Climate Change and Its Impacts on the Planting Regionalization of Potato in Gansu Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
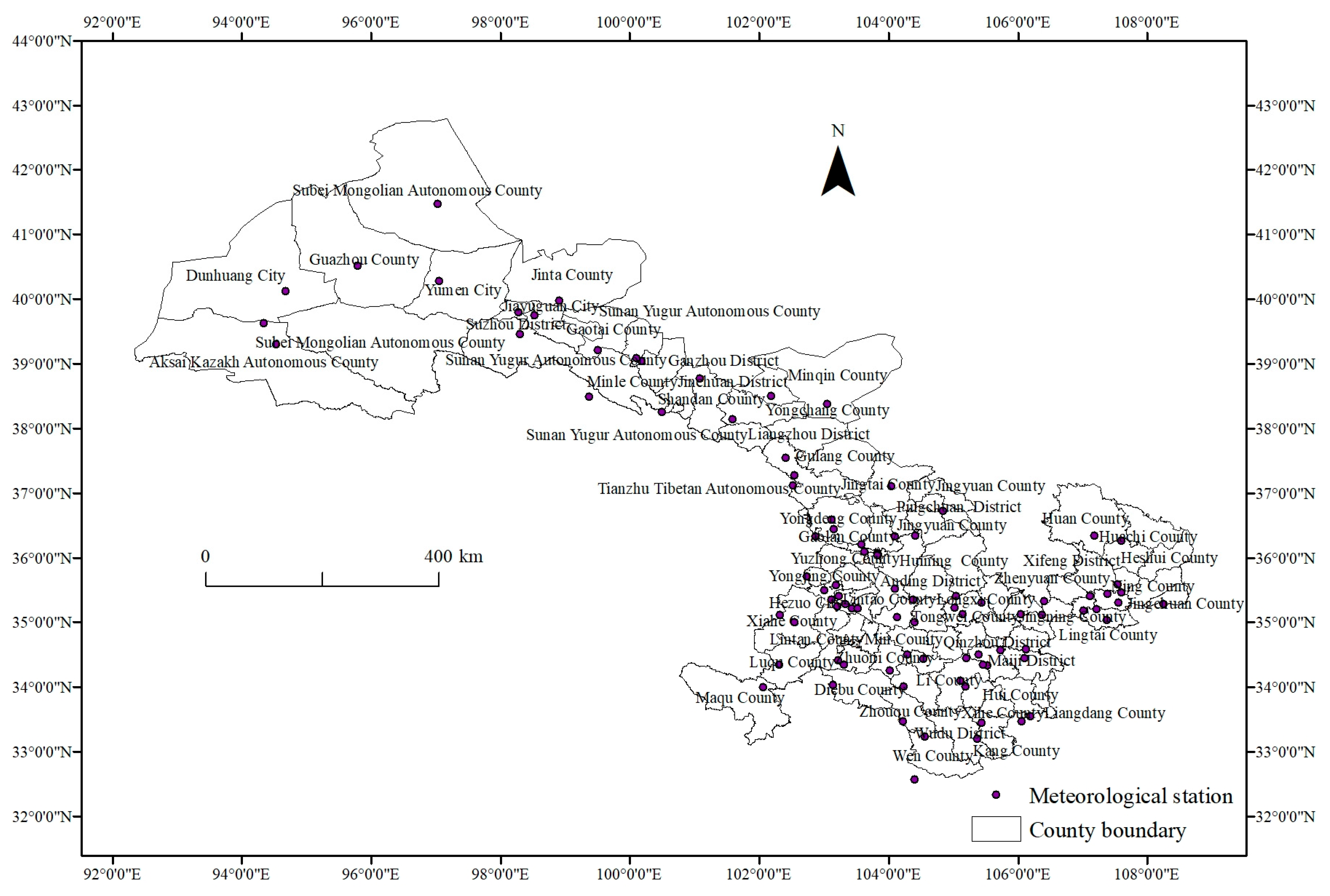
2.1. Regional Overview and Data Sources
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Data Processing
2.4. Research Technique
2.4.1. BP Neural Network Interpolation Method
2.4.2. The Mann–Kendall Mutation Test Method
2.4.3. Maximum Membership Degree Fuzzy Evaluation Method
- (1)
- Selection of climatic zoning factors
- (2)
- Fuzzy comprehensive evaluation of zoning factors
- ①
- Establishment of the factor set and evaluation set for zoning factors
