Cultivated Grassland Types Differently Affected Carbon Flux Downstream of the Yellow River
(This article belongs to the Section Agroecology Innovation: Achieving System Resilience)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
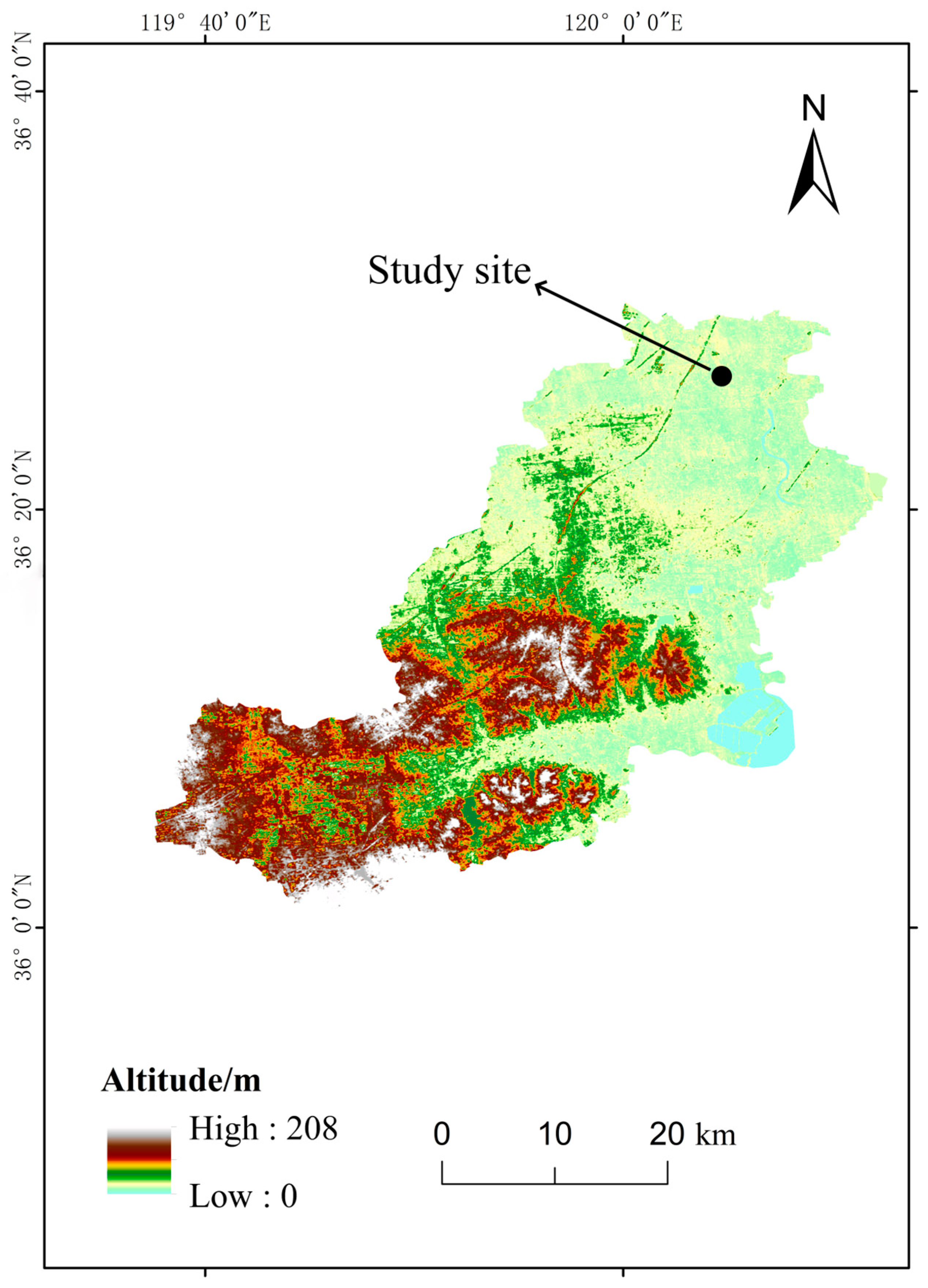
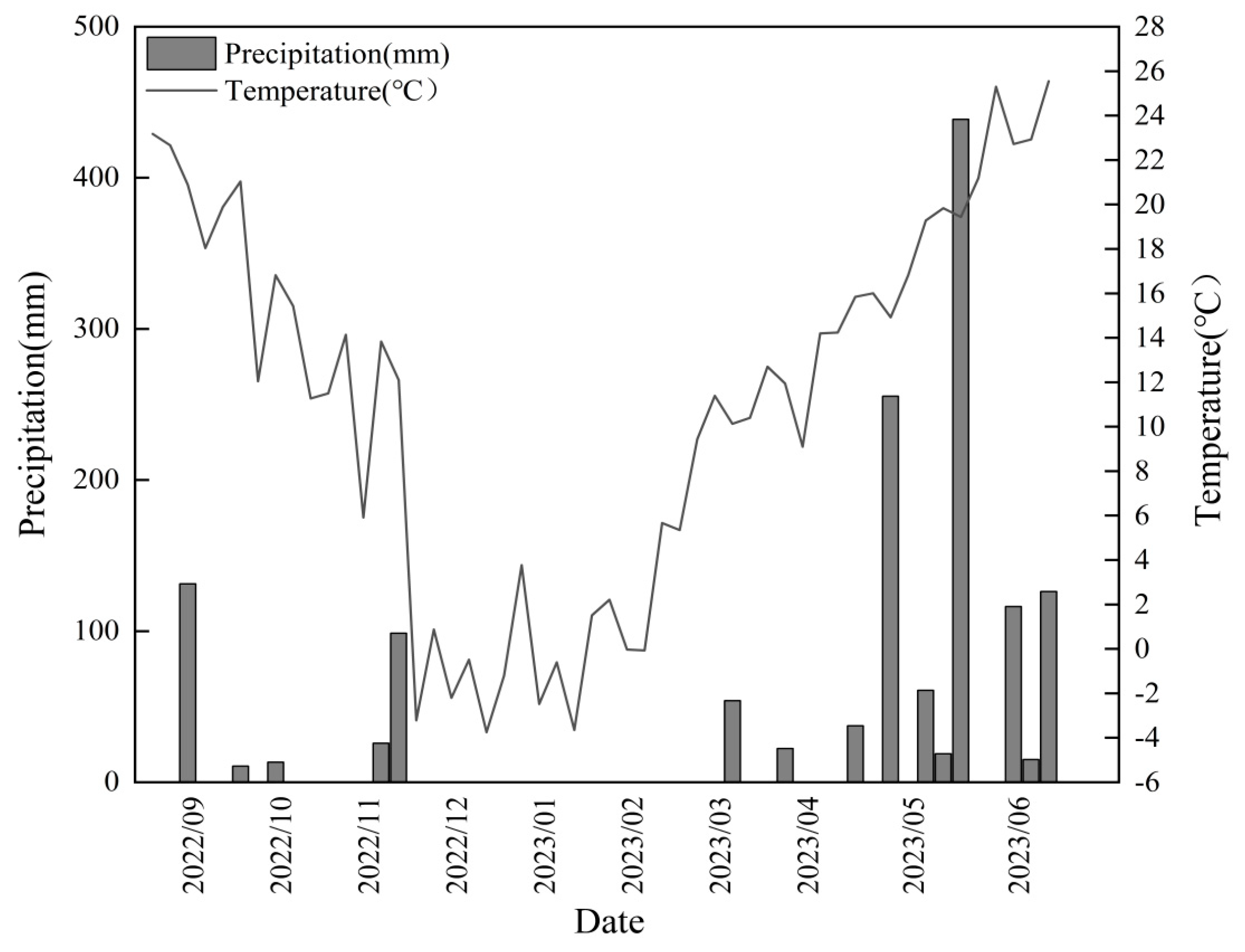
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experiment Design
2.3. Measurement of CO2 Flux
2.4. Soil Physicochemical Property Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
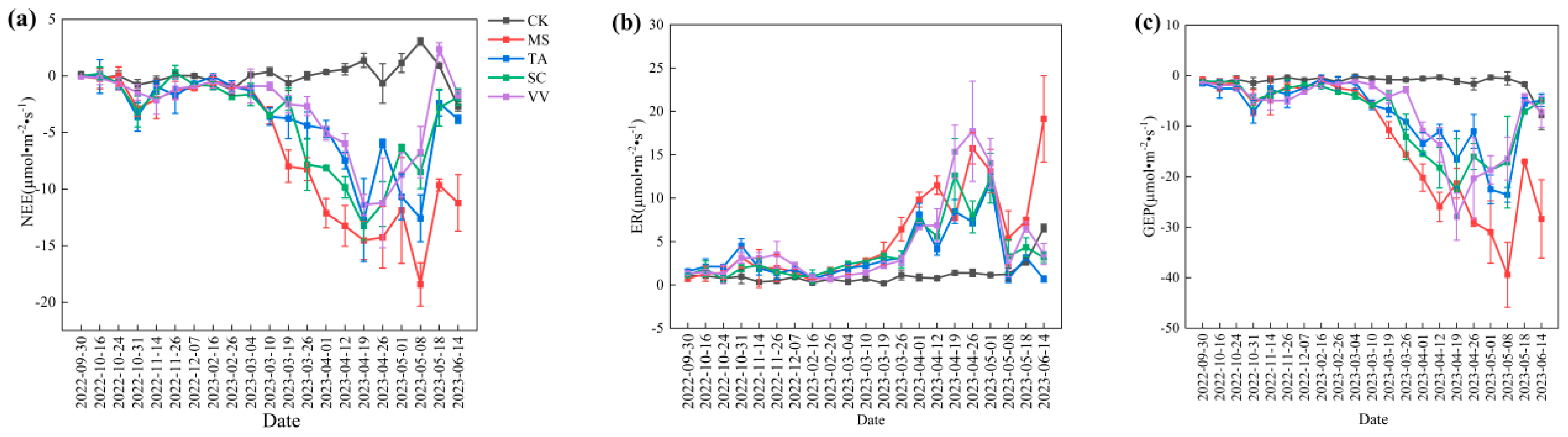
3.1. Treatment Effects on NEE, ER and GEP
3.2. Treatment Effects on Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.3. Factors Affecting CO2 Flux
4. Discussion
4.1. Variation in the Characteristics of Carbon Flux in Cultivated Grasslands
4.2. Effects of Environmental Factors on Carbon Fluxes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Lu, Y.; Wei, X. Effects of rainfall amount and frequency on carbon exchange in a wet meadow ecosystem on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Catena 2022, 219, 106629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Han, H.; Du, Y.; Hui, D.; Xia, J.; Niu, S.; Li, X.; Wan, S. Effects of warming and increased precipitation on net ecosystem productivity: A long-term manipulative experiment in a semiarid grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 232, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjurjav, H.; Hu, G.; Wan, Y.; Li, Y.; Danjiu, L.; Gao, Q. Different responses of ecosystem carbon exchange to warming in three types of alpine grassland on the central Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 8, 1507–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.J.; Li, L.F.; Biederman, J.A.; Hao, Y.B.; Zhang, H.; Kang, X.M.; Cui, X.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Li, M.W.; Xu, Z.H.; et al. Repackaging precipitation into fewer, larger storms reduces ecosystem exchanges of CO2 and H2O in a semiarid steppe. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 247, 356–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.H.; Mou, W.B.; Wang, X.J.; Zhang, R.Y.; Gao, T.P.; Ai, D.X.C.; Yuan, J.L.; Zhang, R.Y.; Fang, X.W. Consistent responses of ecosystem CO2 exchange to grassland degradation in alpine meadow of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Li, G.; Yan, L.J.; Wu, J.Q.; Li, J.; Liu, S.A.; Lu, Y.H. Effects of different vegetation types on ecosystem respiration in semiarid Loess Hilly Region, Central Gansu Province, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Were, D.; Kansiime, F.; Fetahi, T.; Cooper, A.; Jjuuko, C. Carbon Sequestration by Wetlands: A Critical Review of Enhancement Measures for Climate Change Mitigation. Earth Syst. Environ. 2019, 3, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, D.; Zhou, W.