Increased Soil Soluble Nitrogen Stocks and Decreased Nitrogen Leaching Loss in Rice Paddy Soil by Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer with Chinese Milk Vetch
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
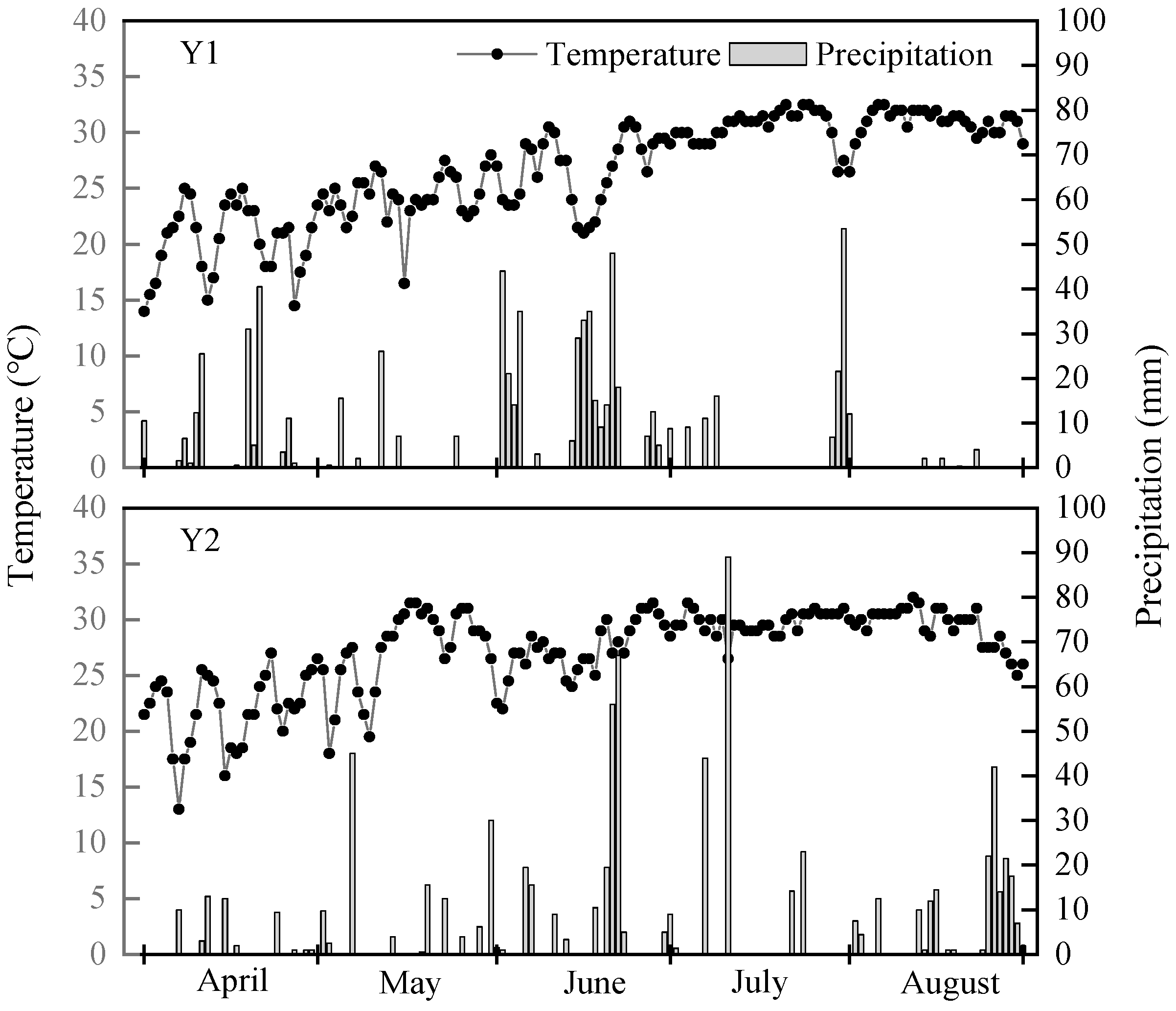
2.1. Experimental Site and Design
2.2. Soil and Soil–Water Sampling
2.3. Soil and Soil Water Analysis
2.3.1. Analysis of Soil Basic Properties
