Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substitution for Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Fertility, Yield, and Quality of Muskmelons
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Plant and Soil Sampling, and Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
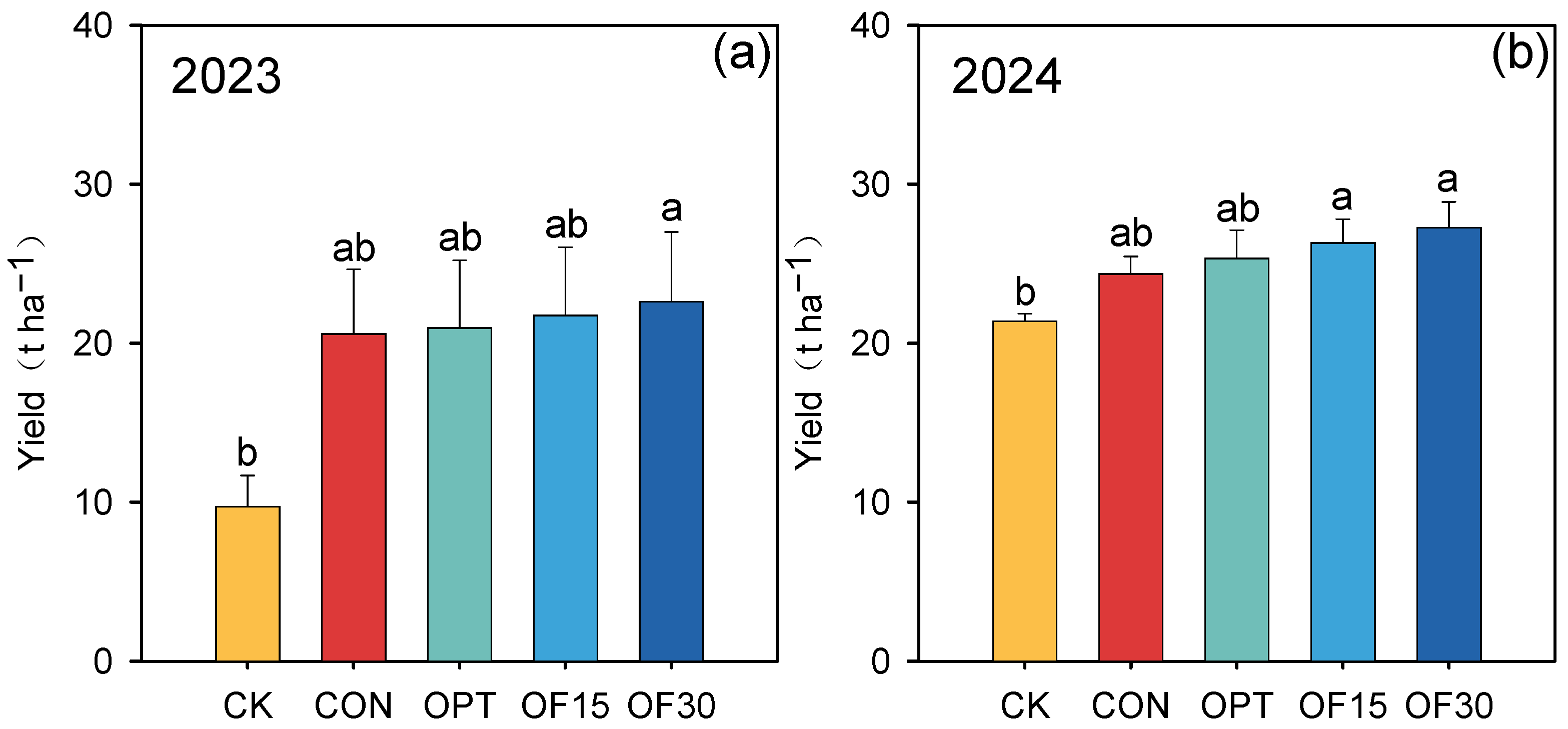
3.1. Impact of Partial Organic Substitution on Yield and Quality of Muskmelon
3.2. Impact of Partial Organic Substitution on Soil Physicochemical Properties
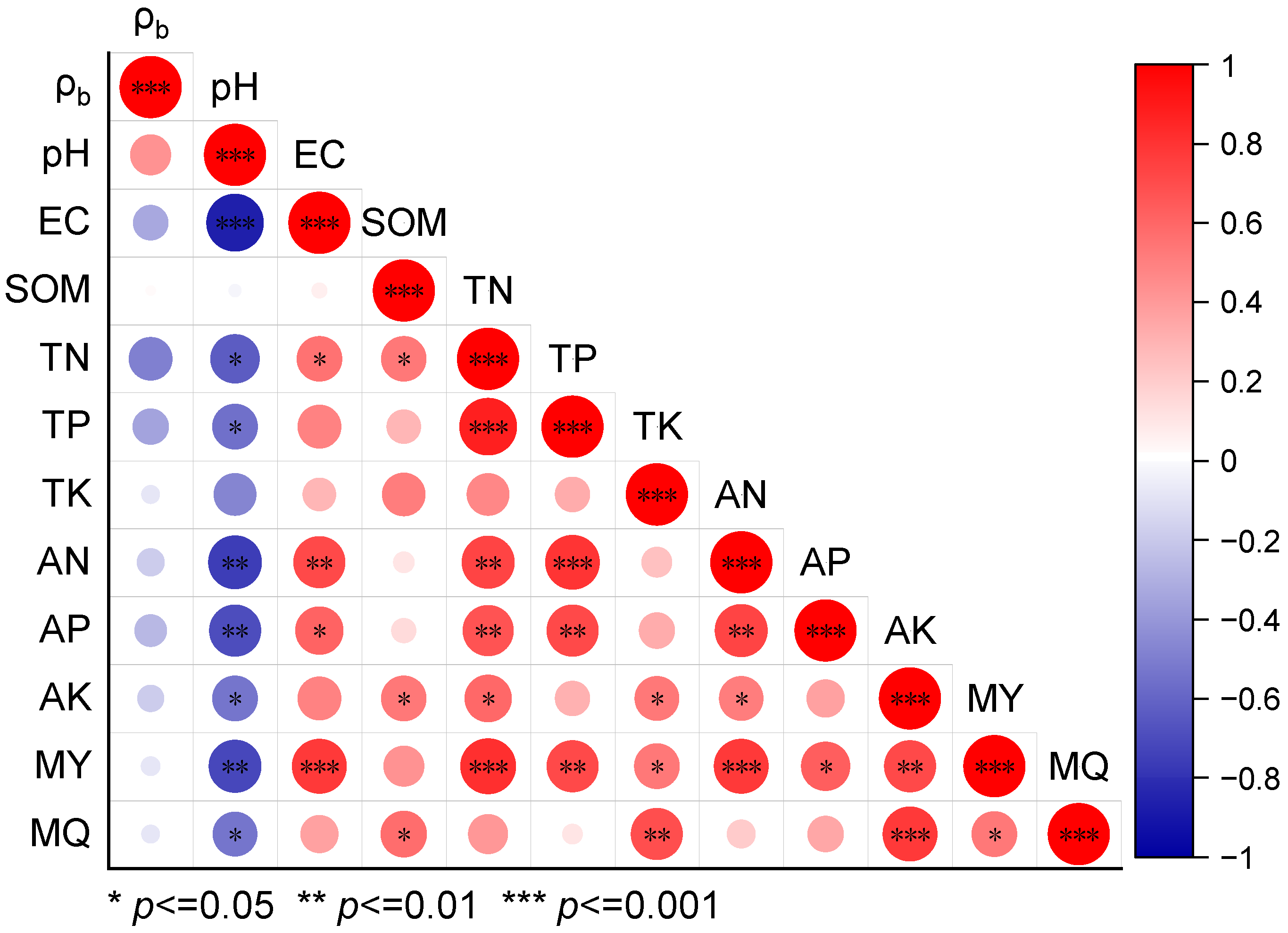
3.3. Correlation Between Soil Physicochemical Properties and the Yield and Quality of Muskmelon
3.4. Impact of Partial Organic Substitution on Economic Benefits of Muskmelon
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Partial Organic Substitution on Muskmelon Productivity, Quality, and Economic Benefits
4.2. Effect of Partial Organic Substitution on Soil Fertility
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhang, Z.D.; Han, X.Y.; Wu, J.H.; Zhang, L.Z.; Wang, J.R.; Wang-Pruski, G. Specific response mechanism to autotoxicity in melon (Cucumis melo L.) root revealed by physiological analyses combined with transcriptome profiling. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 200, 110779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.L.; Xu, X.; Lin, J.Y.; Bing, H.; Wang, X.J.; Zhao, J.W.; Xiang, W.S. Identification and Pathogenicity of Fungi Associated with Leaf Spot of Muskmelon in Eastern Shandong Province, China. Plant Dis. 2022, 106, 872–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing nitrogen for sustainable development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.W.; Chen, H.L.; Liu, M.C. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on aromatic compounds and nutritional quality of melon fruits. Plant Nutr. Fertil. Sci. 2011, 17, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar]
- Goucher, L.; Bruce, R.; Cameron, D.D.; Lenny Koh, S.C.; Horton, P. The environmental impact of fertilizer embodied in a wheat-to-bread supply chain. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaji, H.; Chandran, V.; Mathew, L. Chapter 13—Organic fertilizers as a route to controlled release of nutrients. In Controlled Release Fertilizers for Sustainable Agriculture; Lewu, F.B., Volova, T., Thomas, S., Rakhimol, R.K., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 231–245. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Shafy, H.I.; Mansour, M.S.M. Solid waste issue: Sources, composition, disposal, recycling, and valorization. Egypt. J. Pet. 2018, 27, 1275–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyhorn, F.; Muller, A.; Reganold, J.P.; Frison, E.; Herren, H.R.; Luttikholt, L.; Mueller, A.; Sanders, J.; Scialabba, N.E.-H.; Seufert, V.; et al. Sustainability in global agriculture driven by organic farming. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouhia, Y.; Hafidi, M.; Ouhdouch, Y.; El Boukhari, M.E.; Mphatso, C.; Zeroual, Y.; Lyamlouli, K. Conversion of waste into organo-mineral fertilizers: Current technological trends and prospects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio-Technol. 