Abstract
Conventional fertilizer management can destroy the structure of soil. Replacing chemical fertilizers with organic fertilizers can improve soil quality and nitrogen use efficiency. We aimed to study the effects of organic fertilizer substitutions for chemical nitrogen fertilizer on soil fertility and nitrogen use efficiency in order to clarify the effectiveness of the available nutrient management measures in improving soil quality and increasing foxtail millet yield. A field experiment was carried out over two consecutive years, and a total of six treatments were set up: no fertilizer (CK), chemical nitrogen fertilizer alone (N), the substitution of 25% of chemical nitrogen fertilizer with bio-organic fertilizer (N25A1), the substitution of 25% of chemical nitrogen fertilizer with fermented mealworm manure (N25B1), the substitution of 50% of chemical nitrogen fertilizer with bio-organic fertilizer (N50A2), and the substitution of 50% of chemical nitrogen fertilizer with fermented mealworm manure (N50B2). The results of this study show the following: (1) Compared with chemical nitrogen fertilizer, the substitution of organic fertilizer for nitrogen fertilizer reduced the bulk density and solid phase of the soil, and it increased the total porosity, water content, liquid phase, and gas phase of the soil. (2) Compared with nitrogen fertilizer, the use of an organic fertilizer increased the contents of nitrate nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen, and total nitrogen in the soil by 13.59~52.56%, 4.47~18.27%, and 4.40~12.09%, respectively. The content of alkaline nitrogen increased by 1.70~32.37%, and the contents of soil available potassium, available phosphorus, and organic matter also increased. (3) The activities of sucrase, urease, glutaminase, and asparaginase were improved by replacing chemical nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizer. The N25 treatments performed better than the N50 treatments, and fermented mealworm manure performed better than biological organic fertilizer. (4) A moderate application of organic fertilizer (N25) can increase the grain yield, ear weight, grain weight, and 1000-grain weight of foxtail millet, whereas excessive application of organic fertilizer (N50) can reduce foxtail millet yield. (5) Replacing chemical nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizer can improve the agronomic use efficiency, physiological efficiency, biased productivity, harvest index, and apparent use efficiency of nitrogen fertilizer. In this study, the substitution of 25% of chemical nitrogen fertilizer with fermented mealworm manure was the best combination for restoring crop productivity and soil quality.
1. Introduction
As the earliest coarse grain planted in Shanxi Province in China, foxtail millet has the characteristics of drought resistance, barrenness tolerance, and wide adaptability. It plays an important role in the diet of the Chinese people [1] and is a strategic reserve grain used to cope with extreme weather conditions and ensure food security in the future. Foxtail millet after hulling is currently recognized as a whole-grain, raw food that is rich in nutrients [2].
An “overdose” of fertilizer inputs can lead to soil compaction, soil nutrient imbalances, reduced soil sustainability, and reduced quality of agricultural products [3], limiting the sustainable development of agriculture. Organic fertilizer is rich in organic matter and various nutrients required by crops; it can not only provide nutrients for crops but can also promote the transformation of soil minerals, increasing the bioavailability of soil nutrients [4]; improve soil fertility and structure; effectively alleviate a series of cultivated-land-degradation problems, such as soil acidification, decreased organic matter content, and reduced soil microbial diversity in China [5]; and contribute to the sustainable production of farmland ecosystems [6]. However, organic fertilizer has a low content of available nutrients and a slow decomposition rate, which can lead to a decrease in the crop yield if applied alone. Moreover, most organic fertilizers are fermented from livestock manure, which contains excessive heavy metals, pathogenic microorganisms, and parasite eggs. If the fermentation is not sufficient, excessive application to farmland can cause heavy metal pollution and increase the risk of crop diseases and insect pests [7,8]. In contrast, chemical fertilizer has a high and effective nutrient content. The two can be applied together to maintain the crop yield and improve soil fertility [9,10].
A large number of studies [11] have shown that the substitution of 20–30% of inorganic nitrogen with organic nitrogen can effectively promote crop dry matter and nutrient accumulation; improve the nitrogen use efficiency, chlorophyll content, and physiological stress resistance; and improve the quality and efficiency of the nitrogen fertilizer under the same nitrogen application rate [12]. Studies have shown that organic inputs, as a substitute for or a supplement to chemical fertilizers, can potentially mitigate nitrogen losses and are effective as measures to achieve efficient crop cultivation [11]. The results of these studies showed that, under certain conditions, organic inputs can increase the yield of roots, tubers, and spring-sown cereals, and there was a significant correlation between the crop yield and the soil organic matter content [13,14,15,16]. Redding et al. [17] and Sarkar and Mukherjee [18] showed that the application of organic fertilizer can delay organ senescence, prolong the grain-filling time, increase the grain weight per panicle, and provide balanced nutrients for crops during later reproductive growth, thereby increasing yields. In addition, some studies have shown that the application of organic fertilizer can enrich mineralized nitrogen sources and increase the soil soluble nitrogen content [19,20], and the free amino acids produced by soil microbial decomposition can be directly absorbed by crops [21]. Other studies [22] have shown that the partial substitution of chemical fertilizers with different organic materials (straw, manure, vermicompost, or rapeseed meal) can improve crop yields and soil quality indices in different cropping systems (winter rapeseed–summer sweet potato, winter wheat–summer maize, and continuous-cropping maize). It is clear that the effects of organic manure from different sources and at different application ratios on crop yields and soil fertility are different. As a type of fertilizer composed of inorganic nutrients, organic substances, and beneficial microorganisms, bio-organic fertilizer provides the same advantages as the addition of biological agents and traditional organic fertilizers [23], including a long action time, a wide action, a high fertilizer efficiency, and no pollution in the production process [24].
With the development of the yellow mealworm farming industry, yellow mealworm feces have also become a new biological resource. Mealworm manure is odorless, fine, and sandy, with tiny agglomerated structures and a high natural porosity. The surface of mealworm manure is coated with a microfilm formed by secretions from the digestive tract of the yellow mealworm. This material can be stored for a long period of time [25], and as a raw material for high-quality organic fertilizer, it is rich in nutrients and can be used for agricultural applications and home planting [26]. Yellow mealworm manure is generally directly applied in crop cultivation, and it is rarely applied in a fermented form. Manure fermentation can improve the nutrient content of organic fertilizer, produce a large number of active substances, enable better decomposition of the organic matter, and promote the growth of crops [27]. However, few reports exist on the effects of mealworm manure and bio-organic fertilizer on the productivity, nutrient availability, and nitrogen use efficiency of foxtail millet. Deciphering the ecological mechanisms by which mealworm manure and bio-organic fertilizer promote yield can help in the design of more efficient bio-fertilizers and promote the sustainability of foxtail millet production.
