Identification of qAs1—A Minor-Effect QTL Controlling Grain Arsenic Accumulation in Rice Using Near-Isogenic Lines Under High-Arsenic and Flooded Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Field Experiments
2.3. Determination of Total Arsenic
2.4. Genotyping of the RIL Population and Construction of the Genetic Linkage Map
2.5. Preliminary QTL Mapping
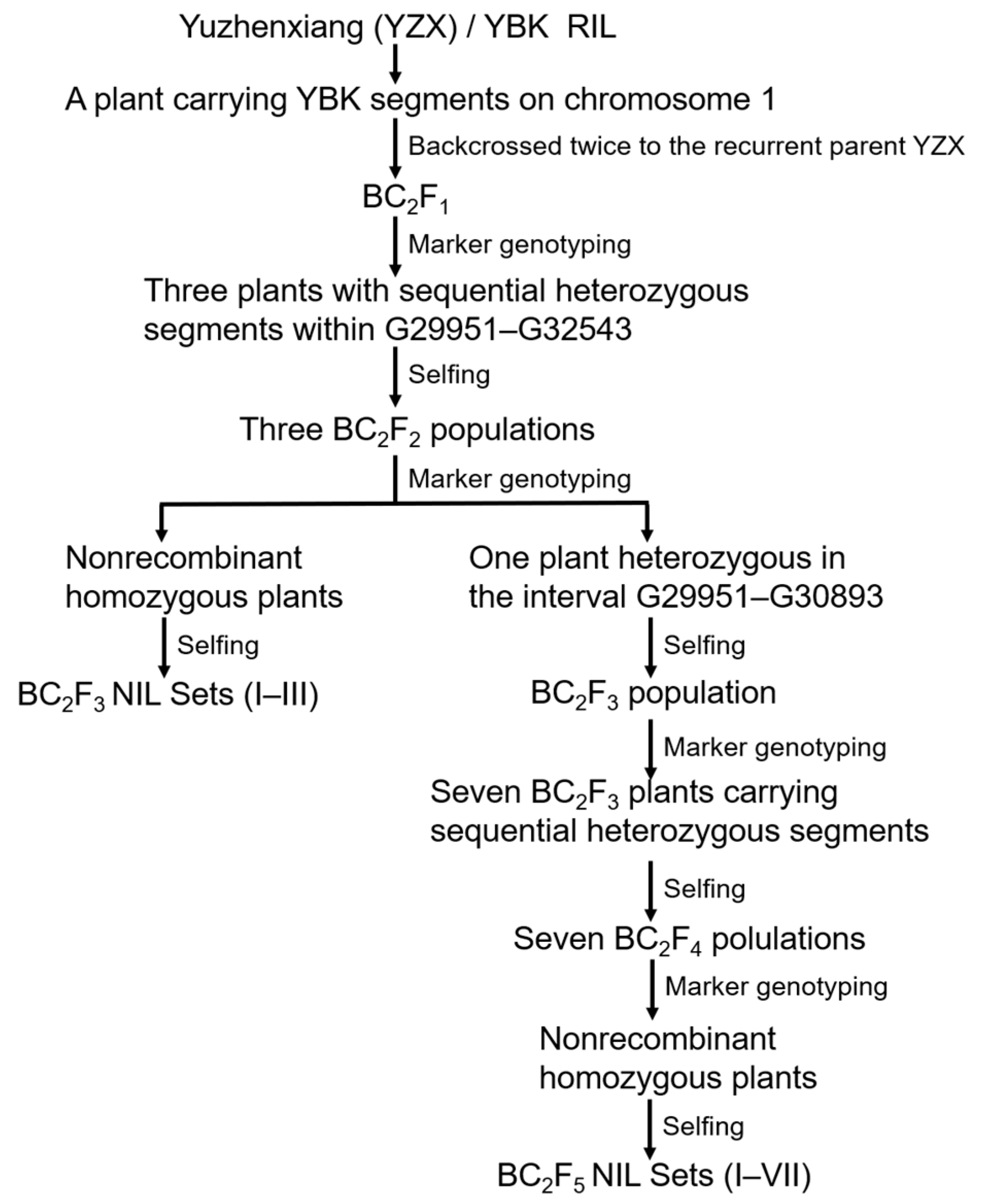
2.6. DNA Marker Genotyping and Fine Mapping
2.7. RNA-Seq and RT-qPCR Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Phenotypic Variation in the YZX/YBK RIL Population
3.2. Preliminary QTL Mapping in the RIL Population
3.3. QTL Effect Verification Using BC2F3 NILs
3.4. Fine Mapping Using BC2F5 NILs
3.5. Identification of Candidate Genes Within the qAs1 Interval
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| As | Arsenic |
| QTL | Quantitative trait locus |
| RIL | Recombinant inbred line |
| YZX | Yuzhenxiang |
| NIL | Near-isogenic line |
| DH | Doubled haploid |
| CSSL | Chromosome segment substitution line |
| MAS | Marker-assisted selection |
| ICIM | Inclusive composite interval mapping |
| PAGE | Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| ANOVA | Analyses of variance |
| CHYR1 | RING finger and CHY zinc finger domain-containing protein |
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SAT | Serine acetyltransferase |
References
- Kandhol, N.; Singh, V.P.; Herrera-Estrella, L.; Tran, L.P.; Tripathi, D.K. Arsenite: The umpire of arsenate perception and responses in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2022, 27, 420–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendorf, S.; Michael, H.A.; Geen, A. Spatial and temporal variations of groundwater arsenic in south and southeast Asia. Science 2010, 328, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagas, M.R.; Punshon, T.; Sayarath, V.; Jackson, B.P.; Folt, C.L.; Cottingham, K.L. Association of rice and rice-product consumption with arsenic exposure early in life. JAMA Pediatr. 2016, 170, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mawia, A.M.; Hui, S.; Zhou, L.; Li, H.; Tabassum, J.; Lai, C.; Wang, J.; Shao, G.; Wei, X.; Tang, S.; et al. Inorganic arsenic toxicity and alleviation strategies in rice. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 408, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Sun, G.; Williams, P.N.; Nunes, L.; Zhu, Y. Inorganic arsenic in Chinese food and its cancer risk. Environ. Int. 2011, 37, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-Y.; McGrath, S.P.; Meharg, A.A.; Zhao, F.-J. Growing rice aerobically markedly decreases arsenic accumulation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5574–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-H.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhao, F.-J. Rice is more efficient in arsenite uptake and translocation than wheat and barley. Plant Soil 2010, 328, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, G.J.; Adomako, E.E.; Deacon, C.M.; Carey, A.M.; Price, A.H.; Meharg, A.A. Effect of organic matter amendment, arsenic amendment and water management regime on rice grain arsenic species. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 177, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Zeng, D.-L.; Cheng, W.-D.; Qian, Q.; Duan, G.-L. Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol. 2008, 177, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, G.J.; Deacon, C.M.; Xiong, L.; Huang, S.; Meharg, A.A.; Price, A.H. Genetic mapping of the rice ionome in leaves and grain: Identification of QTLs for 17 elements including arsenic, cadmium, iron and selenium. Plant Soil 2010, 329, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norton, G.J.; Duan, G.-L.; Lei, M.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Meharg, A.A.; Price, A.H. Identification of quantitative trait loci for rice grain element composition on an arsenic impacted soil: Influence of flowering time on genetic loci. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2012, 161, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuramata, M.; Abe, T.; Kawasaki, A.; Ebana, K.; Shibaya, T.; Yano, M.; Ishikawa, S. Genetic diversity of arsenic accumulation in rice and QTL analysis of methylated arsenic in rice grains. Rice 2013, 6, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Pinson, S.R.M.; Tarpley, L.; Huang, X.-Y.; Lahner, B.; Yakubova, E.; Baxter, I.; Guerinot, M.L.; Salt, D.E. Mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci associated with concentrations of 16 elements in unmilled rice grain. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 137–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Guo, L.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Pan, X. Genome-wide association study of arsenic accumulation in polished rice. Gene 2023, 14, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Feng, Q.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, A.; Guan, J.; Fan, D.; Weng, Q.; Huang, T.; et al. High-throughput genotyping by whole-genome resequencing. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broman, K.W. Mapping quantitative trait loci in the case of a spike in the phenotype distribution. Genetics 2003, 163, 1169–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J. QTL IciMapping: Integrated software for genetic linkage map construction and quantitative trait locus mapping in biparental populations. Crop J. 2015, 3, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCouch, S.R.; CGSNL (Committee on Gene Symbolization, Nomenclature and Linkage, Rice Genetics Cooperative). Gene nomenclature system for rice. Rice 2008, 1, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.L.; Huang, N.; Bennett, J.; Khush, G.S. PCR-Based Marker-Assisted Selection in Rice Breeding: IRRI Discussion Paper Series No. 12; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Temnykh, S.; Xu, Y.; Cho, Y.G.; McCouch, S.R. Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 1997, 95, 553–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAS Institute Inc. SAS/STAT User’s Guide; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jia, G. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.; Trapnell, C.; Donaghey, J.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Improving RNA-Seq expression estimates by correcting for fragment bias. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anders, S.; Pyl, P.T.; Huber, W. HTSeq—A Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 166–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yu, S.; Zhuang, J. Dissection of the qTGW1.1 region into two tightly-linked minor QTLs having stable effects for grain weight in rice. BMC Genet. 2016, 17, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, K.; Chen, J.; Huang, D.; Fan, Y.; Zhuang, J. Dissection of two quantitative trait loci for grain weight linked in repulsion on the long arm of chromosome 1 of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Crop J. 2013, 1, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, D.-R.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Zhu, Y.-J. Identification of qTGW2, a minor-effect QTL controlling grain weight in rice. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Q.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, L.-L.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Mou, T.-M.; Ma, L.Y.; Zhuang, J.-Y. Dissection and fine-mapping of two QTL for grain size linked in a 460-kb region on chromosome 1 of rice. Rice 2018, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Zhuang, J. Fine-mapping of qTGW1.2a, a quantitative trait locus for 1000-grain weight in rice. Rice Sci. 2019, 26, 220–228. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.N.; Wang, L.-L.; Zhu, Y.-J.; Fan, Y.-Y.; Zhuang, J.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-H. Identification through fine mapping and verification using CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis for a minor QTL controlling grain weight in rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2021, 134, 327–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, K.-K.; Yang, H.; Liao, C.-Y.; Song, R.-F.; Hu, X.-Y.; Ren, F.; Liu, W.