Influence of Cropping Regimes on the Availability and Existing Forms of Phosphorus in the Albic Luvisols in Northeast China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Sample Collection
2.4. Soil Analysis
2.5. Determination of Maize Yield
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Influence of Cropping Regimes on Maize Yields
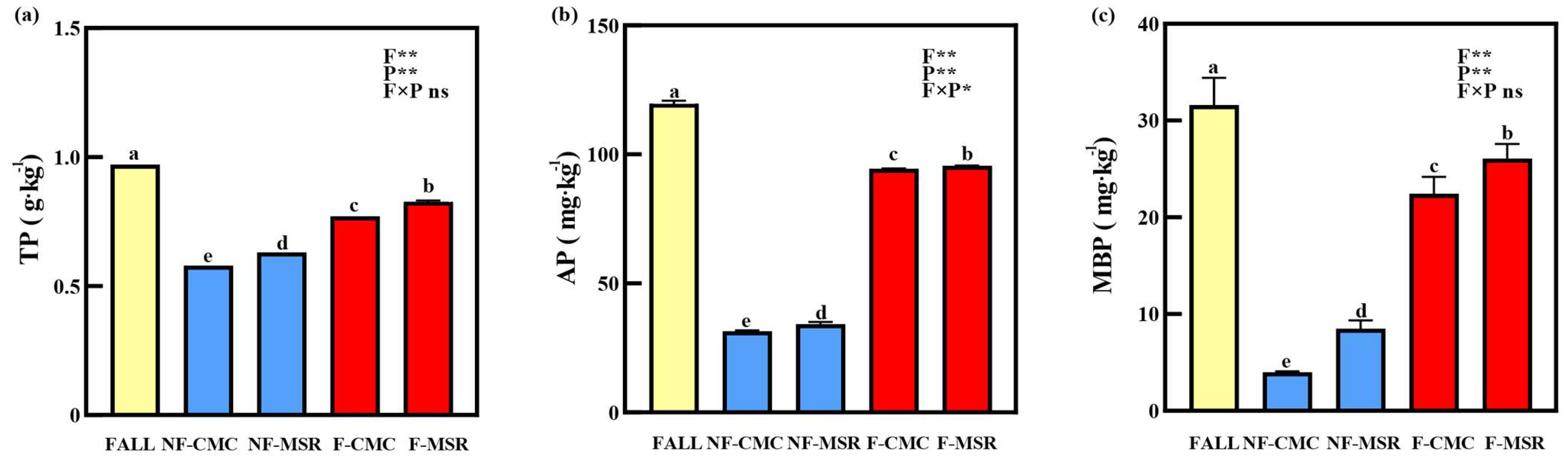
3.2. Effects of Cropping Regimes on TP, AP, and MBP in the Soil
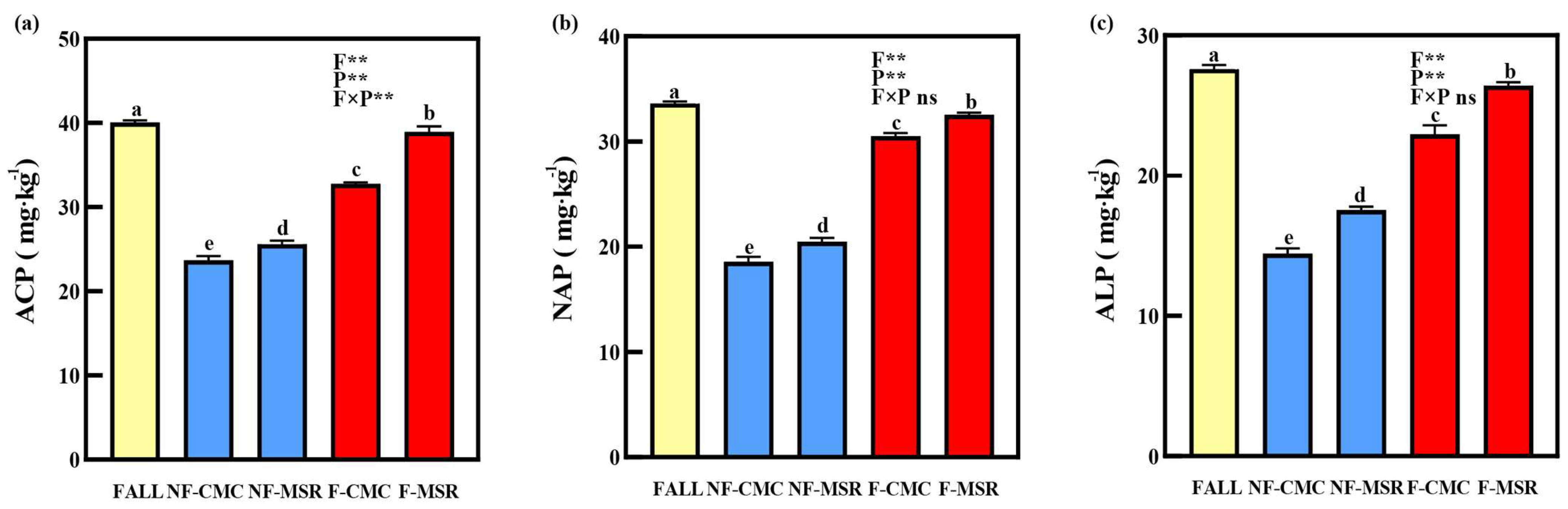
3.3. Impacts of Cropping Regimes on Activity of Phosphatase in Soil
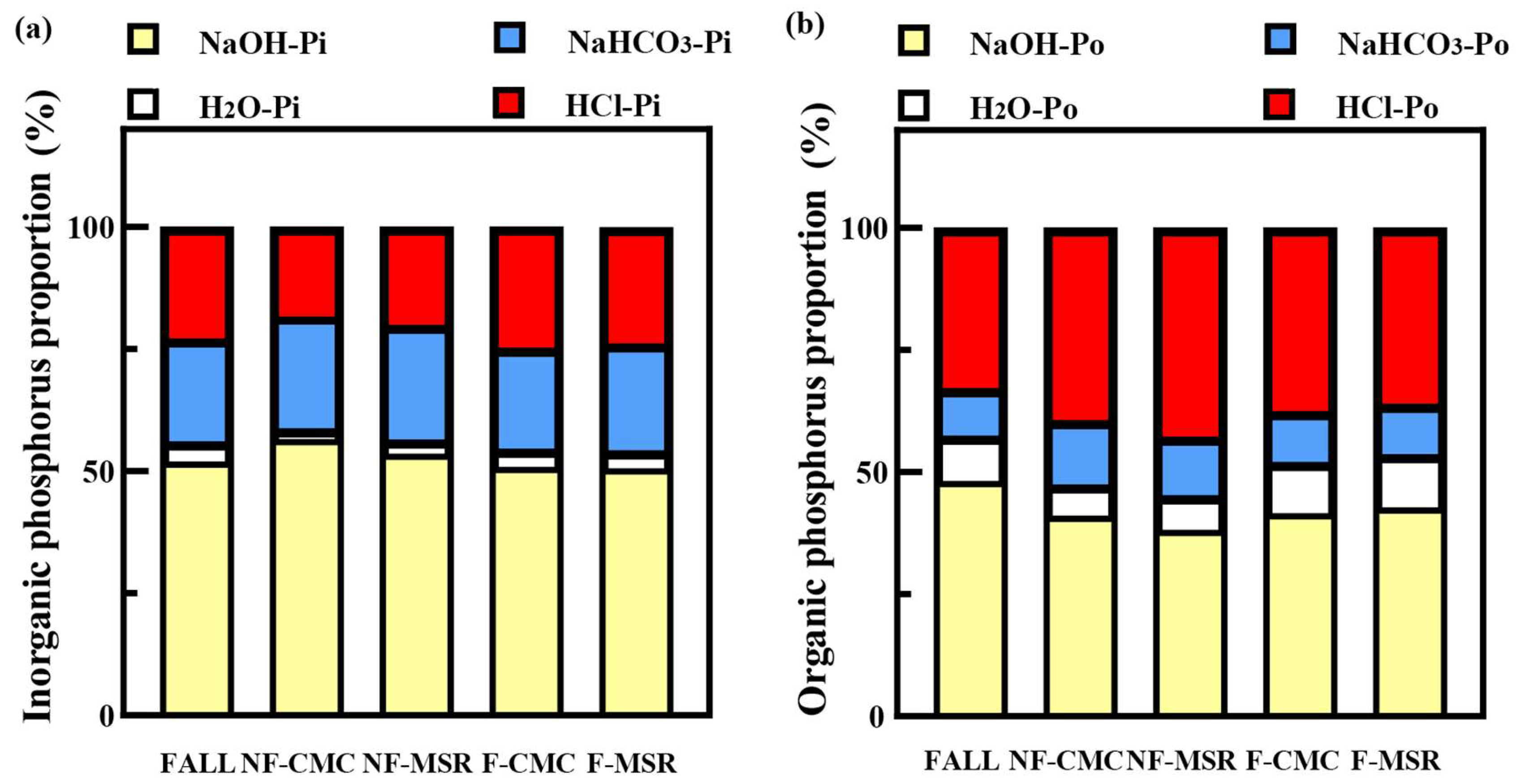
3.4. Impact of Cropping Regimes on the P Forms in Soil
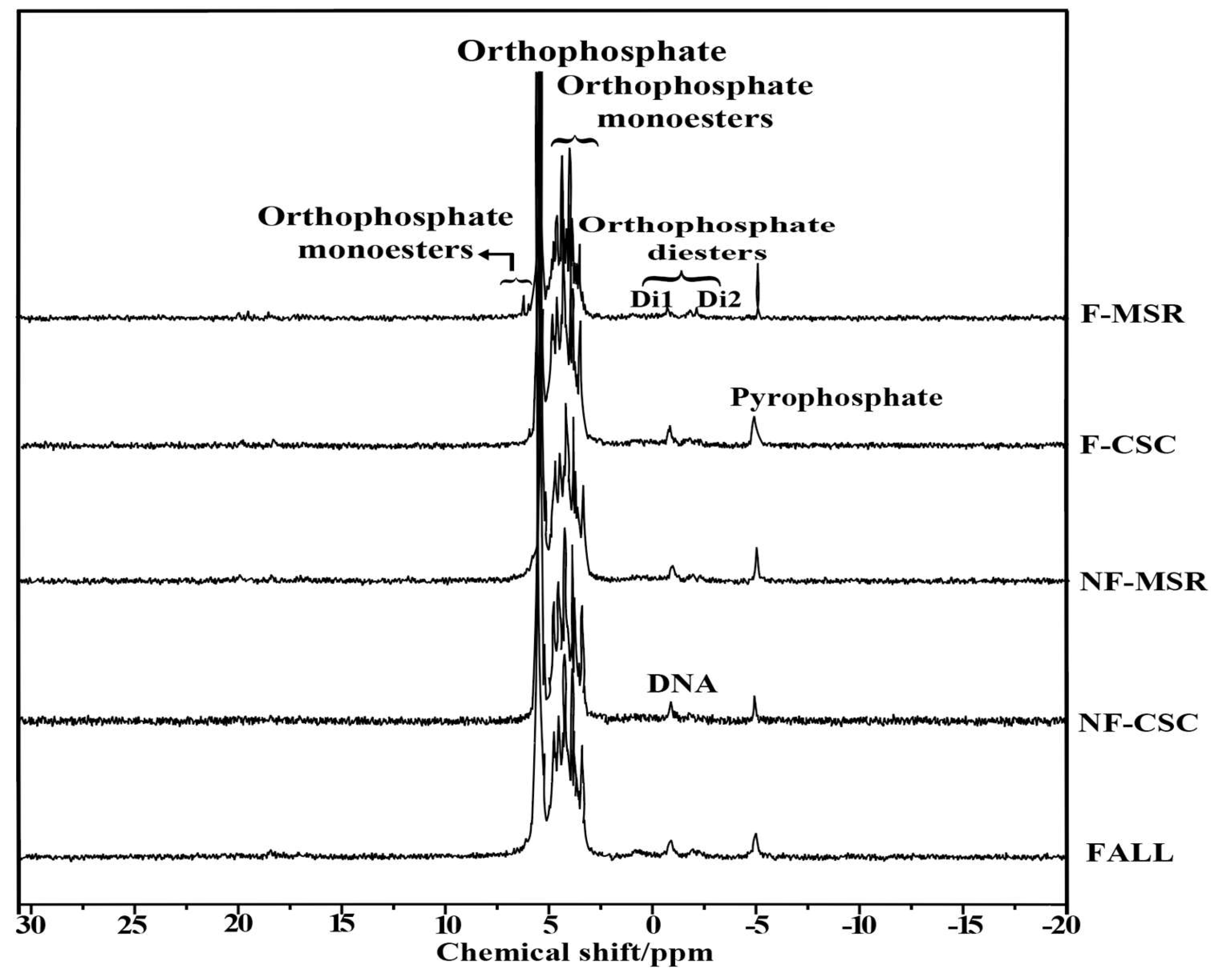
3.5. 31P-NMR Spectroscopy of Soil P Forms Under Different Planting Regimes
3.6. Key Soil Factors Influencing the P Forms in Soil Under Different Cropping Regimes
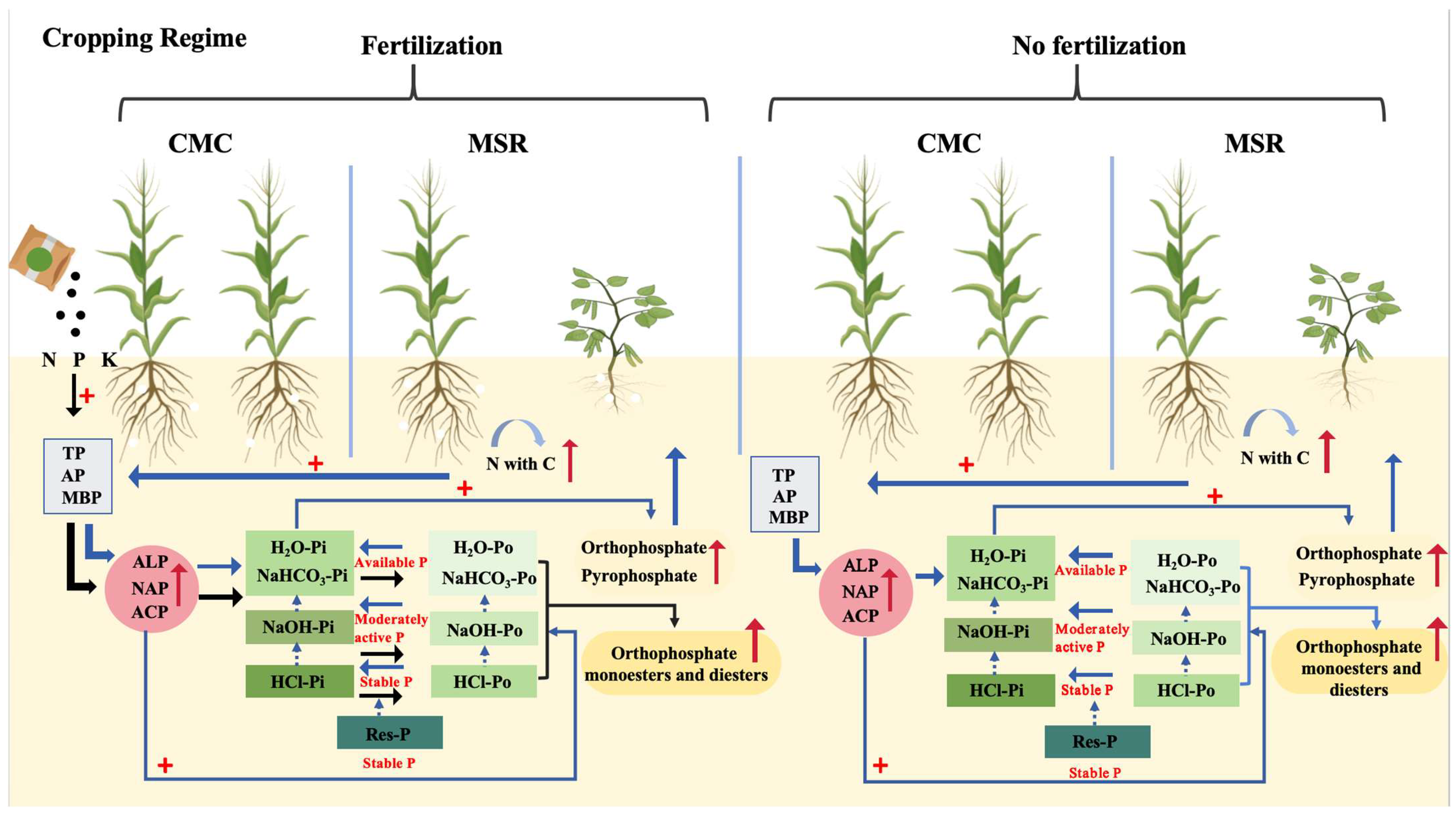
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Maize–Soybean Rotation on Maize Yields and P-Utilization Efficiency
4.2. Impacts of Maize–Soybean Rotation on P Availability and Forms in Soils
4.3. Key Factors Influencing the P Availability and Forms in Soil Under Different Cropping Regimes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F. Phosphorus dynamics: From soil to plant. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.Z.; Tang, C.; Song, C.Y.; Wang, S.Y.; Qiao, Y.F. Phosphorus characteristics correlate with soil fertility of albic luvisols. Plant Soil 2005, 270, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P. Roots of the second green revolution. Aust. J. Bot. 2007, 55, 493–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Li, H.; Yang, X.; Zhou, B.; Shi, X.; Wang, B.; Li, D.; Shen, J.; Chen, Q.; Qin, W.; et al. The critical soil P levels for crop yield, soil fertility and environmental safety in different soil types. Plant Soil 2013, 372, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.M.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Burt, T.P.; Chan, N.I.; Elser, J.J.; Haygarth, P.M.; Howden, N.J.; Jarvie, H.P.; Lyu, Y.; Peterson, H.M.; et al. Long-term accumulation and transport of anthropogenic phosphorus in three river basins. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochian, L.V. Rooting for more phosphorus. Nature 2012, 488, 466–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, G.K.; Bennett, E.M.; Potter, P.A.; Ramankutty, N. Agronomic phosphorus imbalances across the world’s croplands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 3086–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringeval, B.; Demay, J.; Goll, D.S.; He, X.; Wang, Y.P.; Hou, E.; Matej, S.; Erb, K.H.; Wang, R.; Augusto, L.; et al. A global dataset on phosphorus in agricultural soils. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.O.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Change 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elser, J.; Bennett, E. A broken biogeochemical cycle. Nature 2011, 478, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, S.I.; Itahashi, S.; Kimura, R.; Inoue, T. Trends of phosphate fertilizer demand and phosphate balance in farmland soils in Japan. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2003, 49, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Attar, I.; Hnini, M.; Taha, K.; Aurag, J. Phosphorus availability and its sustainable use. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 5036–5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Müller, T.; Lakshmanan, P.; Liu, Y.; Liang, T.; Yang, H.; Chen, X. Soil phosphorus availability and fractionation in response to different phosphorus sources in alkaline and acid soils: A short-term incubation study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfenstein, J.; Ringeval, B.; Tamburini, F.; Mulder, V.L.; Goll, D.S.; He, X.; Alblas, E.; Wang, Y.; Morrill, A.; Frossard, E. Understanding soil phosphorus cycling for sustainable development: A review. One Earth 2024, 7, 1727–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacometti, C.; Mazzon, M.; Cavani, L.; Triberti, L.; Baldoni, G.; Ciavatta, C.; Marzadori, C. Rotation and fertilization effects on soil quality and yields in a long term field experiment. Agronomy 2021, 11, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.M.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, J.Z.; Zhou, Z.J.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Z.H.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhang, L.F. Crop rotations increased soil ecosystem multifunctionality by improving keystone taxa and soil properties in potatoes. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1034761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhametov, A.; Ansabayeva, A.; Efimov, O.; Kamerova, A. Influence of crop rotation, the treatment of crop residues, and the application of nitrogen fertilizers on soil properties and maize yield. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2024, 88, 2227–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Yan, B.; Gao, Y.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Xu, P.; Wang, H.; Wen, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Crop yield and water use efficiency in response to long-term diversified crop rotations. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1024898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Ma, J.; Wu, L.