- ②
- Determination of weight coefficients for zoning factors
- ③
- Determination of membership function
- ④
- Calculation of the fuzzy evaluation matrix
- ⑤
- Comprehensive evaluation
3. Results
3.1. The Temporal Variation Characteristics and Mutation Testing of Zoning Factors
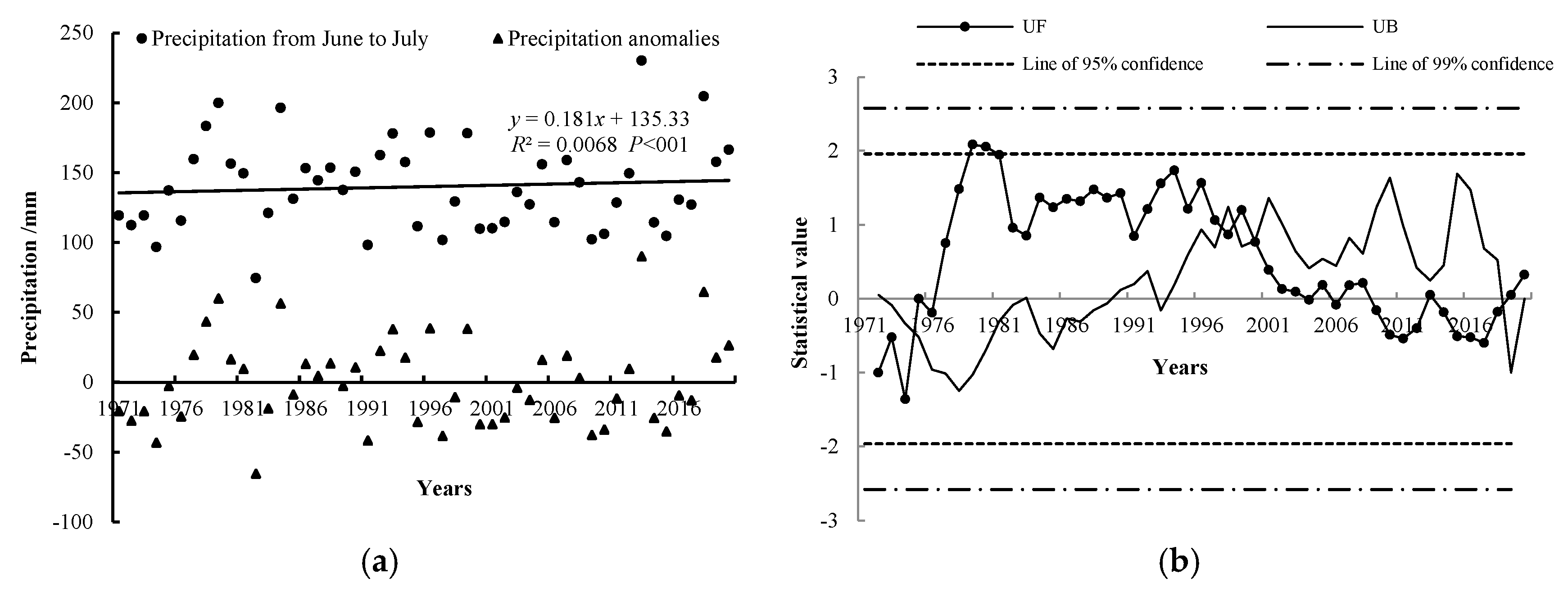
3.1.1. Amount of Precipitation from June to July
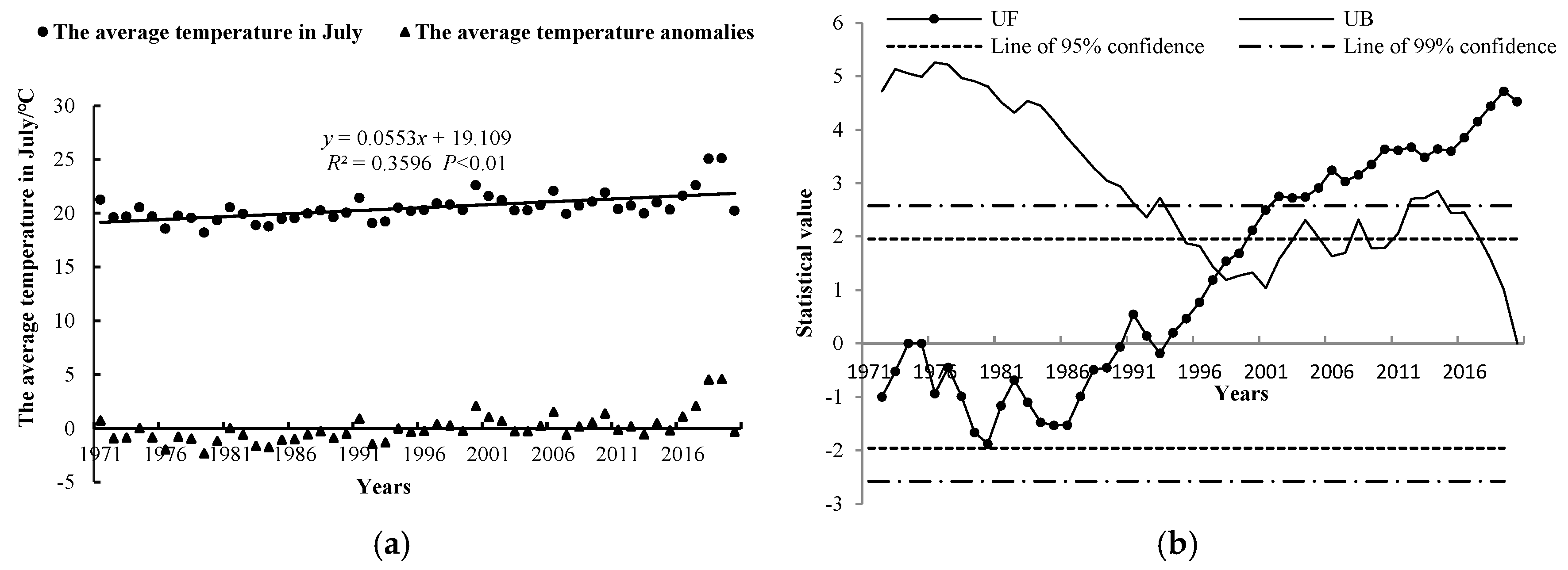
3.1.2. The Average Temperature in July
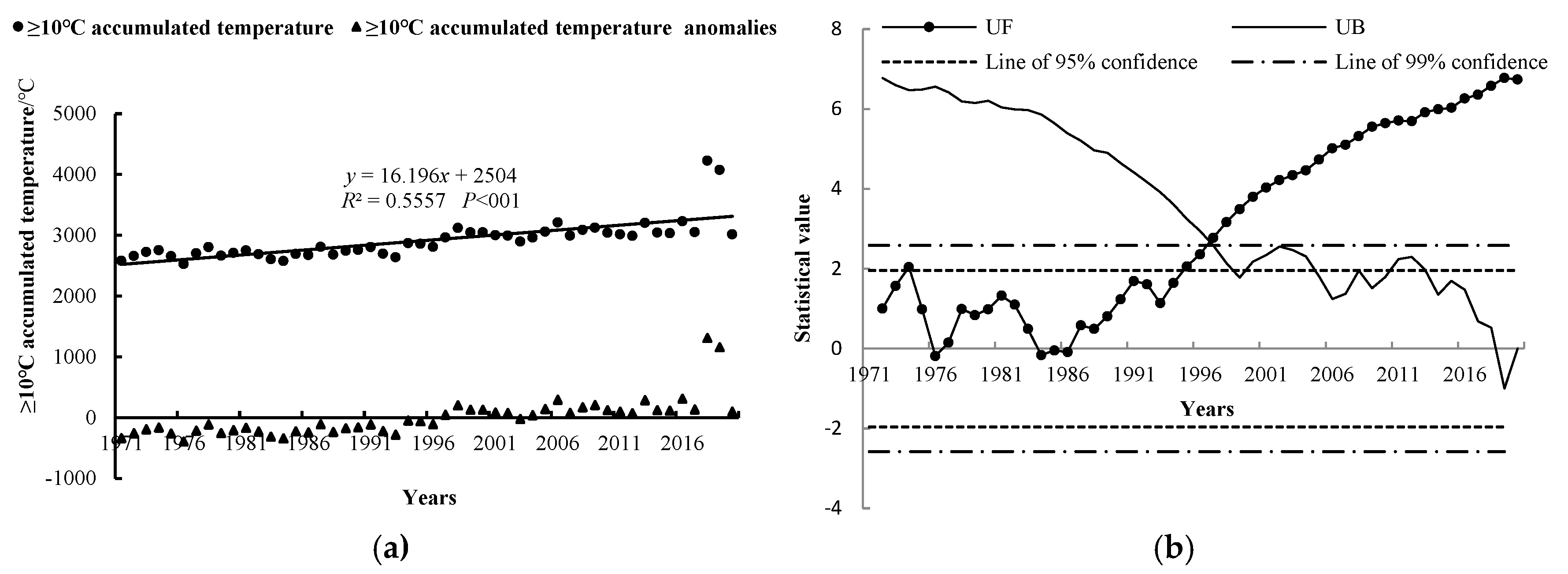
3.1.3. The Accumulated Temperature Above 10 °C
3.2. The Spatial Variation Characteristics of Zoning Factors
