Abstract
Vitamin C industrial residue after evaporation (RAE) acts as both a rapid-release carbon source and a microbial activity promoter. A two-year maize field experiment assessed the effectiveness of RAE in improving soil quality in degraded semi-arid regions. The RAE formulation was applied via drip irrigation during the sixth true leaf unfolded (BBCH 24), fourteenth true leaf unfolded (BBCH 38), and middle of grain filling (BBCH 66) stages, which consisted of three treatments: (1) untreated control (CK), (2) low RAE rate (LR: 150 L/ha), and (3) high RAE rate (HR: 300 L/ha). Soil physicochemical properties, enzyme activities, maize nutrient accumulations, and yields were comprehensively analyzed at the maize maturity stage. RAE application significantly improved the following soil nutrients: dissolved organic carbon (10.40–25.92%), ammonium nitrogen (14.04–70.67%), nitrate nitrogen (14.80–78.63%), and available phosphorus (11.79–42.55%). Soil enzyme activities also increased: sucrase (12.38–30.25%), amidase (1.95–25.69%), peptidase (0.56–48.79%), β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase (3.11–9.48%), protease (17.41–226.29%), and acid phosphatase (8.73–60.04%). These changes enhanced maize nitrogen (17.63–40.73%) and phosphorus (20.09–42.11%) uptake, increasing yield by 7.12–13.46%. Statistical analysis showed strong correlations between yields and nutrient accumulations (r = 0.82, p < 0.01), particularly phosphorus (r = 0.91, p < 0.001). RAE enhances crop productivity in degraded agricultural systems by improving soil nutrient availability and plant assimilation, making it a viable alternative to conventional fertilizers.
1. Introduction
Maize (Zea mays L.) is cultivated worldwide and is one of the most crucial staple crops, providing approximately 30% of the caloric intake for around 4.6 billion people [1]. Meanwhile, maize is the most widely planted cereal crop globally, with 500 million tons produced annually on 130 million hectares [2]. Maize plays a crucial role in livestock production, biofuel generation, and human nutrition [3,4]. Global demand for maize is expected to increase by 16% by 2027 [5]. Therefore, enhancing maize yield through effective fertilization is of significant importance. However, modern agricultural practices rely heavily on the excessive use of fertilizers, such as nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), to enhance crop yields. This approach negatively impacts agricultural sustainability [6]. Nitrogen fertilizer overuse is particularly problematic, with approximately 45% of applied nitrogen being wasted through leaching rather than being absorbed by crops [7]. This inefficiency not only escalates production costs and diminishes soil quality but also contributes to water contamination and soil acidification [8,9,10]. Therefore, there is an urgent need to develop fertilization strategies that promote environmental sustainability and minimize fertilizer dependency. Semi-arid regions cover approximately 15 percent of the world’s total land area and play a major role in agricultural production [11]. In recent years, climate change has exacerbated soil degradation in these areas, resulting in reduced water retention, soil structural deterioration, and reduced organic matter content. These problems have created unprecedented challenges for agricultural production [12]. Thus, restoring soil productivity and increasing crop yields through rationalized fertilization has become a key research focus in contemporary agricultural science.
Residue after evaporation (RAE) is a byproduct of the industrial production process of vitamin C, formed as a residual liquid after the ultrafiltration, concentration, and crystallization of fermented broth. China’s annual vitamin C production (200,000 tons) generates 40,000 tons of RAE, characterized by a high organic content (COD: 0.8–1.0 × 106 mg/L), low pH (<0.5), and extremely low heavy metal levels [13]. Adjusting the low acidity of RAE appropriately can potentially turn it into a valuable fertilizer source. RAE is characterized by the presence of diverse low-molecular-weight organic acids (LMWOAs), with 2-keto-L-gulonic acid (2KGA) being the predominant constituent [14]. Multiple studies have demonstrated that LMWOAs regulate rhizosphere microbial community structure and facilitate biochemical processes within the plant rhizosphere [15,16,17], facilitating the formation and preservation of soil nutrients [18]. In addition, the main active component of RAE, 2KGA, substantially promotes plant resilience to abiotic stresses, thus enhancing plant biomass [19]. Despite evidence that RAE enhances nutrient availability in multiple soil types [20,21], its specific impact on soil property and maize yield under drip irrigation has not been studied. In this study, a two-year maize planting experiment was conducted that aimed to (1) investigate the influence of RAE on soil properties and enzyme activities, (2) investigate how RAE impacts maize nutrient accumulations and yields, and (3) explore the potential relationship between soil nutrients, enzyme activities, maize nutrient accumulations, and yields under RAE application. This study seeks to reduce environmental pollution from RAE disposal while reducing traditional fertilizer inputs and enhancing crop productivity and economic outcomes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
The experiment was conducted at the field experimental station of the Fuxin Dryland Water-saving Technology Experimental Demonstration Base of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Liaoning Province, China (41°44′~42°34′ N, 121°01′~122°26′ E). The study area is located on the southern edge of the Horqin Sandy Land, one of the primary wind and sand corridors in Northeast China. The area has been affected by the surrounding sandy land, leading to notable land degradation [22]. The region experiences a temperate semi-humid continental monsoon climate, with an average elevation of 235 m. The annual average temperature is 7.8 °C, and during the crop growing season, the average temperature is 20.2 °C. There are 169 days with temperatures above 10 °C. The total sunlight hours during the growing season amount to 1295.8 h. The average annual evaporation is 1847.6 mm, while the annual precipitation is 493.1 mm. The experimental site soils are arenosols. Arenosols are highly aerated and well-drained soils, but they have relatively low water and nutrient retention capacities. Drip irrigation has been used as the primary irrigation strategy in agricultural operations at this research station. The soil represents a characteristic form of soil degradation that significantly reduces agricultural productivity in cultivated regions.
