Heavy Metals Distribution and Source Identification in Contaminated Agricultural Soils: Isotopic and Multi-Model Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Preparation
2.3. Chemical Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Soil Properties, Concentrations, Distributions, and Risk Assessments of Heavy Metals in the Study Area
3.2. Properties, Heavy Metal Concentration in Soil Profile
3.3. Source Identification of Heavy Metal in Soil
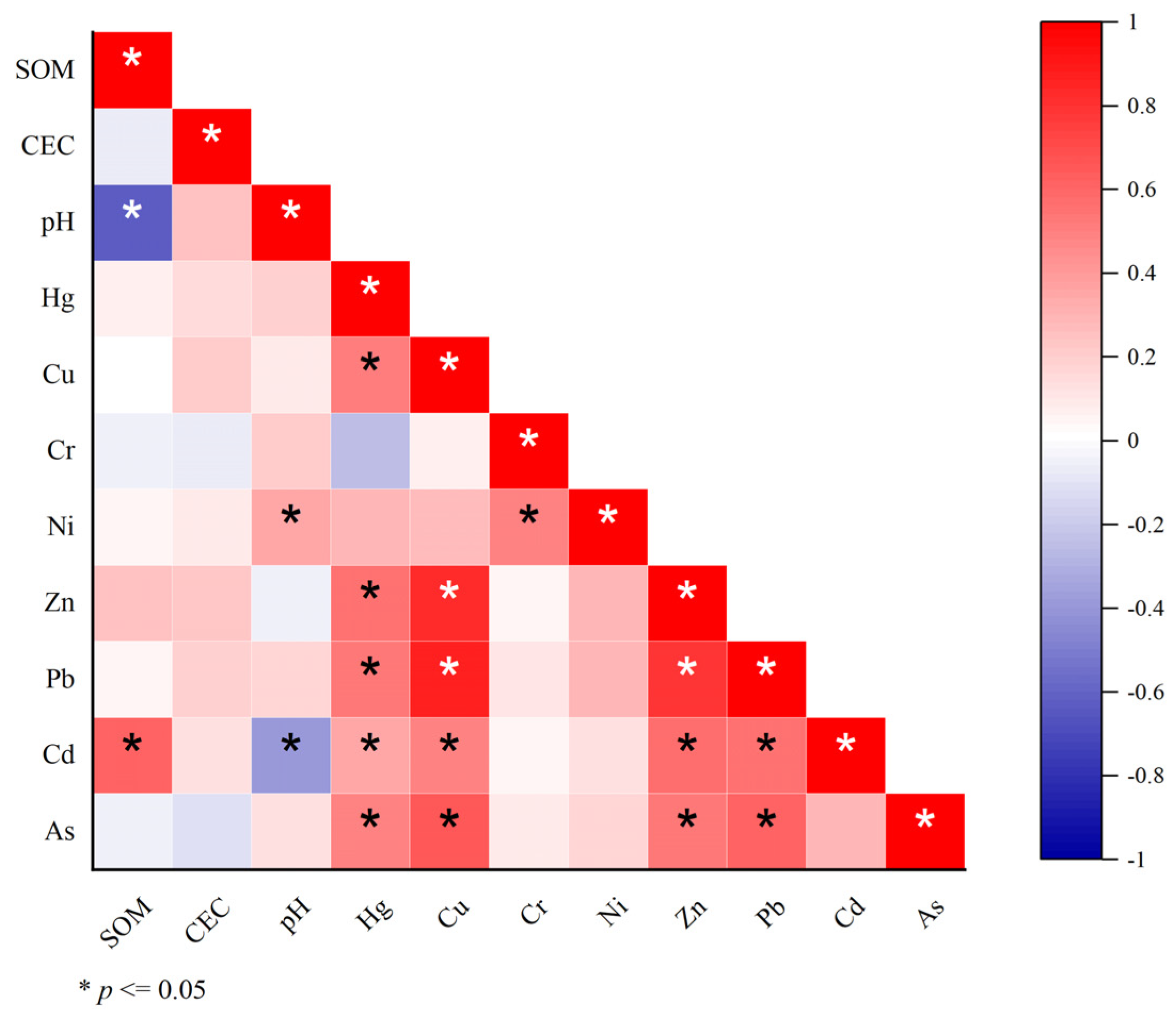
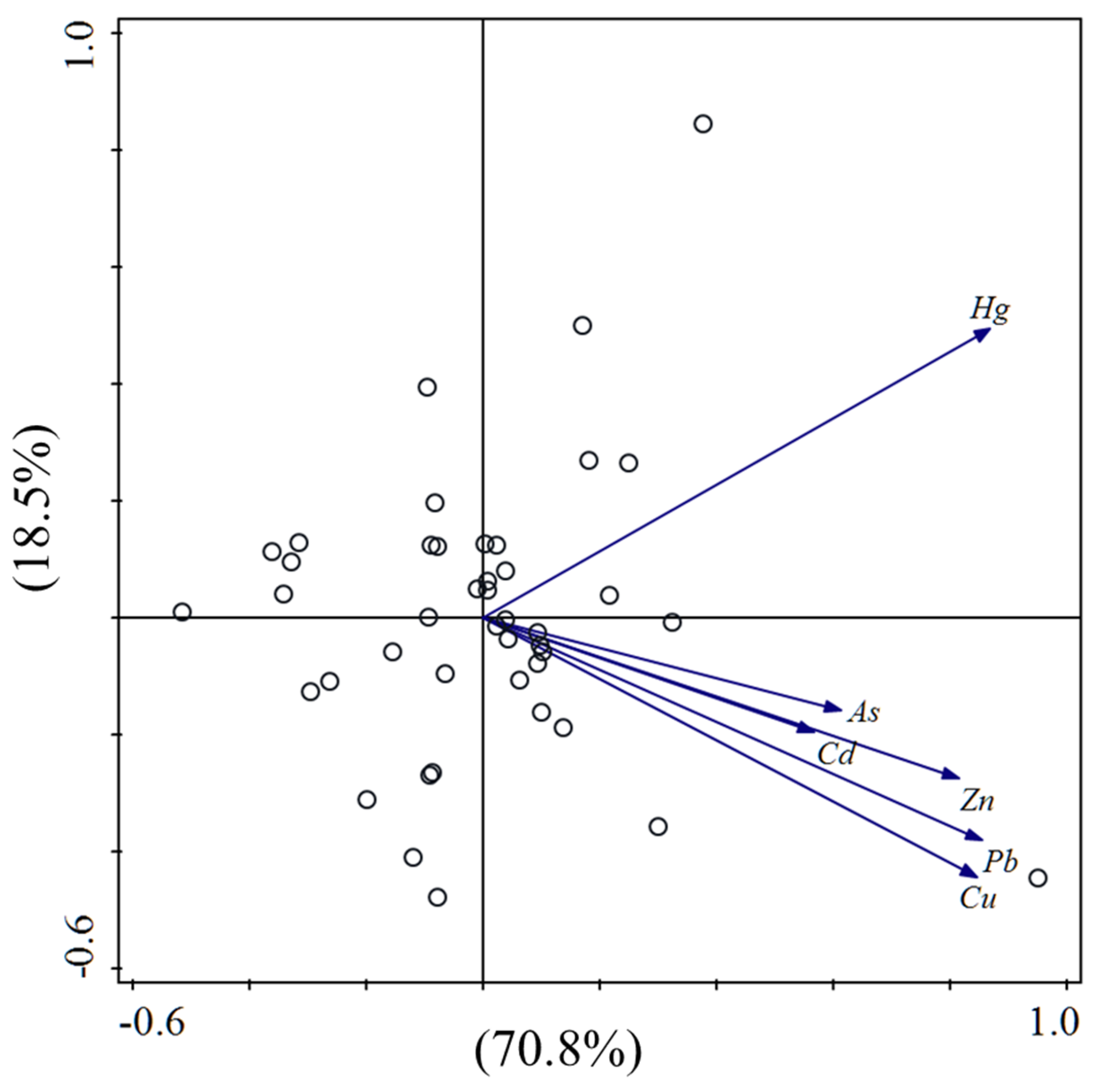
3.3.1. Source Identification by CA and PCA
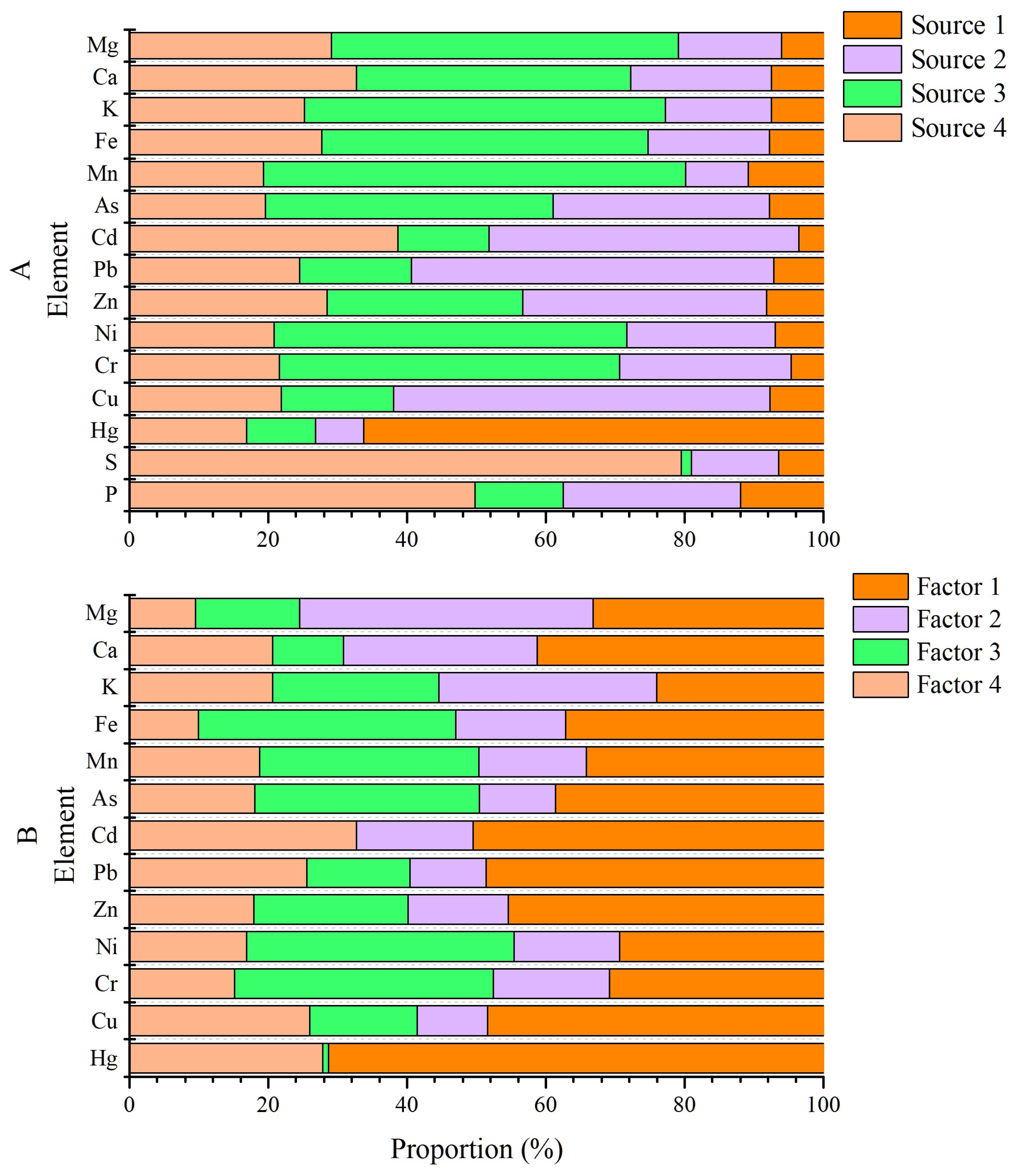
3.3.2. Source Identification by UNMIX
3.3.3. Source Identification by PMF
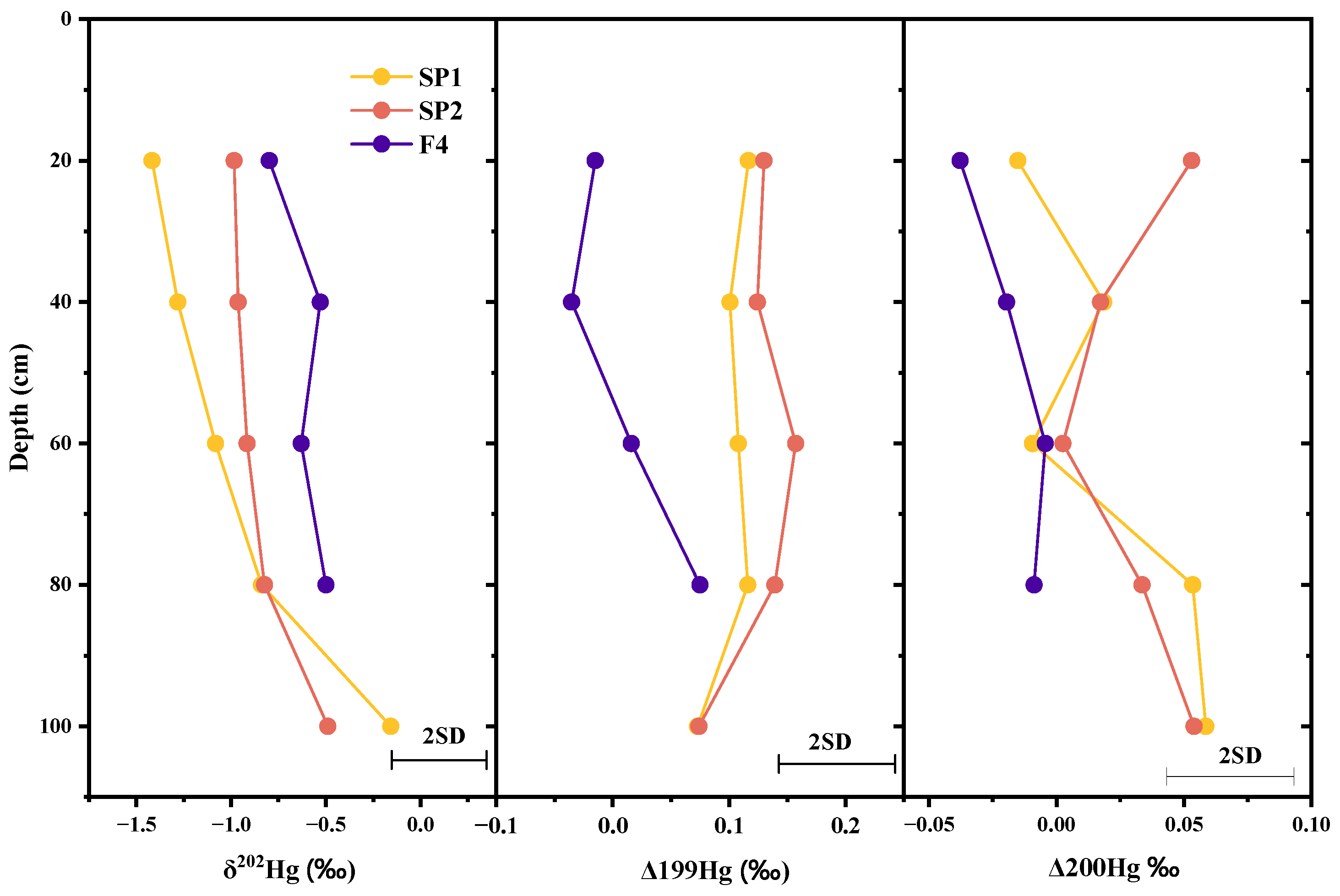
3.3.4. Source Identification by Hg Isotope Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, Q.M.; Hu, W.Y.; Wang, H.F.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.K.; Huang, B. Spatial distribution, ecological risk and sources of heavy metals in soils from a typical economic development area, Southeastern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.L.; Zhang, L.Y.; Dong, J.Q.; Wu, J.S.; Ye, Z.Q.; Zhao, W.M.; Ding, L.Z.; Fu, W.J. Risk assessment, spatial patterns and source apportionment of soil heavy metals in a typical Chinese hickory plantation region of southeastern China. Geoderma 2020, 360, 114011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safari, Y.; Delavar, M.A. The influence of soil pollution by heavy metals on the land suitability for irrigated wheat farming in Zanjan region, northwest Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2019, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, I.C.; Devi, N.L.; Singh, V.K.; Li, J.; Zhang, G. Spatial distribution, source analysis, and health risk assessment of heavy metals contamination in house dust and surface soil from four major cities of Nepal. Chemosphere 2019, 218, 1100–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Parvez, S.; Sayeed, I.; Haque, R.; Bin-Hafeez, B.; Raisuddin, S. Biomarkers of oxidative stress: A comparative study of river Yamuna fish Wallago attu (Bl. & Schn.). Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 309, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Kuang, H.F.; Hu, C.H.; Ge, G. Source apportionment of heavy metal pollution in agricultural soils around the Poyang Lake Region using Unmix model. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda, J.P.; Valente, A.J.; Duraes, L. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution from Anthropogenic Activities and Remediation Strategies: A Review. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 246, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azad, A.M.; Frantzen, S.; Bank, M.S.; Madsen, L.; Maage, A. Mercury bioaccumulation pathways in tusk (Brosme brosme) from Sognefjord, Norway: Insights from C and N isotopes. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 115997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, B.; Teng, Y. Soil environmental quality in greenhouse vegetable production systems in eastern China: Current status and management strategies. Chemosphere 2017, 170, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Hu, W.; Tian, K.; Huang, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, B.; Kwon, B.; Ryu, J.; et al. Accumulation and ecological risk of heavy metals in soils along the coastal areas of the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea: A comparative study of China and South Korea. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wan, Y.Y.; Wu, R.J.; Feng, D.K.; Li, K. Source identification and comprehensive apportionment of the accumulation of soil heavy metals by integrating pollution landscapes, pathways, and receptors. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147436. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Long, Z.J.; Zhu, H.; Bing, H.J.; Tian, X.; Wang, Z.G.; Wang, X.F.; Wu, Y.H. Contamination, sources and health risk of heavy metals in soil and dust from different functional areas in an industrial city of Panzhihua City, Southwest China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 420, 126638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alina, D.S.; Delia, M.T.; Carmen, E.M.; Ciprian, I.; Lavinia, P.; Manuel, G.; Simona, B. Enzymological and Physicochemical Evaluation of the Effects of Soil Management Practices. Rev. Chim. 2017, 68, 2243–2247. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.B.; Ma, J.; Wang, X.L.; Hou, H. Heavy metals in soils from a typical county in Shanxi Province, China: Levels, sources and spatial distribution. Chemosphere 2016, 148, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Guo, D.; Liu, K.; Meng, H.; Zheng, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhu, G. Levels, sources, and spatial distribution of heavy metals in soils from a typical coal industrial city of Tangshan, China. Catena 2019, 175, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simona, B.; Tapan, B.; Lotfi, A.; Pascale, B.; Badr, A.S.; Anamaria, L.P.; Areha, A.; Alina, D.S. Expatiating the impact of anthropogenic aspects and climatic factors on long-term soil monitoring and management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 30528–30550. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Xiao, R.; Wang, C.Q.; Cao, L.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, S.Q.; Yang, L.; Guo, Y. Spatial distribution of soil cadmium and its influencing factors in peri-urban farmland: A case study in the Jingyang District, Sichuan, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Borvka, L.; Vacek, O.; Jehlika, J. Principal component analysis as a tool to indicate the origin of potentially toxic elements in soils. Geoderma 2005, 128, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
