Biological Solutions for Higher Maize Yield and Reduced Stalk Damage Caused by the European Corn Borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
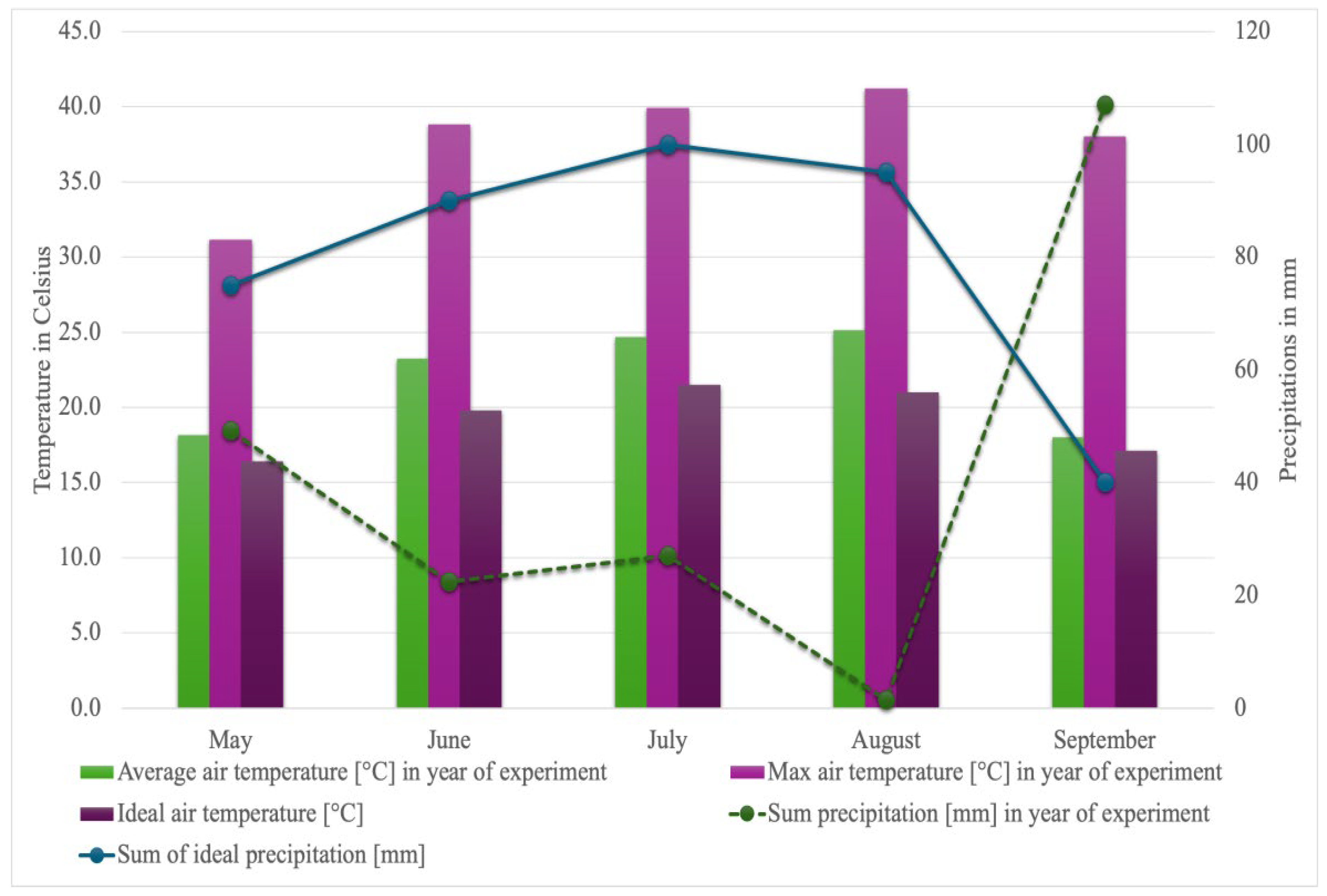
2.1. Weather Conditions
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.2.1. Partial Least Squares Regression (PLSR)
- Full factorial interaction of traits from the ear (number of tunnels, number of larvae, and tunnel length).
