Abstract
Different types of organic materials demonstrate varying efficacy in ameliorating saline–alkali soils, while the combined application of organic materials can potentially enhance the remediation effects on saline–alkali land. To verify this assumption, our study conducted a pot experiment with spinach in saline–alkali soil, observing the improvement effect of saline–alkali soil and the growth of crops when acid fermentation products of vegetables, humic acid-like substances, and corn straw were applied either individually or in combination. The results revealed that both the sole and combined application of organic materials could enhance the yield of spinach. Particularly, humic acid-like substances increased spinach yield to six times that of the chemical fertilizer treatment. Although the application of organic materials led to a decline in the diversity and richness indices of the microbial community in saline–alkali soil (except fungal richness), the combined use of organic materials contributed to a healthier trend in the soil microbial community structure. Beyond its effects on soil nutrients such as total carbon and total nitrogen, the improvement in soil organic matter activity caused by the joint application of organic materials was identified as the primary factor responsible for enhancing the health of the soil microbial community and the remediation effects on saline–alkali soil.
1. Introduction
Globally, there are approximately 1.1 billion hectares of saline–alkali soils, which encompass 45 million hectares of salt-affected agricultural land [1,2]. The area of these soils is expanding at an annual rate of 10% [3]. Saline–alkali soils have poor structure, strong alkalinity, low nutrient and organic matter content, and low microbial activity, which limits soil fertility and is not conducive to crop growth [4,5,6]. Consequently, the enhancement and utilization of saline–alkali soils are critical for the advancement of global agricultural land resources and for augmenting grain production [7].
The application of organic materials has been recognized as an effective strategy for ameliorating saline–alkali soils, and straw, biochar, manure, and vinegar residue are most commonly used [8,9,10]. The primary mechanisms by which organic materials enhance saline–alkali soils include the promotion of soil aggregate formation, regulation of pH, enhancement of nutrient availability, and stimulation of microbial activity [11,12]. Numerous studies have indicated that the combined application of soil amendments yields substantially greater improvements in saline–alkali soils compared to the deployment of a singular amendment [13,14]. The co-application of wheat straw and gypsum not only reduces CO2 emissions but also enhances soil carbon storage [10]. The simultaneous application of humic acid and attapulgite has been found to improve nutrient content in saline–alkali soils while increasing surface area and elemental abundance through synergistic interactions [15]. Mixed amendment applications exhibit superior performance in elevating both biological activity and nutrient cycling capacity in saline–alkali soils, a strategy now receiving expanded research consideration.
Soil microorganisms drive multiple ecosystem functions and play a vital role in maintaining soil health and sustainability [16]. Highly sensitive to soil micro-environmental variations, they are also impacted by fertilization changes [14]. The application of phosphogypsum enhances soil antioxidant enzyme activity and nutrient availability by increasing bacterial diversity, richness, and the relative abundance of dominant bacterial phyla in the soil [17]. Corn straw and fermented chicken manure amendments measurably enhance the relative abundance of specific microbial taxa in soils while alleviating competitive inhibition from other bacteria, and improving crop salinity tolerance [18,19]. The activity of soil microorganisms can also be enhanced by the readily available nutrients introduced through organic amendments [20]. While inorganic amendments alter soil properties and structure to some extent, they bring about limited improvement to the microbial community structure [21].
From both economic and practical standpoints, crop straw serves as a primary source of organic matter for the enhancement of saline–alkali soils [10,22]. Straw application can enhance the enzymatic activity associated with soil carbon cycling, which in turn facilitates the mineralization of soil organic carbon and consequently supplies ample nutrients to soil microbial communities [23]. Nonetheless, the use of straw as a soil amendment for saline–alkali soils presents several challenges, including slow decomposition rates, limited initial ameliorative effects, susceptibility to triggering crop diseases, and disruption of microbial and nutrient equilibrium [24,25]. Consequently, the integration of crop straw with alternative soil conditioners has emerged as a focal point of research [26].
Fermented vegetable waste (FVW) and artificial humic acids (AHAs), as two types of active organic materials, possess potential advantages in enhancing soil microbial activity and providing active functional groups [27,28]. To address the limitations of applying corn straw alone for saline–alkali soil remediation, can it be combined with FVW or AHAs to enhance the effectiveness of the improvement? To verify this hypothesis and better align with actual agricultural production practices, we performed an experiment on the combined application of vegetable fermentation liquid, humic acid-like substances, and crop straws for the remediation of coastal saline–alkali soil, based on the application of chemical fertilizers to compensate for nutrient deficiencies in saline–alkali soil. Our investigation aims to explore (1) the effects of exogenous organic materials on the activity of organic matter and microflora in coastal saline–alkali soils, and (2) the regulatory pathways for edaphic factors affecting crop growth. The outcomes of this research will elucidate the primary regulatory factors associated with exogenous organic materials that contribute to increased crop yields in saline–alkali soils, thereby facilitating the effective utilization of coastal saline–alkali lands.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design and Plant Material
Soils were obtained from coastal saline–alkali regions in the north part of Shouguang City, Shandong Province (118°95′ E, 37°28′ N), where the growth of salt-tolerant vegetation is severely limited. The basic properties of the soil are shown in Table S1.
The coastal saline–alkali soil was backfilled into a specially designed cultivation pot, which measures 900 mm in height and 300 mm in diameter, constructed from 5 mm thick PVC material. The base of the perforated cultivation pots was wrapped in gauze and subsequently placed into a container filled with locally sourced groundwater, which is situated at a depth of 1–2 m and has a total soluble salt (TSS) content of 3 g·kg−1. To replicate the continuous upward movement of salt from the lower layers of the saline–alkali soil, the salt solution was consistently maintained at a height of 30–40 mm (refer to Figure S1). The experimental pots were categorized into four treatment groups: (1) CF (inorganic N-P-K fertilizers), (2) SF (inorganic N-P-K fertilizers combined with corn straw), (3) SHC (inorganic N-P-K fertilizers combined with corn straw and fermentation broth), (4) SHA (inorganic N-P-K fertilizers combined with corn straw and humic acid-like substances). For all treatment groups, organic materials were added according to the carbon content of 10,000 kg·ha−1 straw, and inorganic N-P-K (N:P:K = 15:15:15) fertilizer was added 300 kg·ha−1 and mixed with the surface soils (0–200 mm). The straw utilized in the experiment was all ground and passed through a 2 mm sieve. All treatments were arranged with a randomized complete block design, with three replicates per treatment.
