Constructing and Spatially Differentiating Soil Quality Indices in Qiqihar’s Typical Black Soil Zone: A Case Study of Tailai, Longjiang, and Gannan Counties, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. Construction of the Soil Quality Index
2.3.1. Calculation of Membership Degree
2.3.2. Establishment of the Minimal Dataset
2.3.3. Weight of Soil Quality Indicators
2.3.4. Soil Quality Index
2.4. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of Soil Quality Evaluation Indicators
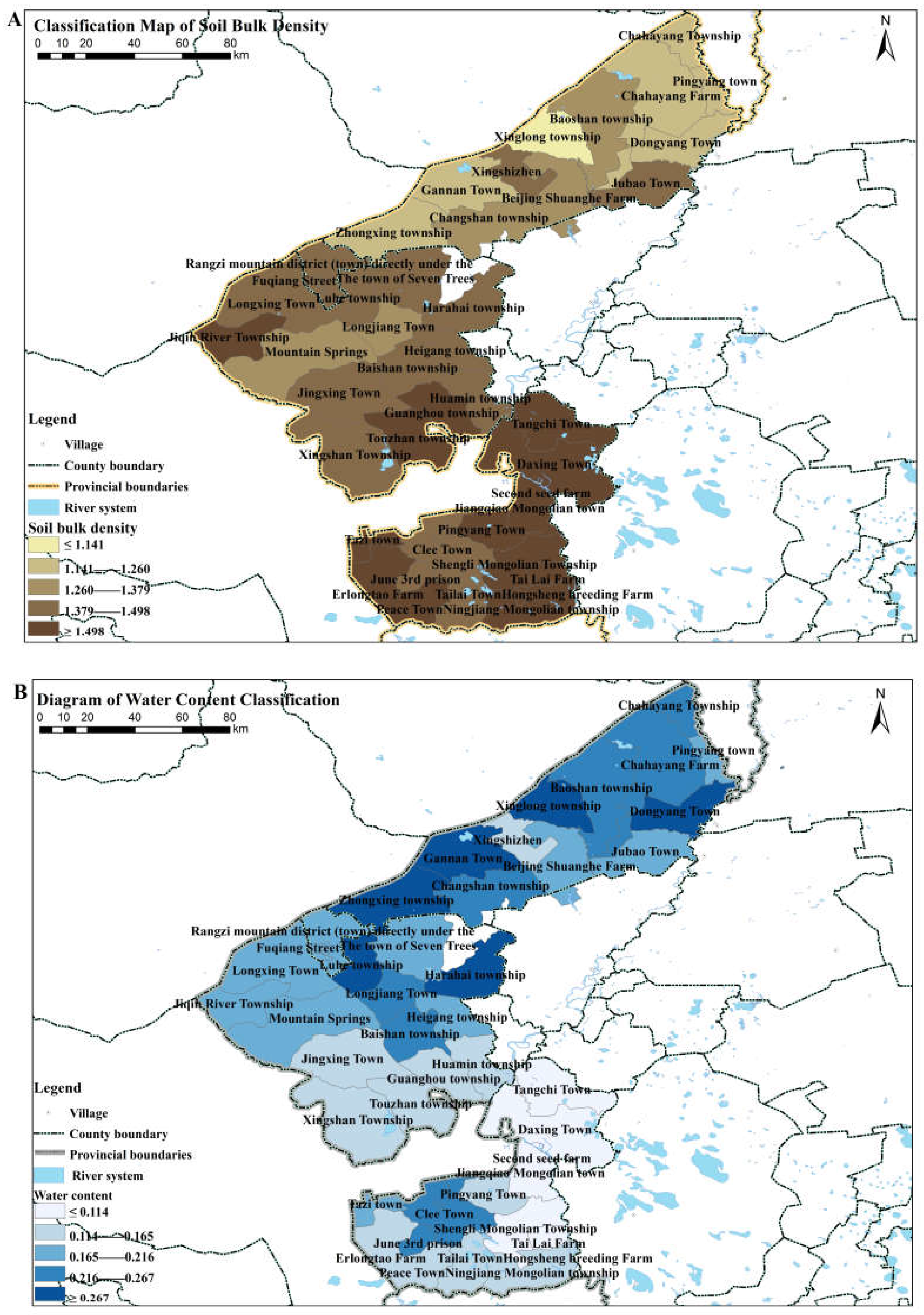
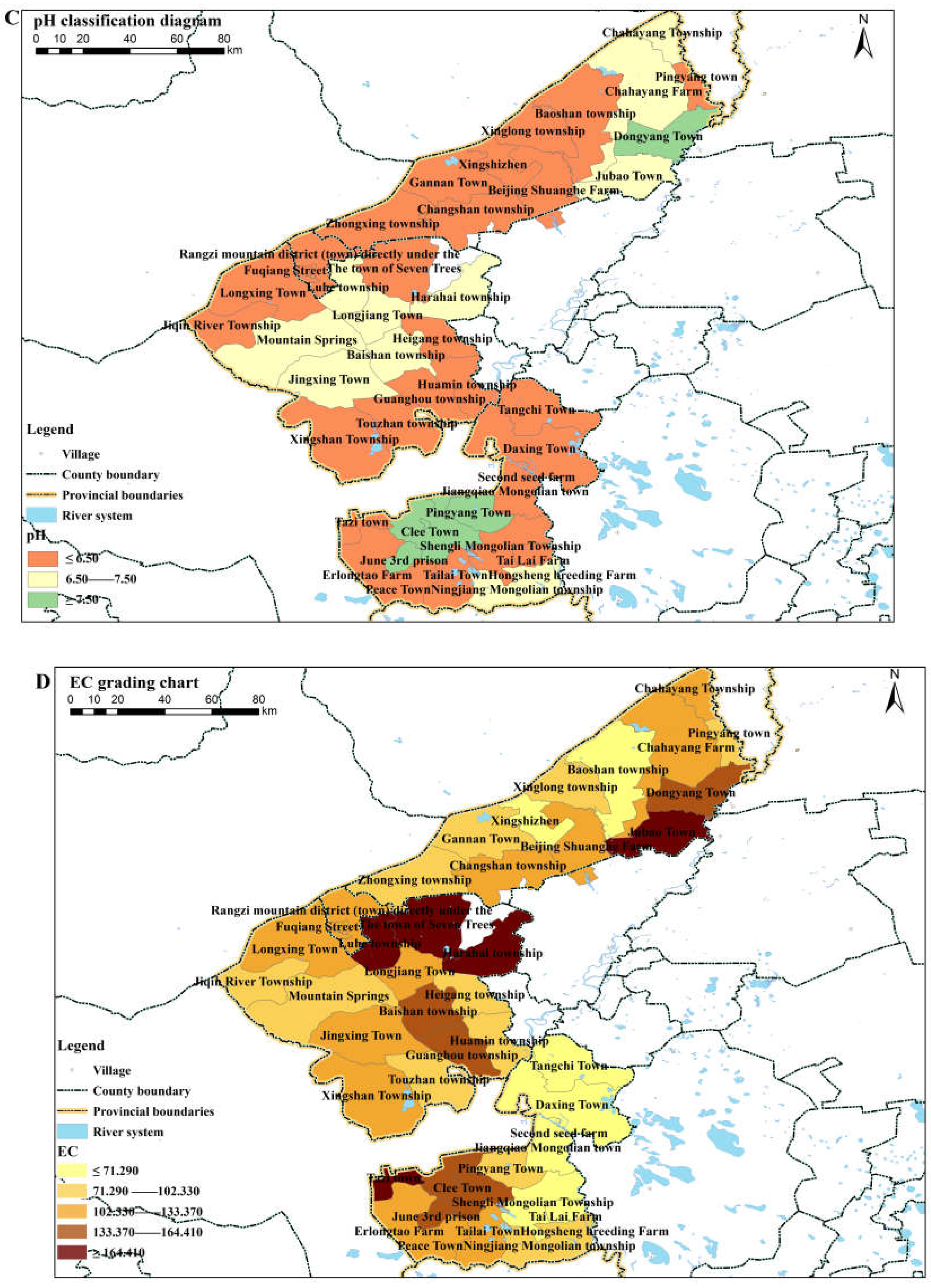
3.1.1. Spatial Analysis of Soil Properties
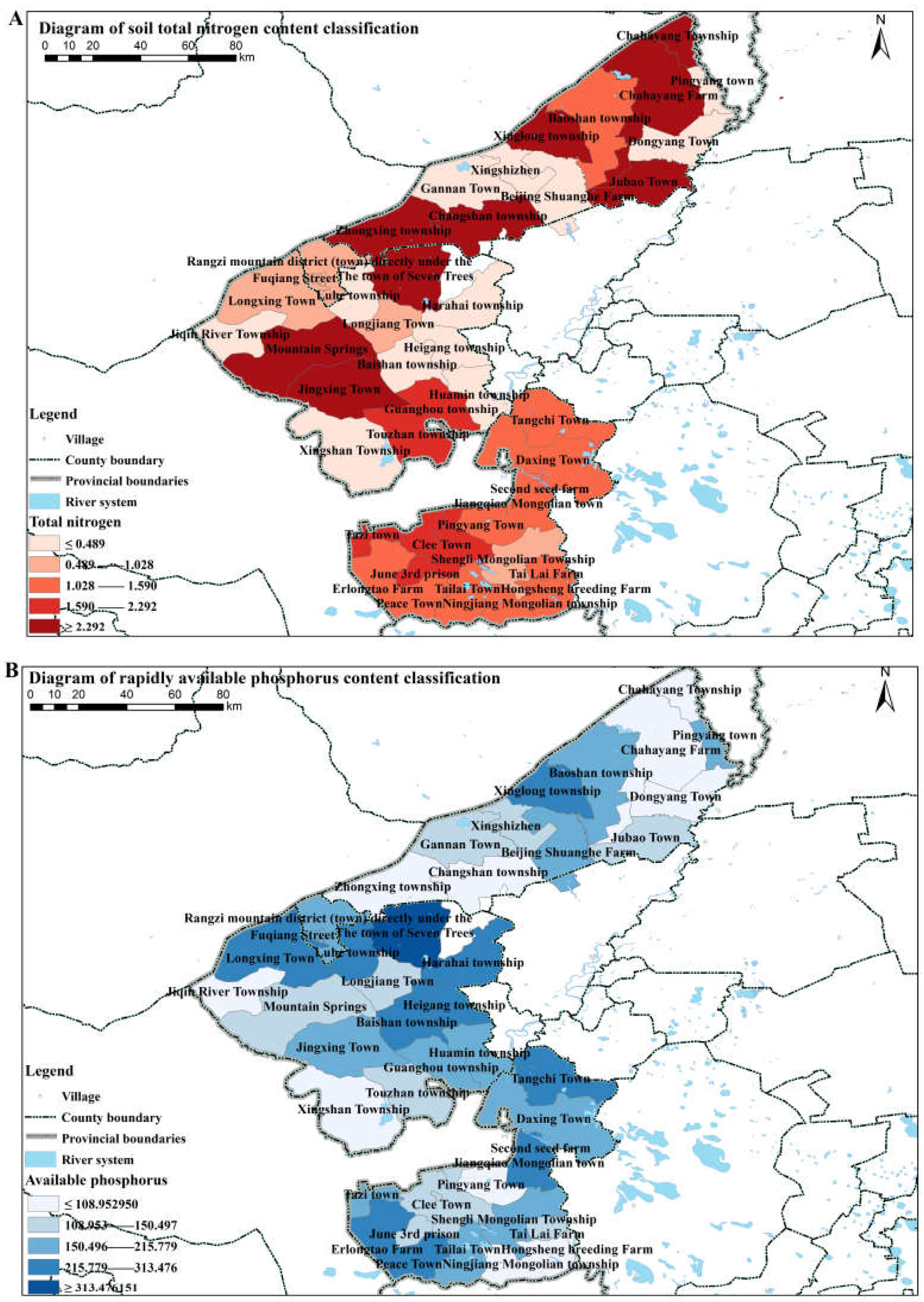
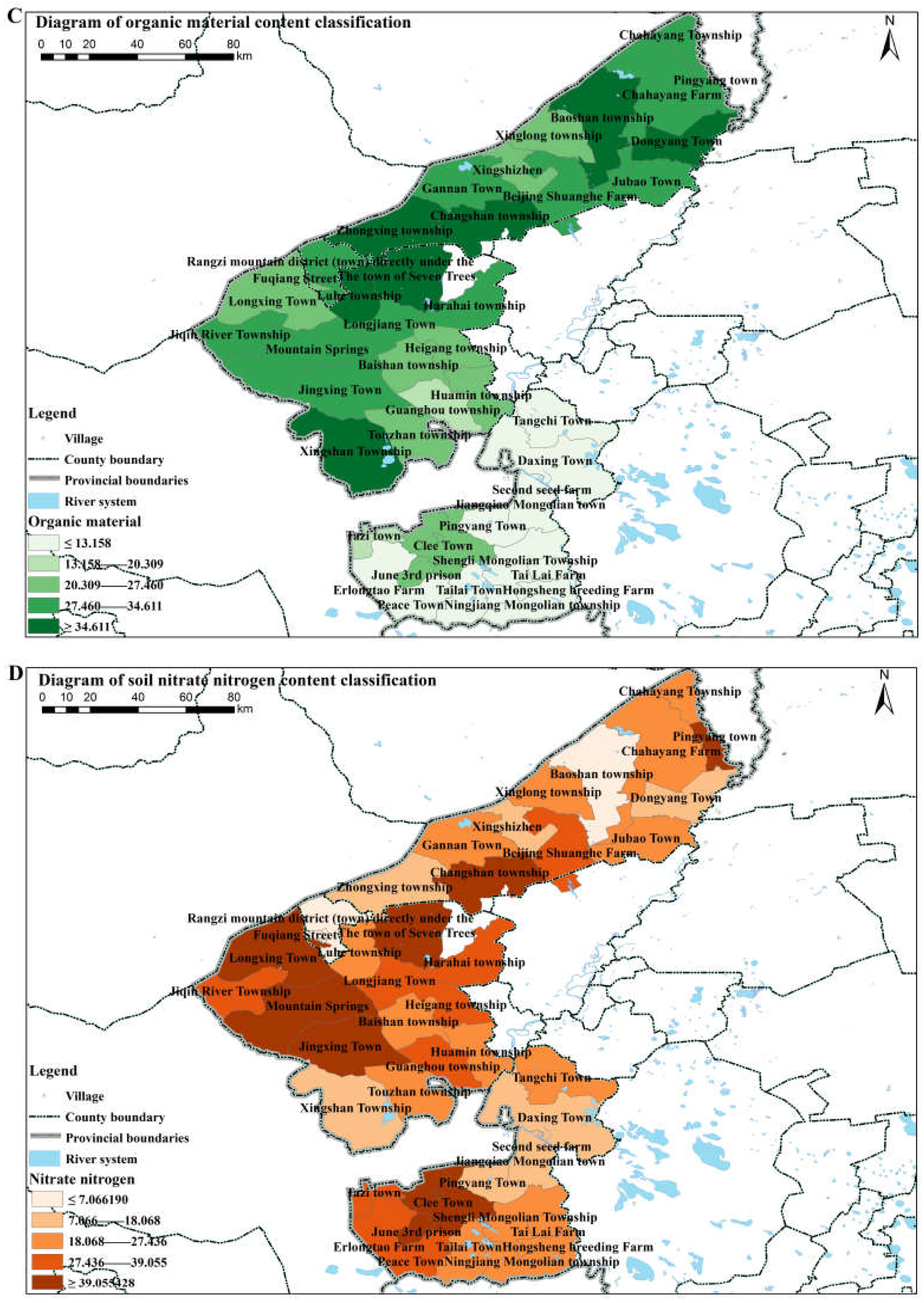
3.1.2. Spatial Characteristics of Soil Nutrients
3.2. Soil Quality Evaluation in Different Regions
3.2.1. Descriptive Analysis of Soil Indicators
3.2.2. Construction of the Minimum Dataset (MDS)
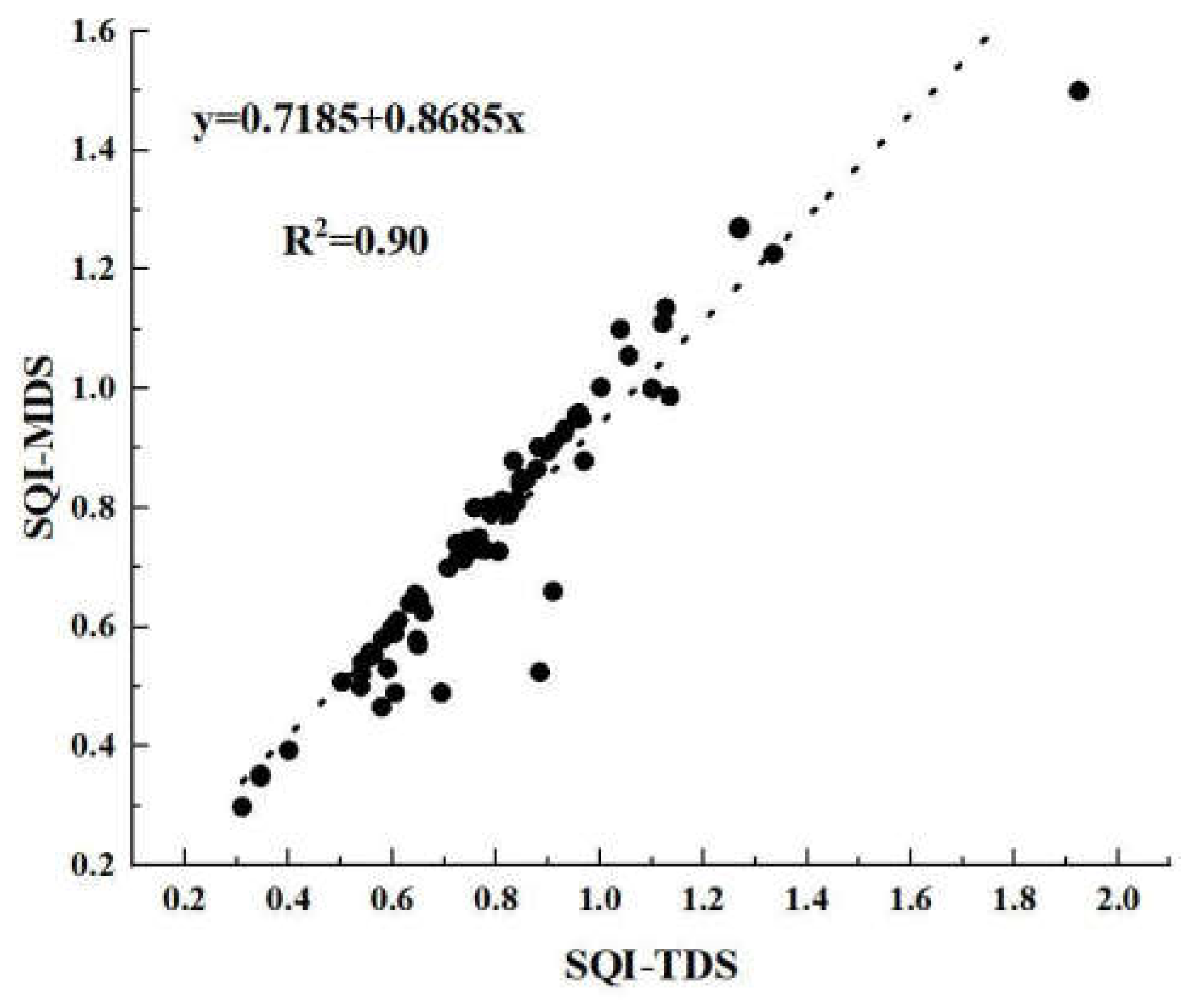
3.2.3. Validating the Minimum Dataset for Soil Quality in Qiqihar
3.2.4. Characteristics of Soil Quality Index Variation
4. Discussion
4.1. Physicochemical Properties of Soil in Different Regions
4.2. MDS Index Screening and Evaluation of Soil Quality
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Compiled by Qiqihar Soil Census Office. Qiqihar Urban Soil; Qiqihar Soil Census Office: Qiqihar, China, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Qiqihar Municipal Water Bureau. Planning of Soil and Water Conservation Ecosystem Construction in Qiqihar City (2001–2010); Qiqihar Municipal Water Bureau: Qiqihar, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ponge, J.F. The soil as an ecosystem. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2015, 51, 645–648. [Google Scholar]
- Nabiollahi, K.; Golmohamadi, F.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R.; Kerry, R.; Davari, M. Assessing the effects of slope gradient and land use change on soil quality degradation through digital mapping of soil quality indices and soil loss rate. Geoderma 2018, 318, 16–28. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Meng, L.; Yin, T.; Wang, X.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Ogundeji, A.O.; Li, S. Maize/soybean intercrop over time has higher yield stability relative to matched monoculture under different nitrogen-application rates. Field Crop. Res. 2023, 301, 109015. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, M.