- Full factorial interaction of traits from the stalk (number of tunnels, number of larvae, and tunnel length).
2.2.2. Comparison of Regression Models and Selection of Distribution
2.2.3. Comparison of Treatments in Terms of Corn Borer Damage
2.2.4. Descriptive Statistics
2.2.5. Software and Tools
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics
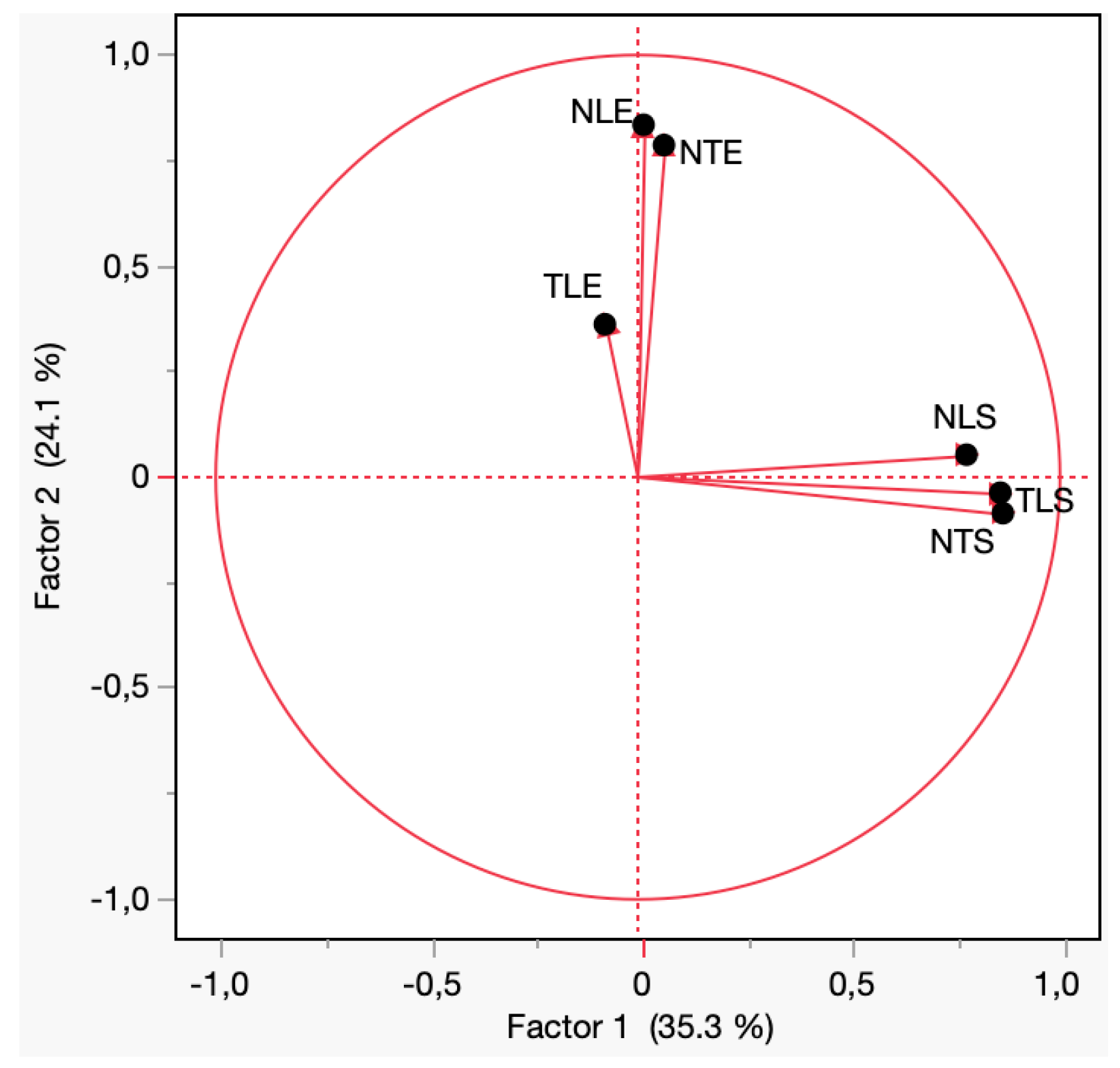
3.2. Initial Selection of Important Traits Impacting Yield Using PLSR
3.3. Final Selection of Important Traits Impacting Yield Using Generalized Regression Model
3.4. Factor and Discriminant Analyses Reveal Differences Between Treatments in Terms of Damage
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#compare (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Čamprag, D. Štetočine kukuruza. In Bolesti, Štetočine i Korovi Kukuruza i Njihovo Suzbijanje; Institut za kukuruz “Zemun Polje”: Novi Sad, Serbia, 2002; pp. 269–271. (In Serbian) [Google Scholar]
- Revillon, S.; Dillmann, C.; Galic, N.; Bauland, C.; Palaffre, C.; Malvar, R.A.; Butron, A.; Rebaudo, F.; Legrand, J. Effects of maize development and phenology on the field infestation dynamics of the European corn borer (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2023, 117, 1913–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keszthelyi, S. An important corn enemy: The European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis Hbn.) in the new approximation. Hung. Agric. Res. 2010, 5, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yanni, S.F.; Whalen, J.K.; Ma, B.L.; Gelinas, Y. European corn borer injury effects on lignin, carbon and nitrogen in corn tissues. Plant Soil 2011, 341, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tărău, A.; Păcurar, A.-M.; Mureșanu, F.; Șopterean, L.; Chețan, F.; Varga, A.; Porumb, I.; Russu, F.; Suciu, L. The research on the chemical control of Ostrinia nubilalis, in natural and artificial infestation conditions, an important link in integrated pest management. Manag. J. 2019, 19, 585–592. [Google Scholar]
- Alma, A.; Lessio, F.; Reyneri, A.; Blandino, M. Relationships between Ostrinia nubilalis (lepidoptera: Crambidae) feeding activity, crop technique and mycotoxin contamination of corn kernel in northwestern Italy. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2005, 51, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias-Martín, M.; Haidukowski, M.; Farinós, G.P.; Patiño, B. Role of Sesamia nonagrioides and Ostrinia nubilalis as Vectors of Fusarium spp. and Contribution of Corn Borer-Resistant bt Maize to Mycotoxin Reduction. Toxins 2021, 13, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimi, M.H.; Hashimi, R.; Ryan, Q. Toxic effects of pesticides on humans, plants, animals, pollinators and beneficial organisms. Asian Plant Res. J. 2020, 5, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission—Questions and Answers: Farm to Fork Strategy—Building a Healthy and Fully Sustainable Food System. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/sr/qanda_20_885 (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Bažok, R.; Igrc Barèiæ, J.; Kos, T.; Goltin Èuljak, T.; Šilović, M.; Jelovčan, S.; Kozina, A. Monitoring and efficacy of selected insecticides for European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis Hubn., Lepidoptera: Crambidae) control. J. Pest Sci. 2009, 82, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biddinger, D.J.; Hull, L.A. Effects of Several Types of Insecticides on the Mite Predator, Stethorus punctum (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae), Including Insect Growth Regulators and Abamectin. J. Econ. Entomol. 