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Bai, L.; Wang, Z. Effect of Organic Manure on Crop Yield, Soil Properties, and Economic Benefit in Wheat-Maize-Sunflower Rotation System, Hetao Irrigation District. Plants 2024, 13, 2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuruzzaman, M.; Lambers, H.; Bolland, M.D.; Veneklaas, E.J. Phosphorus benefits of different legume crops to subsequent wheat grown in different soils of Western Australia. Plant Soil. 2005, 271, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łukowiak, R.; Grzebisz, W.; Sassenrath, G.F. New insights into phosphorus management in agriculture—A crop rotation approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 1062–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Wang, F.; Shao, M.; Huang, L.; Xie, Y.; Xu, Y.; Kong, L. Effects of rotations with legume on soil functional microbial communities involved in phosphorus transformation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 661100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, C.; Li, D.; Wander, M.M.; Kent, A.D. Long-term fertilizer and crop-rotation treatments differentially affect soil bacterial community structure. Plant Soil. 2017, 413, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ren, T.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liao, S.; Li, X.; Cong, R.; Lu, J. Rotation with oilseed rape as the winter crop enhances rice yield and improves soil indigenous nutrient supply. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 212, 105065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Ruan, Y.; Sun, W.; Wang, S.; Wang, H.; Hang, Y.; Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; et al. Metagenomes reveal the effect of crop rotation systems on phosphorus cycling functional genes and soil phosphorus avail–ability. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 364, 108886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xia, K.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Cui, J. Maize, Peanut, and Millet Rotations Improve Crop Yields by Altering the Microbial Community and Chemistry of Sandy Saline–Alkaline Soils. Plants 2024, 13, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X. The characteristic and influence factors of extinction depth of shallow groundwater on the high-latitude region: A case study on the Sanjiang Plain, northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 6695–6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, L.; Zhang, W.; Sun, Y.; Wu, D.; Meng, J.; Chen, W. Effects of biochar and straw returning on the key cultivation limitations of Albic soil and soybean growth over 2 years. Catena 2019, 173, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campdelacreu Rocabruna, P.; Domene, X.; Preece, C.; Peñuelas, J. Relationship