Projection of Land Use and Habitat Quality Under Climate Scenarios: A Case Study of Arid Oasis Urban Agglomerations
Abstract
1. Introduction
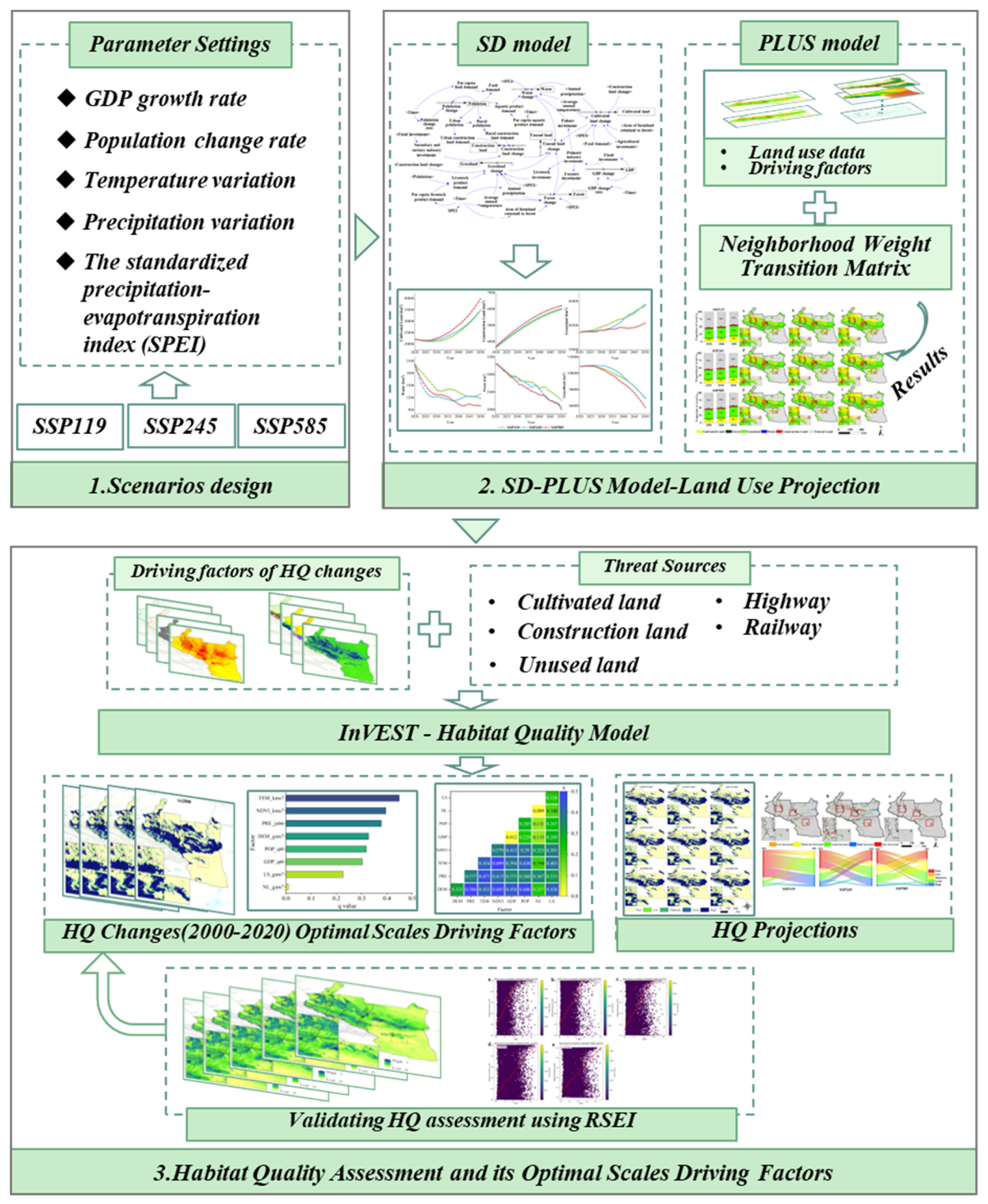
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. The Standardized Precipitation-Evapotranspiration Index (SPEI)
2.3.2. Climate Scenario Framework Derived from CMIP6 Datasets
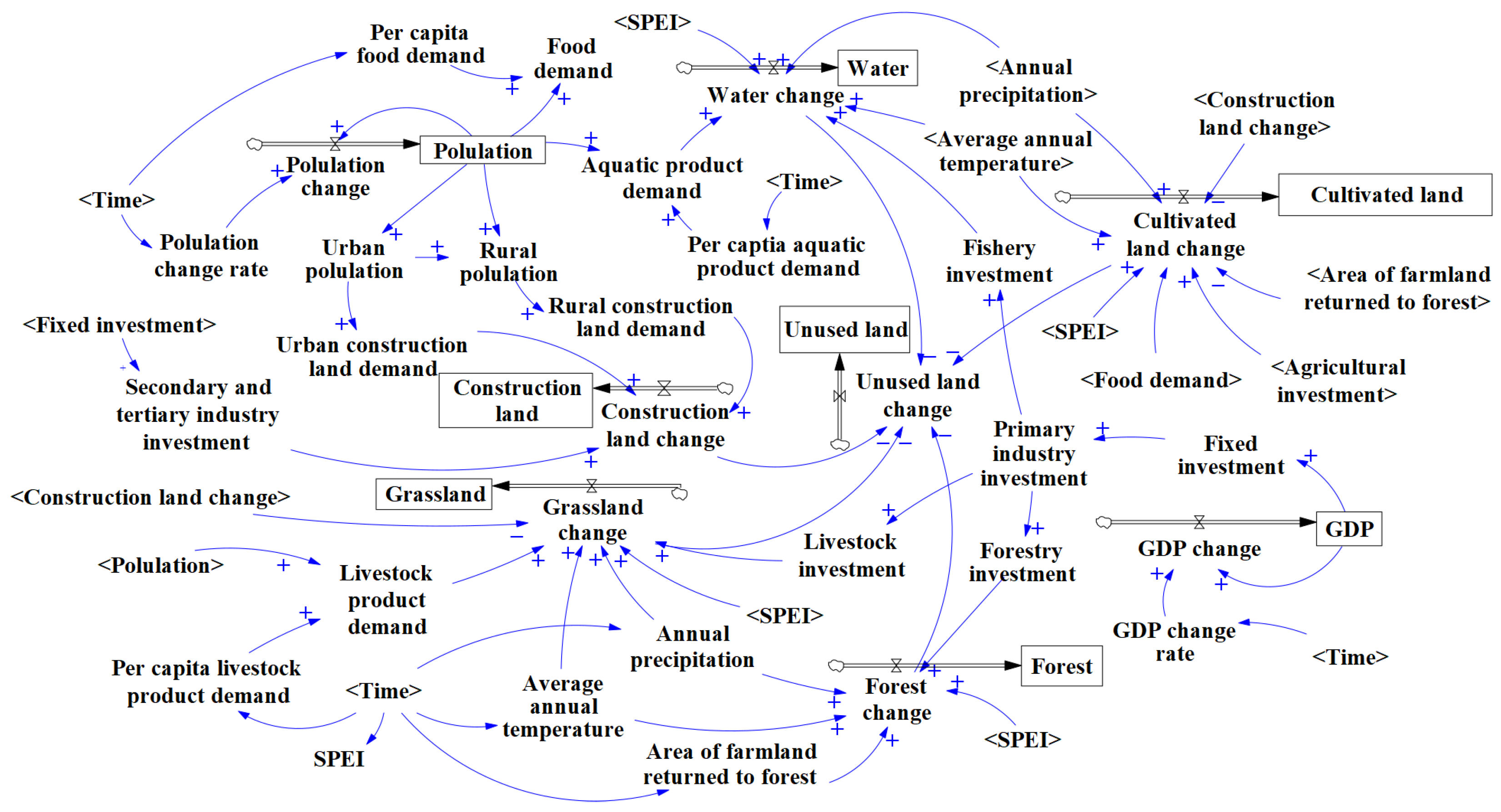
2.3.3. System Dynamics Model
2.3.4. PLUS Model
2.3.5. InVEST—Habitat Quality Model
2.3.6. Validating HQ Using Remote Sensing Ecological Index (RSEI)
2.3.7. Optimal Multivariate-Stratification Geographical Detector Model
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Scenario-Based Projections of LULC Transformation
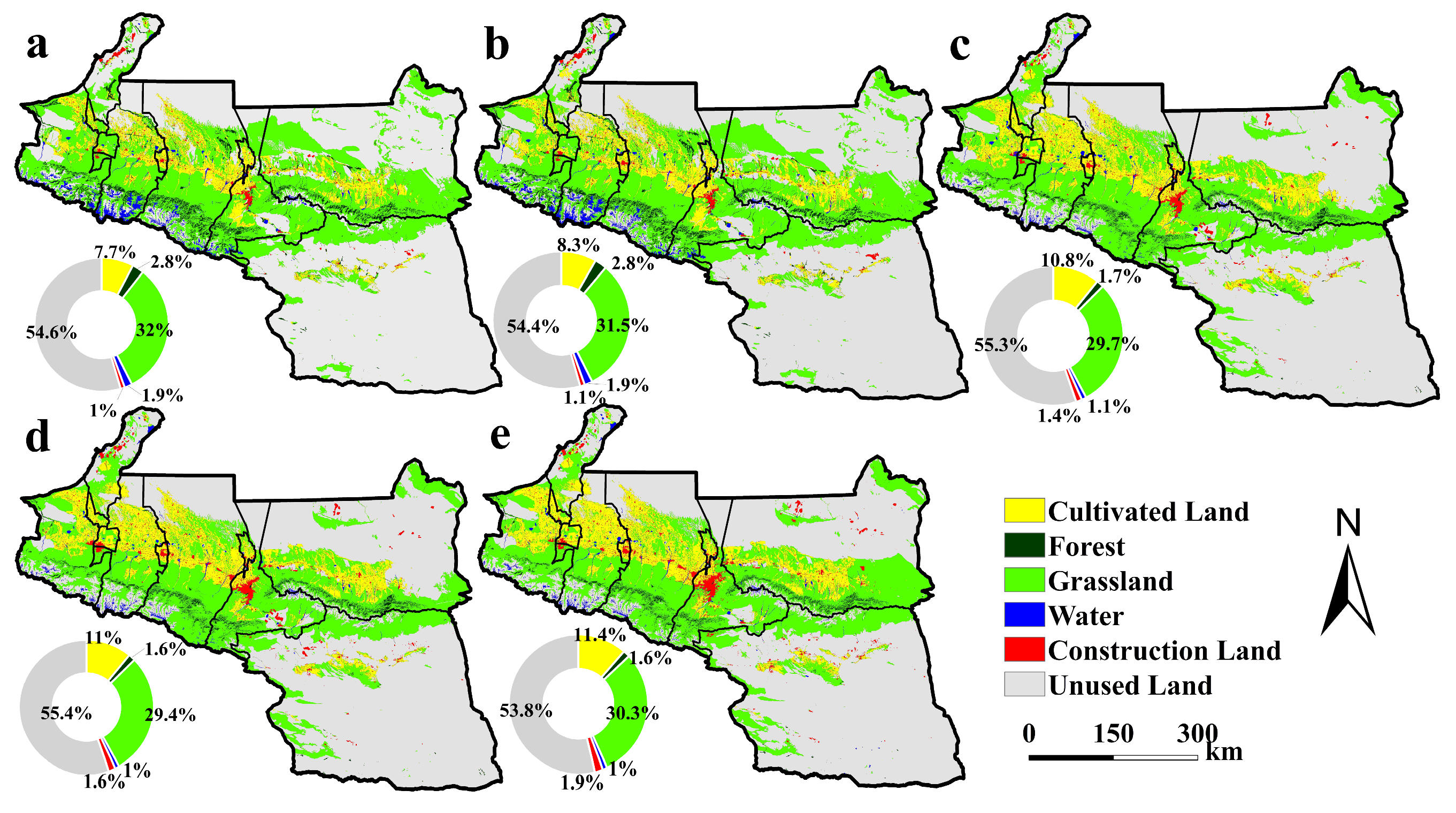
3.1.1. Historical Transition of Land Use
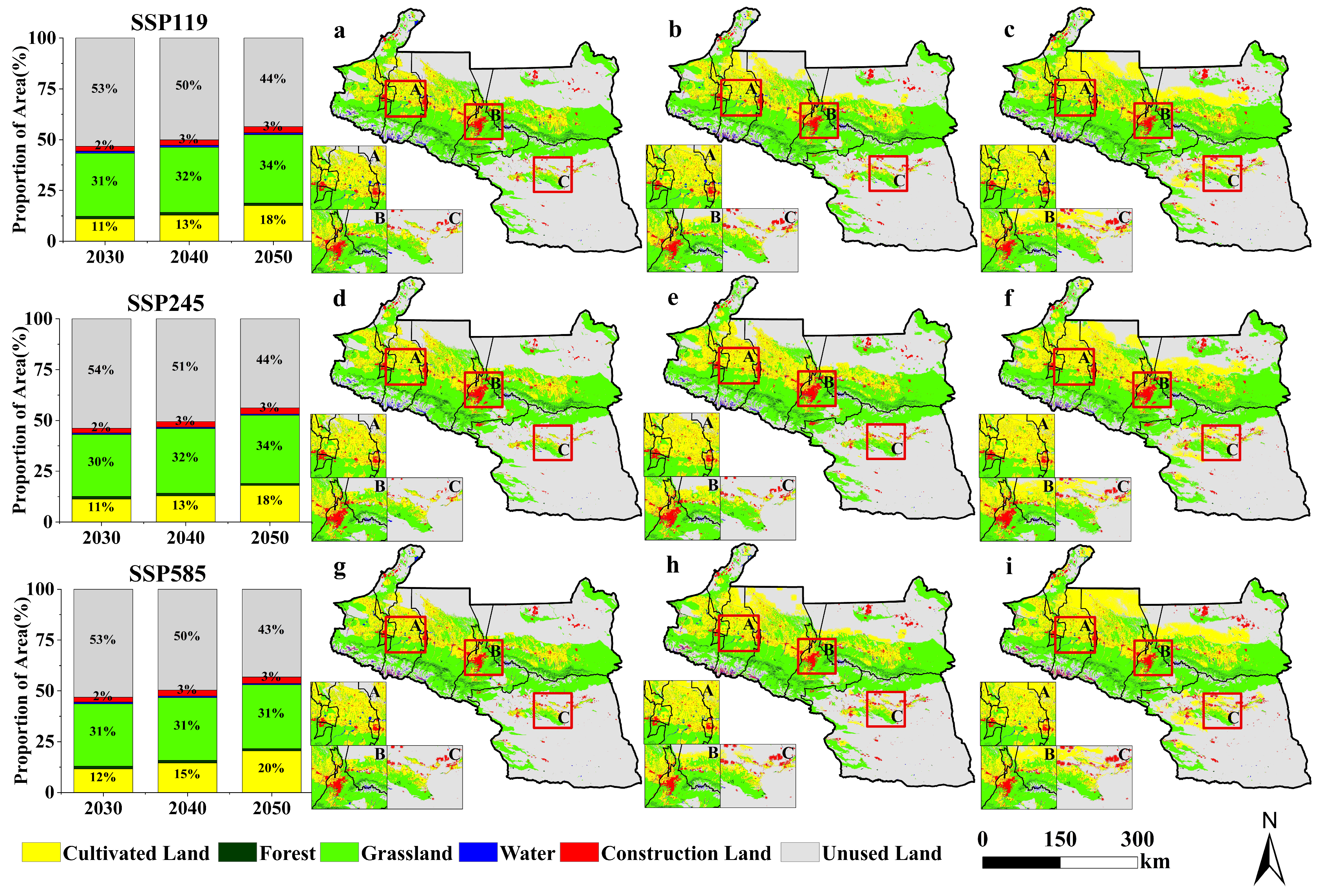
3.1.2. Land-Use Projections
3.2. Habitat Quality and Spatial Distribution Characteristics
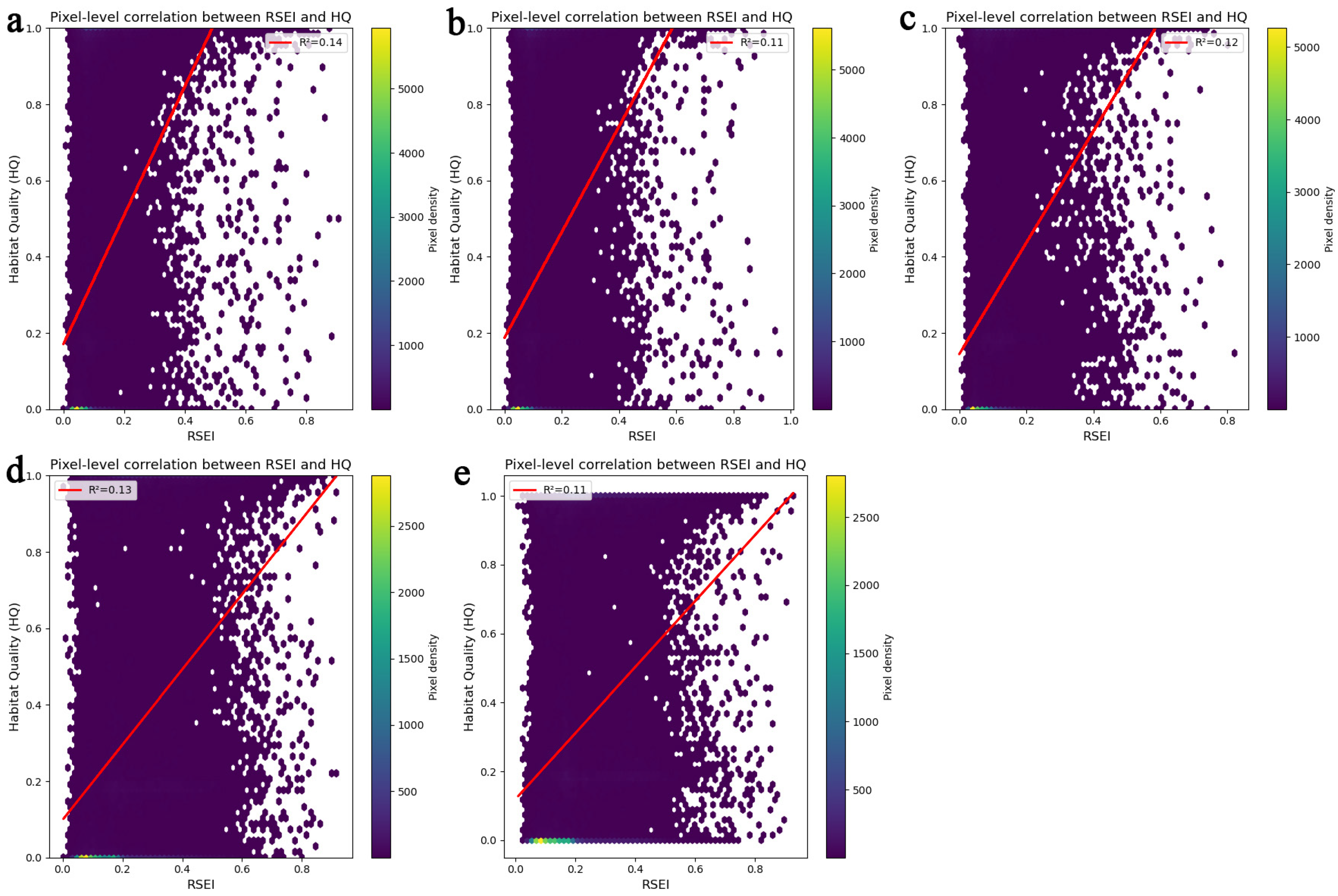
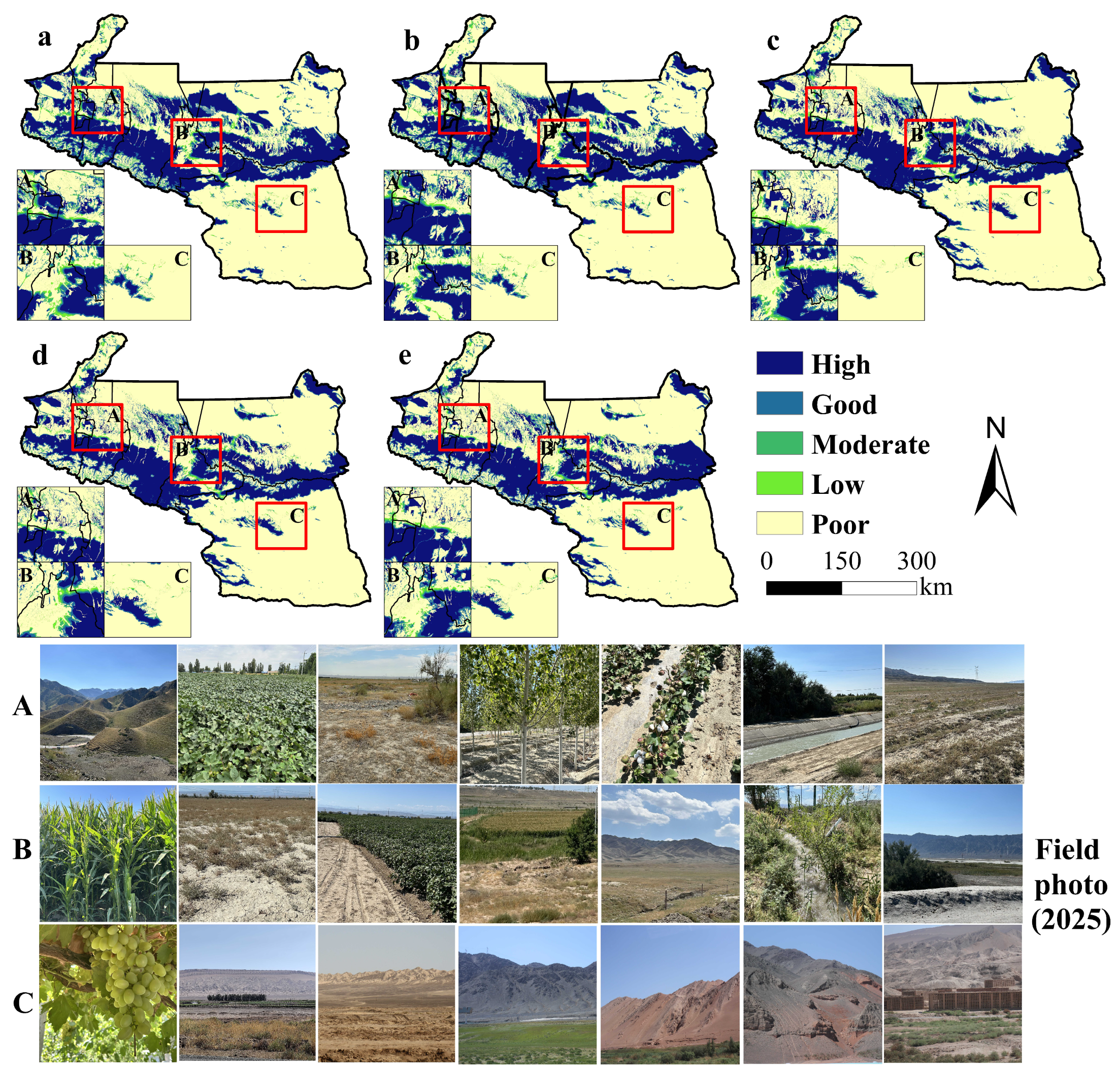
3.2.1. Validating HQ Assessment Using RSEI
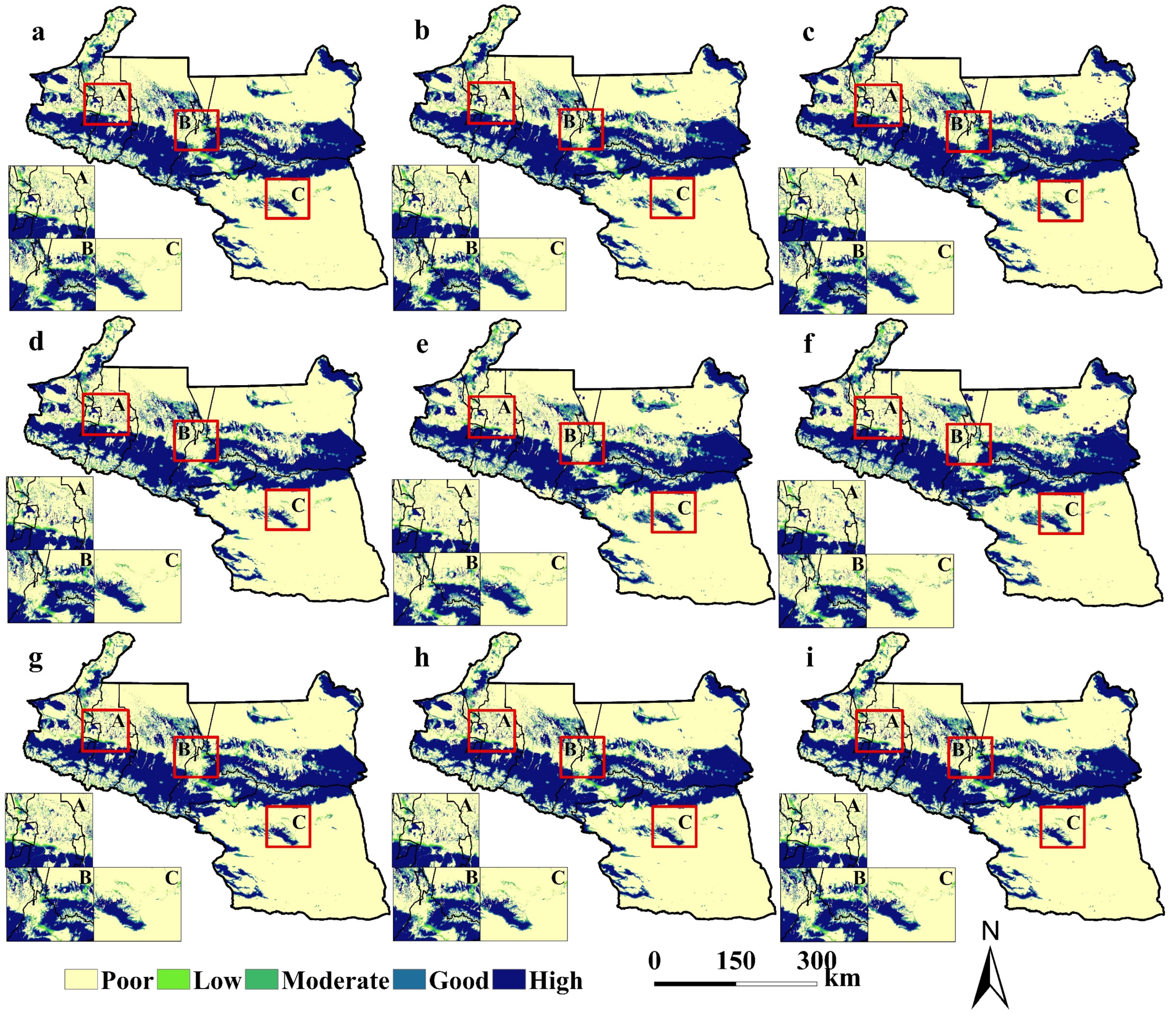
3.2.2. Characteristics of HQ Changes
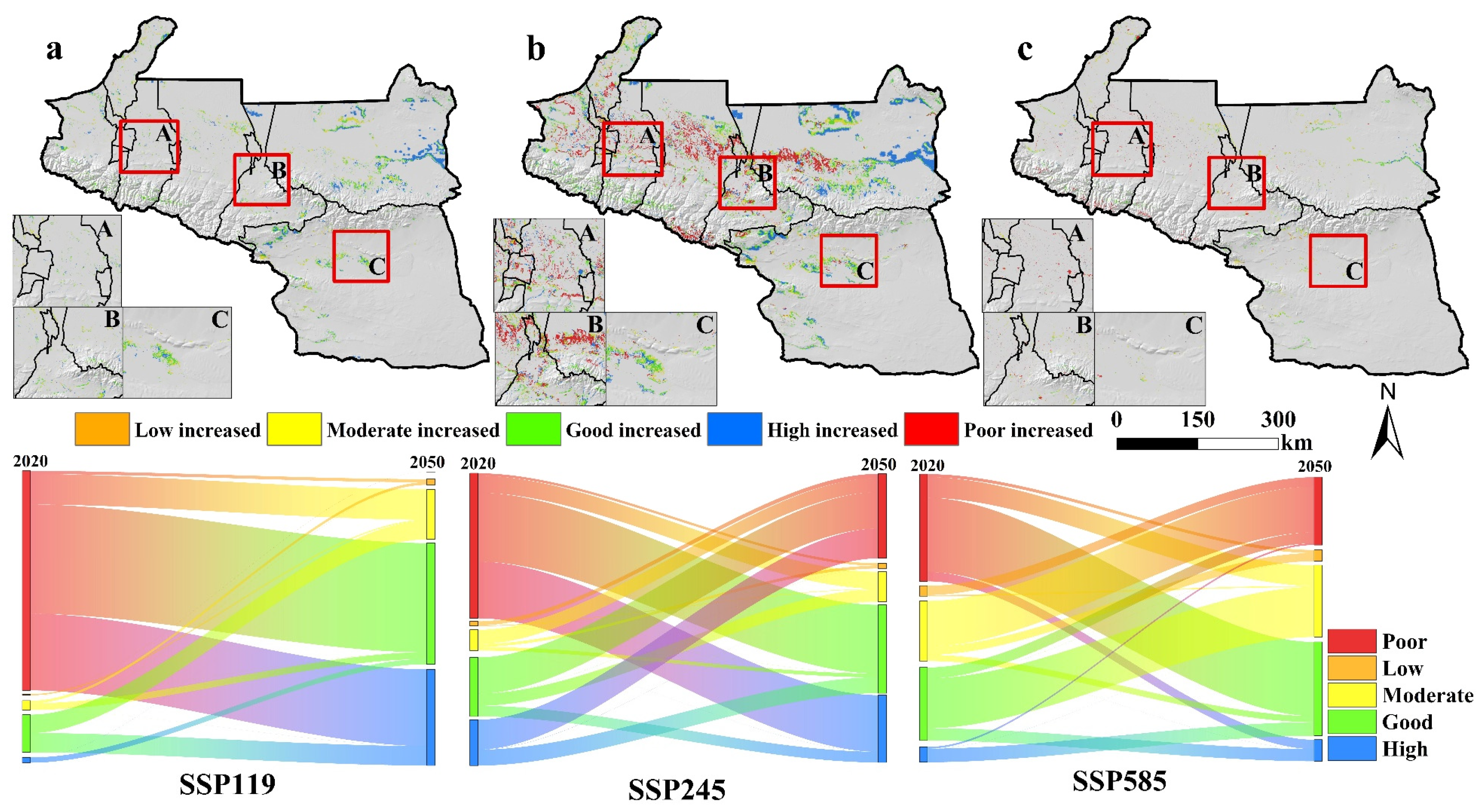
3.2.3. Spatiotemporal Uncertainty of Future HQ Predictions
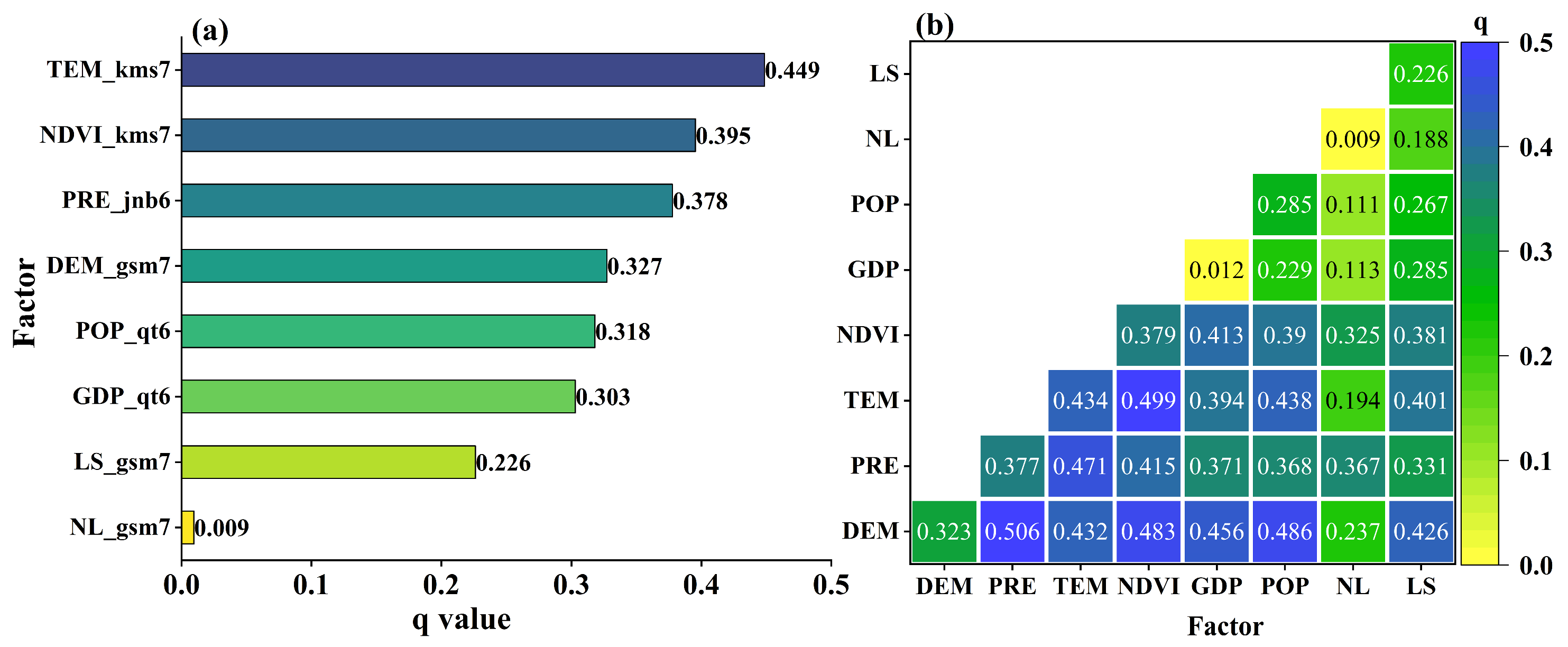
3.3. Analysis of Habitat Quality Drivers
4. Discussion
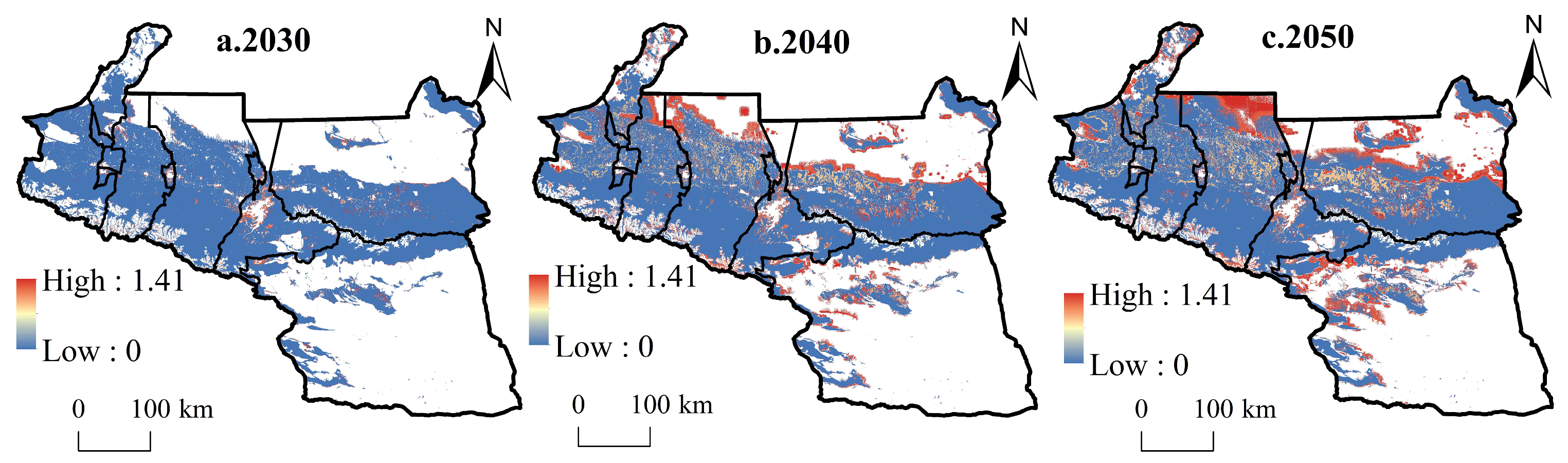
4.1. Drought Scenario Prediction
4.2. The Corresponding Impact of Drought on Habitat Quality
4.3. Land Use Change Response to Habitat Quality
4.4. Assessment of the Framework Established
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1
| SPEI | Categories |
|---|---|
| SPEI > −0.5 | Near normal |
| −1.0 < SPEI ≤ −0.5 | Slight dry |
| −1.5 < SPEI ≤ −1.0 | Moderately dry |
| −2.0 < SPEI ≤ −1.5 | Severely dry |
| SPEI ≥ −2.0 | Extremely dry |
| Parameter Type | 2020–2030 | 2030–2040 | 2040–2050 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSP119 | SSP245 | SSP585 | SSP119 | SSP245 | SSP585 | SSP119 | SSP245 | SSP585 | |
| AGR | 3.78% | 3.53% | 3.85% | 2.94% | 3.27% | 3.73% | 2.63% | 3.08% | 3.31% |
| APR | 0.53‰ | 0.74‰ | 0.61‰ | 0.44‰ | 0.66‰ | 0.52‰ | 0.26‰ | 0.59‰ | 0.35‰ |
| APV (mm) | 2.55 | −0.32 | 7.82 | −4.29 | 2.17 | −3.93 | 3.80 | −0.94 | −1.80 |
| ATV (°C) | 0.08 | 0.08 | 0.09 | 0.05 | −0.01 | 0.09 | −0.02 | 0.18 | −0.03 |
| Main Equations | Unit |
|---|---|
| Population = INTEG (Population change, 530.761) | ten thousand |
| Population change = Population × Population change rate | ten thousand |
| Primary industry investment = 147,072 + 0.041 × Fixed investment | ten thousand |
| Secondary and tertiary industry investment = −147,072 + 0.958933 × Fixed investment | ten thousand |
| Urban population = −185.636 + 1.0238 × Population | ten thousand |
| Rural population = Population − Urban population | ten thousand |
| Urban construction land demand = −450.225 + 2.02 × Urban population | km2 |
| Rural construction land demand = EXP (5.9876 − 124.842/Rural population) | km2 |
| Agricultural investment = 266,071 + 0.146765 × Primary industry investment | ten thousand |
| Fishery investment = −9818.04 + 0.01556 × Primary industry investment | ten thousand |
| Forestry investment = 17,333.4 + 0.018881 × Primary industry investment | ten thousand |
| Livestock investment = −100,921 + 0.274569 × Primary industry investment | ten thousand |
| Construction land change = −621.716 + 3.12953 × Rural construction land demand + 2.26594 × Urban construction land demand + 0.00013 × Secondary and tertiary industry investment | km2 |