1995, 88, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolotti, L.; Porrini, C.; Micciarelli Sbrenna, A.; Giovanni, S. Ovicidal action of fenoxycarb on a predator, Chrysoperla carnea (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2000, 35, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, B.P.; Green, T.A.; Loker, A.J. Biological control and integrated pest management in organic and conventional systems. Biol. Control 2020, 140, 104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruberson, J.R.; Kring, T.J. Parasitism of developing eggs by Trichogramma pretiosum (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae): Host age preference and suitability. Biol. Control 1993, 3, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razinger, J.; Vasileiadis, V.P.; Giraud, M.; van Dijk, W.; Modic, Š.; Sattin, M.; Urek, G. On-farm evaluation of inundative biological control of Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) by Trichogramma brassicae (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) in three European maize-producing regions. Pest Manag. Sci. 2015, 71, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudon, M.; LeRoux, E.J.; Harcourt, D.G. Seventy years of European corn borer (Ostrinia nubilalis) research in North America. In Agricultural Zoology Reviews; Russell, G.E., Ed.; Intercept: Wimborne, UK, 1989; Volume 3, pp. 53–96. [Google Scholar]
- Ismoilov, K.; Wang, M.; Jalilov, A.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Z.; Saidov, A.; Sun, X.; Han, P. First Report Using a Native Lacewing Species to Control Tuta absoluta: From Laboratory Trials to Field Assessment. Insects 2020, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Zhang, H.Z.; Zhang, M.S.; Wang, M.Q.; Mao, J.J.; Zhang, L.S. The green lacewing Chrysopa formosa as a potential biocontrol agent for managing Spodoptera frugiperda and Spodoptera litura. Bull. Entomol. Res. 2022, 113, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boćanski, J.; Jocković, Đ.; Radojičić, S.; Popov, R.; Čapelja, V. Seed production of NS corn hybrids: Possibilities for improvement. In Zbornik Radova Instituta za Ratarstvo i Povrtarstvo; Institut za ratarstvo i povrtarstvo: Novi Sad, Serbia, 2008; Volume 45, pp. 81–87. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, M.D.; Moriarty, T.M.; Cook, D.D.; Mazzeo, B.A. Electrical Capacitance Measurements to Assess European Corn Borer Infestation in Maize. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 187, 106305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Rahman, M.E.; Landmann, T.; Kyalo, R.; Ong’amo, G.; Mwalusepo, S.; Sulieman, S.; LeRu, B. Predicting stem borer density in maize using RapidEye data and generalized linear models. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 57, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trnka, M.; Muška, F.; Semerádová, D.; Dubrovský, M.; Kocmánková, E.; Žalud, Z. European corn borer life stage model: Regional estimates of pest development and spatial distribution under present and future climate. Ecol. Model. 