Design and Optimization of Divider Head Geometry in Air-Assisted Metering Devices for Enhanced Seed Distribution Accuracy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development of Seed Distributor Heads
2.1.1. Funnel Head Distributor (A1)
2.1.2. Closed-Funnel Head Distributor (A2)
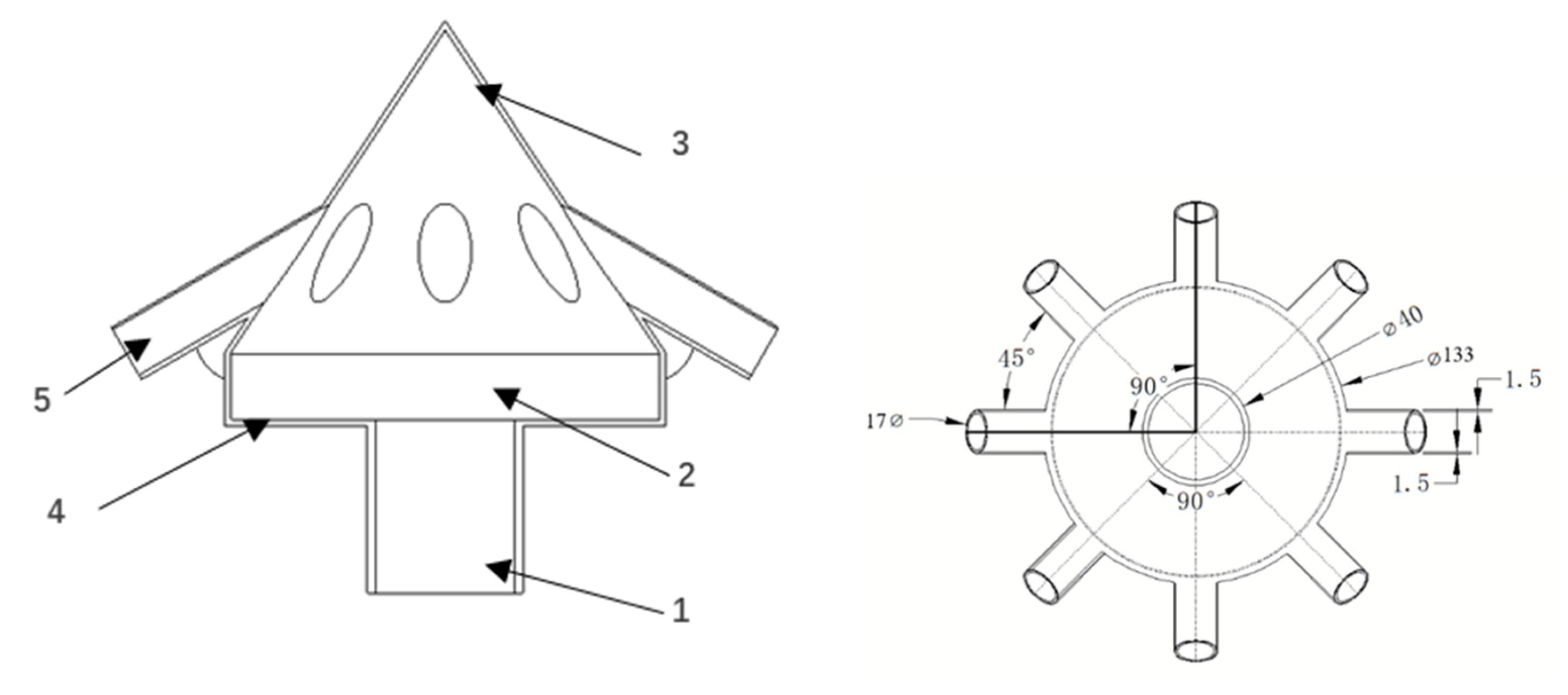
2.1.3. Cone-Shaped Distributor (A3)
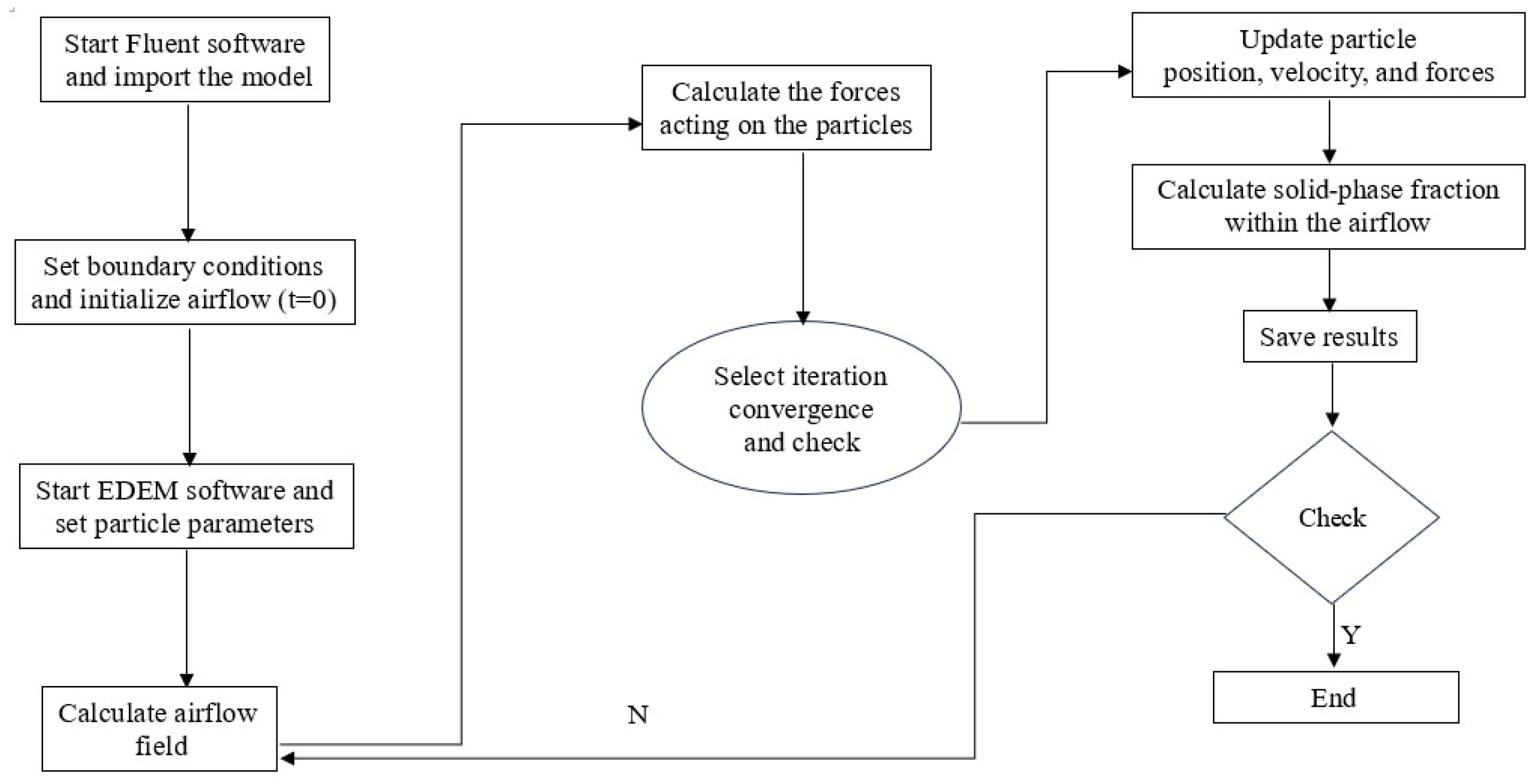
2.2. EDEM-CFD Model Establishment
2.3. Numerical Model of Seed Gas Delivery
2.3.1. Development of a Numerical Model for Seed Gas Delivery Based on Air Pressure
2.3.2. Seed–Gas Delivery Ratio
2.3.3. Inlet Airflow Tube Diameter
2.4. Experiment Design
2.4.1. DEM-CFD Coupling Simulation Experimental Experiment