The field had been under continuous maize cultivation for many years before the experiment. After the harvest of the previous season’s maize, straw was spread evenly over the surface. The following year, no-till planters were used for sowing, and wide, narrow rows were planted alternately (Figure 1). Before starting the experiment in 2023, five soil cores (0–20 cm depth) were extracted from each experimental field with a 5.0 cm diameter soil drill using the five-point method. The soil samples were thoroughly homogenized, passed through a 2 mm sieve, and used for determining soil physicochemical properties. Details of the experimental site are illustrated in Figure 1.
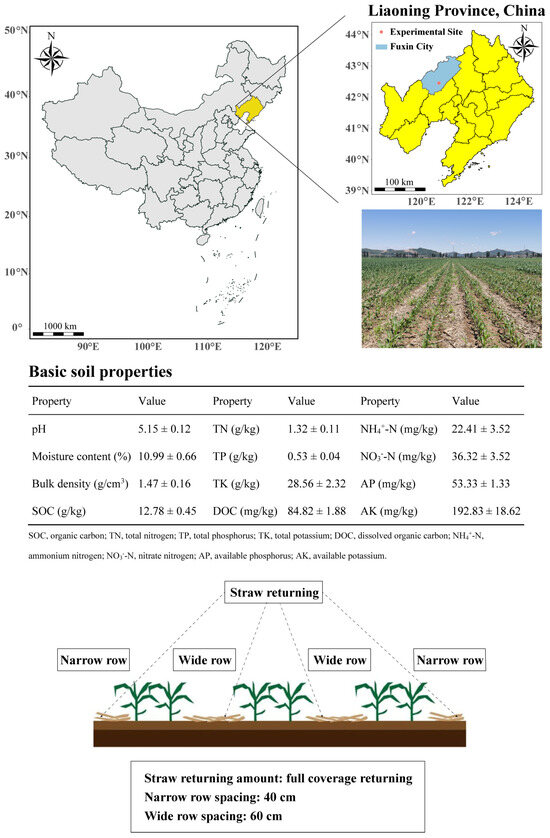
Figure 1.
Information on the experimental site.
2.2. Experimental Design and Treatments
A two-year field experiment was conducted at the same field plot during the maize growing seasons (May to September) in 2023 and 2024 employing a completely randomized block design with four replicates. During the second year, a randomized redesign of the treatment group assignment was implemented. The study comprised three treatments: (1) control (CK, no RAE application), (2) low RAE dosage (LR), and (3) high RAE dosage (HR), each applied to 50 m2 plots (10 m × 5 m). Standardized agronomic practices were maintained across all treatments. Before sowing, compound fertilizer (N:P2O5:K2O = 15:15:15) was uniformly applied as a basal dressing at 450 kg/ha. Fertilizer incorporation was achieved using a rotary tiller to a depth of 15–20 cm, simultaneously mixing with residual straw. Maize was sown at 5 cm depth with a planting density of 55,000 plants per hectare, consistent across all experimental units. The variety “H188” spring maize, classified as late maturing under Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) standards, required 127 days to mature.
The RAE, which was provided by Northeast Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. in Shenyang, China, possesses the physicochemical characteristics outlined in Table 1. With an initial pH below 1, it is unsuitable for direct application to plants and requires adjustment. The pH of the solution was adjusted to 3.5 using NH3·H2O under water bath conditions, which preserved the integrity of LMWOAs and minimized fluctuations in soil pH. Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) was applied to equalize ammonium ion levels across the three treatments, thereby eliminating interference due to variations in RAE dosages. The experimental treatments were applied via drip irrigation at three key maize growth stages: sixth true leaf unfolded (BBCH 24), fourteenth true leaf unfolded (BBCH 38), and middle of grain filling (BBCH 66). Apart from necessary irrigation during the topdressing phase, the water supply in all other growth stages for each treatment was entirely sourced from natural rainfall. The amounts of fertilizer application and water irrigation per topdressing are given in Table 2.

Table 1.
The physical–chemical properties of RAE.

Table 2.
The fertilizer and irrigation information.
2.3. Soil and Maize Sample Collection
Soil sampling was conducted following standardized protocols during the end of maturity stage (BBCH 72) of maize in 2023 and 2024 (15 September 2023 and 15 September 2024). Surface litter and straw were carefully removed before collecting soil cores from the upper 20 cm soil layer. From each experimental plot, eight randomly distributed soil cores were extracted and homogenized to form a composite sample. Subsequently, each composite sample was processed by removing visible maize roots and stones, followed by sieving through a 2 mm mesh. The processed samples were then divided into three aliquots for subsequent analyses. The first portion was placed in an ice box, transported to the lab, and stored at −20 °C for analyzing soil extracellular enzyme activities, ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N), and nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) contents within one week. The second portion was used to determine the soil water content (SWC), while the third portion was air-dried for the analysis of other chemical properties. Additionally, a total of ten maize plants above ground were randomly selected from each plot. Fresh samples underwent drying at 105 °C for 30 min, followed by drying at 75 °C to reach a constant weight, for assessing aboveground dry matter weight. Each plant part was ground using a 100-mesh ring mill for N and P content analysis.
2.4. Soil Properties
The SWC was quantified by drying the soil at 105 °C for 24 h, and pH levels were measured with a pH meter (PHS-3C, INESA, Shanghai, China) using a 2.5:1 water-to-soil ratio [23]. The soil organic carbon (SOC) and total nitrogen (TN) were measured by the K2Cr2O7-H2SO4 oxidation and the Kjeldahl methods, respectively [24,25]. Total phosphorus (TP) was measured by the molybdenum antimony spectrophotometric method [26]. Soil dissolved organic carbon (DOC) was extracted from a soil slurry [27]. Filtered leachate samples were frozen at −18 °C. Then, after thawing at room temperature, the liquid was analyzed for DOC [28] using a high-temperature combustion total C analyzer (TOC-VCPH, Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The NH4+-N and NO3−-N concentrations were analyzed by flow injection after leaching with 2 mol/L KCl [29]. The available phosphorus (AP) was quantified by colorimetry using HCl and NH4F extraction [30]. The total potassium (TK) and available potassium (AK) contents were measured using a flame photometer. The extractants used for TK and AK were 1 mol/L NaOH and NH4OAc, respectively [31].