2.3.2. Analysis of Soil SIN and SON
2.3.3. Analysis of DIN and DON in Soil Water
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
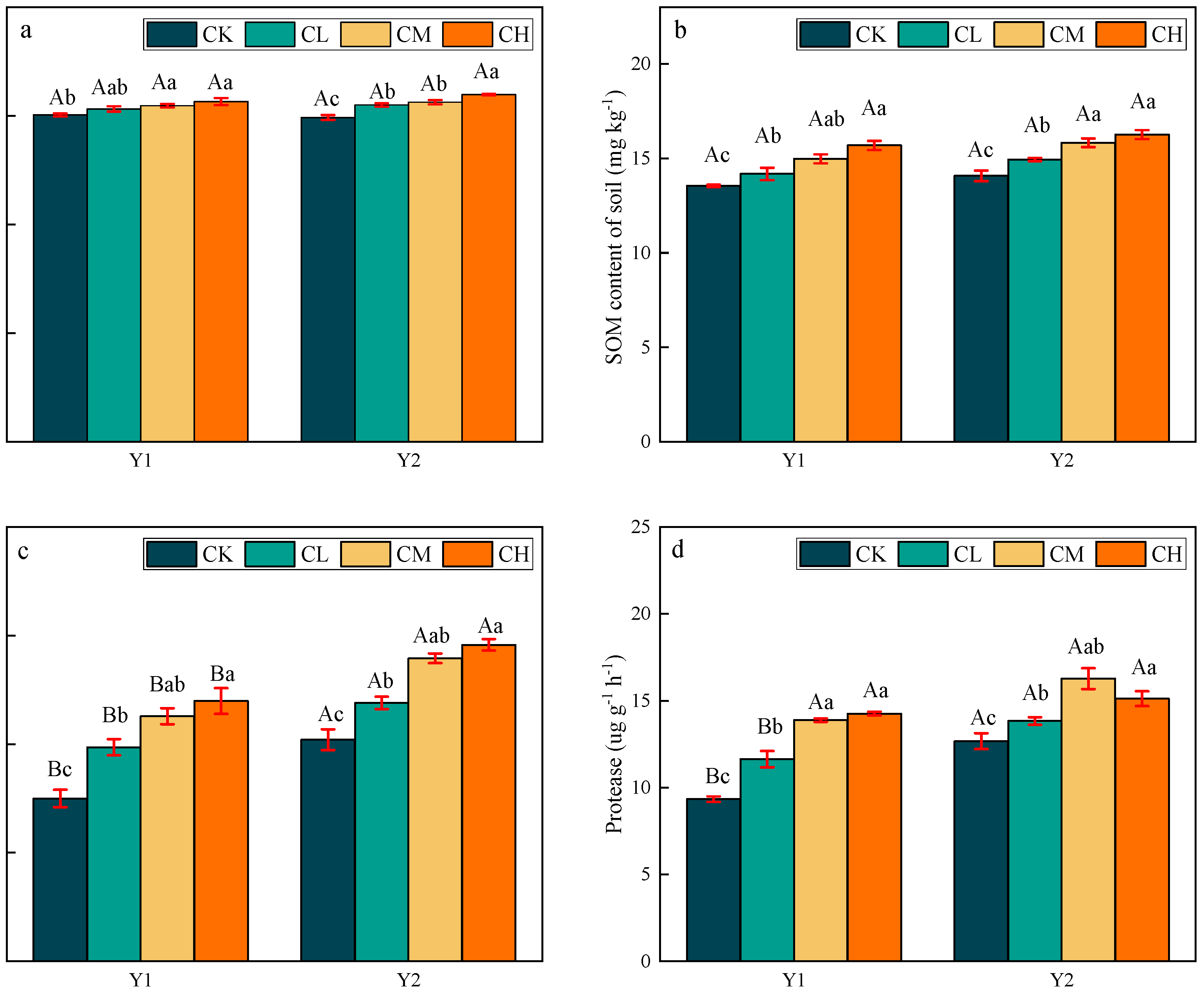
3.1. Soil Properties in Loamy Clay Paddy Soil under Different Treatments
3.2. SIN and SON Stocks in Loamy Clay Paddy Soil under Different Treatments
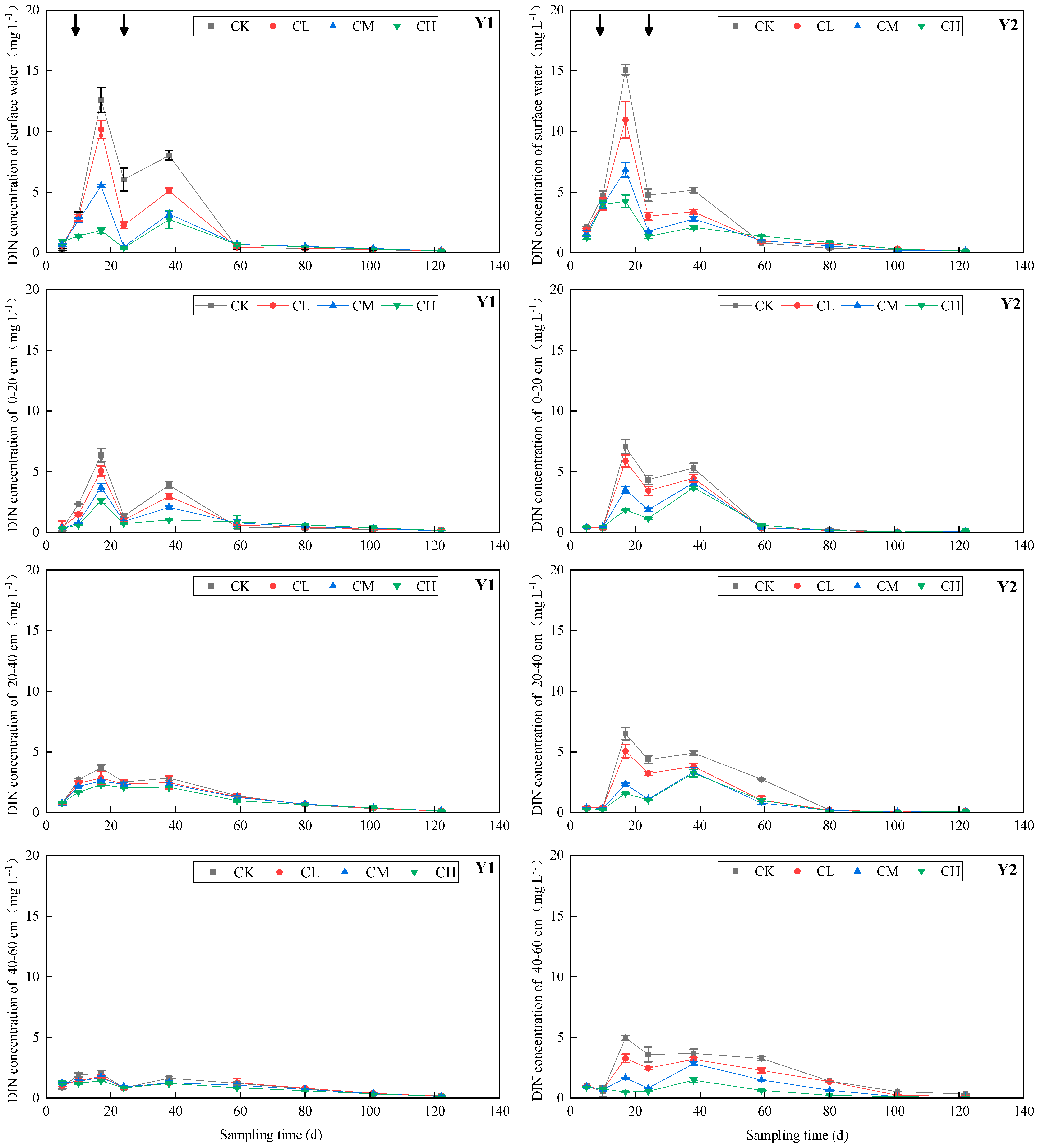
