Contamination of Phthalic Acid Esters in China’s Agricultural Soils: Sources, Risk, and Control Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
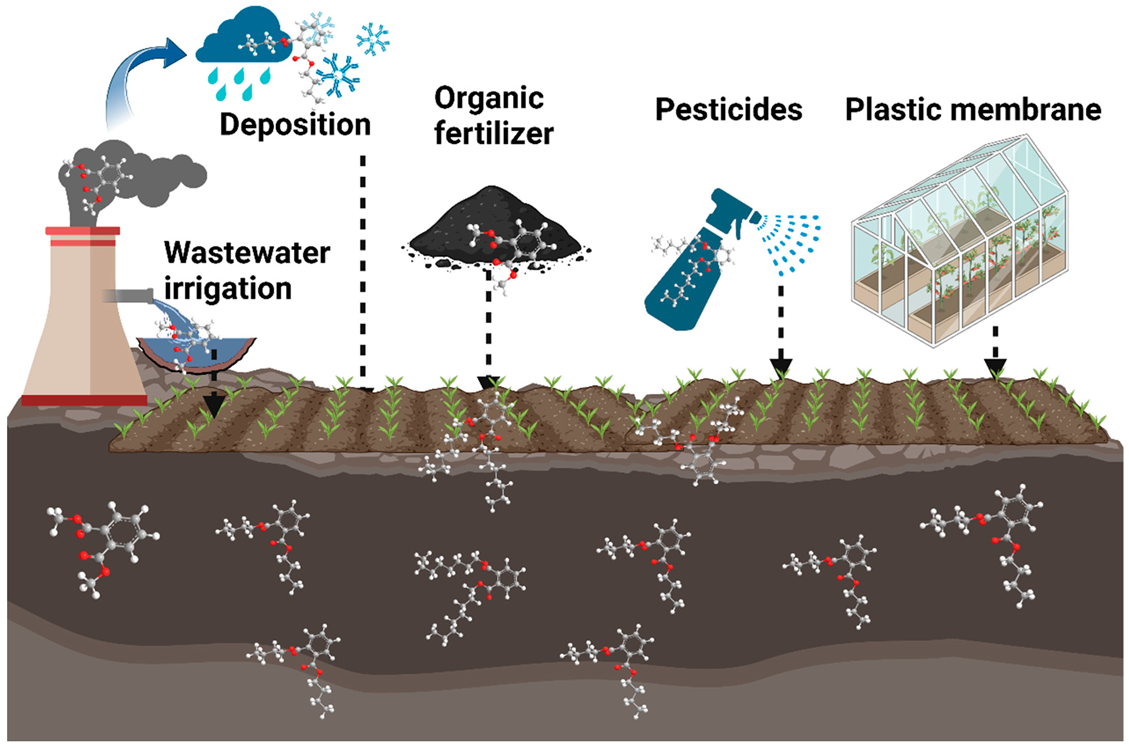
2. Sources of Phthalic Acid Esters
3. Concentration and Risk of PAEs in Agricultural Soil–Crop Systems
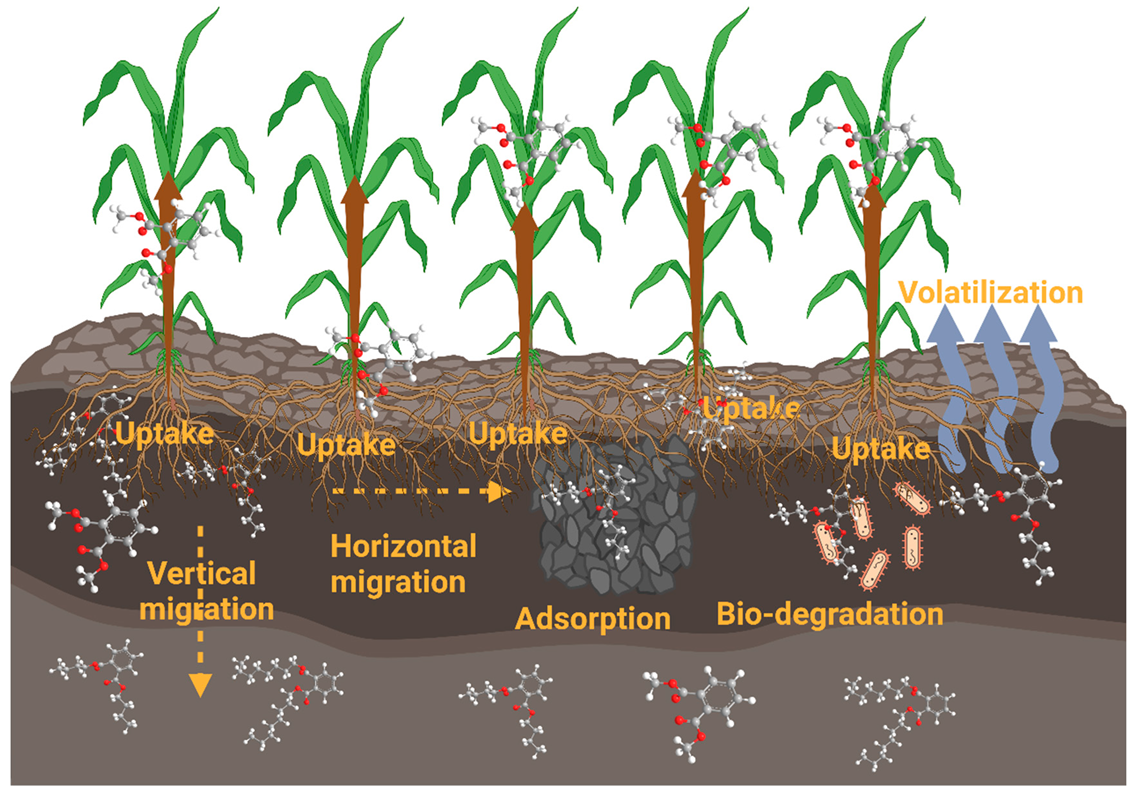
4. Fate and Transformation of PAEs in Agricultural Soils
4.1. Adsorption
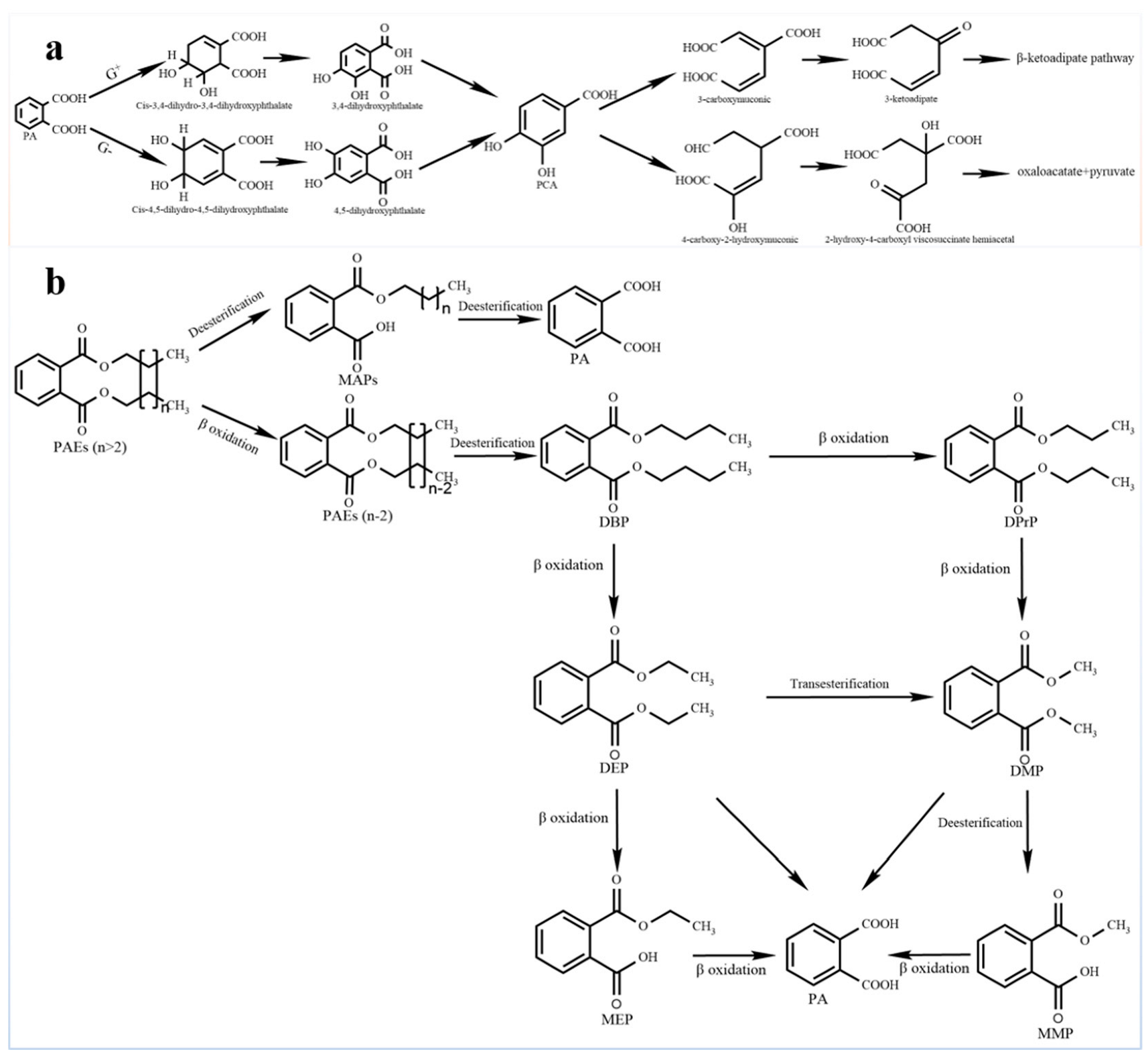
4.2. Biodegradation
4.3. Migration
4.4. Volatilization
5. The Control of PAE Contamination Risks in Soil–Crop Systems
| Methods | Advantage | Disadvantage | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Physical remediation | The bioavailability of pollutants can be reduced in a short time | Adsorbed PAEs are easily desorbed and cannot be removed directly from the soil | [108] |
| Chemical remediation | Strong oxidation capacity, wide application range, no secondary pollution, and strong operability for organic pollutants | Negative effects on soil physicochemical properties and microbial community composition | [109] |
| Bioremediation | High efficiency, complete PAE degradation, low cost, and environmental friendliness | Long processing time, strict requirements for external conditions | [110] |
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qadeer, A.; Kirsten, K.L.; Ajmal, Z.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, X. Alternative plasticizers as emerging global environmental and health threat: Another regrettable substitution? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 1482–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Ma, T.; Ma, K.; Ni, X.; Wu, S. Accumulation and Transport of Phthalic Acid Esters in the Soil-Plant System of Agricultural Fields with Different Years of Film Mulching. Sustainability 2023, 15, 15589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ng, E.L.; Hu, W.; Wang, H.; Galaviz, P.; Yang, H.; Liu, H. Plastic pollution in croplands threatens long-term food security. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 3356–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.M.; Li, X.G.; Javaid, M.M.; Ashraf, M.; Zhang, F. Ridge-furrow plastic film mulching farming for sustainable dryland agriculture on the Chinese loess plateau. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 3284–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Ma, Z.R.; Cai, Y.Y.; Li, H.R.; Ying, G.G. Agricultural plastic pollution in China: Generation of plastic debris and emission of phthalic acid esters from agricultural films. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 12459–12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Gu, C.; Redmile-Gordon, M.; Sheng, H.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Bian, R.; Jiang, X. Risk assessment of agricultural plastic films based on release kinetics of phthalate acid esters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 3676–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Pan, K.; Shoaib, N.; Sun, X.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L. Status of phthalate esters pollution in facility agriculture across China: Spatial distribution, risk assessment, and remediation measures. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Zhang, H.; Huang, C.; Ben, Y.; Zhou, H.; Guo, H.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, P. Occurrence and potential risks of organophosphate esters in agricultural soils: A case study of Fuzhou City, Southeast China. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 150, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Redmile-Gordon, M.; Gu, C.; Yang, X.; Barceló, D. Perspectives on ecological risks of microplastics and phthalate acid esters in crop production systems. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2022, 4, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, N.; Lv, H.; Liang, C.; Yang, H.; Wang, J. Occurrence, source, ecological risk, and mitigation of phthalates (PAEs) in agricultural soils and the environment: A review. Environ. Res. 2023, 220, 115196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddela, N.R.; Ramakrishnan, B.; Dueñas-Rivadeneira, A.A.