2.5. Assays of Soil Enzyme Activities
Soil sucrase (SC) activity was determined by dinitro salicylic acid colorimetry [32]. Amidase (SA) activity was assayed using the method described by Frankenberger and Tabatabai [33]. Soil peptidase (SPE), β-1,4-N-acetylglucosaminidase (NAG), and acid phosphatase (ACP) activity was measured using a fluorescent substrate (7-amino-4-methylcoumarin and 4-MUB) [34]. Full details are provided in Supplementary Method S1. Soil protease activity was measured as described by Ladd and Butler [35].
2.6. Assessment of Soil Quality Index and Enzyme Index
This study evaluated the effect of various treatments on soil quality and enzyme activity by employing the total dataset method to derive the soil quality index (SQI) and soil enzyme activity index (SEI) for MWDS soil. The eight indicators of SQI were considered: SOC, DOC, NH4+-N, NO3−-N, AP, AK, pH, and SWC. The six indicators of SEI were considered: SC, SA, SPE, NAG, NPT, and ACP.
The first step entails standardizing each soil metric into a dimensionless score (Si) bounded by 0 and 1 [36]:
where Si signifies the score for the i-th indicator, xi represents the measured value, and xmax and xmin denote the maximum and minimum values, respectively.
In the second step, the weight (Wi) for each indicator was computed using a principal component analysis, dividing the variance of its common factors by the total variance of all indicators [37].
The SQI [38] and SEI [39] were determined by multiplying the scored values by their weights. Higher SQI and SEI values indicate increased soil quality and enzyme activity.
In this formula, n denotes the total number of indicators, while Si and Wi represent the score and weight of the i-th indicator.
2.7. Maize Nutrient Accumulations and Yields
The N and P contents of the maize plant samples (collected simultaneously with soil samples) were measured by the Kjeldahl method [40] and the vanadomolybdate procedure [41], respectively. The N (or P) accumulation was calculated as the product between aboveground biomass and N (or P) concentration. At maize harvest in 2023 and 2024, the maize was harvested manually, and the grain yield, ear number, kernel number per ear, and 1000-kernel weight were measured. Full details are provided in Supplementary Method S2.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
Significant differences among groups were determined by a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Duncan’s multiple comparisons. Correlations between the metrics were evaluated using Spearman’s correlation coefficient and Mantel’s test. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was constructed using Amos software version 26.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). Random forest analysis was conducted with the rfPermute package in R, while additional statistical analyses were carried out using R software version 4.3 (R Core Team, Vienna, Austria), GraphPad Prism software version 8.0 (GraphPad Software, Inc, San Diego, CA, USA), and IBM SPSS Statistics software version 22.0 (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). The data are the mean of four replicates (n = 4), with error bars showing standard error (SE). A p-value less than 0.05 is considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Fluctuation of Soil Properties
In 2023 and 2024, the application of the RAE (LR and HR) did not significantly shift the total nutrient contents (SOC, TN, and TP) or pH levels in the soil (Figure 2). However, RAE application significantly improved the contents of available nutrients (DOC, NH4+-N, NO3−-N, and AP). The HR treatment demonstrated superior effectiveness over the LR. Compared to the CK in 2023 and 2024, the LR significantly increased the contents of DOC (11.51%–14.14%), NH4+-N (21.74–25.44%), NO3−-N (23.24–30.14%), and AP (16.42–19.23%). In contrast, the HR led to even greater increases of DOC (22.89–23.29%), NH4+-N (44.75–49.32%), NO3−-N (54.78–54.92%), and AP (34.18–37.03%).
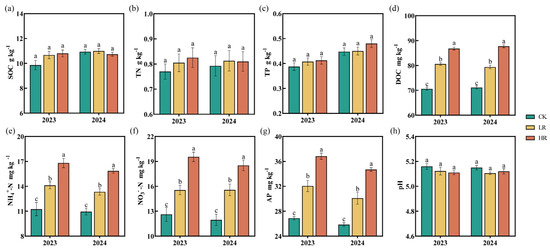
Figure 2.
Effect of RAE on the SOC (a), TN (b), TP (c), DOC (d), NH4+-N (e), NO3—N (f), AP (g), and pH (h) of the maize soil in 2023 and 2024. CK, control; LR, low RAE dosage (150 L/ha); HR, high RAE dosage (300 L/ha). SOC, soil organic carbon; TN, total nitrogen; TP, total phosphorus; DOC, dissolved organic carbon; NH4+-N, ammonium nitrogen; NO3−-N, nitrate nitrogen; AP, available phosphorus. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (n = 4, p < 0.05).
3.2. Changes in Soil Enzyme Activities
Soil enzyme activity varied across treatments and years (Figure 3). In 2023 and 2024, the sucrase activity in soils treated with LR and HR was significantly higher than in the CK, increasing by 17.37–30.25% and 12.38–23.95%, respectively. In 2023, the application of RAE (LR and HR) significantly enhanced the activities of SA, SPE, NAG, NPT, and ACP, with the HR showing the most pronounced effects. In 2024, the HR significantly enhanced the activities of SA (17.75–25.69%), SPE (23.99–48.79%), NAG (6.42–9.48%), NPT (79.37–226.29%), and ACP (50.10–60.04%) compared to the CK, while the LR showed no statistically significant differences from the CK. These improvements were consistent with the trends observed in 2023, demonstrating HR’s sustained positive effects on soil enzyme activities across both experimental years.
