Abstract
Selenium-enriched vegetables are a safe way to combat selenium deficiency in humans. Here, a new microbial selenium-enriched bacterial fertilizer (named “HJ”) was prepared and studied by dipping, and then its application strategy was optimized and compared with other commercially available selenium fertilizers. The results showed that the application of HJ selenium fertilizer to peas by soaking (Se concentration 10 μg/mL) and foliar application (Se concentration 8 μg/mL) could effectively enhance their growth, selenium enrichment ability, stress tolerance and nutritional quality. In particular, the selenium content of peas in the HJ-treated group exhibited a significant increase of 69.86% in comparison with the control group. Moreover, HJ treated pea sprouts demonstrated enhanced antioxidant activity, as well as elevated levels of vitamin C and protein, amongst other observations. The findings of this study offer novel insights into the development of eco-friendly selenium fertilizers and provide guidance for optimal fertilizer application techniques.
1. Introduction
Selenium (Se) is an essential trace element, but high concentrations of selenium can cause irreversible damage to the body. Consequently, selenium was initially considered a carcinogen [1]. As a result of scientific advancement, comprehensive research has demonstrated that selenium is a vital component in maintaining optimal organism health. Its functions include enhancing the body’s antioxidant capacity, strengthening immunity, preserving thyroid gland health, preventing cardiovascular and cerebral vascular diseases, and reducing the risk of cancer [2]. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends a selenium intake of 55 μg/d for adults. It is believed that intakes below 40 μg/d may result in selenium deficiency, which can cause a range of health issues. Conversely, intakes above 400 μg/d may also lead to adverse effects in adults, including alopecia, respiratory problems, skin rashes and neurotoxicity, among others [3]. It is therefore imperative to ensure an appropriate daily intake of selenium.
In comparison to pharmaceutical selenium supplementation, dietary selenium supplementation is a more readily accepted option [4], particularly given that selenium present in plant tissues is the form most readily absorbed by the human body. Furthermore, the enrichment of plants with selenium can be achieved through the application of selenium fertilizers [5]. Additionally, numerous selenium-enriched food products, including Se-rich broccoli, Se-rich garlic, and Se-rich rice, are currently available on the market [6,7]. At present, selenium-enriched foods are cultivated either with inorganic selenium fertilizers or with organic selenium fertilizers.
Inorganic selenium fertilizers are highly toxic, poorly bioavailable, and contribute to environmental pollution and other problems. Consequently, the conversion of inorganic selenium into organic selenium through biotransformation is a significant research topic. Microbial transformation offers several advantages, including rapid growth and metabolism, high yields, and economic viability, making it an important mechanism for the production of organic selenium fertilizers [8,9]. Furthermore, the joint action of microorganisms and selenium can enhance selenium accumulation in crops and boost biological selenium utilization [10].
The efficiency of plant selenium enrichment is contingent upon two key factors: the selenium concentration of the applied selenium fertilizer and the fertilization method. The latter can be broadly classified into two categories: foliar application [11] and rhizosphere irrigation [12]. Additionally, research has demonstrated that selenium fertilizer dipping of seeds can enhance plant resistance, promote growth and development, and increase their selenium content [13].
Humic acid (HA) is a class of natural organic polymer compounds that has been demonstrated to promote plant growth, alleviate adversity stress, improve microbial activity, and more. It is a widely used substance in agriculture, ecology, and other fields of study [14]. Chitosan oligosaccharides (COS) are commonly utilized in biofertilizers and have been demonstrated to enhance plant disease resistance and induce plant immunity [15]. Polyethylene glycol 400 (PEG400) is a nonionic water-soluble polymer that is frequently utilized as a pharmaceutical excipient in the biological field. It has been demonstrated to enhance the solubility of microorganisms in liquid formulations and to improve stability [16]. The three substances can be combined and used as a liquid stabilizer, which has the capacity to enhance liquid viscosity and bacterial stability, facilitate the retention time of fertilizer on plants, and contribute to efficient plant uptake.
Pea (Pisum sativum L.) sprouts are a rich source of selenium and vitamin C, as well as a variety of amino acids, trace elements and other biologically active substances. They have the advantages of low planting technical requirements, a short growth cycle time and strong vitality, and are therefore suitable for selenium-enriched food research and development [17]. Jerse et al. used an inorganic selenium solution to soak pea seeds and found that it significantly increased the selenium content of the resulting pea sprouts [18]. The researchers pre-separated selenium-resistant strains from selenium-enriched fields in Hailun, China, and screened out strain H1 with excellent selenium enrichment ability through tests [19]. In order to enhance the stability of H1 for plant selenium-enriched culture, we elected to prepare an environmentally friendly selenium-enriched bacterial fertilizer with H1 as the principal component. The objective of this study was to develop a novel bacterial fertilizer, designated HJ, that is cost-effective, environmentally benign, non-polluting and exhibits superior selenium enrichment capacity. Additionally, this study aimed to optimize the utilization strategy of the bacterial fertilizer, thereby facilitating a comprehensive investigation into the impact of diverse selenium fertilizers on the growth of pea sprouts. The findings of this study will provide scientific guidance for the cultivation of selenium-enriched crops, thereby promoting the advancement of functional agricultural products.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strain Acquisition and Selenium Rich Cultivation
In this study, we employed a previously isolated microbial strain, designated Enterobacter species H1, which had been optimized for culture conditions to achieve selenium concentrations of up to 3000 µg/g. All strains were stored in a −80 °C ultra-freezer to ensure their continued viability and stability for future use. The detailed methods for screening and characterizing microbial strains have been previously reported [19].
For reconstitution, 1 mL of a glycerol-preserved bacterial solution was inoculated into 20 mL of a sterile liquid medium (yeast extract powder 10 g/L, glucose 20 g/L, peptone 20 g/L, pH 6.0) and incubated at 30 °C with oscillation at 200 rpm. Once the bacterial solution reached a concentration of 1.5 × 107 CFU/mL (colony forming units, CFU), it was inoculated into a liquid medium containing sodium selenite at a concentration of 15 µg/mL, with an inoculum volume of 5%. The culture was then incubated at 30 °C with a shaking speed of 200 rpm for 24 h, allowing the selenium-enriched culture to complete its growth.
2.2. Preparation of Selenium-Enriched Bacterial Fertilizer HJ
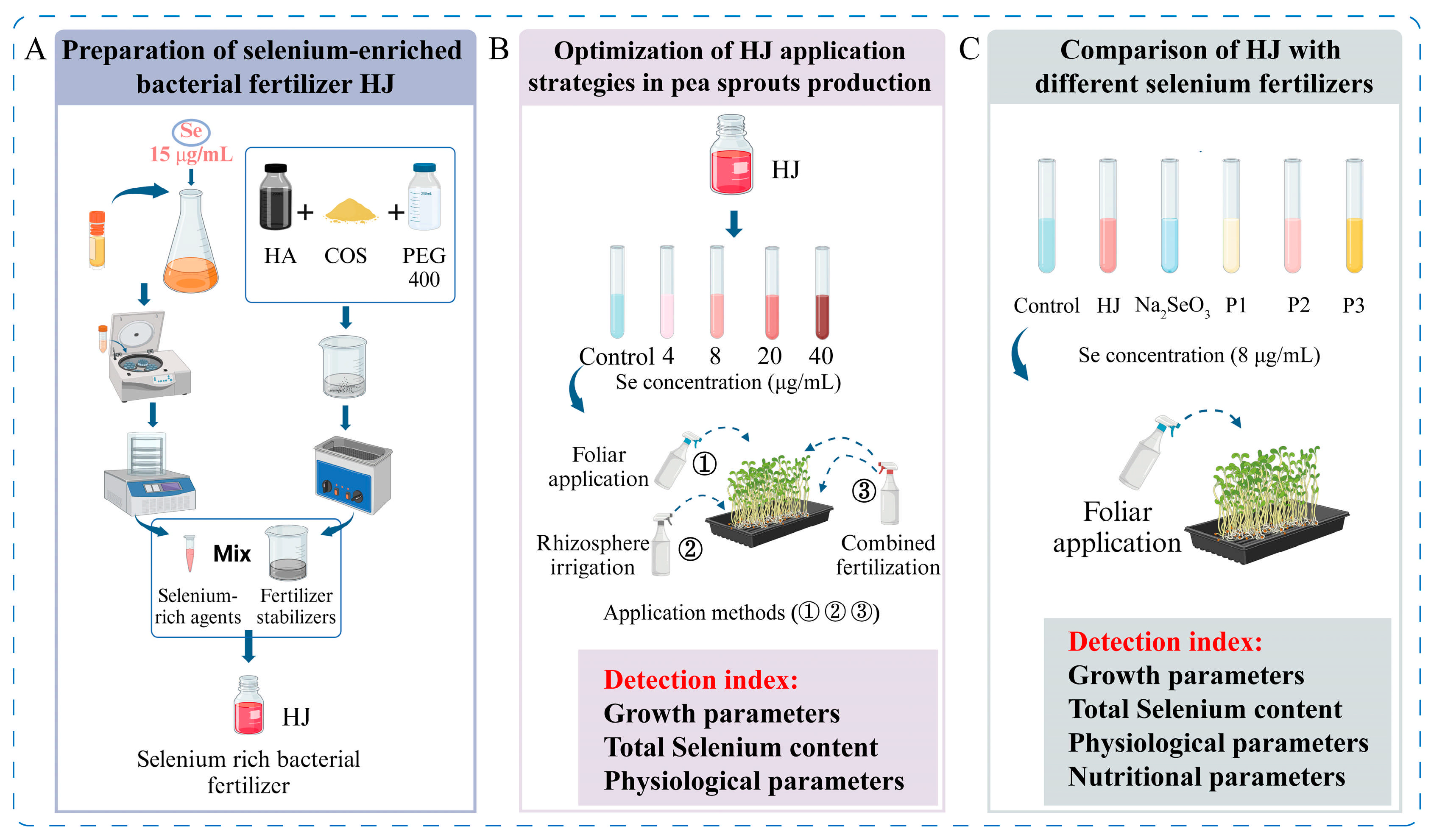
The Enterobacter sp. H1 strain was cultivated in a selenium-rich liquid medium at 30 °C for 24 h with agitation at 180 rpm. The bacterial solution was then collected and subjected to centrifugation at 8000 rpm for a period of 15 min. The supernatant was discarded, and the precipitate was subjected to three washes with deionized water. The precipitate was then freeze-dried and sieved through a 100-mesh sieve, thus obtaining a selenium-rich bacterial agent. A microbial fertilizer stabilizer was prepared by mixing a 60 µg/mL HA solution, 4% COS, and PEG 400 in a ratio of 30:4:1, and sonicating the mixture at 30–35 °C for 30–40 min. Subsequently, the selenium-rich microbial agent was dissolved in the stabilizer at a ratio of 1:15, resulting in a selenium-rich microbial fertilizer with a selenium content of 200 µg/mL, designated as HJ (Figure 1A). Fertilizer HJ is pink in color, and after long term storage in light-proof and cool conditions, it still maintains a homogeneous pink appearance, with no instability such as precipitation, delamination or discoloration, and its activity is maintained, showing good stability.
