Evaluating the Sustainability of Wheat–Maize System with a Long-Term Fertilization Experiment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
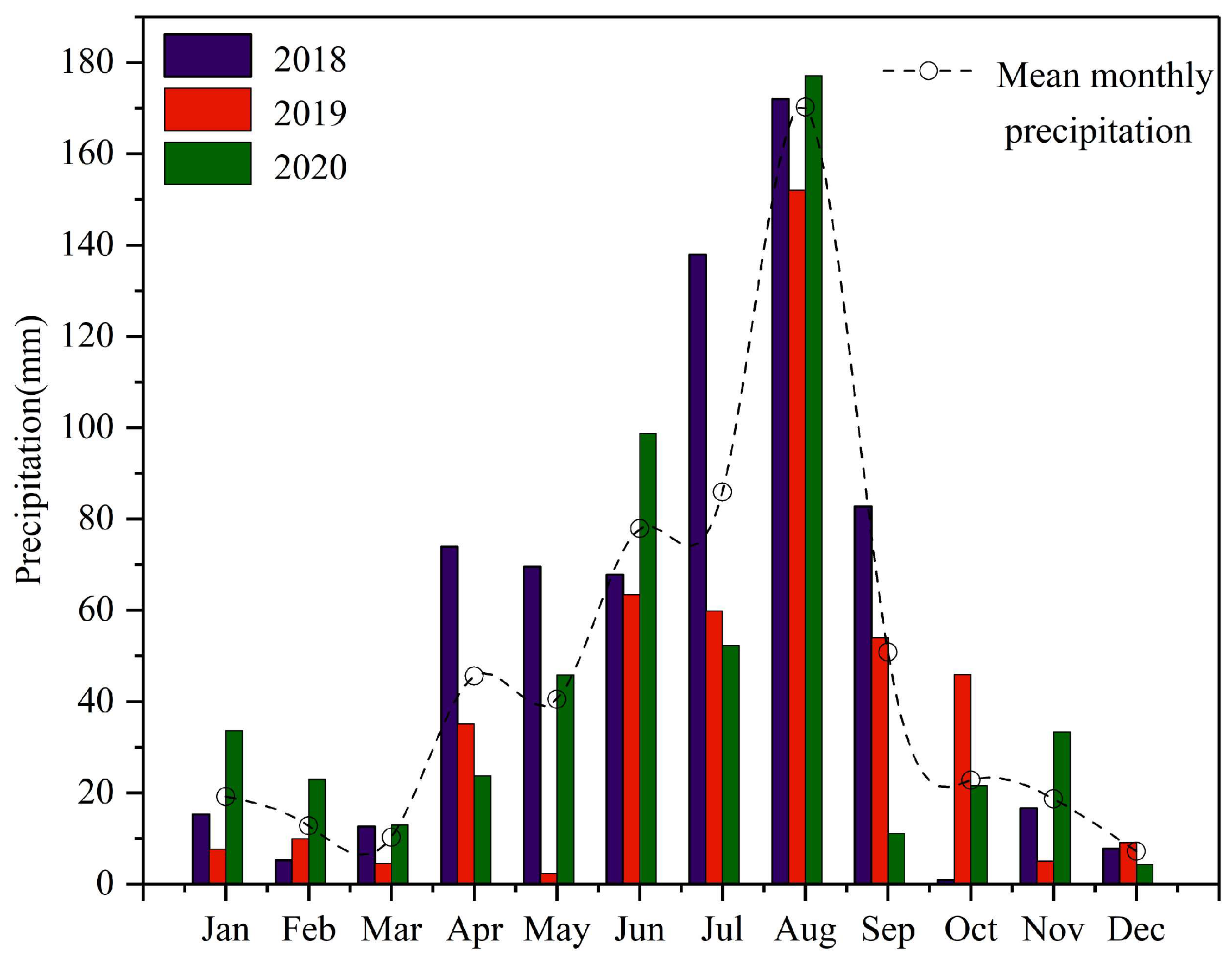
2.1. Profiles of Experimental Field
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Sample Collection and Measurement
2.4. Calculation of Soil Fertility Retention
2.5. Calculation of Crop Yield Stability
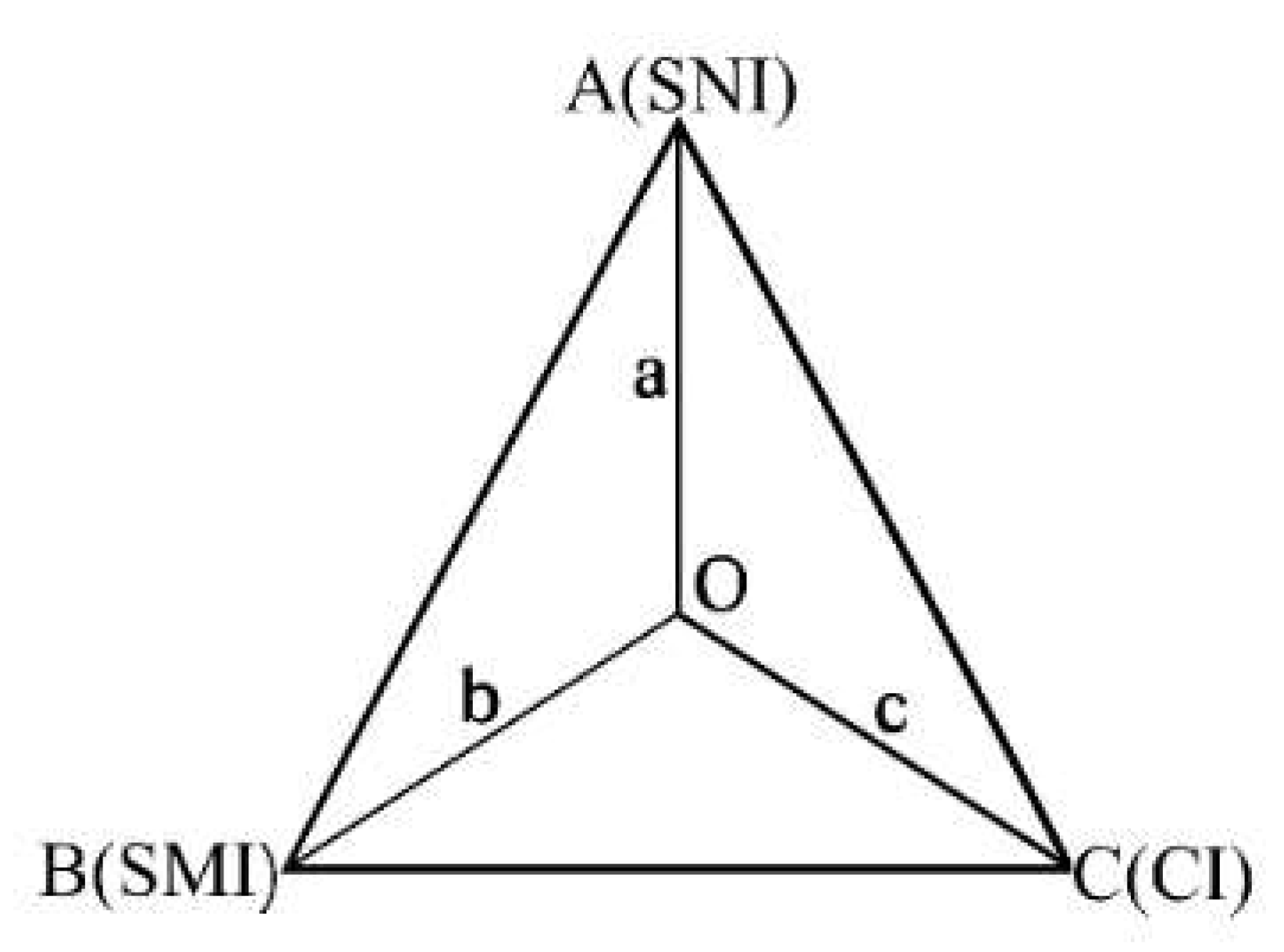
2.6. Calculation of the Sustainability Index
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
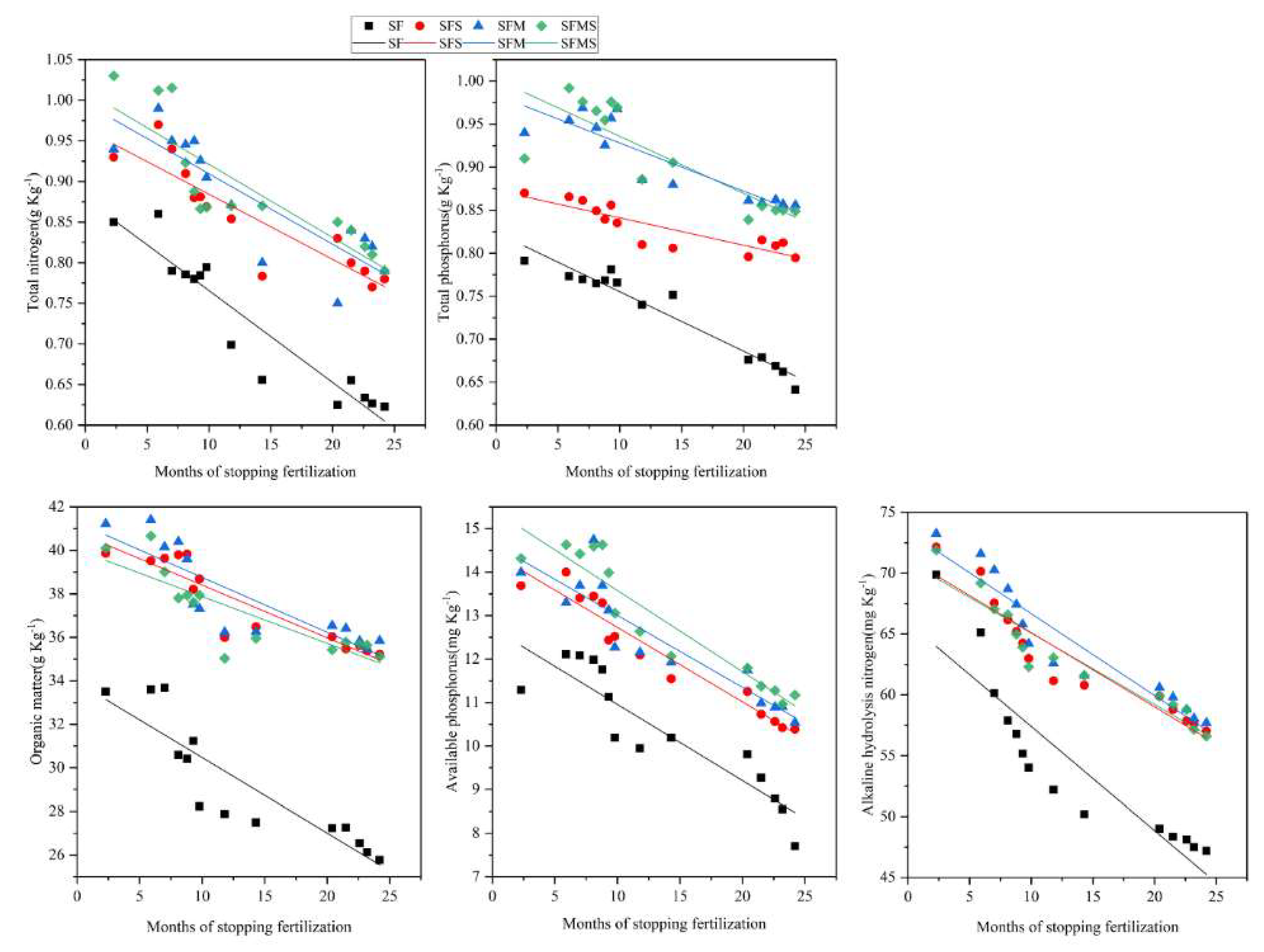
3.1. Effect of Long-Term Fertilization on Soil Nutrient Properties
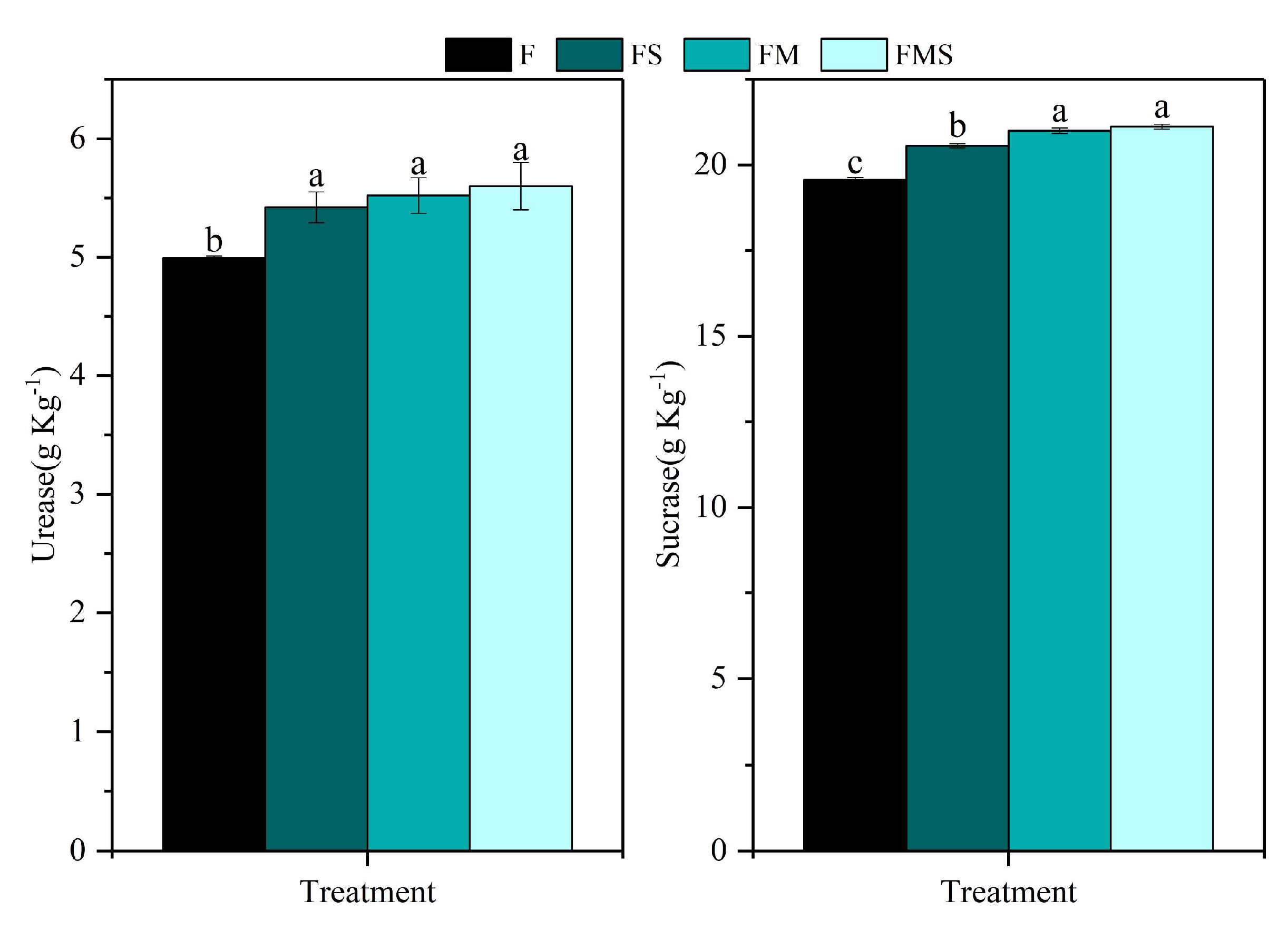
3.2. Effect of Long-Term Fertilization on Microbiological Properties of Soil
3.3. Effect of Long-Term Fertilization on Crop Yield
3.4. Effect of Long-Term Fertilization on the Sustainability Index
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Long-Term Fertilization on Soil Nutrient Properties
4.2. Effect of Long-Term Fertilization on Microbiological Properties of Soil
4.3. Impact of Long-Term Fertilization on Crop Yield and Sustainable Production
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, X.-X.; Huang, M.-M.; Liu, Y.; Si, T.; Zhang, X.-J.; Yu, X.-N.; Guo, F.; Wan, S.-B. Inclusion of peanut in wheat–maize rotation increases wheat yield and net return and improves soil organic carbon pool by optimizing bacterial community. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 3430–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Peng, M.; Hou, Z.; Li, J. Organic substitution contrasting direct fertilizer reduction increases wheat productivity, soil quality, microbial diversity and network complexity. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Stewart, B.A.; Zhang, F. Long-term experiments for sustainable nutrient management in China. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2011, 31, 397–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.-W.; Yang, F.; Feng, H.-X.; Wei, C.-Y. General characteristics of the chemical fertilizers and pesticides use and the analysis of use reduction effect in China. Environ. Pollut. Control 2019, 41, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, K.; Xi, B.; Tan, W.; Song, Q. Long-term application of nitrogen fertilizer alters the properties of dissolved soil organic matter and increases the accumulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Environ. Res. 2022, 215, 114267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, L. Economic and environmental sustainability of maize-wheat rotation production when substituting mineral fertilizers with manure in the North China Plain. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 271, 122683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainan, Z.; Ming, H.; Youjun, L.; Jinzhi, W.; Wenzhong, T.; Junhong, L.; Yuanquan, H.; Shanwei, W.; Jun, Z.; Zhenwang, Z.; et al. Combined Organic Fertilizer and Straw Return Enhanced Summer Maize Productivity and Optimized Soil Nitrate–N distribution in Rainfed Summer Maize–Winter Wheat Rotation on the Southeast Loess Plateau. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 23, 938–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltas, A.; Kebli, H.; Oberholzer, H.R.; Weisskopf, P.; Sinaj, S. The effects of organic and mineral fertilizers on carbon sequestration, soil properties, and crop yields from a long-term field experiment under a Swiss conventional farming system. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 926–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congzhi, Z.; Zhanhui, Z.; Fang, L.; Jiabao, Z. Effects of Organic and Inorganic Fertilization on Soil Organic Carbon and Enzymatic Activities. Agronomy 2022, 12, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Cao, C.; Chen, H. Long-term located fertilization causes the differences in root traits, rhizosphere soil biological characteristics and crop yield. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2021, 69, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chivenge, P.; Vanlauwe, B.; Six, J. Does the combined application of organic and mineral nutrient sources influence maize productivity? A meta-analysis. Plant Soil 2010, 342, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xi, Y.; Wu, X.; Pei, X.; Liang, G.; Bai, J.; Song, X.; Zhang, M.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; et al. Partial substitution of manure reduces nitrous oxide emission with maintained yield in a winter wheat crop. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 326, 116794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Lu, M.; Sun, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhao, J.; Fan, M. Effects of partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic manure on the activity of enzyme and soil bacterial communities in the mountain red soil. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1234904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhongkai, Z.; Siyu, Z.; Na, J.; Weiming, X.; Jianning, Z.; Dianlin, Y. Effects of organic fertilizer incorporation practices on crops yield, soil quality, and soil fauna feeding activity in the wheat-maize rotation system. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1058071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Feng, W.-T.; He, X.-H.; Zhu, P.; Gao, H.-J.; Sun, N.; Xu, M.-G. Chemical fertilizers could be completely replaced by manure to maintain high maize yield and soil organic carbon (SOC) when SOC reaches a threshold in the Northeast China Plain. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Yan, Y.; Cao, J.; Christie, P.; Zhang, F.; Fan, M. Effects of combined application of organic amendments and fertilizers on crop yield and soil organic matter: An integrated analysis of long-term experiments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 225, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Si, B.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Lu, X.; Chen, X.; Han, X.; Zhu, Y.; Zou, W. Drivers of soil quality and maize yield under long-term tillage and straw incorporation in Mollisols. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 246, 106360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Z.; Gao, H.-J.; Peng, C.; Li, Q.; Zhu, P.; Gao, Q. Variation trend of soil organic carbon, total nitrogen and the stability of maizeyield in black soil under long-term organic fertilization. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2019, 25, 1473–1481. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, M.; Panday, S.C.; Meena, V.S.; Singh, S.; Yadav, R.P.; Mahanta, D.; Mondal, T.; Mishra, P.K.; Bisht, J.K.; Pattanayak, A. Long-term effects of organic manure and inorganic fertilization on sustainability and chemical soil quality indicators of soybean-wheat cropping system in the Indian mid-Himalayas. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 257, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.S.; Beri, V.; Sidhu, B.S.; Rupela, O.P. A new index to assess soil quality and sustainability of wheat-based cropping systems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2005, 41, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.-R.; Tian, K. Expermental Tutorial of Soil Science; China forestry Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2012; p. 107. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.-D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; p. 495. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.-Y. Soil Enzyme and Its Research Method; Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 1986; p. 376. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.U.; Guo, Z.; Jiang, F.; Peng, X. Does straw return increase crop yield in the wheat-maize cropping system in China? A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2022, 279, 108447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Bao, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, R.; Sun, C.; Ma, D.; Chen, L.; Zou, H.; Zhang, J. Effects of fertilization applications on soil aggregate organic carbon content and assessment of their influencing factors: A meta-analysis. Catena 2024, 242, 108135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Yan, C.; Mei, X.; He, W.; Bing, S.H.; Ding, L.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Fan, T. Long-term effect of chemical fertilizer, straw, and manure on soil chemical and biological properties in northwest China. Geoderma 2010, 158, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Gao, W.; Huang, S.; Tang, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic amendments affects soil organic carbon composition and stability in a greenhouse vegetable production system. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Wang, D.; Guo, X.; Yang, T.; Oenema, O. Productivity and sustainability of rainfed wheat-soybean system in the North China Plain: Results from a long-term experiment and crop modelling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongyu, G.; Xinyue, Z.; Zhuolei, T.; Yu, Z.; Kaifeng, H. Effects of Rice Straw Combined with Inorganic Fertilizer on Grain Filling and Yield of Common Buckwheat. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Hu, C.-S.; Dong, W.-X.; Li, X.-X.; Liu, X.-P.; Zhang, X.-P.; Zhang, L.-J.; Wen, H.-D. Effects of long-term nutrient recycling pathways on soil nutrient dynamics and fertility in farmland. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2022, 30, 937–951. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, T.; Lei, X.-Y.; Cui, X.-W.; Lu, Y.-X.; Fan, P.-F.; Long, S.-P.; Huang, J.; Gao, J.-S.; Zhang, Z.-H.; et al. Improvement of soil fertility and rice yield after long-term application of cow manure combined with inorganic fertilizers. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Dheri, G.S.; Benbi, D.K. Effect of long-term fertilization in maize-wheat cropping system on carbon mineralization in soil. Carbon Manag. 2019, 10, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Li, W.; Sheng, L. Effects of long-term application of organic fertilizer on improving organic matter content and retarding acidity in red soil from China. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, M.; Fahad, S.; Khan, I.A.; Saeed, M.; Ihsan, M.Z.; Saud, S.; Riaz, M.; Wang, D.; Wu, C. Integration of poultry manure and phosphate solubilizing bacteria improved availability of Ca bound P in calcareous soils. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, X.; He, H.; Cheng, L.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Yu, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. Combined Application of Chemical and Organic Fertilizers: Effects on Yield and Soil Nutrients in Spring Wheat under Drip Irrigation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.-C.; Gao, P.-D.; Wang, B.-Q.; Lin, W.-P.; Jiang, N.-H.; Cai, K.-Z. Impacts of chemical fertilizer reduction and organic amendments supplementation on soil nutrient, enzyme activity and heavy metal content. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 1819–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, A.; He, L.; Ali, I.; Ullah, S.; Khan, A.; Khan, A.; Akhtar, K.; Wei, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, J.; et al. Manure combined with chemical fertilizer increases rice productivity by improving soil health, post-anthesis biomass yield, and nitrogen metabolism. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, X.; Wei, T.; Yang, Z.; Jia, Z.; Yang, B.; Han, Q.; Ren, X. Effects of straw incorporation on the soil nutrient contents, enzyme activities, and crop yield in a semiarid region of China. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 160, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Christie, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Maize yield and soil fertility with combined use of compost and inorganic fertilizers on a calcareous soil on the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 155, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Gao, C.; Zhang, S.; Tang, D.W.S. Soil enzyme activities, soil physical properties, photosynthetic physical characteristics and water use of winter wheat after long-term straw mulch and organic fertilizer application. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1186376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Gu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, H.; Mao, W.; Yang, H.; Mi, W.; Zhao, H. Effects of Organic Fertilizer Combined with Chemical Fertilizer on Nutrients, Enzyme Activities, and Rice Yield in Reclaimed Soil. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2022, 53, 3060–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, P.; Li, R.; Zheng, H.; Wang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, J.; Liu, W. Long-Term Conservation Tillage Practices Directly and Indirectly Affect Soil Micro-Food Web in a Chinese Mollisol. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo, F.S.; Strock, J.S.; Pagliari, P.H. Impacts of corn stover management and fertilizer application on soil nutrient availability and enzymatic activity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borase, D.N.; Nath, C.P.; Hazra, K.K.; Senthilkumar, M.; Singh, S.S.; Praharaj, C.S.; Singh, U.; Kumar, N. Long-term impact of diversified crop rotations and nutrient management practices on soil microbial functions and soil enzymes activity. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, F. Effects of shallow groundwater table and fertilization level on soil physico-chemical properties, enzyme activities, and winter wheat yield. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 208, 307–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linag, L.; Zhang, W.-J.; Xu, B.-H.; Zhuang, Q.-L.; Jiang, X.-F.; Huang, Y.-B. Research Progress on Effects of Combined Application of Organic and Inorganic Fertilizers on Soil Fertility and Soil Environment. J. Henan Agric. Sci. 2022, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maaz, T.M.; Sapkota, T.B.; Eagle, A.J.; Kantar, M.B.; Bruulsema, T.W.; Majumdar, K. Meta-analysis of yield and nitrous oxide outcomes for nitrogen management in agriculture. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2343–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainju, U.M.; Liptzin, D.; Ghimire, R.; Dangi, S. Relationship between soil carbon and nitrogen, soil properties, and dryland crop yields. Agron. J. 2021, 114, 395–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Shah, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Peng, S.; Nie, L. Effect of straw returning on soil organic carbon in rice–wheat rotation system: A review. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Bian, Q.; Dong, Z.; Rao, X.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Y.; Chen, B. The input of organic fertilizer can improve soil physicochemical properties and increase cotton yield in southern Xinjiang. Front. Plant Sci. 2025, 15, 1520272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, W.; Luo, P.; An, N.; Cai, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, K.; Yang, J.; Han, X. Manure application increased crop yields by promoting nitrogen use efficiency in the soils of 40-year soybean-maize rotation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Du, W.; Zhang, L.; Dong, Z. Effects of Sheep Manure Combined with Chemical Fertilizers on Maize Yield and Quality and Spatial and Temporal Distribution of Soil Inorganic Nitrogen. Complexity 2021, 2021, 4330666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welbaum, G.E.; Sturz, A.V.; Dong, Z.; Nowak, J. Managing Soil Microorganisms to Improve Productivity of Agro-Ecosystems. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2004, 23, 175–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhang, Z.S.; Gao, H.Y.; Liu, P.; Dong, S.T.; Zhang, J.W.; Zhao, B. Effects of nitrogen on photosynthetic characteristics of leaves from two different stay-green corn (Zea mays L.) varieties at the grain-filling stage. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 92, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | Total Nitrogen (g Kg−1) | Total Phosphorus (g Kg−1) | Organic Matter (g Kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg Kg−1) | Alkaline Hydrolysis Nitrogen (mg Kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | 0.93 ± 0.03c | 0.79 ± 0.01c | 33.56 ± 0.05c | 11.01 ± 0.04c | 70.54 ± 0.18c |
| FS | 1.03 ± 0.02b | 0.84 ± 0.01b | 39.49 ± 0.02b | 13.69 ± 0.20b | 72.49 ± 0.16b |
| FM | 1.10 ± 0.01a | 0.86 ± 0.01ab | 40.13 ± 0.03a | 13.99 ± 0.06ab | 73.59 ± 0.24a |
| FMS | 1.00 ± 0.02b | 0.88 ± 0.01a | 40.16 ± 0.09a | 14.32 ± 0.13a | 72.23 ± 0.13b |
| Treatment | Organic Matter (g Kg−1) | Total Nitrogen (g Kg−1) | Total Phosphorus (g Kg−1) | Alkaline Hydrolysis Nitrogen (mg Kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg Kg−1) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Value | Slope | R2 | Change Trend | Mean Value | Slope | R2 | Change Trend | Mean Value | Slope | R2 | Change Trend | Mean Value | Slope | R2 | Change Trend | Mean Value | Slope | R2 | Change Trend | |
| SF | 29.25 | −0.3468 | 0.79 ** | Decrease | 0.73 | −0.0113 | 0.89 ** | Decrease | 0.73 | −0.0069 | 0.94 ** | Decrease | 54.39 | −0.1752 | 0.81 ** | Decrease | 10.34 | −0.5874 | 0.81 ** | Decrease |
| SFS | 37.55 | −0.2425 | 0.83 ** | Decrease | 0.86 | −0.0080 | 0.80 ** | Decrease | 0.83 | −0.0032 | 0.76 ** | Decrease | 62.97 | −0.1713 | 0.88 ** | Decrease | 12.13 | −0.6733 | 0.93 ** | Decrease |
| SFM | 37.87 | −0.2526 | 0.71 ** | Decrease | 0.88 | −0.0087 | 0.73 ** | Decrease | 0.91 | −0.0056 | 0.78 ** | Decrease | 64.31 | −0.1656 | 0.90 ** | Decrease | 12.43 | −0.6101 | 0.82 ** | Decrease |
| SFMS | 37.12 | −0.2155 | 0.70 ** | Decrease | 0.89 | −0.0090 | 0.72 ** | Decrease | 0.91 | −0.0066 | 0.85 ** | Decrease | 63.01 | −0.1867 | 0.90 ** | Decrease | 12.92 | −0.8542 | 0.88 ** | Decrease |
| Treatment | Urease (g Kg−1) | Sucrase (g Kg−1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Value | Slope | R2 | Change | Mean Value | Slope | R2 | Change | |
| SF | 3.91 | −0.0671 | 0.89 ** | Decrease | 14.93 | −0.2680 | 0.88 ** | Decrease |