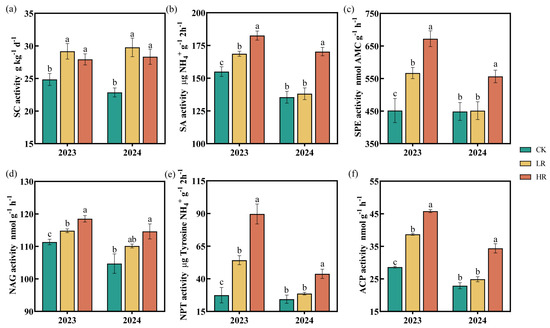
Figure 3.
Effect of RAE on the SC (a), SA (b), SPE (c), NAG (d), NPT (e), and ACP (f) activities of the maize soil in 2023–2024. CK, control; LR, low RAE dosage (150 L/ha); HR, high RAE dosage (300 L/ha). SC, soil sucrase; SA, soil amidase; SPE, soil peptidase; NAG, soil 1,4-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase; NPT, soil protease; ACP, soil acid phosphatase. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (n = 4, p < 0.05).
3.3. The Quality Index and Enzyme Index of Maize Soil
In 2023 and 2024, the SQI values for the CK, LR, and HR ranged from 0.10 to 0.26, 0.51 to 0.59, and 0.75 to 0.90, respectively (Figure 4a). The SEI value for the CK remained at 0 in both years, while the LR and HR showed SEI values of 0.32–0.58 and 0.95–0.96, respectively (Figure 4b). The application of RAE (LR and HR) significantly improved both SQI and SEI, with the HR demonstrating the most pronounced effects.
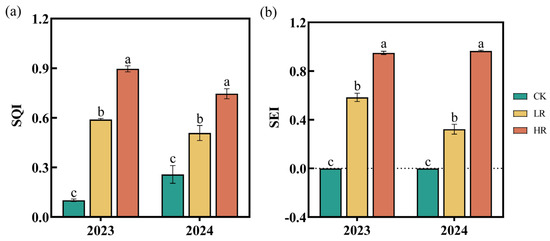
Figure 4.
Effect of RAE on the SQI (a) and SEI (b) of the maize soil in 2023–2024. CK, control; LR, low RAE dosage (150 L/ha); HR, high RAE dosage (300 L/ha). SQI, soil quality index; SEI, soil enzyme index. Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (n = 4, p < 0.05).
3.4. Maize Nutrient Accumulations
The application of the RAE (LR and HR) significantly increased N and P accumulation in the maize plants (Figure 5). In 2023 and 2024, the LR increased N and P accumulation by 17.63–19.77% and 20.09–23.25%, respectively, while the HR achieved increases of 39.19–40.73% and 41.10–42.11%.
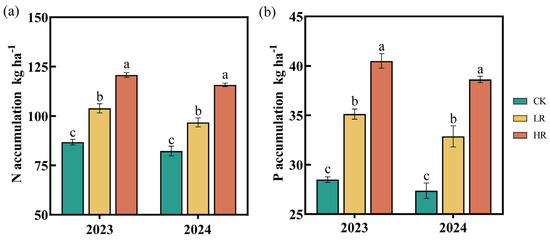
Figure 5.
Effect of RAE on the N accumulation (a) and P accumulation (b) of the maize plant in 2023–2024. CK, control; LR, low RAE dosage (150 L/ha); HR, high RAE dosage (300 L/ha). Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (n = 4, p < 0.05).
3.5. Effects of RAE Addition on Maize Yield
The effects of RAE application (LR and HR) on the maize yield components varied (Figure 6). The RAE significantly increased grain yield, kernel number per ear, and 1000-kernel weight but had no significant impact on the ear number. Compared to the CK, the LR significantly increased grain yield by 7.12–8.26%, kernel number per ear by 3.51–3.54%, and 1000-kernel weight by 2.67–3.85% across both the 2023 and 2024 growing seasons. The HR demonstrated even more pronounced effects, yielding greater improvements of 13.09–13.46% in grain yield, 5.96–6.01% in kernel number per ear, and 6.52–6.94% in 1000-kernel weight.
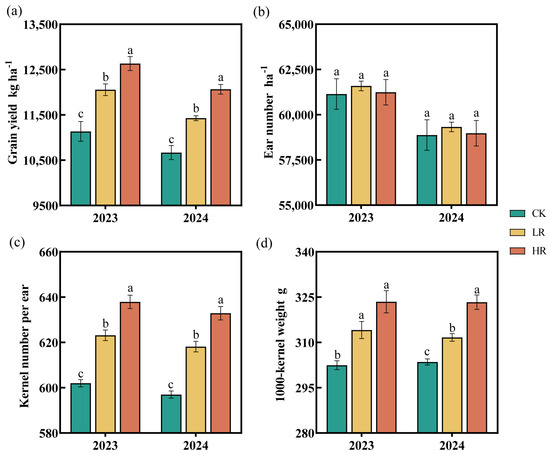
Figure 6.
Effect of RAE on the Grain yield (a), Ear number (b), Kernel number per ear (c), and 1000-kernel weight (d) of the maize in 2023–2024. CK, control; LR, low RAE dosage (150 L/ha); HR, high RAE dosage (300 L/ha). Different letters indicate statistically significant differences (n = 4, p < 0.05).
3.6. Comprehensive Analysis of Soil and Maize Characteristics
RAE, DOC, and AP exhibited significant positive correlations with soil enzyme activity (Figure 7a). NH4+-N and NO3−-N were positively correlated with all soil enzymes in this study except sucrase. No significant correlations were observed between soil enzyme activities and total nutrient contents (SOC, TN, and TP) or pH. Mantel’s test results (Figure 7a) showed significant positive correlations between maize N and P accumulation, yield components, and RAE, as well as available nutrients (DOC, NH4+-N, NO3−-N, and AP). The correlation analysis shown in Figure 7b, c further reveals that grain yield, kernel number per ear, and 1000-kernel weight were significantly positively correlated with maize N and P accumulation, whereas the number of ears showed no significant correlation.
