Effect of Low-Temperature-Fermented Straw Compost on Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Growth and Stress Tolerance
Abstract
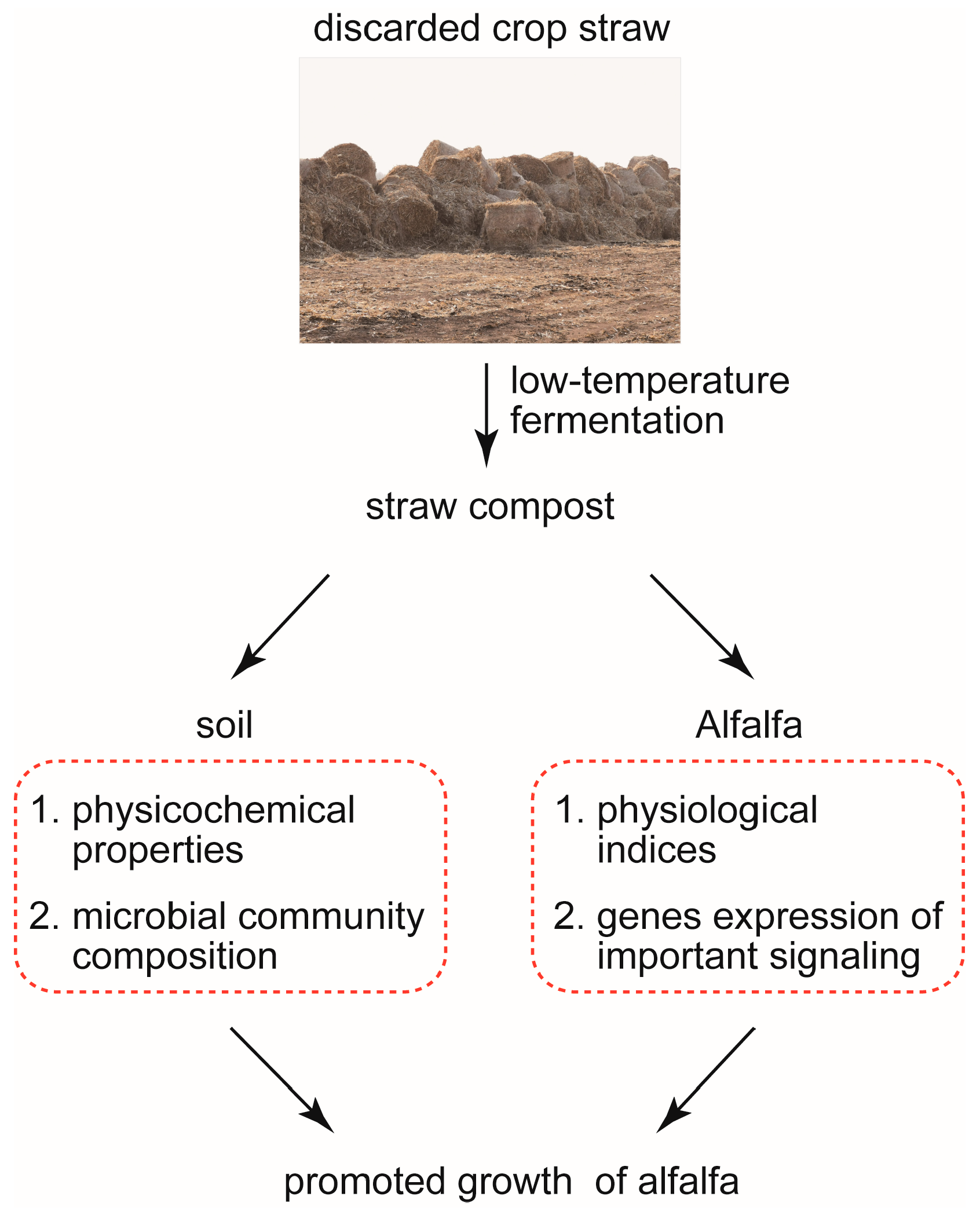
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Determination of Physiological Indicators of Alfalfa
2.3. DAB and NBT Staining of Alfalfa Leaves
2.4. Determination of Alfalfa Blade Length and Leaf Water Loss Rate
2.5. Determination of Soil Physiochemical Properties
2.6. Alfalfa Transcriptome Sequencing and Data Analysis
2.7. RT-qPCR Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
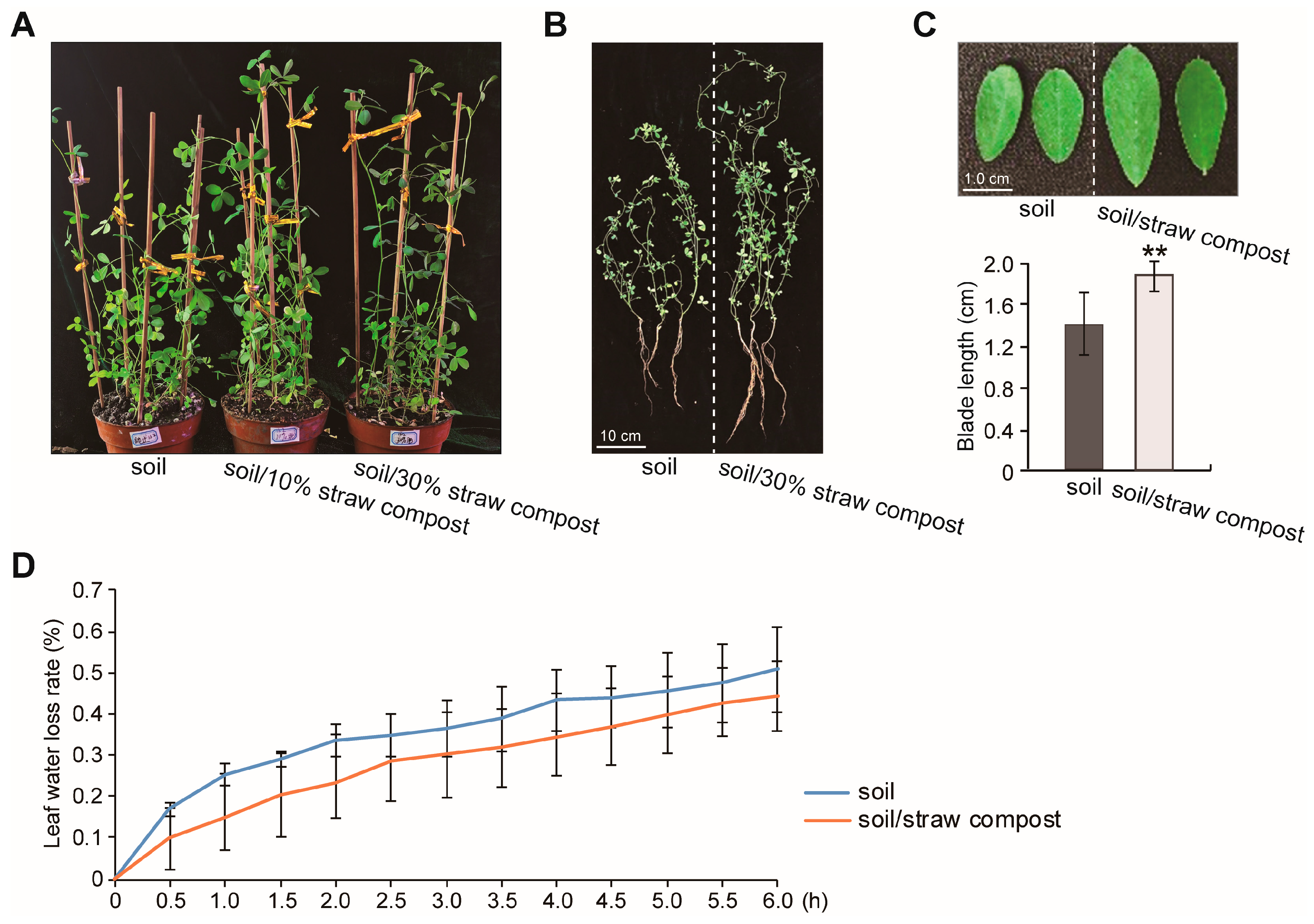
3.1. Straw Compost Influences the Growth of Alfalfa
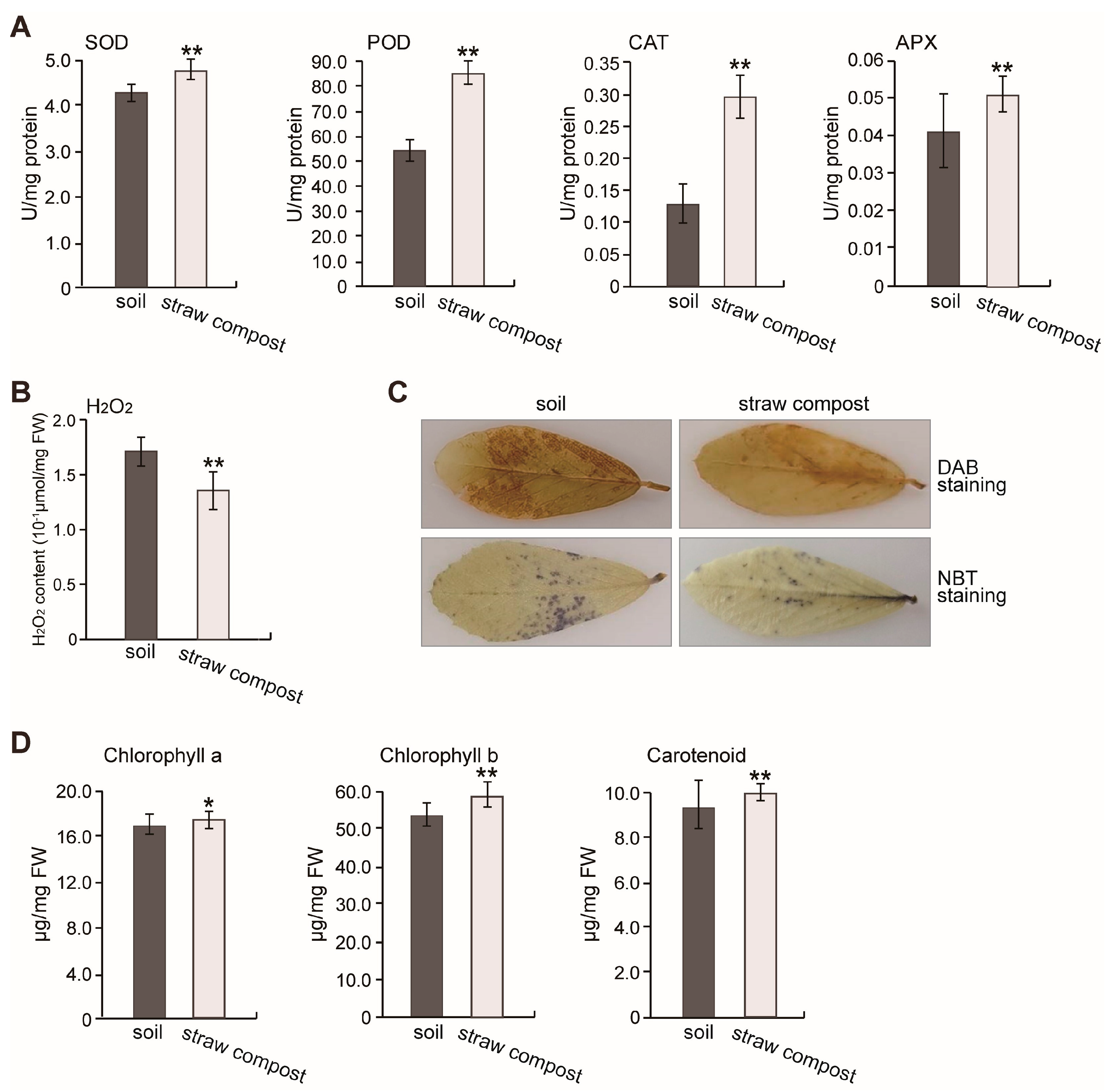
3.2. Effects of Straw Compost on Various Physiological Indicators of Alfalfa
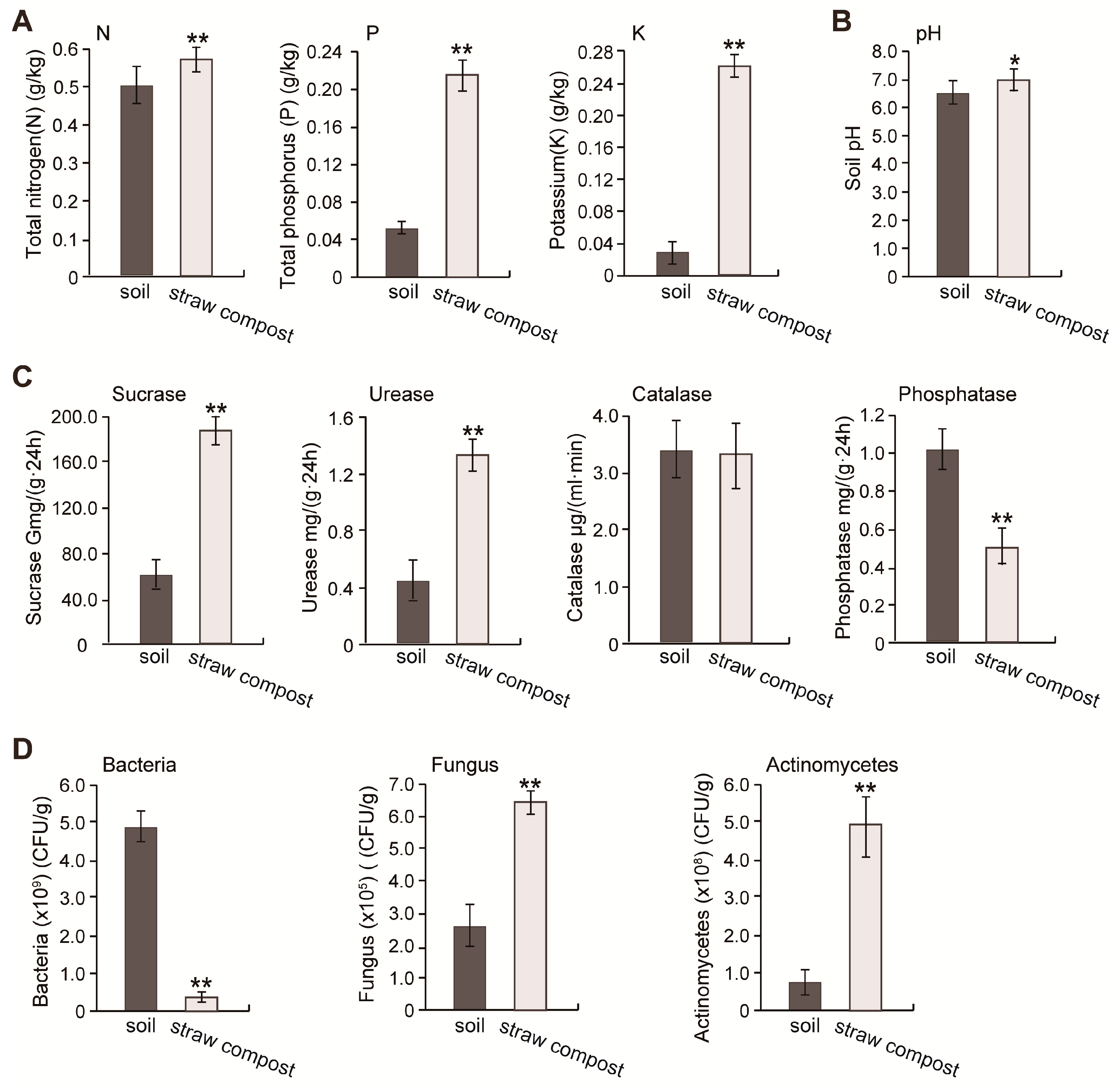
3.3. The Application of Straw Compost Optimizes the Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.4. The Addition of Straw Compost Improved the Soil Microbial Abundance
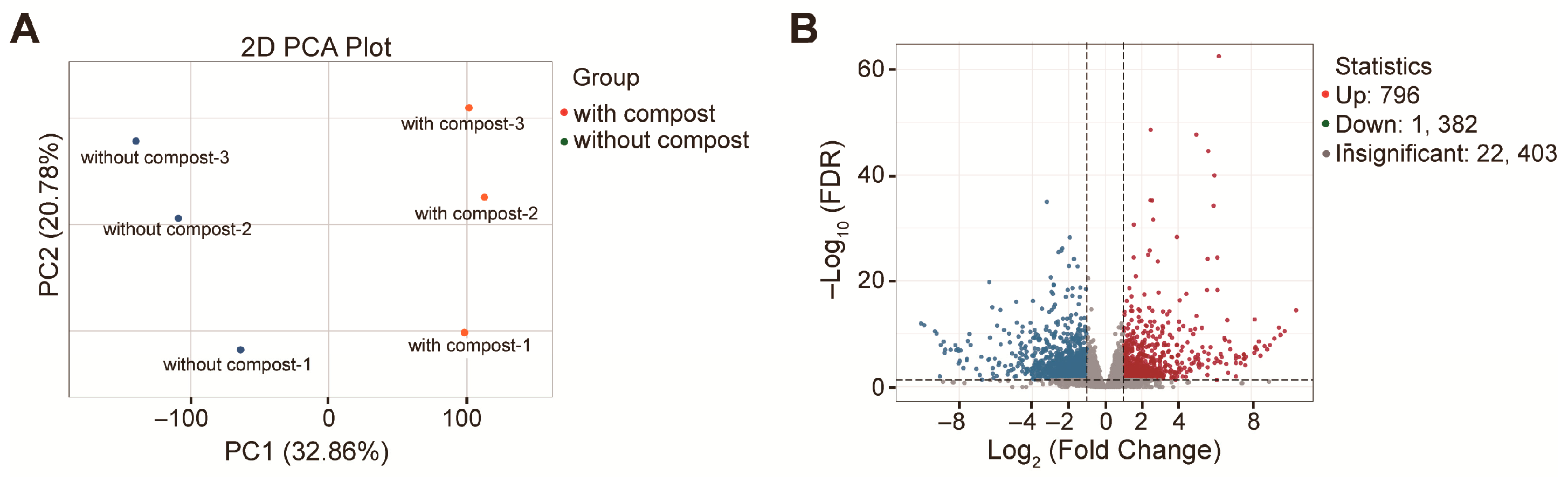
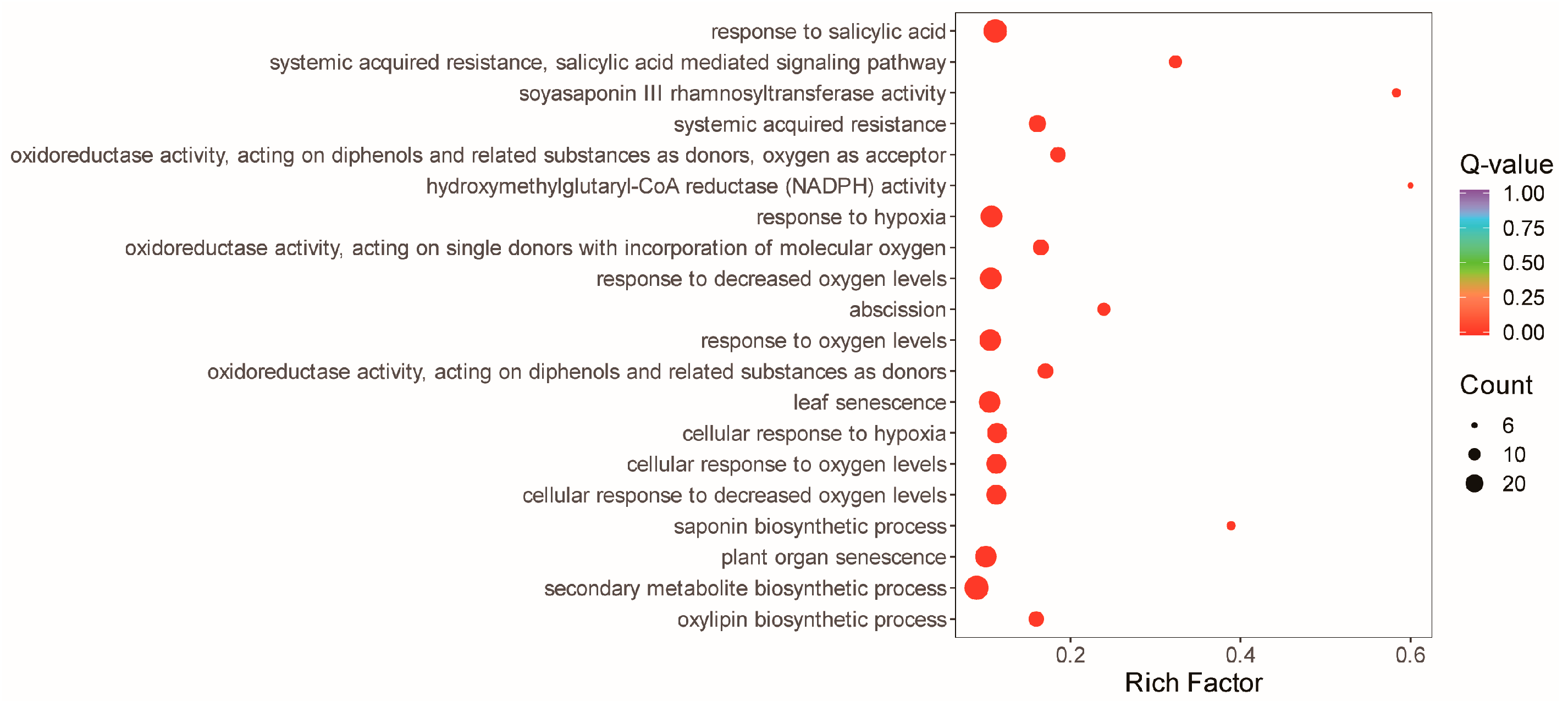
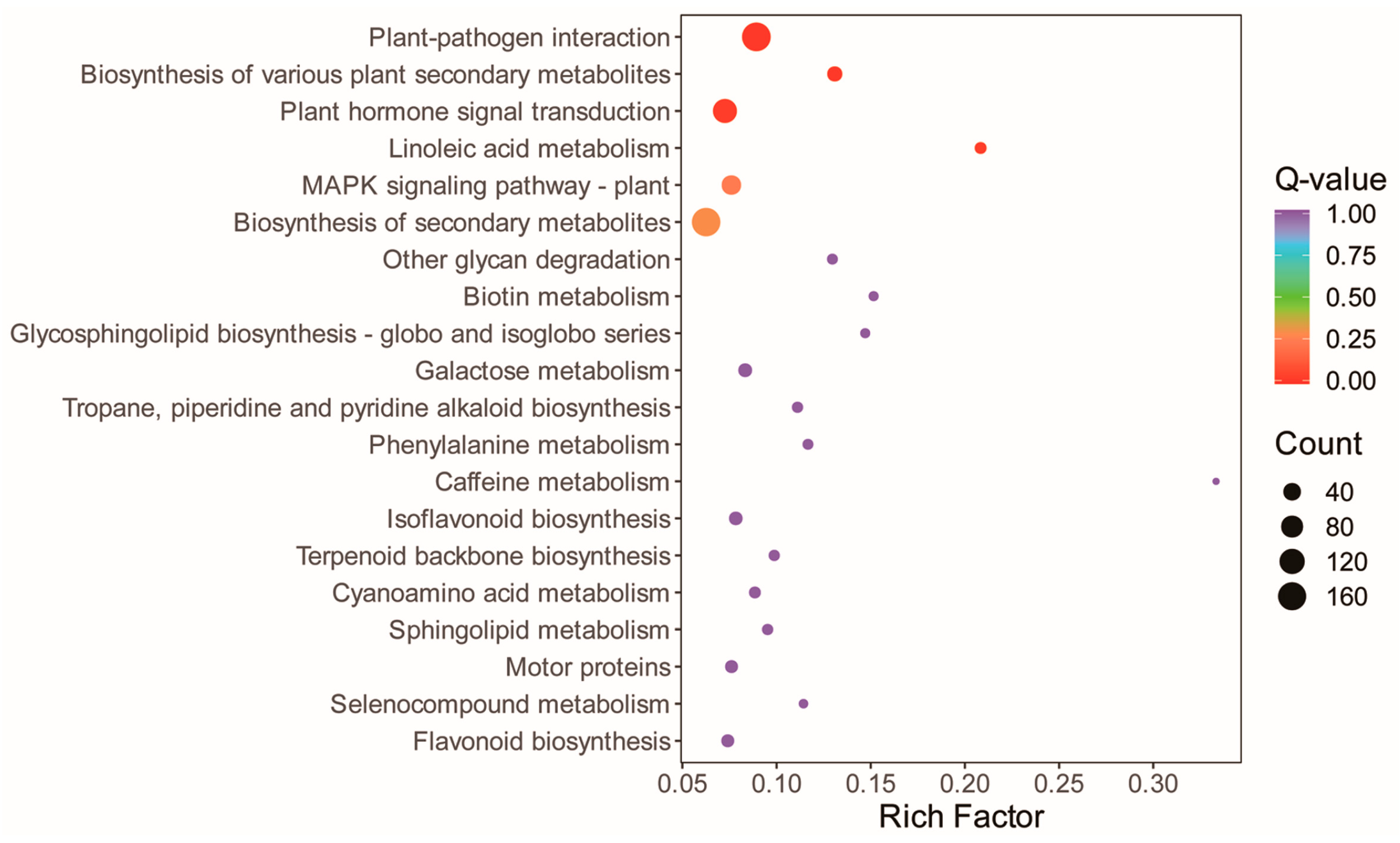
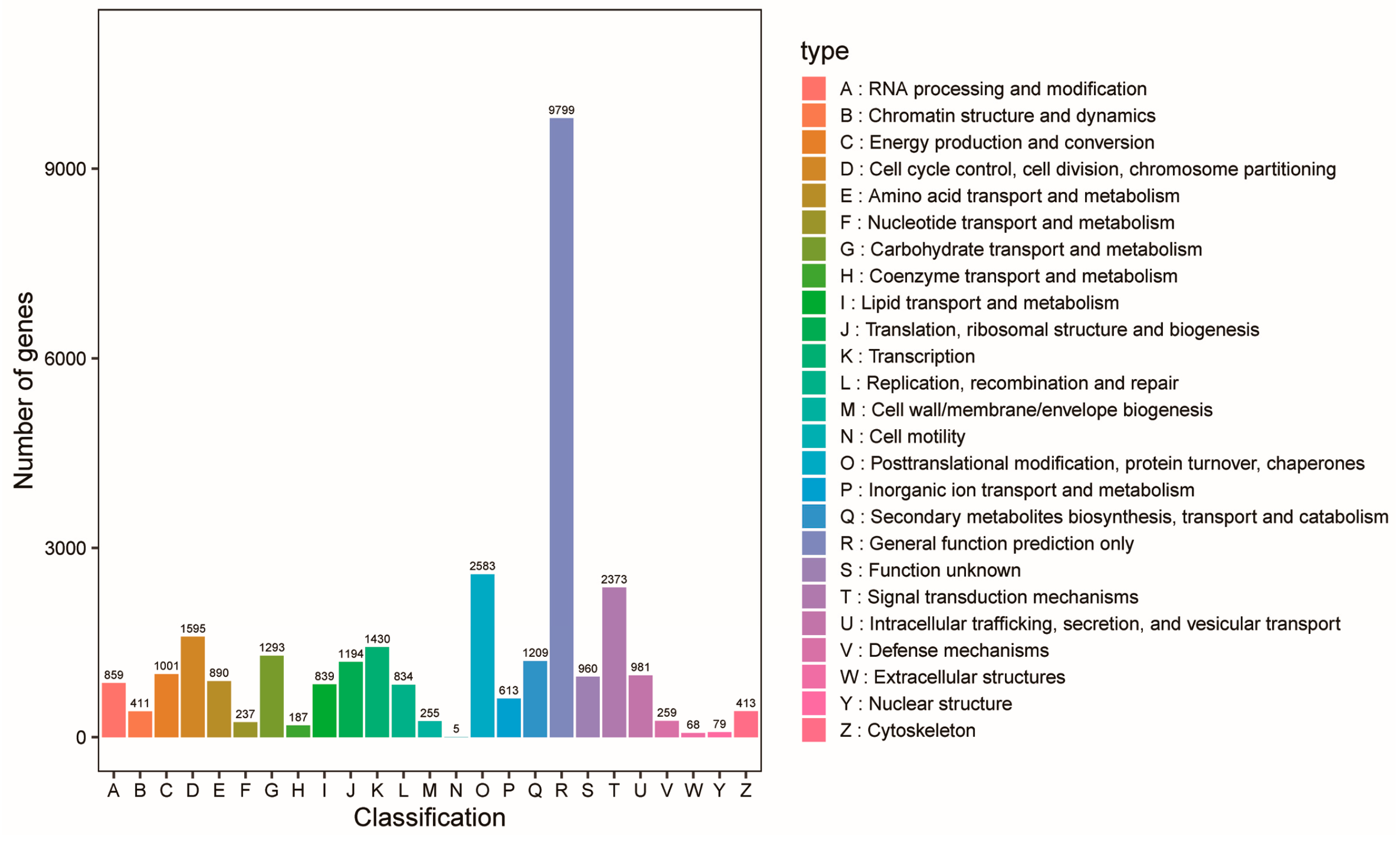
3.5. Reprograms in the Alfalfa Leaf Transcriptome in Response to the Straw Compost Application
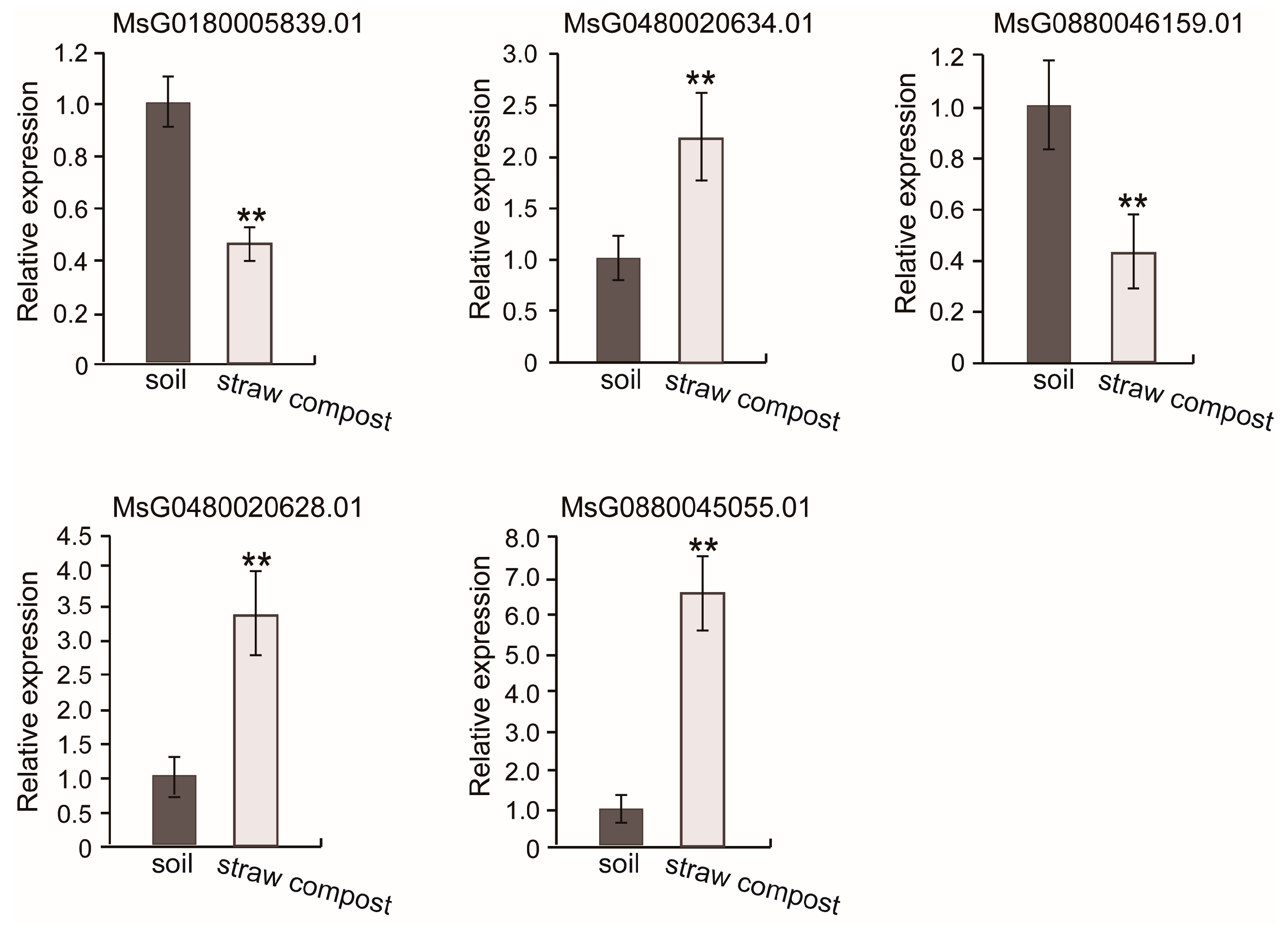
3.6. RT-qPCR Verification for the Transcriptome Sequencing Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Application of Straw Compost in Agricultural Production
4.2. Low-Temperature Fermentation of Straw Compost Promotes the Growth of Alfalfa by Optimizing the Soil Microenvironment and the Physical and Chemical Properties of Alfalfa