The experiment was conducted in 2023 within a greenhouse environment. During the experiment, the air temperature in the greenhouse fluctuated between 20 and 31 °C, and only natural light was utilized. Seeds of large leaf spinach (Spinacia oleracea L. var. Gigantea) were sown directly into the potting soil, with a total of 12 seeds per pot. The exogenous organic materials employed in this study were prepared by the following methods: (1) The fermentation broth was made from tomato vines and litter (with a solid–liquid ratio of 1:3) through microbial anaerobic fermentation. The liquid is acidic (3.60 ≤ pH ≤ 4.20) and contains some small molecular organic acids, such as lactic acid and acetic acid, and amino acids. (2) The humic acid-like substances were made from tomato stems and leaves (solid–liquid ratio 1:10) at 180 °C for 3 h, under hydrothermal conditions, and their total humic acid content was 10.6–12.1%. The humic acid-like substances formed through hydrothermal cracking have the characteristics of uniform composition, good solubility, and a relatively low pH value (6.0 ≤ pH ≤ 7.1). The fundamental properties of the exogenous organic material are presented in Table S2.
2.2. Soil Sampling and Measurements
Soil samples were collected in the maturation period of spinach using a five-point sampling method in all treatments. Fresh soil samples were sieved through a 2 mm mesh and subsequently divided into 2 parts. One part was stored at −80 °C for amplicon sequencing, while the other was air-dried for the assessment of soil chemical properties.
Spinach plants were harvested at the mature period, which were oven-dried at 105 °C for 30 min and then at 65 °C to a constant weight. The dry weights of both the shoots and roots were recorded separately. Soil pH was measured with a glass electrode (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and electrical conductivity (EC) was determined with a conductivity meter (INESA, Shanghai, China) following suspension using deionized water at soil-to-water ratios of 1:2.5 (w/v) and 1:5 (w/v), respectively. The contents of soil organic carbon (SOC) and total nitrogen (TN) were quantified using an elemental analyzer (Elementar Analysensysteme GmbH, Frankfurt, Germany). Total phosphorus (TP) in the soil was assessed using the molybdenum blue method [29].
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) was obtained using a spectrometer in the transmission mode (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). The samples underwent comprehensive scanning across the 400–4000 cm−1 wavenumber range at 4 cm−1 resolution, with each sample subjected to 64 cumulative scans. Background correction was performed using the spectrum of a KBr pellet under ambient conditions, with real-time removal of water and carbon dioxide, followed by automatic baseline correction of the spectra. This study selected the bands at 1030 cm−1, 1440 cm−1, 1630 cm−1, 2925 cm−1, and 3440 cm−1, which correspond to coupled vibrations of complex organic compounds. The band near 1030 cm−1 arises from the C–O stretching and O–H deformation vibrations in polysaccharides [30]. Bands near 1440 cm−1 and 2925 cm−1 were linked to aliphatic-C, which were mainly attributed to aliphatic C–H bending, and asymmetric stretching [31,32]. The band near 1630 cm−1 was assigned to aromatic C=C stretching [33]. The band near 3440 cm−1 was primarily associated with alcohol-C, which represented the H-bonded O–H stretch [34]. The relative absorbance is calculated as the ratio of the intensity of any selected peak to the total intensity of all designated peaks, multiplied by 100% [35]. The ratios at 1630 cm−1 and (1440 + 2925) cm−1 were utilized to predict the complexity of the soil organic matter (SOM) chemical composition [36]. Additionally, the ratios at (1440 + 2925) cm−1 and 1030 cm−1 were employed to assess the degree of SOM decomposition or humification [36]. Noda’s rule indicated that if the corresponding peak coordinates exhibit identical signs in both synchronous and asynchronous maps, the variation sequence is the former preceding the latter; conversely, if the signs are opposite, the variation sequence reverses to the latter preceding the former [37].
2.3. DNA Extraction, 16S, ITS rRNA Gene Amplification, and Sequencing
Total DNA was extracted from 0.50 g of soil samples utilizing the Fast DNA SPIN Kit (MP Biomedicals, Santa Ana, CA, USA). The concentration of the extracted DNA was quantified using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA).
The V3-V4 region of the bacterial 16S rRNA genes was amplified with primer pairs of 338F (5′-ACTCCTACGGGAGGCAGCAG-3′) and 806R (5′-GGACTACHV GGGTWTCTAAT-3′). The ITS2 region of fungi was amplified by using primers of ITS1F (ITS1F, 5′-CTTGGTCATTTAGAGGAAGTAA-3′) and ITS2R (5′-GCTGCGTTCTTCATCG ATGC-3′) [38,39]. The PCR amplification of 16S rRNA was performed at an initial denaturation temperature of 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 27 cycles of denaturing at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 45 s, and a final elongation step at 72 °C was run for 10 min. The PCR amplification of the ITS rRNA gene was performed at an initial denaturation temperature of 95 °C for 3 min, followed by 35 cycles of denaturing at 95 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s, and extension at 72 °C for 45 s, and a final elongation step at 72 °C was run for 10 min. The products of PCR were purified using the AxyPrep DNA Gel Extraction Kit (Axygen Biosciences, Union City, CA, USA) following the manufacturer’s instructions and then were eluted in sterile water. The 2.0% agarose gel electrophoresis was used to quantify the concentration of each gene. The Illumina Miseq PE300 platform (Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) was selected to sequence the purified amplicons were pooled in equimolar and paired-end. The raw sequencing data have been deposited into the NCBI Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database under the accession number PRJNA1274540.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
A one-way ANOVA was conducted to identify significant differences in the soil properties. All analyses were conducted in R 4.2.1 (R Development Core Team, 2022). The synchronous and asynchronous spectra of FTIR were analyzed using 2DShige software (version 1.3) [40]. Alpha diversity was assessed using Mothur software (version 1.30.2), following the methodologies described by Zeng et al. [41]. Redundancy analysis (RDA) was employed to elucidate the relationships between soil microbial community structure and soil properties. Network analyses investigating the interactions between soil properties and microbial taxa were conducted using Gephi software (version 0.9.1) [42]. Spearman correlation heatmaps were generated on the Majorbio i-Sanger Cloud Platform. A structural equation model (SEM) was constructed to analyze the causal relationships between TN, SOC, C–H/C–O, C=C/C–H, root dry weight (RDW), and stem and leaf dry weight (SDW). Data visualization was performed using Origin 2022 Standard Edition (OriginLab Corp., Northampton, MA, USA), AMOS (IBM SPSS AMOS version 21.0.0), and PowerPoint software.
3. Results
3.1. Crop Yield and Basic Soil Properties
The application of exogenous organic matter notably enhanced the biomass accumulation of spinach stems and leaves, particularly in the treatment involving inorganic N-P-K fertilizers combined with corn straw and humic acid-like substances (SHA) (Figure 1A). In contrast, no significant differences were observed in the root dry weight among the inorganic N-P-K fertilizers combined with corn straw (SF), inorganic N-P-K fertilizers combined with corn straw and fermentation broth (SHC), and SHA treatments (Figure 1B).
