The Application of Slow-Release Nitrogen Combined with Soil Conditioner Under the Impact of Alkaline Salinity in Alfalfa Cultivation and Soil Improvement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Harvest
2.4. Forage Analysis
2.5. Soil Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Alfalfa Yield
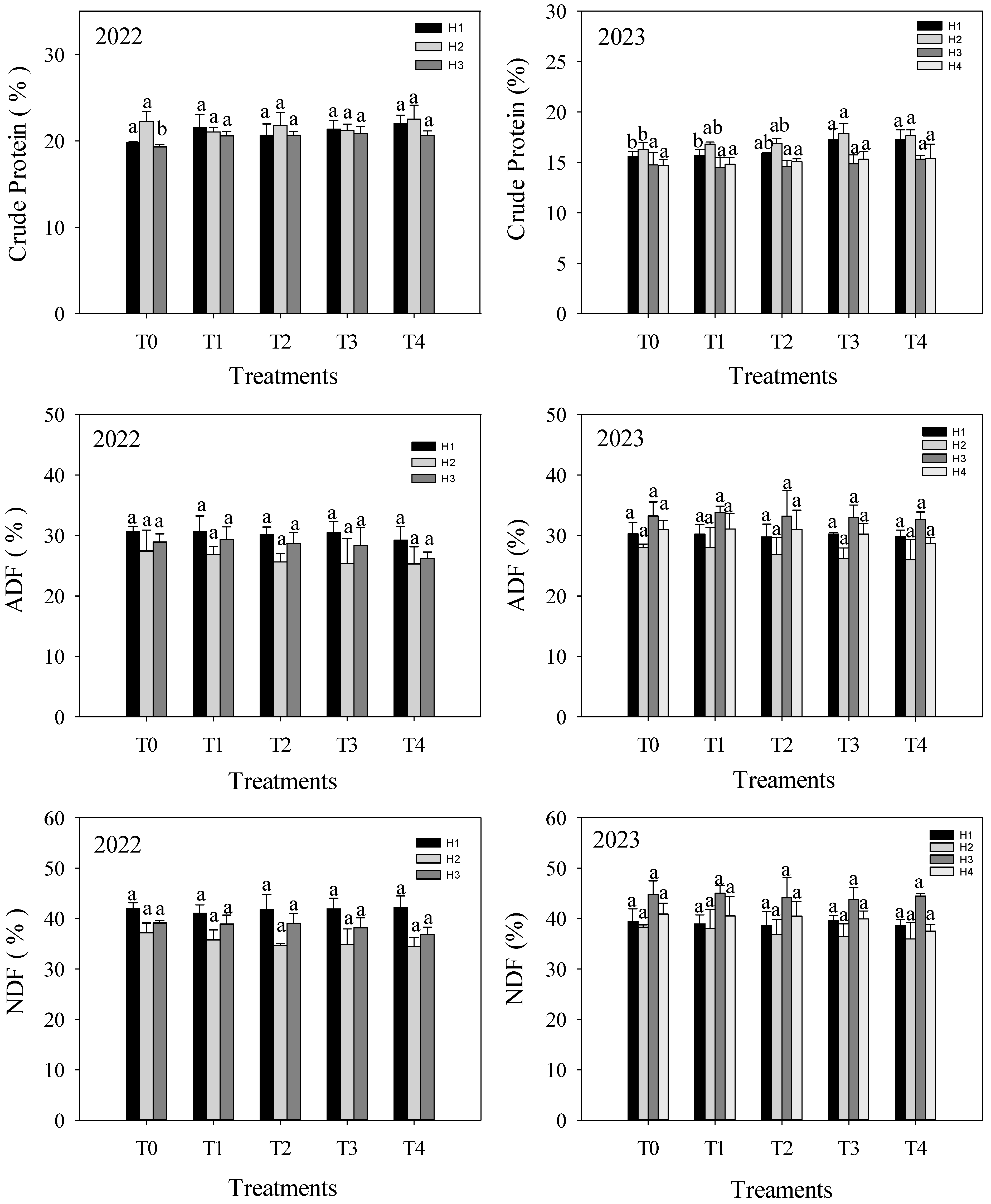
3.2. Alfalfa Quality
3.3. Soil Characteristics
3.4. Correlation Between Alfalfa Yield and Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of CRF on Alfalfa Yield
4.2. Effect of CRF with Soil Conditioner on Alfalfa Yield and Quality
4.3. Amelioration of Saline–Alkali Soil with the Combined Application of CRF and Soil Conditioner
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chhabra, R. Salt-Affected Soils and Marginal Waters; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Ni, G.; Feng, G.; Burrill, H.M.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, F. Saline-alkali soil reclamation and utilization in China: Progress and prospects. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2024, 11, 216–228. [Google Scholar]
- Negacz, K.; Malek, Ž.; De Vos, A.; Vellinga, P. Saline soils worldwide: Identifying the most promising areas for saline agriculture. J. Arid Environ. 2022, 203, 104775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Wang, X.P.; Xie, W.P.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, R.J. Research on salt-affected soils in China: History, status quo and prospect. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 59, 10–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fang, H.L.; Liu, G.H.; Kearney, M. Georelational analysis of soil type, soil salt content, landform, and land use in the Yellow River Delta, China. Environ. Manag. 2005, 35, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Amelioration and Utilization of Saline-Alkali Land. In Study of Ecological Engineering of Human Settlements; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M.; Jiao, S.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Jia, J.W.; Shen, Y.W.; Zhang, Z.X.; Kong, B.S. Effects of controlled release fertilizer on alfalfa grassland yield and soil nutrients in saline-alkali soil region of Yellow River Delta. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 33, 217–222. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ketterings, Q.M.; Godwin, G.; Gami, S.; Dietzel, K.; Lawrence, J.; Barney, P.; Kilcer, T.; Stanyard, M.; Albers, C.; Cherney, J.H. Soil and tissue testing for sulfur management of alfalfa in New York State. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, F.J.; Grattan, S.R.; Reyes, J.A.; Delgado, B.R.; Benes, S.E.; Jiménez, C.; Dorta, M.; Tejedor, M. Using saline soil and marginal quality water to produce alfalfa in arid climates. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 199, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hao, X.M.; Li, S.E.; Kang, S.Z. Response of dry matter and water use efficiency of alfalfa to water and salinity stress in arid and semiarid regions of Northwest China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 254, 106934. [Google Scholar]
- Monirifar, H.; Roudsari, A.M.; Ghassemi, S.; Tavasolee, A. Harvest Time and Cultivar Effects on Growth, Physiological Traits, Yield and Quality of Alfalfa in Saline Condition. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2020, 14, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelling, K.A. Alfalfa Fertilization; rev. Publication—Cooperative Extension Programs; University of Wisconsin-Extension: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.L.; Li, M.N.; Zhuo, Y.; Guo, H.; Yan, H.J.; Yan, X.D. Responses of alfalfa growth and nitrogen utilization to foliar fertilization with different urea concentrations. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 42, 5507–5522. [Google Scholar]
