Partial Replacement of Chemical Fertilizer by Biochar-Based Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield and Soil Quality
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Sampling and Measurements
2.2.1. Yield Measurement
2.2.2. Measurement of Major Rice Quality Indicators
2.2.3. Measurement of Plant Traits
2.2.4. Measurement of Soil Physicochemical Properties
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Rice Yield
3.2. Rice Quality
3.3. Dry Matter
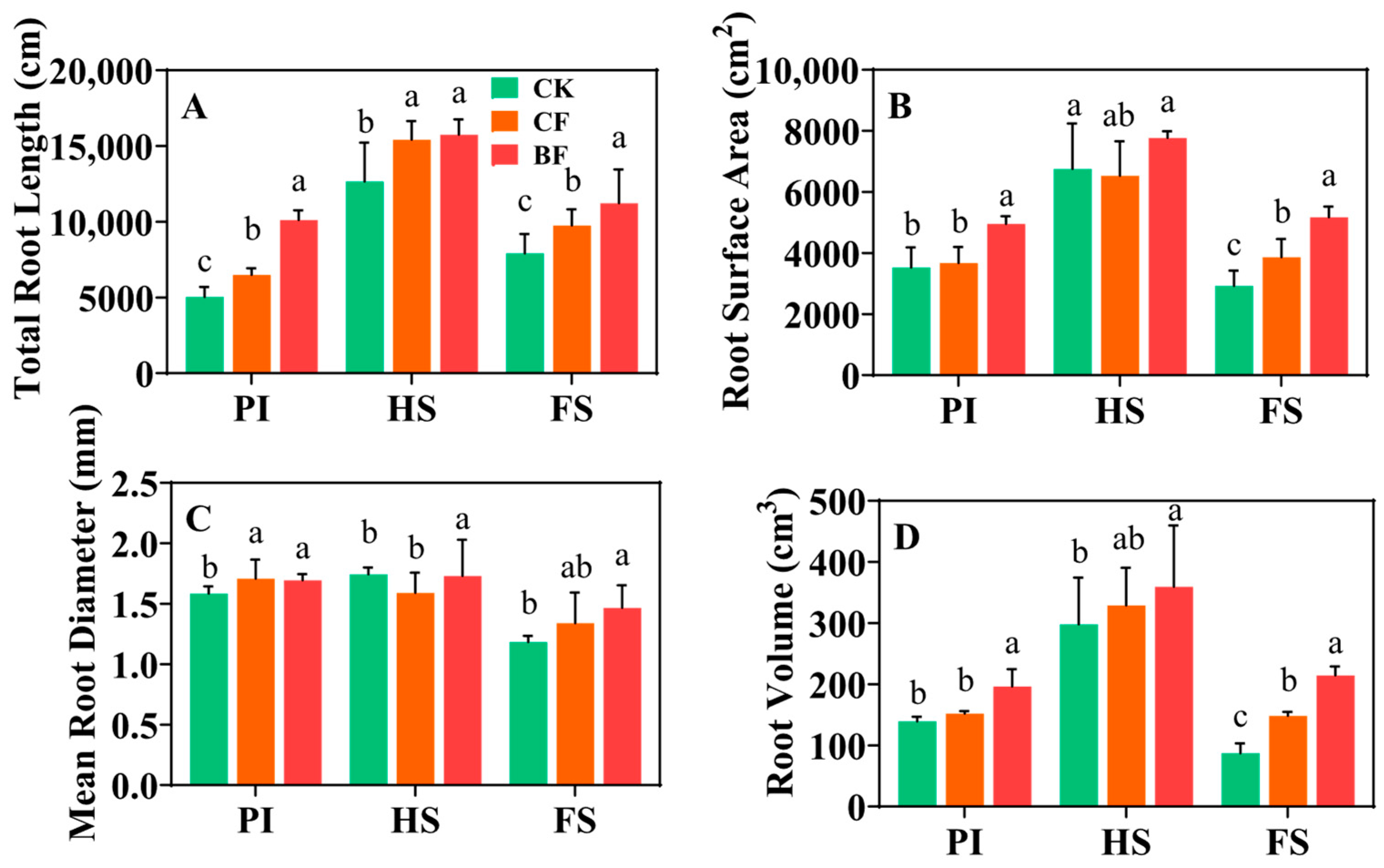
3.4. Root System
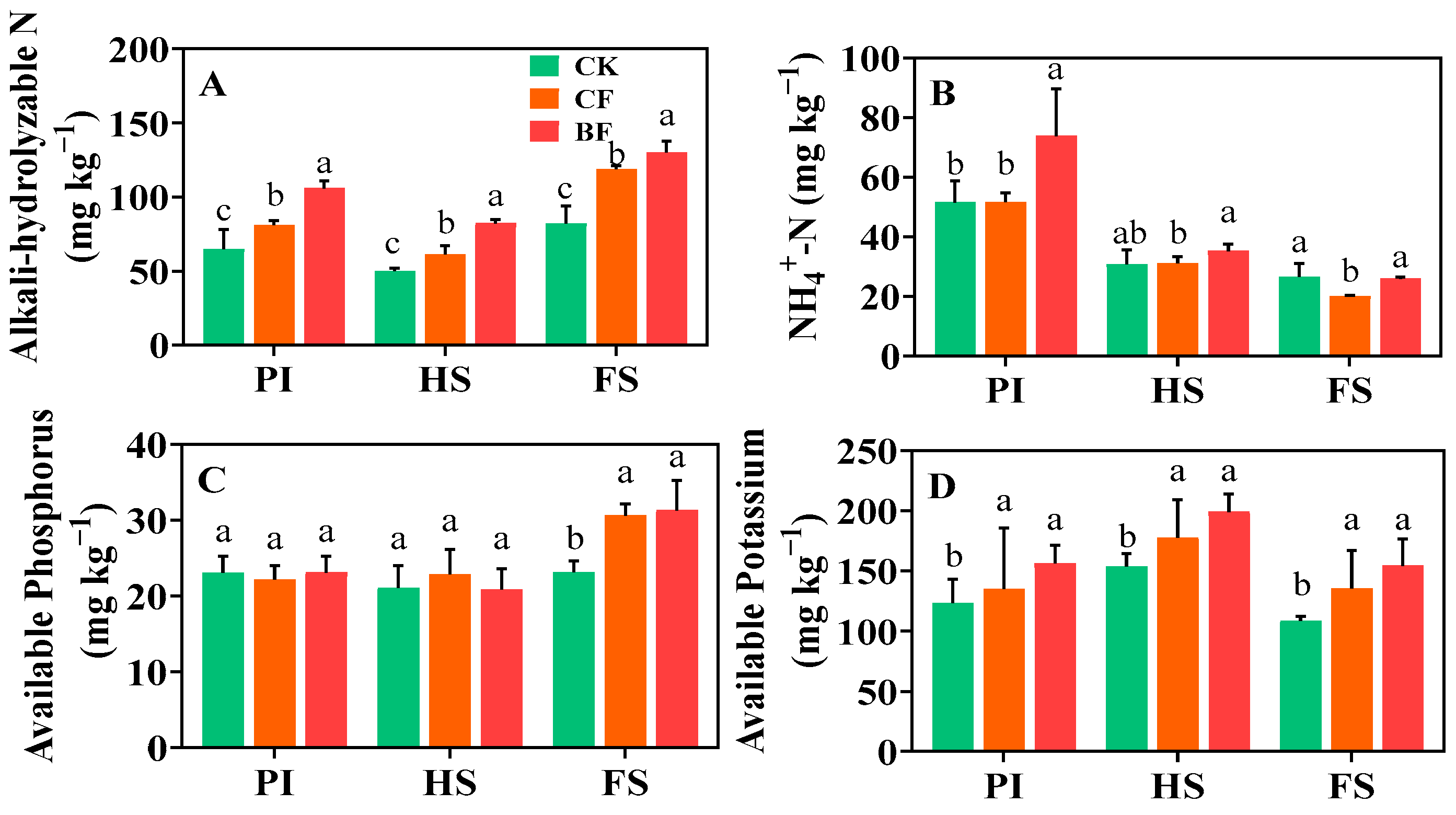
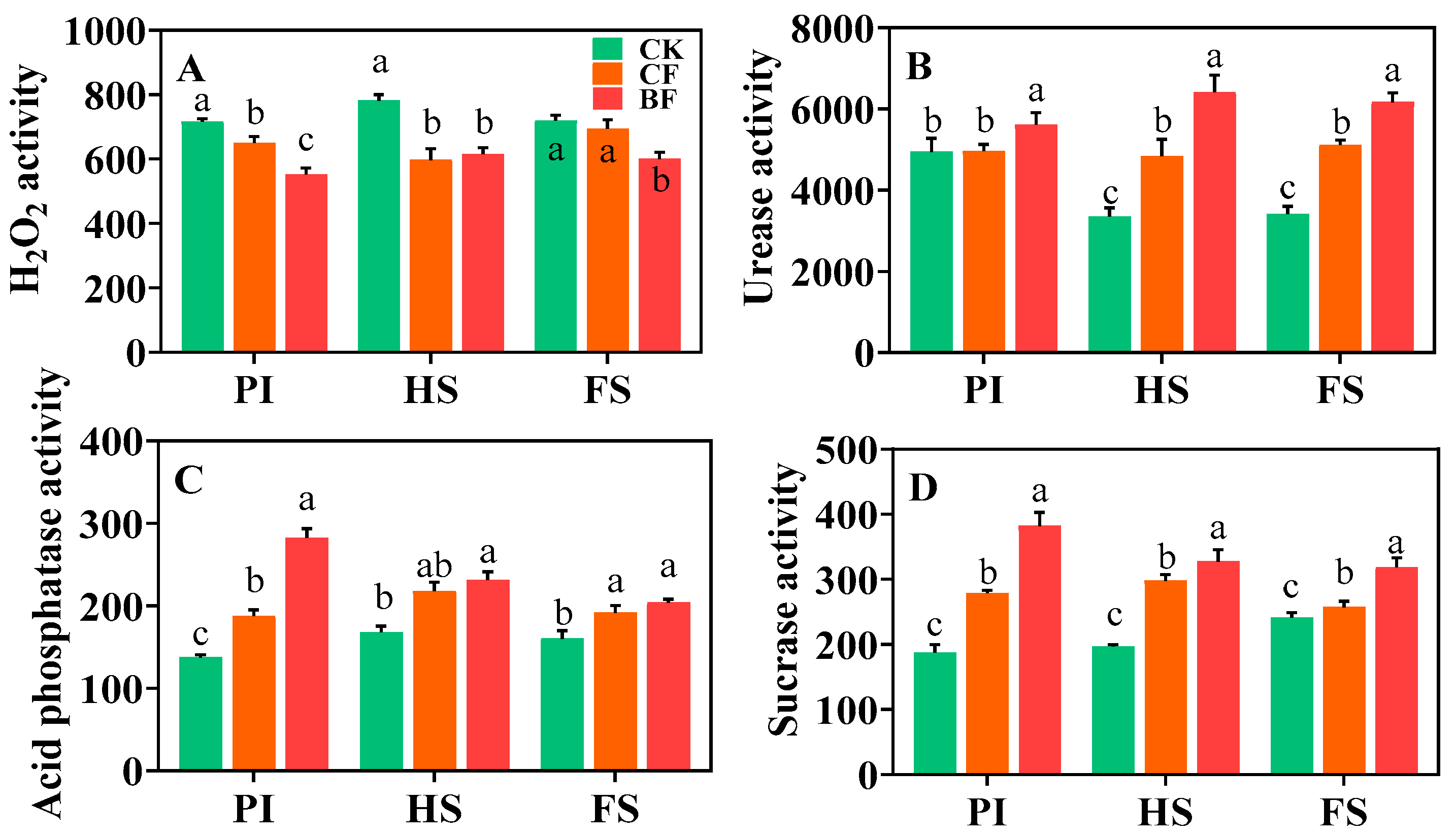
3.5. Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Mechanisms of Organic Fertilizer Substitution in Enhancing Rice Yield
4.2. Key Mechanisms of Organic Fertilizer Substitution in Improving Rice Eating Quality
4.3. Organic Fertilizer Substitution Activates Soil Nutrient Supply
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.F.; Ma, L.; Huang, G.Q.; Wu, L.; Chen, X.P.; Zhang, F.S. The Development and Contribution of Nitrogenous Fertilizer in China and Challenges Faced by the Country. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2013, 46, 3161–3171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ding, W.C. Strategic researches of reducing fertilizer use and increasing use efficiency in China in the new era. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2023, 29, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, K.; Xu, M.; Li, R.; Zheng, L.; Liu, S.; Reis, S.; Wang, H.; Lu, C.; Zhang, W.; Gao, H. Optimizing nitrogen fertilizer use for more grain and less pollution. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 360, 132180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Tian, Y.L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.T.; Zhu, C.X.; Li, H.N. Research on action and technology for reducing fertilizer usage and enhancing efficiency in China. J. Agric. Resour. Environ. 2025, 42, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.F.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.L.; Xu, Z.H.; Miao, Y.Z.; Zhang, N.; Liu, D.Y.; Shen, Q.R. Biofertilizer and organic fertilizer research over thirty years in China: Retrospect and prospect. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2024, 30, 1262–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.H.; Yin, J.; Ma, Z.H.; Yang, Y.P. Effect of Organic Fertilizer Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer on Major Grain Yield in China. Environ. Sci. 2025, 46, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.C.; He, A.B.; Khan, M.N.; Yin, Q.; Song, S.K.; Nie, L.X. Coupling of reduced inorganic fertilizer with plant-based organic fertilizer as a promising fertilizer management strategy for colored rice in tropical regions. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Ni, Y.M.; Huang, S.; Zuo, T.; Wang, J.; NI, W. Effects of substituting chemical fertilizers with manure on rice yield and soil labile nitrogen in paddy fields of China: A meta-analysis. Pedosphere 2023, 33, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayatu, N.G.; Liu, Y.R.; Han, T.F.; Daba, N.; Zhang, L.; Shen, Z.; Li, J.-W.; Muazu, H.; Lamlom, S.F.; Zhang, H.M. Carbon sequestration rate, nitrogen use efficiency and rice yield responses to long-term substitution of chemical fertilizer by organic manure in a rice-rice cropping system. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2848–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasse, D.P.; Weldon, S.; Joner, E.J.; Joseph, S.; Kammann, C.I.; Liu, X.; O’Toole, A.; Pan, G.; Kocaturk-Schumacher, N.P. Enhancing plant N uptake with biochar-based fertilizers: Limitation of sorption and prospects. Plant Soil 2022, 475, 213–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Bian, R.; Li, L.; Lian, W.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, X.; Drosos, M.; Joseph, S. Assessing the impacts of biochar-blended urea on nitrogen use efficiency and soil retention in wheat production. Glob. Change Biol. Bioenergy 2022, 14, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, P.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Lv, S.; Li, J.; Abdo, A.I.; Wang, L. Optimum nitrogen rate combined with biochar increased wheat yield whileimproving lodging resistance. Eur. J. Agron. 2026, 172, 127849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Peng, M.; Lu, W.; Hou, Z.; Li, J. Commercial organic fertilizer substitution increases wheat yield by improving soil quality. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.T.; Feng, X.Y.; Chai, N.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Zhang, F.; Li, F.M. Biochar effects on crop yield variability. Field Crops Res. 2024, 316, 109518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Lv, R.; Hu, T.