2022, 21, 425–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Chen, H.; Gong, Y.; Fan, M.; Yang, H.; Lal, R.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of 15 years of manure and inorganic fertilizers on soil organic carbon fractions in a wheat-maize system in the North China Plain. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 92, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Ju, X.; Shen, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Mi, G.; Fan, M.; et al. Integrated nutrient management for food security and environmental quality in China. In Advances in Agronomy; Sparks, D.L., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 116, pp. 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Christie, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Maize yield and soil fertility with combined use of compost and inorganic fertilizers on a calcareous soil on the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, M.; Nayak, A.K.; Puree, C.; Tripathi, R.; Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, A.; Panda, B.B.; et al. Carbon and nitrogen fractions and stocks under 41 years of chemical and organic fertilization in a sub-humid tropical rice soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 170, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shu, A.; Song, W.; Shi, W.; Li, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, G.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, S.; et al. Long-term organic fertilizer substitution increases rice yield by improving soil properties and regulating soil bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.F.; Shu, A.P.; Liu, J.A.; Shi, W.C.; Li, M.C.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, Z.Z.; Liu, G.R.; Yuan, F.S.; Zhang, S.X.; et al. Effects of long-term fertilization with different substitution ratios of organic fertilizer on paddy soil. Pedosphere 2022, 32, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moe, K.; Htwe, A.Z.; Thu, T.T.P.; Kajihara, Y.; Yamakawa, T. Effects on NPK Status, Growth, Dry Matter and Yield of Rice (Oryza sativa) by Organic Fertilizers Applied in Field Condition. Agriculture 2019, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnaudery, M.; Fournier, P.; LÉChaudel, M. Low-input pineapple crops with high quality fruit: Promising impacts of locally integrated and organic fertilisation compared to chemical fertilisers. Exp. Agric. 2018, 54, 286–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, R. Challenges and opportunities in soil organic matter research. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 60, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, R.; Kukal, S.S.; Hira, G.S. Soil organic carbon and physical properties as affected by long-term application of FYM and inorganic fertilizers in maize–wheat system. Soil Tillage Res. 2008, 101, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niewes, D.; Biegun, M.; Huculak-Maczka, M.; Marecka, K.; Kaniewski, M.; Zielinski, J.; Hoffmann, J. Extraction of humic acid from peat and lignite and the thermal behavior of their mixtures with ammonium nitrate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2023, 148, 13175–13188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qaswar, M.; Jing, H.; Ahmed, W.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; Lu, Z.; Cai, A.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. Yield sustainability, soil organic carbon sequestration and nutrients balance under long-term combined application of manure and inorganic fertilizers in acidic paddy soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 198, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravuer, K.; Gennet, S.; Throop, H.L. Organic amendment additions to rangelands: A meta-analysis of multiple ecosystem outcomes. Glob. Change Biol. 2019, 25, 1152–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edmeades, D.C. The long-term effects of manures and fertilisers on soil productivity and quality: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2003, 66, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.F.; Ni, K.; Wu, Z.D.; Zhang, J.W.; Yi, X.Y.; Yang, X.D.; Ling, N.; You, Z.M.; Guo, S.W.; Ruan, J.Y. Effect of organic substitution rates on soil quality and fungal community composition in a tea plantation with long-term fertilization. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 633–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazcano, C.; Gómez-Brandón, M.; Revilla, P.; Domínguez, J. Short-term effects of organic and inorganic fertilizers on soil microbial community structure and function: A field study with sweet corn. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Gao, W.; Huang, S.; Tang, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic amendments affects soil organic carbon composition and stability in a greenhouse vegetable production system. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheoran, H.; Kakar, R.; Kumar, N. Impact of organic and conventional farming practices on soil quality: A global review. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2019, 17, 951–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, H.E.; Zimmermann, N.E.; McVicar, T.R.; Vergopolan, N.; Berg, A.; Wood, E.F. Present and future Köppen-Geiger climate classification maps at 1-km resolution. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostecka, M.; Szot, I.; Czernecki, T.; Szot, P. Vitamin C content of new ecotypes of cornelian cherry (Cornus mas L.) determined by various analytical methods. Acta Sci. Pol. Hortorum Cultus 2017, 16, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, H. A colorimetric estimation of reducing sugars in potatoes with 3, 5-dinitrosalicylic acid. Potato Res. 1973, 16, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkley, A.; Black, I.A.J.S.s. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Potato Res. 1934, 37, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremner, J.M. Determination of nitrogen in soil by the Kjeldahl method. J. Agric. Sci. 1960, 55, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Mao, Q.; Li, X.; You, Y.; Wang, J.; Zheng, M.; Zhang, W.; Lu, X.J.S.B.; et al. Nitrogen addition reduces soil bacterial richness, while phosphorus addition alters community composition in an old-growth N-rich tropical forest in southern China. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 127, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, G.; English, L. Use of the flame photometer in rapid soil tests for K and Ca. Agron. J. 1949, 41, 446–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Min, X.; Yang, Z.; Chai, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y. Physicochemical and biological quality of soil in hexavalent chromium-contaminated soils as affected by chemical and microbial remediation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogunovic, I.; Trevisani, S.; Seput, M.; Juzbasic, D.; Durdevic, B. Short-range and regional spatial variability of soil chemical properties in an agro-ecosystem in eastern Croatia. Catena 2017, 154, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogunovic, I.; Pereira, P.; Brevik, E.C. Spatial distribution of soil chemical properties in an organic farm in Croatia. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 584–585, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xi, Y.; Wu, X.; Pei, X.; Liang, G.; Bai, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; et al. Partial substitution of manure reduces nitrous oxide emission with maintained yield in a winter wheat crop. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, B.X.; Hou, Y.; Wang, S.Q.; Ma, W.Q. Partial substitution of urea fertilizers by manure increases crop yield and nitrogen use efficiency of a wheat-maize double cropping system. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2023, 127, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Fang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Ma, W.; Velthof, G.L.; Hou, Y.; Oenema, O.; Zhang, F. Benefits and trade-offs of replacing synthetic fertilizers by animal manures in crop production in China: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 888–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, W.B.; Cannon, K.R.; Robertson, J.A.; Cook, F.D. Dynamics of soil microbial biomass and water-soluble organic C in Breton L after 50 years of cropping to two rotations. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1986, 66, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Chen, W.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Q. Soil aggregate size-dependent relationships between microbial functional diversity and multifunctionality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 154, 108143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Yang, S.; Luan, C.S.; Wu, Q.; Lin, L.L.; Li, X.X.; Che, Z.; Zhou, D.B.; Dong, Z.R.; Song, H. Partial organic substitution for synthetic fertilizer improves soil fertility and crop yields while mitigating N2O emissions in wheat-maize rotation system. Eur. J. Agron. 