-A.; Mathes, F.; Loke, M.H.; McGrath, G.; Murphy, D.V.; Leopold, M. Bacillus Subtilis and Surfactant Amendments for the Breakdown of Soil Water Repellency in a Sandy Soil. Geoderma 2019, 344, 108–118. [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Francés, F.; Martínez-Graña, A.; Ávila-Zarza, C.; Criado, M.; Sánchez, Y. Comparison of methods for evaluating soil quality of semiarid ecosystem and evaluation of the effects of physico-chemical properties and factor soil erodibility (Northern Plateau, Spain). Geoderma 2019, 354, 113872. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Li, Z.; Xu, C.; Luo, W. Improvements in soil quality with vegetation succession in subtropical China karst. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145876. [Google Scholar]
- Govaerts, B.; Sayre, K.D.; Deckers, J. A minimum data set for soil quality assessment of wheat and maize cropping in the highlands of Mexico. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Abd-Elwahed, M.S. Effect of long-term wastewater irrigation on the quality of alluvial soil for agricultural sustainability. Ann. Agric. Sci. 2019, 64, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Q.; Zheng, F.L.; Li, Z.; Feng, Z.Z. A novel optimal data set approach for erosion-impacted soil quality assessments—A case-study of an agricultural catchment in the Chernozem region of Northeast China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 1062–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Hedo, J.; Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Wic-Baena, C.; Andrés-Abellán, M.; De lasHeras, J. Effects of thinning and induced drought on microbiologicalsoil properties and plant species diversity at dry and semiarid locations. Land Degrad. Dev. 2014, 27, 1045–1063. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, Y. Characteristics of farmland erosion and degradation in typical water erosion areas of black soil in northeast China. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Rong, G. Experimental Study on the Effects of Erosion and Tillage Measures on Soil Quality. Ph.D. Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xi’an, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Tian, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liang, Y. Response of soil quality degradation to cultivation and soil erosion: A case study in a Mollisol region of Northeast China. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 242, 106159. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, H. Improving organic matter content of black soil with straight ridge tillage and higher ridge tillage. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.Y.; Yang, J.; Jiang, S.N.; Gu, H.Y. Soil quality difference of different age black poplars in typical black soil area based on minimum data set. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 44, 3623–3635. [Google Scholar]
- Bünemann, E.K.; Bongiorno, G.; Bai, Z.; Creamer, R.E.; De Deyn, G.; de Goede, R.; Fleskens, L.; Geissen, V.; Kuyper, T.W.; Mäder, P.; et al. Soil quality—A critical review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 105–125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G. Soil Physical and Chemical Analysis & Description of Soil Profiles; Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, X.; Wang, H.Y.; Zou, J.H.; Du, X.; Meng, H. Soil quality assessment of natural coniferous and broad-leaved mixed forest under different cutting intensities using minimum data set. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2022, 50, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Bremner, J.M.; Mulvaney, C.S. Nitrogen-total. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2: Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Page, A.L., Miller, R.H., Keeney, D.R., Eds.; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982; pp. 595–624. [Google Scholar]
- Santhi, C.; Arnold, J.G.; Williams, J.R.; Hauck, L.M.; Dugas, W.A. Application of a Watershed Model to Evaluate Management Effects on Point and Nonpoint Source Pollution. Trans. ASAE 2001, 44, 1559–1570. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Q.; Luo, Z.Z.; Niu, Y.N.; Cai, L.Q.; Liu, J.H.; Li, L.Z. Soil quality evaluation of alfalfa fields in semi-arid areas of the Loess Plateau based on minimum data set. Chin. J. Grassl. 2023, 45, 81–90. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yemefack, M.; Jetten, V.G.; Rossiter, D.G. Developing a minimum data set for characterizing soil dynamics in shifting cultivation systems. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 86, 84–98. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, S.; Ou, Z.; Shen, W.; Hou, Y.; Huang, X.; Zheng, W. Edaphic characteristics of different regeneration patterns in karst mountainous areas of Guangxi. J. Cent. South. Univ. For. Technol. 2016, 36, 60–66. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, H.; Lei, H. Evaluation of farmland soil quality and obstacle diagnosis in Shawan City, Xinjiang Province based on minimal data set. Geogr. Arid. Reg. 2024, 47, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L.L.; Wu, Z.X.; Sun, R.; Yang, C.; Fu, Q.M.; Tan, Z.H. Soil organic carbon components and influencing factors of rubber plantations of different ages in Qiongzhong, Hainan. J. Yunnan Agric. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2023, 38, 886–893. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Li, R.; Fang, F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J. Soil health evaluation of intensive vineyard based on minimum data set. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 40, 71–79. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.; Yu, S.; Yang, D.; Hutchins, M.G.; Ding, J.; Hong, B.; Chen, P.; Liu, X. Discriminating surface soil inorganic nitrogen cycling under various land uses in a watershed with simulations of energy balanced temperature and slope introduced moisture. J. Hydrol. 2020, 587, 124950. [Google Scholar]
- Abbaspour-Gilandeh, Y.; Abbaspour-Gilandeh, M.; Babaie, H.A.; Shahgoli, G. Modeling agricultural soilbulk density using artificial neural network and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. EarthScience Inform. 2023, 16, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Bruand, A.; Pérez Fernández, P.; Duval, O. Use of class pedotransfer functions based on texture andbulk density of clods to generate water retention curves. Soil Use Manag. 2003, 19, 232–242. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, M.K.; Lal, R.; Ebinger, M. Determining soil quality indicators by factor analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 87, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, C.P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.F.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.Y. Effects of topographic factors on soil moisture and bulk density of sloping farmland in northeast black soil region. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 28, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Han, C.; Zeng, S.; Wu, Q.; Liu, L. Effects of different tillage methods on soil physical properties and maize yield. Maize Sci. 2014, 22, 108–113. [Google Scholar]
- Pires, L.F.; Borges, J.; Rosa, J.A.; Cooper, M.; Heck, R.J.; Passoni, S.; Roque, W.L. Soil structure changes induced by tillage systems. Soil Till Res. 2017, 165, 66–79. [Google Scholar]