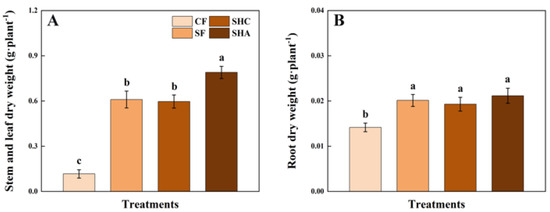
Figure 1.
Stem and leaf (A) and root (B) dry weights per spinach plant in different treatments. Notes: Values are means ± SE (n = 3). Different lowercase letters (a, b, c) above the bars indicate significant (p < 0.05) differences.
No significant differences were observed among all treatments in soil pH and TP (Table 1). In contrast to the conventional fertilization (CF) treatment, the incorporation of organic matter notably increased the levels of soil organic carbon (SOC) and total nitrogen (TN). However, no significant difference was found among the treatments involving exogenous organic matter.

Table 1.
Changes in soil properties following the different treatments.
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
The assignments of the soil organic matter (SOM) functional groups of different treatment soils were characterized by similar spectral signatures (Figure S2). The FTIR spectral behavior can be divided into two spectral regions. The first region extends from 1000 to 1800 cm−1, and the second region extends from 2800 to 3500 cm−1.
Both the synchronous and asynchronous spectra are shown in Figure 2, which analyzes the 750–3750 cm−1 region of the FTIR spectrum. In the synchronous map, four positive auto-peaks were found in different treatments (Figure 2A–D). The SOM structure at 1030 cm−1 is more sensitive than the others in all treatments, which means that the structure of SOM at shorter wavelengths shows a high susceptibility. In the synchronous map, three, four, two, and two cross-peaks were observed above the diagonal line for CF, SF, SHC, and SHA, respectively (Figure 2E–H). According to Noda’s rules, the order for SOM characteristic peaks change were: 1630 cm−1 > 2925 cm−1 > 1440 cm−1 > 1030 cm−1 > 3440 cm−1 for CF, 3440 cm−1 > 1630 cm−1 > 1030 cm−1 > 2925 cm−1 > 1440 cm−1 for SF, 3440 cm−1 > 2925 cm−1 > 1630 cm−1 > 1030 cm−1 > 1440 cm−1 for SHC, and 2925 cm−1 > 3440 cm−1 > 1630 cm−1 > 1030 cm−1 > 1440 cm−1 for SHA (Table S3).
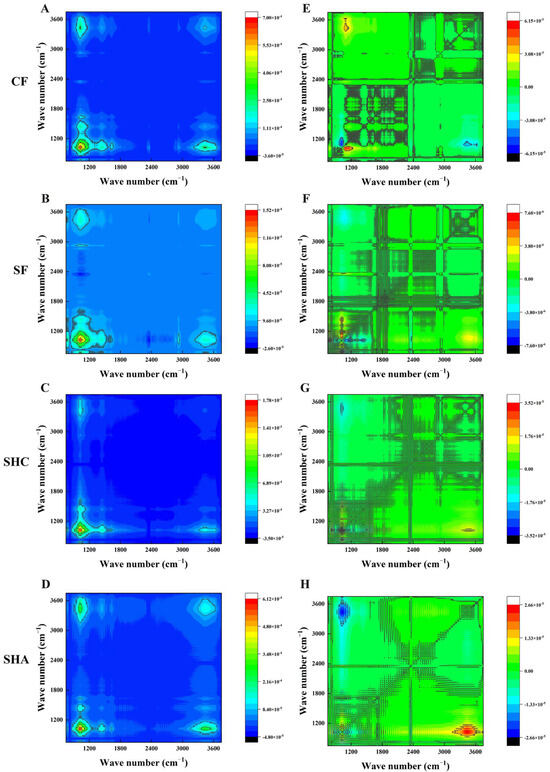
Figure 2.
Synchronous (A–D) and asynchronous (E–H) two-dimensional FTIR correlation spectra maps from the 750–3750 cm−1 region of the FTIR spectra during different treatment of soils.
The average relative abundance of characteristic peaks is listed in Table 2. There was no significant difference in C–O bonds, C–H bonds, C=C bonds, and C=C/C–H ratio among all treatments. Compared to SF treatment, the relative abundances of O–H bonds were significantly lower in SHA treatment, while no significant differences were observed between the other treatments. For the C–H/C–O ratio, only the CF and SHC treatments have a significant difference; the SHC treatment had the highest value, while the CF treatment had the lowest.

Table 2.
Averaged relative abundances of organic compounds from FTIR spectra across the different treatment soils.
3.3. Soil Microbial Community Structure Analysis
SHC treatment significantly decreased bacterial diversity and richness, relative to CF treatment (Figure S3A,B). No significant difference in bacterial diversity and richness was observed among CF, SF, and SHA treatments. Compared to CF treatment, SHC and SHA treatments significantly increased fungal diversity, and SF treatment significantly enhanced fungal richness (Figure S3C,D).
The heat map shows that the soil bacteria community at the phylum level in the four treatments changed significantly, while there was no significant difference in the fungi community (Figure 3). Compared to SF and CF treatments, SHC and SHA treatments appeared to be more closely clustered together in the composition of the bacterial communities. For fungal communities, the composition in SHA and SF treatments clustered more closely together.
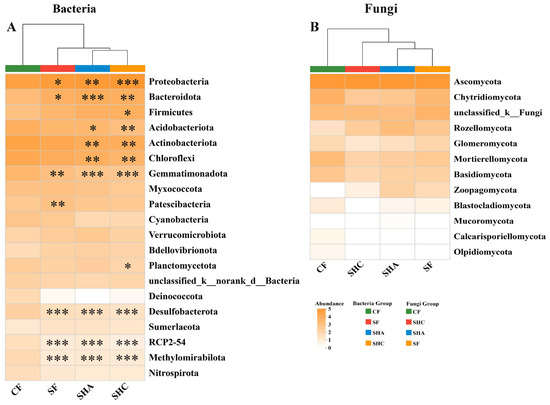
Figure 3.
Heat map showing the relative abundances of the top 20 bacteria (A) and fungi (B) phyla among different treatments. Stars on the squares indicate significant differences in CF to SF, SHC, and SHA, respectively (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001).
Exogenous organic matter significantly changed the sequence proportion of bacterial and fungal genera (Figure S4). SF, SHC, and SHA treatments had a significantly higher sequence proportion of Pseudoxanthomonas, Altererythrobacter, Ensifer, norank-f-Cellvibrionaceae, Schizothecium, and a low sequence proportion of norank-f-JG30-KF-CM45, norank-f-norank-o-Vicinamibacterales, Fusarium than CF treatment. In addition, compared with CF treatment, SF treatment significantly increased the sequence proportion of Devosia (p < 0.01); SHC treatment significantly increased the sequence proportion of Bacillus (p < 0.05), Microbulbifer (p < 0.01), and Muricauda (p < 0.05), and decreased norank-f-Vicinamibacteraceae (p < 0.05), Paraphoma; SHA treatment enhanced the sequence proportion of Devosia (p < 0.01), Subsaxibacter (p < 0.05), Muricauda (p < 0.05), and reduced Paraphoma (p < 0.05).