2024, 154, 127077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.T.; Xiao, C.; Bi, R.Y.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, B.X.; Dong, Y.B.; Xiong, Z.Q. Optimizing organic fertilization towards sustainable vegetable production evaluated by long-term field measurement and multi-level fuzzy comprehensive model. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 368, 109008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.R.; Wang, H.Q.; Jiang, G.Y.; Yin, H.J.; Che, Z.Q. Effects of Nitrogen Application Strategy on Nitrogen Enzyme Activities and Protein Content in Spring Wheat Grain. Agriculture 2022, 12, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Huang, H.M.; Jia, B.B.; Hu, L.L.; Luan, C.S.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, X.X.; Che, Z.; Dong, Z.R.; et al. Partial organic substitution increases soil quality and crop yields but promotes global warming potential in a wheat-maize rotation system in China. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 244, 106274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Yan, P.; Wang, X.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.; Sui, P.; Chen, Y. Integrated assessment of economic and environmental consequences of shifting cropping system from wheat-maize to monocropped maize in the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 193, 524–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufert, V.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J.A. Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture. Nature 2012, 485, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Li, B.; Chen, L.; Liang, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.Q. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer over seven years increases yields and restores soil bacterial community diversity in wheat-rice rotation. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 133, 126445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.C.; Zhang, X.Z.; Luo, J.F.; Zhu, P.; Lindsey, S.; Gao, H.J.; Li, Q.; Peng, C.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.Y.; et al. Changes in soil fertility under partial organic substitution of chemical fertilizer: A 33-year trial. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 7424–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, É.; Angers, D.A. Animal manure application and soil organic carbon stocks: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Shan, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lv, Z.; Ji, J.; Hou, H.; Xia, W.; Liu, Y. Effects of long-term manure substitution regimes on soil organic carbon composition in a red paddy soil of southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 221, 105395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Du, X.; Li, Y.; Han, X.; Li, B.; Zhang, X.; Li, Q.; Liang, W. Organic substitutions improve soil quality and maize yield through increasing soil microbial diversity. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 347, 131323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.-J.; Su, J.-Q.; Sun, G.-X.; Wu, J.-S.; Wei, W.-X. Increased microbial functional diversity under long-term organic and integrated fertilization in a paddy soil. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 1969–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.J.; Guo, J.H.; Vogt, R.D.; Mulder, J.; Wang, J.G.; Zhang, X.S. Soil pH as the chief modifier for regional nitrous oxide emissions: New evidence and implications for global estimates and mitigation. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, E617–E626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Treatment | Basal Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | Topdressing Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | Total Fertilizer Application (kg ha−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compound Fertilizer | Organic Fertilizer | Water-Soluble Fertilizer 1 | Water-Soluble Fertilizer 2 | N | P2O5 | K2O | |
| CK | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| CON | 600 | 0 | 900 | 675 | 364 | 310 | 540 |
| OPT | 0 | 4870 | 900 | 675 | 364 | 322 | 561 |
| OF15 | 0 | 7100 | 695 | 675 | 364 | 327 | 571 |
| OF30 | 0 | 9330 | 540 | 600 | 364 | 338 | 560 |
| Year | Treatment | Vitamin C (mg 100 g−1) | Soluble Protein (g kg−1) | Sugar (%) | Nitrate (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | CK | 11.1 ± 0.039 d | 0.441 ± 0.006 c | 15.6 ± 0.255 ab | 42.9 ± 6.90 b |
| CON | 12.1 ± 0.402 d | 0.948 ± 0.091 a | 15.0 ± 0.749 b | 51.6 ± 3.82 a | |
| OPT | 17.3 ± 0.048 c | 0.853 ± 0.079 ab | 15.5 ± 0.253 ab | 31.6± 5.39 c | |
| OF15 | 22.7 ± 1.22 a | 0.762 ± 0.063 b | 16.4 ± 0.416 a | 26.4 ± 1.40 c | |
| OF30 | 19.7 ± 0.397 b | 0.824 ± 0.022 b | 16.4 ± 0.751 a | 24.7 ± 1.88 c | |
| 2024 | CK | 11.8 ± 2.36 a | 0.319 ± 0.027 a | 10.8 ± 0.402 ab | 72.9 ± 18.4 a |
| CON | 11.1 ± 1.16 a | 0.370 ± 0.043 a | 11.6 ± 2.95 a | 93.3 ± 30.4 a | |
| OPT | 14.3 ± 6.81 a | 0.307 ± 0.054 a | 11.0 ± 2.08 a | 72.5 ± 29.0 a | |
| OF15 | 8.67 ± 1.70 a | 0.313 ± 0.067 a | 11.6 ± 1.54 a | 80.4 ± 28.3 a | |
| OF30 | 10.3 ± 3.56 a | 0.401 ± 0.262 a | 12.7 ± 0.780 a | 84.1 ± 12.7 a |
| Year | Treatment | ρb (g cm−3) | pH | SOM (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | TK (g kg−1) | AN (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | AK (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | CK | 1.34 ± 0.022 a | 7.61 ± 0.021 c | 8.50 ± 0.187 ab | 0.503 ± 0.027 d | 1.43 ± 0.140 b | 15.0 ± 1.60 a | 59.3 ± 2.22 d | 123 ± 2.56 c | 95.0 ± 10.2 d |
| CON | 1.26 ± 0.009 b | 7.75 ± 0.065 c | 6.26 ± 0.104 b | 0.652 ± 0.022 c | 1.83 ± 0.133 a | 13.4 ± 1.13 a | 72.1 ± 2.71 c | 122 ± 1.92 c | 135 ± 5.00 c | |
| OPT | 1.25 ± 0.043 b | 7.77 ± 0.037 c | 10.1 ± 1.64 ab | 0.679 ± 0.019 c | 1.86 ± 0.018 a | 13.2 ± 0.253 a | 77.7 ± 2.24 b | 124 ± 1.89 c | 155 ± 18.0 bc | |