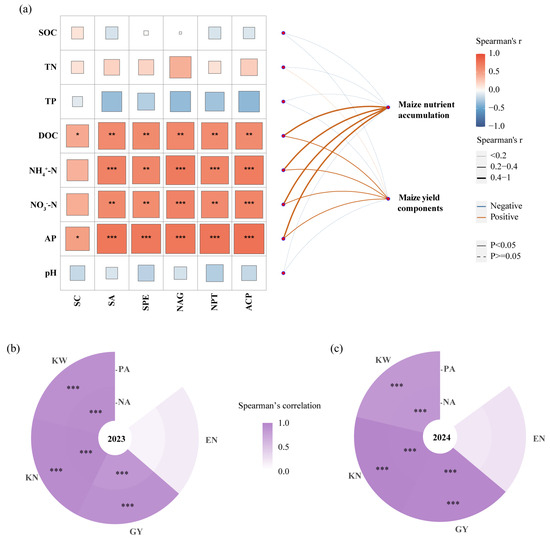
Figure 7.
Correlation analysis by Mantel’s test (a); correlation analysis of maize yield components with plant N and P accumulation in 2023 (b) and 2024 (c). Note, RAE, RAE addition; SOC, organic carbon; TN, total nitrogen; TP, total phosphorus; DOC, dissolved organic carbon; NH4+-N, ammonium nitrogen; NO3−-N, nitrate nitrogen; AP, available phosphorus; GY, grain yield; EN, ear number; KN, kernel number per ear; KW, 1000-kernel weight; NA, maize N accumulation; PA, maize P accumulation. Correlation analysis and Mantel’s test were performed by Spearman’s method. ***, p < 0.001; **, p < 0.01; *, p < 0.05.
3.7. Structural Equation Modeling Analysis
Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) analyzed the relationships between maize yield and nutrient cycling under different treatments (Figure 8a). This improvement ultimately contributed to increased maize yield. Random forest analysis identified the most critical factors affecting maize yield, in agreement with the SEM results. PA was the most significant factor affecting maize yield (Figure 8b). The observed correlations between SQI (or SEI) and yield enhancement suggest a potential relationship that warrants further investigation.
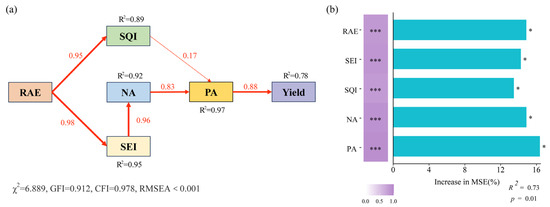
Figure 8.
Relationships of maize yield with nutrient cycle. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was used to identify the nutrient cycle that affected maize yield (a). Red arrows illustrate positive correlations (p < 0.05). The numbers on the arrows correspond to significant standardized path coefficients, and R² indicates the variance of the dependent variable explained by the model. Random forest was used to analyze the importance of impact factors of maize yield (b). Note, RAE, RAE addition; SQI, soil quality index; SEI, soil enzyme index; NA, maize N accumulation; PA, maize P accumulation. ***, p < 0.001; *, p < 0.05.
4. Discussion
The present study employed RAE application to enhance soil nutrient bioavailability and promote crop nutrient assimilation during the growing season. RAE application exhibited minimal impact on total soil nutrient pools (SOC, TN, and TP), as evidenced in Figure 2a–c. This limited effect can be attributed to the RAE’s inherently low nutrient concentration, which precludes direct soil fertility enhancement. However, significant increases in DOC, NH4+-N, NO3−-N, and AP levels were observed (Figure 2d–g), driven by multiple mechanisms. Most microbial communities are limited by energy sources, usually as C, or critical nutrients, usually as N and P, or both [42]. RAE serves as an easily accessible carbon source, reshaping soil bacterial community structures, influencing the expression of functional genes [21], and enhancing microbial activity, accelerating organic matter decomposition [43]. The capacity of RAE to elevate DOC levels effectively mitigates microbial energy limitations, thereby indirectly facilitating nutrient mineralization and availability [20]. The role of LMWOAs within RAE is also critical to the increased levels of NH4+-N, NO3−-N, and AP. LMWOAs enhance nitrogen availability through hydrogen and ionic bond interactions [44] and interact with soil metal ions such as iron, aluminum, and calcium, forming soluble chelates that reduce the binding of these metals to phosphates, thereby releasing fixed phosphorus [45]. This characteristic makes RAE particularly suitable for phosphorus-demanding crops, such as maize, enhancing their growth and development potential. In addition, LMWOAs stimulate microbial activity and enhance nutrient mobilization by increasing soil enzyme activity [44].
Soil enzymes, primarily derived from microbial activity, are essential for catalyzing biochemical reactions that sustain nutrient cycling and soil metabolism [46]. As sensitive indicators of soil biological fertility [47], enzyme activities reflect ecological changes and contribute directly to nutrient dynamics in soil ecosystems [48]. SC was identified as pivotal for sucrose hydrolysis, yielding glucose and fructose, which are critical substrates for carbon and nitrogen cycling [49]. SA hydrolyzes amide bonds to release ammonia and carboxylic acids [50], while SPE and NPT catalyze protein and peptide breakdown, converting organic nitrogen into plant-available forms [51,52]. S-NP, which releases phosphate from esters, serves as an indicator of microbial phosphorus demand [53]. Previous research has demonstrated that organic acids can enhance soil enzyme activities, stimulate nutrient mobilization, and improve soil fertility [54]. Our experimental results revealed significantly enhanced nutrient transformation rates, as indicated by elevated enzymatic activities in soils treated with the HR compared to control plots during both the 2023 and 2024 growing seasons. (Figure 3). Furthermore, ANOVA analyses revealed that RAE application significantly enhanced soil enzyme activities, demonstrating its effectiveness in promoting biochemical processes in the rhizosphere. Enhanced enzyme activity was also significantly associated with increased levels of available soil nutrients, highlighting their critical role in nutrient mobilization. The SQI and SEI evaluations (Figure 4) provided additional evidence that the HR treatment substantially improved soil quality and enzymatic functions, making it a potential fertilization strategy. Notably, soil pH remained consistent across all treatments (Figure 2h) and showed no significant correlation with enzymatic activities (Figure 7a). These findings suggest that RAE’s effects operate independently of pH modification, potentially mediated through alternative biochemical mechanisms.