3.4. Relationships Among Soil Chemical, Microbiological Properties, and Plant Growth
Spearman’s correlation analysis showed that the top 20 most abundant bacterial and fungal genera were both mainly affected by SOC and TN (Figure S5). The 11 edaphic factors explained 93.08% and 88.01% of the total variation in soil bacterial and fungal communities, respectively (Figure 4). Redundancy analysis (RDA) illustrated that TN (p < 0.01) was the significant driver of bacterial community, while SOC (p < 0.05) was the significant driver of fungal community (Figure 4, Table S4).
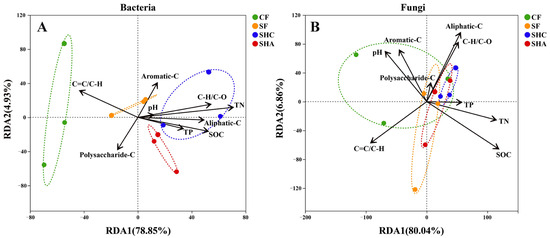
Figure 4.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) showing the associations of bacterial (A) and fungal (B) community composition with soil properties. Notes: The colors indicate the different treatments, with three replicates per treatment. SOC, soil organic carbon; TN, total nitrogen; TP, total phosphorus; C–O, polysaccharide-C; C–H, aliphatic-C; C=C, aromatic-C.
Two-factor correlation network analysis was further used to reveal the correlation between edaphic factors and microbial genus (Figure 5). The top 50 most abundant bacterial and fungal genera and the most important edaphic factors were selected for two-factor correlation analysis. The number of nodes and lines indicated the complexity of the connection between the edaphic factors and microbial genus, in which the node in this figure defaults to significant (p < 0.05). As depicted in Figure 5, bacteria consistently displayed more intricate networks compared to fungi. The top 3 edaphic factors and genera in the network were selected based on the central coefficient value (Table S5). For bacteria, Pseudoxanthomonas and Devosia showed positive correlations with SOC and TN, and the Muricauda showed positive correlations with SOC and C–H/C–O. For fungi, Paraphoma and Mortierella showed negative correlations with SOC, C–H/C–O, and aliphatic-C, while Fusarium showed negative correlations with C–H/C–O and aliphatic-C.
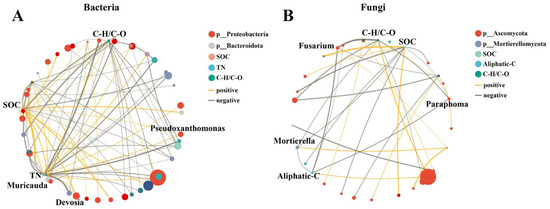
Figure 5.
Two-factor correlation network analysis between soil properties and the top 50 most abundant bacterial (A) and fungal (B) genera in all treatments. Notes: A connection stands for a significant correlation (p < 0.05). Nodes of the same color represent OUTs belonging to the same genus. The size of each node is proportional to the relative abundance. Yellow and gray lines indicate positive and negative correlations, respectively. Line thickness is positively correlated with the correlation between factors.
SEM analysis was used to investigate the influence of edaphic factors on the dry weight of spinach stems and leaves (Figure 6). Soil TN had a positive and direct influence on SOC and C–H/C–O. SOC had significant direct positive effects on stem and leaf dry weight (SDW), while negatively impacting the C–H/C–O. C–H/C–O showed a positive and direct influence on RDW, and a negative and direct influence on C=C/C–H. The effects of these edaphic factors on RDW were soil TN > C–H/C–O > C=C/C–H > SOC (Figure 6B). The standardized total effects indicated that soil TN exerted the highest influence on SDW, followed by C–H/C–O, SOC, RDW, and C=C/C–H (Figure 6C). Only C=C/C–H had a negative effect on SDW.
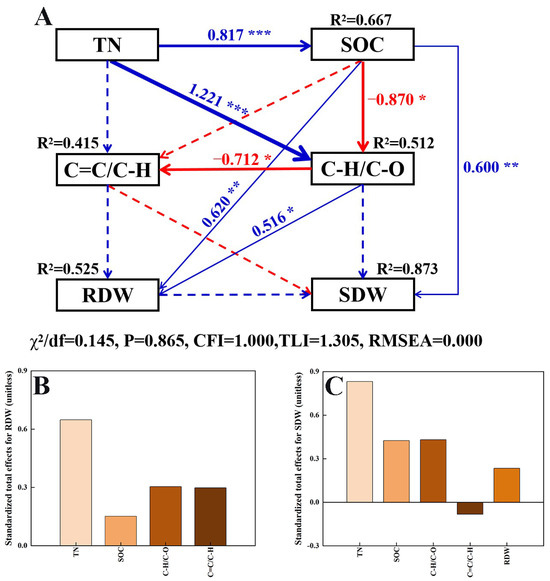
Figure 6.
Effects of multiple factors on the spinach shoot/root dry weight. Structural equation modeling based on the effects of soil properties (TN, SOC, C–H/C–O, and C=C/C–H) (A). Standardized total effects on the spinach root dry weight (B). Standardized total effects on the spinach shoot dry weight (C). Continuous red arrows indicate significant negative relationships, and blue arrows indicate positive relationships. Dashed arrows represent non-significant relationships. Arrow width indicates the strength of the relationships. The numbers on the arrows are standardized path coefficients. Significance levels are as follows: * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001. χ2/df = 0.076, p = 0.783, CFI = 1.000, TLI = 1.254, RMSEA = 0.000. SDW, stem and leaf dry weight; RDW, root dry weight.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Exogenous Organic Materials on SOM Chemical Composition
The addition of organic materials is the most widely adopted approach for saline–alkali soil remediation, as it effectively increases soil nutrient content and bioavailability [10]. Our experiment also yielded similar results. All organic amendments significantly increased soil TN and SOC content, but short-term application did not result in significant differences in nutrient levels among different organic matter treatments. Exogenous organic materials did not alter the complexity of SOM composition, but enhanced the decomposition degree of it, especially the SHC treatment (Table 2). This is attributed to the carbon-equivalent input of exogenous organic materials. In addition, the functional group composition of SOM is determined by the duration of mineralization and humification processes [43]. Conventional tillage and organic fertilizer application have not been observed to alter the composition of SOM functional groups in the short term, but prolonged implementation (>10 years) may lead to significant changes in SOM properties [44,45]. Consequently, short-term disturbances do not lead to significant alterations in its properties.