-J.; Ji, H.-L.; Grace, J.; Bai, X.-L.; Song, Q.-H.; Liu, Y.-T.; Sha, L.-Q.; Fei, X.-H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Environmental and management controls of soil carbon storage in grasslands of southwestern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 254, 109810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Quesada, B.; Xia, L.; Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Goodale, C.L.; Kiese, R. Effects of climate warming on carbon fluxes in grasslands—A global meta-analysis. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2019, 25, 1839–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dangal, S.R.S.; Tian, H.Q.; Pan, S.F.; Zhang, L.; Xu, R.T. Greenhouse gas balance in global pasturelands and rangelands. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 104006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.F.; Cotrufo, M.F. Grassland soil carbon sequestration: Current understanding, challenges, and solutions. Science 2022, 377, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poncehernandez, R.J.W.P. A Modelling Framework for Addressing the Synergies between Global Conventions through Land Use Changes: Carbon Sequestration, Biodiversity Conservation, Prevention of Land Degradation and Food Security in Agricultural and Forested Lands in Developing Count. In Working Papers; Trent University: Peterborough, ON, Canada, 2007; Volume 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, B.Y.; Yan, H.M.; Liu, H.; Pan, L.H.; Feng, Z.M. Keep sustainable livestock production without Grassland degradation: Future cultivated pasture development simulation based on agent-based model. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 417, 138072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuaijun, H. Effects of Multiple Mowing on Forage Yield and Greenhouse Gas Emissions of Sown Grassland on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau Cultivated Grassland. Master’s Thesis, Lanzhou University, Lanzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, F. Adaptation of mixed crop-livestock systems in Asia. CABI 2014, 5, 155–166. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tian, F.; Jia, P.; Zhang, J.; Hou, F.; Wu, G. Leguminous species sequester more carbon than gramineous species in cultivated grasslands of a semi-arid area. Solid Earth 2017, 8, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soussana, J.F.; Allard, V.; Pilegaard, K.; Ambus, P.; Domingues, R. Full accounting of the greenhouse gas (CO2, N2O, CH4) budget of nine European grassland sites. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2007, 121, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhai, X.; Wilkes, A.; Han, G.