3.2.1. The Spatial Variation Characteristics of Precipitation from June to July
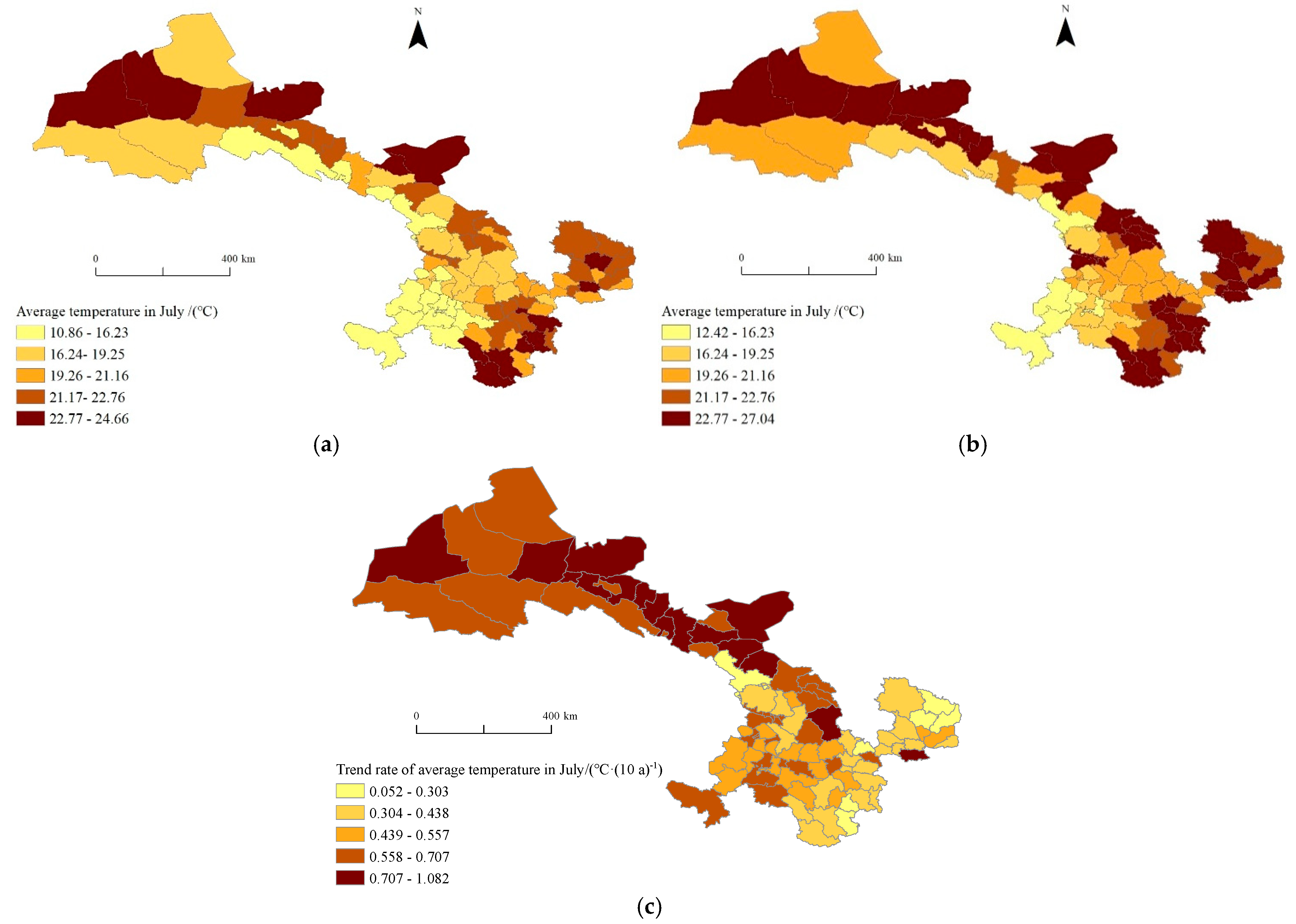
3.2.2. The Spatial Variation Characteristics of the Average Temperature in July
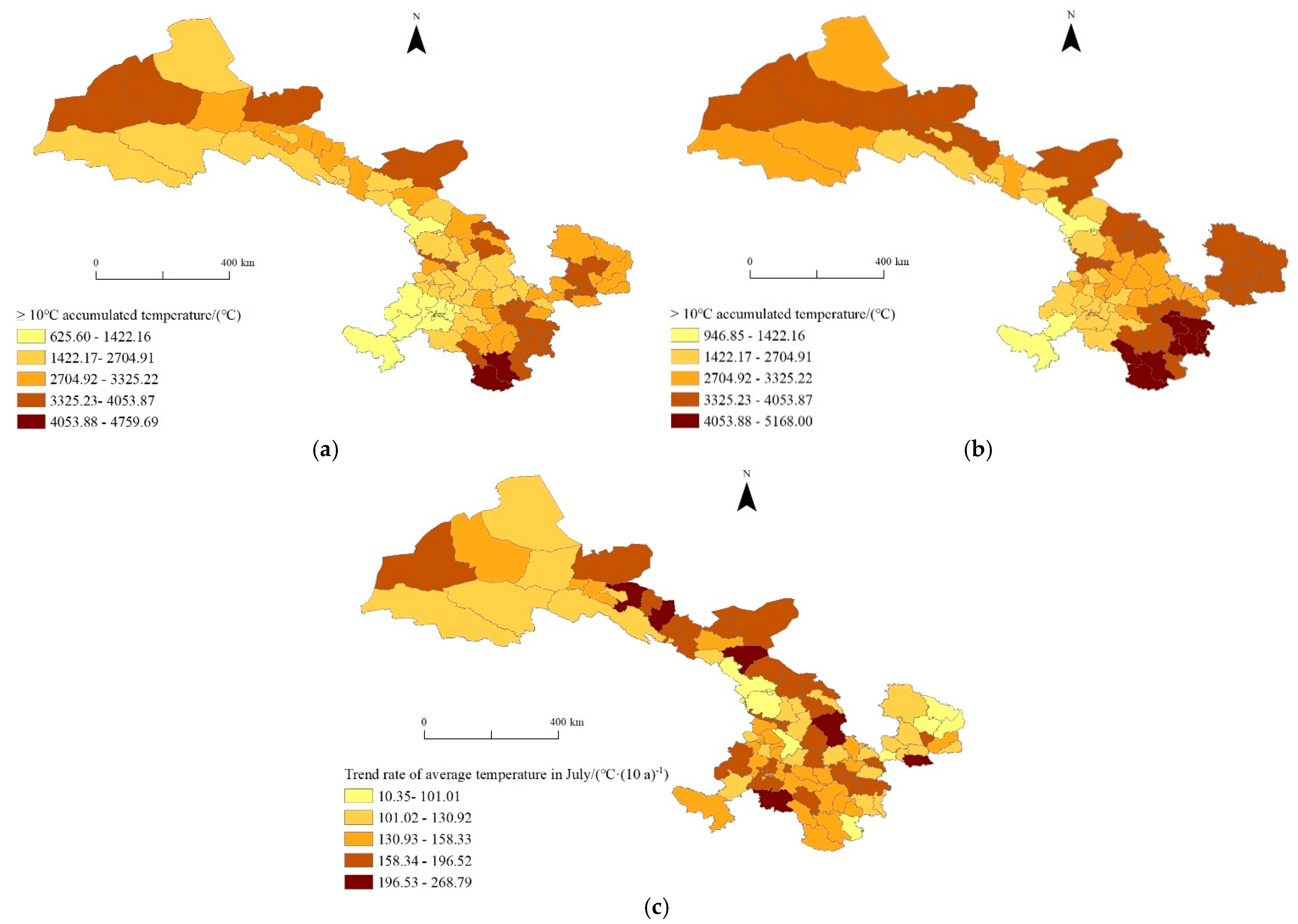
3.2.3. The Spatial Variation Characteristics of the Accumulated Temperature Above 10 °C
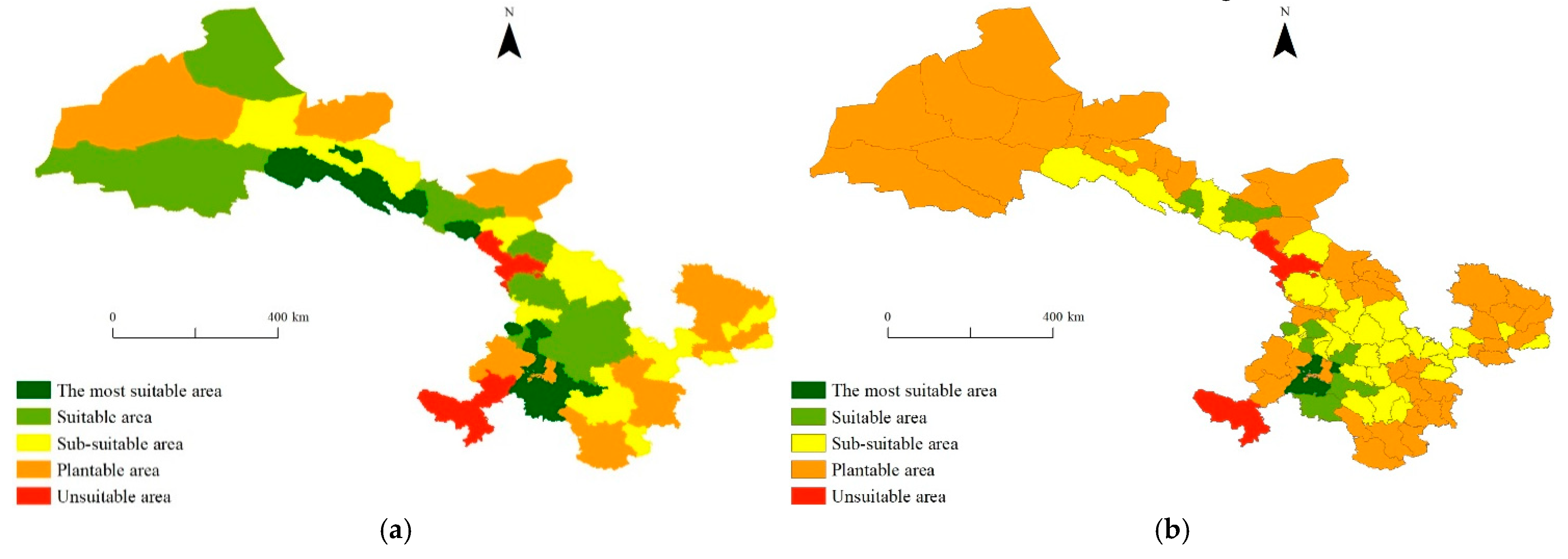
3.3. The Spatial Changes in Potato Planting Areas
3.3.1. The Spatial Changes in the Most Suitable Areas
3.3.2. The Spatial Changes in the Suitable Areas
3.3.3. The Spatial Changes in the Sub-Suitable Areas