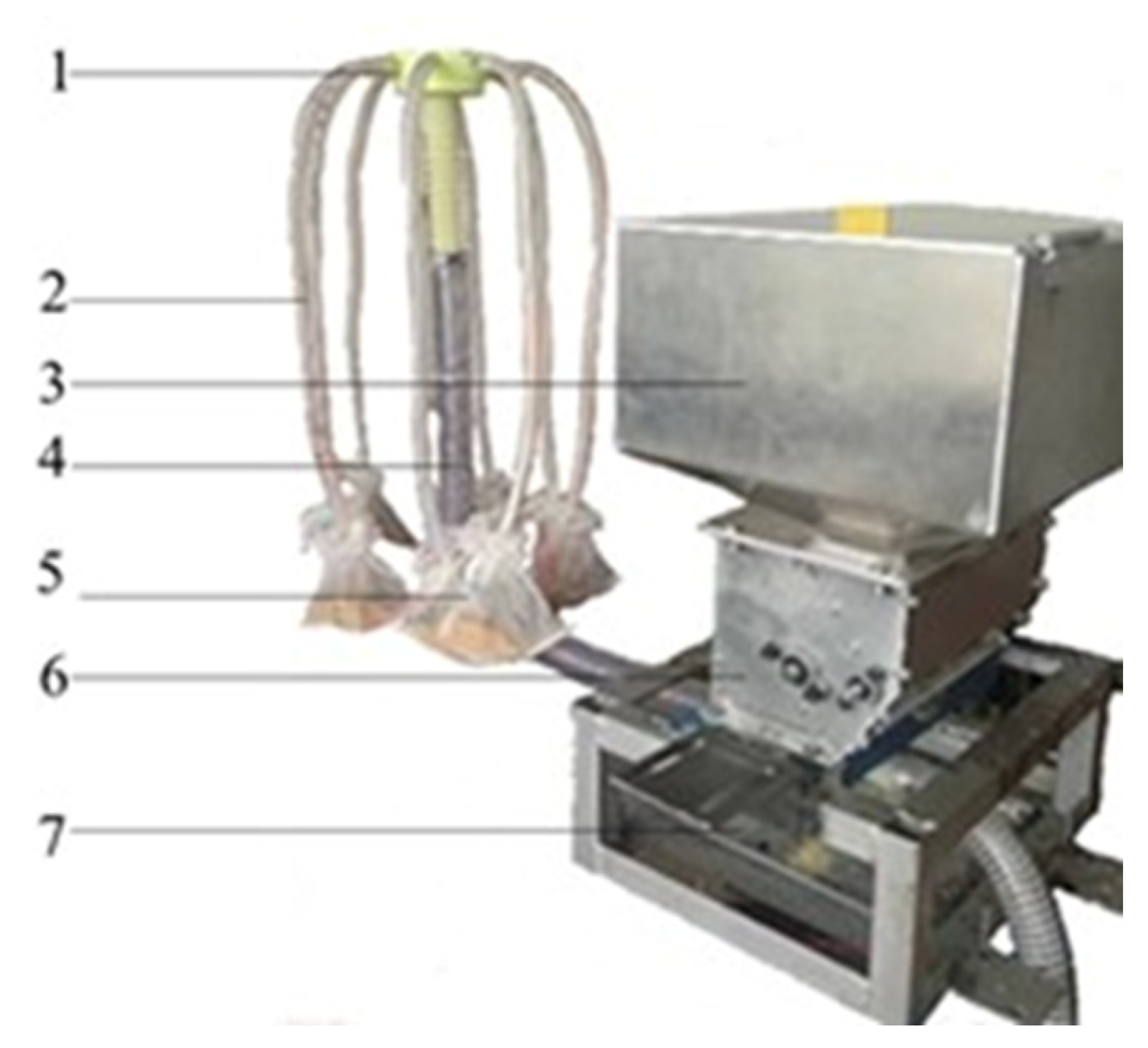
2.4.2. Description of Distributor Head’s Bench Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Analysis of DEM-CFD Coupling Simulation Experimental Results
3.2. Analysis of Bench Test Experimental Results
3.2.1. Influence of Wheat–Air Mixture on Distributing Performance
3.2.2. Influence of Rice–Air Mixture on Distributing Performance
3.2.3. Influence of Rapeseed–Air Mixture on Distributing Performance
3.3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- The A2 distributor consistently outperforms A1 and A3 across all seed–air mixtures (wheat, rice, and rapeseed) regarding distribution uniformity and stability due to its barrier design, which effectively mitigates turbulence.