Exogenous organic materials trigger the transformation of the SOM molecular conformation. The addition of straw alone only altered the sequence of changes in aliphatic-C and polysaccharide-C. The combined application of straw with fermentation broth or humic acid-like substances modified the sequence of changes in aromatic-C and aliphatic-C. Fermentation broth and humic acid-like substances exhibit high decomposition rates and low stability [46]. Their co-application with straw increases the content of labile functional group compounds while decreasing the content of recalcitrant functional group compounds in soil, thereby delaying the onset of aromatization processes [34,47].
4.2. Effects of Exogenous Organic Materials on Soil Microbial Community Composition
The application of organic fertilizers is an effective strategy for improving the quality of saline–alkali soils [11,48]. Organic materials can significantly improve soil nutrient availability and have been shown to provide abundant carbon sources for soils, with their active and inert chemical components increasing the relative abundance of key microbial groups and organic carbon content [21]. Consequently, the application of organic materials has been shown to stimulate plant growth [17]. The contrary results observed in this study (Figure S3) may be intrinsically linked to the distinctive properties of saline–alkali soils. Under nutrient-sufficient conditions, the return of straw to the soil stimulates microbial diversity and richness while accelerating straw decomposition [49]. In contrast, in saline–alkali soils with nutrient deficiencies, the elevated C/N ratio of crop straw induces soil C/N ratio imbalance, resulting in intensified competition for nitrogen between crops and microorganisms and leading to the inhibition of the activities of soil microorganisms [50,51]. Research has shown that fertilization with both chemical fertilizers and cow manure does not significantly modify either the alpha diversity or the community composition of soil fungi, in contrast to the pronounced alterations observed in bacterial communities, suggesting that bacterial communities exhibit greater sensitivity to fertilization than their fungal counterparts [52]. The increased fungal richness observed in saline–alkali soils following the addition of exogenous organic materials can be attributed to fungi’s inherently higher C/N ratio, which results in lower nitrogen requirements, improved carbon use efficiency, and ultimately confers a competitive advantage in nutrient-depleted environments [53].
Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteriota, Chloroflexi, and Bacteroidota were the dominant phyla identified in saline–alkali soil [26,54]. The addition of exogenous organic materials did not alter the dominant bacterial composition at the phylum level in saline–alkali soil; however, it did enhance their relative abundance. The dominant bacterial phyla have adapted to the saline–alkali soil environment, and their widespread distribution stems from their rapid utilization of organic matter [55]. The composition of these microbial communities is generally stable, so the input of organic matter primarily affects the relative abundance of species rather than the structural composition [26,54,56]. In contrast, no such alterations were observed in the fungal communities (Figure 3). Proteobacteria, Actinobacteriota, and Acidobacteriota play pivotal roles in degrading soil macromolecular substances (e.g., lignin, cellulose, and xylan) and facilitating carbon cycling, while the Chloroflexi phylum enhances nitrogen uptake in crops, thereby promoting crop growth [57,58]. Additionally, Proteobacteria can alleviate abiotic stress through nitrogen fixation, and both Proteobacteria and Firmicutes are bacterial groups capable of resisting and mitigating saline–alkali stress [59]. Treatments of straw with humic acid-like substances and fermentation broth demonstrate superior efficacy in improving the microorganism community composition of saline–alkali soils [60]. Notably, SHA treatment not only elevated the relative abundance of Chloroflexi phylum linked to recalcitrant compound degradation, but also enhanced the relative abundance of Firmicutes phylum, which decomposed labile organic compounds [61,62]. This might be attributed to the fact that humic acid can act as an electron shuttle, facilitating electron transfer between microorganisms and enhancing their collaborative metabolic capabilities [63]. Meanwhile, humic acid contains various functional groups (such as carboxyl groups, phenolic hydroxyl groups, quinone groups, etc.), which can be utilized by certain microorganisms as carbon and energy sources to compensate for nutrient deficiencies caused by SOM leaching [64,65]. Through the above mechanisms, humic acid can promote the shift in soil bacterial communities towards aerobic heterotrophic community structures [66]. The increased relative abundance of dominant soil bacteria optimizes the soil microenvironment by altering the bacterial-to-fungal ratio and enhancing nutrient cycling and utilization.
4.3. Relationships Between Edaphic Factors and Soil Microbial Community Composition
Soil microorganisms play a crucial role in the processes of soil nutrient cycling. Although environmental factors influencing microbial composition and diversity vary across ecosystems [67], soil pH, SOC, and TN remain recognized primary influencing factors in forest [68], grassland [69], and cropland soils [70,71]. No significant relationship was observed between soil pH and microbial community composition in this study (Figure 4), which was attributed to the inherently high pH of saline–alkali soils and the lack of pH changes caused by exogenous organic material. In this study, redundancy analysis, two-factor network analysis, and structural equation modeling revealed that TN. SOC, and the C–H/C–O ratio are the primary environmental factors influencing microbial community composition, with TN exhibiting positive regulatory relationships with both SOC and the C–H/C–O ratio. Soil microorganisms, particularly the bacterial community composition, are highly sensitive to changes in fertilization and are therefore considered early indicators of soil ecosystem quality changes [72]. Given that fungi require less nitrogen than bacteria and exhibit lower mineralization rates for their byproducts, nitrogen addition not only suppresses fungal growth and their contribution to organic carbon but also indirectly bolsters exogenous organic matter in soil through increased bacterial residues [73,74]. The study demonstrated that nitrogen fertilizer application had no significant effect on phospholipid fatty acids (PLFAs) produced by fungi but significantly increased the content of bacterial-derived PLFAs, thereby elevating the bacterial-to-fungal ratio [74]. This phenomenon may be attributed to the competition between high-nitrogen-demand bacteria and low-nitrogen-demand fungi [75].
The input of mixed exogenous organic materials delays the onset of soil aromatization, supplying the microbial community with more readily decomposable labile functional group compounds. This is empirically demonstrated by elevated soil SOC content and C–H/C–O ratio, which collectively drive a transition toward bacterial dominance in the microbial community. In addition to the significant increase in the relative abundance of dominant bacterial phyla, the relative abundances of cellulose-degrading Pseudoxanthomonas and nitrogen-fixing, plant growth-promoting Devosia also showed significant increases [76,77]. Certain strains within these bacterial genera produce metabolites that create a water-retaining microenvironment in the soil to protect plant roots from drought, while specific gene clusters in other strains exhibit the capacity to mitigate the toxicity of heavy metals and antibiotics [77,78]. Conversely, the relative abundances of Fusarium and Paraphoma were significantly reduced. Fusarium can infect plants from the root tip and spread along the xylem, leading to plant lodging or root rot, while Paraphoma not only causes root rot in crops but also induces crown rot [79,80]. SHA treatment resulted in the highest stem and leaf dry matter accumulation in crops, not only because it significantly increased soil nutrient content but also due to its most pronounced improvement in saline–alkaline soil microorganisms. Although the SHC treatment also enhanced soil nutrient content, it exhibited stronger inhibitory effects on microbial diversity and richness. This is related to the fact that vegetable fermentation solutions can bring in more vegetable inorganic salts and tend to exacerbate soil salinization (Figure S6).