2007, 207, 61–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piekutowska, M.; Hara, P.; Pentoś, K.; Lenartowicz, T.; Wojciechowski, T.; Kujawa, S.; Niedbała, G. Predicting Starch Content in Early Potato Varieties Using Neural Networks and Regression Models: A Comparative Study. Agronomy 2024, 14, 3010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.P.; Johnson, R. High temperature stress and pollen viability of maize. Crop Sci. 1980, 20, 796–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harri, A.; Erdem, C.; Coble, K.H.; Knight, T.O. Crop yield distributions: A reconciliation of previous research and statistical tests for normality. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 2010, 31, 163–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.F.; Reynolds, H.T. Principles, Definition and Scope of Integrated Pest Control. In Proceedings of the FAO Symposium on Integrated Pest Control, Rome, Italy, 11–15 October 1965; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1996; Volume 1, pp. 11–18. [Google Scholar]
- Deguine, J.P.; Aubertot, J.N.; Flor, R.J.; Lescourret, F.; Wyckhuys, K.A.; Ratnadass, A. Integrated pest management: Good intentions, hard realities. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2021, 41, 38. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, M.G.; Kuhar, T.P.; Hoffmann, M.P.; Chenus, S.A. Effect of inoculative releases of Trichogramma ostriniae on populations of Ostrinia nubilalis and damage to sweet corn and field corn. Biol. Control 2002, 23, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gagnon, A.E.; Audette, C.; Duval, B.; Boisclair, J. Can the Use of Trichogramma ostriniae (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) to Control Ostrinia nubilalis (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) Be Economically Sustainable for Processing Sweet Corn? J. Econ. Entomol. 2017, 110, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.X.; Jaworski, C.C.; Desneux, N.; Zhang, F.; Yang, P.Y.; Wang, S. Long-term and large-scale releases of Trichogramma promote pesticide decrease in maize in northeastern China. Entomol. Gen. 2020, 40, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Lin, Y.; Ma, G.; Liu, J.; Hao, Z.; Han, S.; Peng, Z. Biocontrol potential of Trichogramma species against Spodoptera frugiperda and their field efficacy in maize. Crop Prot. 2021, 150, 105790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hou, Y.-Y.; Benelli, G.; Desneux, N.; Ali, A.; Zang, L.-S. Trichogramma ostriniae is more effective than Trichogramma dendrolimi as a biocontrol agent of the Asian corn borer, Ostrinia furnacalis. J. Insects 2022, 13, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Babendreier, D.; Wang, Z.; Il, K.S.; Zheng, L.; Pyon, Y.C.; Bai, S.; Song, K.; Ri, J.O.; Grossrieder, M.; et al. Mass releases of Trichogramma ostriniae increase maize production in DPR Korea. J. Appl. Entomol. 2010, 134, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivezić, A.; Rugman-Jones, P.; Malausa, T.; Ris, N.; Ignjatović-Ćupina, A. Molecular identification of Trichogramma species parasitizing Ostrinia nubilalis in corn and pepper in south–east border of Europe. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2020, 67, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tancik, J. Natural parasitism of the second generation European corn borer eggs Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner) (Lepidoptera, Pyralidae) by Trichogramma spp. in sweet corn fields in Vojvodina, Serbia—Short communication. CAAS Agric. J. 2017, 53, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cascone, P.; Tabebordbar, F.; Cencetti, G.; Michelozzi, M.; Shishehbor, P.; Guerrieri, E.; Giorgini, M. Phytophagy of Nesidiocoris tenuis triggers the response of Trichogramma achaeae to tomato plants infested by Tuta absoluta. J. Pest Sci. 2024, 97, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, I.J.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, R. Efficacy of the green lace wing, Chrysoperla zastrowi sillemi (Esben-Peterson) (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae), against sucking pests of tomato: An appraisal under protected conditions. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Nordlund, D.A. Use of Chrysoperla spp. (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) in augmentative release programmes for control of arthropod pests. Biocontrol News Inf. 1994, 15, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Xie, R.; Gu, M.; Qin, H. Green lacewing Chrysoperla rufilabris (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae) is a potential biological agent for crapemyrtle bark scale (Hemiptera: Eriococcidae) pest management. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, R.E.; Chiang, H.C. Reduction of an Ostrinia nubilalis population by predatory insects attracted by sucrose sprays. Entomophaga 1973, 18, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Ferro, D.; Hosmer, D. Effectiveness of Trichogramma ostriniae and T. nubilale for controlling the European corn borer Ostrinia nubilalis in sweet corn. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1999, 91, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navik, O.; Yele, Y.; Kedar, S.C.; Sushil, S.N. Biological control of fall armyworm Spodoptera frugiperda (JE Smith) using egg parasitoids, Trichogramma species (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae): A review. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2023, 33, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar Aghdam, H.; Nemati, Z. Modeling of the effect of temperature on developmental rate of common green lacewing, Chrysoperla carnea (Steph.)(Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2020, 30, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Trait | Mean | Std. Dev | CV (%) | Min | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield (t ha−1) | 1.97 | 0.76 | 38.83 | 1.28 | 3.60 |
| NTE | 0.54 | 0.17 | 32.03 | 0.25 | 0.86 |
| NLE | 0.16 | 0.19 | 118.37 | 0.00 | 0.75 |
| TLE | 3.49 | 1.30 | 37.28 | 1.00 | 5.33 |
| NTS | 2.38 | 0.34 | 14.09 | 1.40 | 2.80 |
| NLS | 1.12 | 0.26 | 23.56 | 0.65 | 1.55 |
| TLS | 22.75 | 4.31 | 18.94 | 10.97 | 30.38 |
| Traits | VIP |
|---|---|
| NTE | 1.2281 |
| NLE | 0.2336 |
| NTE × NLE | 0.1398 |
| TLE | 1.5282 |
| NTE × TLE | 0.1969 |
| NLE × TLE | 0.3992 |
| NTE × NLE × TLE | 0.2129 |
| NTS | 1.3137 |
| TLS | 1.5827 |
| NTS × TLS | 1.0932 |
| NLS | 0.9656 |
| NTS × NLS | 1.1280 |
| TLS × NLS | 1.0598 |
| NTS × TLS × NLS | 1.0417 |
| Response | Yield | |||||
| Distribution | Best subset | |||||
| Validation method | Holdback | |||||
| Location model link | Identity | |||||
| Scale model link | Identity | |||||
| Measure | Training | Validation | ||||
| −LogLikelihood | 4.69 | −2.80 | ||||
| BIC | 26.77 | 2.10 | ||||
| Generalized R2 | 0.74 | 0.84 | ||||