3.3.4. The Spatial Changes in the Plantable Areas
3.3.5. The Spatial Changes in the Unsuitable Areas
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- During the study period, the amount of precipitation from June to July fluctuated; however, there was a slight increasing trend with an overall rate of 1.81 mm/10 a. The average temperature in July showed a general warming trend at a rate of 0.55 °C/10 a. Moreover, the accumulated temperature above 10 °C showed a significant warming trend at a rate of 161.96 °C/10 a. The abrupt change in precipitation from June to July and in the average temperature for July occurred in 1998. However, no sudden alteration was observed for the accumulated temperature above 10 °C.
- (2)
- The spatial distribution of potato regionalization indexes has exhibited significant regional disparities in Gansu Province over the past 50 years. The spatial distribution of precipitation from June to July exhibited distinct regional variations, characterized by a gradual decrease from south to north and from east to west. Additionally, the spatial change in the precipitation tendency rate during this period showed a gradual decrease from north to south and from east to west. The average temperature in July showed a decreasing spatial pattern from northeast to southwest. Furthermore, the trend rate for the average temperature in July exhibited a decreasing trend from west to east and from north to south. The accumulated temperature above 10 °C in the study area showed a spatial pattern of higher accumulated temperatures in the northwestern and southeastern regions and lower accumulated temperatures in other regions, while the trend rate for the accumulated temperature above 10 °C displayed a decreasing trend from west to east and from north to south.