| SFS | 4.68 | −0.0513 | 0.84 ** | Decrease | 16.82 | −0.1832 | 0.77 ** | Decrease |
| SFM | 4.87 | −0.0433 | 0.61 ** | Decrease | 17.32 | −0.2301 | 0.92 ** | Decrease |
| SFMS | 4.76 | −0.0636 | 0.89 ** | Decrease | 17.94 | −0.2274 | 0.91 ** | Decrease |
| Treatment | Average Production for 2007–2018 | Treatment | 2019 (Wheat) | 2019 (Maize) | 2020 (Wheat) | 2020 (Maize) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat | Maize | Crop Yield (kg ha−1) | Sustainability Index | Crop Yield (kg ha−1) | Sustainability Index | Crop Yield (kg ha−1) | Sustainability Index | Crop Yield (kg ha−1) | Sustainability Index | ||
| F | 6986.67 | 8862.50 | SF | 6105.00c | 0.87 | 8461.00b | 0.95 | 5872.00c | 0.84 | 7461.00c | 0.84 |
| FS | 7931.67 | 9283.0 | SFS | 7743.35b | 0.98 | 9034.0a | 0.97 | 7389.25b | 0.93 | 8683.00b | 0.94 |
| FM | 8134.5 | 9082.50 | SFM | 7821.46ab | 0.96 | 8925.00a | 0.98 | 7523.75a | 0.92 | 8749.00a | 0.96 |
| FMS | 8103 | 9123.00 | SFMS | 7916.00a | 0.98 | 9070.00a | 0.99 | 7550.00a | 0.93 | 8735.00a | 0.96 |
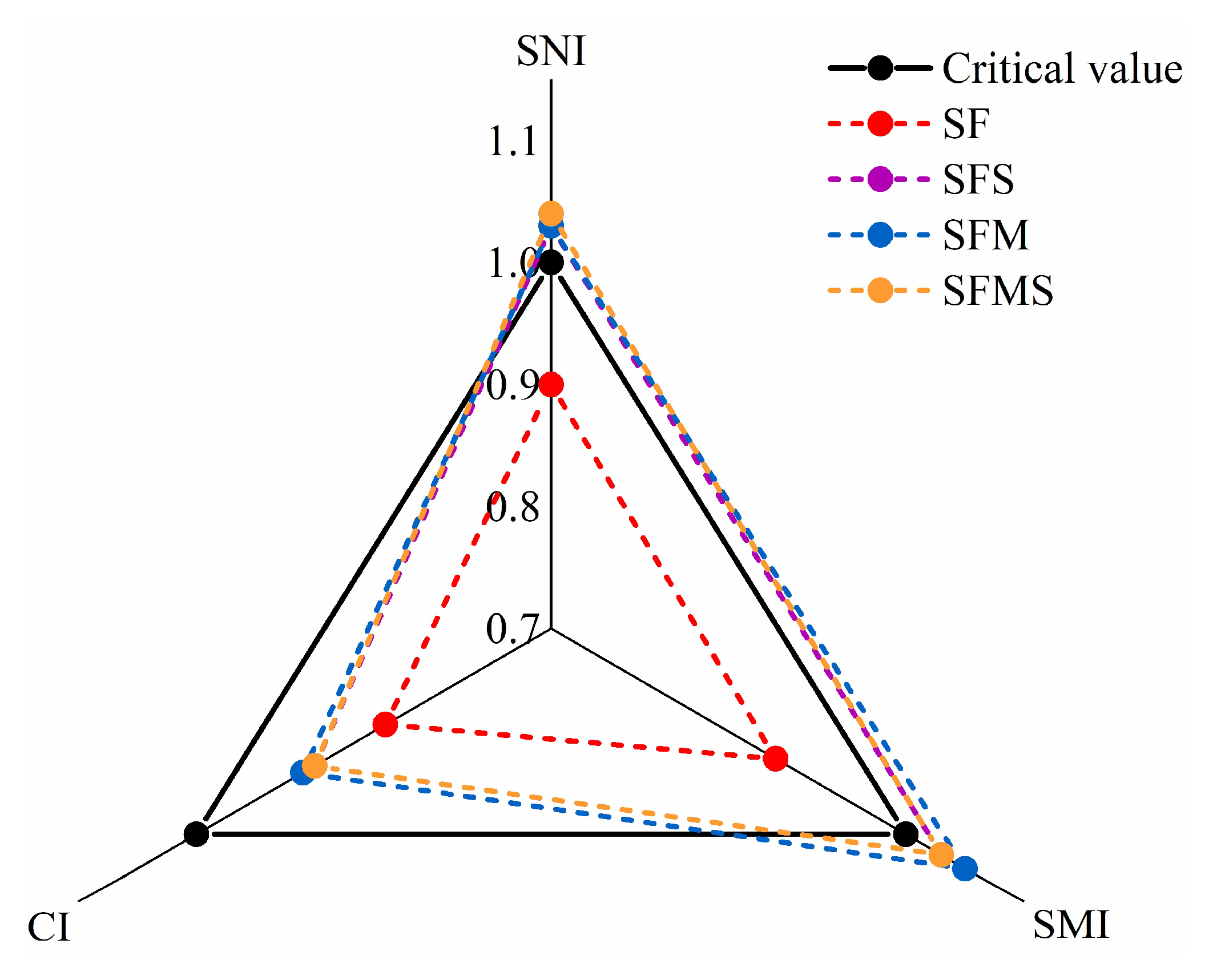
| Treatment | Soil Nutrient Index | Soil Microbial Index | Crop Index | Sustainability Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF | 0.90 | 0.89 | 0.84 | 1.00 |
| SFS | 1.03 | 1.03 | 0.90 | 1.26 |
| SFM | 1.03 | 1.05 | 0.91 | 1.29 |
| SFMS | 1.04 | 1.03 | 0.91 | 1.27 |
| critical value | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.30 |
| CV (%) | 6.67% | 7.45% | 3.84% | 11.62% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shao, Y.; An, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, S.; Meng, Y.; Gao, Y.; Ma, S. Evaluating the Sustainability of Wheat–Maize System with a Long-Term Fertilization Experiment. Agronomy 2025, 15, 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010210
Shao Y, An J, Wang X, Ma S, Meng Y, Gao Y, Ma S. Evaluating the Sustainability of Wheat–Maize System with a Long-Term Fertilization Experiment. Agronomy. 2025; 15(1):210. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010210
Chicago/Turabian StyleShao, Yun, Jiahui An, Xueping Wang, Shouchen Ma, Ye Meng, Yang Gao, and Shoutian Ma. 2025. "Evaluating the Sustainability of Wheat–Maize System with a Long-Term Fertilization Experiment" Agronomy 15, no. 1: 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010210
APA StyleShao, Y., An, J., Wang, X., Ma, S., Meng, Y., Gao, Y., & Ma, S. (2025). Evaluating the Sustainability of Wheat–Maize System with a Long-Term Fertilization Experiment. Agronomy, 15(1), 210. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010210










