Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water in Controlling Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato in Tomato Crops
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electrolyzed Water Treatments for Tomato Plants
2.2. Quality Tests on the Fruit
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Fruit Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- SADER—Secretaria de Agricultura y Desarrollo Rural, México, Referente Mundial en el Cultivo y Exportación de Jitomate: Agricultura, March 2022. Available online: https://www.gob.mx/agricultura/prensa/mexico-referente-mundial-en-el-cultivo-y-exportacion-de-jitomate-agricultura#:~:text=M%C3%A9xico%20se%20ha%20constituido%20como,y%20Singapur%2C%20entre%20otros%20mercados%2C (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- The Observatory of Economic Complexity: OEC. Available online: https://oec.world/es/profile/hs92/tomatoes?redirect=true (accessed on 25 May 2023).
- Morán-Diez, M.E.; Tranque, X.F.; He, S.Y. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000: A Model Pathogen for Probing Disease Susceptibility and Hormone Signaling in Plants. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2013, 51, 473–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, G.M. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato: The right pathogen, of the right plant, at the right time. Mol. Plan Pathol. 2000, 1, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunnac, S.; Lindeberg, M.; Collmer, A. Pseudomonas syringae type III secretion system effectors: Repertoires in search of functions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiga, Y.; Ichinose, Y. Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato OxyR Is Required for Virulence in Tomato and Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2016, 29, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Uppalapati, S.R.; Ishiga, Y.; Wangdi, T.; Urbanczyk-Wochniak, E.; Ishiga, T.; Mysore, K.S.; Bender, C.L. Pathogenicity of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato on tomato seedlings: Phenotypic and gene expression analyses of the virulence function of coronatine. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2008, 21, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morán-Diez, M.E.; Tranque, E.; Bettiol, W.; Monte, E.; Hermosa, R. Differential Response of Tomato Plants to the Application of Three Trichoderma Species When Evaluating the Control of Pseudomonas syringae Populations. Plants 2020, 9, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsharkawy, M.; Derbalah, A.; Hamza, A.; El-Shaer, A. Zinc oxide nanostructures as a control strategy of bacterial speck of tomato caused by Pseudomonas syringae in Egypt. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 19049–19057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quattrucci, A.; Balestra, G.M. Antibacterial activity of natural extracts in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato control. Acta Hortic. 2009, 808, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quaglia, M.; Bocchini, M.; Orfei, B.; D’Amato, R.; Famiani, F.; Moretti, C.; Buonaurio, R. Zinc phosphate protects tomato plants against Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. J. Plant Dis. Prot. 2021, 128, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, F.P. Agriculture, pesticides, food security and food safety. Environ. Sci. Policy. 2006, 9, 685–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canzoniere, P.; Francesconi, S.; Giovando, S.; Balestra, G.M. Antibacterial activity of tannins towards Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato, and their potential as biostimulants on tomato plants. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2021, 60, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aktar, M.W.; Sengupta, D.; Chowdhury, A. Impact of pesticides use in agriculture: Their benefits and hazards. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vásquez-López, A.; Villarreal-Barajas, T.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, G. Effectiveness of neutral electrolyzed water on incidence of fungal rot on tomato fruits (Solanum lycopersicum L.). J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1802–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yue, H.; Xu, S.; Tian, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, J. The effect of electrolyzed water on fresh-cut eggplant in storage period. LWT. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 123, 109080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guentzel, J.L.; Callan, M.A.; Liang Lam, K.; Emmons, S.A.; Dunham, V.L. Evaluation of electrolyzed oxidizing water for phytotoxic effects and pre-harvest management of gray mold disease on strawberry plants. Crop Prot. 2011, 30, 1274–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, K.; Fujii, T.; Park, J. Successive spraying efficacy of acidic electrolyzed oxidizing water and alkalic electrolyzed reducing water on controlling powdery mildew infection and suppressing visible physiological disorder on cucumber leaves. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2011, 52, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, B.; Jadeja, R.; Hung, Y. Effects of electrolyzed oxidizing water on inactivation of bacillus subtilis and bacillus cereus spores in suspension and on carriers. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, M144–M149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangloli, P.; Hung, Y. Efficacy of slightly acidic electrolyzed water in killing or Reducing Escherichia coli O157:H7 on iceberg lettuce and tomatoes under simulated food service operation conditions. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, M361–M366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiroodi, S.G.; Ovissipour, M. Electrolyzed Water Application in Fresh Produce Sanitation. In Postharvest Disinfection of Fruits and Vegetables, 1st ed.; Mohammed, W.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Kolkata, India, 2018; pp. 67–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Hung, Y.; Hsu, S.; Huang, Y.; Hwang, D. Application of electrolyzed water in the food industry. Food Control 2008, 19, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, S.M.E.; Khan, I.; Oh, D.H. Electrolyzed water as a novel sanitizer in the food industry: Current trends and future perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 471–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovissipour, M.; Al-Qadiri, H.M.; Sablani, S.S.; Govindan, B.N.; Al-Alami, N.; Rasco, B. Efficacy of acidic and alkaline electrolyzed water for inactivating Escherichia coli O104:H4, Listeria monocytogenes, Campylobacter jejuni, Aeromonas hydrophila, and Vibrio parahaemolyticus in cell suspensions. Food Control 2015, 53, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Li, H.; Wan, Y.; Liu, H. Effect of slightly acidic electrolyzed water (SAEW) treatment on the microbial reduction and storage quality of Fresh-Cut cilantro. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2015, 39, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, R.; Bryant, M.; Degala, H.L.; Mahapatra, A.K.; Kannan, G. Effectiveness of a low-cost household electrolyzed water generator in reducing the populations of Escherichia coli K12 on inoculated beef, chevon, and pork surfaces. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2018, 42, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, S.; Burkhardt, W. Efficacy of electrolyzed oxidizing water against Listeria monocytogenes and Morganella morganii on conveyor belt and raw fish surfaces. Food Control 2012, 24, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Qadiri, H.M.; Smith, S.; Sielaff, A.C.; Govindan, B.N.; Ziyaina, M.; Al-Alami, N.; Rasco, B. Bactericidal activity of neutral electrolyzed water against Bacillus cereus and Clostridium perfringens in cell suspensions and artificially inoculated onto the surface of selected fresh produce and polypropylene cutting boards. Food Control 2019, 96, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Mahendran, R.; Alagusundaram, K.; Norton, T.; Tiwari, B.K. Novel disinfectants for fresh produce. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 34, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Orejel, J.C.; Cano-Buendía, J.A. Applications of Electrolyzed Water as a Sanitizer in the Food and Animal-By Products Industry. Processes 2020, 8, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoyo, L.M.; Saavedra, T.M.; Elos, M.M.; García, U.M.L.; López, M.A.C.; Martínez, T.O.M. Antibacterial activity of electrolyzed water on Pseudomonas syringae and Clavibacter michiganensis and its effect on seed germination. Cienc. Rural 2024, 54, e20220416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, P.A.; Lazarovits, G. Effect of acidic electrolyzed water on the viability of bacterial and fungal plant pathogens and on bacterial spot disease of tomato. Can. J. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aires, A.; Dias, C.; Carvalho, R.; Oliveira, M.; Monteiro, A.; Simões, M.; Rosa, E.; Bennett, R.; Saavedra, M. Correlations between disease severity, glucosinolate profiles and total phenolics and Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris inoculation of different Brassicaceae. Sci. Hortic. 2011, 129, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casierra-Posada, F.; Aguilar-Avendaño, Ó.E. Calidad en frutos de tomate (Solanum lycopersicum L.) cosechados en diferentes estados de madurez. Agron. Colomb. 2008, 26, 300–307. [Google Scholar]