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, J.; Lin, X.; Liu, Q.; Xie, Z. 12-year continuous biochar application: Mitigating reactive nitrogen loss in paddy fields but without rice yield enhancement. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2024, 375, 109223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 17891-2017; High Quality Paddy. Standardization Administration of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Liu, S.B.; Wang, J.Y.; Pu, S.Y.; Blagodatskaya, E.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Razavi, B.S. Impact of manure on soil biochemical properties: A global synthesis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 141003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Sun, L.J.; Sun, Y.F.; Yang, S.; Qin, Q.; Xue, Y. Integrated enzyme activities and untargeted metabolome to reveal themechanism that allow long-term biochar-based fertilizer substitution improves soil quality and maize yield. Environ. Res. 2025, 270, 120935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Guo, J.; Fan, L.; Ji, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, F.; Pu, Z.; Ling, N.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. The source-sink balance during the grain filling period facilitates rice production under organic fertilizer substitution. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 134, 126468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.Z.; Deng, Q.; Duan, H.L.; Guo, Y. Effects of biochar application on root traits: A meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. Bioenergy 2017, 9, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Ju, Y.Y.; Bian, R.J.; Li, L.; Pan, G. Biochar bound urea boosts plant growth and reduces nitrogen leaching. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 701, 134424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omokaro, G.O.; Kornev, K.P.; Nafula, Z.S.; Chikukula, A.A.; Osayogie, O.G.; Efeni, O.S. Biochar for sustainable soil management: Enhancing soil fertility, plant growth and climate resilience. Farming Syst. 2025, 3, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahery, S.; Munroe, P.; Marjo, C.E.; Rawal, A.; Horvat, J.; Mohammed, M.; Webber, J.B.W.; Arns, J.-Y.; Arns, C.H.; Pan, G.; et al. A comparison between the characteristics of a biochar-NPK granule and a commercial NPK granule for application in the soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 832, 155021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.C.; Zhou, R.; Xu, G.R. Global analysis on potential effects of biochar on crop yields and soil quality. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2025, 7, 240267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, K.; Xuan, T.D.; Noori, Z.; Aryan, S.; Gulab, G. Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizer Application on Growth, Yield, and Grain Quality of Rice. Agriculture 2020, 10, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Iqbal, A.; Ullah, S.; Muhammad, I.; Yuan, P.L.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, M.; Zhang, H.; Huang, M.; Liang, H.; et al. Effects of Biochar Amendment and Nitrogen Fertilizer on RVA Profile and Rice Grain Quality Attributes. Foods 2022, 11, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; Liang, H.; McBride, S.G.; Yuan, P.L.; Ali, I.; Zaman, M.; Zeeshan, M.; Khan, R.; Akhtar, K.; Wei, S.Q.; et al. Manure applications combined with chemical fertilizer improves soil functionality, microbial biomass and rice production in a paddy field. Agron. J. 2022, 114, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Shu, A.P.; Song, W.F.; Shi, W.C.; Li, M.C.; Zhang, W.X.; Li, Z.Z.; Liu, G.R.; Yuan, F.S.; Zhang, S.X.; et al. Long-term organic fertilizer substitution increases rice yield by improving soil properties and regulating soil bacteria. Geoderma 2021, 404, 115287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, B.; Chen, L.; Liang, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.Q. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer over seven years increases yields and restores soil bacterial community diversity in wheat-rice rotation. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 133, 126445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.H.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, A.R.; Bilyera, N.; Wang, J.Q.; Wang, X.Q.; Han, Y.H.; Ma, B.X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Li, F.; Zhou, J.; et al. Mechanisms of biochar-based organic fertilizers enhancing maize yield on a Chinese Chernozem: Root traits, soil quality and soil microorganisms. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Khan, Z.; Khan, M.N.; Luo, T.; Luo, L.J.; Bi, J.G.; Hu, L.Y. The application of biochar improves the nutrient supply efficiency of organic fertilizer, sustains soil quality and promotes sustainable crop production. Food Energy Secur. 2024, 13, e520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | Base Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | Tillering Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | Panicle Fertilizer (kg ha−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic Fertilizer | Urea | Urea | Urea | |