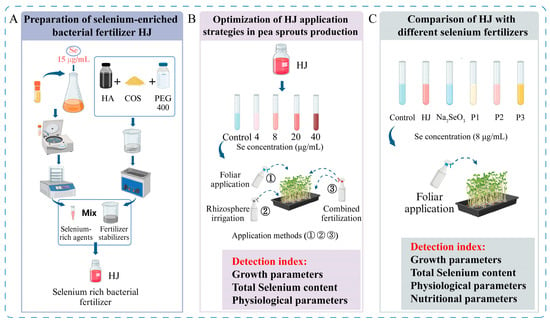
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the experimental procedure. (A) Preparation of selenium-enriched bacterial fertilizer HJ. (B) Optimization of HJ application strategies in pea sprouts production. (C) Comparison of HJ with different selenium fertilizers. In the Figure, HA refers to humic acid, COS denotes chitosan oligosaccharides, and PEG400 denotes polyethylene glycol 400. HJ is the experimental group, and P1, P2 and P3 of the positive control group represent three kinds of commercial selenium fertilizers, “KaiJin”, “ZhenXi” and “SiJiFeng”.
2.3. Experimental Design
Seed pretreatment: The selected experimental material is composed of flattened spherical pea seeds of a similar size and plump appearance, with a mean weight of 17.03 ± 0.43 g per hundred seeds. The seeds were washed twice with deionized water, followed by a 30 s immersion in a 75% ethanol solution. Subsequently, the ethanol was rinsed off with deionized water, and the seeds were dried with filter paper.
2.3.1. Effects of HJ Soaking Solution at Different Selenium Concentrations on Seed Germination and Growth Indices
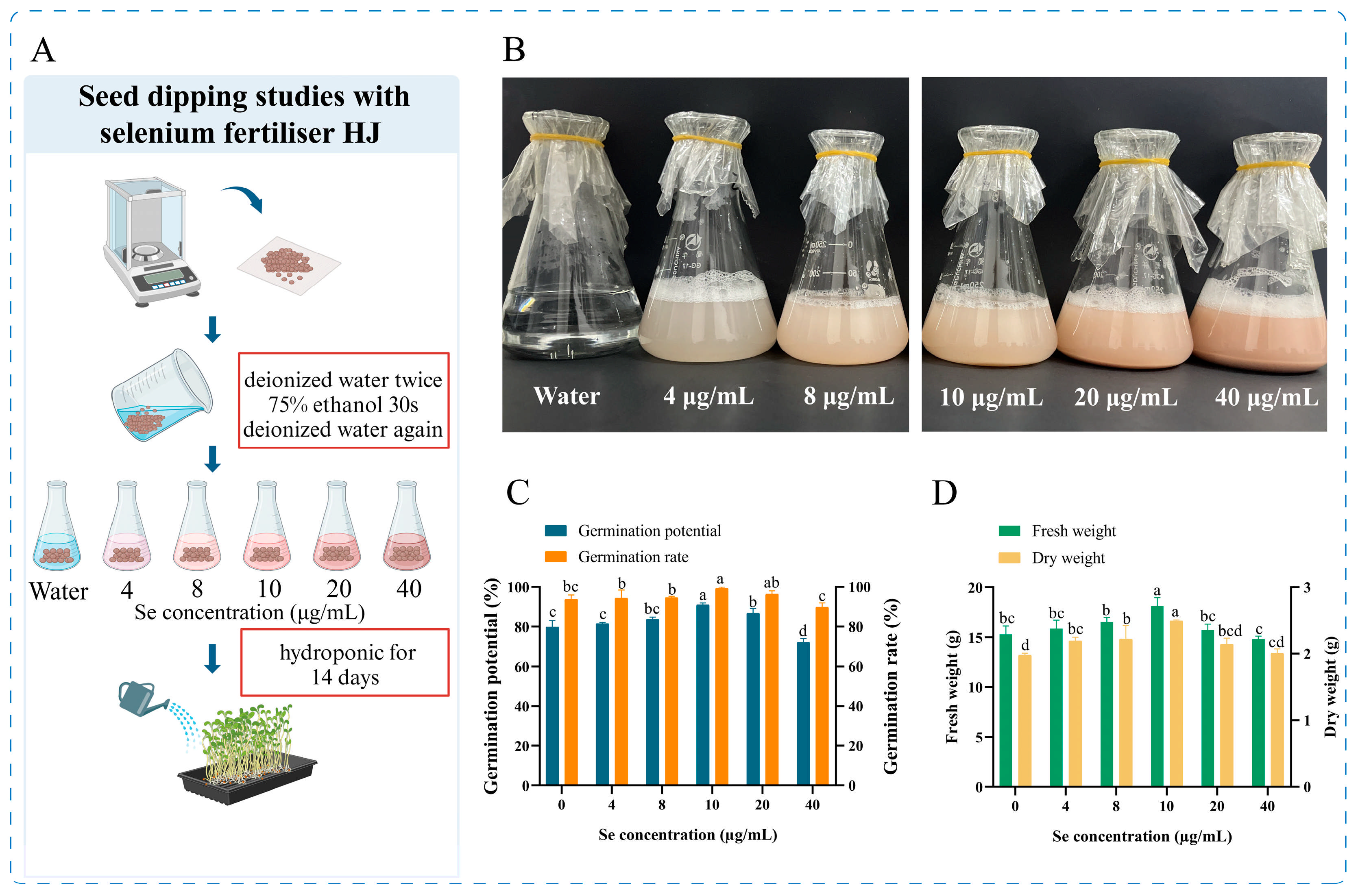
Six seed soaking solutions were used, consisting of deionized water and bacterial fertilizer HJ with different concentrations of selenium (4 μg/mL, 8 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL, 20 μg/mL, or 40 μg/mL), and 500 mL of each solution was prepared, 300 seeds were added and soaked for 12 h. At the end of the soaking period, the seeds were washed twice with water and then evenly distributed in groups of 100 seeds each on the 22.5 cm × 14.4 cm seedling trays and covered with moist gauze. Harvesting was carried out after 14 days of hydroponics, protected from light, and the indicators were measured after harvesting, with three sets of parallel replicates for each treatment (Figure 2A).
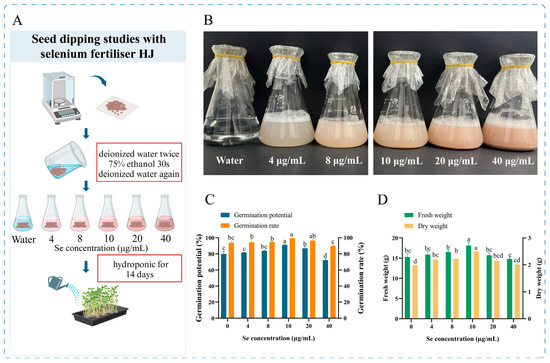
Figure 2.
Pea seeds soaking experiment. (A) Flow chart of the experiment, (B) Graph of the imbibing solution, (C) Results of seed germination potential and germination rate, and (D) Results of fresh weight and dry weight of pea sprouts after imbibition. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between the two groups.
2.3.2. Experimental Design for the Optimization of HJ Application Strategies in Pea Sprouts Production
In line with the outcomes of the seed dipping experiment, the optimal HJ selenium concentration was employed to treat all seeds via dipping. A methodology was devised whereby the HJ was diluted into four selenium concentrations (4 μg/mL, 8 μg/mL, 20 μg/mL and 40 μg/mL). Subsequently, the solutions were applied using three distinct fertilization techniques (foliar application, rhizosphere irrigation, and combined fertilization, which was a combination of the former two in equal proportions), namely, the four selenium concentrations were combined with the three fertilization methods to create 12 treatment groups. The control group was treated with deionized water. The specific grouping of the experiment is presented in the Supplementary Materials (Table S1). Subsequently, the plants were protected from light using a hydroponic system, and fertilizer was applied at two-day intervals following germination. Subsequently, the growth and physiological indexes of the pea sprouts in each group were evaluated in order to identify the optimal application strategy for the HJ bacterial fertilizer (Figure 1B).
2.3.3. Experimental Design for Comparative Analysis of the Effect of Application of HJ, Na2SeO3 and Three Commercial Selenium Fertilizers on Pea Sprouts
In accordance with the findings of the Section 2.3.2 trial, the most efficacious HJ application strategy was employed in subsequent trials. The seeds were treated by dipping in deionized water, protected from light through the use of hydroponics, and fertilizer was applied once every two days. The study employed six treatment groups, comprising a control group and five experimental groups. The experimental groups included the HJ group and the Na2SeO3 group, as well as three commercial selenium fertilizers, which were included as positive control groups (Figure 1C). The three commercial selenium fertilizers were the P1 group, commercial selenium-enriched bacterial fertilizer “KaiJin” (purchased from Zhengzhou Kaijin Agricultural Technology Co., Ltd., Zhengzhou, China); the P2 group, commercial selenium-enriched bacterial fertilizer “ZhenXi” (purchased from Guilin Jiqi Biochemical Co., Ltd., Guilin, China); and the P3 group, commercial selenium-enriched bacterial fertilizer “SiJiFeng” (purchased from Qingdao Sijifengyuan Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Qingdao, China). The selenium fertilizers were diluted in accordance with the selenium content of the HJ dilution solution and subsequently applied.