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhou, P.; Wang, K.; et al. Changes of soil CO2 flux under different stocking rates during spring-thaw period in a northern desert steppe, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, W. Study on Carbon Flux and Its Controlling Mechanisms in a Degraded Alpine Meadow and an Artificial Pasture in the Three-River Source Region of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau; Nankai University: Tianjin, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.S.; Cao, L.; Bai, Y.F.; Xin, X.P.; Zhou, Y.; Xie, Z.G.; Hu, T.M.; Yang, P.Z. Dynamics of SOC density and driving factors during the restoration of artificial grassland and abandoned farmland in Mu Us Desert, China. Catena 2023, 224, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Treuren, R.; Bas, N.; Goossens, P.J.; Jansen, J.; Van Soest, L.J.M. Genetic diversity in perennial ryegrass and white clover among old Dutch grasslands as compared to cultivars and nature reserves. Mol. Ecol. 2005, 14, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, S.X.; Chi, Y.G.; Yang, X.J.; Li, W.H.; Lan, Z.C.; Bai, Y.F. Direct and indirect effects of nitrogen enrichment and grazing on grassland productivity through intraspecific trait variability. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 598–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagle, P.; Xiao, X.; Scott, R.L.; Kolb, T.E.; Cook, D.R.; Brunsell, N.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Basara, J.; Matamala, R.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Biophysical controls on carbon and water vapor fluxes across a grassland climatic gradient in the United States. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 214, 293–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Ma, Y.; Luo, Y.; Hu, Z.; Li, F.; Li, Y.; Gu, L.; Li, Z.; Yuan, L. Carbon fluxes and environmental controls across different alpine grassland types on the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 311, 108694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Li, Y.; Yun, H.; Wang, X.; Gong, X.; Duan, Y.; Liu, J. Variations in diurnal and seasonal net ecosystem carbon dioxide exchange in a semiarid sandy grassland ecosystem in China’s Horqin Sandy Land. Biogeosciences 2020, 17, 6309–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Li, T.; Wang, D.; Wang, F.; Fu, B.; Liu, G.; Lv, Y. Soil properties mediate the freeze-thaw-related soil N2O and CO2 emissions from temperate grasslands. Catena 2020, 195, 104797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.B.; Zhou, C.T.; Liu, W.J.; Li, L.F.; Kang, X.M.; Jiang, L.L.; Cui, X.Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhou, X.Q.; Xu, C.Y. Aboveground net primary productivity and carbon balance remain stable under extreme precipitation events in a semiarid steppe ecosystem. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 240, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Quan, Q.; Chen, W.; Tian, D.; Ciais, P.; Crowther, T.W.; Mack, M.C.; Poulter, B.; Tian, H.; Luo, Y.; et al. Increased CO2 emissions surpass reductions of non-CO2 emissions more under higher experimental warming in an alpine meadow. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 769, 144559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, B.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Cao, F. Vertical and seasonal variations of soil carbon pools in ginkgo agroforestry systems in eastern China. Catena 2018, 171, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Wu, J.; Gong, Y.; Wei, X.; Lu, Y. Responses of CH4 flux and microbial diversity to changes in rainfall amount and frequencies in a wet meadow in the Tibetan Plateau. Catena 2021, 202, 105253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, U.K.; Sonon, L.; Biswas, B.K. A Comparison of Diffusion-Conductimetric and Distillation-Titration Methods in Analyzing Ammonium- and Nitrate-Nitrogen in the KCl-Extracts of Georgia Soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Chen, S.; Huang, J.; Lin, G.J.G.C.B. Water regulated effects of photosynthetic substrate supply on soil respiration in a semiarid steppe. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2011, 17, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui-Lin, X.; Xi-Jian, Z.J.S.; Sciences, E. Effects of Soil Warming on Some Soil Chemical Properties. Soil Environ. Sci. 2000, 9, 316–321. [Google Scholar]
- Hong-Ai, S.; Lu-Jun, L.I.; Meng-Yang, Y.; Jiao, D.; Shuai, W.; Zeng, X. Impact of Soil Temperature and Moisture on Soil N2O Emission from Mollisols under Different Land-use Types. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2013, 32, 2286–2292. [Google Scholar]
- Heisler-White, J.L.; Blair, J.M.; Kelly, E.F.; Harmoney, K.; Knapp, A.K.J.B.P.L. Contingent productivity responses to more extreme rainfall regimes across a grassland biome. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2009, 15, 2894–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Chang, Q.-R.; Qi, Y.-B.; Liu, J.; Chen, T. Aggregation and soil organic carbon fractions under different land uses on the tableland of the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2014, 115, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larondelle, N.; Haase, D. Urban ecosystem services assessment along a rural-urban gradient: A cross-analysis of European cities. Ecol. Indic. 