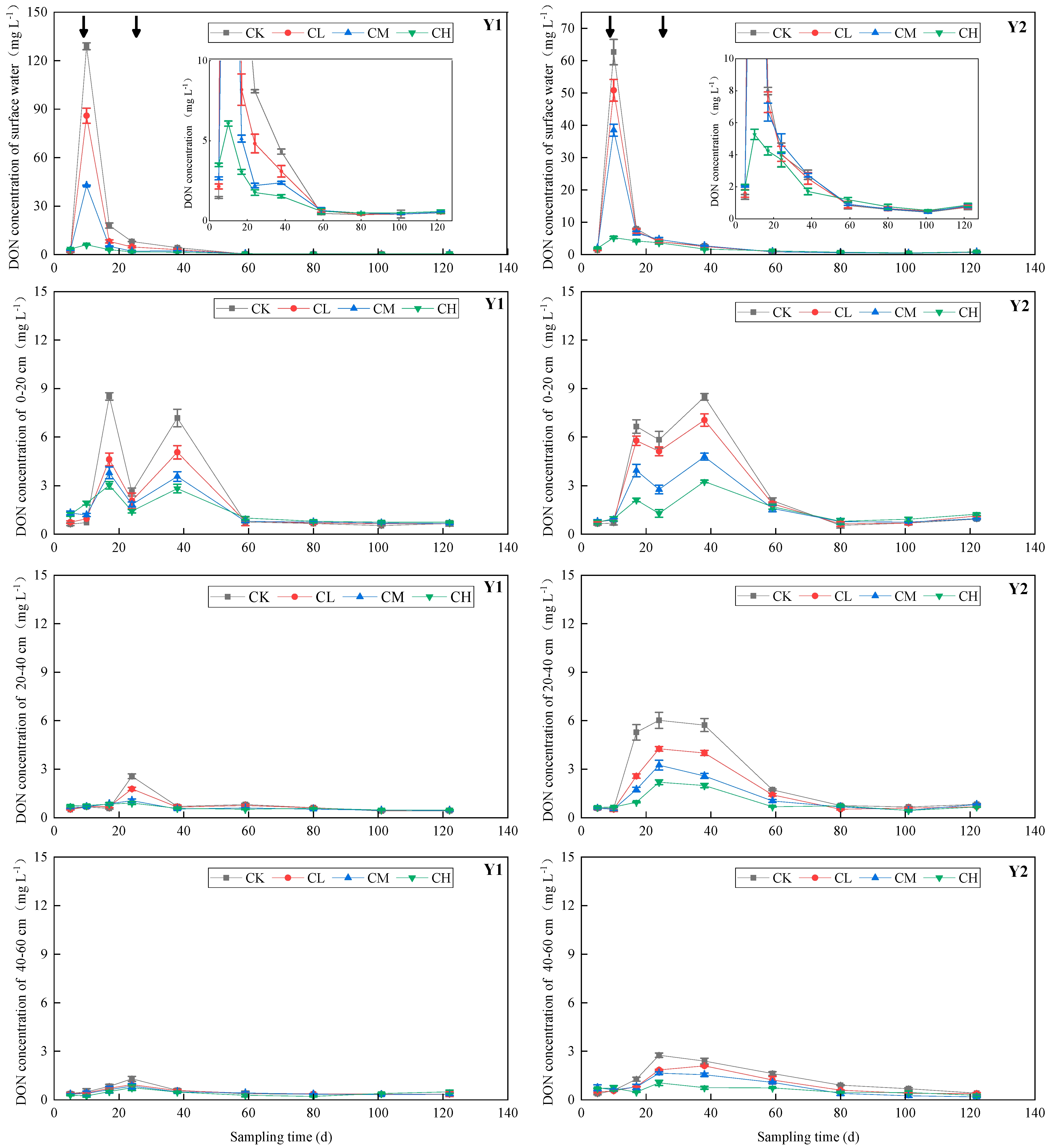
3.3. DIN and DON Concentrations in Soil Water at Different Depths
3.3.1. DIN Concentration in Soil Water
3.3.2. DON Concentration in Soil Water
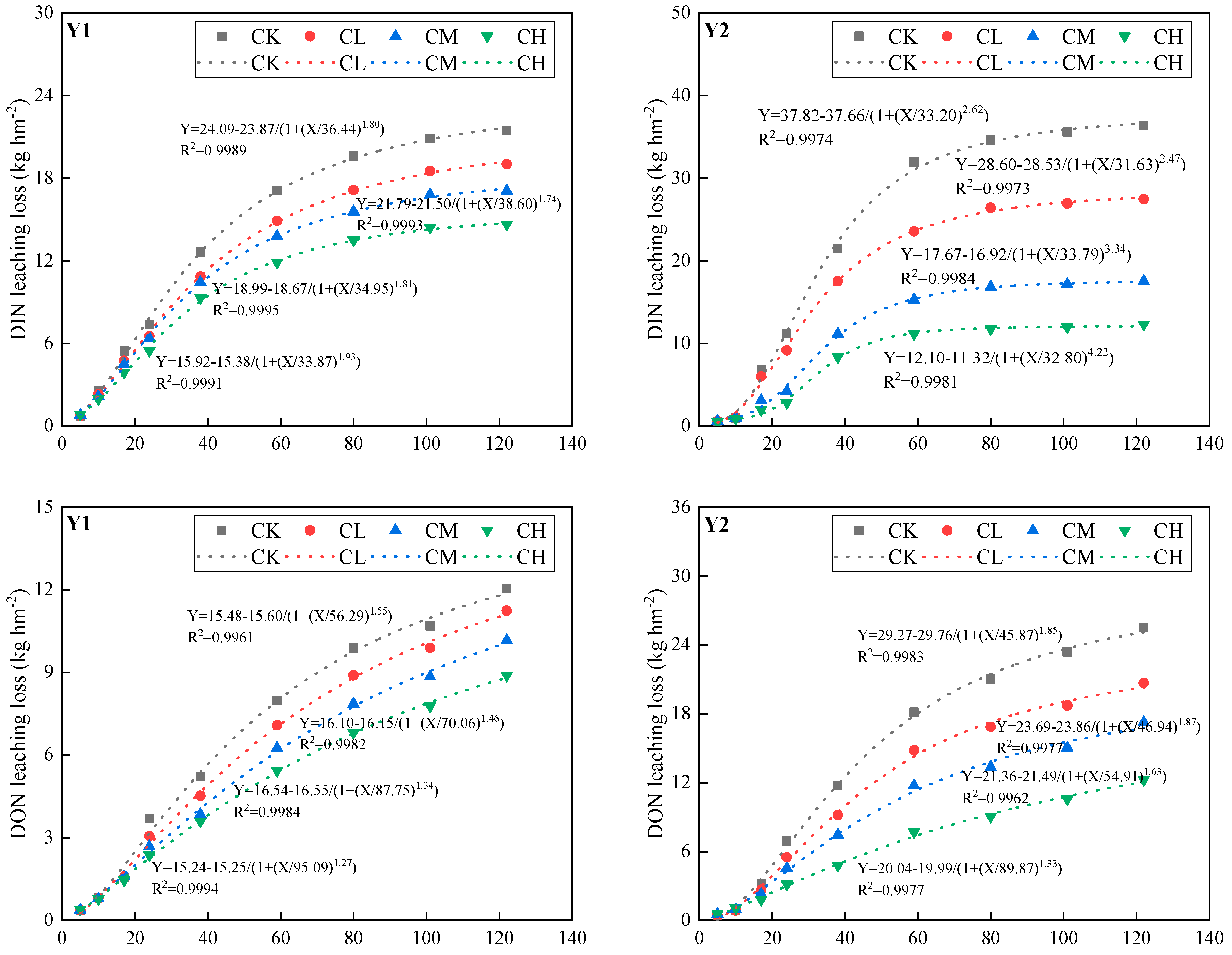
3.4. Potential Leaching Loss of DIN and DON in Loamy Clay Paddy Soil under Different Treatments
3.4.1. Leaching Rates of DIN and DON in Loamy Clay Paddy Soil
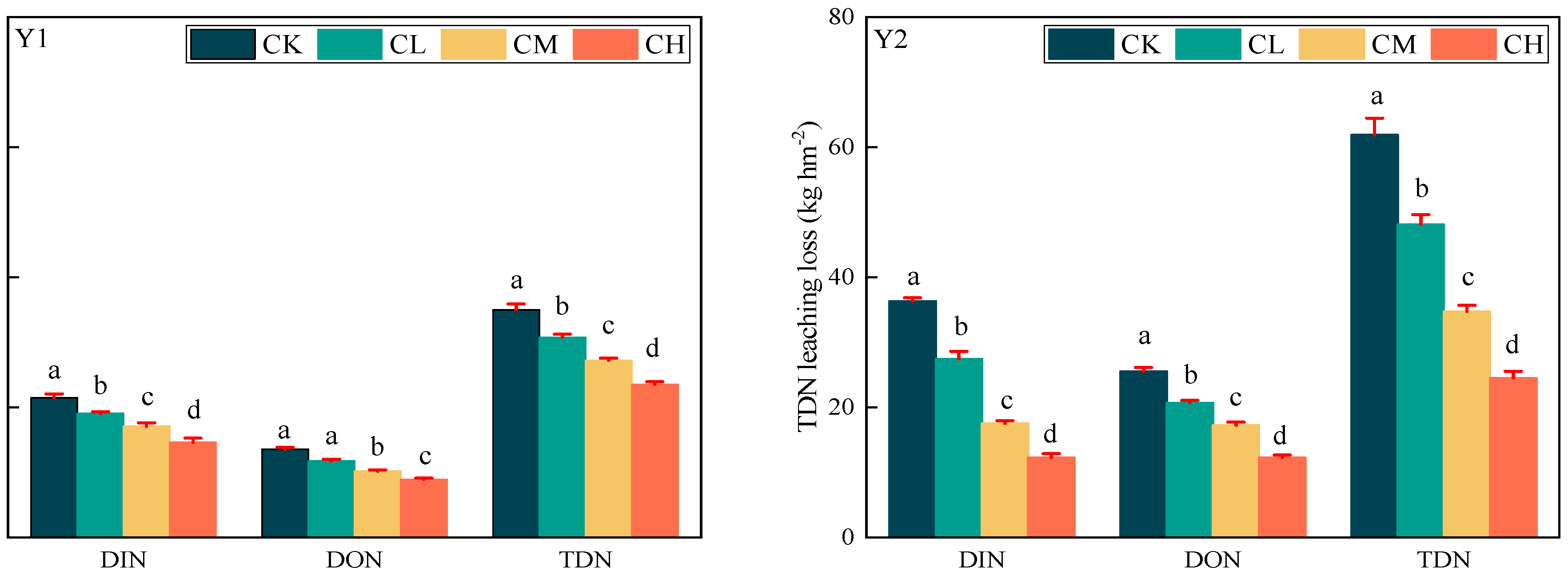