2.4. Measurement of Indicators
2.4.1. Measuring Growth Indicators
The number of germinated seeds was counted at 2 d and 6 d after sowing, and the criterion of germination was the radicle breaking through the whiteness of the seed coat. The seed germination potential and germination rate were calculated using Formulas (1) and (2) [20]. After 14 d of cultivation, 20 pea sprouts from each treatment were sampled and this was repeated three times. The sprouts’ shoot length and root length were measured using a ruler, and the fresh weight and fresh weight of edible parts were determined using an electronic balance, after which the pea sprouts were placed in an oven to kill greening at 105 °C for 10 min, and then dried at 60 °C to a constant weight to determine their dry weight. The water content of the pea sprouts was calculated from their fresh weight and dry weight using Formula (3) [21]. The edible rate of the pea sprouts, defined as the ratio of edible fresh weight to total fresh weight, was determined by first weighing the total fresh weight of the pea sprouts, then removing the inedible portion (e.g., roots), and weighing the fresh weight of the edible portion, and was calculated using Formula (4) [22].
Germination potential = (number of seeds germinated on day 2/total number of seeds) × 100%
Germination rate = (number of seeds germinated on day 6/total number of seeds) × 100%
Water content = (fresh weight − dry weight)/fresh weight × 100%
Edibility rate = (edible fresh weight/total fresh weight) × 100%
2.4.2. Determination of Total Se Content
To determine the total Se content, 0.01 g sample of dried and ground pea sprouts was weighed and digested with 1 mL of a mixed nitric acid–perchloric acid solution (v/v, 4:1), protected from light overnight and heated the next day to clear the solution according to the method of Tan et al. [23]. Heating was stopped when the liquid was close to evaporation. After cooling, the solution was diluted to 10 mL with deionized water and then measured for selenium, expressed as μg/g.
2.4.3. Methods for Measuring Physiological Indicators
The soluble protein content of the pea sprouts was determined according to the method of Abbas [24] and Kanwal [25]. The samples were measured using a BCA kit (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China).
The soluble sugar content was determined by the enthrone colorimetric method [26], where 0.05 g of each fresh sample from different treatments was placed in a 20 mL graduated test tube, 2.5 mL of water was added, and the extract was sonicated for 30 min and then centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min. Then, 0.25 mL of the supernatant was collected and the supernatant was diluted 3 times in deionized water before adding 0.25 mL of enthrone ethyl acetate and 2.5 mL of concentrated sulphury acid. The absorbance was measured at 620 nm and the soluble sugar content was calculated using a microplate reader (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
Fresh pea sprouts were weighed (0.1 g), minced, added to 5 mL of 95% ethanol and kept in the dark for 24 h. After the leaves had turned white, the absorbance values at 470 nm, 645 nm and 663 nm were measured and the values of chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, total chlorophyll and carotenoids were calculated.
2.4.4. Determination of Antioxidant Enzymes
A 0.5 g sample of fresh pea sprouts was weighed and added to 3 mL phosphate buffer (pH 7.8, 50 mM) and ground on ice to form a homogenate, which was adjusted to 5 mL with phosphate buffer and centrifuged at 8500 rpm for 20 min at 4 °C, and the supernatant was collected as the enzyme solution to be assayed.
The activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) (U/g FW) was determined by the nitrogen blue tetrazolium (NBT) photochemical reduction method, and the absorbance value was measured at 560 nm. The peroxidase (POD) activity (U/g min) was determined by the guaiacol method. The catalase (CAT) activity (U/g min) was determined by preparing a reaction system containing 1 mL of 0.3% hydrogen peroxide, 1.9 mL deionized water and 0.1 mL enzyme solution. The rate of decrease in absorbance of the reaction system was determined at 240 nm and a decrease in absorbance of 0.01 units per minute was defined as one unit of viability [25].
2.4.5. Determination of Malondialdehyde (MDA) Content
The MDA content was determined by the thiobarbituric acid (TBA) method and the absorbance values were measured at 532 nm using a malondialdehyde test kit (Nanjing Jiancheng Bioengineering Institute, Nanjing, China).
2.4.6. Methods for Determining Nutritional Quality
The amino acid content was determined by the ninhydrin colorimetric method utilizing an amino acid content detection kit (Beijing Solarbio Science & Technology Co., Ltd., Beijing, China). The absorbance value was subsequently measured at 570 nm, enabling the calculation of the amino acid content of the samples. The concentration of vitamin C was determined by the molybdenum blue colorimetric method, employing ascorbic acid as the standard curve for the samples. The absorbance values were obtained at 760 nm using a UV spectrophotometer (752 N, Shanghai Yi electric Analytical Instrument Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) [23]. Each treatment used 3 g of chopped pea sprouts, and the nitrate nitrogen content was calculated by measuring the absorbance at 410 nm using the colorimetric method with salicylic acid.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
SPSS 26.0 software was used for statistical analyses, and Duncan’s multiple significance test was used for one-way analysis of variance (p ≤ 0.05). All experimental data were based on three independent replicates. The data are presented as mean ± SD and were plotted using Graphpad Prism 8.0.2. Radar analysis was performed with Origin 2021.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optimization of HJ Application Strategies in Pea Sprouts Production
A selenium-enriched HJ bacterial fertilizer was prepared, which is a pink liquid that is readily soluble in water, has no irritating aroma and is highly stable. The impact of the selenium fertilizer on pea sprouts was contingent upon two primary factors: the concentration of selenium in the fertilizer, and the combined effect of pre-germination seed soaking treatments and post-germination fertilizer application methods. The judicious application of selenium fertilizer has been demonstrated to promote plant growth, enhance crop nutritional quality and stimulate enzyme activity. Conversely, excessive selenium fertilizer concentrations have been observed to impede plant growth, induce oxidative stress and diminish the accumulation of specific nutrients [27]. Consequently, scientific regulation of selenium fertilizer concentration is imperative for optimal plant growth and nutritional quality of the products. In this study, we initially investigated the impact of seed dipping treatment and identified the optimal seed dipping selenium concentration of HJ as 10 μg/mL (Table 1, Figure 2C,D). Subsequently, we proceeded to optimize the application strategy of HJ in sprouts production.

Table 1.
Effect of different selenium concentrations in HJ soaking on growth indexes of pea sprouts.
3.1.1. Shoot Length, Root Length and Edibility Rate
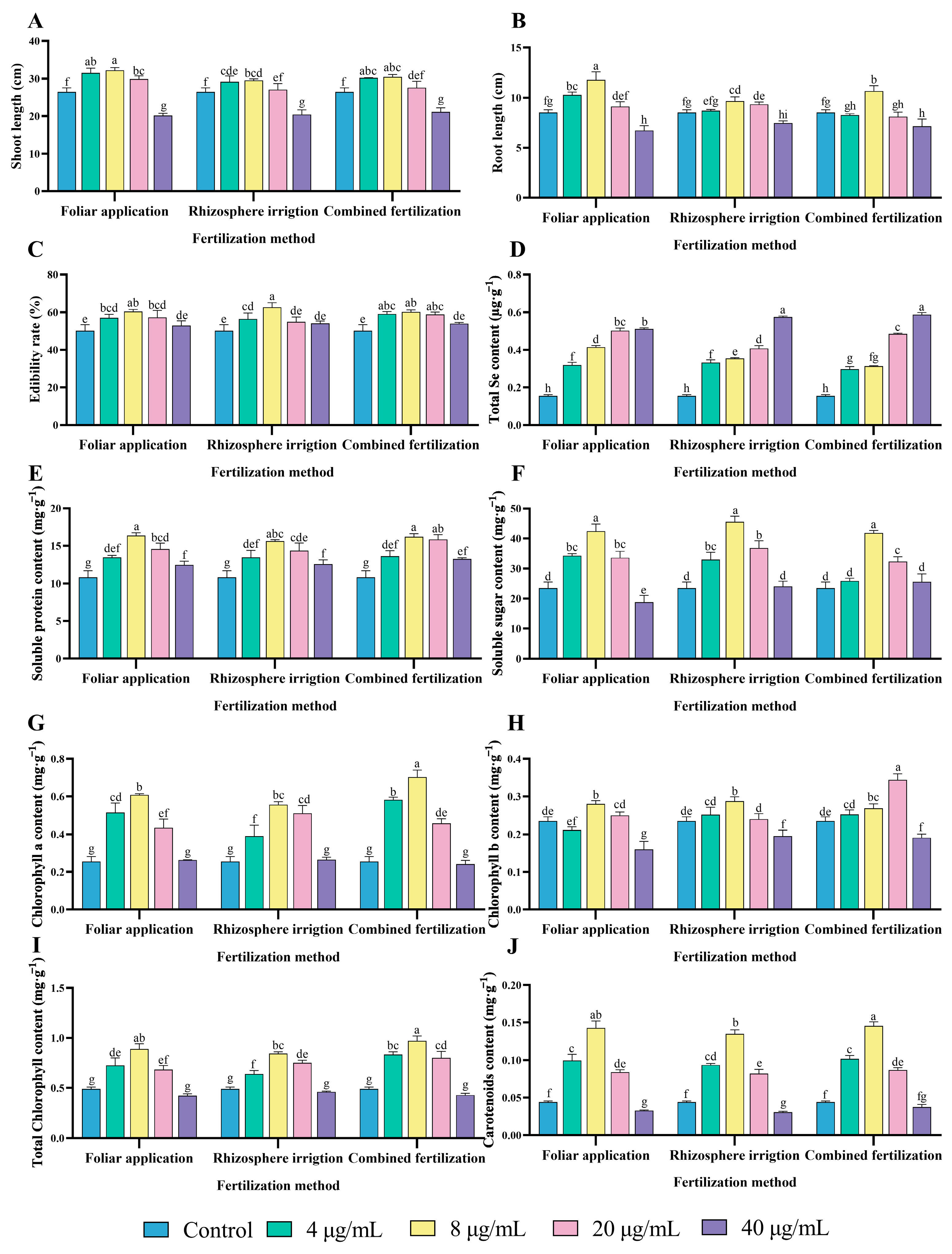
The application of fertilizers via spraying can provide plants with essential nutrients for growth, promote shoot and root growth, and improve crop yield and quality [28]. Following a 14-day period, the shoot and root length of pea sprouts was measured and the edibility rate was calculated. Amongst the three application methods, there was an observed trend of increasing and subsequently declining values for the shoot length, root length, and edibility rate of different treatments as the concentration of selenium in the bacterial fertilizer (HJ) increased. The concentration of 8 μg/mL was identified as the most efficacious in promoting pea sprouts growth. The F8 (foliar application, 8 μg/mL) treatment group was the most effective in promoting shoot growth, with an increase of 21.60% compared to the control group and an increase of 9.13% and 5.81% compared to the R8 (rhizosphere irrigation, 8 μg/mL) and C8 (combined fertilization, 8 μg/mL) groups, respectively (Figure 3A). The root length of the F8, R8 and C8 treatments was significantly higher than that of the control group by 38.51%, 13.79% and 25.5%, respectively (Figure 3B). The application of different selenium concentration treatments and methods resulted in a notable enhancement in the edibility rate of pea sprouts. The F8, R8 and C8 treatment groups exhibited the most pronounced increase in edibility rate, with values of 20.31%, 24.73% and 19.87%, respectively, when compared to the control group (Figure 3C).