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M. Chemicals/materials of emerging concern in farmlands: Sources, crop uptake and potential human health risks. Environ. Sci. Process. Impacts 2022, 24, 2217–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masinga, P.; Simbanegavi, T.T.; Makuvara, Z.; Marumure, J.; Chaukura, N.; Gwenzi, W. Emerging organic contaminants in the soil–plant-receptor continuum: Transport, fate, health risks, and removal mechanisms. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti, M.; Fasano, M.; Palandri, L.; Righi, E. A review of European and international phthalates regulation: Focus on daily use products. Eur. J. Public Health 2022, 32 (Suppl. S3), ckac131.226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Barone, G.D.; Ding, D.; Mao, Y.; Nan, F.; Xu, L.; Wang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Cernava, T. Pollution Status, Ecological Effects, and Bioremediation Strategies of Phthalic Acid Esters in Agricultural Ecosystems: A Review. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2024, 72, 27668–27678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puri, M.; Gandhi, K.; Kumar, M.S. The occurrence, fate, toxicity, and biodegradation of phthalate esters: An overview. Water Environ. Res. 2023, 95, e10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljoen, S.J.; Brailsford, F.L.; Murphy, D.V.; Hoyle, F.C.; Chadwick, D.R.; Jones, D.L. Leaching of phthalate acid esters from plastic mulch films and their degradation in response to UV irradiation and contrasting soil conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 443, 130256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Liu, C.; He, D.; Xu, J.; Sun, J.; Li, J.; Pan, X. Environmental behaviors of microplastics in aquatic systems: A systematic review on degradation, adsorption, toxicity and biofilm under aging conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.Y.; Mo, C.H.; Wu, Q.T.; Zeng, Q.Y. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalic acid esters in the soil–radish (Raphanus sativus) system with sewage sludge and compost application. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 1830–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.W.; Wen, Z.D. Phthalate esters in the environment: A critical review of their occurrence, biodegradation, and removal during wastewater treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billings, A.; Jones, K.C.; Pereira, M.G.; Spurgeon, D.J. Plasticisers in the terrestrial environment: Sources, occurrence and fate. Environ. Chem. 2021, 18, 111–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.Y.; Zhou, S.G.; Hong, W.; Feng, W.F.; Tao, L. Pollution characteristics of volatile organic compounds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and phthalate esters emitted from plastic wastes recycling granulation plants in Xingtan Town, South China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 71, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hab, S.A.; Talpur, F.N.; Baig, J.A.; Afridi, H.I.; Surhio, M.A.; Talpur, M.K. Leaching and exposure of phthalates from medical devices; health impacts and regulations. Environ. Contam. Rev. 2018, 1, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.J.; Shi, Y.J.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Y.; Teng, S.X.; Wang, S.G.; Zhao, R. Degradation of phthalate esters (PAEs) in soil and the effects of PAEs on soil microcosm activity. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1108–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; Wang, T.; Han, W.; Yuan, B.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G. Spatial and vertical distribution of short chain chlorinated paraffins in soils from wastewater irrigated farmlands. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 2100–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Teng, Y.; Christie, P.; Luo, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ye, M.; Huang, Y. A new procedure combining GC-MS with accelerated solvent extraction for the analysis of phthalic acid esters in contaminated soils. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2013, 7, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y. Study on the High-Performance Liquid Chromatography detection method of phthalic acid esters in soils. China Environ. Sci. 2022, 43, 756–763. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, J.; Cui, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, G. Determination of phthalate esters in soil by microemulsion electrokinetic chromatography coupled with accelerated solvent extraction. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 3717–3725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowski, A.; Dybowski, M.P.; Oleszczuk, P.; Gao, Y.; Czech, B. Fast and reliable determination of phthalic acid esters in soil and lettuce samples based on QuEChERS GC–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2024, 440, 138222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, L.; Xu, Y.; Xu, C.; Yun, L.; Liu, W. Status of phthalate esters contamination in agricultural soils across China and associated health risks. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 195, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Tao, Y.; Xu, J.; He, Y.; Lu, Z. Release of additives from agricultural plastic films in water: Experiment and modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 10053–10061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škrbić, B.D.; Ji, Y.; Đurišić-Mladenović, N.; Zhao, J. Occurence of the phthalate esters in soil and street dust samples from the Novi Sad city area, Serbia, and the influence on the children’s and adults’ exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 312, 272–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, B.C.; Teil, M.J.; Blanchard, M.; Alliot, F.; Chevreuil, M. Fate of phthalates and BPA in agricultural and non-agricultural soils of the Paris area (France). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 11118–11126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhind, S.M.; Kyle, C.E.; Kerr, C.; Osprey, M.; Zhang, Z.L.; Duff, E.I.; Lilly, A.; Nolan, A.; Hudson, G.; Towers, W.; et al. Concentrations and geographic distribution of selected organic pollutants in Scottish surface soils. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikelsøe, J.; Thomsen, M.; Carlsen, L. Phthalates and nonylphenols in profiles of differently dressed soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 296, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, T.; Xu, D.; Xue, Y.; Xi, B.; Sun, J.; Peng, K.; Zhang, J.; Jin, D. Analysis of phthalate esters pollution in 59 top soils of long-term film mulching plots in China. Asian J. Eco-Toxicol. 2022, 17, 462–471. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Li, C.; Luan, Y.; Wang, J.; Lu, A.X. Pollution characteristics and pollution level of phthalic acid ester in soils of facility vegetable bases of Beijing. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2016, 7, 472–477. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Gu, H.; Huang, Q.; Huang, G.; Li, L. Assessment of contamination risk of PAEs in soils and crops of irrigation district located at southeastern suburbs of Beijing. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 203–212. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, L.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Weng, L.; Li, Y. Contamination and human health risks of phthalate esters in vegetable and crop soils from the Huang-Huai-Hai region of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Ji, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, L.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Sun, Z. Diversities of phthalate esters in suburban agricultural soils and wasteland soil appeared with urbanization in China. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 170, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.Y.; Wen, B.; Shan, X.Q. Survey of phthalate pollution in arable soils in China. J. Environ. Monit. 2003, 5, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Hao, J.; Xiong, Y.; Cao, J. Accumulation Characteristics and Sources of PAEs in Agricultural Soils in Gansu Province. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2022, 43, 4622–4629. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yi, Y.; Xie, F.; Hu, H.; Wu, H.; Jing, C.; Zulikeerjiang, T.; Jing, C. Residual characteristics of phthalate acid esters (PAEs) in cotton fields with different mulching film years in Wujiaqu area, Xinjiang. J. Xinjiang Agric. Univ. 2020, 43, 221–227. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guo, D.M.; Wu, Y. Determination of phthalic acid esters of soil in south of Xinjiang cotton fields. Arid Environ. Monit. 2011, 25, 76–79. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Tao, H. Study on pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of phthalates in soil of Ningxia. China Environ. Sci. 2020, 40, 3930–3941. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tuohutaerhan, M.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Q.; Tuersibieke, G.; He, W.; Kong, L.; Wang, C. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of phthalates in melon field soil. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 36, 287–295. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Tao, H. Pollution characteristics of phthalate esters (PAEs) in soils of facility vegetable bases and health risk assessment in eastern suburb of Yinchuan. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 3703–3713. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, H. Study on Pollution Characteristics of Phthalic Acid Esters in Agricultural Soil and It’s Microbial Remediation in Yinchuan City (M); Ningxia University: Yinchuan, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, H.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Li, J. Pollution characteristics of phthalate acid esters in agricultural soil of Yinchuan, northwest China, and health risk assessment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2020, 42, 4313–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Pan, L.; Zhan, Y.; Lu, H.; Tsang, D.C.; Liu, W.; Zhu, L. Contamination of phthalate esters, organochlorine pesticides and polybrominated diphenyl ethers in agricultural soils from the Yangtze River Delta of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhu, L. Pollution characteristics and health risk assessment of phthalate esters in agricultural soil and vegetables in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 137978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.P.; Ying, R.R.; Lin, Y.S.; Wang, G.Q. Distribution characteristics of phthalic acid esters in soil and vegetables under greenhouse in different areas of Jiangsu Province, China. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2017, 33, 308–316. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, B.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; Li, Y. Spatial distribution of phthalate esters and the associated response of enzyme activities and microbial community composition in typical plastic-shed vegetable soils in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 195, 110495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Ma, D.; Wu, J.; Chai, C.; Shi, Y. Distribution of phthalate esters in agricultural soil with plastic film mulching in Shandong Peninsula, East China. Chemosphere 2016, 164, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.A.; Xue, Y.H.; Li, X.H.; Duan, Q.H.; Gao, S.B. Phthalate acid esters (PAEs) pollution in soils and agricultural products of vegetable greenhouses in Shouguang City, Shandong Province. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 492–499. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Song, D.; Sun, H.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, M.; Feng, C.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Status of phthalate esters in tobacco cultivation soils and its health risk to Chinese people. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, C.; Cheng, H.; Ge, W.; Ma, D.; Shi, Y. Phthalic acid esters in soils from vegetable greenhouses in Shandong Peninsula, East China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewlaoyoong, A.; Vu, C.T.; Lin, C.; Liao, C.S.; Chen, J.R. Occurrence of phthalate esters around the major plastic industrial area in southern Taiwan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, L.; Han, B.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Tao, S.; Liu, W. Pollution characteristics and affecting factors of phthalate esters in agricultural soils in mainland China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 466, 133625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, H.; Yu, X.; Huang, J.; Du, X.; Wang, M.; Sun, J.; Tao, X. Characteristics and health risks of phthalate ester contamination in soil and plants in coastal areas of South China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 9516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, F.; Cui, K.; Xie, Z.; Wu, L.; Liu, M.; Sun, G.; Zeng, Z. Phthalate esters (PAEs): Emerging organic contaminants in agricultural soils in peri-urban areas around Guangzhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 156, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wu, S.; Liang, J.M.; Liang, W.L.; Chen, G.X.; Li, Y.J.; Yang, G.Y. Characteristics of phthalic acid esters in agricultural soils and products in areas of Zhongshan City, South China. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2015, 36, 2283–2291. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, Z.L.C.M.C.; Li, C.; Mo, C. Distribution of phthalic acid esters in agricultural soils of Huizhou City. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2012, 37, 120–123. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, R.; Wang, M.J.; Padgett, E.; Beck, A.J. Analysis of 4-nonylphenols, phthalates, and polychlorinated biphenyls in soils and biosolids. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 1336–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, Z.; Wang, B.; Tian, X.Y.; Zhang, H.; Duan, L.Q.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.Z. Contamination Status and Health Risk of Phthalate Esters in Facility Agricultural Soil of 11 Cities of Hainan, China. Chin. J. Trop. Crops 2021, 42, 806–815. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Lai, Y.; Zhu, H.; Yang, X.; Ye, X.; Zhang, A.; Sun, J. Phthalate esters and their metabolites in paired soil-crop systems from farmland in major provinces of eastern China: Pollution characteristics and implications for human exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 882, 163645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Christie, P.; Zhang, M.; Luo, Y.; Teng, Y. Occurrence and risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in vegetables and soils of suburban plastic film greenhouses. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 523, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, X.; Gan, J. Uptake and metabolism of phthalate esters by edible plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8471–8478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Tan, F. Characteristics, prediction, and risk assessment of phthalates, organophosphate esters, and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in vegetables from plastic greenhouses of Northeast China. Chemosphere 2024, 368, 143743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.A.; Chen, X.B.; Zhao, H.M.; Mo, C.H.; Li, H.; Li, Y.W.; Cai, Q.Y. Distribution of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) in paddy soil and grains of rice in the Pearl River Delta region and the health risk assessment. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2016, 35, 1242–1248. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, M.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, G.; Quan, H.; He, H. Plastic film mulching increased the accumulation and human health risks of phthalate esters in wheat grains. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, B.; Wang, L. Phthalic acid esters in grains, vegetables, and fruits: Concentration, distribution, composition, bio-accessibility, and dietary exposure. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 2787–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ling, W.; Liu, R.; Liu, J.; Kang, F.; Gao, Y. Contamination and health risk assessment of PAHs in soils and crops in industrial areas of the Yangtze River Delta region, China. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 976–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartwright, C.D.; Thompson, I.P.; Burns, R.G. Degradation and impact of phthalate plasticizers on soil microbial communities. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. Int. J. 2000, 19, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Gao, J.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Phthalate induced oxidative stress and DNA damage in earthworms (Eisenia fetida). Environ. Int. 2019, 129, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Liu, Y.; Dong, Y.; Song, Z. Photosynthetic and antioxidant response of wheat to di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) contamination in the soil. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaaban, M.; Nunez-Delgado, A. Soil adsorption potential: Harnessing Earth’s living skin for mitigating climate change and greenhouse gas dynamics. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Sheng, H.; Gu, C.; Song, Y.; Willbold, S.