This study used the cultivated foxtail millet variety “Jin gu 21” to explore the effects of replacing chemical fertilizers with different organic materials (bio-organic fertilizer and mealworm manure) on the physical properties, chemical nutrients, and enzyme activities of soil and the nitrogen content in various parts of foxtail millet. This study also aimed to clarify the mechanism used by different organic fertilizers to improve soil fertility and nitrogen use efficiency, as well as provide information on the selection of suitable organic fertilizers and combined application ratios, so as to provide suggestions and references for the formulation of efficient and sustainable fertilization measures.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Test Site
The two-year trial (2021–2022) was conducted at the Shenfeng Experimental Base of Shanxi Agricultural University, Taigu District, Jinzhong City, Shanxi Province, China (112°28′, 37°12″ E), which has a temperate continental climate with an average annual temperature of 10 °C, a frost-free period of 175 days, annual rainfall of 462.9 mm, an elevation of 900–1200 m, and an accumulated temperature ranging from 3250–3500 °C.
The soil at the study site is sandy loam. The crop planted at the test site prior to the 2021 season was corn, and the crop planted at the test site prior to the 2022 season was foxtail millet. At the beginning of the experiment, initial soil samples were collected in a surface soil profile of 0–20 cm, and the soil-testing method used was the same as that described in Section 2.4.2. The specific physical and chemical properties of the soil are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Soil physical and chemical properties.
2.2. Test Materials
The foxtail millet variety used in this experiment was “Jin gu 21”. The bio-organic test fertilizer was purchased from Beijing Taiwan Sifang Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China); it was made through the fermentation of 70% chicken manure and 30% corn stalk. The number of effective viable bacteria (compound probiotics) in the fertilizer was ≥300 million/g, its organic matter content was ≥60%, nitrogen content was 1.46%, phosphorus pentoxide content was 1.69%, potassium oxide content was 1.11%, and water content was 45%. Homemade fermented mealworm manure was made using the following procedure. Mealworm manure was mixed with water in a 1:1 ratio, and double superphosphate in an amount of 3% of the mealworm manure mass was added. The mixture was stirred evenly and then packed into an airtight plastic bag, tied tightly at the mouth of the bag, and allowed to anaerobically ferment until brown. The bag was opened and the mixture was turned once during fermentation. The fermented mealworm manure contained 50% water content, 67% organic matter, 2.87% nitrogen, 1.98% phosphorus pentoxide, and 1.26% potassium oxide. Urea (N ≥ 46%) was produced by Shanxi Tianze Coal Chemical Group Co., Ltd. (Jincheng, China); double superphosphate (P2O5 ≥ 46%) was produced by Kunming Dongsheng Metallurgical Co., Ltd. (Kunming, China); and potassium chloride (K2O ≥ 60%) was produced by Golmud Zanghuada Granule Potash Fertilizer Co., Ltd. (Golmud, China).
2.3. Experimental Design
A random block design was adopted. The following six treatments were established: a no-fertilizer control (CK), a single-chemical-fertilizer treatment (N), the substitution of 25% of the chemical nitrogen fertilizer with bio-organic fertilizer (N25A1), the substitution of 25% of the chemical nitrogen fertilizer with fermented mealworm manure (N25B1), the substitution of 50% of the chemical nitrogen fertilizer with bio-organic fertilizer (N50A2), and the substitution of 50% of the chemical nitrogen fertilizer with fermented mealworm manure (N50B2). The N:P2O5:K2O ratio was 5:3:4, and when the phosphorus and potassium were insufficient after the application of organic fertilizer, the soil was supplemented with double superphosphate and potassium chloride. The specific fertilizer amount is shown in Table 2. Each treatment was repeated 3 times for a total of 18 cells, with a plot area of 15 m2 (3 m × 5 m) and a 1 m buffer row around it.

Table 2.
Fertilization schemes for different treatments.
All fertilizers were applied as basic fertilizers only once during the sowing period, and then the millet was sown after plowing all of the treatment areas with a rotary tiller, with a row spacing of 50 cm and a plant spacing of 6 cm at the 4–6 leaf stage. The seedling density was 450,000 plants/ha, no watering was performed, no top dressing was used, and cultivation and weeding were performed 2 times during the whole growth period. Sowing occurred on 21 May 2021 and 18 May 2022; harvesting occurred on 30 September 2021 and 3 October 2022.
2.4. Test Methods and Calculation Formulas
2.4.1. Soil Physical Properties
The ring-knife method [28] was used to determine the bulk density, total porosity, water content, solid deviation, liquid deviation, and gas deviation of the soil samples from the 0~20 cm soil layer during the crop’s mature stage. The initial weight was m1, the weight after water absorption was m2, the weight after drying was m3, and the weight of the ring knife was m0. The formulas for calculating each indicator are shown below.
The soil bulk density was calculated as follows:
In this formula, ρb is the bulk density of soil (g/cm3), and V is the volume of the ring knife (cm3).
The soil mass moisture content was calculated using Equation (2):
where θg is the water content of the soil (%).
The soil porosity was calculated using Equation (3):
where Pt is the total porosity of the soil (%); Pd is the soil (grain) density, which is usually 2.65 g/cm3; and ρb is the same as in Equation (1).
The solid, liquid, and gas phases of the soil were calculated using Equations (4)–(6):
where X in Equation (4) is the soil’s solid-phase value, Y in Equation (5) is the soil’s liquid-phase value, Z in Equation (6) is the soil’s gas-phase value, 0.4 is the weight of the soil’s solid-phase data, and 0.6 is the weight of the soil’s gas sample data. Pb, θg, and Pt are the same as in Equations (1)–(3), respectively.
2.4.2. Soil Chemical Properties
When the foxtail millet was harvested, soil samples were taken from the 0~20 cm soil layer using a multi-point mixed sampling method with a soil drill in each community. Stones, plant residues, and other impurities were removed and the samples were mixed, bagged, and brought back to the laboratory. The soil samples were then naturally air-dried, ground, screened, and divided into components for the determination of nutrient contents.
The soil’s chemical properties were determined according to a soil agrochemical analysis [29]. The alkaline-hydrolyzable nitrogen was determined using the 1.0 mol/L NaOH alkaline hydrolysis and dispersion method, the available potassium was determined using NH4OAc leaching flame photometry, the available phosphorus was determined using the 0.5 mol/L NaHCO3 method, the organic carbon was determined through external heating (potassium dichromate oxidation method) and then organic matter was derived from organic carbon content × 1.724, and the total nitrogen content was determined by boiling at 380 °C using H2SO4 and a mixed catalyst (Kjeldahl method). The pH was determined to be 5. The ratio of water to soil was determined using a pH meter, soil nitrate nitrogen was determined using a spectrophotometric method with phenol disulfonic acid, and soil ammonium nitrogen was determined using the 2 mol/L KCl–indophenol blue spectrophotometric method.
2.4.3. Soil Enzyme Activity
Before harvesting, soil samples were collected from the 0–20 cm soil layer from each plot using a multi-point mixed sampling method and immediately stored in a −20 °C freezer after removing stones, plant residues, and other debris. These samples were then used for the determination of soil enzyme activity within one week.