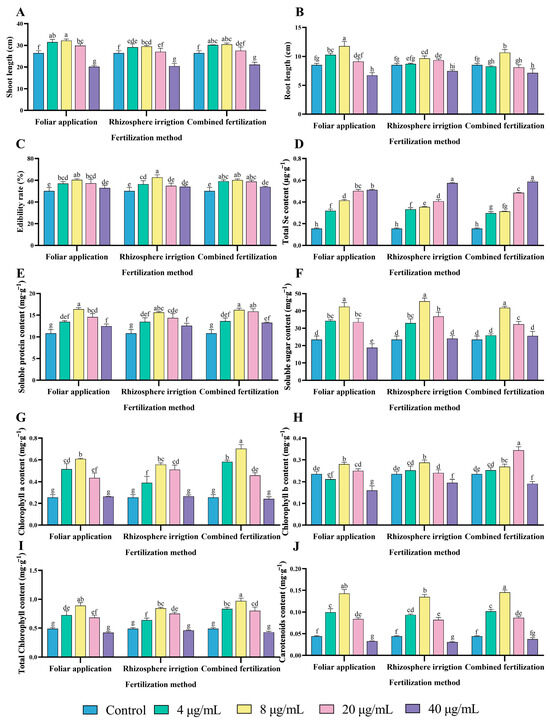
Figure 3.
Optimization of HJ application strategies in pea sprouts production. (A) Shoot length, (B) Root length, (C) Edibility rate, (D) Total Se content, (E) Soluble protein content, (F) Soluble sugar content, (G) Chlorophyll a content, (H) Chlorophyll b content, (I) Total chlorophyll content, and (J) Carotenoids content. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between the two groups.
The findings demonstrated that the HJ selenium concentration of 8 μg/mL and foliar application exhibited the most pronounced growth-promoting effect on pea sprouts shoot length and root length. The highest edibility rate of pea sprouts was observed when the HJ selenium concentration was 8 μg/mL and the fertilization method was rhizosphere irrigation.
3.1.2. Total Se Content
Selenium, an essential micronutrient, plays a role in a variety of physiological processes, including the maintenance of immune function, thyroid hormone metabolism, and the maintenance of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular health [2]. The addition of exogenous selenium does not typically exert a deleterious effect on plant growth. Indeed, selenium fertilization of plants represents an efficacious approach to the production of selenium-enriched plants [29]. The selenium contents of the treatment groups with different selenium concentrations of HJ applied according to different fertilization methods are presented in Figure 3D. The application of HJ was found to significantly increase the total Se content of pea sprouts, with a positive correlation observed between the increase in selenium concentration of HJ and the total Se content of the pea sprouts. Among the treatments, the 40 μg/mL treatment demonstrated the highest total Se content under the same fertilization method. The F40, R40, and C40 treatments exhibited significant increases over the control group by 231.49%, 272.62%, and 280.62%, respectively. The total Se content of the foliar application method was, on average, higher than that of rhizosphere irrigation and combined fertilization. The total Se content of the F8 group was significantly higher than that of the R8 and C8 groups, with a mean increase of 17.24% and 33.08%, respectively.
The consumption of vegetables with an appropriate selenium content is beneficial to human health. Pea sprouts sprayed with HJ at a selenium concentration of 8 μg/mL foliarly not only met the recommended daily intake of selenium (55–400 μg) but also provided optimal nutritional value [30]. However, excessive selenium intake can cause gastrointestinal disorders, alopecia, and other symptoms, and may even cause neurological disorders [31]. These findings suggest that the selenium content of pea sprouts increased in line with the HJ selenium concentration, with foliar application proving more effective than the other two application methods. This aligns with the results of a previous study [32].
3.1.3. Soluble Protein and Soluble Sugar Content
Soluble proteins and soluble sugars provide essential proteins and energy to the body, and soluble sugars are also important cellular osmoregulators. Li et al. observed that selenium treatment enhanced the soluble protein content of cowpea [33], while Xue et al. demonstrated that nanosized selenium application to pea sprouts led to a notable increase in soluble sugar content and a reduction in starch and crude fiber content [34].
The application of different concentrations of HJ bacterial fertilizer elevated the soluble protein content of pea sprouts in a manner demonstrating a general trend of increasing and then decreasing (Figure 3E). Among the three different fertilization methods, foliar application, rhizosphere irrigation, and combined fertilization, the bacterial fertilizer selenium concentration of 8 μg/mL demonstrated the most pronounced enhancement effect, with increases of 51.19%, 44.29%, and 49.65%, respectively, compared with the control.
The application of HJ was observed to result in a discernible increase in the soluble sugar content of pea sprouts. As illustrated in the Figure 3F, the application of HJ with a selenium concentration of 8 μg/mL had an extremely significant effect on the enhancement of soluble sugar content. In comparison to the control group, the soluble sugar contents of the F8, R8 and C8 treatment groups were increased by 80.48%, 93.54% and 77.72%, respectively. There was no significant difference between F8 and R8, while there was a significant difference between R8 and C8. The elevated soluble protein and soluble sugar content of pea sprouts following the application of HJ may be attributed to the uptake of organic selenium in the selenium fertilizer by the pea sprouts in the form of amino acids. This subsequently regulates protein synthesis, while selenium application promotes the metabolism of sugars in pea sprouts, which has a positive effect on the sugar content. Therefore, selenium fertilizer treatments at an appropriate concentration result in an increase in the soluble protein and soluble sugar content of pea sprouts.
3.1.4. Photosynthetic Pigment Content
Chlorophylls and carotenoids represent two of the most significant natural pigments found in plants. Chlorophylls a and b are responsible for the conversion of light energy into chemical energy, thereby promoting plant growth. Additionally, carotenoids possess functions such as photoprotection and antioxidant activity [35]. The application of appropriate concentrations of selenium to plants has been demonstrated to promote growth, improve overall quality, facilitate the synthesis of photosynthetic pigments and enhance photosynthesis [36].
The application of HJ in the selenium concentration range of 4–20 μg/mL was observed to significantly increase the chlorophyll a content (Figure 3G). Furthermore, the four treatment groups of F8, R8, C8, and C20 were found to be more effective in increasing the chlorophyll b content (Figure 3H). Both total chlorophyll and carotenoid content demonstrated a tendency to increase and subsequently decline with elevated HJ selenium concentrations. The most pronounced improvement relative to the control was observed at a selenium concentration of 8 μg/mL. Conversely, the application of 40 μg/mL HJ resulted in a reduction in total chlorophyll and carotenoid content. Upon analysis, the total chlorophyll content was increased by 81.50%, 72.23%, and 98.08% (Figure 3I), while the carotenoid content was increased by 223.54%, 205.88%, and 229.79% in the F8, R8, and C8 groups, respectively, in comparison to the control group (Figure 3J). HJ promoted the synthesis of chlorophyll a, total chlorophyll, and carotenoids in pea sprouts. However, the effect on chlorophyll b varied depending on the selenium content and application method.