- Paatero, P.; Tapper, U. Positive Matrix Factorization: A nonnegative factor model with optimal utilization of error estimates of data values. Environmetrics 1994, 5, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefania, G.A.; Rotiroti, M.; Buerge, I.J.; Zanotti, C.; Nava, V.; Leoni, B.; Fumagalli, L.; Bonomi, T. Identification of groundwater pollution sources in a landfill site using artificial sweeteners, multivariate analysis and transport modeling. Waste Manag. 2019, 95, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Feng, K.; Pei, Z.P.; Meng, F.; Sun, J. Multivariate analysis combined with GIS to source identification of heavy metals in soils around an abandoned industrial area, Eastern China. Ecotoxicology 2016, 25, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lv, J. Multivariate Receptor models and robust geostatistics to estimate source apportionment of heavy metals in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Deng, M.H.; Zhu, Y.W.; Shao, K.; Zhang, Q.; Ye, G.H.; Shen, J. Metals source apportionment in farmland soil and the prediction of metal transfer in the soil-rice-human chain. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 260, 110092. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.T.; Guo, G.H.; Zhang, D.G.; Lei, M. An integrated method for source apportionment of heavy metal(loid)s in agricultural soils and model uncertainty analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116666. [Google Scholar]
- Iakovidesa, M.; Stephanoua, E.G.; Apostolaki, M.; Hadjicharalambousc, M.; Evansd, J.; Koutrakisd, P.; Achilleosd, S. Study of the occurrence of airborne Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons associated with respirable particles in two coastal cities at Eastern Mediterranean: Levels, source apportionment, and potential risk for human health. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 213, 170–184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, H.H.; Cui, Z.J. Evaluation and analysis of soil migration and distribution characteristics of heavy metals in iron tailings. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- dos Santos, G.C.G.; Valladares, G.S.; Abreu, C.A.; de Camargo, O.A.; Grego, C.R. Assessment of copper and zinc in soils of a vineyard region in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2013, 10, 790795. [Google Scholar]
- Bashir, M.A.; Rehim, A.; Liu, J.; Imran, M.; Liu, H.B.; Suleman, M.; Naveed, S. Soil survey techniques determine nutrient status in soil profile and metal retention by calcium carbonate. Catena 2019, 173, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Facchinelli, A.; Sacchi, E.; Mallen, L. Multivariate statistical and gis-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 114, 313–324. [Google Scholar]
- Giri, S.; Singh, A.K.; Mahato, M.K. Metal contamination of agricultural soils in the copper mining areas of Singhbhum shear zone in India. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 126, 49. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cang, L.; Xu, B.; Ding, J. Source identification and apportionment of heavy metals in urban soil profiles. Chemosphere 2015, 127, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, R.S.; Feng, X.B.; Hurley, J.P.; Krabbenhoft, D.P.; Lepak, R.F.; Hu, R.Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.G.; Bi, X.W. Mercury isotopes as proxies to identify sources and environmental impacts of mercury in sphalerites. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Liao, L.F.; Li, G.G.; Lin, Y.; Meng, B.; Feng, X.B. Mercury isotopes trace historical mercury pollution from Pb-Zn smelter in China. Chem. Geol. 2023, 635, 121622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gmochowska, W.; Pietranik, A.; Tyszka, R.; Ettler, V.; Mihaljevic, M.; Dlugosz, M.; Walenczak, K. Sources of pollution and distribution of Pb, Cd and Hg in Wroclaw soils: Insight from chemical and Pb isotope composition. Geochemistry 2019, 79, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.J.; Liu, H.Y.; Dinis, F.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Jing, P.; Liu, F.; Ju, X.H. Contamination Evaluation and Source Analysis of Heavy Metals in Karst Soil Using UNMIX Model and Pb-Cd Isotopes. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 12478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.D.; Bergquist, B.A. Reporting of variations in the natural isotopic composition of mercury. Anal. Bioanal Chem. 2007, 388, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Analytical Methods for Soil and Agricultural Chemistry; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Simpson, S.; Angel, B.; Jolley, D. Metal equilibration in laboratory contaminated (spiked) sediments used for the development of whole sediment toxicity tests. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 597–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakanson, L. An ecological risk index for aquatic pollution control. A sedimentological approach. Water Res. 1980, 14, 975–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Pan, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Ma, R.; Shen, Z.; Dong, S. Risk assessment of soil heavy metals associated with land use variations in the riparian zones of a typical urban river gradient. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 181, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Monitoring Administration of China. The Background Values of Heavy Metals for Agricultural Soil in Zhejiang Province; Environmental Monitoring Administration of China: Beijing, China, 1990.