The soil urease content was determined colorimetrically using sodium phenolate–sodium hypochlorite [30]. We measured 5 g of air-dried soil sample into a 50 mL triangular flask, added 1 mL of toluene, and let it stand for 15 min; we then added 10 mL of 10% urea solution and 20 mL of citrate buffer with pH 6.7 to the triangular flask, shook it well, and then incubated the solution for 24 h at 37 °C. After filtration, 3 mL of the filtrate was placed into a 50 mL volumetric flask and distilled water was added to make the solution reach 20 mL. After filtration, 3 mL of the filtrate was injected into a 50 mL volumetric flask, and distilled water was added to bring the solution to 20 mL. Then, 4 mL of sodium phenol solution and 3 mL of sodium hypochlorite solution were added, and the solution was well shaken. The color and volume developed after 20 min. At 1 h, the colorimetric analysis was conducted at a wavelength of 578 nm using an intrinsic spectrophotometer. The urease activity is expressed in milligrams of NH3-N in 1 g of soil after 24 h.
The sucrase content was determined colorimetrically using 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid [31]. An amount of 2 g of air-dried soil was placed into a 50 mL triangular bottle, 5 drops of toluene were added and left for 15 min. Then 15 mL of 8% sucrose solution and 5 mL of phosphate buffer with pH 5.5 were added and shaken well. The soil was then incubated in an incubator at 37 °C for 24 h, followed by rapid filtration. Then 1 mL of filtrate was pipetted and filled into a small test tube; 3 mL of DNS reagent was added, and the mixture was heated in a boiling water bath for 5 min. The tube was then immediately transferred to tap water and cooled for 3 min. Finally, the liquid in the test tube was transferred to a 50 mL volumetric flask and diluted to 50 mL with distilled water solution and tested colorimetrically on a spectrophotometer at 508 nm. Sucrase activity was expressed as milligrams of glucose produced by 1 g of dry soil in 24 h.
The glutaminase and asparaginase contents were determined using Kneyer’s reagent colorimetric method [32]. An amount of 5 g of soil was placed into a 50 mL triangular flask and treated with 0.5 mL of toluene. After 15 min, 10 mL of 3% asparagine and 10 mL of a phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 6.7 were added. After shaking, the mixture was incubated at a constant temperature of 37 °C for 24 h. At the end of the incubation, 30 mL of a 1 N KCl solution was added, and the mixture was shaken for 30 min and then filtered. An amount of 5 mL of filtrate was transferred to a 50 mL volumetric flask and 5 mL of 5% NaOH, 2 mL of 50% potassium sodium tartrate, and 30 mL of distilled water were added. After shaking, 2 mL of Kneyer’s reagent was added, the volume was set, and a colorimetric determination was performed using a spectrophotometer at 420 nm after 10 min. The asparaginase activity was expressed as the number of milligrams of ammonia released after 24 h by 1 g of soil.
An amount of 5 g of soil was placed into a 50 mL triangular flask and treated with 0.5 mL of toluene, and 10 mL of a 3% glutamine solution was added after 15 min. After mixing, the solution was incubated in a 37% incubator for 24 h. The procedure after culturing was the same as for the determination of asparaginase. The glutaminase activity was expressed as the number of milligrams of ammonia released after 24 h by 1 g of soil.
2.4.4. Yield and Composition
At the ripening stage of the foxtail millet, plant samples with consistent growth were randomly selected from each treatment in a sampling area of 4 m2. All selected ears were cut off, placed into a net bag, naturally dried, threshed, weighed, and converted into density (per hectare) according to the area of each community. A total of 10 ears were selected for each cell for an indoor examination. The weight of a single ear, the grain weight of a single ear, and 1000 grains were measured and recorded.
2.4.5. Dry Matter Accumulation and Nitrogen Content in Each Part of the Plant
Three representative foxtail millet plants were selected for each treatment and divided into four parts: roots, stems, leaves, and spikes, dried in an oven at 105 °C for 30 min and then dried to constant weight at 75 °C. The dry weights of the four parts were used to calculate the proportion of foxtail millet in each part of the plant. The dried plant samples were weighed and pulverized, passed through a 0.5 mm sieve, and the nitrogen content of the plant parts was determined by Kjeldahl method: 0.5 g of the sieved sample was weighed into a digestion tube and 5 mL of H2SO4 was added, the mixture was boiled at 380 °C, and the nitrogen content determined using a Kjeldahl meter after the boiling liquid became transparent [33].
2.4.6. Calculation Method for Nitrogen Fertilizer Utilization Efficiency
The following equations were used to calculate the nitrogen fertilizer utilization efficiency:
Agronomic efficiency of nitrogen fertilizer (ANUE kg/kg) = (yield in nitrogen application area − yield in control area)/nitrogen application rate.
Physiological efficiency of nitrogen fertilizer (PNUE kg/kg) = (yield in nitrogen application area − yield in control area)/(nitrogen uptake in shoots in nitrogen application area − nitrogen uptake in the shoots of plants in the control area).
Apparent nitrogen use efficiency (NRE) = (nitrogen uptake in shoots in nitrogen application area − nitrogen uptake in the shoots of plants in the control area)/nitrogen application rate × 100%.
Nitrogen harvesting index (NHI %) = nitrogen uptake in grain/nitrogen uptake in the shoots of plants × 100.
Nitrogen partial productivity (PFP kg/kg) = grain yield/nitrogen application rate.
2.5. Data Analysis
The differences between different fertilization treatments were analyzed by one-way ANOVA, and then Tukey’s HSD test was performed using SPSS (20.0, IBM SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) software at a significance level of p = 0.05. Pearson correlation was used to analyze the correlation between soil properties. Excel (2010, Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA) software was used to organize the data and charts, and Origin (2021, OriginLab, Hampden, MA, USA) was used for plotting.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Replacing Chemical Nitrogen Fertilizer with Different Organic Fertilizers on Soil Physical Properties
The analysis of the physical quality of the 0~20 cm soil layer after applying different fertilization treatments over two consecutive years showed (Table 3) that fertilization can reduce the soil’s bulk density (ρb) and increase its total porosity (Pt) and water content (θg). For the N25 treatments, the application of fermented mealworm manure reduced the total porosity and increased the water content of the soil. For the N50 treatments, the application of fermented mealworm manure significantly reduced the bulk density and increased the water content of the soil. For the same N level, fermented mealworm manure was beneficial for increasing the water content of the soil. The highest total porosity in 2021 was observed for the N50B2 treatment, and the highest in 2022 was observed for the N50A2 treatment, with these treatments showing an increase of 7.99% and 3.81%, respectively, compared with N25B1. The highest soil water content in both years was observed for the N25B1 treatment, which increased by 9.73% and 10.06% compared with N50A2. Overall, the N50B2 fertilization effect was the best, and organic substitution was shown to reduce the bulk density of the soil while also reducing the amount of chemical fertilizer, which is conducive to improving the soil structure and increasing the circulation of air and water in soil.

Table 3.
Effects of replacing chemical fertilizer with different organic fertilizers on soil physical quality in 0–20 cm soil layer.