3.4.2. Leaching Loss of DIN and DON in Loamy Clay Paddy Soil
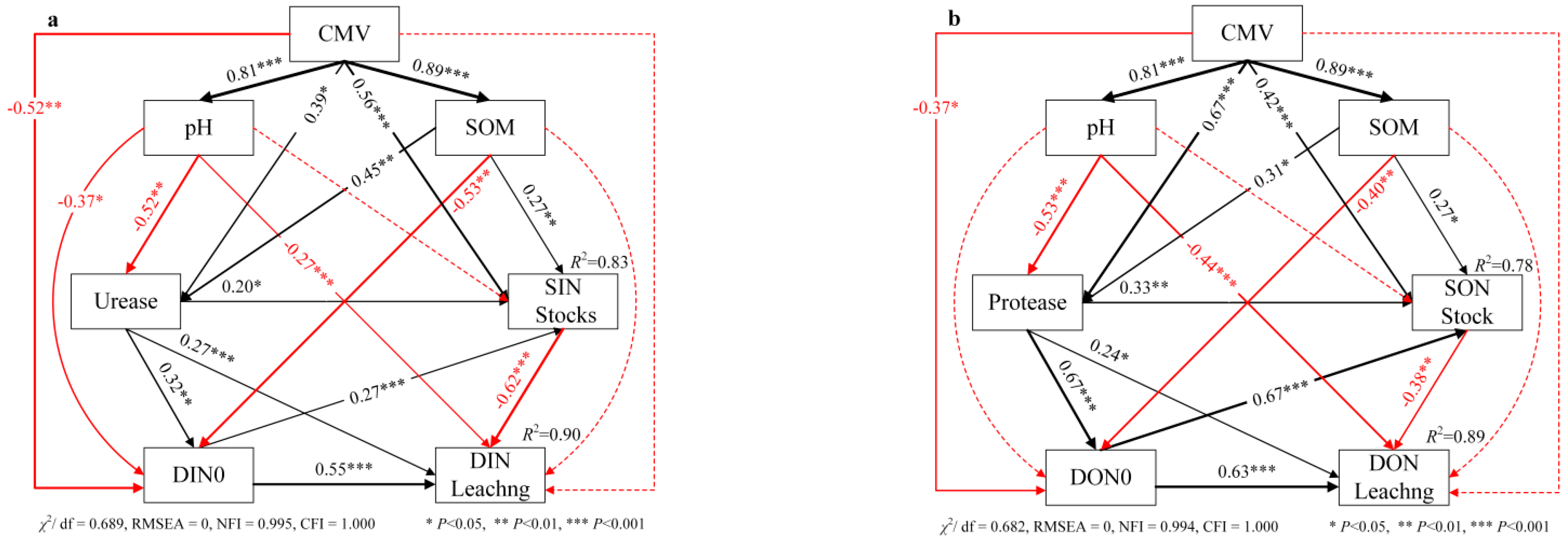
3.5. Influencing Factors of DIN and DON Leaching in Loamy Clay Paddy Soil under Different Treatments
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of CMV Application on SIN and SON Stocks in Loamy Clay Paddy Soil
4.2. Effects of CMV Application on DIN and DON Concentrations in Soil Water
4.3. Effects of CMV Application on DIN and DON Leaching in Loamy Clay Paddy Soil
4.4. Potential Risk of Nitrogen Leaching in Loamy Clay Paddy Soil
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. FAO Statistical Yearbook 2014 Asia and the Pacific Food and Agriculture. 2014. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-i3590e.pdf (accessed on 1 March 2014).