- (3)
- The impact of climate change on potato planting in Gansu Province was primarily characterized by a reduction in the most suitable areas and suitable areas, an expansion of the sub-suitable areas and plantable areas, as well as a decrease in the unsuitable areas. Compared with before 1998, the arable land area for planting potato had increased by 2.96 × 103 hm2, an increase of 0.065% in proportion, and the altitude of potato planting areas had moved up by 176.3 m. After 1998, the cultivated land area of the most suitable areas for potato decreased by 0.30 × 106 hm2, while the suitable area experienced a reduction of 0.96 × 106 hm2. Conversely, the sub-suitable area witnessed an increase of 0.47 × 106 hm2, and the plantable area expanded by 0.79 × 106 hm2. Moreover, there was a decrease in the unsuitable area of 0.30 × 104 hm2. In the future, a more scientific and comprehensive potato planting plan should be formulated by considering the influence of climate resources, the economy and human factors on the zoning for potato planting. The results of the study will contribute to regional decision-making and the development of strategies for the rational utilization of climate resources, thereby promoting sustainable agricultural development as well as achieving high yields and quality potatoes in Gansu Province. Furthermore, comprehensive measures are proposed based on these findings to offer scientific insights into the agricultural production layout in arid areas worldwide.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, X.S.; Wang, Z.L.; Zhou, X.W.; Lai, C.G.; Lin, W.X.; Chen, X.H. Observed changes in precipitation extremes across 11 basins in China during 1961–2013. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2866–2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.H.; Wang, Y.B.; Zhang, Z.Y. Climatic characteristics of precipitation change and its multiscale causes over Central Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 7966–7986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.M.; Liu, Y.J.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Ge, Q.S. Spatial difference of climate change effects on wheat protein concentration in China. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 124011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.J.; Sun, J.Y.; Gao, J.L.; Qiao, S.S.; Zhang, B.L.; Bao, H.Z.; Feng, X.W.; Wang, S.Y. Effects of Climate Change on Cultivation Patterns and Climate Suitability of Spring Maize in Inner Mongolia. Sustainability 2021, 13, 8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bak, G.R.; Lee, K.K.; Clark, I.M.; Mauchline, T.H.; Kavamura, V.N.; Lund, G.; Jee, S.; Lee, J.T.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.H. The potato rhizosphere microbiota correlated to the yield of three different regions in Korea. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 4536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Pan, Y.Y.; Han, G.L.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Ma, S.Q.; Sun, G.F.; Liu, C.; Pan, Z.H. The adaptation mechanism based on an integrated vulnerability assessment of potato production to climate change in Inner Mongolia, China. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2022, 27, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L. Impacts of Climate Change on Potato Production in the Northwest Semi-Arid Region. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, Nanjing, China, 2015. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Xie, K.Y.; Wang, X.X.; Zhang, R.F.; Gong, X.F.; Zhang, S.B.; Mares, V. Partial root-zone drying irrigation and water utilization efficiency by the potato crop in semi-arid regions in China. Sci. Hortic. 2012, 134, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.J.; Zheng, F.J.; Qiu, Z.J.; Yao, Y.B. Impact of climate change on water use efficiency by wheat, potato and corn in semiarid areas of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 181, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.F.; Zhang, Y.H.; Qian, Y.L.; Pan, Z.H.; Zhu, Y.J.; Zhang, Y. Coincidence of variation in potato yield and climate in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 573, 965–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.B.; Zhou, Y.F.; Cai, W.M.; Wang, Z.Z.; Duan, D.D.; Luo, S.J. Using a process-oriented methodology to precisely evaluate temperature suitability for potato growth in China using GIS. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, R.Y.; Lv, X.D.; Wang, L.; Zhang, L.; Qi, Y. Effects of climate change on agro climatic resources and potential primary cropping patterns in Gansu Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2017, 37, 6099–6110. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hong, W.X.; Zheng, N.N.; Xiong, Z.A.; Hu, Z.Q. A Parallel Deep Neural Network Using Reviews and Item Metadata for Cross-Domain Recommendation. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 41774–41783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.S.; Tong, X.X.; Gan, R.; Liu, P.F.; Guo, L.; Zhao, S.S. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors of water resources in Henan Province. Hydrol. Res. 2023, 54, 508–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.D.; Wei, W.; Xue, S. Analysis on the variation of temperature and precipitation in Dingxi based on R/S and Mann-Kendall Test. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2015, 22, 183–189. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Wang, S.H.; Qiao, L.P. Cloud Model Membership Degree of Rock Slope Stability Evaluation: Method and a Case Study. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2022, 31, 3181–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.F.; Zhan, X.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Xu, J.W. Variations in climatic suitability and planting regionalization for potato in northern China under climate change. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0203538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.Y.; Cherry, T.L.; GlomrØd, S.; Zhang, T.Y. Climate change impacts on crop yield: Evidence from China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Donnelly, A.; Liu, X.J. Interannual variations in spring phenology and their response to climate change across the Tibetan Plateau from 1982 to 2013. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2016, 60, 1563–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.W.; Niu, J.Z. Evaluating the Adaptation of Chinese Torreya Plantations to Climate Change. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ma, L.; Liu, T.X.; Sun, B.L.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, Z.X.; Liang, L.T. Response relationship between the abrupt temperature change-climate warming hiatus and changes in influencing factors in China. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 5178–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Kawamura, K. Grassland degradation in China: Methods of monitoring, management and restoration. Grassl. Sci. 2007, 53, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee for the preparation of the Second National Assessment Report on Climate Change. In The Second National Assessment Report on Climate Change; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. (In Chinese)
- Huang, D.; Wang, K.; Wu, W. Problems and strategies for sustainable development of farming and animal husbandry in the agro-pastoral transition zone in Northern China (APTZNC). Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2007, 14, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.J.; Chen, J.B.; Liu, H.Y. Soil respiration and its autotrophic and heterotrophic components in response to nitrogen addition among different degraded temperate grasslands. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 124, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Q.; Yang, S.L. Regional climatic response to global warming: Trends in temperature and precipitation in the Yellow, Yangtze and Pearl River basins since the 1950s. Quat. Int. 2017, 440, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daccache, A.; Weatherhead, E.K.; Stalham, M.A.; Knox, J.W. Impacts of climate change on irrigated potato production in a humid climate. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1641–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J. The effect of climate change on global potato production. Am. J. Potato Res. 2003, 80, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HolzkaÈmper, A.; Calanca, P.; Fuhrer, J. Identifying climatic limitations to grain maize yield potentials using a suitability evaluation approach. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 168, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, E.L.; Yu, Q.; Yin, H.; He, D.; Pan, X.B. Identifying key meteorological factors to yield variation of potato and the optimal planting date in the agro-pastoral ecotone in North China. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 256, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Index | Altitude/m | Precipitation in June and July/mm | Average Temperature in July/°C | Accumulated Temperature Above 10 °C/°C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| The most suitable area | 2000~2600 | 130~140 | 14~16 | 1500~2200 |
| The suitable area | 1700~2000 | 60~130 | 16~18 | 2200~3000 |
| The sub-suitable area | 1300~1700 | 40~60 | 18~22 | 3000~3500 |
| The plantable area | 2600~2900 <1300 | 140~180 20~40 | 12~14 >22 | 1000~1500 >3500 |
| The unsuitable area | >2900 | >180 | <12 | <1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, Y.; Han, J.; Li, G.; Yan, Z.; Dong, L.; Nie, Z.; Liu, Q. Climate Change and Its Impacts on the Planting Regionalization of Potato in Gansu Province, China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020257
Lu Y, Han J, Li G, Yan Z, Dong L, Nie Z, Liu Q. Climate Change and Its Impacts on the Planting Regionalization of Potato in Gansu Province, China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(2):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020257
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Yulan, Junying Han, Guang Li, Zhengang Yan, Lixia Dong, Zhigang Nie, and Qiang Liu. 2025. "Climate Change and Its Impacts on the Planting Regionalization of Potato in Gansu Province, China" Agronomy 15, no. 2: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020257
APA StyleLu, Y., Han, J., Li, G., Yan, Z., Dong, L., Nie, Z., & Liu, Q. (2025). Climate Change and Its Impacts on the Planting Regionalization of Potato in Gansu Province, China. Agronomy, 15(2), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020257