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Rosa, J.; Pontolillo, D.M.; Di Maio, C.; Di Maio, C.; Vassallo, R. Chemical clay soil improvement: From laboratory to field test. Procedia Eng. 2016, 158, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrynkiewicz, K.; Baum, C.; Leinweber, P. Density, metabolic activity, and identity of cultivable rhizosphere bacteria on Salix viminalis in disturbed arable and landfill soils. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2010, 173, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, M.; Gao, X.; Fang, F. Corn straw mulching affects Parthenium hysterophorus and rhizosphere organisms. Crop Prot. 2018, 113, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Li, S.; Liu, J.; Cai, L.; Zhang, W.; Yu, C. Additives change microbiota to promote humic acid formation in composting of vegetable wastes. Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 232, 121307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Liu, J.; Deng, F.; Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Li, D. Screening of lignin-degrading fungi and bioaugmentation on the directional humification of garden waste composting. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 203, 117208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Lu, Y.; Yan, H.; Yi, Y.; Shan, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, X. Screening of cellulolytic bacteria from rotten wood of Qinling (China) for biomass degradation and cloning of cellulases from Bacillus methylotrophicus. BMC Biotechnol. 2020, 20, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Kang, Z.; Kong, X.; Qiu, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T.; Han, X.; Zhu, G.; Wen, L.; Xu, X.; et al. Development of a novel low-temperature-tolerant microbial consortium for efficient degradation and recycling of farmland straw. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 115884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, N.; Xuan, H.; Luo, F.; Dai, X. Isolation, identification, and characterization of a cold-adapted cellulase-producing psychotropic Streptomyces sp. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2015, 36, 159–163, 168. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, H.; Zou, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Bing, W.; Aman, K.; Wei, D.; Wang, W. Isolation of Pseudomonas psychrophila BYAU-6 and Analysis of its Low-temperature Straw Degradation Capacity. Acta Microbiol. 2025, 65, 3273–3286. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, W.; Liu, R.; Jiang, H.; Yu, X.; Gao, J.; Hu, S.; Borjigin, Q. Study on the effect of microbial agent M44 on straw decay promoting in cold soils. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 22539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J.R.; Chen, Z.; Ka, Q.; Jiang, P.; Lan, X.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Z. The effects of fungal straw compost inoculation on soil fertility, wheat biomass, and microbial community structure. Soil 2025, 57, 586–596. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, D.; Liang, H.; Hu, J.; Xu, D. The effect of eggplant and fruit vegetable straw compost on the growth, yield, and quality of spinach. North. Hortic. 2024, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, M.; Alotaibi, M.O.; Li, J.; Mahmoud, E.; Ghoneim, A.M.; Ramadan, M.S.; Shabana, M. Effect of Nano-Zinc Oxide, Rice Straw Compost, and Gypsum on Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Yield and Soil Quality in Saline–Sodic Soil. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, A.; Naveed, M.; Azeem, M.; Yaseen, M.; Ullah, R.; Alamri, S.; Farooq, Q.; Siddiqui, M. Efficiency of wheat straw biochar in combination with compost and biogas slurry for enhancing nutritional status and productivity of soil and plant. Plants 2020, 9, 1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Li, G.; Cui, Y.; Xie, J.; Liang, Z.; Guan, F.; Li, Z. Response of Alfalfa Leaf Traits and Rhizosphere Fungal Communities to Compost Application in Saline-Sodic Soil. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, K.; Chen, H.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, N.; Liu, D.; He, X. Low-temperature fermented straw compost regulates rice growth and yield by affecting soil physicochemical properties and the expression of important signaling pathway genes. Agronomy 2023, 13, 3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, W.; Li, M.; Liu, B.; Zhao, S.; Hu, M.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Shi, Y.; Sun, H.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the nutritional value and contaminants of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) in China. Front. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1539462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.L.; Xu, Y.Y.; Xu, Y.Q.; Feng, Y.Z.; Yang, X.M.; Yuan, Q.; Wang, L.J. Bacterial Strains of Low Temperature Fermentation of Corn Stover and Their Fermentation and Cultivation Methods and Applications. Chinese Patent CN108865927B, 6 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhang, H. Impacts of corn straw compost on rice growth and soil microflora under saline-alkali stress. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Dai, J.; Hu, T.M. Study on Salt Tolerance of Eight Alfalfa Varieties during Seedling Stage under Aseptic Culture Conditions. J. N. W. AF Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2010, 38, 176–182. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, E.; Xia, X.; Ji, W.; Li, T.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Zhu, X. Effects of High Temperature Stress on the Physiological and Biochemical Characteristics of Paeonia ostii. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porra, R.J. The chequered history of the development and use of simultaneous equations for the accurate determination of chlorophylls a and b. Photosynth. Res. 2002, 73, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, A.; Pang, Q. Enhancement of sulfur metabolism and antioxidant machinery confers Bacillus sp. Jrh14-10–induced alkaline stress tolerance in plant. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 203, 108063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, V.P.; Mishra, S.; Ahmed, H. Comparison of Total Nitrogen estimation by Kjeldahl Method CHNSAnalyzer in Dry Tropical Grassland. Int. J. Plant Environ. 2023, 9, 180–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xie, Z.; Yang, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, S. Effects of biochar application and water-saving drip irrigation on phosphorus leaching in farmland fluvo-aquic soil. J. Univ. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2021, 38, 2095–2134. [Google Scholar]
- Grewal, I.; Ali, S.; Ali, I.; Li, F.; Lin, S.; Liu, D. Effects of biochar and organic-inorganic fertilizer on pomelo orchard soil properties, enzymes activities, and microbial community structure. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 980241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W.; Xin, X.L.; Zhu, A.; Huang, S. Soil nutrients and aggregate composition of four soils with contrasting textures in a long-term experiment. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2021, 54, 1746–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Wang, Z.; Leng, X.; Liu, J.; Cao, J. Improvement of soil phosphatase activity measurement method. Exp. Technol. Manag. 2016, 33, 48–49. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Shi, H. Changes of microbes population in the different degraded alpine meadows on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Acta Agric. Boreali-Occident. Sin. 2011, 20, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nature Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varet, H.; Brillet-Guéguen, L.; Coppée, J.Y.; Dillies, M.A. SARTools: A DESeq2-and EdgeR-based R pipeline for comprehensive differential analysis of RNA-Seq data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fu, Y.; Ban, L.; Wang, Z.; Feng, G.; Li, J.; Gao, H. Selection of reliable reference genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR in alfalfa. Genes Genet. Syst. 2015, 90, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Huang, D.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, S.; Cao, X. The effects of straw incorporation on physicochemical properties of soil: A review. J. Irrig. Drain. 2022, 41, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Producing high-quality cultivation substrates for cucumber production by in-situ composting of corn straw blocks amended with biochar and earthworm casts. Waste Manag. 2022, 139, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarangi, S.; Swain, H.; Adak, T.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Mukherjee, A.K.; Kumar, G.; Mehetre, S.T. Trichoderma-mediated rice straw compost promotes plant growth and imparts stress tolerance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 44014–44027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, X.; Sun, Z.; Shuai, W.; Xia, Z.; Xie, C.; Gou, M.; Tang, Y. Evaluation of physicochemical properties, bacterial community, and product fertility during rice straw composting supplemented with different nitrogen-rich wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 369, 128462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qiao, Y.; Tie, J.; Zhang, W.; Wei, B.; Liu, Z.; Yu, J.; Hu, L. Sheep Manure-Tail Vegetable-Corn Straw Co-Composting Improved the Yield and Quality of Mini Chinese Cabbage. Foods 2025, 14, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Wang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. Effect of corn straw manure as dairy manure on productivity and profitability of wheat at Huang-Huai-Hai plain. J. Environ. Biol. 2019, 40, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Nie, X.; Dai, Q.; Huo, Z.; Xu, K. Effect of interplanting with zero tillage and straw manure on rice growth and rice quality. Rice Sci. 2007, 14, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Qin, T.; Dong, W.; Pan, G.; Gong, M.; Zhao, K. The Effects of Biological Fungi and Corn Straw Returning on the Growth of Repeating Sweet Peppers and the Relationship between Greenhouse Temperature and Humidity and Agricultural Measures. North. Hortic. 2013, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Hou, P.; Zheng, C.; Yang, X.; Tao, Q.; Sun, J. Wheat Straw Biochar Amendment Increases Salinity Stress Tolerance in Alfalfa Seedlings by Modulating Physiological and Biochemical Responses. Plants 2025, 14, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, B.; Liu, C.; Wang, Q.; Liu, C.; Duan, W.; Hang, X. Research on flower cultivation substrate based on straw compost fermentation. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2024, 52, 245–252. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, V.L.; Fansler, S.J.; Smith, J.L.; Bolton, H. Reconciling apparent variability in effects of biochar amendment on soil enzyme activities by assay optimization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, R.; Kruijt, M.; de Bruijn, I.; Dekkers, E.; van der Voort, M.; Schneider, J.H.M.; Piceno, Y.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Bakker, P.A.H.M.; et al. Deciphering the rhizosphere microbiome for disease-suppressive bacteria. Science 2011, 332, 1097–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Shao, T.