| CK | 0 | 195.6 | 195.6 | 260.8 |
| CF | 4500 | 0 | 195.6 | 260.8 |
| BF | 4500 | 0 | 195.6 | 260.8 |
| Treatment | Panicle Number (m−2) | Spikelets Per Panicle | Seed Setting Rate (%) | Grain Weight (mg) | Yield (t ha−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 268.5 C | 149.2 A | 94.0 A | 26.6 B | 10.0 C |
| CF | 296.1 B | 148.5 A | 90.8 B | 27.3 AB | 10.9 B |
| BF | 318.8 A | 147.6 A | 87.0 C | 27.9 A | 11.4 A |
| Treatment | Amylose Content (%) | Protein Content (%) | Taste Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 11.0 A | 11.8 A | 79.7 C |
| CF | 10.5 B | 9.5 B | 82.3 B |
| BF | 9.1 C | 9.0 B | 85.3 A |
| Treatment | Peak Viscosity | Trough Viscosity | Breakdown | Final Viscosity | Setback |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 2720.3 C | 1710.7 B | 1009.7 C | 2336.7 B | −383.7 A |
| CF | 2894.0 B | 1776.0 A | 1118.0 B | 2484.3 A | −409.7 B |
| BF | 3011.0 A | 1789.0 A | 1222.0 A | 2425.3 A | −585.7 C |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, C.; Luo, X.; Wang, Y.; Long, W.; Guan, Y.; Hou, Q.; Yuan, C.; Wang, L. Partial Replacement of Chemical Fertilizer by Biochar-Based Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield and Soil Quality. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122716
Ding C, Luo X, Wang Y, Long W, Guan Y, Hou Q, Yuan C, Wang L. Partial Replacement of Chemical Fertilizer by Biochar-Based Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield and Soil Quality. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122716
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Chao, Xikun Luo, Yuhui Wang, Weihua Long, Yongxiang Guan, Qiong Hou, Cansheng Yuan, and Lin Wang. 2025. "Partial Replacement of Chemical Fertilizer by Biochar-Based Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield and Soil Quality" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122716
APA StyleDing, C., Luo, X., Wang, Y., Long, W., Guan, Y., Hou, Q., Yuan, C., & Wang, L. (2025). Partial Replacement of Chemical Fertilizer by Biochar-Based Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield and Soil Quality. Agronomy, 15(12), 2716. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122716