-C. A transcriptional recognition site within SOS1 coding region controls salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2025, 60, 2626–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Zhang, B.; Qin, F. Arabidopsis RZFP34/CHYR1, a ubiquitin E3 ligase, regulates stomatal movement and drought tolerance via SnRK2.6-mediated phosphorylation. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 3228–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, B.; Lou, S.; Bi, H.; Tang, H.; Tong, S.; Song, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, Y.; et al. CHYR1 ubiquitinates the phosphorylated WRKY70 for degradation to balance immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kussmaul, L.; Hirst, J. The mechanism of superoxide production by NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) from bovine heart mitochondria. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 7607–7612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.; Piyatida, P.; da Silva, J.A.T.; Fujita, M. Molecular mechanism of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance in plants: Central role of glutathione in detoxification of reactive oxygen species and methylglyoxal and in heavy metal chelation. J. Bot. 2012, 2012, 872875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.; Chiba, Y.; Hirai, M.Y. Metabolism and regulatory functions of O-acetylserine, S-adenosylmethionine, homocysteine, and serine in plant development and environmental responses. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 643403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howarth, J.R.; Dominguez-Solis, J.R.; Gutierrez-Alcala, G.; Wray, J.L.; Romero, L.C.; Gotor, C. The serine acetyltransferase gene family in Arabidopsis thaliana and the regulation of its expression by cadmium. Plant Mol. Biol. 2003, 51, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| QTL | Chromosome | Region (Mb) | LOD | A | R2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qAs1 | 1 | 29.97–32.34 | 4.85 | −0.054 | 10.81 |
| Population | Segregating Region | Phenotypic Mean (mg/kg) | p | A | R2 (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YZX | YBK | |||||
| BC2F3-I | G29987-G30807 | 0.618 | 0.307 | 0.0019 | −0.156 | 25.9 |
| BC2F3-II | G29987-G31634 | 0.653 | 0.321 | 0.0013 | −0.166 | 28.7 |
| BC2F3-III | G30893-G32543 | 0.586 | 0.609 | 0.5644 | ||
| BC2F5-I | G29987-G30045 | 0.648 | 0.334 | <0.0001 | −0.157 | 44.2 |
| BC2F5-II | G29987-G30110 | 0.580 | 0.309 | <0.0001 | −0.136 | 39.9 |
| BC2F5-III | G29987-G30178 | 0.564 | 0.290 | <0.0001 | −0.137 | 42.0 |
| BC2F5-IV | G29987-G30343 | 0.601 | 0.342 | <0.0001 | −0.130 | 37.3 |
| BC2F5-V | G30117-G30807 | 0.613 | 0.539 | 0.9765 | ||
| BC2F5-VII | G30213-G30807 | 0.628 | 0.649 | 0.7709 | ||
| BC2F5-VIII | G30407-G30807 | 0.665 | 0.581 | 0.9003 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, L.; Dong, Z.; Xiong, H.; Pan, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, X. Identification of qAs1—A Minor-Effect QTL Controlling Grain Arsenic Accumulation in Rice Using Near-Isogenic Lines Under High-Arsenic and Flooded Conditions. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2699. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122699
Guo L, Dong Z, Xiong H, Pan X, Liu W, Chen Z, Li X. Identification of qAs1—A Minor-Effect QTL Controlling Grain Arsenic Accumulation in Rice Using Near-Isogenic Lines Under High-Arsenic and Flooded Conditions. Agronomy. 2025; 15(12):2699. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122699
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Liang, Zheng Dong, Haibo Xiong, Xiaowu Pan, Wenqiang Liu, Zuwu Chen, and Xiaoxiang Li. 2025. "Identification of qAs1—A Minor-Effect QTL Controlling Grain Arsenic Accumulation in Rice Using Near-Isogenic Lines Under High-Arsenic and Flooded Conditions" Agronomy 15, no. 12: 2699. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122699
APA StyleGuo, L., Dong, Z., Xiong, H., Pan, X., Liu, W., Chen, Z., & Li, X. (2025). Identification of qAs1—A Minor-Effect QTL Controlling Grain Arsenic Accumulation in Rice Using Near-Isogenic Lines Under High-Arsenic and Flooded Conditions. Agronomy, 15(12), 2699. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15122699