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Sun, Q.; Long, X.; Yue, Y.; Gao, X.; Rengel, Z. Effects of planting Melia azedarach L. on soil properties and microbial community in saline-alkali soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2951–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Su, L.; Lv, A.; Wang, S.; Huang, B.; An, Y. Gene Expression Analysis of Alfalfa Seedlings Response to Acid-Aluminum. Int. J. Genom. 2016, 2016, 2095195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
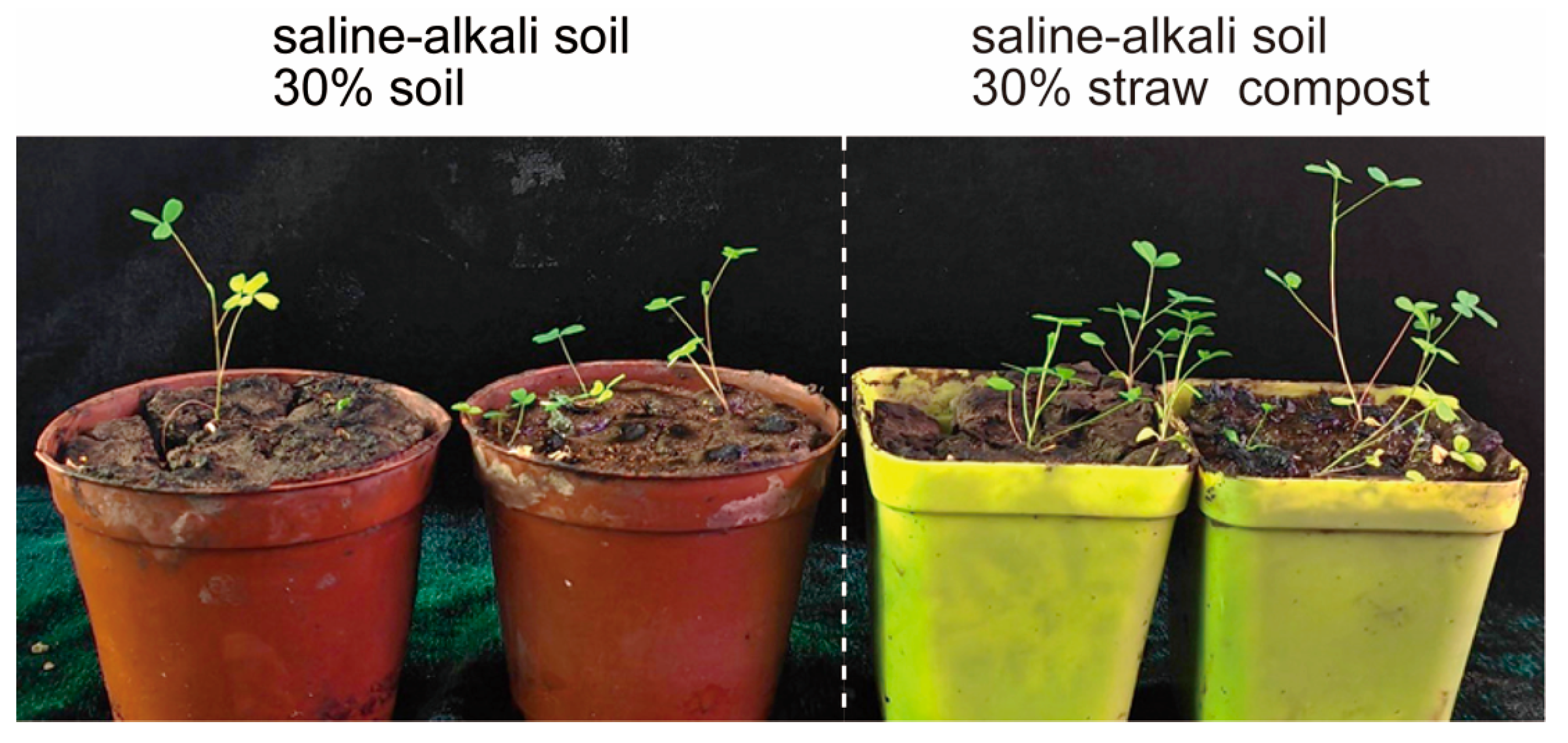

| Mixture Components |
|---|
| 0% straw compost + 100% soil (control) |
| 10% straw compost + 90% soil |
| 30% straw compost + 70% soil |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chang, L.; Sun, W.; Cai, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Effect of Low-Temperature-Fermented Straw Compost on Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Growth and Stress Tolerance. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122723
Zhao Z, Liu Z, Chang L, Sun W, Cai H, Li Y, Wu J. Effect of Low-Temperature-Fermented Straw Compost on Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Growth and Stress Tolerance. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122723
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Ziyi, Ziguang Liu, Lingyun Chang, Wenchao Sun, Haoyu Cai, Yumei Li, and Juan Wu. 2025. "Effect of Low-Temperature-Fermented Straw Compost on Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Growth and Stress Tolerance" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122723
APA StyleZhao, Z., Liu, Z., Chang, L., Sun, W., Cai, H., Li, Y., & Wu, J. (2025). Effect of Low-Temperature-Fermented Straw Compost on Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Growth and Stress Tolerance. Agronomy, 15(12), 2723. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122723