The experimental results demonstrate that RAE application significantly enhances maize productivity in degraded agricultural soils, offering a promising solution for sustainable crop production in marginal lands. The enhancement of soil nutrient availability, particularly N and P, emerges as a critical factor governing maize yield potential [55]. During grain formation, maize needs to recycle accumulated nutrients in the plant, such as N and P, to meet the demands of developing kernels [56]. Therefore, increasing N and P accumulation in maize plants is essential for achieving higher yields. In this study, RAE application significantly enhanced N and P accumulation (Figure 5), which can be attributed to the improvement in soil nutrient conditions. Mantel’s test (Figure 7a) revealed a significant correlation between available soil nutrient and maize nutrient (N or P) accumulation. Elevated nutrient levels were associated with enhanced root nutrient uptake, plant biomass growth, and nutrient storage. The RAE significantly improved grain yield, kernel number per ear, and 1000-kernel weight in this study (Figure 6). These improvements were largely due to the enhanced levels of NH4+-N, NO3−-N, and AP, which promoted N and P accumulation and provided optimal conditions for grain formation. The correlation analysis (Figure 7b,c) revealed significant positive associations between N and P accumulation and yield components, highlighting the pivotal role of these nutrients in yield improvement.
The SEM and random forest analyses (Figure 8) further clarified the pathways by which RAE affects yield, identifying RAE, soil quality, enzyme activity, and maize N and P accumulation as significant contributing factors. Among these, maize P accumulation was identified as the most critical determinant of yield (Figure 8b), emphasizing the indispensable role of phosphorus in maize production. As an essential element in energy transfer, photosynthesis, and metabolic processes, phosphorus directly influences root system development, flowering, and grain formation [57]. An adequate phosphorus supply is thus vital for high-yield production [58]. This study also identified a significant positive relationship between maize N and P accumulation (Figure 8a), which is attributed to the synergistic interaction between N and P uptake. Nitrogen accumulation stimulates the expression of phosphate transporters in the root, enhancing phosphorus absorption, and phosphorus accumulation can boost energy metabolism again, thereby increasing nitrogen assimilation efficiency [59]. Although prior studies have suggested that elevated microbial enzyme activity may exacerbate soil carbon loss and intensify competition for nitrogen between plants and microbes [60], the SEM results (Figure 8a) indicated a significant positive influence of SEI on maize N accumulation. This finding highlights the mitigating role of RAE, which supplies carbon to microbes, alleviating competitive pressures and enhancing nutrient accumulations for maize. Notably, the HR group consistently outperformed the LR group, achieving higher soil nutrient levels, enzyme activity, maize nutrient accumulations, and yields across two years (2023 and 2024). These results demonstrated the potential of RAE as an effective strategy in maize cultivation.
5. Conclusions
RAE application demonstrated dual beneficial effects: (1) significantly increasing soil available nutrient concentrations (DOC, NH4+-N, NO3−-N, and AP) and enzymatic activities while minimizing nutrient competition between soil microbiota and maize plants and (2) exhibiting substantial potential for improving maize yields in low-fertility, degraded soils. These findings position RAE as a promising sustainable solution for enhancing agricultural productivity in marginal lands. These improvements contribute to the efficient accumulation of N and P in maize, ultimately leading to improved yields. Given its demonstrated capacity to potentially reduce fertilizer requirements while enhancing crop productivity (as evidenced in our study), RAE emerges as a sustainable and effective alternative to conventional fertilizers. These findings highlight its strong potential for broader agricultural adoption.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15040897/s1, Supplementary Method S1: Soil extracellular enzyme activity determination methods; Supplementary Method S2: Maize nutrient accumulation sampling and yield measurement methods. References [61,62,63] are cited in the Supplementary Materials.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.S. and H.X.; methodology, H.C.; software, H.C. and H.S.; formal analysis, W.Y., M.G. and X.Z.; investigation, H.C.; resources, W.Y. and H.X.; data curation, H.C. and H.S.; writing—original draft preparation, H.C.; writing—review and editing, H.C., H.S. and H.X.; visualization, H.C. and M.G.; supervision, W.Y. and H.X. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Key R&D Program of China, grant number 2023YFD1501200; the Key R&D Program of Liaoning Province, grant number 2024JH2/102400011; the Science and Technology Plan Project of Liaoning Province, grant number 2023JH2/101700358; and the Science and Technology Plan Project of Shenyang, grant number 24-216-2-02.