In 2021 and 2022, compared with the CK treatment, the substitutions of chemical nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizers reduced the solid fraction and increased the liquid fraction. As can be seen in Table 4, the solid fraction of the N25B1 treatment was significantly lower than that of other treatments, and it decreased by 4.63% compared with N. The liquid fraction resulting from the substitutions of chemical nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizer was significantly increased; compared with N, the N50A2 treatment resulted in an increase of 10.97% and 7.83% over two years, respectively. In 2021, the gas fraction of the N25B1 treatment was significantly higher than that of other treatments and was 33.51% higher than that of CK. For the N50 treatments, the solid fraction and gas fraction after the two-year application of bio-organic fertilizer were lower than those after the application of fermented mealworm manure.

Table 4.
Effects of replacing chemical fertilizer with different organic fertilizers on the values of the solid, liquid, and gas fraction.
3.2. Effect of Replacing Chemical Fertilizer with Different Organic Fertilizers on Soil Nutrients
The effects of different fertilization treatments on the nitrogen content in the 0~20 cm soil layer are shown in Table 5. Compared with N, the nitrate nitrogen content decreased by 25.19~52.56% and 13.59~30.41%, respectively. The ammonium nitrogen content decreased significantly by 14.13~18.27% and 4.46~14.81%, respectively. The content of alkaline-hydrolyzable nitrogen increased by 5.07~27.79% and 1.69~32.37%, and the N25B1 fertilization treatment resulted in a higher content than that of the other treatments. In 2021, the total nitrogen content was significantly reduced by 4.35~7.6%, and that of the N25B1 treatment increased by 12.09% in 2022. For the N25 treatments, the application of fermented mealworm manure increased the content of alkaline-hydrolyzable nitrogen in the soil. For the N50 treatments, the contents of soil nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen were increased by the application of fermented mealworm manure, indicating that fermented mealworm manure was more conducive to an increase in the various soil nitrogen forms. Overall, the content of various nitrogen forms was increased by the fertilization treatments, and the nitrogen content of each treatment was higher in 2022 than in 2021.

Table 5.
Effects of replacing chemical fertilizer with different organic fertilizers on contents of different forms of soil nitrogen.
The effects of different fertilization treatments on soil available potassium, available phosphorus, and organic content are shown in Figure 1A–C. In 2021, the soil available potassium content of N50B2 was appreciably higher than that of the other treatments. In 2022, the N25A1 treatment had the highest soil available potassium content, which was appreciably higher than the N treatment by 49.58%. In N50 treatments, soil available potassium content was higher after application of fermented yellow mealworm manure than after application of bio-organic manures. Compared to N, N25B1, N50A2, and N50B2 treatments significantly increased soil available phosphorus content. Soil available phosphorus content after application of fermented yellow mealworm manure was higher than that of bio-organic fertilizer treatments at the same rate of substitution. The organic fertilizer replacements improved soil organic matter content significantly as shown in Figure 1C. After 2 years, the organic matter content of N25A1 and N25B1 treatments was significantly higher than that of other treatments, indicating that the application of various materials from N25 organic fertilizer treatments was more beneficial in improving soil organic matter content.
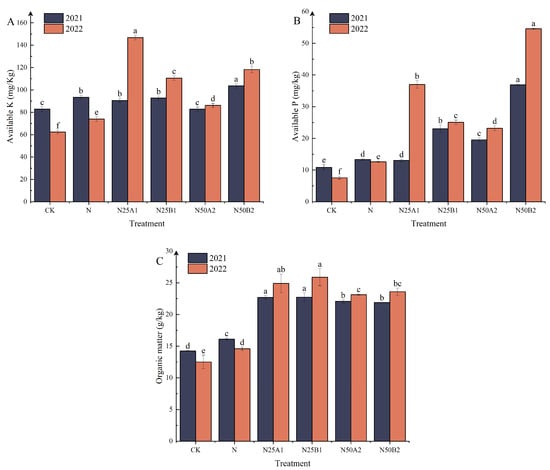
Figure 1.
Effects of replacing chemical fertilizer with different organic fertilizers on soil (A) available potassium, (B) available phosphorus, and (C) organic matter. Note: Different letters in the figure indicate that the mean values of different treatments in the same year are significantly different (Tukey’s HSD test, p ≤ 0.05).
3.3. Effects of Replacing Chemical Fertilizer with Different Organic Fertilizers on Soil Enzyme Activities
As can be seen in Figure 2A, the soil sucrase activity following the organic fertilizer treatments was significantly higher than that resulting from the chemical nitrogen fertilizer treatment alone. At the N25 level, the two-year treatment with fermented mealworm manure resulted in a significantly higher sucrase activity than that resulting from the bio-organic fertilizer, showing an increase of 10.8% and 14.87%, respectively. At the N50 level, N50B2 demonstrated a significantly higher sucrase activity than the N50A2 fertilization treatment in 2021. From Figure 2B, it can be seen that soil urease activity was higher in 2022 than in 2021, and soil urease activity was significantly higher in 2021 for the N25B1 fertilizer treatment, with an increase of 38.16% compared to the N treatment. The N25B1 application in 2022 resulted in a significantly higher urease activity than the other matching treatments, and the N25A1 application treatment increased the urease activity by 13.34%. The urease activity of N25 treatments was greater than that of N50 treatments. Figure 2C shows that the soil glutaminase activity of organic fertilizer treatments was significantly higher than that of N treatments, with the N25A1 treatment having the highest glutaminase activity. The soil glutaminase activity of the N50 treatment was higher than that of the N25 treatment. At the same substitution level, the glutaminase activity of fermented mealworm manure was higher than that of the bio-organic fertilizer. Figure 2D illustrates that asparaginase activities of CK, N, N25A1, and N50B2 were lower in 2022 than in 2021, while the opposite was true for the other treatments. At the same nitrogen level, asparaginase activity after application of fermented yellow mealworm manure was greater than that of the bio-organic fertilizer treatments, and asparaginase activity was significantly higher in the N25B1 treatment than in the N treatment.
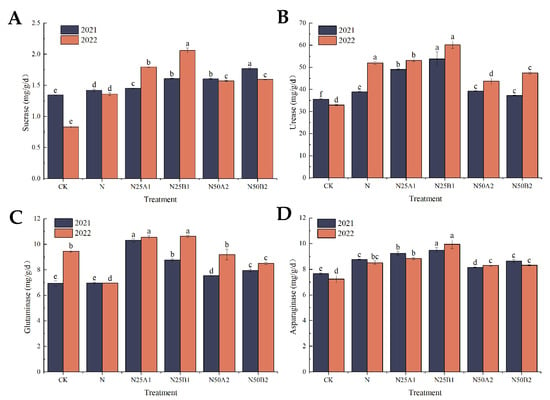
Figure 2.
Effects of replacing chemical fertilizer with different organic fertilizers on soil enzyme activities. Note: Different letters in the figure indicate that the mean values of different treatments in the same year are significantly different after Tukey’s HSD test (p ≤ 0.05). (A) Sucrase, (B) urease, (C) glutaminase, (D) asparaginase.