- Rabot, E.; Wiesmeier, M.; Schlüter, S.; Vogel, H.-J. Soil structure as an indicator of soil functions: A review. Geoderma 2018, 314, 122–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Q.; Zhu, H.S.; Wei, X.R.; Liu, B.Y.; Shao, M.A. Soil erosion leads to degradation of hydraulic properties in the agricultural region of Northeast China. Agric Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 314, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Sheng, Y. Effect of various salt–alkaline mixed stress conditions on sunflower seedlings and analysis of their stress factors. Environ. Exp. Botany. 2005, 54, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, W.; Zhao, J.; Xue, C.; Zhang, G.; Ran, W.; Wang, B.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, R. Significant alteration of soil bacterial communities and organic carbon decomposition by different long-term ferilization management conditions of extremely low-productivity arable soil in South China. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18 (Suppl. S6), 1907–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Guo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Hai, C.; Hu, Z. Evaluation of soil quality in Inner Mongolia desert steppe-A case study of Siziwang Banner. PLoS ONE 2023, 21, e0290301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Long, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, J.; Cai, C. Construction and spatial differentiation of soil quality index in eroded farmland in Northeast China. J. Agric. Eng. 2019, 40, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Xiao, M.; Cui, X.; Lu, S.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, T. Soil health assessment of non-grain cultivated land: A case study of Dongwu Town, Ningbo, Zhejiang Province. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 2785–2793. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, G.C.; Saha, S.; Ghosh, K.G. Assessing the soil quality of Bansloi river basin, eastern India using soil-quality indices (SQIs) and Random Forest machine learning technique. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.F.; Shi, D.M.; Chen, Z.F.; Liu, Y.J.; Lou, Y.B.; Yang, X. Evaluation index of topsoil quality in red soil slope cultivated land based on clustering and PCA analysis. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 155–164. [Google Scholar]