| OF15 | 1.23 ± 0.041 b | 7.88 ± 0.014 b | 10.5 ± 0.082 ab | 0.733 ± 0.011 b | 1.75 ± 0.559 a | 12.4 ± 0.491 a | 86.4 ± 1.21 a | 140 ± 5.06 a | 175 ± 10.0 ab | |
| OF30 | 1.21 ± 0.037 b | 8.00 ± 0.058 a | 11.2 ± 1.31 a | 0.801 ± 0.020 a | 1.48 ± 0.021 a | 12.7 ± 0.948 a | 89.1 ± 3.48 a | 132 ± 2.44 b | 202 ± 20.2 a | |
| 2024 | CK | 1.25 ± 0.018 a | 8.94 ± 0.114 a | 10.1 ± 1.68 ab | 0.646 ± 0.009 b | 1.23 ± 0.051 b | 8.88 ± 0.339 b | 53.5 ± 2.39 b | 57.4 ± 7.26 b | 140 ± 33.5 c |
| CON | 1.21 ± 0.036 a | 8.59 ± 0.347 b | 7.41 ± 4.22 b | 0.864 ± 0.101 a | 1.56 ± 0.152 a | 8.73 ± 0.725 b | 71.7 ± 5.97 a | 82.7 ± 14.7 a | 157 ± 16.5 c | |
| OPT | 1.28 ± 0.027 a | 8.66 ± 0.093 ab | 11.1 ± 2.22 ab | 0.820 ± 0.129 ab | 1.47 ± 0.109 a | 8.82 ± 0.654 b | 69.8 ± 6.93 a | 75.8 ± 1.62 ab | 210 ± 2.08 b | |
| OF15 | 1.19 ± 0.128 a | 8.44 ± 0.079 b | 12.2 ± 1.03 a | 0.941 ± 0.131 a | 1.54 ± 0.112 a | 12.1 ± 1.16 a | 68.0 ± 3.70 a | 83.4 ± 1.51 a | 233 ± 21.1 ab | |
| OF30 | 1.21 ± 0.032 a | 8.40 ± 0.082 b | 12.0 ± 1.43 ab | 0.939 ± 0.058 a | 1.48 ± 0.103 a | 10.2 ± 0.728 b | 72.2 ±0.762 a | 91.1 ± 18.8 a | 258 ± 35.6 a |
| Year | Treatment | Total Income | Chemical Fertilizer | Organic Fertilizer | Total Cost | Net Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | CK | 26.2 | / | / | 6.57 | 19.6 |
| CON | 55.0 | 4.59 | / | 11.2 | 43.8 | |
| OPT | 56.3 | 4.09 | 0.990 | 11.7 | 44.6 | |
| OF15 | 58.1 | 3.47 | 1.82 | 11.9 | 46.3 | |
| OF30 | 60.3 | 2.88 | 2.64 | 12.1 | 48.2 | |
| 2024 | CK | 40.9 | / | / | 6.57 | 34.3 |
| CON | 48.2 | 4.59 | / | 11.2 | 37.0 | |
| OPT | 49.3 | 4.09 | 0.990 | 11.7 | 37.6 | |
| OF15 | 52.4 | 3.47 | 1.82 | 11.9 | 40.6 | |
| OF30 | 54.6 | 2.88 | 2.64 | 12.1 | 42.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Z.; Guo, B.; Sun, T.; Li, R.; Zhao, Z.; Yao, L. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substitution for Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Fertility, Yield, and Quality of Muskmelons. Agronomy 2025, 15, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030639
Yu Z, Guo B, Sun T, Li R, Zhao Z, Yao L. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substitution for Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Fertility, Yield, and Quality of Muskmelons. Agronomy. 2025; 15(3):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030639
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Zhanlonggang, Bing Guo, Tao Sun, Ran Li, Zichao Zhao, and Li Yao. 2025. "Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substitution for Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Fertility, Yield, and Quality of Muskmelons" Agronomy 15, no. 3: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030639
APA StyleYu, Z., Guo, B., Sun, T., Li, R., Zhao, Z., & Yao, L. (2025). Effects of Organic Fertilizer Substitution for Mineral Fertilizer on Soil Fertility, Yield, and Quality of Muskmelons. Agronomy, 15(3), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030639