- A2 achieved the lowest coefficients of variation (CV): 2.6% for wheat (compared to A1′s 4.3% and A3′s 6.9%), 3.4% for rice (compared to A1′s 4.5% and A3′s 6.2%), and 0.1% for rapeseed (compared to A1′s 0.3% and A3′s 1%).
- CFD-DEM simulations demonstrate significant CV reductions for A2 compared to A1 and A3—45.65% and 73.68% for rapeseed, 19.09% and 54.55% for wheat, and 17.33% and 31.11% for rice, respectively.
- The optimized structure of the A2 distributor minimizes turbulence, reduces velocity differences and pressure loss, and prevents seed particle accumulation, ensuring consistent and uniform feed distribution.
- Further research using finite element analysis (ANSYS) is recommended to study airflow dynamics, refine head configurations, and enhance distribution efficiency for practical applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A1 | Funnel distributor |
| A2 | Closed-funnel distributor |
| A3 | Con-shaped distributor |
| CV | Coefficient of variation |
| CFD-DEM | Computational fluid dynamics–discrete element method coupling |
| df | Degree of freedom |
References
- Babu, U. Effect of Sowing Methods and Nutrients on Growth and Yield of Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): A Review. Curr. Res. Agric. Farming 2021, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Finch-Savage, W.E.; Bassel, G.W. Seed vigour and crop establishment: Extending performance beyond adaptation. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 567–591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, A.D.; Qingxi, L.; Ibrahim, E.J.; Lei, W. Design and experiment of the pneumatic cylinder type precision metering system for wheat. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2023, 16, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, P.; Xia, X.; Gao, P.; Ren, D.; Hao, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, R.; Hu, B.; Huang, Y. Double-Setting Seed-Metering Device for Precision Planting of Soybean at High Speeds. Trans. ASABE 2019, 62, 187–196. [Google Scholar]
- Yazgi, A.; Degirmencioglu, A. Optimisation of the seed spacing uniformity performance of a vacuum-type precision seeder using response surface methodology. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 97, 347–356. [Google Scholar]
- Lachuga, Y.; Akhalaya, B.; Shogenov, Y.; Meskhi, B.; Rudoy, D.; Olshevskaya, A. Innovative pneumatic device for combined seeding of various tilled crops. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 210, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, F.; Adeel, M.; Qui, B.; Ma, J.; Shoaib, M.; Shakoor, A.; Chandio, F.A. Sowing uniformity of bed-type pneumatic maize planter at various seedbed preparation levels and machine travel speeds. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.J.F.; Durairaj, C.D. Influence of head geometry on the distributive performance of air-assisted seed drills. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2000, 75, 81–95. [Google Scholar]
- Pareek, C.M.; Tewari, V.K.; Nare, B. A mechatronic seed metering control system for improving sowing uniformity of planters. J. Eng. Res. 2023, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.; Gao, N.; An, X.; Zhang, J. Study on Precision Application Rate Technology for maize no-tillage planter in North China Plain. IFAC-Pap. 2018, 51, 412–417. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yang, H.; He, J.; Kang, K.; Li, H. The Influence of Seed Variety and High Seeding Speed on Pneumatic Precision Seed Metering. Eng. Agrícola 2023, 43, e20220183. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Na, Y.; Chen, M.; Ge, Z.; Pan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wu, W.; Luo, X. Design and Experiment on a Distributed Seed Delivery System with a Pneumatic Central-Cylinder Seeder. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCartney, D.; Hultgreen, G.; Boyden, A.; Stevenson, C. Development of Agitators for Seeding Forages Using Air Delivery Systems. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2005, 58, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Cong, J.; Ren, N.; Ying, J.; Wang, X.; Liao, Y.; Liao, Q. Influence of surface slope on the seeding performance of air-assisted centralized metering device for rapeseed based on numerical simulation. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 218, 108–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kamgar, S.; Noei-Khodabadi, F.; Shafaei, S.M. Design, development and field assessment of a controlled seed metering unit to be used in grain drills for direct seeding of wheat. Inf. Process. Agric. 2015, 2, 169–176. [Google Scholar]
- ASABE S506 OCT2010 (R2024ED); Terminology & Definitions for Planters, Drills & Seeders. ASABE American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineering: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2024.
- ASABE S506 OCT2010 (R2019); Terminology & Definitions for Planters, Drills & Seeders. American society of agricultural and biological engineers: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2010.