3.2. Comparative Analysis of the Effect of Application of HJ, Na2SeO3 and Three Commercial Selenium Fertilizers on Pea Sprouts
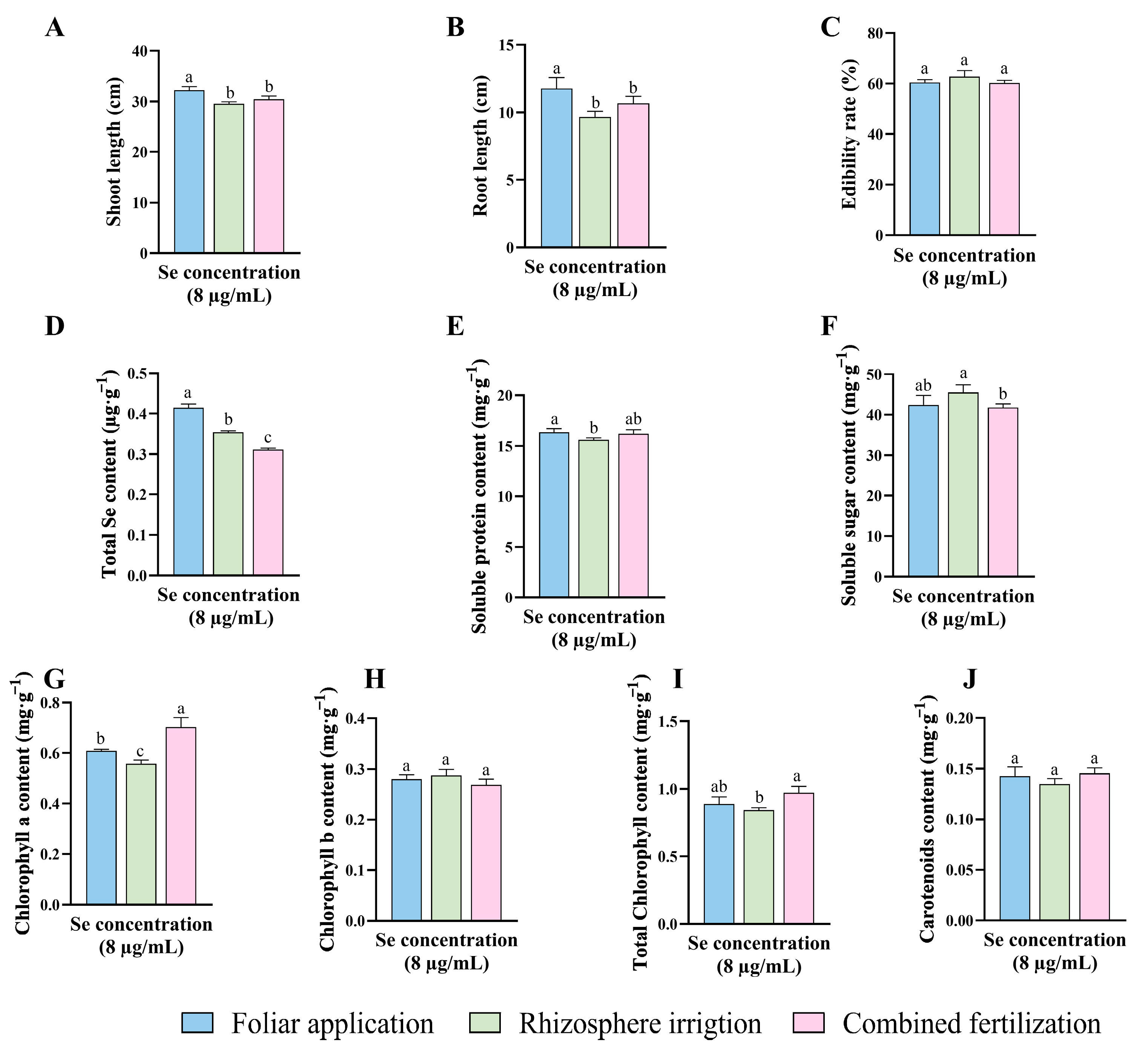
The results of the study of HJ selenium application concentrations and patterns indicated that the HJ selenium concentration of 8 μg/mL had the most pronounced effect on a range of indicators. Furthermore, the data demonstrated that foliar applications were more effective than combined fertilization and rhizosphere irrigation (Figure 4). To fully assess the effectiveness of the HJ selenium fertilizer, it was compared with sodium selenite (Na2SeO3). Additionally, three commercially available selenium fertilizers of the same type (“KaiJin”, “ZhenXi”, and “SiJiFeng”) were used as positive controls (P1, P2 and P3). A detailed comparative study and preliminary application assessment were conducted based on the HJ optimal fertilizer application strategy.
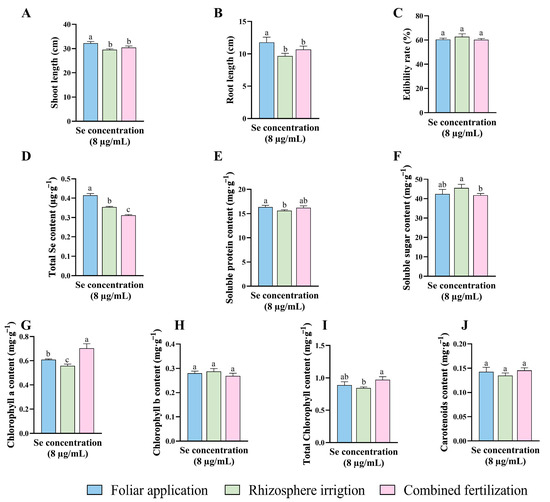
Figure 4.
Comparison of the effects of different application methods for selenium concentration of 8 μg/mL HJ. (A) Shoot length, (B) Root length, (C) Edibility rate, (D) Total Se content, (E) Soluble protein content, (F) Soluble sugar content, (G) Chlorophyll a content, (H) Chlorophyll b content, (I) Total chlorophyll content, and (J) Carotenoids content. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between the two groups.
3.2.1. Integrated Determination of Growth and Physiological Status and Total Se Content in Pea Sprouts
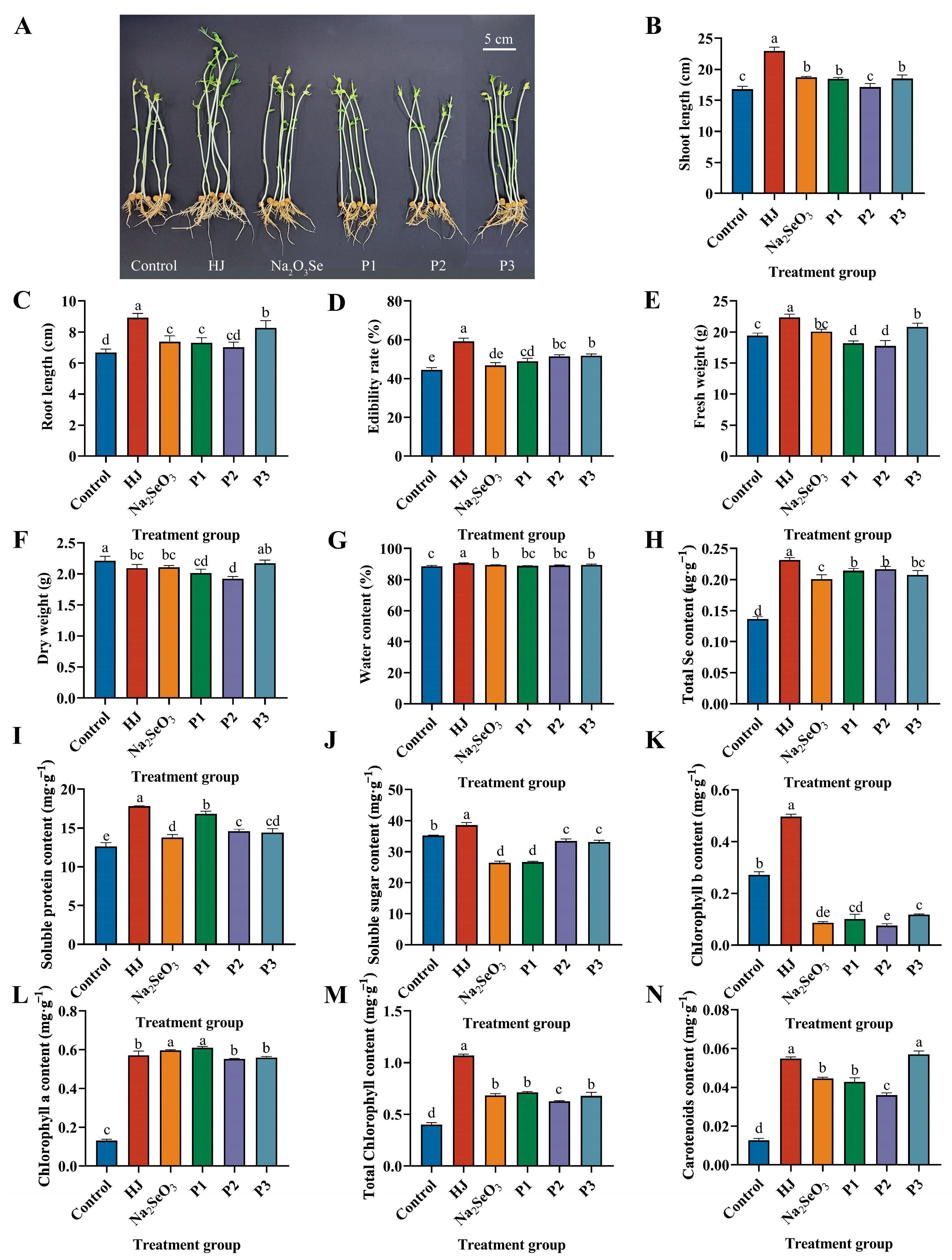
The effects of different selenium fertilizers on pea sprouts are illustrated in Figure 5A. Significant differences were observed between the HJ group and the other groups in terms of shoot length, root length, edibility rate, fresh weight, and water content. Among the positive control groups, the P3 group demonstrated the most favorable outcomes. In terms of shoot length, the HJ group increased by 36.59%, 22.79% and 24.10% compared to the control, Na2SeO3 and P3 groups (Figure 5B). In terms of root length, the HJ group increased by 33.36%, 21.06% and 7.83% compared to the control, Na2SeO3 and P3 groups (Figure 5C). In terms of edibility rate, the HJ group increased by 33.13%, 26.52%, 21.04%, 15.44% and 14.33% over all other treatment groups (Figure 5D). In terms of fresh weight, the HJ group increased by 15.19%, 11.29%, 22.87%, 25.83% and 7.23% compared to all other treatment groups (Figure 5E). The dry weight of the HJ group demonstrated a 5.42% reduction in comparison with the control group (Figure 5F). Meanwhile, the water content of the HJ group was as high as 90.63%, representing a 2.31% increase compared to the control group (Figure 5G).