Data Availability Statement
All data presented in this study are contained within the article and the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the Fuxin Dryland Water-saving Technology Experimental Demonstration Base of the Chinese Academy of Sciences for offering the experimental site and assisting with relevant agronomical measures. We would like to thank Shuang Kong, Xiaohuan Lyu, and Yongqi Liu for their support in the experimental approach. We also thank Wenqiang Guo and Xiangyu Gao for their support in the collection of soil samples.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Nyirenda, H.; Mwangomba, W.; Nyirenda, E.M. Delving into possible missing links for attainment of food security in Central Malawi: Farmers’ perceptions and long term dynamics in maize (Zea mays L.) production. Heliyon 2021, 7, e07130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowswell, C. Maize in the Third World; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Vitousek, P.M.; Cassman, K.G.; Matson, P.A.; Bai, J.; Meng, Q.; Hou, P.; Yue, S.; Römheld, V. Integrated soil–crop system management for food security. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6399–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grassini, P.; Cassman, K.G. High-yield maize with large net energy yield and small global warming intensity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- OECD/FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2018–2027; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, X.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Liang, W. Organic substitutions improve soil quality and maize yield through increasing soil microbial diversity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; You, L.; Amini, M.; Obersteiner, M.; Herrero, M.; Zehnder, A.J.; Yang, H. A high-resolution assessment on global nitrogen flows in cropland. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8035–8040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Van Groenigen, K.J.; Hungate, B.A.; Cao, J.; Zhou, X.; Wang, R.-W. A keystone microbial enzyme for nitrogen control of soil carbon storage. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaaq1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, M.; Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Jiang, R.; Chen, X.; Davies, W.J.; Zhang, F. Improving crop productivity and resource use efficiency to ensure food security and environmental quality in China. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Bom, F.; Nunes, I.; Raymond, N.S.; Hansen, V.; Bonnichsen, L.; Magid, J.; Nybroe, O.; Jensen, L.S. Long-term fertilisation form, level and duration affect the diversity, structure and functioning of soil microbial communities in the field. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 122, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Wang, G.; Fan, C.; Zhuo, X.; Sha, L.; Kuang, Z.; Bi, J.; Cheng, T. Temporal accumulation and lag effects of precipitation on carbon fluxes in terrestrial ecosystems across semi-arid regions in China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2024, 356, 110189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tilman, D.; Jin, Z.; Smith, P.; Barrett, C.B.; Zhu, Y.; Burney, J.; D’Odorico, P.; Fantke, P.; Fargione, J. Climate change exacerbates the environmental impacts of agriculture. Science 2024, 385, eadn3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Yang, W.; Li, J. New progress on the second step of the mixed fermentation for vitamin C. J. Microbiol. 2021, 41, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, H.; Wang, L. Effect of a residue after evaporation from industrial vitamin C fermentation on chemical and microbial properties of alkali-saline soil. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 27, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Yuan, J.; He, X.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Q.; Shen, Q. Enrichment of beneficial cucumber rhizosphere microbes mediated by organic acid secretion. Hortic. Res. 2020, 7, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Hua, Y.; Wan, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, D. The abundance of nirS-type denitrifiers and anammox bacteria in rhizospheres was affected by the organic acids secreted from roots of submerged macrophytes. Chemosphere 2020, 240, 124903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.; Yan, Z.; Li, X. Effects of exogenous organic acids and flooding on root exudates, rhizosphere bacterial community structure, and iron plaque formation in Kandelia obovata seedlings. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Lu, Q.; Li, M.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wei, Z. Impact of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria inoculation methods on phosphorus transformation and long-term utilization in composting. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 241, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Sun, H.; Shi, M.; Wu, Q.; Ji, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.; Han, L.; Ruan, X.; et al. 2-Keto-L-Gulonic Acid Improved the Salt Stress Resistance of Non-heading Chinese Cabbage by Increasing L-Ascorbic Acid Accumulation. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 7184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.T.; Gao, M.F.; Yang, W.C.; Sun, H.; Kong, T.; Xu, H. Combined application of organic wastes and Trichoderma longibraciatum to promote vegetation restoration and soil quality on mining waste dump sites. Plant Soil 2025, 508, 567–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Sun, H.; Yang, W.; Gao, M.; Zhong, X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Z.; Xu, H. Potential utilization of vitamin C industrial effluents in agriculture: Soil fertility and bacterial community composition. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.; Yin, G.; Gu, J. Effects of stubble and mulching on soil erosion by wind in semi-arid China. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widdig, M.; Schleuss, P.M.; Biederman, L.A.; Borer, E.T.; Crawley, M.J.; Kirkman, K.P.; Seabloom, E.W.; Wragg, P.D.; Spohn, M. Microbial carbon use efficiency in grassland soils subjected to nitrogen and phosphorus additions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 146, 107815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.; Mulvaney, C. Nitrogen-total. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; Agronomy Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Hui, R.; Sui, T.; Yang, L.; Du, W.; Dong, Z. A 4-year field measurement of N2O emissions from a maize-wheat rotation system as influenced by partial organic substitution for synthetic fertilizer. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 263, 110384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsolnay, Á. Dissolved organic matter: Artefacts, definitions, and functions. Geoderma 2003, 113, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Wieder, W.R.; Reed, S.C.; Townsend, A.R. Experimental drought in a tropical rain forest increases soil carbon dioxide losses to the atmosphere. Ecology 2010, 91, 2313–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, P.; Liang, C.; Rubert-Nason, K.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Bao, X. Secondary successional forests undergo tightly-coupled changes in soil microbial community structure and soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, R.H.; Kurtz, L.T. Determination of total, organic, and available forms of phosphorus in soils. Soil Sci. 1945, 59, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pribyl, D.W. A critical review of the conventional SOC to SOM conversion factor. Geoderma 2010, 156, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimha, G.; Sridevi, A.; Reddy, A.V.S.; Banu, M.T.; Reddy, B.R. Effect of cotton ginning mill industrial effluents on soil dehydrogenase, phosphatase, amylase and invertase enzyme activities. Int. J. Agric. Food Sci. 2012, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Frankenberger, W.T., Jr.; Tabatabai, M. Amidase activity in soils: I. Method of assay. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiya-Cork, K.; Sinsabaugh, R.; Zak, D. The effects of long term nitrogen deposition on extracellular enzyme activity in an Acer saccharum forest soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2002, 34, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladd, J.; Butler, J. Short-term assays of soil proteolytic enzyme activities using proteins and dipeptide derivatives as substrates. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1972, 4, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, B.T.; Le, L.B.; Pham, L.P.; Nguyen, H.T.; Tran, T.D.; Van Thai, N. The effects of biochar on the biomass yield of elephant grass (Pennisetum purpureum Schumach) and properties of acidic soils. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 161, 113224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, M.; Lal, R.; Ebinger, M. Determining soil quality indicators by factor analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Y. Long-term straw mulching with nitrogen fertilization increases nutrient and microbial determinants of soil quality in a maize–wheat rotation on China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Liang, J.H.; He, Y.Y.; Hu, Q.J.; Yu, S. Effect of land use on soil enzyme activities at karst area in Nanchuan, Chongqing, Southwest China. Plant Soil Environ. 2014, 60, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sun, J.; Zhang, F.; Li, X.; Yang, S.; Rengel, Z. Wheat/maize or wheat/soybean strip intercropping: I. Yield advantage and interspecific interactions on nutrients. Field Crops Res. 2001, 71, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Sun, J.; Bao, X.; Christie, P.; Zhang, F.; Li, L. Contribution of interspecific interactions and phosphorus application to sustainable and productive intercropping systems. Field Crops Res. 2013, 154, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, B.; Yue, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhai, B.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, W.; Li, Z.; Zamanian, K. Effects of plastic and straw mulching on soil microbial P limitations in maize fields: Dependency on soil organic carbon demonstrated by ecoenzymatic stoichiometry. Geoderma 2021, 388, 114928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Hou, Z.; Su, T.; Lin, Z.; Liu, A.; Cai, L. Characteristics and correlation of soil low-molecular-weight organic acids and nutrients in four plantations in red soil area of south China. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 6339–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Li, X.; Wei, M.; Zeng, G.; Hou, S.; Li, D.; Xu, H. Elucidation of the mechanisms into effects of organic acids on soil fertility, cadmium speciation and ecotoxicity in contaminated soil. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, M.; Jalali, M. Effect of low-molecular-weight organic acids on the release of phosphorus from amended calcareous soils: Experimental and modeling. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 4179–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Tarin, M.W.K.; Zhang, Y.; Han, Y.; Rong, J.; Cai, X.; Chen, L.; Shi, C.; Zheng, Y. Patterns of soil microorganisms and enzymatic activities of various forest types in coastal sandy land. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 28, e01625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, X.; Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, G. Effects of green manure continuous application on soil microbial biomass and enzyme activity. J. Plant Nutr. 2014, 37, 498–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G.; DeForest, J.L.; Marxsen, J.; Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Stromberger, M.E.; Wallenstein, M.D.; Weintraub, M.N.; Zoppini, A. Soil enzymes in a changing environment: Current knowledge and future directions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 58, 216–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stemmer, M.; Gerzabek, M.H.; Kandeler, E. Invertase and xylanase activity of bulk soil and particle-size fractions during maize straw decomposition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Li, J.; Liu, K.; Zhang, H.; Wei, X.; Shao, X. Variations in soil properties rather than functional gene abundances dominate soil phosphorus dynamics under short-term nitrogen input. Plant Soil 2021, 469, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhu, Q.; Wen, D.; Yang, L.; Ni, K.; Xu, X.; Cao, J.; Meng, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, J. Stimulation of organic N mineralization by N-acquiring enzyme activity alleviates soil microbial N limitation following afforestation in subtropical karst areas. Plant Soil 2024, 504, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddela, N.R.; Golla, N.; Vengatampalli, R.; Naga Raju, M.; Golla, N.; Vengatampalli, R. Soil Protease. In Soil Enzymes: Influence of Sugar Industry Effluents on Soil Enzyme Activities; Springer International Publishing: Cham, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.Q.; Dou, Y.X.; Cheng, H.; Liu, L.X.; An, S.S. Linkage between soil ectoenzyme stoichiometry ratios and microbial diversity following the conversion of cropland into grassland. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 314, 107418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macias-Benitez, S.; Maria Garcia-Martinez, A.; Caballero Jimenez, P.; Miguel Gonzalez, J.; Tejada Moral, M.; Parrado Rubio, J. Rhizospheric organic acids as biostimulants: Monitoring feedbacks on soil microorganisms and biochemical properties. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Rodríguez, J.V.; Salazar-Vidal, M.N.; Chávez Montes, R.A.; Massange-Sánchez, J.A.; Gillmor, C.S.; Sawers, R.J. Low nitrogen availability inhibits the phosphorus starvation response in maize (Zea mays ssp. mays L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, P.; Li, S.; Yu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C. Post-silking accumulation and partitioning of dry matter, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium in maize varieties differing in leaf longevity. Field Crops Res. 2013, 144, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, N.C.M.; Galindo, F.S.; Gazola, R.P.D.; Dupas, E.; Rosa, P.A.L.; Mortinho, E.S.; Filho, M.C.M.T. Corn yield and phosphorus use efficiency response to phosphorus rates associated with plant growth promoting bacteria. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Zhang, L.; Cui, R.; Liu, Q.; Du, J.; Cao, G.; Xiang, C. Effects of Combined Application of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Fertilizers on Photosynthetic Characteristics of Silage Corn, Laying the Foundation of Agricultural Information. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Machine Learning and Big Data Analytics for IoT Security and Privacy: SPIoT-2020, Fuyang, China, 20–21 October 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; Volume 1, pp. 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Spohn, M. Interactions of nitrogen and phosphorus in plant nutrition—Analysis of a 60-years old field experiment. Plant Soil 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, M.E.; Fraterrigo, J.M. Plant–microbial competition for nitrogen increases microbial activities and carbon loss in invaded soils. Oecologia 2017, 184, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossard, A.; Gerull, L.; Mutz, M.; Gessner, M.O. Disconnect of microbial structure and function: Enzyme activities and bacterial communities in nascent stream corridors. ISME J. 2012, 6, 680–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, M.-C.; Wood, M.; Jarvis, S. A microplate fluorimetric assay for the study of enzyme diversity in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1633–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- German, D.P.; Weintraub, M.N.; Grandy, A.S.; Lauber, C.L.; Rinkes, Z.L.; Allison, S.D. Optimization of hydrolytic and oxidative enzyme methods for ecosystem studies. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1387–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).