- Lei, X.L. Design and experiment of seed feed device in air-assisted centralized seed-metering device for rapeseed and wheat. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H. Distribution characteristics and parameter optimisation of an air-assisted centralised seed-metering device for rapeseed using a CFD-DEM coupled simulation. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 208, 246–259. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Su, Y.; Xu, Y.; Huang, Y. Investigation of seeding performance of a novel high-speed precision seed metering device based on numerical simulation and high-speed camera. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108563. [Google Scholar]
- He, S. Design of and Experiment on a Cleaning Mechanism of the Pneumatic Single Seed Metering Device for Coated Hybrid Rice. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatskul, A.; Lemiere, J. Establishing the conveying parameters required for the air-seeders. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 166, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Hu, H.; Yang, W.; Liu, L.; Liao, Q.; Ren, W. Seeding performance of air-assisted centralized seed-metering device for rapeseed. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, H.; Yang, S.; Huang, Y.; Gao, X.; Fu, Z. Simulation and experiment of distributors of different outlet types of pneumatic collection and discharging systems based on CFD-DEM coupling. J. Intell. Agric. Mech. J. Intell. Agric. Mech. 2024, 5, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yatskul, A.; Lemiere, J.; Cointault, F. Influence of the divider head functioning conditions and geometry on the seed’s distribution accuracy of the air-seeder. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 161, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Liao, Q. Numerical simulation of seed motion characteristics of distribution head for rapeseed and wheat. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 150, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Ni, X.; Li, S.; Li, K.; Qi, Q. Simulation and Experimental Study of a Split High-Speed Precision Seeding System. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R. Numerical Simulation of Seed-Movement Characteristics in New Maize Delivery Device. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ognev, I.I.; Zyryanov, A.P.; Pyataev, M.V.; Gulyarenko, A.A. Influence of parameters of a pneumatic grain seeder distributor on the uniform distribution of seeds. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 193, 01031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierz, Ł.; Markowski, P. The effect of the distribution head tilt and diffuser variants on the evenness of sowing rye and oat seeds with a pneumatic seed drill. Materials 2020, 13, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourges, G.; Medina, M. Evaluación de la performance neumática del sistema de transporte de semillas en sembradoras ‘air drill’. Mecánica Comput. 2007, 10, 1131–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.Q.; Liu, Y.Q.; Hu, Y.W. An Airflow Field Finite Element Analysis of the Seed Adsorption Hole of Pneumatic Seeder. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2011, 117–119, 1810–1815. [Google Scholar]