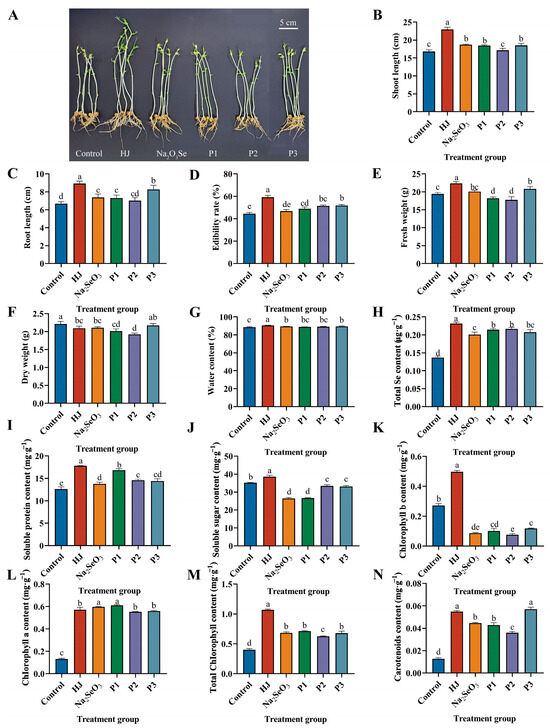
Figure 5.
Effects of various selenium fertilizers on growth indexes, total Se content and physiological indexes of pea sprouts. (A) Comparison of pea sprouts in each treatment group, (B) Shoot length, (C) Root length, (D) Edibility rate, (E) Fresh weight, (F) Dry weight, (G) Water content, (H) Total Se content, (I) Soluble protein content, (J) Soluble sugar content, (K) Chlorophyll b content, (L) Chlorophyll a content, (M) Total chlorophyll content, and (N) Carotenoids content. In the Figure, HJ is the experimental group and P1, P2 and P3 of the positive control group represent three kinds of commercial selenium fertilizers, “KaiJin”, “ZhenXi” and “SiJiFeng”. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between the two groups.
The total Se content and soluble protein content were found to be significantly elevated in each treatment group in comparison to the control group. The HJ group exhibited the most pronounced effect (Figure 5H,I). The increase of the total Se content in the HJ group in comparison to the control group was as high as 69.86%. The soluble protein content increased by 40.93% compared to the control. These results demonstrated that the HJ group exhibited the most pronounced elevation in soluble sugar content, which was 9.67% higher than that observed in the control group (Figure 5J). In contrast, the remaining treatment groups exhibited a decline in soluble sugar content, with decreases of 24.95%, 24.38%, 4.88%, and 5.85%, respectively, compared to the control group.
The application of various selenium fertilizers was found to significantly increase the content of chlorophyll a, total chlorophyll and carotenoids in pea sprouts. Conversely, the application of Na2SeO3, as well as three commercial selenium fertilizers, was observed to cause a decrease in the content of chlorophyll b in pea sprouts (Figure 5K). This may be attributed to the interaction of selenium with sulfhydryl-containing enzymes that play a crucial role in the process of chlorophyll synthesis [18]. The application of HJ was found to significantly increase the content of chlorophyll a in pea sprouts, with a 337.07% increase compared to the control (Figure 5L). Furthermore, the HJ group demonstrated the greatest efficacy in increasing chlorophyll b, total chlorophyll and carotenoids, with increases of 83.00%, 165.53% and 335.03%, respectively, compared to the control (Figure 5M). The P3 group exhibited a more pronounced effect on carotenoid content than the HJ group, although the effects of the two treatments did not differ significantly (Figure 5N).
The selenium-enriched bacterial fertilizer HJ was observed to effectively promote the growth of pea sprouts and improve their growth status. The total Se content of pea sprouts was significantly increased by all selenium fertilizers, and no difference in the effects was observed among the three commercial selenium fertilizer groups. However, HJ demonstrated the most effective selenium enrichment. Furthermore, the application of HJ was observed to enhance the accumulation of soluble protein and soluble sugar in pea sprouts, thereby improving the quality of the shoots. With the exception of HJ, the reduction in soluble sugar content observed in other treatment groups may be attributed to the accumulation of starch [34].
3.2.2. SOD, POD, CAT Enzyme Activity and MDA Content
Antioxidant enzymes are a category of biocatalysts produced by living cells in organisms. They are capable of effectively removing reactive oxygen species generated by the metabolic activities of organisms. The antioxidant enzyme system primarily comprises superoxide dismutase (SOD), peroxidase (POD), catalase (CAT), and other enzymes. Malondialdehyde (MDA) is a lipid peroxidation product generated from the peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids in cell membranes when attacked by free radicals. It is one of the most important indicators of the degree of oxidative damage to cells [37].
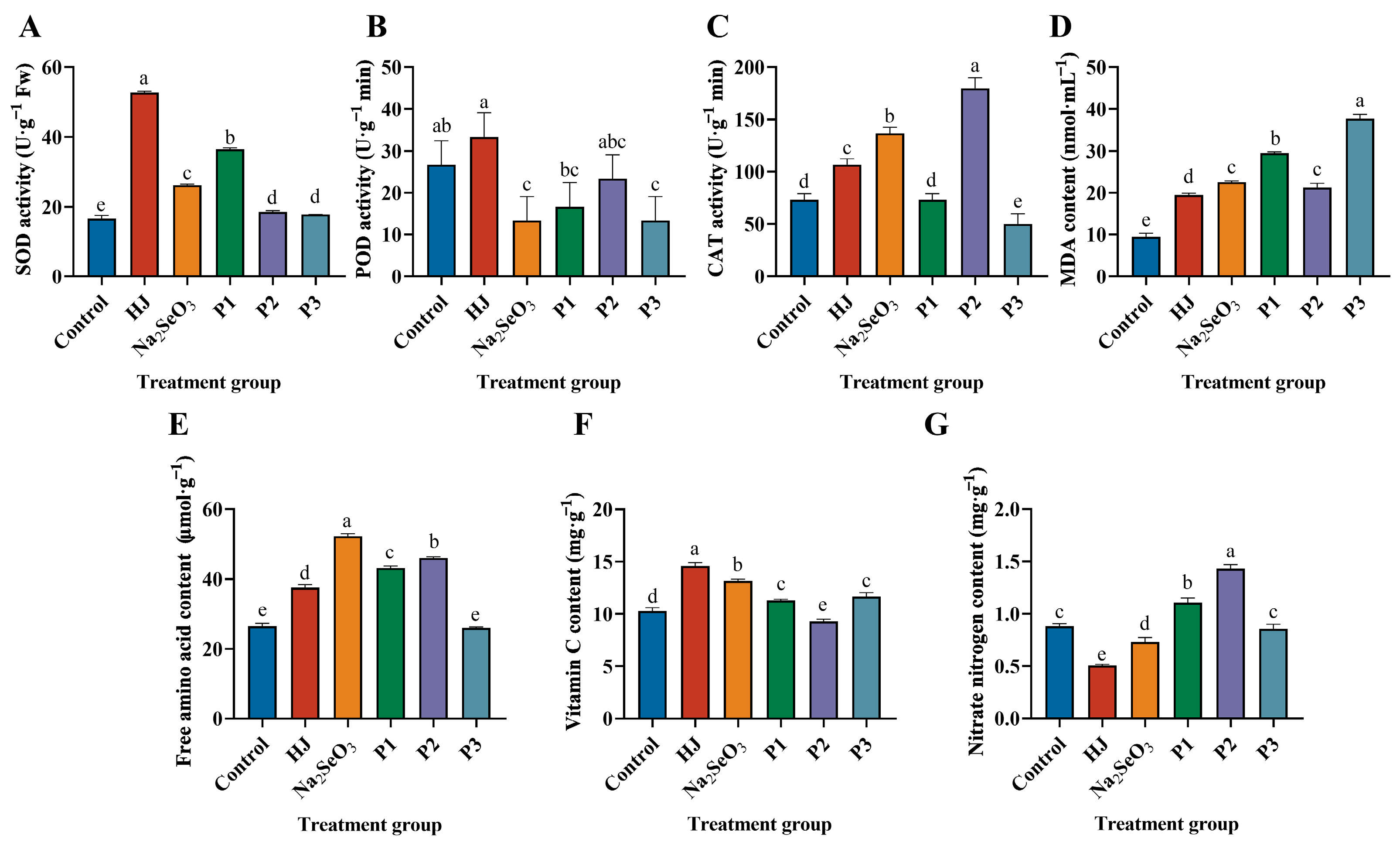
As illustrated in Figure 6A, the SOD activity of each selenium fertilizer treatment was markedly elevated in comparison to the control group. The HJ group exhibited the greatest enhancement in SOD activity, with an increase of 219.23%, while the P3 group demonstrated the least significant elevation, with an increase of 7.69%. Figure 6B illustrates that the elevation in POD activity in the HJ group was less pronounced in comparison to the control group, while the POD activity in the remaining groups was observed to be lower than that of the control group. As illustrated in Figure 6C, the CAT activities of the HJ, Na2SeO3, and P2 groups exhibited a notable increase, reaching 45.46%, 86.36%, and 145.45%, respectively, in comparison to the control group. However, the P1 and P3 groups demonstrated a contrasting trend, displaying a decline in CAT activity relative to the control group. As illustrated in Figure 6D, the application of selenium fertilizers to pea sprouts resulted in an MDA content that was 2.05, 2.37, 3.11, 2.24 and 3.97 times higher than that of the control group, respectively. It can be observed that the application of HJ has the potential to enhance the antioxidant capacity of pea sprouts, improve their resistance to stress and elevate the activities of SOD, POD and CAT enzymes.
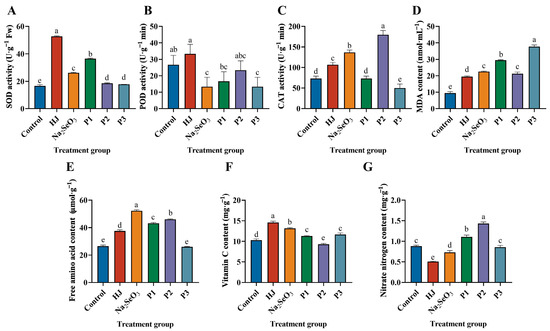
Figure 6.