| Grassland change = 4741.63 + 0.000346 × Livestock investment + 9.27408 × Construction land change − 0.2622 × Livestock product demand − 241.191 × Average annual temperature + 5.02998 × Annual precipitation − 71.4336 × SPEI | km2 |
| Forest change = −44.2848 − 2.5 × 10−5 × Forestry investment − 83.145 × Area of farmland returned to forest + 1.32188 × Average annual temperature + 0.5896 × Annual precipitation − 11.7385 × SPEI | km2 |
| Water change = 392.3513 + 0.00768 × Fishery investment − 0.13233 × Aquatic product demand − 69.08913 × Average annual temperature + 1.96969 × Annual precipitation + 0.69345 × SPEI | km2 |
| Cultivated land change = 725.398 − 0.01212 × Food demand + 366.8 × Area of farmland returned to forest + 0.001607 × Agricultural investment − 9.43386 × Construction land change − 67.8428 × Average annual temperature + 3.39966 × Annual precipitation − 58.0908 × SPEI | km2 |
| Unused land change = −(Construction land change + Grassland change + Forest change + Water change + Cultivated land change) | km2 |
| Land Use Types | Actual Value in 2020 | Predicted Value in 2020 | Relative Error |
|---|---|---|---|
| (km2) | (km2) | (%) | |
| Cultivated Land | 22,063.72 | 22,067.3 | 0.016 |
| Forest | 3047.4 | 3045.55 | −0.061 |
| Grassland | 58,798.62 | 58,795.8 | −0.005 |
| Water | 2025.04 | 2023.46 | −0.078 |
| Construction Land | 3644.75 | 3646.94 | 0.060 |
| Unused Land | 104,408.69 | 104,405 | −0.004 |
| Parameter | Reduced by 10% | Increase by 10% |
|---|---|---|
| Population change rate | 0.012 | 0.002 |
| GDP change rate | 0.019 | 0.019 |
| Primary industry investment | 0.060 | 0.060 |
| Secondary and tertiary industry investment | −0.004 | −0.004 |
| Urban construction land demand | −0.283 | −0.281 |
| Rural construction land demand | −0.189 | −0.176 |
| Agricultural investment | 0.164 | 0.164 |
| Fishery investment | 0.032 | 0.032 |
| Forestry investment | 0.129 | 0.129 |
| Livestock investment | 0.030 | 0.030 |
| Cultivated Land | Forest | Grassland | Water | Construction Land | Unused Land | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Forest | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Grassland | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Water | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Construction Land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Unused Land | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Weight of neighborhood | 0.3705 | 0.0282 | 1 | 0 | 0.2406 | 0.2308 | ||||||||||||
| Parameter Variation | Pearson’s r | RMSE | Stability Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Threat weight + 10% | 1 | 0 | High |
| Threat weight − 10% | 1 | 0 | High |
| Decay distance + 10% | 0.999964 | 0.004528 | High |
| Decay distance − 10% | 0.999961 | 0.004723 | High |
| Land Use | Slope | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | 386.47 | 0.874 | 0.0197 |
| Forest | −143.54 | 0.786 | 0.0452 |
| Grassland | −211.37 | 0.585 | 0.1319 |
| Water | −97.2 | 0.77 | 0.0505 |
| Construction Land | 89.55 | 0.98 | 0.0012 |
| Unused Land | −23.13 | 0.019 | 0.8241 |
| Start_Year | End_Year | FoM | Kappa |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 2020 | 0.9761 | 0.8991 |
| 2010 | 2015 | 0.9933 | 0.9849 |
| Land Use Types | SSP119 | SSP245 | SSP585 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
| Cultivated Land | 21,219.8 | 25,051.3 | 34,709.1 | 21,812.6 | 25,863.0 | 34,733.2 | 22,475.5 | 28,290.4 | 39,762.7 |
| Forest | 2721.6 | 2495.7 | 2216.0 | 2728.1 | 2464.0 | 2057.9 | 2631.9 | 2339.0 | 2008.6 |