- Liu, K.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Zhang, W.Y.; Zhang, H.; Gu, J.F.; Yang, J.C.; Liu, L.J. Differing responses of root morphology and physiology to nitrogen application rates and their relationships with grain yield in rice. Crop. J. 2023, 11, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.B.; Huang, J.L.; Zhong, X.H.; Yang, J.C.; Wang, H.G.; Zou, Y.B.; Zhang, F.S.; Zhu, Q.S.; Buresh, R.; Witt, C. Research strategy in improving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2002, 35, 1095–1103. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ross, S.M.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Janzen, H.H.; Robertson, J.A.; McGill, W.B. The nitrogen balance of three long-term agroecosystems on a boreal soil in western Canada. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2008, 127, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Zhang, Y.W.; Yan, W.M.; Shangguan, Z.P. Effect of biochar application method on nitrogen leaching and hydraulic conductivity in a silty clay soil. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 183, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, T.Q.; Li, P.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.Q.; Deng, W.P. Runoff velocity controls soil nitrogen leaching in subtropical restored forest in southern China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 548, 121412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.N.; Grant, B.B.; Desjardins, R.L.; Kroebel, R.; Li, C.; Qian, B. Assessing the effects of climate change on crop production and GHG emissions in Canada. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 179, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanhee, L.; Feyereisen, G.W.; Hristov, A.N.; Dell, C.J.; Kaye, J.; Beegle, D. Effects of dietary protein concentration on ammonia volatilization, nitrate leaching, and plant nitrogen uptake from dairy manure applied to lysimeters. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 398–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, Y.J.; Park, J.H. Reducing nitrogen leaching using wood vinegar treated in urea-fertilized soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 7138–7145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Yao, Y.L.; Zeng, K.; Li, B.Y.; Tian, Y.H.; Yin, B. Study on mechanism of reducing nitrate leaching with organic addition from paddy field in Taihu Lake region. Soil 2020, 52, 766–772. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastrocicco, M. Intense rainfalls trigger nitrite leaching in agricultural soils depleted in organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Ti, C.; Xia, L.; Xia, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yan, X. Ecosystem services of partial organic substitution for chemical fertilizer in a peri-urban zone in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 224, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lam, S.K.; Yan, X.; Chen, D. How does recycling of livestock manure in agroecosystems affect crop productivity, reactive nitrogen losses, and soil carbon balance? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 7450–7457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, G. Litter quality and nitrogen release in tropical agriculture: A synthesis. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 31, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.J.; Ju, X.T.; Ingwersen, J.; Guo, Z.D.; Stange, C.F.; Bisharat, R.; Streck, T.; Chistie, P.; Zhang, F.S. Role of carbon substrates added in the transformation of surplus nitrate to organic nitrogen in a calcareous soil. Pedosphere 2013, 23, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.Y.; Xu, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Xie, J.C.; Zhou, G.P.; Hu, F.; Gao, S.J.; Cao, W.D. Application of milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) with reduced chemical fertilizer improves rice yield and nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium use efficiency in southern China. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 144, 126762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Y.; Liu, X.D.; Hua, Z.L.; Xue, H.Q.; Mei, S.C.; Wang, P.; Wang, S.W. Comparison of Nitrogen Loss Weight in Ammonia Volatilization, Runoff, and Leaching between Common and Slow-Release Fertilizer in Paddy Field. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Li, J.; Aamer, M.; Huang, G. Increasing methane (CH4) emissions and altering rhizosphere microbial diversity in paddy soil by combining Chinese milk vetch and rice straw. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.V.; Macdonald, A.J.; Stockdale, E.A.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Fortune, S.; Gaunt, J.L.; Poulton, P.R.; Wakefield, J.A.; Webster, C.P.; Wilmer, W.S. Soluble organic nitrogen in agriculture soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 30, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.S.J. Soil solution and extractable soil nitrogen response to climate change in two boreal forest ecosystems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2005, 41, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.L.; Laubach, J.; Hunt, J.E.; Mudge, P.L.; Nuñez, J.; Rogers, G.N.D.; Buxton, R.P.; Carrick, S.; Whitehead, D. Irrigation and grazing management affect leaching losses and soil nitrogen balance of lucerne. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 259, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.Y.; Chen, S.; Liang, B.; Qin, W.; Chen, Q. Catch crop planting and residue incorporation to reduce nitrogen leaching in intensive vegetable greenhouse field. J. Environ. Qual. 2022, 51, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, S.A.; Zhao, L.X.; Lei, X.M.; Sarfraz, R.; Xing, S.H. Dissolved organic nitrogen distribution in differently fertilized paddy soil profiles: Implications for its potential loss. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 262, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tribouillois, H.; Constantin, J.; Guillon, B.; Willaume, M.; Aubrion, G.; Fontaine, A.; Hauprich, P.; Kerveillant, P.; Laurent, F.; Therond, O. AqYield-N: A simple model to predict nitrogen leaching from crop fields. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 284, 107890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, G.H.; Hoffland, E.; Kessel, C.V.; Temminghoff, E.J.M. Extractable and dissolved soil organic nitrogen—A quantitative assessment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2009, 41, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitzmana, J.N.; Brooksb, J.R.; Comptonb, J.E.; Faulknerc, B.R.; Mayerb, P.M.; Peacheyd, R.E.; Rughb, W.D.; Coulombee, R.A.; Hatteberge, B.; Hutchins, S.R. Deep soil nitrogen storage slows nitrate leaching through the vadose zone. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 332, 107949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Yang, J.L.; Zhao, X.R.; Yang, S.H.; Mulder, J.; Dörschc, P.; Zhang, G.L. Nitrate leaching and N accumulation in a typical subtropical red soil with N fertilization. Geoderma 2022, 407, 115559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, N.; Han, J.C.; Mu, X.M.; Sun, Z.H.; Wang, H.Y. Effects of improved materials on reclamation of soil properties and crop yield in hollow villages in China. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2374–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Methods of Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Guan, S.Y. Soil Enzyme and Research Methods for Soil Enzyme; Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 1986. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, S.L.; Keay, P. Soluble organic nitrogen pools in forest soils of subtropical Australia. Plant Soil 2005, 277, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Li, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, X. Storage and sequestration potential of topsoil organic carbon in China’s paddy soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2003, 10, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Z.; Chang, D.N.; Li, B.Y.; Cao, W.D.; Lv, Y.H.; Pan, Z.L. Effects of planting and incorporation of Chinese milk vetch coupled with application of chemical fertilizer on active organic carbon and nitrogen in paddy soil. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2017, 54, 657–669. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.D.; Lu, Y.H.; Nie, J.; Zhu, Q.J.; Nie, X.; Cao, W.D.; Gao, Y.J.; Liao, Y.L. Effects of reducing chemical fertilizer combined with Chinese milk vetch on soil carbon and nitrogen in paddy fields. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2020, 39, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Xin, J.; Nai, H.; Zheng, X.L. Effects of different fertilizer applications on nitrogen leaching losses and the response in soil microbial community structure. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.M.; Xiao, X.P.; Tang, W.G.; Lin, Y.C.; Wang, K.; Yang, G.L. Effects of winter cover crops residue returning on soil enzyme activities and soil microbial community in double-cropping rice fields. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, J.; Xing, Y.; Xie, X.Y.; Wang, L.C. Influence of intercropping Chinese milk vetch on the soil microbial community in rhizosphere of rape. Plant Soil 2019, 440, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, W.H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.M.; Zhou, B.Q.; Sarfraz, R.; Xing, S.H. Driving factor of soluble organic nitrogen dynamics in paddy soils: Structure equation modeling analysis. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Y.; Lian, J.; Zeng, H.Q.; Liu, G.; Di, T.J.; Shen, Q.R.; Guo, H. Involvement of Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase in Adaption of Rice to Ammonium Nutrient. Rice Sci. 2011, 18, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, B.H.; Schmitt, J.; Chen, Z.H.; Liang, L.Y.; McCarthy, J.F. Adsorption and desorption of different organic matter fractions on iron oxide. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1995, 59, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filep, T.; Rékási, M. Factors controlling dissolved organic carbon (DOC), dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and DOC/DON ratio in arable soils based on a dataset from Hungary. Geoderma 2011, 162, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Sha, Z.M.; Wu, F.J.; Fang, K.K.; Xu, C.H.; Yang, X.L.; Zhu, Y.H.; Cao, L.K. Effect of rice-frog cultivation on ammonia volatilization in rice-Chinese milk vetch rotation system. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2021, 29, 792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Shannon, D.; Murphy, D.V.; Farrar, J. Role of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in soil N cycling in grassland soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2004, 36, 749–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Guggenberger, G. The role of DOM sorption to mineral surfaces in the preservation of organic matter in soils. Org. Geochem. 2000, 31, 711–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.E.; Rothstein, D.E. The dynamic exchange of dissolved organic matter percolating through six diverse soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 69, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, E.; Jones, D.L.; Hill, P.W.; Trivelin, P.C.O. Mineralisation and sorption of dissolved organic nitrogen compounds in litter and soil from sugarcane fields. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 103, 522–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.N.; Zhang, J.L.; Peng, C.R.; Li, D.H. Replacing nitrogen fertilizer with nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria reduced nitrogen leaching in red soil paddy fields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 312, 107320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skiba, U.; Wainwright, M. Urea hydrolysis and transformations in coastal dune sands and soil. Plant Soil 1984, 82, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, K.; Zech, W. Sorption of dissolved organic nitrogen by acid subsoil horizons and individual mineral phases. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2000, 51, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yin, B.; Zhu, Z. The assessment of nitrate leaching in a rice-wheat rotation system using an improved agronomic practice aimed to increase rice crop yields. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 241, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, D.J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, C. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer application rate on nitrogen leaching in paddy field incorporated with straw. Environ. Sci. 2010, 30, 1650–1657. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeney, D.R. Nitrogen management for maximum efficiency and minimum pollution. Nitro. Agri. Soil 1982, 22, 605–649. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.R.; Qin, W.J.; Chen, X.F.; Cao, W.D.; Qian, G.M.; Liu, J.; Xu, C.X. Application of Chinese milk vetch affects rice yield and soil productivity in a subtropical double-rice cropping system. J. Integr. Agric. 2020, 19, 2116–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wen, J.; Wen, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.N.; Bai, L.Y.; Su, S.M.; Zeng, X.B. Alteration of soil-surface electrochemical properties by organic fertilization to reduce dissolved inorganic nitrogen leaching in paddy fields. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.J.; Cao, W.D.; Zhou, G.P.; Rees, R.M. Bacterial communities in paddy soils changed by milk vetch as green manure: A study conducted across six provinces in South China. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.I.; Hossain, M.B.; Schmidhalter, U. Carbon and nitrogen mineralization in different upland soils of the subtropics treated with organic materials. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulo, E.N.D.; Galindo, F.S.; Rabêlo, F.H.S.; Frazão, J.J.; Lavres, J. 3,4-Dimethylpyrazole phosphate (DMPP) reduces nitrogen leaching in three tropical soils improves the agronomic efficiency of nitrogen fertilizers applied to cotton. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 2520–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.T.; Cai, H.J.; Wang, X.Y.; Ma, C.G.; Lu, Y.Y.; Ding, Y.B.; Wang, X.W.; Chen, H.; Wang, Y.F.; Saddique, Q. Exploring optimal irrigation and nitrogen fertilization in a winter wheat-summer maize rotation system for improving crop yield and reducing water and nitrogen leaching. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 228, 105904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Min, J.; Wang, S.Q.; Shi, W.M.; Xing, G.X. Nitrogen runoff dominates water nitrogen pollution from rice-wheat rotation in the Taihu Lake region of China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 156, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.Q.; Huang, X.; Chen, H.; Godfray, H.C.J.; Wright, J.S.; Hall, J.W.; Gong, P.; Ni, S.Q.; Qiao, S.C.; Huang, G.R. Managing nitrogen to restore water quality in China. Nature 2019, 567, 516–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, K.; Amano, H.; Takao, Y.; Berndtsson, R. On the use of coprostanol to identify source of nitrate pollution in groundwater. J. Hydrol. 2017, 550, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.M.; Akter, A.; Jahangir, M.M.; Ahmed, T. Leaching and runoff potential of nutrient and water losses in rice field as affected by alternate wetting and drying irrigation. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopácek, J.; Hejzlar, J.; Posch, M. Quantifying nitrogen leaching from diffuse agricultural and forest sources in a large heterogeneous catchment. Biogeochemistry 2013, 115, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Guo, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, B.; Yang, W.; Xing, S.; Ding, F. Increased Soil Soluble Nitrogen Stocks and Decreased Nitrogen Leaching Loss in Rice Paddy Soil by Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer with Chinese Milk Vetch. Agronomy 2024, 14, 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040715
Yang J, Guo W, Zhao C, Zhou B, Yang W, Xing S, Ding F. Increased Soil Soluble Nitrogen Stocks and Decreased Nitrogen Leaching Loss in Rice Paddy Soil by Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer with Chinese Milk Vetch. Agronomy. 2024; 14(4):715. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040715
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jing, Wenqi Guo, Chengsen Zhao, Biqing Zhou, Wenhao Yang, Shihe Xing, and Fenghua Ding. 2024. "Increased Soil Soluble Nitrogen Stocks and Decreased Nitrogen Leaching Loss in Rice Paddy Soil by Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer with Chinese Milk Vetch" Agronomy 14, no. 4: 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040715
APA StyleYang, J., Guo, W., Zhao, C., Zhou, B., Yang, W., Xing, S., & Ding, F. (2024). Increased Soil Soluble Nitrogen Stocks and Decreased Nitrogen Leaching Loss in Rice Paddy Soil by Replacing Nitrogen Fertilizer with Chinese Milk Vetch. Agronomy, 14(4), 715. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14040715