3.4. Correlation between Soil Quality Evaluation Indicators
The correlation analysis of the above indicators related to soil physico-chemical and enzyme activities showed (Figure 3) that the six indicators of soil physical properties (total porosity, bulk density, mass water content, solid phase, liquid phase, and gas phase) were not correlated with the various forms of nitrogen (nitrate nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen, alkaline-hydrolyzable nitrogen, and total nitrogen), available potassium, or available phosphorus. The various forms of nitrogen were positively correlated with soil enzymes (sucrase, urease, glutaminase, and asparaginase) and soil nutrients (available potassium, available phosphorus, and organic matter). The total porosity and soil gas phase showed a significant positive correlation, and the soil solid phase and soil bulk density showed a significant negative correlation. Ammonium nitrogen, alkaline-hydrolyzable nitrogen, and organic matter were also positively correlated with soil nutrients and soil enzymes.
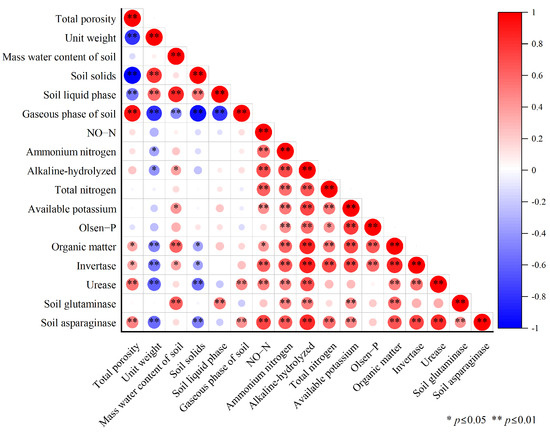
Figure 3.
Correlation between soil quality evaluation indicators.
3.5. Effects of Different Organic Fertilizers on Foxtail Millet Yield and Nitrogen Accumulation
It can be seen from Table 6 that the pattern of change in the foxtail millet yield over 2 years was essentially the same for the different fertilization treatments, and the yield of the CK and N treatments in 2022 increased by 3.89% and 0.89%, respectively, compared with the yields in 2021. Compared with N, the N50 organic fertilizer treatment significantly reduced foxtail millet yield in both years; in contrast, the yield of the N25B1 treatment was significantly higher than that of the other treatments; and the yield increased by 6.21% and 7.83%, respectively, over the two years compared with the N treatment. Compared with N, the average yield of foxtail millet increased by 18.87% and 14.88% over the two years after the application of organic fertilizer. After application of organic fertilizer, the above-ground nitrogen accumulation of foxtail millet and grain nitrogen accumulation were significantly higher than those under N and CK treatment, and the highest value was reached under N25 organic fertilizer treatment. In 2021, the grain weight per spike of the N25B1 treatment was significantly higher than that of the other treatments. On the whole, the yield, nitrogen accumulation, single-ear weight, and single-ear grain weight achieved by the 2 year N25B1 treatment were better than those of the other treatments, and the fermented mealworm manure treatments resulted in better weights than the treatments with bio-organic fertilizer. This indicates that the fertilizer effect of fermented mealworm manure lasted longer and the effect was better.

Table 6.
Effects of different organic fertilizers on foxtail millet yield and nitrogen accumulation.
3.6. Effects of Replacing Chemical Fertilizer with Different Organic Fertilizers on Nitrogen Content in Different Parts of Foxtail Millet
The nitrogen content in different parts of foxtail millet resulting from different fertilization treatments at the plant’s mature stage was analyzed, and it can be seen in Figure 4 that the nitrogen content in the different parts of foxtail millet was in the order of panicles > leaves > stems > roots. In 2022, the nitrogen content of each part of foxtail millet was significantly higher for the N25B1 treatment than for the other treatments. Compared with N, the nitrogen content of each part of the foxtail millet that received an N25 treatment increased by 9.36%, 15.13%, 44.97%, and 31.73%, respectively. Under the same nitrogen level, the nitrogen content of all parts of the foxtail millet treated with fermented mealworm manure was higher than that of the plants treated with bio-organic fertilizer. Overall, N25B1 performed the best in both years, and the fermented mealworm manure treatment was better than that of the bio-organic fertilizer at the same level of organic fertilizer substitution.
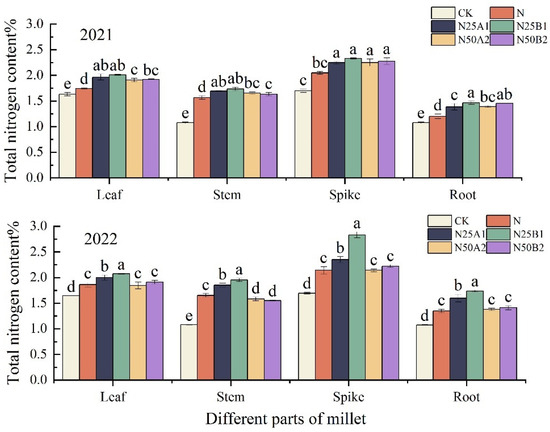
Figure 4.
Effects of replacing chemical fertilizer with different organic fertilizers on nitrogen content in different parts of foxtail millet. Note: Different letters in the figure indicate that the mean values of different treatments in the same year are significantly different (Tukey’s HSD test, p ≤ 0.05).
3.7. Effects of Replacing Chemical Fertilizer with Different Organic Fertilizers on Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Foxtail Millet
It can be seen from Table 7 that, compared with N, the treatments with organic fertilizer instead of chemical fertilizer increased the ANUE by 11.67%, 43.27%, 41.97%, 38.48%, 87.93%, 82.02%, 21.78%, and 25.56%, respectively. In 2022, the NRE of the N25 treatments was higher than that of the N50 treatments. In 2021, the N25A1, N25B1, and N50B2 treatments decreased by 12.23%, 16.11%, and 17.41%, respectively, compared with the N treatment. In 2022, the ANUE of the N25 treatment was higher than that of the N treatment, while the opposite was true for the N50 treatment. At the same level of organic fertilizer substitution, the treatments with bio-organic fertilizer resulted in a higher nitrogen use efficiency than that resulting from the fermented mealworm manure treatments, indicating that bio-organic fertilizer was conducive to an improvement in the nitrogen use efficiency. Under the same level of organic fertilizer substitution, the PFP of the 2-year biological organic fertilizer treatments was greater than that of the fermented mealworm manure treatments. Two years of fermented mealworm manure application resulted in a superior NHI compared to that achieved by the bio-organic fertilizer treatment. Compared with N, N25B1 resulted in a significant increase in the NHI of 18.78% and 25.16% in 2021 and 2022, respectively. During the 2 years, the bio-organic fertilizer treatments resulted in a significantly higher NPE than the nitrogen treatment for various materials. In 2021, the NPE was better at the N25 fertilization level compared to that at the N50 level, and vice versa in 2022.

Table 7.