- Han, D. DEM-CFD coupling simulation and optimization of an inside-filling air-blowing maize precision seed-metering device. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 150, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, T.; Su, Y.; Geng, J.; Niu, Z. Numerical simulation of feed pellet breakage in pneumatic conveying. Biosyst. Eng. 2022, 218, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieckhefen, P.; Pietsch, S.; Dosta, M.; Heinrich, S. Possibilities and Limits of Computational Fluid Dynamics–Discrete Element Method Simulations in Process Engineering: A Review of Recent Advancements and Future Trends. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2020, 11, 397–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Y.; Su, Y.; Cui, T. Numerical simulation of particle motion characteristics in quantitative seed feeding system. Powder Technol. 2020, 367, 643–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinzing, G.E. A review of pneumatic conveying status, advances and projections. Powder Technol. 2018, 333, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, F.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, L. CFD–DEM simulation of material motion in air-and-screen cleaning device. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2012, 88, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Y.; Chen, Z.; Yang, M.L.; Huang, Y.X. Mechanized corn production systems based on the combination of machinery and agronomy. Transact. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 8, 83–88. [Google Scholar]
- Romaní Fernández, X.; Nirschl, H. Simulation of particles and sediment behaviour in centrifugal field by coupling CFD and DEM. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 94, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salikov, V.; Antonyuk, S.; Heinrich, S.; Sutkar, V.S.; Deen, N.G.; Kuipers, J.A.M. Characterization and CFD-DEM modelling of a prismatic spouted bed. Powder Technol. 2015, 270, 622–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albasheer, A.H.; Liao, Q.; Wang, L.; Abdallah, A.D.; Lin, J. Design and Preliminary Evaluation of a Precision Cylindrical Air-Assisted Drill Sowing Device for Rapeseed, Wheat, and Rice. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 9478-2005; Quality Inspection PressGrain Seed Drill Test Method. China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2005.