among soil biophysicochemical properties, agricultural practices and climate factors influencing soil phosphatase activity in agricultural land. Agriculture 2024, 14, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesołowska, S.; Futa, B.; Myszura, M.; Kobyłka, A. Residual effects of different cropping systems on physicochemical properties and the activity of phosphatases of soil. Agriculture 2022, 12, 693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In The International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, R.K. Methods for Soil Agrochemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Brookes, P.C.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiessen, H.; Moir, J.O. Characterization of Available P by Sequential Extraction; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1993; pp. 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, B.L.; Mahieu, N.; Condron, L.M. Phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectral assignments of phosphorus compounds in soil NaOH–EDTA extracts. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2003, 67, 497–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 37Aspila, K.I.; Agemian, H.; Chau, A.S.Y. A semi-automated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphate in sediments. Analyst 1976, 101, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cade-Menun, B.; Liu, C.W. Solution phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of soils from 2005 to 2013: A review of sample preparation and experimental parameters. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2014, 78, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Yang, Y.; Song, J.; Shan, F.; Lyu, X.; Yan, S.; Wang, C.; Song, Q.; Ma, C. Analysis of the beneficial effects of prior soybean cultivation to the field on corn yield and soil nitrogen content. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1413507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havlin, J.; Heiniger, R. Soil fertility management for better crop production. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinkwater, L.E.; Wagoner, P.; Sarrantonio, M. Legume-based cropping systems have reduced carbon and nitrogen losses. Nature 1998, 396, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, H. Optimizing the nitrogen use efficiency in vegetable crops. Nitrogen 2024, 5, 106–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, T.O.; Post, W.M. Soil organic carbon sequestration by tillage and crop rotation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2022, 66, 1930–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiemann, L.K.; Grandy, A.S.; Atkinson, E.E.; Marin-Spiotta, E.; McDaniel, M.D. Crop rotational diversity enhances soil microbial networks and organic carbon. Ecol. Appl. 2015, 18, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.E.; Lynch, J.P.; Ryan, P.R.; Delhaize, E.; Smith, F.A.; Smith, S.E.; Simpson, R.J. Plant and microbial strategies to improve phosphorus efficiency in agriculture. Plant Soil 2011, 349, 121–156. [Google Scholar]