- Jiru, E.B.; Wegari, H.T. Soil and water conservation practice effects on soil physicochemical properties and crop yield in Ethiopia: Review and synthesis. Ecol. Process. 2022, 11, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Dong, Y.; Song, M.; Gu, J.; Shi, Y.; Wu, H.; Song, X.; Yang, J.; Li, D.; Zhang, G.-L. Deep nitrate accumulation in typical black soil critical zones of Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176050. [Google Scholar]
- Obade, V.D.; Lal, R. Soil quality evaluation under different land management practices. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 4531–4549. [Google Scholar]
- Raiesi, F. A minimum data set and soil quality index to quantify the effect of land use conversion on soil quality and degradation in native rangelands of upland arid and semiarid regions. Ecol. Indic. 2017, 75, 307–320. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.L.; Rao, C.S.; Chandrika, D.S.; Nandini, N.; Munnalal, R.K.S.; Indoria, A.K.; Kumar, T.S. Assessment of GMean biological soil quality indices under conservation agriculture practices in rainfed Alfisol soils. Curr. Sci. 2016, 111, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhong, X.; Miao, S.; Li, Q.; Lu, X. Evaluation indicators of soil quality in plough layer of aeolian sandy land in Northeast China based on minimum data set. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 26, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, L.; Zhang, X.; Ran, Q. Quality assessment of oasis soil in the upper reaches of Tarim River based on minimum data set. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2015, 52, 682–689. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, F.; Yu, Y.; Dong, X.; Gu, H. Soil Quality Evaluation Based on a Minimum Data Set (MDS)—A Case Study of Tieling County, Northeast China. Land 2023, 12, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Xi, M.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, Q.; Jia, J. Soil quality assessment of coastal wetlands in the Yellow River Delta of China based on the minimum data set. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 458–466. [Google Scholar]
- Karlen, D.L.; Ditzler, C.A.; Andrews, S.S. Soil quality: Why and how? Geoderma 2003, 114, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S.S.; Flora, C.B.; Mitchell, J.P.; Karlen, D.L. Growers’ perceptions and acceptance of soil quality indices. Geoderma 2003, 114, 187–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, Q.; Wu, X.; Wu, H.; Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ding, W.