| Grassland | 60,167.0 | 62,105.0 | 65,347.7 | 59,483.2 | 61,768.8 | 65,085.5 | 59,493.3 | 60,022.7 | 61,048.1 |
| Water | 1394.3 | 1336.5 | 1285.3 | 1218.7 | 1151.7 | 1181.1 | 1272.0 | 1042.4 | 1000.9 |
| Construction Land | 4620.5 | 5423.3 | 5970.0 | 4679.5 | 5497.0 | 6019.3 | 4818.4 | 5678.4 | 6190.5 |
| Unused Land | 103,082 | 96,984.1 | 84,541.4 | 104,498 | 98,068.9 | 84,751.1 | 102,405 | 93,733.9 | 79,063.6 |
| SSP119 | Poor | Low | Moderate | Good | High | |
| Poor | 124,695.1 | 78.57 | 755.96 | 2717.56 | 1909.11 | |
| Low | 0.11 | 1238.91 | 30.98 | 0.02 | 0 | |
| Moderate | 0 | 65.74 | 4439.68 | 166.66 | 1.23 | |
| Good | 0 | 0.07 | 456.61 | 14,384.95 | 483.03 | |
| High | 0 | 0 | 0.37 | 131.77 | 14,384.95 | |
| SSP245 | Poor | Low | Moderate | Good | High | |
| Poor | 119,560.9 | 181.93 | 1244.43 | 5029.69 | 4139.35 | |
| Low | 304.24 | 916.59 | 48.68 | 0.51 | 0 | |
| Moderate | 1041.77 | 203.99 | 3151.48 | 273.31 | 2.76 | |
| Good | 2651.15 | 2.9 | 888.8 | 10,997.49 | 784.32 | |
| High | 2177.89 | 0 | 15.55 | 1164.85 | 39,243.99 | |
| SSP585 | Poor | Low | Moderate | Good | High | |
| Poor | 128,924.6 | 35.37 | 237.18 | 851.43 | 107.69 | |
| Low | 108.05 | 1148.28 | 13.69 | 0 | 0 | |
| Moderate | 525.33 | 94.91 | 3982.15 | 70.82 | 0.1 | |
| Good | 125.73 | 0.17 | 573.91 | 14,484.11 | 140.74 | |
| High | 20.09 | 0 | 0.57 | 157.35 | 42,424.27 |
Appendix A.2
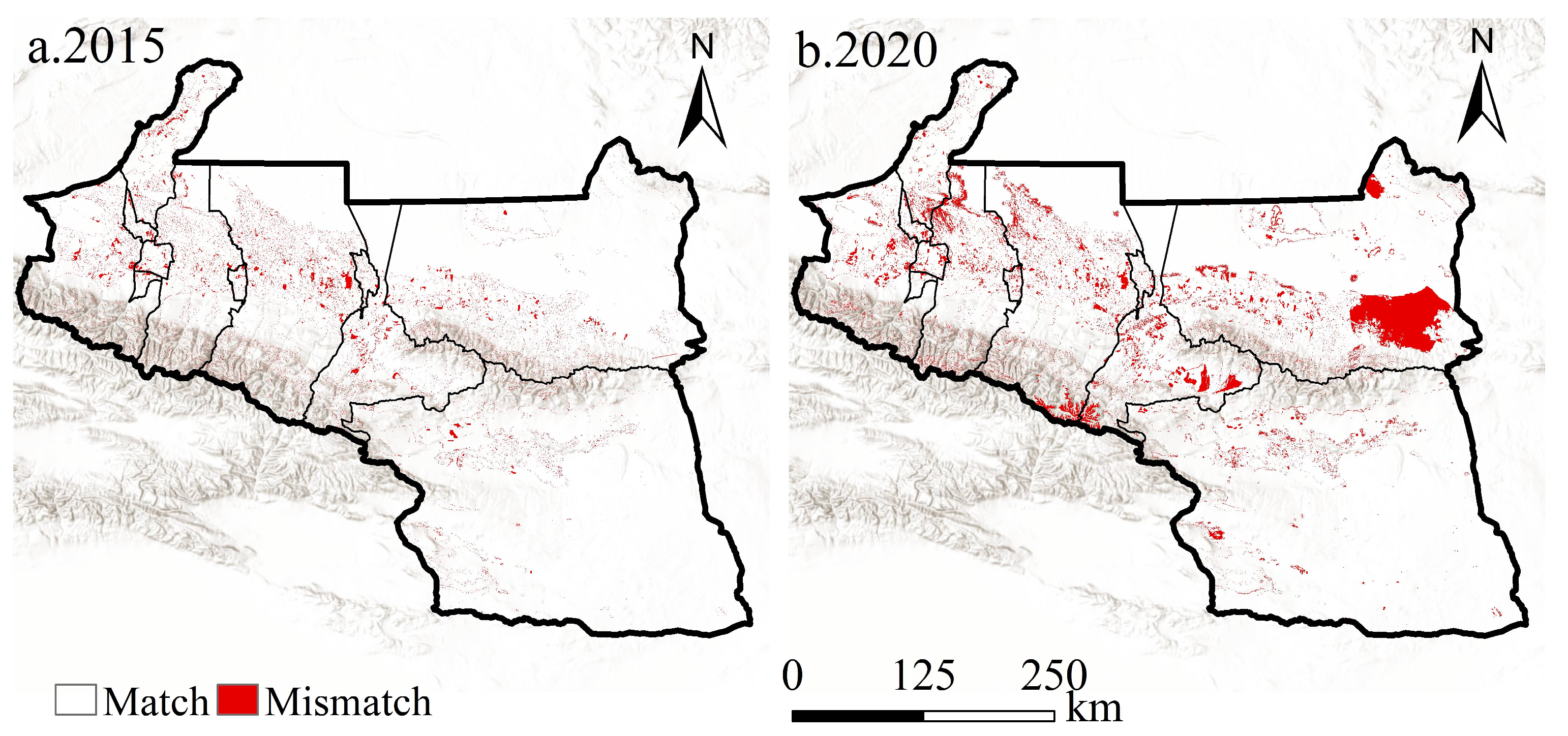

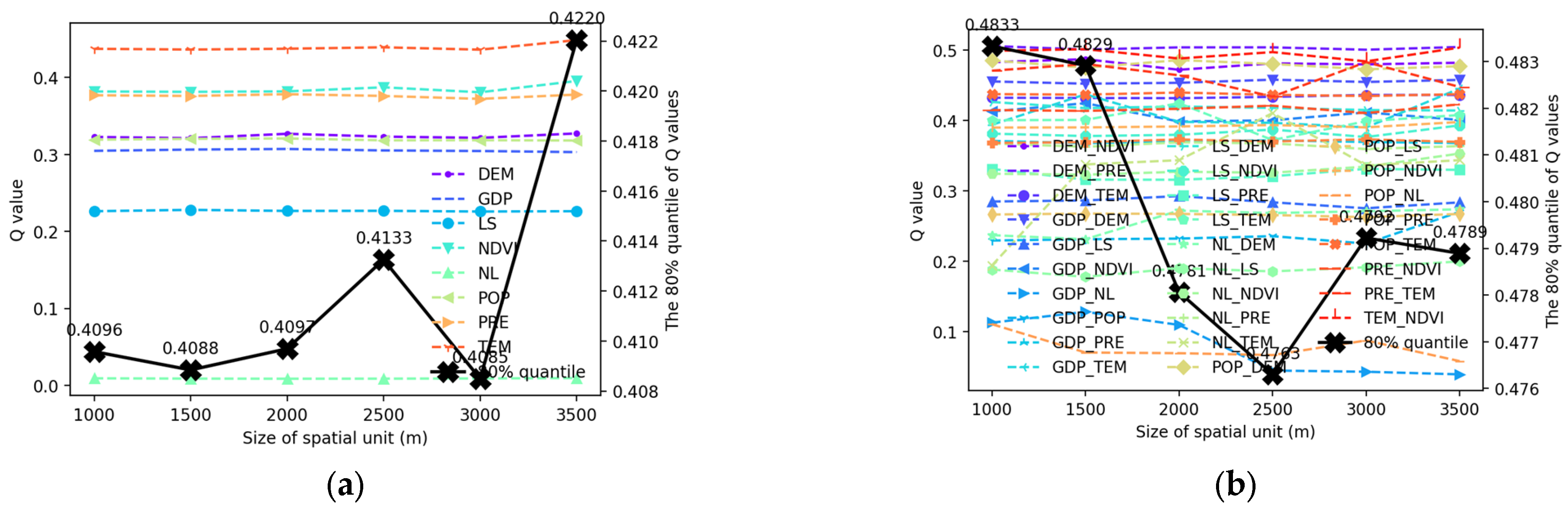
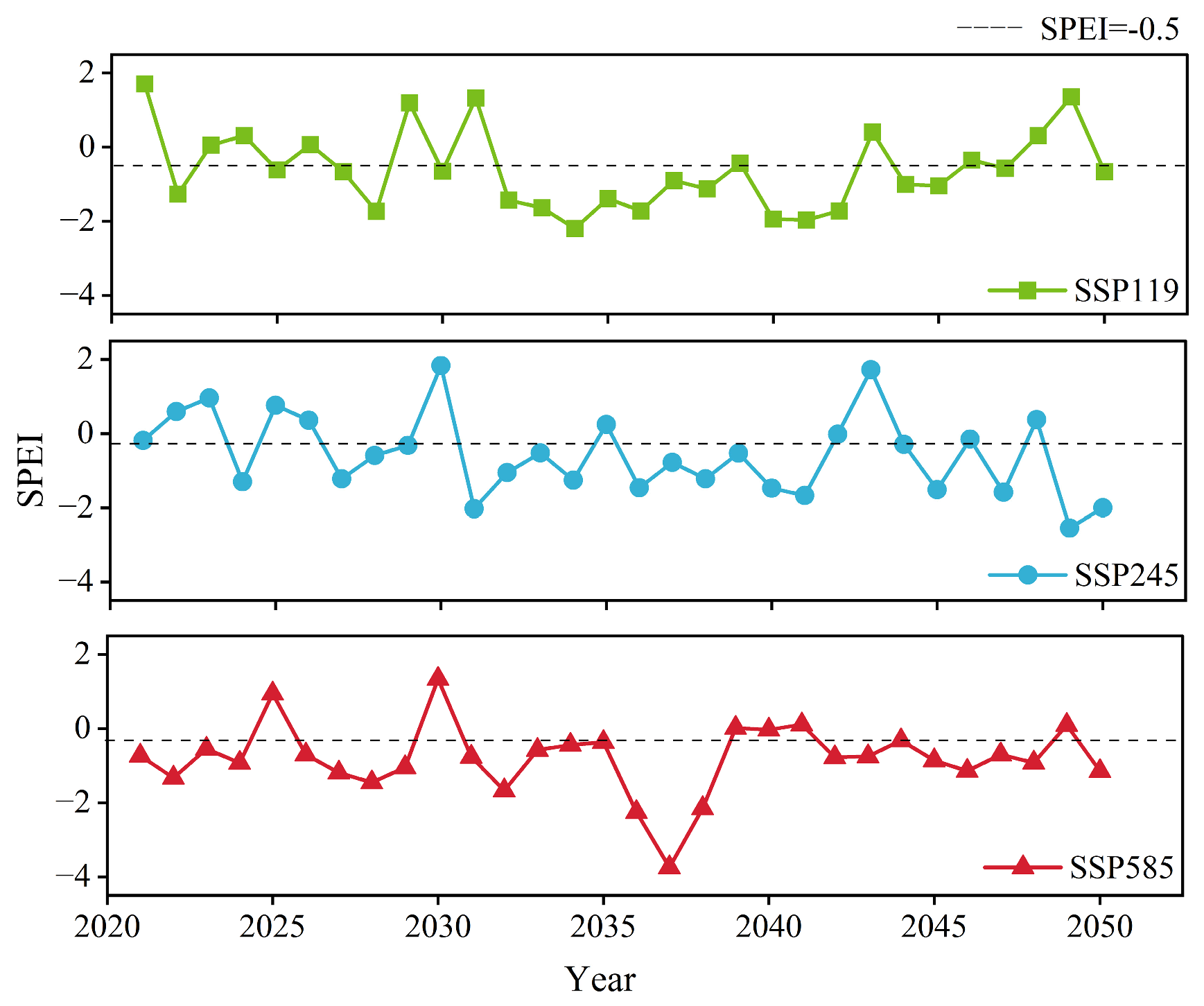
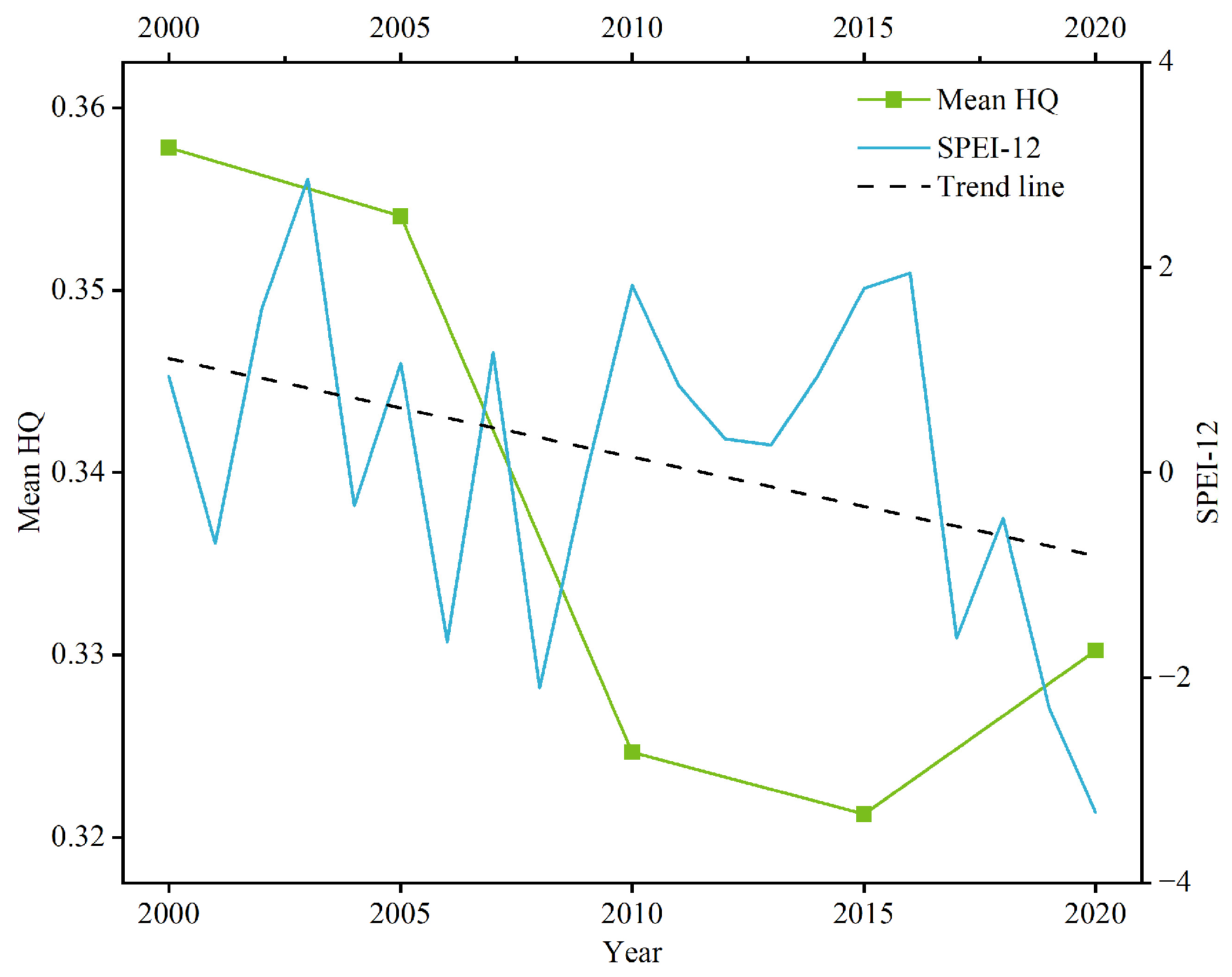
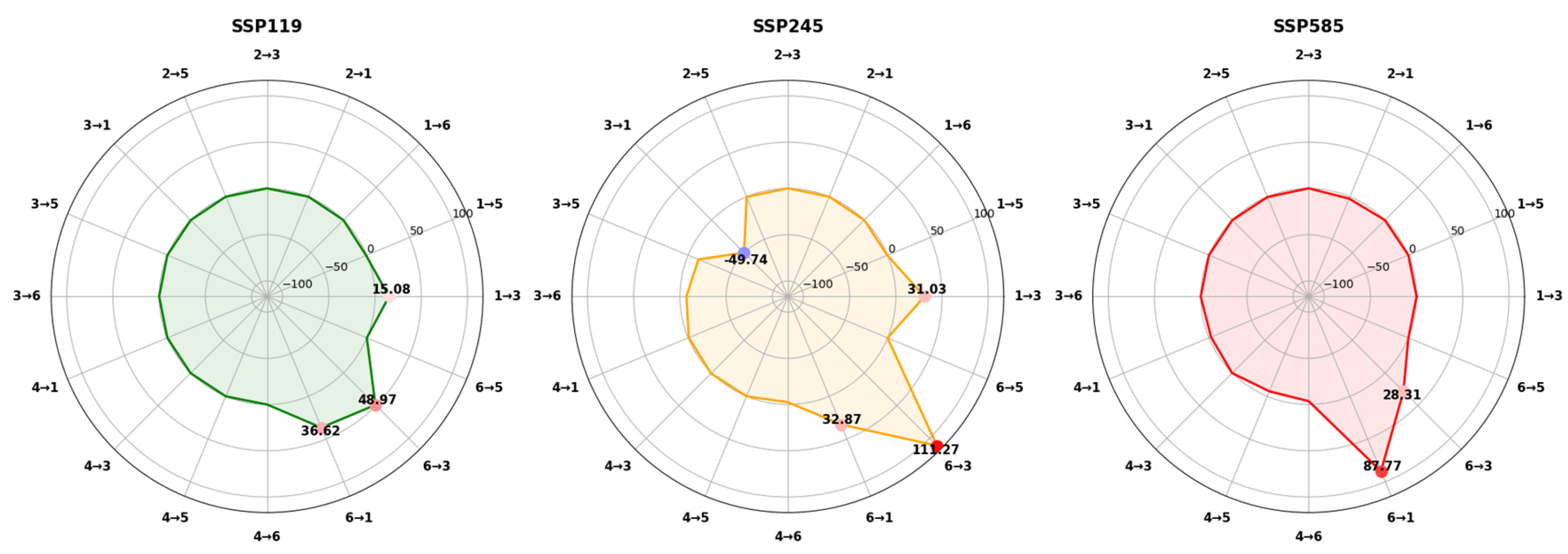
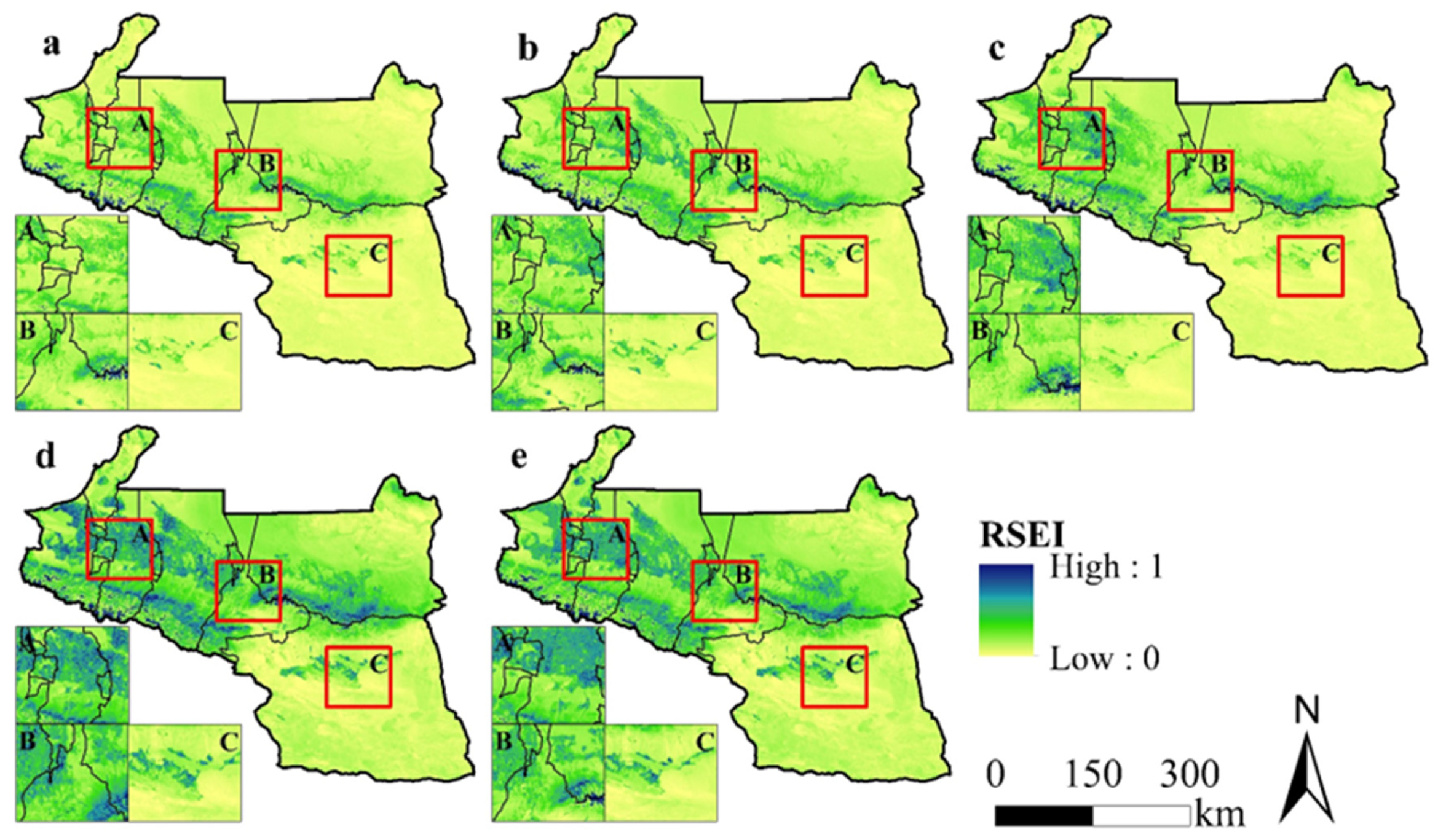
Appendix B. Field Quadrat Validation
| Sample | HQ Value | Vegetation Coverage |
|---|---|---|
| a | 0.183 | 8% |
| b | 0.836 | 65% |
| c | 0.908 | 99% |
| d | 0.200 | 9% |
| e | 0.593 | 42% |
| f | 0 | 4% |
| g | 0.784 | 80% |
| h | 0.609 | 65% |
| i | 0.453 | 16% |

References
- Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Gou, A. Research on the Evolution Characteristics, Driving Mechanisms and Multi-Scenario Simulation of Habitat Quality in the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Based on Multi-Model Coupling. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L. The Evolution of Habitat Quality and Its Response to Land Use Change in the Coastal China, 1985–2020. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 952, 175930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Xiu, C.; Feng, X.; Liu, D. Influence of Urbanization on Regional Habitat Quality:A Case Study of Changchun City. Habitat Int. 2019, 93, 102042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Tang, Z.; Liu, D.; He, J. Ecological Response to Urban Development in a Changing Socio-Economic and Climate Context: Policy Implications for Balancing Regional Development and Habitat Conservation. Land Use Policy 2020, 97, 104772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Xu, Y.; Hao, F.; Yin, G. Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Synergies under Influence of Climate and Land Cover Change in an Afforested Semiarid Basin, China. Ecol. Eng. 2021, 159, 106083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulford, R.S.; Russell, M.; Myers, M.; Malish, M.; Delmaine, A. Models Help Set Ecosystem Service Baselines for Restoration Assessment. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, X. The Role of Land Use Change in Affecting Ecosystem Services and the Ecological Security Pattern of the Hexi Regions, Northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Hong, Z.; Xue, X.; Zheng, X.; Du, S.; Liu, X. Evolution Characteristics and Multi-Scenario Prediction of Habitat Quality in Yulin City Based on PLUS and InVEST Models. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, H. Local Perceptions of Ecosystem Services and Human-Induced Degradation of Lake Ziway in the Rift Valley Region of Ethiopia. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 127, 107786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, R.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, S. Effects of Multi-Temporal Scale Drought on Vegetation Dynamics in Inner Mongolia from 1982 to 2015, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 136, 108666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabel, F.; Putzenlechner, B.; Mauser, W. Global Agricultural Land Resources—A High Resolution Suitability Evaluation and Its Perspectives until 2100 under Climate Change Conditions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guise, I.; Silva, B.; Mestre, F.; Muñoz-Rojas, J.; Duarte, M.F.; Herrera, J.M. Climate Change Is Expected to Severely Impact Protected Designation of Origin Olive Growing Regions over the Iberian Peninsula. Agric. Syst. 2024, 220, 104108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, G.; Gu, T.; Fang, C.; Pan, S.; Zeng, J.; Wu, J. Simulating the Impact of Urban Expansion on Ecosystem Services in Chinese Urban Agglomerations: A Multi-Scenario Perspective. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2023, 103, 107275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; He, Z.; Bai, W.; He, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, J. Identification of Ecological Security Patterns of Alpine Wetland Grasslands Based on Landscape Ecological Risks: A Study in Zoigê County. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, S.; Kerachian, R.; Pourmoghim, P.; Behboudian, M.; Motlaghzadeh, K. Evaluating and Improving the Sustainability of Ecosystem Services in River Basins under Climate Change. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polasky, S.; Nelson, E.; Pennington, D.; Johnson, K.A. The Impact of Land-Use Change on Ecosystem Services, Biodiversity and Returns to Landowners: A Case Study in the State of Minnesota. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2011, 48, 219–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, P.; Lv, S.; Zhang, C. Spatial and temporal changes in land use and habitat quality in the Weihe River Basin based on the PLUS and InVEST models and predictions. Arid. Land Geogr. 2022, 45, 1125–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, C.; Zhong, J.; You, Q.; Fang, C.; Hu, Q.; Liang, J.; He, J.; Yang, W. Land Use Modeling and Habitat Quality Assessment under Climate Scenarios: A Case Study of the Poyang Lake Basin. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 172, 113292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Fang, S.; Wu, H.; Zhou, X.; He, Z.; Gao, L. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Habitat Quality and Its Shrinkage Effect in Shrinking Cities: Evidence from Northeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 161, 111919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Li, Z.; Liang, Y. Tempo-Spatial Changes of Ecological Vulnerability in the Arid Area Based on Ordered Weighted Average Model. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 133, 108398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, C.; Zhu, C.; Gao, Q. Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Identification of Eco-Optimal Regions in Urban Agglomerations in Arid Regions of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 373, 133823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Wang, B. Temporal and Spatial Change of Habitat Quality and Its Driving Forces: The Case of Tacheng Region, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1118179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Abudureheman, M.; Halike, A.; Yao, K.; Yao, L.; Tang, H.; Tuheti, B. Temporal and Spatial Variation Analysis of Habitat Quality on the PLUS-InVEST Model for Ebinur Lake Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Ning, Y. Projecting LUCC Dynamics and Ecosystem Services in an Emerging Urban Agglomeration under SSP-RCP Scenarios and Their Management Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 949, 175100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Luo, J.; Zhang, H.; Qin, S.; Yu, M. Projections of Land Use Change and Habitat Quality Assessment by Coupling Climate Change and Development Patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 847, 157491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Fan, Y.; Wu, H.; Zheng, K.; Fan, J.; Liu, Z.; Xuan, J.; Zhou, J. The Value of Ecosystem Services in Arid and Semi-Arid Regions: A Multi-Scenario Analysis of Land Use Simulation in the Kashgar Region of Xinjiang. Ecol. Model. 2024, 488, 110579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Huang, J.; Mondal, S.K.; Zhai, J.; Wang, Y.; Wen, S.; Gao, M.; Lv, Y.; Jiang, S.; Jiang, T.; et al. Insight from CMIP6 SSP-RCP Scenarios for Future Drought Characteristics in China. Atmos. Res. 2021, 250, 105375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathbout, S.; Martin-Vide, J.; Bustins, J.A.L. Drought Characteristics Projections Based on CMIP6 Climate Change Scenarios in Syria. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 50, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wang, C.; Feng, T.; Du, C.; Zhang, B. Multi-Scenario Prediction of Land Use Change and Carbon Storage in Shaanxi Province Based on the SD-PLUS Coupled Model. Chin. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 195–206+215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Xue, J.; Feng, X.; Zhao, J.; Sun, H.; Hu, Y.; Ma, Y. Thriving Arid Oasis Urban Agglomerations: Optimizing Ecosystem Services Pattern under Future Climate Change Scenarios Using Dynamic Bayesian Network. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 350, 119612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, L.; Yan, Z.; Li, K.; He, P.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, R. Prediction of habitat quality in the Ili River Valley under the influence of human activities and climate change. Arid. Land Geogr. 2024, 47, 104–116. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, X.; Sun, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhao, C.; Li, K. Land Use and Habitat Quality Change in the Yellow River Basin: A Perspective with Different CMIP6-Based Scenarios and Multiple Scales. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.; Xiao, C.; Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yan, H. Accelerating Decline of Habitat Quality in Chinese Border Areas. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2024, 206, 107665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Li, X. An Optimal Multivariate-Stratification Geographical Detector Model for Revealing the Impact of Multi-Factor Combinations on the Dependent Variable. GIScience Remote Sens. 2024, 61, 2422941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Ding, Y.; Wen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ren, J. Spatiotemporal Change and Trend Analysis of Potential Evapotranspiration over the Loess Plateau of China during 2011–2100. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Su, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Luo, Y.; Zhai, J.; Huang, J.; Jing, C.; Gao, M.; Lin, Q.; et al. Gridded datasets for population and economy under Shared Socioeconomic Pathways for 2020–2100. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2022, 18, 381–383. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, J.; Zhu, R.; Yin, Z.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Fang, C. Spatial and temporal variation of drought in Northwest China based on CMIP6 model. Arid Zone Res. 2024, 41, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, Y.; Lv, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, D. The Characteristics and Evaluation of Future Droughts across China through the CMIP6 Multi-Model Ensemble. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Borth, H.; Fraedrich, K.; Su, B.; Zhu, X. Drought and Wetness Variability in the Tarim River Basin and Connection to Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulation. Int. J. Climatol. 2014, 34, 2678–2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, F.; Lagos, O.; Gil, P.M.; Jara, J.; Zaccaria, D. Assessment of Reference Evapotranspiration Forecasting in the Mediterranean Climate of Central Chile Using the ASCE Standardized Penman-Monteith Equation, the Hargreaves-Samani Equation, and Weather Predictions from the Global Forecast System Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 957, 177606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, G.H.; Allen, R.G. History and Evaluation of Hargreaves Evapotranspiration Equation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2003, 129, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, K. Dynamic Simulation and Projection of Land Use Change Using System Dynamics Model in the Chinese Tianshan Mountainous Region, Central Asia. Ecol. Model. 2024, 487, 110564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Qin, D.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhai, J.; Cao, L.; Chao, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, G.; et al. Effect of Fertility Policy Changes on the Population Structure and Economy of China: From the Perspective of the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways. Earth’s Future 2019, 7, 250–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Wang, W.; Cai, W.; Chen, N.; Hu, S.; Luo, X.; Li, J.; Zhan, C. Land Use/Land Cover Prediction and Analysis of the Middle Reaches of the Yangtze River under Different Scenarios. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 833, 155238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Y.; Qi, Y.; Ma, X.; Cao, L. Exploring the Response of Ecosystem Service Value to Land Use Changes under Multiple Scenarios Coupling a Mixed-Cell Cellular Automata Model and System Dynamics Model in Xi’an, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 110009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Ye, C.; Li, X.; Hu, M. Scenario Simulation of Land Use Change in Jiangxi Province Based on SD Model. Geogr. Geo-Inf. Sci. 2022, 38, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y. Understanding the Drivers of Sustainable Land Expansion Using a Patch-Generating Land Use Simulation (PLUS) Model: A Case Study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, C.; Liu, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q. Comparison