- Gentry, L.F.; Ruffo, M.L.; Below, F.E. Identifying factors controlling the continuous corn yield penalty. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellazzi, M.S.; Wood, G.A.; Burgess, P.J.; Morris, J.; Conrad, K.F.; Perry, J.N. A systematic representation of crop rotations. Agric. Syst. 2008, 97, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvagiotti, F.; Cassman, K.G.; Specht, J.E.; Walters, D.T.; Weiss, A.; Dobermann, A. Nitrogen uptake, fixation and response to fertilizer N in soybeans: A review. Field Crops Res. 2008, 108, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snapp, S.S.; Blackie, M.J.; Gilbert, R.A.; Bezner-Kerr, R.; Kanyama-Phiri, G.Y. Biodiversity can support a greener revolution in Africa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 20840–20845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, S.; Mathesius, U. The role of flavonoids in root-rhizosphere signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 3429–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartini, N.L.; Saifulloh, M.; Trigunasih, N.M.; Sukmawati, N.M.S.; Mega, I. Impact of Long-Term Continuous Cropping on Soil Nutrient Depletion. Ecol. Eng. Environ. Technol. 2024, 25, 191953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Sui, P. Changes in soil microbial biomass, diversity, and activity with crop rotation in cropping systems: A global synthesis. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 186, 104815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsinger, P. Bioavailability of soil inorganic P in the rhizosphere as affected by root-induced chemical changes: A review. Plant Soil. 2001, 237, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, F.; Li, Q.; Solanki, M.K.; Wang, Z.; Xing, Y.X.; Dong, D.F. Soil phosphorus transformation and plant uptake driven by phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1383813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagno, L.N.; Sannazzaro, A.I.; Gonzalez, M.E.; Pieckenstain, F.L.; Estrella, M.J. Phosphobacteria as key actors to overcome phosphorus deficiency in plants. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2021, 178, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, G.; Sheng, E.; Chen, Z.; Yuan, J.; Lu, G.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Y. The forms and classification methods of phosphorus in soil: Research progress. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2023, 39, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Hu, M.; Wu, H.; Chen, D. National estimates of environmental thresholds for upland soil phosphorus in China based on a meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Giagnoni, L.; Renella, G.; Puglisi, E.; Ceccanti, B.; Masciandaro, G.; Fornasier, F.; Marinari, S.A.R.A. Soil enzymology: Classical and molecular approaches. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2012, 48, 743–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgaroui, N.; Berthomieu, P.; Rouached, H.; Hanin, M. The secretion of the bacterial phytase PHY-US 417 by Arabidopsis roots reveals its potential for increasing phosphate acquisition and biomass production during co-growth. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2016, 14, 1914–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, M.; El-Naggar, A.H.; Usman, A.R.A.; Abduljabbar, A.; Vithanage, M.; Elfaki, J.; Al-Faraj, A.; Al-Wabel, M. Aging effects of organic and inorganic fertilizers on phosphorus fractionation in a calcareous Sandy Loam Soil. Pedosphere 2018, 28, 873–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltangheisi, A.; Rodrigues, M.; Coelho, M.J.A.; Gasperini, A.M.; Sartor, L.R.; Pavinato, P.S. Changes in soil phosphorus lability promoted by phosphate sources and cover crops. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 179, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltangheisi, A.; Teles, A.P.B.; Sartor, L.R.; Pavinato, P.S. Cover cropping may alter legacy phosphorus dynamics under long-term fertilizer addition. Front. Environ. Sci. 2020, 8, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margalef, O.; Sardans, J.; Maspons, J.; Molowny-Horas, R.; Fernández-Martínez, M.; Janssens, I.A.; Richter, A.; Ciaia, P.; Obersteiner, M.; Peñuelas, J. The effect of global change on soil phosphatase activity. Global Change Biol. 2021, 27, 5989–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, P.; Turner, B.L.; Lambers, H.; Laliberté, E. Foliar nutrient concentrations and resorption efficiency in plants of contrasting nutrient-acquisition strategies along a 2-million-year dune chronosequence. J. Ecol. 2014, 102, 396–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Hu, Z.; Fan, Y.; Hua, B.; Yang, W.; Pang, S.; Mao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, K.; Fadda, C.; et al. Effects of leguminous green manure–crop rotation on soil enzyme activity and stoichiometry. J. Plant Ecol. 2024, 17, rtae065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, D.; Wei, Y.; He, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, S. Changes in soil phosphorus availability and microbial community structures in rhizospheres of oilseed rapes induced by intercropping with white lupins. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, H.Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, D.; Guan, Q. Soil labile organic carbon and carbon-cycle enzyme activities under different thinning intensities in Chinese fir plantations. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 107, 162–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickings, K.; Grandy, A.S.; Reed, S.C.; Cleveland, C.C. The origin of litter chemical complexity during decomposition. Ecol. Lett. 2012, 15, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Pu, Y.; Li, T.; Xu, X.; Jia, Y.; Deng, O.; Gong, G. Dynamics of soil labile organic carbon fractions and C-cycle enzyme activities under straw mulch in Chengdu Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, S.M.; Sun, J.H.; Zhou, L.L.; Bao, X.G.; Zhang, H.G.; Zhang, F.S. Diversity enhances agricultural productivity via rhizosphere phosphorus facilitation on phosphorus-deficient soils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11192–11196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Berumen, J.A.; de la Torre, J.A.F.; de Los Santos-Villalobos, S.; Espinoza-Canales, A.; Echavarría-Cháirez, F.G.; Gutiérrez-Bañuelos, H. Phosphorus dynamics and sustainable agriculture: The role of microbial solubilization and innovations in nutrient management. Curr. Res. Microb. Sci. 2025, 8, 100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ren, T.; Yan, J.; Zhu, D.; Liao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Cong, R.; Li, X.; Lu, J. Straw returning mediates soil microbial biomass carbon and phosphorus turnover to enhance soil phosphorus availability in a rice-oilseed rape rotation with different soil phosphorus levels. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 335, 107991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redel, Y.D.; Escudey, M.; Alvear, M.; Conrad, J.; Borie, F. Effects of tillage and crop rotation on chemical phosphorus forms and some related biological activities in a Chilean Ultisol. Soil Use Manag. 2011, 27, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleixo, S.; Gama-Rodrigues, A.C.; Gama-Rodrigues, E.F.; Campello, E.F.C.; Silva, E.C.; Schripsema, J. Can soil phosphorus availability in tropical forest systems be increased by nitrogen-fixing leguminous trees? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Xu, L.; Zong, N.; Zhang, J.; He, N. Impacts of climate warming on soil phosphorus forms and transformation in a Tibetan alpine meadow. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 2545–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, K.; Glaser, K.; Mutz, J.E.; Karsten, U.; MacLennan, A.; Hu, Y.; Michalik, D.; Kruse, J.; Eckhardt, K.U.; Schall, P.; et al. Biological soil crusts of temperate forests: Their role in P cycling. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 109, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmieder, F.; Bergström, L.; Riddle, M.; Gustafsson, J.P.; Klysubun, W.; Zehetner, F.; Gondron, L.; Kirchmann, H. Phosphorus speciation in a long-term manure-amended soil profile–Evidence from wet chemical extraction, 31P-NMR and P K-edge XANES spectroscopy. Geoderma 2018, 322, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


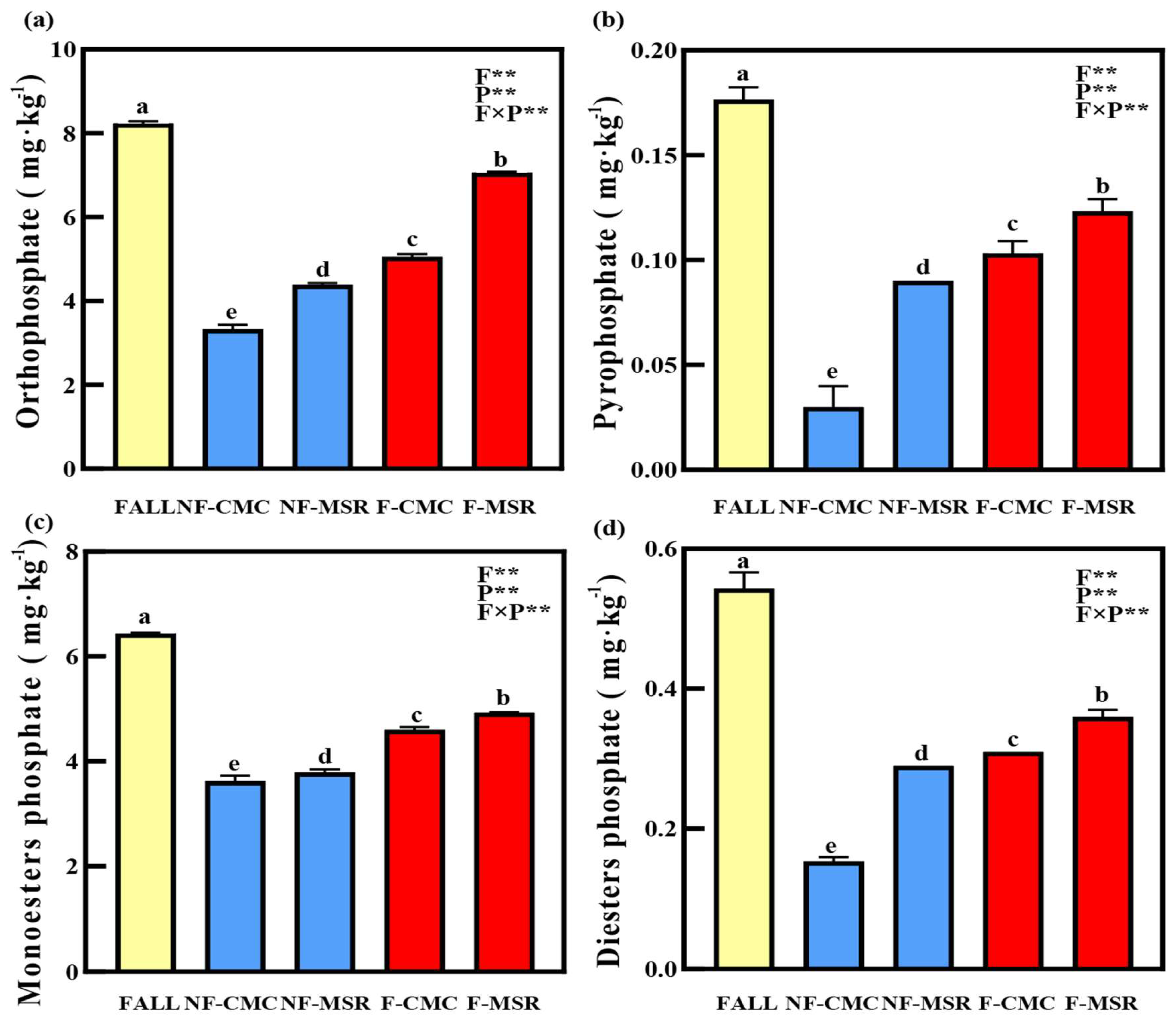
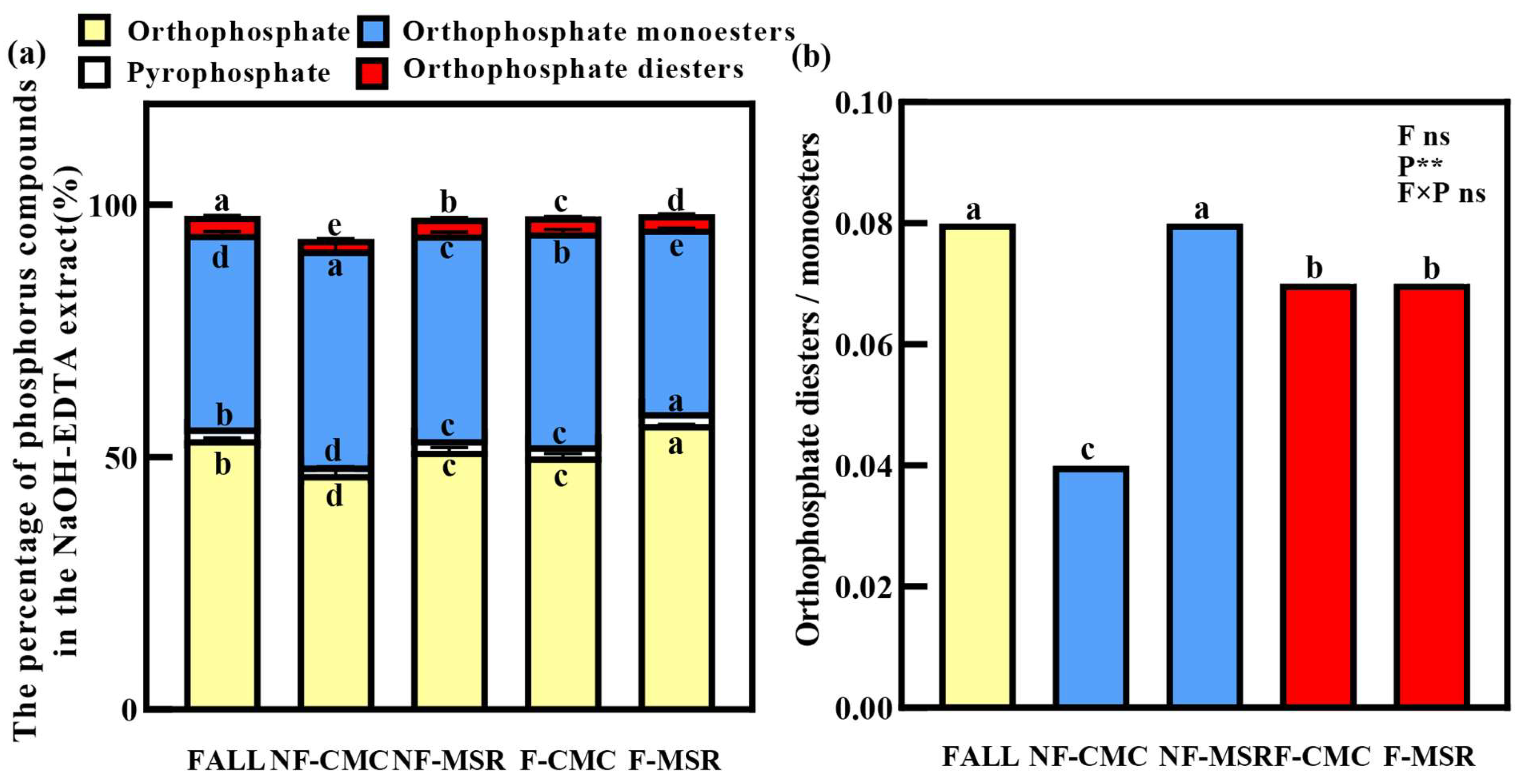

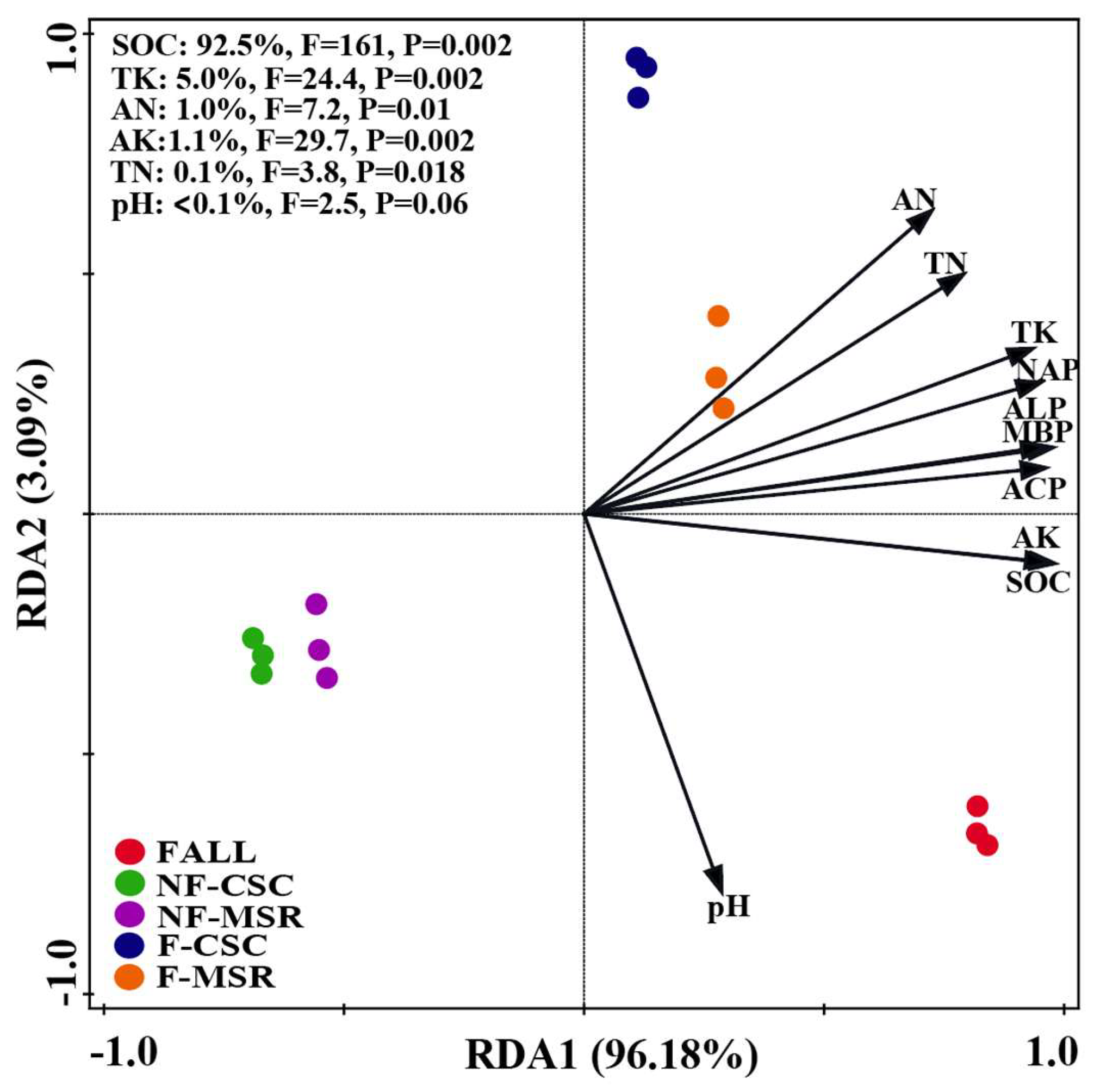

| Soil Samples | pH | SOC (g·kg−1) | TN (g·kg−1) | AN (mg·kg−1) | TK (g·kg−1) | AK (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Original soil | 5.25 ± 0.01 | 25.65 ± 0.87 | 3.35 ± 0.29 | 153.12 ± 3.44 | 8.18 ± 0.02 | 31.08 ± 0.53 |
| FALL | 5.68 ± 0.01 a | 24.90 ± 0.54 a | 2.20 ± 0.00 c | 275.40 ± 1.98 c | 21.44 ± 0.19 a | 655.38 ± 1.73 a |
| NF-CMC | 5.15 ± 0.02 b | 14.13 ± 0.18 e | 2.10 ± 0.00 e | 170.51 ± 0.75 e | 12.09 ± 0.04 e | 217.33 ± 1.52 e |
| NF-MSR | 5.14 ± 0.03 b | 16.48 ± 0.06 d | 2.13 ± 0.00 d | 195.55 ± 1.30 d | 12.74 ± 0.09 d | 316.34 ± 2.06 d |
| F-CMC | 4.87 ± 0.01 c | 19.44 ± 0.02 c | 2.25 ± 0.00 b | 325.48 ± 1.50 b | 20.40 ± 0.07 c | 401.99 ± 1.52 c |
| F-MSR | 4.66 ± 0.04 d | 20.01 ± 0.04 b | 2.28 ± 0.00 a | 339.72 ± 0.75 a | 20.90 ± 0.05 b | 545.29 ± 1.13 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geng, Y.; Yu, H.; Sun, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Li, C.; Zhang, J. Influence of Cropping Regimes on the Availability and Existing Forms of Phosphorus in the Albic Luvisols in Northeast China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040827
Geng Y, Yu H, Sun Y, Cao Z, Li S, Liu H, Li C, Zhang J. Influence of Cropping Regimes on the Availability and Existing Forms of Phosphorus in the Albic Luvisols in Northeast China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040827
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeng, Yidan, Honghao Yu, Yuanhong Sun, Zhiyuan Cao, Siyu Li, Hang Liu, Cuilan Li, and Jinjing Zhang. 2025. "Influence of Cropping Regimes on the Availability and Existing Forms of Phosphorus in the Albic Luvisols in Northeast China" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040827
APA StyleGeng, Y., Yu, H., Sun, Y., Cao, Z., Li, S., Liu, H., Li, C., & Zhang, J. (2025). Influence of Cropping Regimes on the Availability and Existing Forms of Phosphorus in the Albic Luvisols in Northeast China. Agronomy, 15(4), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040827