Effect of various selenium fertilizers on antioxidant enzyme activities and nutritional quality of pea sprouts. (A) SOD activity, (B) POD activity, (C) CAT activity, (D) MDA content, (E) free amino acids, (F) vitamin C, and (G) nitrate nitrogen. In the Figure, HJ is the experimental group and P1, P2 and P3 of the positive control group represent three kinds of commercial selenium fertilizers, “KaiJin”, “ZhenXi” and “SiJiFeng”. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) between the two groups.
3.2.3. Free Amino Acid, Vitamin C, Nitrate Nitrogen Content
A high concentration of free amino acids is an indicator of a healthy, high-quality crop [38]. An increase in the vitamin C content of crops can enhance their nutritional value and improve their resilience to adverse conditions [39]. Nitrate nitrogen can be rapidly absorbed by plants and can be converted to nitrite when ingested by the human body. Excessive consumption of nitrate-containing plants can lead to gastrointestinal distress or, in extreme cases, cancerous growths [40]. However, appropriate agricultural management and food processing techniques can be employed to reduce the nitrate nitrogen content of plant species [41].
We compared the effects of five different selenium fertilizers on free amino acids, vitamin C and nitrate nitrogen in pea sprouts. The results demonstrated that, with the exception of the P3 group, the remaining treatment groups exhibited a notable increase in the free amino acid content of pea sprouts. Of these, the Na2SeO3 group exhibited the most pronounced effect. Additionally, with the exception of the P2 group, the remaining treatment groups demonstrated a significant improvement in the vitamin C content of pea sprouts, with the HJ group displaying the most favorable outcome. The free amino acid content of the HJ, Na2SeO3, P1 and P2 groups increased by 41.81%, 97.27%, 62.77% and 73.55%, respectively, in comparison to the control group (Figure 6E). Similarly, the vitamin C content of the HJ, Na2SeO3, P1 and P3 groups increased by 42.05%, 28.14%, 10.18% and 13.66% (Figure 6F). The nitrate nitrogen content decreased in the HJ, Na2SeO3 and P3 groups in comparison to the control group by 42.95%, 17.18% and 2.86%, respectively. However, the difference was not significant in the P3 group (Figure 6G). These findings demonstrated that both HJ and Na2SeO3 were efficacious in augmenting the free amino acid and vitamin C contents of pea sprouts, while concurrently reducing the nitrate nitrogen content and enhancing the nutritional quality of pea sprouts.
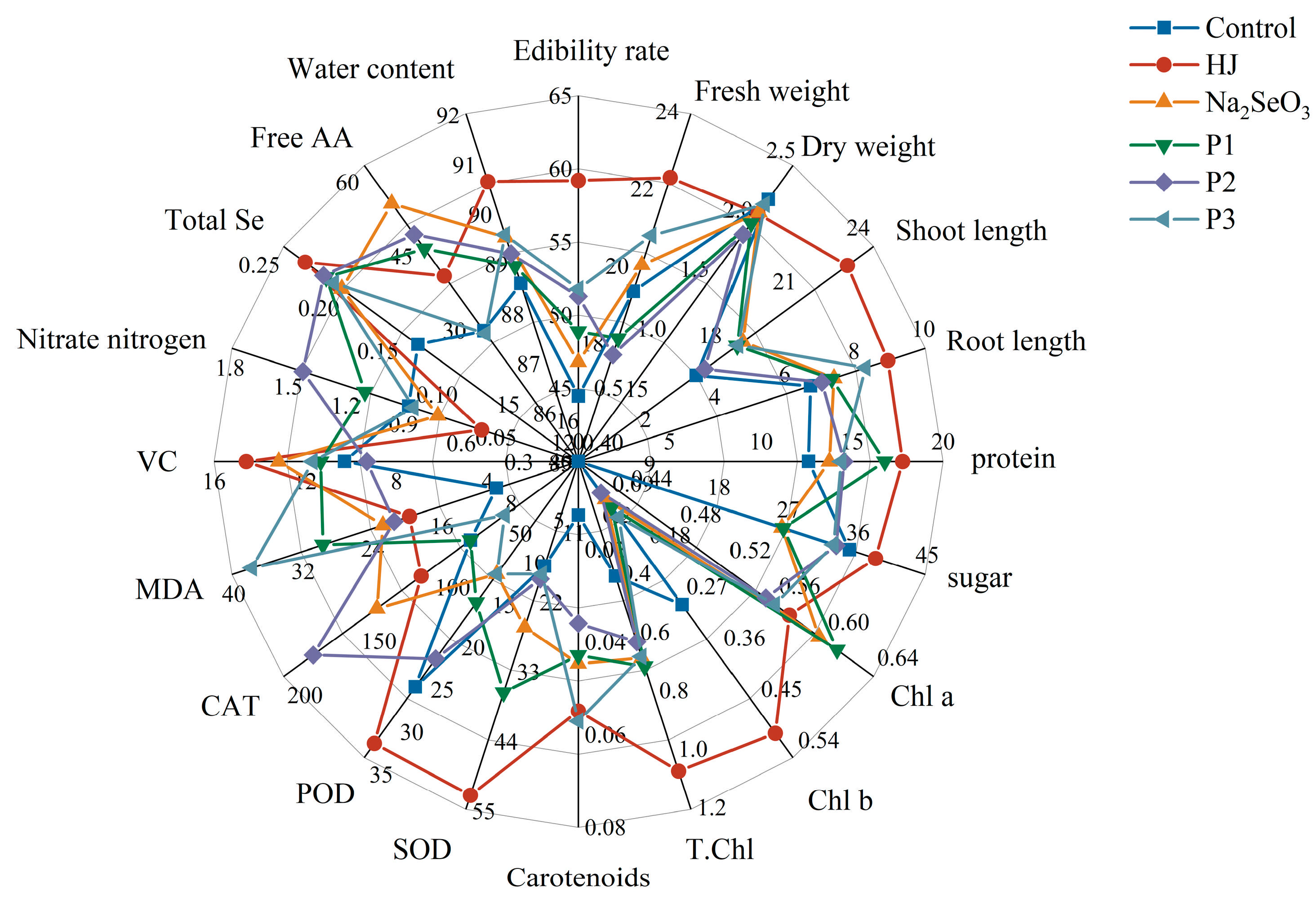
3.2.4. Radar Analysis
Radar analysis demonstrated that the mean observed values of the parameters influenced by foliar application of diverse selenium fertilizers on pea sprouts, including growth indexes, total Se content, soluble protein content, soluble sugar content, photosynthetic pigments, antioxidant enzyme activities, MDA content, free amino acids content, vitamin C content, and nitrate nitrogen content (Figure 7), were affected by the application of these fertilizers. The results demonstrated that among the diverse selenium fertilizers employed, the selenium-enriched bacterial fertilizer HJ exhibited the most pronounced benefits in promoting pea sprouts growth, water content, edibility rate, fresh weight, shoot length, root length, soluble protein, soluble sugar, chlorophyll b, total chlorophyll, SOD, POD, vitamin C, and total Se, while concurrently demonstrating the lowest MDA and nitrate nitrogen content. The advantages of the Na2SeO3 and the three commercial selenium fertilizers were compared. The application of Na2SeO3 was found to significantly enhance the free amino acid content of pea sprouts. The “KaiJin” treatment demonstrated the most pronounced effect on the capacity of pea shoots to synthesize chlorophyll a, while the “ZhenXi” treatment exhibited a notable impact on the ability of pea sprouts to elevate the activity of the CAT enzyme. The application of “SiJiFeng” had the most pronounced effect on the synthesis of carotenoids in pea sprouts.
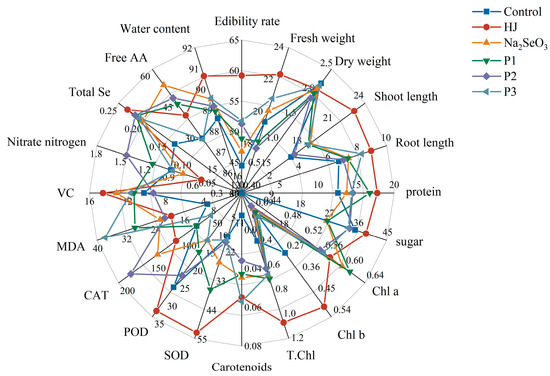
Figure 7.
Radar analysis of the effects of different selenium fertilizers on various indicators of pea sprouts. In the Figure, HJ is the experimental group, and P1, P2 and P3 of the positive control group represent three kinds of commercial selenium fertilizers, “KaiJin”, “ZhenXi” and “SiJiFeng”.