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, F. Extraneous dissolved organic matter enhanced adsorption of dibutyl phthalate in soils: Insights from kinetics and isotherms. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631, 1495–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, H.; Zhou, Y.; Beiyuan, J.; Li, X.; Min, J.; Su, L.; Zhang, L.; Ji, R.; Xue, J. Insights into the effect of hydrochar-derived dissolved organic matter on the sorption of diethyl phthalate onto soil: A pilot mechanism study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Si, Y.; Zhou, D.; Gao, J. Adsorption of diethyl phthalate ester to clay minerals. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 690–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, J.; Sun, K.; Wang, Z.; Han, L.; Pan, Z.; Wu, F.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Xing, B. Characterization and phthalate esters sorption of organic matter fractions isolated from soils and sediments. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 24–31. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Wang, M.; Wang, Z. Sorption behavior of 17 phthalic acid esters on three soils: Effects of pH and dissolved organic matter, sorption coefficient measurement and QSPR study. Chemosphere 2013, 93, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, F.; Sohi, S.P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J. Insight into mechanism of aged biochar for adsorption of PAEs: Reciprocal effects of ageing and coexisting Cd2+. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 1098–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhu, G.; Zhong, G.; Zhang, Y. Fate, ecotoxicity, and remediation of phthalic acid ester in soils. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2023, 32, 100440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennartz, S.; Byrne, H.A.; Kümmel, S.; Krauss, M.; Nowak, K.M. Hydrogen isotope labeling unravels origin of soil-bound organic contaminant residues in biodegradability testing. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gates, E.; Crook, N. The biochemical mechanisms of plastic biodegradation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 48, fuae027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Li, H.; Gu, J.; Shi, H.; Han, S.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Metabolism of diethyl phthalate (DEP) and identification of degradation intermediates by Pseudomonas sp. DNE-S1. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 173, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.M.; Du, H.; Lin, J.; Chen, X.B.; Li, Y.W.; Li, H.; Cai, Q.; Mo, C.; Qin, H.; Wong, M.H. Complete degradation of the endocrine disruptor di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate by a novel Agromyces sp. MT-O strain and its application to bioremediation of contaminated soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 562, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, L.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.L.; Jia, Y.; Hu, H.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Biodegradation of phthalic acid esters by a novel marine bacterial strain RL-BY03: Characterization, metabolic pathway, bioaugmentation and genome analysis. Chemosphere 2024, 366, 143530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dueñas-Moreno, J.; Mora, A.; Cervantes-Avilés, P.; Mahlknecht, J. Groundwater contamination pathways of phthalates and bisphenol A: Origin, characteristics, transport, and fate—A review. Environ. Int. 2022, 170, 107550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGrath, G.; Hinz, C.; Sivapalan, M. Assessing the impact of regional rainfall variability on rapid pesticide leaching potential. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2010, 113, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, X.X.; Zhu, T.K.; Li, X.; Chen, X.H.; Mo, C.H.; Wong, M.H. Variation in accumulation, transport, and distribution of phthalic acid esters (PAEs) in soil columns grown with low-and high-PAE accumulating rice cultivars. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 17768–17780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, S.; Fang, H.