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, F. Regional differences in the effects of no-tillage on soil water holding capacity and organic carbon storage in farmland. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2020, 53, 3729–3740. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Gao, G.; Ding, G.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Soil particle size distribution of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in the Horqin Sandy Land. Arid Land Geogr. 2020, 43, 1051–1058. [Google Scholar]


| Soil Indicator | Factor Loadings | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PC-1 | PC-2 | PC-3 | PC | Norm Value | |
| Soil Moisture Content (%) | 0.833 | −0.334 | −0.016 | 1 | 1.465 |
| Soil Bulk Density (g·cm−3) | −0.705 | 0.454 | 0.223 | 1 | 1.351 |
| Soil pH | 0.236 | −0.024 | 0.899 | 3 | 1.088 |
| Electrical Conductivity (μS cm−1) | 0.668 | 0.355 | 0.341 | 1 | 1.275 |
| Available Phosphorus (g kg−1) | 0.197 | 0.666 | −0.32 | 2 | 1.017 |
| Ammonium Nitrogen (g kg−1) | 0.086 | −0.553 | −0.349 | 2 | 0.851 |
| Nitrate Nitrogen (g kg−1) | 0.533 | 0.633 | −0.258 | 2 | 1.265 |
| Total Nitrogen (g kg−1) | 0.4 | 0.365 | −0.071 | 1 | 0.833 |
| Organic Matter (g kg−1) | 0.789 | −0.255 | −0.013 | 1 | 1.365 |
| Principal Component Eigenvalues | 2.804 | 1.793 | 1.270 | - | - |
| Variance Contribution of Principal Components (%) | 31.155 | 19.918 | 14.114 | - | - |
| Cumulative Contribution of Principal Components (%) | 31.155 | 51.073 | 65.187 | - | - |
| Soil Moisture Content | Soil Bulk Density | Soil pH | Electrical Conductivity | Available Phosphorus | Ammonium Nitrogen | Nitrate Nitrogen | Total Nitrogen | Organic Matter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soil Moisture Content | 1 | ||||||||
| Soil Bulk Density | −0.71 ** | 1 | |||||||
| Soil pH | 0.24 * | −0.02 | 1 | ||||||
| Electrical Conductivity | 0.51 ** | −0.11 | 0.38 ** | 1 | |||||
| Available Phosphorus | −0.03 | 0.05 | −0.15 | 0.26 * | 1 | ||||
| Ammonium Nitrogen | 0.16 | −0.20 | −0.14 | −0.05 | −0.18 | 1 | |||
| Nitrate Nitrogen | 0.23 | −0.11 | −0.12 | 0.53 ** | 0.40 ** | −0.14 | 1 | ||
| Total Nitrogen | 0.14 | −0.18 | 0.10 | 0.14 | 0.15 | −0.11 | 0.40 ** | 1 | |
| Organic Matter | 0.65 ** | −0.61 ** | 0.14 | 0.34 ** | 0.01 | 0.08 | 0.21 | 0.20 | 1 |
| Indicator | Total Dataset | Minimum Dataset | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Common Factor Variance | Weight | Common Factor Variance | Weight | |
