ab | 27.61 ± 0.72 a | 572.29 ± 14.90 c | 5.05 ± 0.13 ab | ||
| Mild water deficit | 115.23 ± 3.32 c | 37.37 ± 1.08 b | 0.26 ± 0.01 a | 23.53 ± 0.19 b | 762.90 ± 6.14 b | 5.24 ± 0.11 a | ||
| No water deficit | 110.93 ± 5.23 c | 43.66 ± 2.06 a | 0.23 ± 0.01 ab | 23.33 ± 0.35 b | 918.24 ± 13.82 a | 4.89 ± 0.02 b | ||
| 2018 | 1st harvest | Severe water deficit | 144.56 ± 0.28 ab | 77.47 ± 9.42 bc | 0.61 ± 0.10 a | 19.59 ± 0.68 a | 1050.46 ± 36.51 c | 8.25 ± 0.35 a |
| Moderate water deficit | 127.58 ± 6.18 c | 56.23 ± 5.95 c | 0.30 ± 0.03 b | 19.26 ± 0.51 a | 857.62 ± 22.63 d | 4.53 ± 0.14 c | ||
| Mild water deficit | 154.94 ± 3.67 a | 97.43 ± 8.41 b | 0.39 ± 0.03 ab | 18.64 ± 0.20 a | 1169.02 ± 12.49 b | 4.74 ± 0.07 c | ||
| No water deficit | 136.81 ± 2.90 bc | 133.25 ± 12.40 a | 0.47 ± 0.04 ab | 18.18 ± 0.13 a | 1766.36 ± 13.11 a | 6.18 ± 0.04 b | ||
| 2nd harvest | Severe water deficit | 200.00 ± 7.75 a | 31.63 ± 2.90 d | 0.73 ± 0.12 a | 24.36 ± 0.83 a | 386.32 ± 13.24 c | 8.79 ± 1.02 ab | |
| Moderate water deficit | 145.12 ± 4.98 c | 47.87 ± 6.57 c | 0.49 ± 0.07 a | 22.18 ± 0.28 b | 732.19 ± 9.14 b | 7.55 ± 0.10 b | ||
| Mild water deficit | 175.82 ± 7.83 b | 65.65 ± 1.18 b | 0.65 ± 0.01 a | 20.90 ± 0.30 bc | 782.32 ± 11.17 b | 7.72 ± 0.28 b | ||
| No water deficit | 119.87 ± 3.69 c | 90.88 ± 0.73 a | 0.61 ± 0.00 a | 19.43 ± 0.45 c | 1476.36 ± 34.17 a | 9.90 ± 0.24 a | ||
| 3rd harvest | Severe water deficit | 207.48 ± 3.08 a | 26.25 ± 6.99 c | 0.65 ± 0.18 a | 23.08 ± 0.27 a | 289.83 ± 3.34 d | 7.15 ± 0.09 a | |
| Moderate water deficit | 166.75 ± 13.28 bc | 34.78 ± 3.99 c | 0.32 ± 0.04 a | 23.43 ± 0.49 a | 490.40 ± 10.33 c | 4.58 ± 0.12 c | ||
| Mild water deficit | 189.10 ± 12.55 ab | 70.83 ± 4.65 b | 0.50 ± 0.04 a | 21.95 ± 0.26 b | 822.26 ± 9.60 b | 5.76 ± 0.15 b | ||
| No water deficit | 137.56 ± 3.53 c | 94.72 ± 4.17 a | 0.51 ± 0.02 a | 20.03 ± 0.19 c | 1377.83 ± 13.19 a | 7.37 ± 0.12 a | ||
| 4th harvest | Severe water deficit | 189.78 ± 15.84 a | 73.60 ± 7.88 b | 0.51 ± 0.05 a | 20.82 ± 0.36 a | 808.69 ± 14.15 c | 5.66 ± 0.09 b | |
| Moderate water deficit | 153.66 ± 15.12 ab | 58.87 ± 6.22 b | 0.38 ± 0.02 bc | 20.59 ± 0.18 ab | 787.88 ± 6.81 c | 5.13 ± 0.08 c | ||
| Mild water deficit | 146.11 ± 4.86 b | 67.84 ± 0.58 b | 0.31 ± 0.00 c | 19.63 ± 0.23 bc | 913.46 ± 10.74 b | 4.12 ± 0.03 d | ||
| No water deficit | 138.93 ± 2.34 b | 106.54 ± 3.72 a | 0.50 ± 0.02 ab | 19.26 ± 0.47 c | 1476.44 ± 36.18 a | 6.93 ± 0.17 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gao, K.; Han, L.; Li, X.; He, J.; Su, D. Deficit Irrigation Provides a Trade-Off Between Water Use and Alfalfa Quality. Agronomy 2025, 15, 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040932
Wang Y, Zhang Q, Gao K, Han L, Li X, He J, Su D. Deficit Irrigation Provides a Trade-Off Between Water Use and Alfalfa Quality. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040932
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yadong, Qiuchi Zhang, Kai Gao, Liliang Han, Xingfu Li, Jing He, and Derong Su. 2025. "Deficit Irrigation Provides a Trade-Off Between Water Use and Alfalfa Quality" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040932
APA StyleWang, Y., Zhang, Q., Gao, K., Han, L., Li, X., He, J., & Su, D. (2025). Deficit Irrigation Provides a Trade-Off Between Water Use and Alfalfa Quality. Agronomy, 15(4), 932. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040932