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, F. Composition, distribution, health risks, and drivers of phthalates in typical red paddy soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 94814–94826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; He, T.; Hu, H. Health risk assessment of phthalate esters (PAEs) in drinking water sources of China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 3620–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Net, S.; Sempéré, R.; Delmont, A.; Paluselli, A.; Ouddane, B. Occurrence, fate, behavior and ecotoxicological state of phthalates in different environmental matrices. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4019–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otton, S.V.; Sura, S.; Blair, J.; Ikonomou, M.G.; Gobas, F.A. Biodegradation of mono-alkyl phthalate esters in natural sediments. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 2011–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Park, J.; Clausen, P.A.; Benning, J.L.; Little, J.C. Measuring and predicting the emission rate of phthalate plasticizer from vinyl flooring in a specially-designed chamber. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 12534–12541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.T.; Kumar, S.S.; Ghosh, P.; Shah, G.; Malyan, S.K.; Bajar, S.; Singh, L. Remediation strategies for mitigation of phthalate pollution: Challenges and future perspectives. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H. In-situ soil remediation via heterogeneous iron-based catalysts activated persulfate process: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, T.F.; Baumgartner, R.; Jaggi, M.; Bernasconi, S.M.; Battagliarin, G.; Sinkel, C.; Sander, M. Biodegradation of poly (butylene succinate) in soil laboratory incubations assessed by stable carbon isotope labelling. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taglialegna, A. Fungi feed bacteria for biodegradation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazeer, A.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, F.; Ahmad, S. Microbial Biodegradation of Plastics and Microplastics: Recent Development. In Plastic Pollution: Challenges and Green Solutions; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2024; pp. 231–248. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Zhou, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y. Biodegradation of phthalates degrading bacteria in agriculture soil and its application. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 44, 1542–1553. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Cifuentes, I.E.; Werner, J.; Jehmlich, N.; Will, S.E.; Neumann-Schaal, M.; Öztürk, B. Synergistic biodegradation of aromatic-aliphatic copolyester plastic by a marine microbial consortium. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Zhou, X.; Wei, T.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y. Potential mechanisms of synthetic endophytic bacterial community to reduce PAHs accumulation in vegetables. Environ. Int. 2024, 194, 109129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Sun, Y.; Wang, T.; Tang, L.; Ling, W.; Mosa, A.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y. Remediation potential of an immobilized microbial consortium with corn straw as a carrier in polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons contaminated soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 469, 134091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Dagar, V.K.; Khasa, Y.P.; Kuhad, R.C. Genetically modified microorganisms (GMOs) for bioremediation. In Biotechnology for Environmental Management and Resource Recovery; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 191–218. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, B. Plastic-eating bacteria boost growing business of bioremediation. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1481–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sarmah, A.K.; Bolan, N.S.; He, L.; Lin, X.; Che, L.; Wang, H. Effect of aging process on adsorption of diethyl phthalate in soils amended with bamboo biochar. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Liu, X.; Sun, K.; Lin, C.; Ma, J.; He, M.; Ouyang, W. Persulfate-based advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) for organic-contaminated soil remediation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 372, 836–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Lu, W.; Ling, W.; Czech, B.; Oleszczuk, P.; Chen, X.; Gao, Y. Biodegradation of PAEs in contaminated soil by immobilized bacterial agent and the response of indigenous bacterial community. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 361, 124925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Extraction | Detection | LOD (μg L−1) | Time (min) | Recovery (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASE | GC–MS system | 20–70 | 17.2 | 75–120 | [25] |