of Various Models for Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use/Land Cover to Predict Ecosystem Service Value: A Case Study of Harbin-Changchun Urban Agglomeration, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 478, 144012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zeng, X.; Xia, L. Assessment Impacts of Weather and Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) Change on Urban Vegetation Net Primary Productivity (NPP): A Case Study in Guangzhou, China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4125–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Liao, J.; Zhu, W.; Qiu, Q.; Wang, L.; Tang, L. The weight of neighborhood setting of the FLUS model based on a historical scenario: A case study of land use simulation of urban agglomeration of the Golden Triangle of Southern Fujian in 2030. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2019, 39, 4284–4298. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, L.; Li, S.; Lewis, B.J.; Wu, J.; Yu, D.; Zhou, W.; Zhou, L.; Wu, S. The influence of land use change on the spatial–temporal variability of habitat quality between 1990 and 2010 in Northeast China. J. For. Res. 2019, 30, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, S.S.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Su, W. Impacts of Land-Use Change on Habitat Quality during 1985–2015 in the Taihu Lake Basin. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-Scale Geospatial Analysis for Everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; He, M. Dynamic Changes and Driving Factors of the Quality of the Ecological Environment in Sanjiangyuan National Park. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yang, J.; Ma, P.; Yue, P.; Yu, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P.; Duan, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, B.; et al. The enhancement and eastward expansion of climate warming and humidification, formation mechanism and important environmental impacts in Northwest China. J. Arid Meteorol. 2023, 41, 351–358. [Google Scholar]
- Su, T.; Meng, X.; Yang, X.; An, Y.; Zhao, C. Drought evolution characteristics and vegetation response in the midwestern region of northwest China from 1963 to 2022. J. Arid Meteorol. 2025, 43, 163–175. [Google Scholar]
- Rehmanrukiya, R.; Kasimu Alimjiang, K.; Ablaiti Halimulati, A.; Doraiti Xilina, D.; Xu, J. Research on the Temporal and Spatial Evolution of Habitat Quality in Urban Agglomeration on the Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountains Based on InVEST Model. J. Ecol. Rural Environ. 2022, 38, 1112–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Ju, C. Spatio-temporal Evolution of Land Use and Ecological Service Value in Urban Agglomeration on Northern Slope of Tianshan Mountains. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 40, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Shen, A.; Liu, C.; Wen, B. Impacts of Ecological Land Fragmentation on Habitat Quality in the Taihu Lake Basin in Jiangsu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Xiao, X.; Jia, Y. Habitat Quality Changes and Influencing Factors in Huixian Wetland Based on InVEST & GEO-detectors Model. J. Guangxi Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 41, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
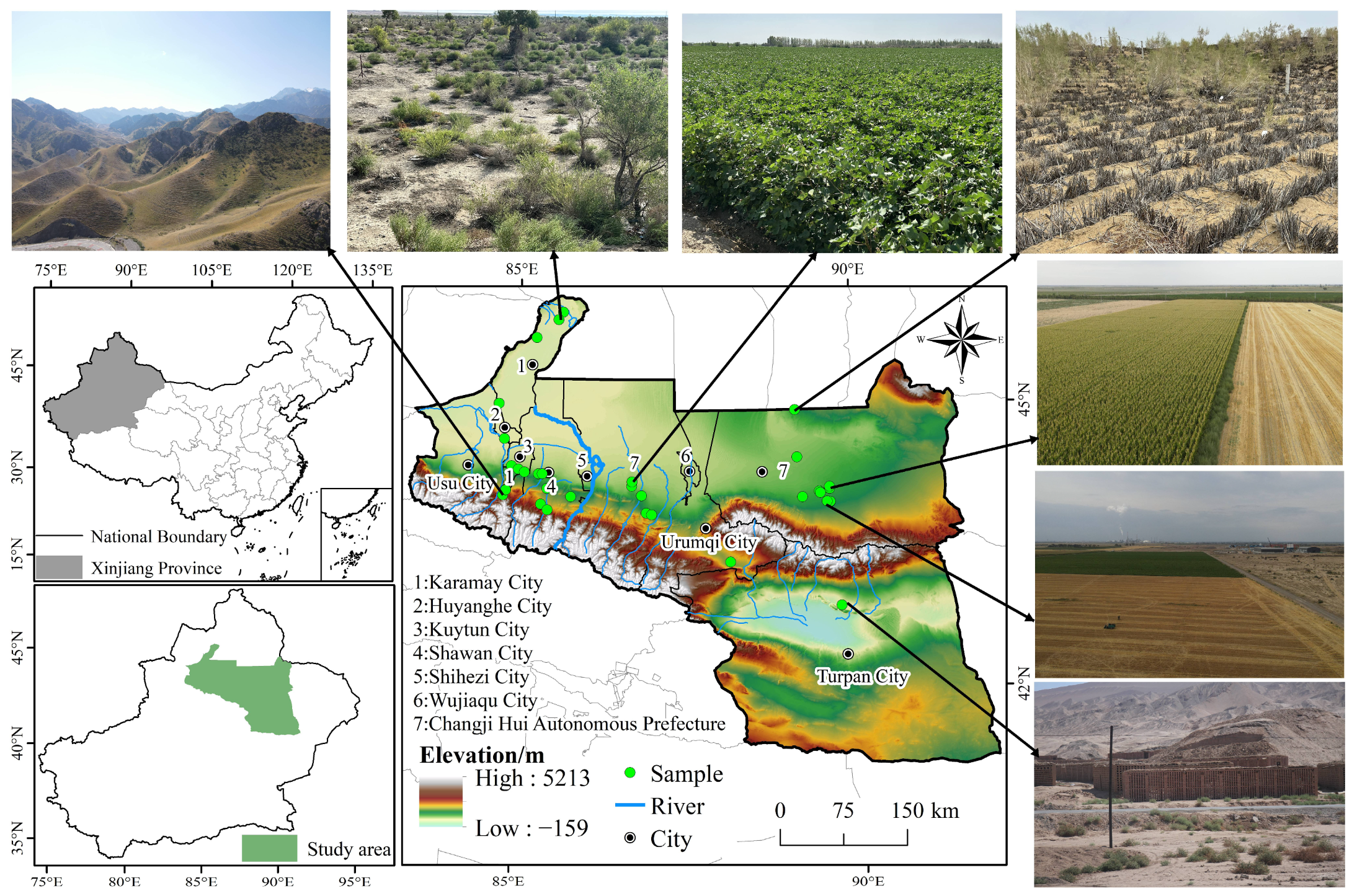
| Data | Application | Period | Resolution | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross domestic product (GDP) | PLUS, OMGD | 2000–2020 | 1 km | Resource and Environment Science Data Platform (https://www.resdc.cn/) |