5. Conclusions
Light and moderate saline–alkali land could be a reserve of arable land resources after appropriate remediation, which is critical for the sustainable development of agriculture. The combined application of organic materials demonstrates superior improvement effects on coastal saline–alkali soils compared to singular applications, with the combination of straw and humic acid-like substances exhibiting the most pronounced efficacy. Beyond elevating soil nutrient content, the combined application of organic materials primarily enhances remediation efficacy in saline–alkali soils by improving SOM activity and delaying the onset of aromatization were key drivers of microbial community health. The increased relative abundance of beneficial bacteria, coupled with decreased relative abundance of harmful bacteria, has optimized soil microbial community structure, thereby enhancing the foundation for soil nutrient cycling. Thus, the combined application of low-cost straw and humic acid-like substances shows great potential for improving coastal saline–alkali soil under controlled conditions. However, further validation under field conditions is required to confirm these findings, which will facilitate the direct utilization of saline–alkali land in the future.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15102382/s1. Figure S1: Schematic diagram of cultivation pots; Figure S2: FTIR changes in different treatment soils; Figure S3: Bacteria (A-B) and fungi (C-D) diversity and abundance under different treatments; Figure S4: Genus with significant changes in sequence proportion among the top 20 bacteria and fungi; Figure S5: Correlation relationships between soil properties and the top 20 most abundant bacterial (A) and fungl (B) genus in all treatments; Figure S6: Total salinity in different treatments; Table S1: Basic properties of 0–20 cm soil; Table S2: Exogenous organic materials properties; Table S3: The signs of characteristic peak coordinates in synchronous and asynchronous spectral maps; Table S4: Environmental explanation of the changes in soil bacterial and fungal community by RDA analysis; Table S5: The central coefficient value of top 3 edaphic factors and genus in the network.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.C. and J.M.; methodology, X.C. and C.L.; software, Y.H. and G.C.; validation, Q.S., H.C., J.M., Y.H., G.C. and C.L.; formal analysis, H.C. and Q.S.; investigation, J.M. and Q.S.; resources, Y.H. and G.C.; data curation, J.M. and Q.S.; writing—original draft preparation, J.M. and Q.S.; writing—review and editing, X.C. and G.C.; visualization, Q.S., J.M. and C.L.; supervision, H.C.; project administration, X.C.; funding acquisition, J.M., Q.S. and G.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, grant number XDA28090300; the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation, grant number 2023M733676; and the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number U2106214.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Acknowledgments
The DeepSeek AI tool was used to refine the language after writing (grammar and structure of the sentences). All the design, data, tables, and figures in the article were completed manually.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wicke, B.; Smeets, E.; Dornburg, V.; Vashev, B.; Gaiser, T.; Turkenburg, W.; Faaij, A. The global technical and economic potential of bioenergy from saltaffected soils. Energ. Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2669–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schofield, R.V.; Kirkby, M.J. Application of salinization indicators and initial development of potential global soil salinization scenario under climatic change. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2003, 17, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrivastava, P.; Kumar, R. Soil salinity: A serious environmental issue and plant growth promoting bacteria as one of the tools for its alleviation. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.F.; Jiang, F.; Liu, X.S.; Sun, K.; Wang, W.; Zhang, M.X.; Li, H.L.; Xu, H.F.; Kong, W.J.; Yu, F.H. Biochar-amended coastal wetland soil enhances growth of Suaeda salsa and alters rhizosphere soil nutrients and microbial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Cao, X.F.; Li, Y.Y.; Sun, Q.; Dai, L.N.; Li, J.W.; Guo, Z.J.; Zhang, L.; Ci, L.J. Functional carbon nanodots improve soil quality and tomato tolerance in saline–alkali soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.H.; Jia, X.X.; Zhao, C.L.; Shao, M.G. A review of saline–alkali soil improvements in China: Efforts and their impacts on soil properties. Agric. Water Manag. 2025, 317, 109617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, S.; Ghadiri, H.; Chen, C.R.; Marschner, P. Salt-affected soils, reclamation, carbon dynamics, and biochar: A review. J. Soils Sediments 2016, 16, 939–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.P.; Li, Y.; Si, B.C.; Wang, Y.Z.; Chen, X.G.; Wang, X.F.; Chen, H.R.; Wang, H.R.; Zhang, F.C.; Bai, Y.G.; et al. Optimizing biochar application to improve soil physical and hydraulic properties in saline–alkali soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 771, 144802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, W.G.; Xu, L.; Qiu, M.H.; Yi, S.Q.; Wang, Y.M.; Shen, C.; Zhao, Y.L.; Li, Y.L.; Gu, C.H.; Shan, Y.H.; et al. Effects of different exogenous organic materials on improving soil fertility in coastal saline–alkali soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Wang, J.Y.; Wang, J.P. Seasonality of soil respiration under gypsum and straw amendments in an arid saline–alkali soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 277, 111494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Q.; Chen, H.Q.; Gong, Y.S.; Fan, M.S.; Yang, H.F.; Lal, R.; Kuzyakov, Y. Effects of 15 years of manure and inorganic fertilizers on soil organic carbon fractions in a wheat-maize system in the North China Plain. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2012, 92, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Garcia, E.; Siebe, C. Rehabilitation of a highly saline-sodic soil using a rubble barrier and organic amendments. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 189, 176–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Shar, A.G.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.L.; Shi, J.L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tian, X.H. Effect of straw return mode on soil aggregation and aggregate carbon content in an annual maize-wheat double cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.N.; Liang, B.J.; Zhao, H.L.; Zhao, Y. Impacts of various amendments on the microbial communities and soil organic carbon of coastal saline–alkali soil in the Yellow River Delta. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1239855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.B.; Wang, S.F.; Tang, L.; Xiao, J.; Chen, G.C. Combined application of humic acid and attapulgite improves physical structure and nutrients in coastal saline–alkali soils. Land Degrad. Dev. 2025, 36, 4415–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Maestre, F.T.; Reich, P.B.; Jeffries, T.C.; Gaitan, J.J.; Encinar, D.; Berdugo, M.; Campbell, C.D.; Singh, B.K. Microbial diversity drives multifunctionality in terrestrial ecosystems. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Guo, L.; Wang, S.B.; Wang, X.Y.; Ren, M.; Zhao, P.J.; Huang, Z.Y.; Jia, H.J.; Wang, J.H.; Lin, A.J. Effective strategies for reclamation of saline–alkali soil and response mechanisms of the soil-plant system. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Bian, Q.; Jiang, Y.J.; Zhu, L.Y.; Chen, Y.; Liang, Y.T.; Sun, B. Organic amendments drive shifts in microbial community structure and keystone taxa which increase C mineralization across aggregate size classes. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 153, 108062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.K.; Liu, H.; Liu, X.X.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y.; Shen, M.C.; Dang, K.K.; Zhao, Y.; Dong, Y.H.; Li, Q.Y.; et al. Organic fertilizer enhances rice growth in severe saline–alkali soil by increasing soil bacterial diversity. Soil Use Manag. 