| Soil Moisture Content | 0.805 | 0.137 | 0.791 | 0.226 |
| Soil Bulk Density | 0.752 | 0.128 | 0.731 | 0.209 |
| Soil pH | 0.864 | 0.147 | 0.683 | 0.195 |
| Electrical Conductivity | 0.689 | 0.117 | - | |
| Available Phosphorus | 0.585 | 0.100 | - | |
| Ammonium Nitrogen | 0.435 | 0.074 | - | |
| Nitrate Nitrogen | 0.751 | 0.128 | 0.558 | 0.160 |
| Total Nitrogen | 0.299 | 0.051 | - | |
| Organic Matter | 0.688 | 0.117 | 0.732 | 0.209 |
| SQI-TDS | SQI-MDS | |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Value | 0.21 | 0.18 |
| Maximum Value | 2.32 | 2.59 |
| Average Value | 0.96 | 1.15 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.45 | 0.51 |
| Median | 1.1 | 1.15 |
| Coefficient of Variation | 46.88% | 44.19% |
| Region | Minimum Value | Maximum Value | Average Value | Standard Deviation | Median | Coefficient of Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tailai County | 0.18 | 2.02 | 0.97 | 0.51 | 0.90 | 52.14% |
| Longjiang County | 0.20 | 2.17 | 1.06 | 0.48 | 1.02 | 45.48% |
| Gannan County | 0.48 | 2.59 | 1.44 | 0.41 | 1.46 | 28.18% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Pang, M.; Wang, N.; Wei, D.; An, Z.; Xie, J.; Jin, L. Constructing and Spatially Differentiating Soil Quality Indices in Qiqihar’s Typical Black Soil Zone: A Case Study of Tailai, Longjiang, and Gannan Counties, China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040773
Wang L, Pang M, Wang N, Wei D, An Z, Xie J, Jin L. Constructing and Spatially Differentiating Soil Quality Indices in Qiqihar’s Typical Black Soil Zone: A Case Study of Tailai, Longjiang, and Gannan Counties, China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):773. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040773
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lei, Min Pang, Na Wang, Dan Wei, Zhizhuang An, Jianzhi Xie, and Liang Jin. 2025. "Constructing and Spatially Differentiating Soil Quality Indices in Qiqihar’s Typical Black Soil Zone: A Case Study of Tailai, Longjiang, and Gannan Counties, China" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040773
APA StyleWang, L., Pang, M., Wang, N., Wei, D., An, Z., Xie, J., & Jin, L. (2025). Constructing and Spatially Differentiating Soil Quality Indices in Qiqihar’s Typical Black Soil Zone: A Case Study of Tailai, Longjiang, and Gannan Counties, China. Agronomy, 15(4), 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040773