2013, 29, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinther, F.P.; Eiland, F.; Lind, A.M.; Elsgaard, L. Microbial biomass and numbers of denitriers related to macropore channels in agricultural and forest soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1999, 31, 0–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.B.; Wang, D.L.; Shi, B.K.; Sun, W. Differential effects of grazing, water, and nitrogen addition on soil respiration and its components in a meadow steppe. Plant Soil 2020, 447, 581–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzluebbers, A.J.; Haney, R.L.; Honeycutt, C.W.; Arshad, M.A.; Schomberg, H.H.; Hons, F.M. Climatic influences on active fractions of soil organic matter. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Qi, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Z.; Li, L. Effects of biochar addition on CO2 and CH4 emissions from a cultivated sandy loam soil during freeze-thaw cycles. Plant Soil Environ. 2017, 63, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Kang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, K.; Kang, E.; Yan, Z.; Li, M.; Wang, X.; Niu, Y.; et al. Alpine wetland degradation reduces carbon sequestration in the Zoige Plateau, China. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2022, 10, 980441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinsinger, P. Bioavailability of Trace Elements as related to Root-Induced Chemical Changes in the Rhizosphere. Plant Soil 2001, 237, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, H.J.; Yang, J.Q.; Hao, J.; Yan, X.D.; Dong, K.H.; Wang, C.H. Seasonal precipitation regulates magnitude and direction of the effect of nitrogen addition on net ecosystem CO2 exchange in saline-alkaline grassland of northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 877, 162907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.; Xie, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Shen, X.J.A.e.S. Effect of annual variation in soil pH on available soil nutrients in pear orchards. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2011, 31, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Can, C. Effects of Green Fertilizer Cover on Soil Erosion Prevention and Heavy Metal Pollution Control in Purple Soil Citrus Orchard. Ph.D. Thesis, Southwest University, El Paso, TX, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z. Effects of Earthworm Fertilizer on Soil Properties and Growth of Leymus chinensis in Mu Us Sandy Land; YU LIN University: Yulin, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicke, M.; Picon-Cochard, C.; Morvan-Bertrand, A.; Prud’homme, M.-P.; Volaire, F. What functional strategies drive drought survival and recovery of perennial species from upland grassland? Ann. Bot. 2015, 116, 1001–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correa-Araneda, F.J.; Urrutia, J.; Soto-Mora, Y.; Figueroa, R.; Hauenstein, E. Effects of the hydroperiod on the vegetative and community structure of freshwater forested wetlands, Chile. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2012, 27, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vannoppen, W.; De Baets, S.; Keeble, J.; Dong, Y.; Poesen, J. How do root and soil characteristics affect the erosion-reducing potential of plant species? Ecol. Eng. 2017, 109, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassink, J. Density fractions of soil macroorganic matter and microbial biomass as predictors of C and N mineralization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1995, 27, 0–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.M.; Kay, B.D. Rotation and tillage effects on soil organic carbon sequestration in a typic Hapludalf in Southern Ontario. Soil Tillage Res. 2001, 59, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatments | pH | BD (g·cm−3) | SOC (g·kg−1) | TN (g·kg−1) | NH4+ -N (mg·kg−1) | NO3_ N (mg·kg−1) | MBC (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | 6.33 ± 0.54 a | 1.68 ± 0.05 a | 5.52 ± 0.79 b | 1.24 ± 0.04 a | 5.45 ± 0.95 a | 7.85 ± 3.16 a | 237.68 ± 27.80 c |
| MS | 5.87 ± 0.40 a | 1.53 ± 0.11 b | 10.26 ± 0.54 a | 1.23 ± 0.12 a | 6.37 ± 1.13 a | 9.80 ± 1.95 a | 1030.02 ± 44.29 a |
| TA | 6.17 ± 0.50 a | 1.61 ± 0.08 ab | 11.64 ± 1.67 a | 1.28 ± 0.06 a | 6.61 ± 0.44 a | 1.43 ± 0.26 b | 873.50 ± 166.35 ab |
| SC | 6.14 ± 0.36 a | 1.61 ± 0.02 ab | 11.83 ± 0.03 a | 1.26 ± 0.03 a | 6.32 ± 1.05 a | 1.24 ± 0.09 b | 691.76 ± 51.21 b |
| VV | 6.24 ± 0.45 a | 1.63 ± 0.14 ab | 11.12 ± 0.60 a | 1.25 ± 0.02 a | 7.72 ± 2.01 a | 4.05 ± 2.50 b | 770.31 ± 175.48 b |
| Dependent Variables | Step Regression Equation | R2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| NEE | y = −11.653x1 + 0.409x2 − 1.847x3 + 29.454 | 0.776 | <0.01 |
| ER | y = −8.160x1 + 0.316x2 + 0.003x4 + 12.070 | 0.798 | <0.05 |
| GEP | y = −19.954x1 + 0.663x2 + 0.005x4 + 29.025 | 0.729 | <0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Qu, X.; Li, M.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Z. Cultivated Grassland Types Differently Affected Carbon Flux Downstream of the Yellow River. Agronomy 2024, 14, 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050974
Wang Y, Qu X, Li M, Sun J, Zhang Z. Cultivated Grassland Types Differently Affected Carbon Flux Downstream of the Yellow River. Agronomy. 2024; 14(5):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050974
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yibo, Xudong Qu, Meixuan Li, Juan Sun, and Zhenchao Zhang. 2024. "Cultivated Grassland Types Differently Affected Carbon Flux Downstream of the Yellow River" Agronomy 14, no. 5: 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050974
APA StyleWang, Y., Qu, X., Li, M., Sun, J., & Zhang, Z. (2024). Cultivated Grassland Types Differently Affected Carbon Flux Downstream of the Yellow River. Agronomy, 14(5), 974. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050974