2022, 38, 964–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saqib, A.; Ahmed, K.; Naseem, A.; Qadir, G.; Nawaz, M.; Khalid, M.; Warraich, I.; Arif, M. Integrated use of humic acid and gypsum under saline-sodic conditions. Pak. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 33, 684–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Yao, Y.Y.; Yang, M.C.; Zhang, Y.P.; Zhang, S.G.; Shen, T.L.; Ding, F.J.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, W.Z.; Cui, J.T.; et al. Effects of different amendments on aggregate stability and microbial communities of coastal saline–alkali soil in the Yellow River Delta. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 34, 1694–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.S.; Shao, T.Y.; Liu, J.Y.; Li, N.; Long, X.H.; Gao, X.M.; Rengel, Z. Improvement of physico-chemical properties and microbiome in different salinity soils by incorporating jerusalem artichoke residues. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 158, 103791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Wu, F.P.; Jia, Z.K.; Wang, S.G.; Cai, Y.J.; Chang, S.X. Wheat straw and its biochar differently affect soil properties and field-based greenhouse gas emission in a Chernozemic soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2020, 56, 1023–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.L.; Ning, P.; Chen, Y.L.; Liu, J.F.; Ghaffar, S.A.; Tian, X.H.; Shi, J.L. Effect of straw amendment modes on soil organic carbon, nitrogen sequestration and crop yield on the North-Central Plain of China. Soil Use Manag. 2018, 35, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, A.Q.; Pan, J.Q.; Kang, K.J.; Pan, M.H.; Wang, G.; Wang, M.; He, Z.L.; Yang, X.E. Effects of straw return with N fertilizer reduction on crop yield, plant diseases and pests and potential heavy metal risk in a Chinese rice paddy: A field study of 2 consecutive wheat-rice cycles. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.L.; Yu, X.W.; Chen, J.; Li, X.F.; Chen, J.; Li, J.H. Effects of compost as a soil amendment on bacterial community diversity in saline–alkali soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1253415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Corato, U. Agricultural waste recycling in horticultural intensive farming systems by on-farm composting and compost-based tea application improves soil quality and plant health: A review under the perspective of a circular economy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Antonietti, M. Artificial humic acids: Sustainable materials against climate change. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1902992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Methods for Soil Agro-Chemistry Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Grube, M.; Lin, J.G.; Lee, P.H.; Kokorevicha, S. Evaluation of sewage sludge-based compost by FT-IR spectroscopy. Geoderma 2006, 130, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, D.; Lehmann, J.; Kinyangi, J.; Liang, B.Q.; Schäfer, T. Carbon K-Edge NEXAFS and FTIR-ATR spectroscopic investigation of organic carbon speciation in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2005, 69, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fultz, L.M.; Jennifer, M.K.; Calderón, F.; Acosta-Martínez, V. Using fourier-transform mid-infrared spectroscopy to distinguish soil organic matter composition dynamics in aggregate fractions of two agroecosystems. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 1940–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.J.; Wen, J.; Wang, Q.; Bai, L.Y.; Wang, Y.N.; Su, S.M.; Wu, C.X.; Zeng, X.B. Organic carbon preservation promoted by aromatic compound-iron complexes through manure fertilization in red soil. J. Soil Sediments 2021, 21, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wu, Z.N.; He, C.H.; Zhang, Y.H.; Huang, W.J.; Wang, D. Source identification and chemical compositions of particulate and mineral-associated organic matter in the deposited sediments of a dam-controlled watershed. Catena 2022, 219, 106618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.Y.; Pan, Q.; Teng, P.J.; Yu, J.C.; Li, N. How does soil organic matter stabilize with soil and environmental variables along a black soil belt in Northeast China? An explanation using FTIR spectroscopy data. Catena 2023, 228, 107152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lv, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X. Tillage impacts on the fractions and compositions of soil organic carbon. Geoderma 2012, 189, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.F.; Li, Q.; Wang, M.X.; Ji, D.B.; Tan, W.F. XPS and two-dimensional FTIR correlation analysis on the binding characteristics of humic acid onto kaolinite surface. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 724, 138154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.C.; An, S.S. Identifying the biogeographic patterns of rare and abundant bacterial communities using different primer sets on the Loess Plateau. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.J.; Gao, W.Q.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.T.; Kong, W.B.; Niu, S.Q.; Gao, K.; Yang, H.Q. Community composition and trophic mode diversity of fungi associated with fruiting body of medicinal Sanghuangporus vaninii. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, I.; Ozaki, Y. Two-Dimensional Correlation Spectroscopy-Applications in Vibrational and Optical Spectroscopy; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.Y.; Li, S.W.; Leng, Y.; Kang, X.H. Structural and functional responses of bacterial and fungal communities to multiple heavy metal exposure in arid loess. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 723, 138081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, M.; Heymann, S.; Jacomy, M. Gephi an Open Source Software for Exploring and Manipulating Networks. In Proceedings of the Third International ICWSM Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 May 2009; Volume 3, pp. 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakov, V.; Abakumov, E. Assessments of organic carbon stabilization using the spectroscopic characteristics of humic acids separated from soils of the Lena River Delta. Separations 2021, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.Q.; Cao, X.Y.; Mao, J.D.; Ohno, T.; Waldrip, H.M. Analysis of carbon functional groups in mobile humic acid and recalcitrant calcium humate extracted from eight us soils. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.Q.; Guo, L.J.; Cao, C.G.; Tan, W.F.; Li, C.F. Long-term rice-oilseed rape rotation increases soil organic carbon by improving functional groups of soil organic matter. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 319, 107548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.Q.; Li, M.X.; Xi, B.D.; Tan, W.B.; Ding, J.; Hao, Y.; Liu, D.M.; Liu, H.L. Short-duration hydrothermal fermentation of food waste: Preparation of soil conditioner for amending organic-matter-impoverished arable soils. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 21283–21297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.R.; Wei, L.H.; Jiang, J.Y.; He, C.J.; Sun, X.; Song, H.Y. New insights into the effect of pyrolysis temperature on the spectroscopy properties of dissolved organic matter in manure-based biochar. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 18527–18539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, S.; Tian, H.; Wang, Z.; Fang, X. Varieties with a high level of resistance provide an opportunity to manage root rot caused by Rhizoctonia solani in alfalfa. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2021, 160, 983–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.X.; Feng, H.J.; Zhang, M.; Shao, Y.Q.; Wang, J.Q.; Liu, Y.L.; Li, C.L. Straw returning combined with controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer affected organic carbon storage and crop yield by changing humic acid composition and aggregate distribution. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 415, 137783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzyakov, Y.; Xu, X. Competition between roots and microorganisms for nitrogen: Mechanisms and ecological relevance. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 656–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.D.; Zhu, Z.K.; Shahbaz, M.; Chen, L.; Liu, S.L.; Inubushi, K.; Wu, J.S.; Ge, T.D. Split N and P addition decreases straw mineralization and the priming effect of a paddy soil: A 100-day incubation experiment. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.X.; Wang, X.Q.; Nie, J.W.; Wang, Y.; Zang, H.D.; Peixoto, L.; Yang, Y.D.; Zeng, Z.H. Manure application increases soil bacterial and fungal network complexity and alters keystone taxa. J. Plant Nutr. Soil SC. 2022, 22, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, M.S.; Rousk, J. Considering fungal: Bacterial dominance in soils-methods, controls, and ecosystem implications. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2010, 42, 1385–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.D.; Zu, M.T.; Li, R.Z.; Zou, J.J.; Tao, J. Soil properties, microbial diversity, and changes in the functionality of saline–alkali soil are driven by microplastics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 446, 130712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, M.; Jia, H.B.; Wang, Q.Y. The effect of land use on bacterial communities in saline–alkali soil. Curr. Microbiol. 2017, 74, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, K.J.; Lv, D.T.; Jiang, S.Y.; Sun, J.Q.; Lin, H.; Sun, J. Inconsistent response of bacterial phyla diversity and abundance to soil salinity in a Chinese delta. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 12870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, N.L.; Challacombe, J.F.; Janssen, P.H.; Henrissat, B.; Coutinho, P.M.; Wu, M.; Xie, G.; Haft, D.H.; Sait, M.; Badger, J.; et al. Comparative genomic and physiological analysis provides insights into the role of Acidobacteria in organic carbon utilization in Arctic tundra soils. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 82, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.Y.; Shao, T.Y.; Gao, X.M.; Long, X.H.; Rengel, Z. Effects of planting quinoa on soil properties and microbiome in saline soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2022, 33, 2689–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, J.Y.; Li, J.X.; Xin, Y.Y.; Hao, Z.Y.; Chen, C.; Li, H.X.; Wang, B.; Ding, M.; Li, W.W.; et al. Insights into bacterial diversity in compost: Core microbiome and prevalence of potential pathogenic bacteria. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 137304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Gao, M.; Chen, H.T.; Chen, Y.W.; Wang, L.; Wang, R. Organic amendments promote saline–alkali soil desalinization and enhance maize growth. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1177209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Qiu, S.; Xu, X.; Ciampitti, I.A.; Zhang, S.; He, P. Change in straw decomposition rate and soil microbial community composition after straw addition in different long-term fertilization soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 138, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; He, X.Y.; Wang, G.H.; Xu, X.C.; Hu, Y.J.; Chen, X.B.; Zhang, W.; Su, Y.R.; Wang, K.L.; Soromotin, A.V.; et al. Network analysis reveals bacterial and fungal keystone taxa involved in straw and soil organic matter mineralization. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 173, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.G.; Chen, S.S.; Yuan, Y.; Lu, Q. Influence of humic acid complexation with metal ions on extracellular electron transfer activity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo, B.A.G.D.; Motta, F.L.; Santana, M.H.A. Humic acids: Structural properties and multiple functionalities for novel technological developments. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 62, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Y.; Li, G.; Bai, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, K.; Wang, Q.; Cao, L. Effects of gypsum combined with different amounts of biochemical humic acid on soil improvement and cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) yield on saline–alkali land. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2022, 20, 841–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.L.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.L.; Lu, Y.C.; Wang, Y.F. Saline–alkali soil applied with vermicompost and humic acid fertilizer improved macroaggregate microstructure to enhance salt leaching and inhibit nitrogen losses. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 156, 103705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, X.; Sanders, N.J.; Shi, Y.; Chu, H.; Classen, A.T.; Zhao, K.; Chen, L.T.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, Y.X.; He, J.S. The links between ecosystem multifunctionality and above- and belowground biodiversity are mediated by climate. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Dong, Y.F.; Gong, Y.B.; Zhu, Q.L.; Wang, Y.P. Climatic and edaphic factors affecting soil bacterial community biodiversity in different forests of China. Catena 2021, 207, 105675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Wu, J.J.; Zhang, D.D.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.L. Soil bacterial community composition and diversity in relation to edaphic properties and plant traits in grasslands of southern China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 128, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Jackson, R.B. The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bainard, L.D.; Hamel, C.; Gan, Y.T. Edaphic properties override the influence of crops on the composition of the soil bacterial community in a semiarid agroecosystem. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2016, 105, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Roy, M.M.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Baitha, A. Soil arthropods in maintaining soil health: Thrust areas for sugarcane production systems. Sugar Tech. 2018, 20, 376–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Cui, Y.; Lu, X.; Bai, E.; He, H.; Xie, H.; Liang, C.; Zhang, X. High nitrogen deposition decreases the contribution of fungal residues to soil carbon pools in a tropical forest ecosystem. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 97, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.Y.; Liu, T.Q.; Ding, H.N.; Li, C.F.; Tan, W.F.; Yu, M.; Liu, J.; Cao, C.G. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on soil microbial residues and their contribution to soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in a rice-wheat system. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 181, 104648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Diepen, L.T.A.; Lilleskov, E.A.; Pregitzer, K.S.; Miller, R.M. Decline of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi in northern hardwood forests exposed to chronic nitrogen additions. New Phytol. 2007, 176, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Revathi, K.; Khanna, S. Biodegradation of cellulosic and lignocellulosic waste by Pseudoxanthomonas sp R-28. Carbohyd. Polym. 2015, 134, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhetri, G.; Kim, I.; Seo, T. Devosia oryzisoli sp. nov., a novel moderately halotolerant bacterium isolated from the roots of rice plants and genome mining revealed the biosynthesis potential as plant growth promoter. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2023, 116, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhya, V.; Ali, S.K.Z.; Grover, M.; Reddy, G.; Venkateswarlu, B. Alleviation of drought stress effects in sunflower seedlings by the exopolysaccharides producing Pseudomonas putida strain GAP-P45. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2009, 46, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyvad, B.; Fejerskov, O. An ultrastructural-study of bacterial invasion and tissue breakdown in human experimental root-surface caries. J. Dent. Res. 1990, 69, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemi, A.; Adesb, P.K.; Crous, P.W.; Groom, T.; Scott, J.B.; Nicolas, M.E.; Taylor, P.W.J. Paraphoma chlamydocopiosa sp. nov. and Paraphoma pye sp. nov., two new species associated with leaf and crown infection of pyrethrum. Plant Pathol. 2018, 67, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).