| Population density (POP) | PLUS, OMGD | 2000–2020 | 1 km | |
| Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) | OMGD | 2000–2020 | 30 m | |
| Soil type | PLUS | / | 1 km | |
| River | PLUS | 2019 | / | National catalog Service For Geographic Information (https://www.webmap.cn/) |
| Level 1 road | PLUS | 2019 | / | |
| Level 2 road | PLUS | 2019 | / | |
| Level 3 road | PLUS | 2019 | / | |
| Highway | PLUS | 2019 | / | |
| Railway | PLUS | 2019 | / | |
| Government | PLUS | 2019 | / | |
| Elevation (DEM) | PLUS, OMGD | / | 30 m | Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/) |
| Slope | PLUS | / | 30 m | |
| Nighttime light data | OMGD | 2000–2020 | 1 km | National Tibetan plateau Data center (https://data.tpdc.ac.cn/) |
| Temperature | PLUS, OMGD | 2000–2020 | 1 km | |
| Precipitation | PLUS, OMGD | 2000–2020 | 1 km | |
| Livestock Density | OMGD | 2000–2020 | 1 km | The Food and Agriculture Organization (https://data.apps.fao.org/) |
| Land-Use Type | Habitat Suitability | Sensitivity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | Construction Land | Unused Land | Highway | Railway | ||
| Cultivated Land | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Forest | 1 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| Grassland | 1 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Water | 0.9 | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| Construction Land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Unused Land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Threat Factors | Max_Dist (km) | Weight | Decay Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | 3 | 0.5 | Linear |
| Construction Land | 8 | 0.8 | Exponential |
| Unused Land | 4 | 0.4 | Linear |
| Highway | 5 | 0.5 | Linear |
| Railway | 6 | 0.6 | Linear |
| 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2020 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metric | Value | p-Value | Value | p-Value | Value | p-Value | Value | p-Value | Value | p-Value |
| Pearson r | 0.375 | 0 | 0.328 | 0 | 0.345 | 0 | 0.367 | 0 | 0.329 | 0 |
| Spearman ρ | 0.530 | 0 | 0.507 | 0 | 0.466 | 0 | 0.457 | 0 | 0.446 | 0 |
| Moran’s I (RSEI) | 0.785 | 0.001 | 0.785 | 0.001 | 0.791 | 0.001 | 0.855 | 0.001 | 0.846 | 0.001 |
| Moran’s I (HQ) | 0.941 | 0.001 | 0.941 | 0.001 | 0.942 | 0.001 | 0.942 | 0.001 | 0.942 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, R.; He, L.; He, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Luo, F.; Li, D.; Lin, Z.; Huang, Y. Projection of Land Use and Habitat Quality Under Climate Scenarios: A Case Study of Arid Oasis Urban Agglomerations. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122704
Jin R, He L, He Z, Zhao Y, Luo F, Li D, Lin Z, Huang Y. Projection of Land Use and Habitat Quality Under Climate Scenarios: A Case Study of Arid Oasis Urban Agglomerations. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122704
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Run, Li He, Zhengwei He, Yang Zhao, Fang Luo, Dan Li, Zhiyu Lin, and Yuna Huang. 2025. "Projection of Land Use and Habitat Quality Under Climate Scenarios: A Case Study of Arid Oasis Urban Agglomerations" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122704
APA StyleJin, R., He, L., He, Z., Zhao, Y., Luo, F., Li, D., Lin, Z., & Huang, Y. (2025). Projection of Land Use and Habitat Quality Under Climate Scenarios: A Case Study of Arid Oasis Urban Agglomerations. Agronomy, 15(12), 2704. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122704