Nitrogen use efficiency under different fertilization modes.
4. Discussion
4.1. Effect of Replacing Chemical Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Physical Quality
Soil physical parameters can be used to evaluate the changes in the soil physical quality under farm land management measures. The soil bulk density is not only an important indicator of soil physical quality but is also a limiting factor that affects crop productivity and soil fertility production, thus directly or indirectly affecting soil quality and affecting crop water uptake as well as yield [34]. The distribution of large and small pores in the soil and the soil’s continuity and stability are directly related to water storage and transport, root growth and development, gas diffusion, and the distribution of soil microbial communities and nutrient transport [35]. The results of this study showed that, compared with the nitrogen treatment, the soil bulk density of the organic alternative treatments was significantly reduced by 1.30~8.43%, and the total porosity and soil mass moisture content were increased by 7.61~11.72% and 1.33~17.08%, respectively. This was because the addition of organic fertilizer increased the content of soil organic matter, and the humus and root exudates formed during the decomposition of organic matter promoted the combination of Al3+ and Ca2+ as well as the formation of aggregates and micro-aggregates through the combination of small soil particles. These micro-aggregates formed macro-aggregates through cementation, which increased the dilution of dense mineral components in the soil [36,37]. The organic fertilizers reduced the infiltration capacity of soil moisture, so that water collected in the 10~20 cm soil layer, which is conducive to maintaining soil moisture [38]. The ideal soil ratio for agriculture is 50% solid phase, 25% liquid phase, and 25% gas phase, and these three ratios, with reasonable regulation, can provide excellent water, fertilizer, gas, and heat conditions for crop growth [39]. This study showed that, compared with N, the organic fertilizer treatments significantly reduced the soil’s solid phase and increased the proportion of the soil’s liquid and gas phases, indicating that organic fertilizer can effectively improve the water-holding capacity of soil, alleviate the compaction state of the soil itself, and promote the effective rooting of foxtail millet.
4.2. Effect of Replacing Chemical Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Nutrients
Soil available nutrients are important indicators used to evaluate soil fertility, which is the basic attribute of soil and the most basic guarantee of a continual supply of nutrients for plants. The results of Gao et al. [40] showed that the use of organic fertilizers can significantly increase the content of available phosphorus and available potassium in the soil. Alkaline-hydrolyzable nitrogen contains nitrate nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen, and organic nitrogen, which can be absorbed and utilized by crops. In this experiment, compared with the CK treatment, the contents of total nitrogen and alkaline-hydrolyzable nitrogen in the soil were increased to varying degrees, and the comprehensive application effect of fermented mealworm manure was better. This may be related to the content of organic matter, as well as the increase in the soil organic nitrogen content and the soil nitrogen supply capacity with an increase in the fermented mealworm manure input. With an increase in the amount of bio-organic fertilizer, the mass fraction of nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen in the soil tillage layer decreased to a certain extent, which may have been due to the addition of a large number of microbial strains to the bio-organic fertilizer, as the organic matter would have provided a sufficient carbon source for microbial activities. Therefore, the organic substitution of chemical fertilizers had an effect on the contents of nitrate nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen, alkaline-hydrolyzable nitrogen, and total nitrogen in the tillage layer, and improved the nitrogen supply level of the soil tillage layer to a certain extent.
4.3. Effect of Replacing Chemical Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Soil Enzyme Activity
Soil enzymes are effective sensors that can be used to study soil ecological effects [41], and they are an active reservoir of plant nutrients. Organic fertilizer substitutions significantly improved the soil enzyme activity and promoted the conversion of soil organic matter [42]. Urease, sucrase, glutaminase, and asparaginase play important roles in soil carbon–nitrogen conversions, and they can be used as ideal biochemical indicators to measure soil fertility. Tripathy [43] and other authors have found that the content of organic matter in soil, the number of microorganisms, and the respiration intensity all affect the activity of sucrase and urease, and urease is deeply involved in the transformation and decomposition of organic matter. The results of this study showed that the substitutions of chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer promoted soil urease, sucrase, glutaminase, and asparaginase activities. The soil enzyme activities were also higher in the N25 treatments than in the N50 treatments, which may be attributed to the increase in the adsorption of soil colloids in organic fertilizer by the reactive substrate in the soil of the plant root system. Soil colloids adsorb enzyme molecules in the soil, thus inhibiting soil enzyme activities [44]. In addition, this study found significant correlations between soil enzyme activities, soil organic matter, and total nitrogen, indicating that soil enzyme activities are coordinated by multiple factors. The application of carbon-rich porous organic fertilizer to the soil changed the soil physicochemical properties; altered the soil microbial environment, nutrient coordination, and bacterial survival; promoted soil enzyme activities; increased the activity of the multi-enzyme system; and synergistically supported the enzyme-promoted reaction [45].
4.4. Effect of Replacing Chemical Fertilizer with Organic Fertilizer on Foxtail Millet Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
The final yield of a crop is closely related to the accumulation, distribution, transportation, and transformation of dry matter in a single plant population [46]. The present study showed that, compared with nitrogen fertilizer alone, replacing chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer increased the seed yield by 13.97% to 65.88% and increased the spike length, spike thickness, and spike weight by 0.80% to 14.28%, 1.57% to 17.65%, and 12.24% to 37.05%, respectively. Compared with N, N25 organic fertilizer treatment significantly increased grain yield. This may have been due to a more appropriate and moderate ratio of organic and inorganic nitrogen fertilizers in the N25 treatments, which may have slowed down the rate of nutrient release from the soil; i.e., organic nutrients were gradually released in the later stages of foxtail millet growth, which ensured an effective number of grains per spike and prevented the premature aging of the foxtail millet [47]. When the substitution ratio of organic fertilizer was N50, the yield of millet was lower than that of the N treatment, which may be because when the substitution ratio is too high, the nitrogen release rate of organic fertilizer is very slow, which cannot keep up with the high nitrogen demand of crops in the early growth period, resulting in crop yield reduction [24,48]. The N content of cereal leaves, stems, roots, and spikes increased by 1.03% to 6.25%, 0.59% to 16.07%, 0.72% to 26.08%, and 0.44% to 25.22%, respectively, compared with N. The N content of foxtail millet increased by 0.72% to 26.08% and 0.44% to 25.22% with the organic fertilizer. It is possible that the application of organic fertilizer promoted microbial cycling and the transport of nitrogen; facilitated crop root colonization and growth; increased crop root activity [49]; and increased the nitrogen uptake by the crop root system and the transfer of nitrogen to the seeds, thus increasing the crop nitrogen uptake and seed yield [50].