- Yuan, G.L.; Sun, T.H.; Han, P.; Li, J.; Lang, X.X. Source identification and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in topsoil using environmental geochemical mapping: Typical urban renewal area in Beijing, China. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 136, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Z.; Huang, L.; Lei, B.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Xiong, H.; Li, X. Identification and prevention of agricultural non-point source pollution risk based on the minimum cumulative resistance model. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 23, e01149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dana, C.F.; Simona, G.B.; Laura, E.; Paul, A.N.; Alexa, F.B.; Bianca, P.; Andrei-Flavius, R.; Alexandra, G.T.; Mihaela, A.B.; Tapan, B.; et al. Characterization of the Toxicological Impact of Heavy Metals on Human Health in Conjunction with Modern Analytical Methods. Toxics 2022, 10, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.W.; Zhan, Y.; Zhou, W.J.; Zhu, L.Z. Current status and temporal trend of heavy metals in farmland soil of the Yangtze River Delta Region: Field survey and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Guan, Q.; Tian, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Pan, N. Contamination characteristics, source apportionment, and health risk assessment of heavy metals in agricultural soil in the Hexi corridor. Catena 2020, 191, 104573. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira, A.; Sfredo, G.J.; Moraes, L.A.C.; Fageria, N.K. Lime and cattle manure in soil fertility and soybean grain yield cultivated in tropical soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2015, 46, 1157–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkowska, K.; Teper, L.; Czech, T.; Hulok, T.; Olszak, M.; Zogala, J. Quality of Peri-Urban Soil Developed from Ore-Bearing Carbonates: Heavy Metal Levels and Source Apportionment Assessed Using Pollution Indices. Minerals 2020, 10, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutkowska, K.; Teper, L.; Krzykawski, T.; Czech, T. Heavy Metals Soil Contamination Induced by Historical Zinc Smelting in Jaworzno. Ecol. Chem. Eng. A 2013, 20, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda Sonke, J.E.; Blum, J.D. Advances in mercury stable isotope biogeochemistry. Chem. Geol. 2013, 336, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Li, T.Q.; Wu, C.X.; Japenga, J.; Deng, M.H.; Yang, X.E. An integrated approach to assess heavy metal source apportionment in peri-urban agricultural soils. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 299, 540–549. [Google Scholar]
- UNEP. Global Mercury Assessment 2018; UN Environment Programme, Chemicals and Health Branch: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, D.Y.; O’Connor, D.; Nathanail, P.; Tian, L.; Ma, Y. Integrated gis and multivariate statistical analysis for regional scale assessment of heavy metal soil contamination: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Adamiec, E. Chemical fractionation and mobility of traffic-related elements in road environments. Environ. Geochem. Health 2017, 39, 1457–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.M.; Jiang, H.H.; Luo, J. Metals in soils from a typical rapidly developing county, southern China: Levels, distribution, and source apportionment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 19282–19293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, K.H.; Aydi, S.S.; Aydi, S.; Rahmani, R.; Haddad, M.; Lante, A.; Tinello, F.; BIenvenuti, S.; Bousnina, H. Soil fertilization practices affect growth, yield and quality of essential oil of Matricaria recutita grown in Tunisian oases. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2023, 10, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quantin, C.; Ettler, V.; Garnier, J.; Sebek, O. Sources and extractability of chromium and nickel in soil profiles developed on Czech serpentinites. Geoscience 2008, 340, 872–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.Y.; Du, B.Y.; Yin, R.S.; Meng, B.; Fu, X.W.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.M.; Feng, X.B. Isotopic fractionation and source appointment of methylmercury and inorganic mercury in a Paddy ecosystem. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 14334–14342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritee, K.; Blum, J.D.; Johnson, M.W.; Bergquist, B.A.; Barkay, T. Mercury stable isotope fractionation during reduction of Hg (II) to Hg (0) by mercury resistant microorganisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 1889–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritee, K.; Blum, J.D.; Barkay, T. Mercury stable isotope fractionation during reduction of Hg (II) by different microbial pathways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 9171–9177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Obrist, D.; Weis, D.; Bergquist, B.A. Mercury isotope compositions across north American forests. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2016, 30, 1475–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, R.; Feng, X.; Wang, J.; Li, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zheng, L.; Hu, T. Mercury speciation, mercury isotope fractionation during ore roasting process and their implication to source identification of downstream sediment in Wanshan mercury mining area, SW China. Chem. Geol. 2012, 04, 030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.D. Mercury isotopes in earth and environmental sciences. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet Sci. 2014, 42, 249–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucher, D.; Ogrinc, N.; Hintelmann, H. Tracing mercury contamination from the Idrija mining region (Slovenia) to the Gulf of Trieste using Hg isotope ratio measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demers, J.D.; Blum, J.D.; Zak, D.R. Mercury isotopes in a forested ecosystem: Implications for air-surface exchange dynamics and the global mercury cycle. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2013, 27, 222–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolison, J.M.; Landing, W.M.; Luke, W.; Cohen, M.; Salters, V.J.M. Isotopic composition of species-specific atmospheric Hg in a coastal environment. Chem. Geol. 2012, 10, 007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, L.S.; Blum, J.D.; Johnson, K.P.; Keeler, G.J.; Barres, J.A.; Douglas, T.A. Mass-independent fractionation of mercury isotopes in Arctic snow driven by sunlight. Nat. Geosci. 2010, 3, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variable | SOM (g kg−1) | pH | CEC (cmol kg−1) | Hg (mg kg−1) | Cd (mg kg−1) | As (mg kg−1) | Pb (mg kg−1) | Cr (mg kg−1) | Ni (mg kg−1) | Zn (mg kg−1) | Cu (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Max | 59.3 | 7.59 | 40.2 | 5.40 | 0.18 | 12.7 | 82.4 | 107 | 50.0 | 162 | 103 |
| Min | 15.3 | 5.09 | 24.7 | 1.09 | 0.07 | 7.03 | 33.3 | 75.0 | 32.0 | 83.0 | 31.0 |
| Mean | 42.1 | 6.42 | 31.5 | 2.87 | 0.13 | 8.76 | 43.5 | 83.3 | 38.2 | 108 | 45.1 |
| SD | 11.9 | 0.74 | 4.74 | 1.35 | 0.03 | 1.07 | 8.79 | 6.48 | 3.53 | 11.9 | 11.5 |
| CV (%) | 28.3 | 11.5 | 14.9 | 64.9 | 20.3 | 12.2 | 20.3 | 7.68 | 9.18 | 11.3 | 25.6 |
| Reference Bi a | / | / | / | 0.09 | 0.07 | 9.20 | 23.7 | 52.9 | 27.6 | 70.6 | 17.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mu, T.; Cao, B.; Yang, M.; Gan, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Li, M.; Lu, Y.; Xu, J. Heavy Metals Distribution and Source Identification in Contaminated Agricultural Soils: Isotopic and Multi-Model Analysis. Agronomy 2025, 15, 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040812
Mu T, Cao B, Yang M, Gan X, Chen L, Wang X, Li M, Lu Y, Xu J. Heavy Metals Distribution and Source Identification in Contaminated Agricultural Soils: Isotopic and Multi-Model Analysis. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):812. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040812
Chicago/Turabian StyleMu, Tingting, Benyi Cao, Min Yang, Xinhong Gan, Lin Chen, Xiaohan Wang, Ming Li, Yuanyuan Lu, and Jian Xu. 2025. "Heavy Metals Distribution and Source Identification in Contaminated Agricultural Soils: Isotopic and Multi-Model Analysis" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040812
APA StyleMu, T., Cao, B., Yang, M., Gan, X., Chen, L., Wang, X., Li, M., Lu, Y., & Xu, J. (2025). Heavy Metals Distribution and Source Identification in Contaminated Agricultural Soils: Isotopic and Multi-Model Analysis. Agronomy, 15(4), 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040812