- Scola, R.; Rossi, I.; Bourges, S. Gast, Air drill Seeder Distributor Head Evaluation: A Comparison between Laboratory Tests and Computational Fluid Dynamics Simulations. In Information and Communication Technologies for Agriculture—Theme II: Data; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; Volume 2, pp. 189–205. [Google Scholar]
- Allam, R.K.; Wiens, H. An Investigation of Air Seeder Component Characteristics; Prairie Agricultural Machinery Institute: Lethbridge, AB, Canada, 1983; Volume 82, p. 20. [Google Scholar]



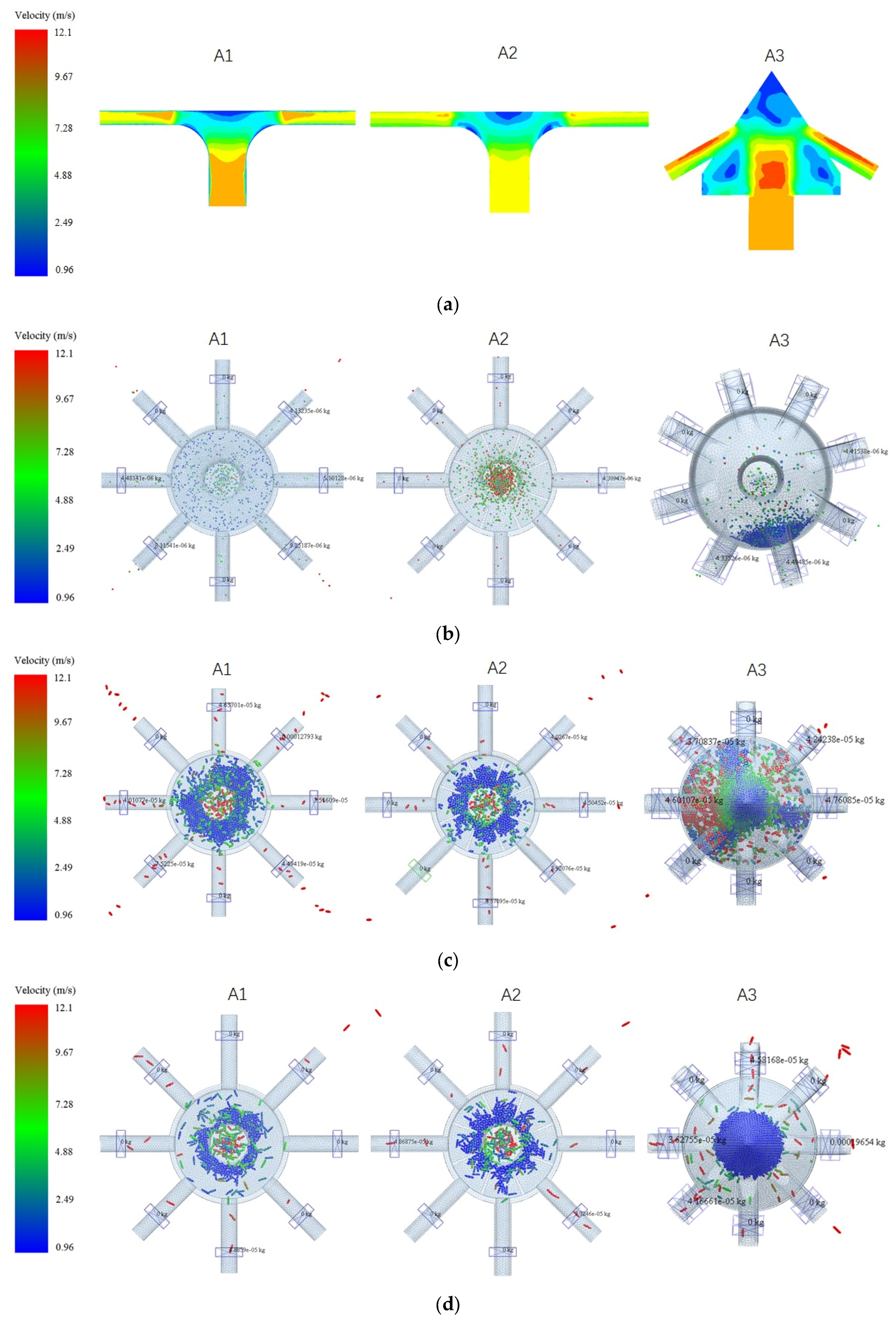

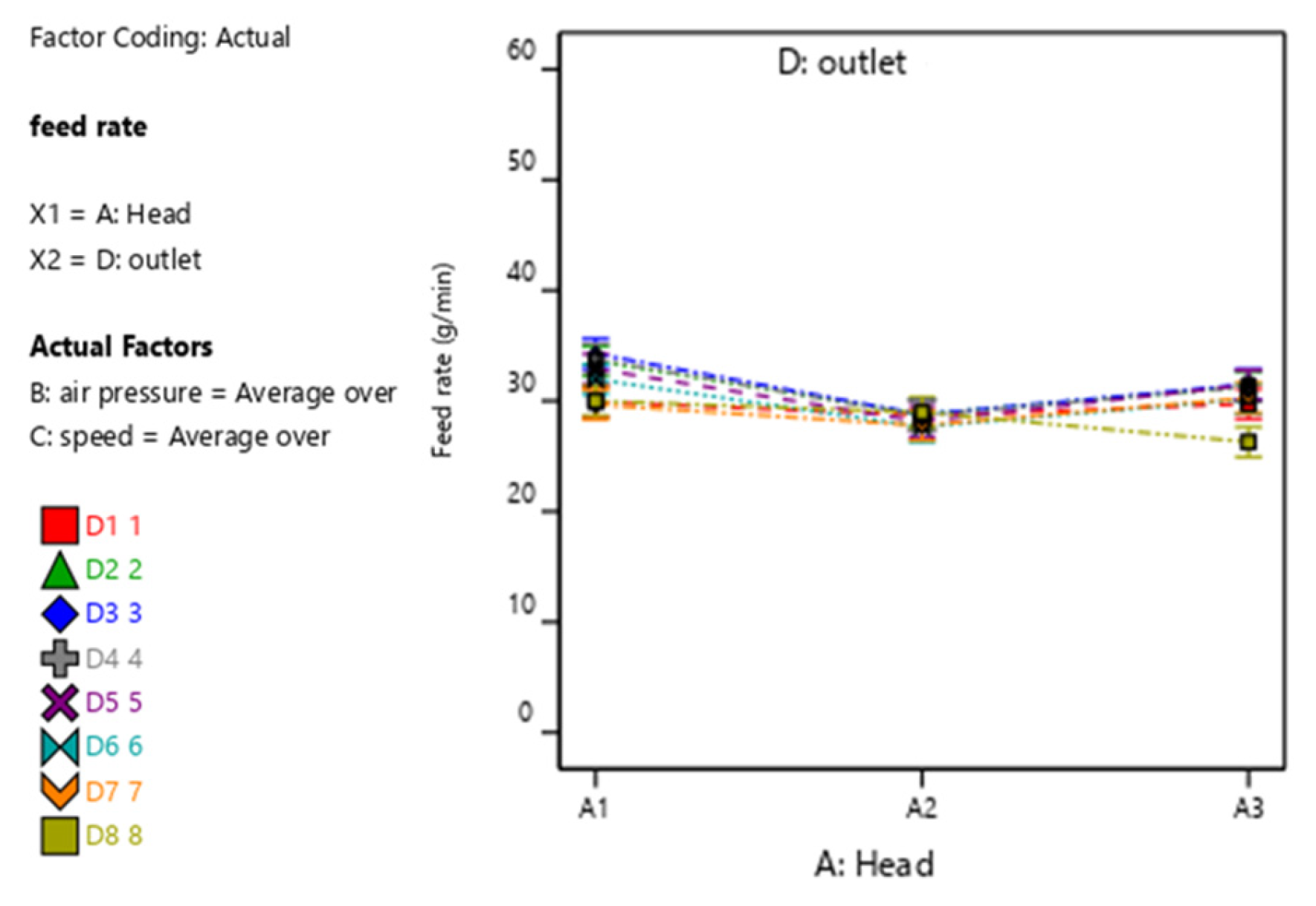
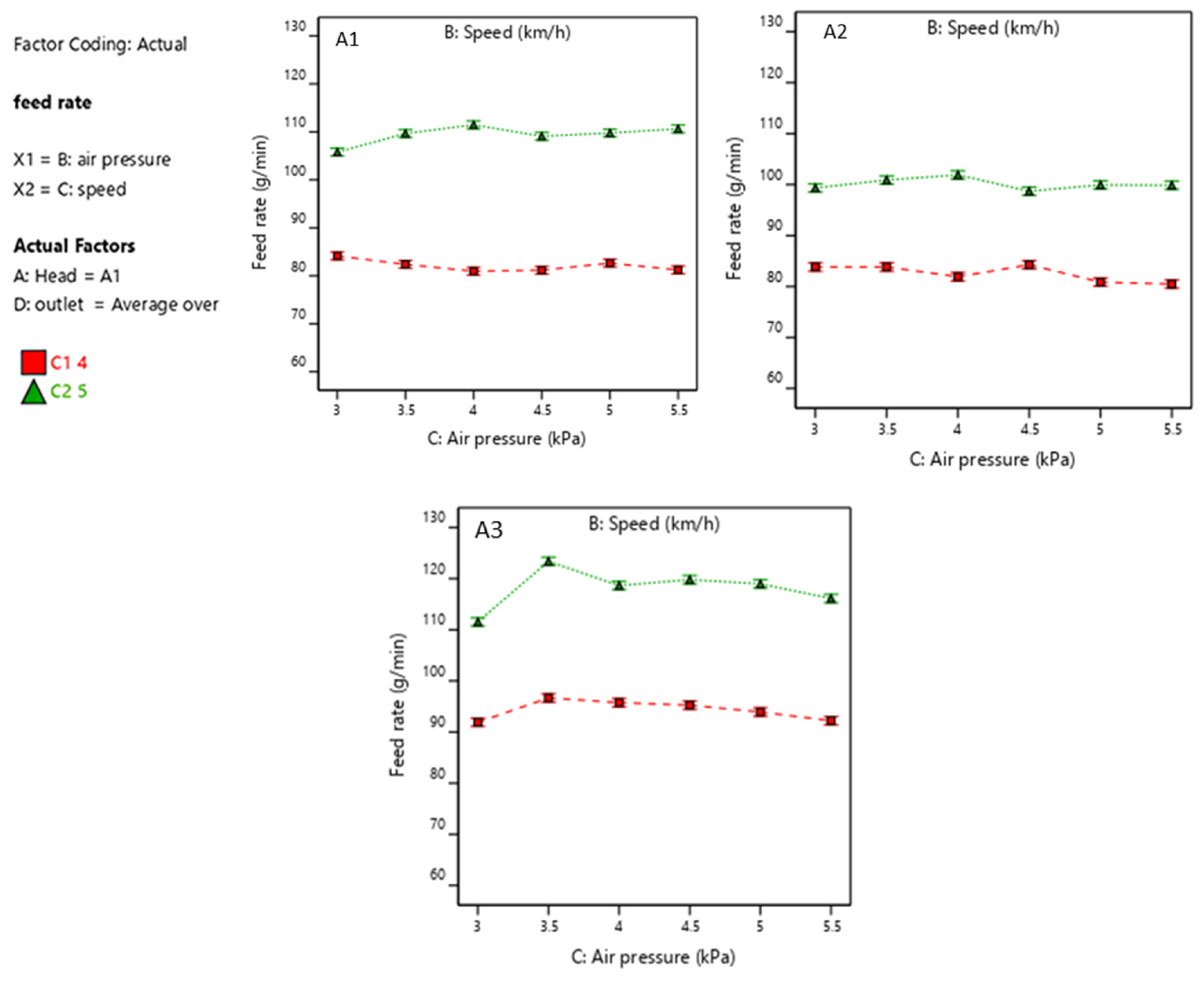


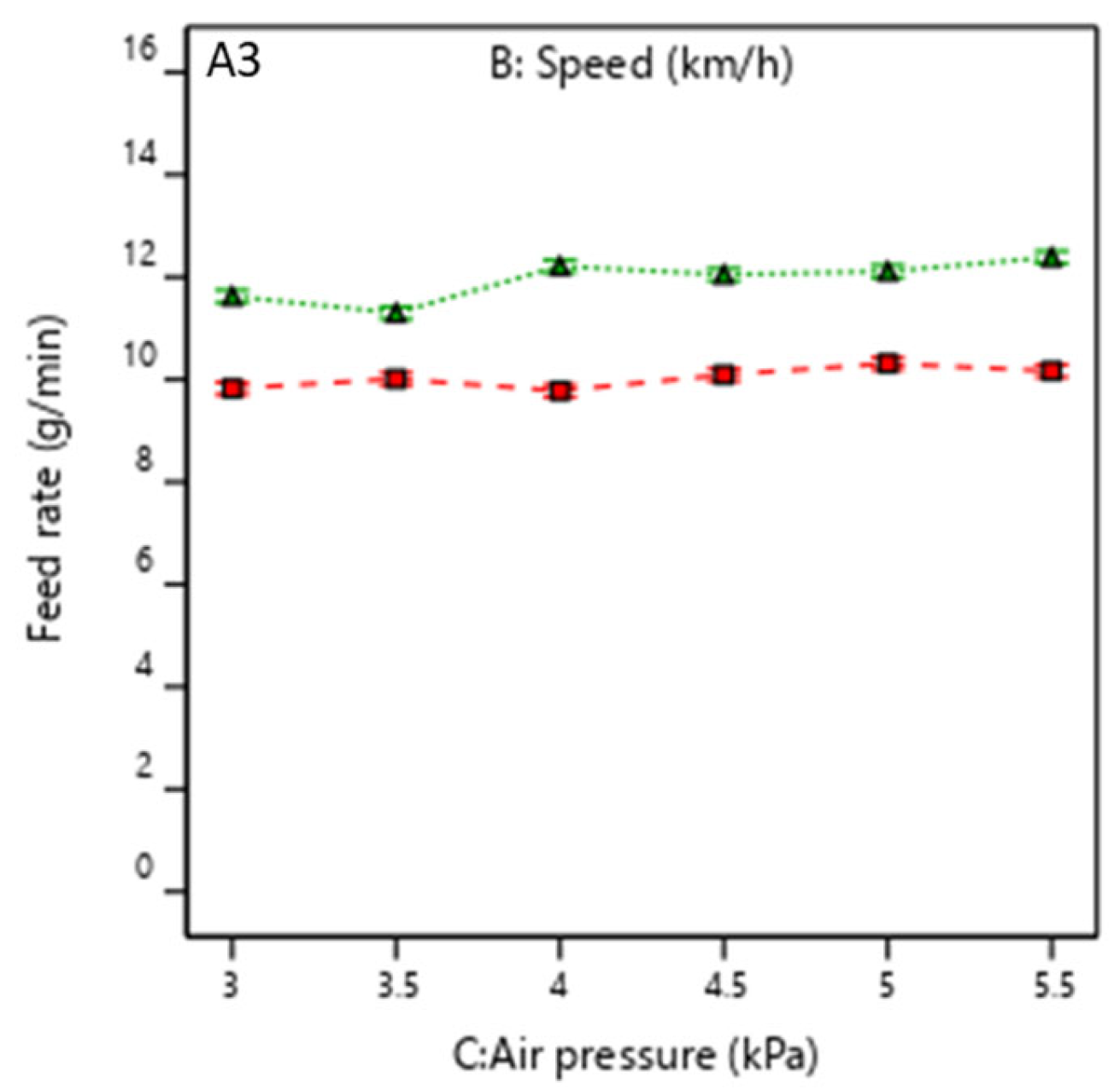

| Study | Objective | Design/Methodology | Key Findings | Limitations | Novelty of Current Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kumar and Durairaj [8] | Analyze head geometry’s role in seed distribution. | Experimental testing with different head shapes | Head geometry directly affects seed uniformity. | Limited to standard geometries and seed types. | Expands the analysis to three advanced designs (A1, A2, A3) across multiple seed types (wheat, rice, rapeseed). |
| Bourges and Medina [31] | Numerical simulation of air-seed distribution in air drills. | CFD simulations | Focused on the impact of air speed on distribution. | Did not include experimental validation or new geometry designs. | Performs CFD-DEM simulations with real-world validation, highlighting the superior performance of A2. |
| Yatskul et al. [25] | Investigate the effect of divider head geometry on seed distribution accuracy. | CFD simulations and experimental testing | Identified the impact of different geometries on distribution uniformity. | Focused only on basic funnel and pipe geometries. | Introduces barrier-based designs (A2) for improved seed flow control. |
| Lei et al. [26] | Study seed motion characteristics in pneumatic systems. | CFD-DEM coupled simulations | Found that CFD-DEM coupling improves prediction of seed distribution. | Did not explore barrier effects in distributor heads. | A2 design with barriers minimizes turbulence for better uniformity. |
| Gierz and Markowski [30] | Study distribution head tilt and diffuser variants. | Experimental testing and simulations | Found that tilting the distribution head improves sowing quality. | Only focused on oat seeds, limited analysis of geometry. | Introduces multi-seed analysis (wheat, rice, rapeseed) and new geometric configurations (A1, A2, A3). |
| Item | Parameter | Value |
|---|---|---|
| EDEM software v. 2018 | Fixed time steps (s) | 5 × 10−6 |
| Target save interval (s) | 1 × 10−3 | |
| Gravity (m s−2) | 9.81 | |
| CFD software v. 19.0 | Time step size (s) | 5 × 10−4 |
| Time step (s) | 1 × 10−3 | |
| Airflow density (kg m−3) | 1.225 | |
| Velocity (Pa s−1) | 15 (rapeseed); 24 (wheat and rice) |
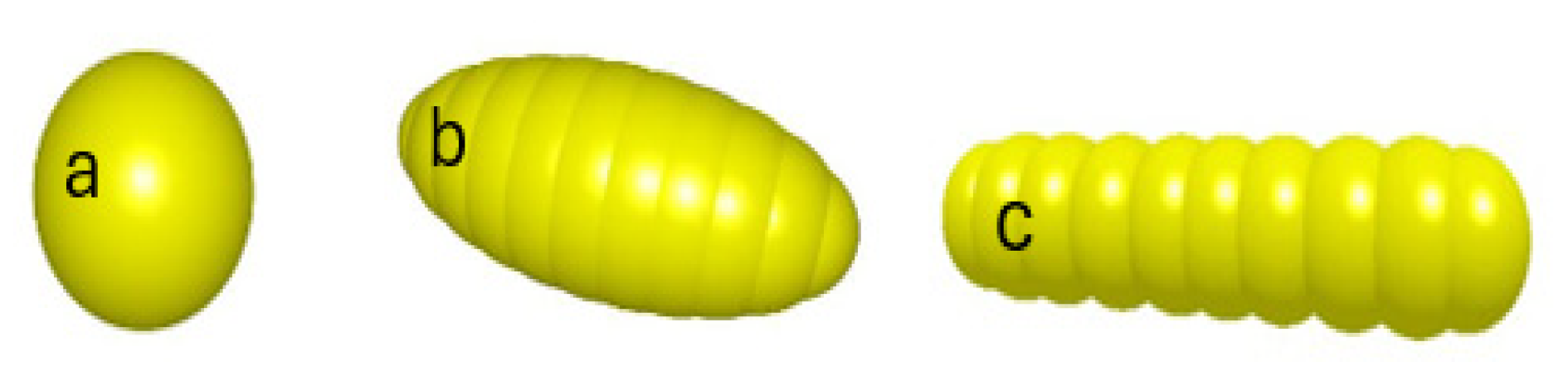