Low nitrogen fertilizer utilization efficiency is a prominent problem of crop production in China; thus, optimizing and improving nitrogen fertilizer management is one of the effective measures used to improve nitrogen fertilizer utilization efficiency. The combination of organic and inorganic nitrogen fertilizers can promote the effective regulation of nitrogen fertilizer by soil microorganisms, ensure a balanced supply of the nutrients required by the crop, and improve the fertilizer efficiency from the perspective of fertilizer supply intensity and supply capacity, thus improving the nitrogen utilization efficiency of crops [51]. The results of this study showed that the organic fertilizer partial productivity and the apparent nitrogen use efficiency increased by 31.77~82.86% and 3.45%~9.56%, respectively. This may have been because the addition of organic fertilizers not only improved the physicochemical properties of the soil [52], but more importantly, it also increased the carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in the soil. When the fertilizer demand increases, the fixed portion of nitrogen in microorganisms is released for crop uptake and utilization [53]. Therefore, an organic–inorganic fertilizer application is one of the effective ways to achieve the efficient utilization of nutrient resources in cereals.
5. Conclusions
This study investigated the effects of different kinds of organic fertilizers and substitution ratios on soil physicochemical properties, soil enzyme activities, and nitrogen fertilizer utilization rate in grain fields. The appropriate proportion of organic fertilizer substitutions for chemical fertilizers improved the soil physicochemical properties in the 0–20 cm soil layer of the grain field. The application of organic fertilizer improves the physical structure of soil; increases soil enzyme activity; promotes the transformation and decomposition of organic matter; reduces the content of nitrate nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen, and total nitrogen in the soil; increases quick-acting nutrients in the soil; ensures that the demand for nutrients in the late stage of the grain is met; and improves the utilization rate of nitrogen fertilizer for the grain, increasing the yield. However, too high a proportion of organic fertilizer substitutions can result in lower grain yields. Fermented yellow mealworm manure was superior to bio-organic fertilizers. These findings will help to establish sustainable fertilization practices and reduce soil degradation in semi-arid regions of China.
Author Contributions
J.W. and G.H., Investigation, Resources, Methodology, Data curation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—review & editing. Y.D., X.S., R.H., C.W. and M.N., Investigation, Resources, Methodology. L.Z., Writing—original draft. H.D., S.D. and X.Y., Supervision, Funding acquisition, Project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Projects of Shanxi Province Key R&D (2022ZDYF119), the National Key R&D Project of China (2021YFD1901103-5), the Special Plan for Scientific and Technological Innovation Talent Team of Shanxi Province (202204051002036), Shanxi Agricultural University scientific research projects (2020xshf42), and the Shanxi Province Postgraduate Practice Innovation Project (2022Y352).
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed in this study are included in this published article. For further information, please contact the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Y.X.’s group for their guidance and advice on our experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the experimental design, data collection, or analysis.
References
- Yousaf, L.; Hou, D.; Liaqat, H.; Shen, Q. Millet: A review of its nutritional and functional changes during processing. Food Res. Int. 2021, 142, 110197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, X.M. Progresses in stress tolerance and field cultivation studies of orphan cereals in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2019, 52, 3943–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qin, L.; Cheng, J.; Shang, C.; Li, B.; Dang, Y.; He, H. Suitable chemical fertilizer reduction mitigates the water footprint of maize production: Evidence from Northeast China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 22589–22601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lv, Z.; Hou, H.; Lan, X.; Ji, J.; Liu, X. Long-term effects of combination of organic and inorganic fertilizer on soil properties and microorganisms in a Quaternary Red Clay. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0261387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaswar, M.; Huang, J.; Ahmed, W.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, L.; Cai, A.; Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. Yield sustainability, soil organic carbon sequestration and nutrients balance under long-term combined application of manure and inorganic fertilizers in acidic paddy soil. Soil Till. Res. 2020, 198, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Manuel, D.B.; Op de Beeck, M.; Shahbaz, M.; Chen, Y.; Deng, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Z. Rotation cropping and organic fertilizer jointly promote soil health and crop production. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 315, 115190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gong, Z.; Allinson, G.; Xiao, M.; Li, X.; Jia, C.; Ni, Z. Environmental risks caused by livestock and poultry farms to the soils: Comparison of swine, chicken, and cattle farms. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 317, 115320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhu, F.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, Y.; Hong, L.; Zhu, W.; Hong, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, H.; et al. Physicochemical properties and risk assessment of perishable waste primary products. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 337, 117549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.; Li, J.; Luo, T.; Chen, L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, S. Effects of different organic fertilizer replacement rates on wheat yield and soil nutrients over three consecutive years. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2021, 27, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zheng, C.; Qiao, Y.; Du, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, C.; Zhang, W. Long-term organic and inorganic fertilization alters the diazotrophic abundance, community structure, and co-occurrence patterns in a vertisol. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Hoffland, E.; Zhuang, M.; Hellegers, P.; Cui, Z. Organic inputs to reduce nitrogen export via leaching and runoff: A global meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 291, 118176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, F.; Sun, N.; Misselbrook, T.; Wu, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, F.; Xu, W. Responses of crop productivity and reactive nitrogen losses to the application of animal manure to China’s main crops: A meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 850, 158064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Hao, X.; Khan, A.; Li, N.; Li, J.; Shi, F.; Tian, Y.; Nepal, J.; Wang, J.; Luo, H. Increase in cotton yield through improved leaf physiological functioning under the soil condition of reduced chemical fertilization compensated by the enhanced organic liquid fertilization. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1225939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Zhang, G.-C.; Ding, H.; Yang, X.; Li, Z.-L.; Liang, X.-B. Effects of reducing nitrogen fertilizer application on agronomic traits and yield of peanut in dry land. Peanut Sci. 2019, 48, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, D.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Wu, S.; Meng, Q.; Feng, H.; Siddique, K.H.M. Mitigating greenhouse gas emissions by replacing inorganic fertilizer with organic fertilizer in wheat-maize rotation systems in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Niu, X.; Chen, B.; Pu, S.; Ma, H.; Li, P.; Feng, G.; Ma, X. Chemical fertilizer reduction combined with organic fertilizer affects the soil microbial community and diversity and yield of cotton. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1295722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redding, M.R.; Lewis, R.; Kearton, T.; Smith, O. Manure and sorbent fertilisers increase on-going nutrient availability relative to conventional fertilisers. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569, 927–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Mukherjee, I. Effect of organic amendment on mobility behavior of flupyradifurone in two different Indian soils. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrell, M.; Hill, P.W.; Farrar, J.; Bardgett, R.D.; Jones, D.L. Seasonal variation in soluble soil carbon and nitrogen across a grassland productivity gradient. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Ye, J.; Perez, P.G.; Tang, D.M.; Huang, D.F. The impact of organic farming on the soluble organic nitrogen pool in horticultural soil under open field and greenhouse conditions: A case study. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, N.; Jin, L.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Liu, F.; Liu, Z.; Luo, S.; Wu, Y.; Lyu, J.; Yu, J. Reduced Chemical Fertilizer Combined with Bio-Organic Fertilizer Affects the Soil Microbial Community and Yield and Quality of Lettuce. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 863325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, H.; Ren, L.; Jin, X.; Fang, W.; Yan, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Cao, A. Organic fertilizers activate soil enzyme activities and promote the recovery of soil beneficial microorganisms after dazomet fumigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 309, 114666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Näsholm, T.; Huss-Danell, K.; Högberg, P. Uptake of organic nitrogen in the field by four agriculturally important plant species. Ecology 2000, 81, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, M.; Gu, X.; Li, C.; Jiang, G. Using organic fertilizers to increase crop yield, economic growth, and soil quality in a temperate farmland. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xu, H.; Luo, H.; Liang, W.; Hu, S.; Huang, H.; Chen, S. Effect of Mealworm Worm Sand and Microbial Functional Bacteria on Nutritional Quality of Roman Lettuce. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2016, 44, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Cao, Y.; Ou, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, G.; Xiong, X. Effect of mealworm manure organic fertilizer on the growth of cold-water flowers. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2021, 38, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyon, L.; Burton, C.H.; Misselbrook, T.; Webb, J.; Philippe, F.X.; Aguilar, M.; Doreau, M.; Hassouna, M.; Veldkamp, T.; Dourmad, J.Y.; et al. Best available technology for European livestock farms: Availability, effectiveness and uptake. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.F.; Ren, A.X.; Li, H.; Gao, Z.Q.; Du, T.Q. Soil physical properties response to tillage practices during summer fallow of dryland winter wheat field on the Loess Plateau. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, S. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 25–114. [Google Scholar]
- Sneha, G.R.; Swarnalakshmi, K.; Sharma, M.; Reddy, K.; Bhoumik, A.; Suman, A.; Kannepalli, A. Soil type influence nutrient availability, microbial metabolic diversity, eubacterial and diazotroph abundance in chickpea rhizosphere. World J. Microb. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Cheng, Z.; Meng, H. Soil properties, nutrient dynamics, and soil enzyme activities associated with garlic stalk decomposition under various conditions. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, H.; Phillips, B.P. Automated determination of bacterial asparaginase and glutaminase. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wu, Y.; Du, R.; Liu, J.; Yu, F.; Liu, S. Soil, leaf and fruit nutrient data for pear orchards located in the Circum-Bohai Bay and Loess Plateau regions. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karami, A.; Homaee, M.; Afzalinia, S.; Ruhipour, H.; Basirat, S. Organic resource management: Impacts on soil aggregate stability and other soil physico-chemical properties. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 148, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, A.; Hdider, C.; Sanaa, M.; Tarchoun, N.; Ben Kheder, M.; Guezal, I. The influence of different organic fertilizers on yield and physico-chemical properties of organically grown tomato. Sustain. Agric. 2009, 33, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Gu, F.; Xin, M.; Kang, G.; Feng, W.; Guo, T. Effects of cultivation management on the winter wheat grain yield and water utilization efficiency. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, R.; Nayak, A.K.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Shukla, A.K.; Shahid, M.; Raja, R.; Panda, B.B.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, A.; Thilagam, V.K. Soil aggregation and distribution of carbon and nitrogen in different fractions after 41 years long-term fertilizer experiment in tropical rice–rice system. Geoderma 2014, 213, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.A.; Li, F.R.; Zhou, L.M.; Zhang, R.H.; Jia, Y.; Lin, S.L.; Wang, L.J.; Siddique, K.H. Effect of organic manure and fertilizer on soil water and crop yields in newly-built terraces with loess soils in a semi-arid environment. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 117, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papini, R.; Valboa, G.; Favilli, F.; L’Abate, G. Influence of land use on organic carbon pool and chemical properties of Vertic Cambisols in central and southern Italy. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 140, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Zhu, P.; Lindsey, S.; Gao, H.; Li, Q.; Peng, C.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; et al. Changes in soil fertility under partial organic substitution of chemical fertilizer: A 33-year trial. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 7424–7433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Lauber, C.L.; Weintraub, M.N.; Ahmed, B.; Zeglin, L.H. Stoichiometry of soil enzyme activity at global scale. Ecol. Lett. 2008, 11, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Wang, Y.C.; Wang, L.G.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, L.M.; Li, Y.H. Effects of subsoiling combined with fertilization on the fractions of soil active organic carbon and soil active nitrogen, and enzyme activities in black soil in northeast China. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2020, 57, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathy, S.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Equeenuddin, S.M.; Kim, K.; Kulkarni, H.D. Comparison of microbial indicators under two water regimes in a soil amended with combined paper mill sludge and decomposed cow manure. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supradip Saha, B.L.; Mina, K.A.; Gopinath, S.; Kundu, H.S. GuptaOrganic amendments affect biochemical properties of a subtemperate soil of the Indian Himalayas. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2008, 80, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Liu, W.; Tang, S.; Yang, Q.; Meng, L.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, L.; Wu, M.; Xue, X.; et al. Long-term partial substitution of chemical nitrogen fertilizer with organic fertilizers increased SOC stability by mediating soil C mineralization and enzyme activities in a rubber plantation of Hainan Island. Appl. Soil. Ecol. 2023, 182, 104691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhiipao, R.R.; Pooniya, V.; Biswakarma, N.; Kumar, D.; Shivay, Y.S.; Dass, A.; Mukri, G.; Lakhena, K.K.; Pandey, R.K.; Bhatia, A.; et al. Timely sown maize hybrids improve the post-anthesis dry matter accumulation, nutrient acquisition and crop productivity. Sci. Rep. 2023, 30, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Lv, Z.; Qin, B.; Yang, J.; Ren, K.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, F.; Zhang, W.; Ma, S.; Ma, C.; et al. Night warming at the vegetative stage improves pre-anthesis photosynthesis and plant productivity involved in grain yield of winter wheat. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 186, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seufert, V.; Ramankutty, N.; Foley, J. Comparing the yields of organic and conventional agriculture. Nature 2012, 485, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Chai, Q.; Hu, F.; Fan, Z.; Yin, W. N-fertilizer postponing application improves dry matter translocation and increases system productivity of wheat/maize intercropping. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraclough, P.B.; Lopez-Bellido, R.; Hawkesford, M.J. Genotypic variation in the uptake, partitioning and remobilisation of nitrogen during grain-filling in wheat. Field Crop Res. 2014, 156, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Basir, A.; Fahad, S.; Adnan, M.; Saleem, M.H.; Iqbal, A.; Amanullah Al-Huqail, A.A.; Alosaimi, A.A.; Saud, S.; Liu, K.; et al. Biochar Optimizes Wheat Quality, Yield, and Nitrogen Acquisition in Low Fertile Calcareous Soil Treated with Organic and Mineral Nitrogen Fertilizers. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 879788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Xu, M.; Gao, S.; Yang, X.; Huang, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, B. Nitrogen use efficiency in a wheat–corn cropping system from 15 years of manure and fertilizer applications. Field Crop Res. 2014, 157, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.F.; Chen, P.; Wang, F.H.; Han, W.X.; Qiao, M.; Dong, W.X.; Hu, C.S.; Zhu, D.; Chu, H.Y.; Zhu, Y.G. The ecological clusters of soil organisms drive the ecosystem multifunctionality under long-term fertilization. Environ. Int. 2022, 161, 107133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).