4. Conclusions
In order to improve the selenium enrichment capacity of plants, we developed a novel selenium-enriched bacterial fertilizer (HJ), which is not only economical and environmentally friendly, but also has significant selenium-enrichment effects. Using pea sprouts as a model plant, we explored the effects of HJ on growth, soluble protein, soluble sugar, photosynthetic pigments and selenium-enriched capacity when applied in different ways. The results showed that HJ had significant advantages in promoting the growth of pea sprouts, improving the resistance to stress, enhancing nutrient accumulation, and improving the quality of the product. The results also showed that HJ had less accumulation of MDA and nitrate nitrogen than the Na2SeO3 treatment group, and it was non-toxic, green, healthy, and environmentally friendly and economical. In view of the discrepancies between crop requirements and growing environments, further exploration of the effectiveness of selenium fertilizer HJ for various crops is required. The above results are of great significance for the cultivation of selenium-enriched agricultural products and promoting the development of functional foods.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15020430/s1, Table S1: Experimental groupings for the optimization of HJ application strategies in pea sprout production.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.W. (Yaqi Wang); methodology, Y.W. (Yaqi Wang), Y.Z. and X.J.; validation, Y.Z. and X.J.; formal analysis, Y.W. (Yaqi Wang); investigation, Y.L. (Ying Li) and Y.W. (Yu Wu); data curation, Y.W. (Yaqi Wang) and Y.L. (Ying Li); writing—original draft preparation, Y.W. (Yaqi Wang), Y.Z. and X.J.; writing—review and editing, Y.L. (Ying Li), Y.Z. and X.J.; supervision, Y.L. (Ying Li), Y.W. (Yu Wu), Y.L. (Yang Liu) and Y.C.; project administration, Y.Z. and X.J.; funding acquisition, Y.Z. and X.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82303743), Heilongjiang Province Outstanding Youth Project (No. YQ2024H030).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Materials. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Genchi, G.; Lauria, G.; Catalano, A.; Sinicropi, M.S.; Carocci, A. Biological Activity of Selenium and Its Impact on Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieliszek, M. Selenium-Fascinating Microelement, Properties and Sources in Food. Molecules 2019, 24, 1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.H.; Sun, X.Y.; Li, P.; Shen, X.C.; Fang, Y. Selenium in cereals: Insight into species of the element from total amount. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2914–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.Q.; Liu, K.L. Selenium and selenoproteins: Their function and development of selenium-rich foods. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 7026–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Peng, Q.; Wang, M.; Liu, N.N.; Dinh, Q.T.; Zhai, H.; Xue, M.Y.; Liang, D.L. Influence of processing methods and exogenous selenium species on the content and in vitro bioaccessibility of selenium in Pleurotus eryngii. Food Chem. 2021, 338, 127661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, J.-Y.; Rao, S.; Gou, Y.; Xu, F.; Cheng, S. Comparative study of the effects of selenium yeast and sodium selenite on selenium content and nutrient quality in broccoli florets (Brassica oleracea L. var. italica). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 102, 1707–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, T. Selenium transformation and selenium-rich foods. Food Biosci. 2021, 40, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.H.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhou, L.; Chang, M.J.; Yue, T.L.; Yuan, Y.H.; Shi, Y.H. Distribution characteristics of organic selenium in Se-enriched Lactobacillus (Lactobacillus paracasei). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 165, 113699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, B.; Xu, W.J.; Xie, H.Y.; Wu, Z.Q. Biosynthesis and characterization of selenium nanoparticles by Se-tolerant Lactiplantibacillus plantarum. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Guo, Y.; Li, H. Effects of Different Forms of Selenium Fertilizers on Se Accumulation, Distribution, and Residual Effect in Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Rotation System. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1116–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesam, S.M.; Wenli, S.; Qi, C. Foliar application of nutrients on medicinal and aromatic plants, the sustainable approaches for higher and better production. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2022, 11, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.P.; Zhang, J.P.; Zhang, K.Y.; Wen, Q.Y.; Ming, K.; Xiong, H.; Ning, F.J. Peanut selenium distribution, concentration, speciation, and effects on proteins after exogenous selenium biofortification. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, L.; Silva, E.; Pavia, I.; Ferreira, H.; Matos, C.; Osca, J.M.; Moutinho-Pereira, J.; Lima-Brito, J. Seed Soaking with Sodium Selenate as a Biofortification Approach in Bread Wheat: Effects on Germination, Seedling Emergence, Biomass and Responses to Water Deficit. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.F.; Hou, S.M.; Yang, Y.C.; Cheng, D.D.; Gao, B.; Wan, Y.S.; Li, Y.C.; Yao, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.G.; Xie, J.Z. Activation of Humic Acid in Lignite Using Molybdate-Phosphorus Hierarchical Hollow Nanosphere Catalyst Oxidation: Molecular Characterization and Rice Seed Germination-Promoting Performances. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 13620–13631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.C.; Han, A.H.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Y.; Xu, L.; Ma, F.X.; Liu, R.Q. Chitosan oligosaccharide alleviates the growth inhibition caused by physcion and synergistically enhances resilience in maize seedlings. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, M.; Li, C.; Shang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P.; Gao, X. Study on the Effect of Pharmaceutical Excipient PEG400 on the Pharmacokinetics of Baicalin in Cells Based on MRP2, MRP3, and BCRP Efflux Transporters. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, J.Z.; Li, J.X.; Zhu, F.M.; Chen, X.N.; Du, B.; Tian, H.L.; Li, J. Plant sprout foods: Biological activities, health benefits, and bioavailability. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e13777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jerse, A.; Kacjan-Marsic, N.; Sircelj, H.; Germ, M.; Kroflic, A.; Stibilj, V. Seed soaking in I and Se solutions increases concentrations of both elements and changes morphological and some physiological parameters of pea sprouts. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 118, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.D.; Liu, Z.H.; Zeng, W.M.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.D.; Zhang, Y.L.; Jia, X.Q. Screening and Identification of Soil Selenium-Enriched Strains and Application in Auricularia auricula. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.; Sharma, R.; Kumari, S.; Kumari, A. Enhancing wheat crop production with eco-friendly chitosan encapsulated nickel oxide nanocomposites: A safe and sustainable solution for higher yield. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Dou, G.; Zhao, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, S.; Qin, A. Inversion of Crop Water Content Using Multispectral Data and Machine Learning Algorithms in the North China Plain. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Chen, S.; Cai, Z.; Guo, Z.; Yang, J.; Zheng, R.; Hu, R. Expansion of Pleioblastus amarus in tea plantations significantly enhances the appearance and nutritional composition of bamboo shoots but adversely affects palatability. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, C.; Zhang, L.; Duan, X.; Chai, X.; Huang, R.; Kang, Y.; Yang, X. Effects of exogenous sucrose and selenium on plant growth, quality, and sugar metabolism of pea sprouts. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, T.; Fan, R.; Hussain, S.; Sattar, A.; Khalid, S.; Butt, M.; Shahzad, U.; Atif, H.M.; Batool, M.; Ullah, S.; et al. Protective effect of jasmonic acid and potassium against cadmium stress in peas (Pisum sativum L.). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 2626–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, R.; Maqsood, M.F.; Shahbaz, M.; Naz, N.; Zulfiqar, U.; Ali, M.F.; Jamil, M.; Khalid, F.; Ali, Q.; Sabir, M.A.; et al. Exogenous ascorbic acid as a potent regulator of antioxidants, osmo-protectants, and lipid peroxidation in pea under salt stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Guo, X.L.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Yang, Y.M.; Zheng, W.A.; Xue, X.Z. Effects of light-emitting diode spectral combinations on growth and quality of pea sprouts under long photoperiod. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 978462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, J.; Cui, J.; Lin, A. Effects of selenium fertilizer application and tomato varieties on tomato fruit quality: A meta-analysis. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 304, 111242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.J.; Xiao, H.J.; Li, J.Q.; Zhang, J.X.; Zhou, L.Y.; Wang, J.Q. Effects of different fertilization rates on growth, yield, quality and partial factor productivity of tomato under non-pressure gravity irrigation. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Gao, M.F.; Shi, R.; Song, S.W.; Zhang, Y.T.; Su, W.; Liu, H.C. The Combination of Selenium and LED Light Quality Affects Growth and Nutritional Properties of Broccoli Sprouts. Molecules 2020, 25, 4788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.A.X.; Yue, L.; Cheng, B.X.; Chen, F.R.; Zhao, X.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Xing, B.S. Mechanisms of growth-promotion and Se-enrichment in Brassica chinensis L. by selenium nanomaterials: Beneficial rhizosphere microorganisms, nutrient availability, and photosynthesis. Environ. Sci. Nano 2022, 9, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somagattu, P.; Chinnannan, K.; Yammanuru, H.; Reddy, U.K.; Nimmakayala, P. Selenium dynamics in plants: Uptake, transport, toxicity, and sustainable management strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Ali, F.; Qi, M.X.; Peng, Q.; Wang, M.K.; Bañuelos, G.S.; Miao, S.Y.; Li, Z.; Dinh, Q.T.; Liang, D.L. Insights into uptake, accumulation, and subcellular distribution of selenium among eight wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars supplied with selenite and selenate. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xiong, Y.Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Xiao, C.M.; Wang, S.Y.; Cheng, S.Y.; Cheng, H. Effect of Nano-Selenium on Nutritional Quality of Cowpea and Response of ABCC Transporter Family. Molecules 2023, 28, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.T.; Kang, Y.F.; Pan, C.P.; Hu, T.T.; Yu, M.; Chen, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.J. Nano-selenium regulates the sugar metabolism in pea (Pisum sativum L.) sprouts. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 167, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, M.; Pérez-Gálvez, A. Metabolomics of Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: Analytical Methods and Metabolome-Based Studies. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.D.; Xiao, C.M.; Qiu, T.C.; Deng, J.; Cheng, H.; Cong, X.; Cheng, S.Y.; Rao, S.; Zhang, Y. Selenium Regulates Antioxidant, Photosynthesis, and Cell Permeability in Plants under Various Abiotic Stresses: A Review. Plants 2023, 12, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Peng, Y.X.; Zheng, L.J.; He, C.; Peng, S.; Huang, Y.W.; Wang, L.X.; Liu, H.P.; Feng, G.F. Chitosan-Se Engineered Nanomaterial Mitigates Salt Stress in Plants by Scavenging Reactive Oxygen Species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2023, 72, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.H.; Li, K.F.; Zhang, X.; Yang, C.W.; Zhang, R.; Guo, H.C. The Impact of the Foliar Application of Amino Acid Aqueous Fertilizer on the Flavor of Potato Tubers. Foods 2023, 12, 3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciolla, C.; Fortunato, S.; Dipierro, N.; Paradiso, A.; De Leonardis, S.; Mastropasqua, L.; de Pinto, M.C. Vitamin C in Plants: From Functions to Biofortification. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, D.; Babu, B. A Review on N-nitrosamine Impurity. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 20, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, T.; Grundy, S.; Yang, Q.C.; Cheng, R.F. A Review of Environment Effects on Nitrate Accumulation in Leafy Vegetables Grown in Controlled Environments. Foods 2020, 9, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).