| Parameter | Rapeseed | Wheat | Rice | ABS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Three axes diminution, mm3 | 2 × 2 × 2 | 6 × 3 × 3 | 10.2 × 3 × 2 | ||
| Density kg/m3 | 1060 | 1350 | 1125 | 1060 | |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.25 | 0.42 | 0.30 | 0.394 | |
| Shear modules/pa | 1.1 × 107 | 5.1 × 107 | 1.01 × 108 | 8.96 × 108 | |
| Collision recovery coefficient | Seed–seed Seed–ABS | 0.60 | 0.42 | 0.50 | |
| 0.75 | 0.60 | 0.001 | |||
| Static friction coefficient | Seed–seed Seed–ABS | 0.50 | 0.35 | 0.50 | |
| 0.30 | 0.40 | 1.0 | |||
| Dynamic friction coefficient | Seed–seed Seed–ABS | 0.01 | 0.05 | 0.01 | |
| 0.01 | 0.05 | 1.03 | |||
| Type of Seed | Recommended Sowing Rate kg/ha | Air Pressure, Kpa | Seed Feed Rate with the Air Plenum, Sowing Rate, Distributing System, g/min Travel Speed, km/h | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 km/h | 5 km/h | |||
| Wheat | 187.5 | 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5 | 2000 | 3100 |
| Rice | 60 | 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5 | 600 | 1000 |
| Rapeseed | 6 | 3.0, 3.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0, 5.5 | 60 | 100 |
| Crop | Type of Distributor | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 CV (%) | A2 CV (%) | A3 CV (%) | |
| Rapeseed | 0.46 | 0.25 | 0.95 |
| Wheat | 3.09 | 2.5 | 5.5 |
| Rice | 3.75 | 3.1 | 4.5 |
| Source | df | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 287 | 16,944.5 | 59.04 | 10.34 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A—Head | 2 | 366.28 | 183.14 | 32.07 | <0.0001 | ** |
| B—Air pressure | 5 | 210.79 | 42.16 | 7.38 | <0.0001 | ** |
| C—Speed | 1 | 12,275.26 | 12,275.26 | 2149.37 | <0.0001 | ** |
| D—Outlet | 7 | 306.14 | 43.73 | 7.66 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AB | 10 | 297.18 | 29.72 | 5.2 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AC | 2 | 442.08 | 221.04 | 38.7 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AD | 14 | 394.82 | 28.2 | 4.94 | <0.0001 | NS |
| BC | 5 | 70.23 | 14.05 | 2.46 | 0.0322 | NS |
| BD | 35 | 502.85 | 14.37 | 2.52 | <0.0001 | ** |
| CD | 7 | 71.18 | 10.17 | 1.78 | 0.0886 | NS |
| ABC | 10 | 327.95 | 32.8 | 5.74 | <0.0001 | ** |
| ABD | 70 | 644.05 | 9.2 | 1.61 | 0.002 | NS |
| ACD | 14 | 133.3 | 9.52 | 1.67 | 0.0584 | NS |
| BCD | 35 | 246.77 | 7.05 | 1.23 | 0.1701 | NS |
| ABCD | 70 | 655.6 | 9.37 | 1.64 | 0.0014 | |
| Pure Error | 576 | 3289.59 | 5.71 | |||
| Total | 863 | 20,234.08 |
| Source | df | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 287 | 1.87 × 105 | 652.62 | 80.92 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A—Head | 2 | 33,563.29 | 16,781.64 | 2080.69 | <0.0001 | ** |
| B—Speed | 1 | 1.13 × 105 | 1.13 × 105 | 14,034.54 | <0.0001 | ** |
| C—Pressure | 5 | 1047.95 | 209.59 | 25.99 | <0.0001 | ** |