- Firmanda, A.; Fahma, F.; Syamsu, K.; Sari, Y.W.; Suryanegara, L.; Wood, K.; Saito, Y. Factors influencing the biodegradability of agro-biopolymer based slow or controlled release fertilizer. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 13, 1706–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.T.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Shen, Y.W.; Jiang, L.H.; Tan, D.S.; Song, X.Z.; Liu, P. The match of the nitrogen uptake in winter wheat and nitrogen release of water borne resin coated urea. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2018, 51, 3852–3862. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Gao, B.; Li, Y.C.; Xie, J.Z. Bio-based elastic polyurethane for controlled-release urea fertilizer: Fabrication, properties, swelling and nitrogen release characteristics. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 209, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.Y.; Sulaiman, S.A. Slow release coating remedy for nitrogen loss from conventional urea: A review. J. Control. Release 2016, 225, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.K.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Z.G.; Zhou, H.Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, W.T.; Yang, Y.C.; Li, C.L.; Chen, B.C. Combining controlled-release urea and normal urea to improve the nitrogen use efficiency and yield under wheat-maize double cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2016, 197, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, L.; Cheng, D.D.; Liu, M.; Geng, Y.Q. Controlled release urea improved nitrogen use efficiency, yield, and quality of wheat. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Geng, J.B.; Li, C.L.; Zhang, M.; Chen, B.C.; Tiao, X.F.; Zheng, W.K.; Liu, Z.G.; Wang, C. Combined application of polymer coated potassium chloride and urea improved fertilizer use efficiencies, yield and leaf photosynthesis of cotton on saline soil. Field Crop Res. 2016, 197, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, T.A.; Minh, V.Q. Improving soil properties and rice yield on saline-affected acid sulfate soil by controlled-release fertilizer. Indian J. Agric. Res. 2023, 57, 475–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motojima, H.; Yamada, P.; Irie, M.; Ozaki, M.; Shigemori, H.; Isoda, H. Amelioration effect of humic acid extracted from solubilized excess sludge on saline-alkali soil. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2012, 14, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, J.A.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Cunningham, S.C.; Jackson, W.R.; Patti, A. Does biochar improve establishment of tree seedlings in saline sodic soils? Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia-Ur-Rehman, M.; Rizwan, M.; Sabir, M.; Ali, S.; Ahmed, H. Comparative effects of different soil conditioners on wheat growth and yield grown in saline-sodic soils. Sains Malay 2016, 45, 339–346. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, Y.Y.; Li, G.; Bai, Y.G.; Liu, H.B.; Zhang, J.H.; Wei, K.; Wang, Q.J.; Cao, L. Effects of gypsum combined with different amounts of biochemical humic acid on soil improvement and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) yield on saline-alkali land. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2022, 20, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.S. Principles and Techniques of Plant Physiological Biochemical Experiment; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2001. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vansoest, P.J.; Robertson, J.B.; Lewis, B.A. Methods for dietary fiber, neutral detergent fiber, and nonstarch polysaccharides in relation to animal nutrition. J. Dairy Sci. 1991, 74, 3583–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohweder, D.A.; Barnes, R.F.; Jorgensen, N. Proposed hay grading standards based on laboratory analyses for evaluating quality. J. Anim. Sci. 1978, 47, 747–759. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jungers, J.M.; Kaiser, D.E.; Lamb, J.F.S.; Lamb, J.A.; Noland, R.L.; Samac, D.A.; Wells, S.; Sheaffer, C.C. Potassium fertilization affects alfalfa forage yield, nutritive value, root traits, and persistence. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 2843–2852. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, W.F.; Li, Y.J.; Li, H.G. Yield and quality of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) in response to fertilizer application in China: A meta-analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1051725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lu, F.; Zhu, Y.; Wu, H.; Ahmed, I.; Dong, G.C.; Zhou, G.S.; Wu, Y.Q. The effects of planting density and nitrogen application on the growth quality of alfalfa forage in saline soils. Agriculture 2024, 14, 302–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.L.; Li, M.N.; Guo, J.L.; Yan, H.J. Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) nitrogen utilization, yield and quality respond to nitrogen application level with center pivot fertigation system. Agronomy 2024, 14, 48–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharably, A.; Benes, S. Alfalfa biomass yield and nitrogen fixation in response to applied mineral nitrogen under saline soil conditions. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 744–755. [Google Scholar]
- Regmi, P.; Devkota, N.R. Effects of nitrogen fertilization and cutting height on the forage yield and feeding value of Eleusine indica in the dry season in Nepal. Weed Biol. Manag. 2009, 9, 106–111. [Google Scholar]
- Angima, S.D.; Kallenbach, R.L.; Riggs, W.W. Forage yield of selected cool-season grasses in response to varying rates of nitrogen. Forage Grazinglands 2009, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Tucak, M.; Ravlić, M.; Horvat, D.; Čupić, T. Improvement of forage nutritive quality of alfalfa and red clover through plant breeding. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugar, G.M. Effect of soil organic carbon on perviousness and conservation property of soil. Indian Geotech. J. 2017, 47, 559–570. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.L.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.L.; Lu, Y.C.; Wang, Y.F. Saline-alkali soil applied with vermicompost and humic acid fertilizer improved macroaggregate microstructure to enhance salt leaching and inhibit nitrogen losses. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103705. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Fang, H.; Mooney, S.J.; Peng, X.H. Effects of long-term inorganic and organic fertilizations on the soil micro and macro structures of rice paddies. Geoderma 2016, 266, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.M.; Zhang, S.R.; Liu, L.L.; Liu, J.G.; Ding, X.D. Organic fertilization increased soil organic carbon stability and sequestration by improving aggregate stability and iron oxide transformation in saline-alkaline soil. Plant Soil 2022, 474, 233–249. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, M.; Liu, G.H.; Zhou, B.B.; Chen, X.P.; Wang, Q.J.; Zhu, H.Y.; Li, Z.J. Effects of modified biochar on water and salt distribution and water-stable macro-aggregates in saline alkaline soil. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2192–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, G.; Abrar, M.M.; Naeem, M.A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Ali, H.M.; Li, Y.; Ahmed, K.; Sun, N.; Xu, M. Biochar increases salt tolerance and grain yield of quinoa on saline-sodic soil: Multivariate comparison of physiological and oxidative stress attributes. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 1446–1459. [Google Scholar]
- Magally, O.D.S.M.R.; Josinaldo, L.A.; Vital dos Santos, R.; Soares de Lima, G.; Da Nóbrega Santos, E.; Correia da Costa, R. Vermiculite mining waste enriched with elemental sulfur as a chemical conditioner for alkaline saline soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2022, 53, 2271–2284. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, A.; Biswas, D.R.; Saha, M.; Kumar, R.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Biswas, S.S.; Ghosh, A.; Roy, T. Development of controlled release fertilizer from double-boiled linseed and mustard oil-based formulations: Surface morphology, nutrient release and performance of wheat in sub-tropical inceptisol. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 1096–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, K.R.; Yang, J.E.; Ok, Y.S.; Owens, G.; Nehls, T.; Wessolek, G.; Kim, K.H. Effect of biochar on reclaimed tidal land soil properties and maize (Zea mays L.) response. Chemosphere 2015, 142, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.W.; Zhang, S.D.; Zhang, X.T.; Chen, J.H.; He, X.Y.; Zhang, Q.Z. Effects of pyrolysis temperature on soil-plant-microbe responses to Solidago canadensis L.-derived biochar in coastal saline-alkali soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 138938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soil Layer | pH | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | SOM † (g kg−1) | Salinity (g kg−1) | EC † (µS cm−1) | Available N (mg kg−1) | Available P (mg kg−1) | Available K (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~20 cm | 9.19 | 1.29 | 10.46 | 1.52 | 312 | 49.64 | 10.24 | 132.67 |
| 20~40 cm | 9.17 | 1.32 | 7.72 | 2.63 | 907 | 35.18 | 8.02 | 106.67 |
| Year | Treatment | T0 § | T1 § | T2 § | T3 § | T4 § |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2022 | H1 † | 4020 ± 90.8 b | 4294 ± 103.9 a | 4269 ± 89.7 a | 4308 ± 98.2 a | 4284 ± 86.7 a |
| H2 † | 2742 ± 95.2 b | 2826 ± 99.2 ab | 2903 ± 85.1 a | 2853 ± 80.9 ab | 2922 ± 82.3 a | |
| H3 † | 2126 ± 103.5 a | 2145 ± 98.4 a | 2163 ± 92.8 a | 2225 ± 96.8 a | 2242 ± 87.2 a | |
| Total | 8889 ± 280.6 b | 9265 ± 289.8 ab | 9335 ± 253.9 ab | 9386 ± 273.3 ab | 9448 ± 247.9 a | |
| 2023 | H1 † | 3625 ± 131.5 b | 3977 ± 160.1 a | 3917 ± 126.5 a | 4110 ± 162.6 a | 4079 ± 160.1 a |
| H2 † | 3242 ± 158.1 b | 3484 ± 194.2 ab | 3599 ± 95.6 a | 3650 ± 217.8 a | 3776 ± 146.7 a | |
| H3 † | 3325 ± 109.0 c | 3343 ± 55.3 c | 3635 ± 141.5 ab | 3481 ± 66.8 bc | 3794 ± 89.9 a | |