| ASE-SPE | GC–MS system | 0.03–270 | 15.1 | 86–111 | Proposed method |
| ASE | HPLC/FLD | 0.99–19.80 | 30 | 73.03–91.89 | [26] |
| ASE | MEEKC/UV | 0.2–0.4 (mg kg−1) | 16 | 88.5–119.7 | [27] |
| QuEChERS | GC–MS/MS | 0.09–0.43 ng g−1 | 30 | 97.2–99.1 | [28] |
| Location | Location Specification | Min | Max | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| North China | ||||
| Shanxi (Lvliang) | Crop soils | / | 512 (Σ6PAEs) | [35] |
| Beijing | Vegetable soil | 46.25 | 1287.96 (Σ15PAEs) | [36] |
| Agricultural soil | 1800 | 12200 (Σ6PAEs) | [37] | |
| Heibei | Vegetable soil | / | 910 (Σ12PAEs) | [38] |
| Crop soil | / | 842 (Σ12PAEs) | ||
| Tianjin | Agricultural soil | 50 | 10400 (Σ6PAEs) | [39] |
| Huhehaote | Agricultural soil | / | 3280 (Σ4PAEs) | [40] |
| Shanxi (Changzhi) | Agricultural soil | / | 2380 (Σ4PAEs) | |
| Henan | Vegetable soil | / | 965 (Σ12PAEs) | [38] |
| Crop soil | / | 760 (Σ12PAEs) | ||
| Northwestern China | ||||
| Gansu | Agricultural soil | 31.1 | 1141.7 (Σ6PAEs) | [41] |
| Greenhouse soil | 394.7 | 2961.8 (Σ6PAEs) | ||
| Xinjiang | Melon patch soil | 57.3 | 3272.7 (Σ6PAEs) | [42] |
| Cotton field soil | 123,925 | 1232076 (Σ6PAEs) | [43] | |
| Ningxia | Cotton field soil | 1360 | 4490 (Σ16PAEs) | [44,45,46,47,48] |
| Vegetable soil | 2123 | 17271(Σ11PAEs) | ||
| Agricultural soil | 727 | 8728 (Σ16PAEs) | ||
| Greenhouse soil | 1121 | 11924 (Σ16PAEs) | ||
| Agricultural soil | 3171 | 5355 (Σ16PAEs) | ||
| Agricultural soil | 2106 | 5124 (Σ16PAEs) | ||
| Agricultural soil | 391 | 11924 (Σ16PAEs) | ||
| Qinghai (Weinan) | Agricultural soil | / | 522 (Σ4PAEs) | [40] |
| Qinghai (Yulin) | Agricultural soil | / | 279 (Σ4PAEs) | |
| East China | ||||
| Yangtze River Delta | Agricultural soils | 167 | 9370 (Σ15PAEs) | [49] |
| Agricultural soils | 5.4 | 1580 (Σ6PAEs) | [50] | |
| Jiangsu | Greenhouse soil | 42.5 | 276.8 (Σ6PAEs) | [51] |
| Zhejiang | Agricultural soil | 307 | 25219 (Σ12PAEs) | [38] |
| Shandong | Vegetable soil | 756 | 1590 (Σ16PAEs) | [52] |
| Vegetable soil | 1374 | 18810 (Σ16PAEs) | [53] | |
| Greenhouse soil | 453 | 1615 (Σ6PAEs) | [54] | |
| Agricultural soil | 218.4 | 1168.9 (Σ6PAEs) | [55] | |
| Greenhouse soil | 1939 | 35442 (Σ16PAEs) | [56] | |
| Henan | Vegetable soil | / | 965 (Σ12PAEs) | [38] |
| Crop soil | / | 760 (Σ12PAEs) | ||
| Taiwan | Agricultural soil | / | 700 (Σ6PAEs) | [57] |
| Anhui | Agricultural soil | 234.5 | 304.8 (Σ16PAEs) | [58] |
| Fujian | Agricultural soil | / | 1018 (Σ15PAEs) | [59] |
| Jiangxi | Agricultural soil | 274.8 | 737.7 (Σ16PAEs) | [58] |
| Shanghai | Agricultural soil | 284.5 | 589.2 (Σ16PAEs) | [58] |
| South China | ||||
| Guangzhou | Agricultural soil | 195 | 33600 (Σ16PAEs) | [60] |
| Guangdong | Agricultural soil | 183 | 2037.6 (Σ6PAEs) | [61,62] |
| Vegetable soil | 140 | 1140 (Σ16PAEs) | ||
| Leizhou Peninsula | Agricultural soil | ND | 1770 (Σ6PAEs) | [63] |
| Hainan | Agricultural soils | 46 | 614 (Σ16PAEs) | [64] |
| Guangxi | Agricultural soils | 78.8 | 902.5 (Σ16PAEs) | [48] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X. Contamination of Phthalic Acid Esters in China’s Agricultural Soils: Sources, Risk, and Control Strategies. Agronomy 2025, 15, 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020433
Han J, Jiang Z, Li P, Wang J, Zhou X. Contamination of Phthalic Acid Esters in China’s Agricultural Soils: Sources, Risk, and Control Strategies. Agronomy. 2025; 15(2):433. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020433
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jin, Zhenying Jiang, Pengfei Li, Jian Wang, and Xian Zhou. 2025. "Contamination of Phthalic Acid Esters in China’s Agricultural Soils: Sources, Risk, and Control Strategies" Agronomy 15, no. 2: 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020433
APA StyleHan, J., Jiang, Z., Li, P., Wang, J., & Zhou, X. (2025). Contamination of Phthalic Acid Esters in China’s Agricultural Soils: Sources, Risk, and Control Strategies. Agronomy, 15(2), 433. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020433