| D—Outlet | 7 | 8623.73 | 1231.96 | 152.75 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AB | 2 | 3503.09 | 1751.54 | 217.17 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AC | 10 | 1203.4 | 120.34 | 14.92 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AD | 14 | 16,268.31 | 1162.02 | 144.07 | <0.0001 | ** |
| BC | 5 | 781.24 | 156.25 | 19.37 | <0.0001 | ** |
| BD | 7 | 510.98 | 73 | 9.05 | <0.0001 | ** |
| CD | 35 | 1456.48 | 41.61 | 5.16 | <0.0001 | ** |
| ABC | 10 | 440.23 | 44.02 | 5.46 | <0.0001 | ** |
| ABD | 14 | 1018.94 | 72.78 | 9.02 | <0.0001 | ** |
| ACD | 70 | 3894.36 | 55.63 | 6.9 | <0.0001 | ** |
| BCD | 35 | 488.76 | 13.96 | 1.73 | 0.0064 | ** |
| ABCD | 70 | 1307.27 | 18.68 | 2.32 | <0.0001 | ** |
| Error | 576 | 4645.69 | 8.07 | |||
| Total | 863 | 1.92 × 105 |
| Source | df | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 287 | 1602.91 | 5.59 | 31.26 | <0.0001 | significant |
| A—Head | 2 | 74.12 | 37.06 | 207.42 | <0.0001 | ** |
| B—Speed | 1 | 1136.67 | 1136.67 | 6361.86 | <0.0001 | ** |
| C—Pressure | 5 | 37.92 | 7.58 | 42.45 | <0.0001 | ** |
| D—Outlet | 7 | 55.1 | 7.87 | 44.06 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AB | 2 | 26.16 | 13.08 | 73.2 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AC | 10 | 19.22 | 1.92 | 10.76 | <0.0001 | ** |
| AD | 14 | 194.18 | 13.87 | 77.63 | <0.0001 | ** |
| BC | 5 | 2.61 | 0.5213 | 2.92 | 0.013 | NS |
| BD | 7 | 1.39 | 0.1988 | 1.11 | 0.3534 | NS |
| CD | 35 | 8.59 | 0.2455 | 1.37 | 0.0774 | NS |
| ABC | 10 | 13.45 | 1.34 | 7.53 | <0.0001 | ** |
| ABD | 14 | 3.05 | 0.218 | 1.22 | 0.2557 | NS |
| ACD | 70 | 14.23 | 0.2034 | 1.14 | 0.2174 | NS |
| BCD | 35 | 4.48 | 0.128 | 0.7164 | 0.8878 | NS |
| ABCD | 70 | 11.74 | 0.1677 | 0.9384 | 0.6199 | NS |
| Error | 576 | 102.91 | 0.1787 | |||
| Total | 863 | 1705.82 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Albasheer, A.H.; Liao, Q.; Wang, L.; Ibrahim, E.J.; Xiao, W.; Li, X. Design and Optimization of Divider Head Geometry in Air-Assisted Metering Devices for Enhanced Seed Distribution Accuracy. Agronomy 2025, 15, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040769
Albasheer AH, Liao Q, Wang L, Ibrahim EJ, Xiao W, Li X. Design and Optimization of Divider Head Geometry in Air-Assisted Metering Devices for Enhanced Seed Distribution Accuracy. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040769
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlbasheer, Alfarog H., Qingxi Liao, Lei Wang, Elebaid Jabir Ibrahim, Wenli Xiao, and Xiaoran Li. 2025. "Design and Optimization of Divider Head Geometry in Air-Assisted Metering Devices for Enhanced Seed Distribution Accuracy" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040769
APA StyleAlbasheer, A. H., Liao, Q., Wang, L., Ibrahim, E. J., Xiao, W., & Li, X. (2025). Design and Optimization of Divider Head Geometry in Air-Assisted Metering Devices for Enhanced Seed Distribution Accuracy. Agronomy, 15(4), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040769