| Term | Estimate | Std Error | Wald ChiSquare | Prob > ChiSquare | Lower 95% | Upper 95% |
| Intercept | 9.286 | 0.241 | 1489.105 | <0.0001 ** | 8.814 | 9.757 |
| NTE | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| TLE | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| NTS | −2.576 | 0.091 | 798.593 | <0.0001 ** | −2.755 | −2.398 |
| TLS | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| NTS × TLS | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| NLS | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| NTS × NLS | −6.731 | 0.307 | 481.716 | <0.0001 ** | −7.332 | −6.130 |
| TLS × NLS | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| NTS × TLS × NLS | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Treatment [T3–T4] | −1.234 | 0.091 | 182.328 | <0.0001 ** | −1.413 | −1.055 |
| Treatment [T1–T4] | −0.994 | 0.073 | 186.499 | <0.0001 ** | −1.137 | −0.852 |
| Treatment [T2–T4] | −0.707 | 0.041 | 292.813 | <0.0001 ** | −0.788 | −0.626 |
| Treatment | −Treatment | Difference (t ha−1) | Std Error | t Ratio | Prob > |t| | Lower 95% | Upper 95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T3 | T1 | −0.240 | 0.105 | −2.278 | 0.2053 | −0.604 | 0.125 |
| T3 | T2 | −0.527 | 0.091 | −5.788 | 0.0047 ** | −0.842 | −0.212 |
| T3 | T4 | −1.234 | 0.091 | −13.503 | <0.0001 ** | −1.550 | −0.918 |
| T1 | T2 | −0.287 | 0.070 | −4.124 | 0.0239 * | −0.528 | −0.046 |
| T1 | T4 | −0.994 | 0.073 | −13.656 | <0.0001 ** | −1.246 | −0.742 |
| T2 | T4 | −0.707 | 0.041 | −17.112 | <0.0001 ** | −0.851 | −0.564 |
| Average yield (t ha−1) | T1 = 1.988 (C) | ||||||
| T2 = 2.275 (B) | |||||||
| T3 = 1.748 (C) | |||||||
| T4 = 2.983 (A) |
| Ear Damage | Stalk Damage | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Prob > F | Prob > F | ||
| Treatment | 0.0170 * | 0.2829 | |
| Level | T1 | 0.86A | 0.34A |
| T2 | 0.87A | 0.19A | |
| T3 | 0.90A | 0.46A | |
| T4 | 0.42B | 0.11A | |
| Correlation with average yield | r = −0.93 | r = −0.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Franeta, F.; Đurić, A.; Dunđerski, D.; Stanisavljević, D.; Konjević, A.; Ivezić, A.; Popović, T.; Milovac, Ž. Biological Solutions for Higher Maize Yield and Reduced Stalk Damage Caused by the European Corn Borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner). Agronomy 2025, 15, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040764
Franeta F, Đurić A, Dunđerski D, Stanisavljević D, Konjević A, Ivezić A, Popović T, Milovac Ž. Biological Solutions for Higher Maize Yield and Reduced Stalk Damage Caused by the European Corn Borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner). Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040764
Chicago/Turabian StyleFraneta, Filip, Anja Đurić, Dušan Dunđerski, Dušan Stanisavljević, Aleksandra Konjević, Aleksandar Ivezić, Tamara Popović, and Željko Milovac. 2025. "Biological Solutions for Higher Maize Yield and Reduced Stalk Damage Caused by the European Corn Borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner)" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040764
APA StyleFraneta, F., Đurić, A., Dunđerski, D., Stanisavljević, D., Konjević, A., Ivezić, A., Popović, T., & Milovac, Ž. (2025). Biological Solutions for Higher Maize Yield and Reduced Stalk Damage Caused by the European Corn Borer, Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner). Agronomy, 15(4), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040764