| H4 † | 2134 ± 177.3 b | 2188 ± 102.0 ab | 2296 ± 175.5 ab | 2313 ± 116.3 ab | 2445 ± 73.4 a | |
| Total | 12,326 ± 556.0 c | 12,992 ± 483.2 bc | 13,447 ± 533.8 ab | 13,553 ± 533.6 ab | 14,077 ± 421.3 a |
| Soil Layer | T0 § | T1 § | T2 § | T3 § | T4 § | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 0~20 cm | 8.49 ± 0.22 a | 8.76 ± 0.18 a | 8.64 ± 0.07 a | 8.67 ± 0.09 a | 8.72 ± 0.13 a |
| 20~40 cm | 8.94 ± 0.21 a | 8.84 ± 0.10 a | 8.87 ± 0.17 a | 8.71 ± 0.28 a | 8.88 ± 0.15 a | |
| 40~60 cm | 9.01 ± 0.22 a | 8.77 ± 0.17 a | 8.88 ± 0.19 a | 9.02 ± 0.07 a | 8.76 ± 0.20 a | |
| Salinity (g kg−1) | 0~20 cm | 1.54 ± 0.11 b | 1.88 ± 0.17 a | 1.78 ± 0.16 ab | 1.59 ± 0.10 b | 1.56 ± 0.18 b |
| 20~40 cm | 1.91 ± 0.15 a | 2.13 ± 0.20 a | 2.05 ± 0.21 a | 2.03 ± 0.30 a | 1.95 ± 0.24 a | |
| 40~60 cm | 2.27 ± 0.33 a | 2.49 ± 0.19 a | 2.40 ± 0.16 a | 2.34 ± 0.31 a | 2.29 ± 0.25 a |
| Soil Layer | T0 § | T1 § | T2 § | T3 § | T4 § | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SOM (g kg−1) | 0~20 cm | 9.12 ± 0.23 a | 9.20 ± 0.36 a | 9.29 ± 0.33 a | 9.54 ± 0.28 a | 9.63 ± 0.34 a |
| 20~40 cm | 6.18 ± 0.51 a | 6.44 ± 0.31 a | 6.39 ± 0.05 a | 6.46 ± 0.23 a | 6.45 ± 0.35 a | |
| 40~60 cm | 3.74 ± 0.58 a | 3.73 ± 0.47 a | 3.77 ± 0.45 a | 3.79 ± 0.42 a | 3.80 ± 0.49 a | |
| Available N (mg kg−1) | 0~20 cm | 59.64 ± 1.50 a | 58.42 ± 3.54 a | 60.06 ± 3.70 a | 65.18 ± 7.84 a | 67.62 ± 5.27 a |
| 20~40 cm | 38.76 ± 2.13 b | 43.64 ± 5.79 ab | 46.83 ± 4.79 ab | 47.77 ± 5.02 ab | 49.27 ± 5.54 a | |
| 40~60 cm | 25.81 ± 3.94 a | 26.13 ± 4.17 a | 26.69 ± 4.05 a | 27.11 ± 4.32 a | 27.22 ± 2.56 a | |
| Available P (mg kg−1) | 0~20 cm | 3.32 ± 1.14 b | 4.33 ± 0.80 b | 5.21 ± 1.30 ab | 7.31 ± 1.31 a | 7.49 ± 1.41 a |
| 20~40 cm | 3.23 ± 0.65 b | 3.96 ± 0.26 b | 4.03 ± 0.30 b | 5.28 ± 0.39 a | 5.72 ± 0.85 a | |
| 40~60 cm | 3.07 ± 0.66 a | 3.76 ± 0.56 a | 3.87 ± 0.59 a | 3.95 ± 0.89 a | 4.00 ± 0.89 a | |
| Available K (mg kg−1) | 0~20 cm | 92.67 ± 8.74 b | 124.67 ± 5.51 a | 120.67 ± 12.01 a | 118.67 ± 10.26 a | 128.33 ± 7.51 a |
| 20~40 cm | 63.67 ± 5.13 b | 94.00 ± 12.49 a | 89.33 ± 10.44 a | 87.00 ± 7.23 a | 96.00 ± 5.29 a | |
| 40~60 cm | 39.00 ± 5.00 b | 60.67 ± 5.13 a | 58.67 ± 2.08 a | 56.67 ± 7.37 a | 62.00 ± 8.72 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Wu, B.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, G.; Liu, Z. The Application of Slow-Release Nitrogen Combined with Soil Conditioner Under the Impact of Alkaline Salinity in Alfalfa Cultivation and Soil Improvement. Agronomy 2025, 15, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040923
Liu P, Wu B, Zhao Z, Wang G, Liu Z. The Application of Slow-Release Nitrogen Combined with Soil Conditioner Under the Impact of Alkaline Salinity in Alfalfa Cultivation and Soil Improvement. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040923
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ping, Bo Wu, Zichao Zhao, Guoliang Wang, and Zhaohui Liu. 2025. "The Application of Slow-Release Nitrogen Combined with Soil Conditioner Under the Impact of Alkaline Salinity in Alfalfa Cultivation and Soil Improvement" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040923
APA StyleLiu, P., Wu, B., Zhao, Z., Wang, G., & Liu, Z. (2025). The Application of Slow-Release Nitrogen Combined with Soil Conditioner Under the Impact of Alkaline Salinity in Alfalfa Cultivation and Soil Improvement. Agronomy, 15(4), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040923