- Peñaloza-Vázquez, A.; Preston, G.M.; Collmer, A.; Bender, C.L. Regulatory interactions between the Hrp type III protein secretion system and coronatine biosynthesis in Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato DC3000. Microbiology 2000, 146, 2447–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Arah, I.K.; Ahorbo, G.K.; Anku, E.K.; Kumah, E.K.; Amaglo, H. Postharvest Handling Practices and Treatment Methods for Tomato Handlers in Developing Countries: A Mini Review. Adv. Agric. 2016, 2016, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thole, V.; Vain, P.; Yang, R.; Almeida Barros da Silva, J.; Enfissi, E.M.A.; Nogueira, M.; Martin, C. Analysis of Tomato Post-Harvest Properties: Fruit Color, Shelf Life, and Fungal Susceptibility. Curr. Protoc. Plant Biol. 2020, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilahy, R.; Tlili, I.; Siddiqui, M.W.; Hdider, C.; Lenucci, M.S. Inside and Beyond Color: Comparative Overview of Functional Quality of Tomato and Watermelon Fruits. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Hung, Y. Inactivation of E. coli O157:H7 on blueberries by electrolyzed water, ultraviolet light, and ozone. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, M206–M211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Han, B. Efficacy of acidic and basic electrolyzed water in eradicating staphylococcus aureus biofilm. Can. J. Microbiol. 2012, 58, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buck, J.W.; Van-Iersel, M.W.; Oetting, R.D.; Hung, Y. Evaluation of acidic electrolyzed water for phytotoxic symptoms on foliage and flowers of bedding plants. Crop Prot. 2003, 22, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, Y.; Asano, S.; Watanabe, K.; Sakamoto, Y.; Ozaki, M.; Okayama, K.; Tojo, M. Control of Colletotrichum fructicola on strawberry with a foliar spray of neutral electrolyzed water through an overhead irrigation system. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2016, 82, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, D.S.; Hung, Y.; Oetting, R.D.; Van Iersel, M.W.; Buck, J.W. Evaluation of electrolyzed oxidizing water for management of powdery mildew on gerbera daisy. Plant Dis. 2003, 87, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarattini, M.; De Bastiani, M.; Bernacchia, G.; Ferro, S.; De Battisti, A. The use of ECAS in plant protection: A green and efficient antimicrobial approach that primes selected defense genes. Ecotoxicology 2015, 24, 1996–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassiri, S.M.; Tahavoor, A.; Jafari, A. Fuzzy logic classification of mature tomatoes based on physical properties fusion. Inf. Process. Agric. 2022, 9, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiharta, L.; Maretta, G.; Pawhestri, S.; Eka, A. Electrolysis of Water Using Iron Electrode to Boost the Growth of Hydroponic Plant of Water Spinach. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2019, 1155, 012054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Pei, L.; Zhao, J.; Gao, W.; Qi, F.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, S. Effect of Irrigating with Slightly Acidic Electrolyzed Water on Lettuce Photosynthesis under Mild Water Stress. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2014, 30, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeshiwas, Y.; Tolessa, K. Postharvest quality of tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) varieties grown under greenhouse and open field conditions. Int. J. Biotechnol. Mol. Biol. Res. 2018, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantwell, M.; Stoddard, S.; LeStrange, M.; Aegerter, B. Report to the California Tomato Commission. Tomato Variety Trials: Postharvest Evaluations for 2006; UCCE Fresh Market Tomato Variety Trial 2006 Postharvest Evaluation; UC Davis: Davis, CA, USA, 2006; 16p. [Google Scholar]
- Okolie, N.; Sanni, T. Effect of post harvest treatments on quality of whole tomatoes. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2012, 6, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.R.; Singha, A.; Faruquee, M.; Jiku, M.A.S.; Rahaman, M.A.; Alam, M.A.; Kader, M.A. Post-harvest assessment of fruit quality and shelf life of two elite tomato varieties cultivated in Bangladesh. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2019, 43, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardona, C.; Arjona, H.; Araméndiz-Tatis, H. Influencia de la fertilización foliar con Ca sobre la pudrición apical en tomate (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). Agron. Colomb. 2005, 23, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Urrieta-Velázquez, J.A.; Rodríguez-Mendoza, M.; Ramírez-Vallejo, P.; Baca-Castillo, G.A.; Ruiz-Posadas, L.; Cueto-Wong, J.A. Production and Quality Variables of Three Selections of Ribbed Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Rev. Chapingo Ser. Hortic. 2012, 18, 371–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Crespo, E.; Martínez-Rodríguez, O.G.; García-Paredes, J.D.; Can-Chulim, A. Influencia del riego y sustrato en el rendimiento y calidad de tomate. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Agríc. 2017, 8, 51–63. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, K.P.; Sargent, S.A.; Fox, A.J. Effect of Storage Temperature on Ripening and Postharvest Quality of Grape and Mini-Pear Tomatoes. Proc. Fla. State Hortic. Soc. 2002, 11, 80–84. [Google Scholar]
- Camelo, A.; Gómez, P. Comparison of color indexes for tomato ripening. Hortic. Bras. 2004, 22, 534–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
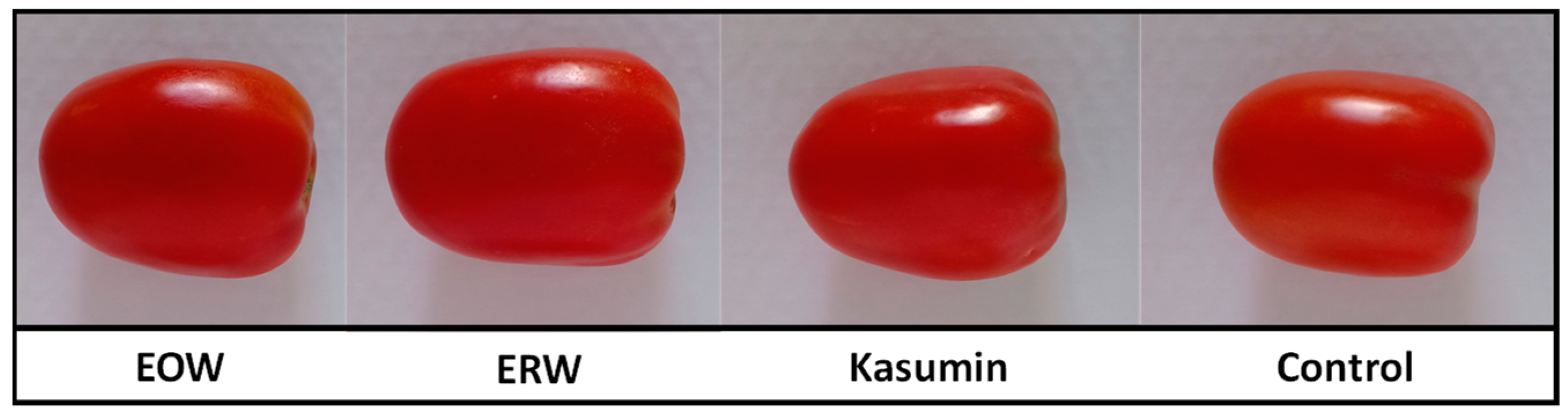

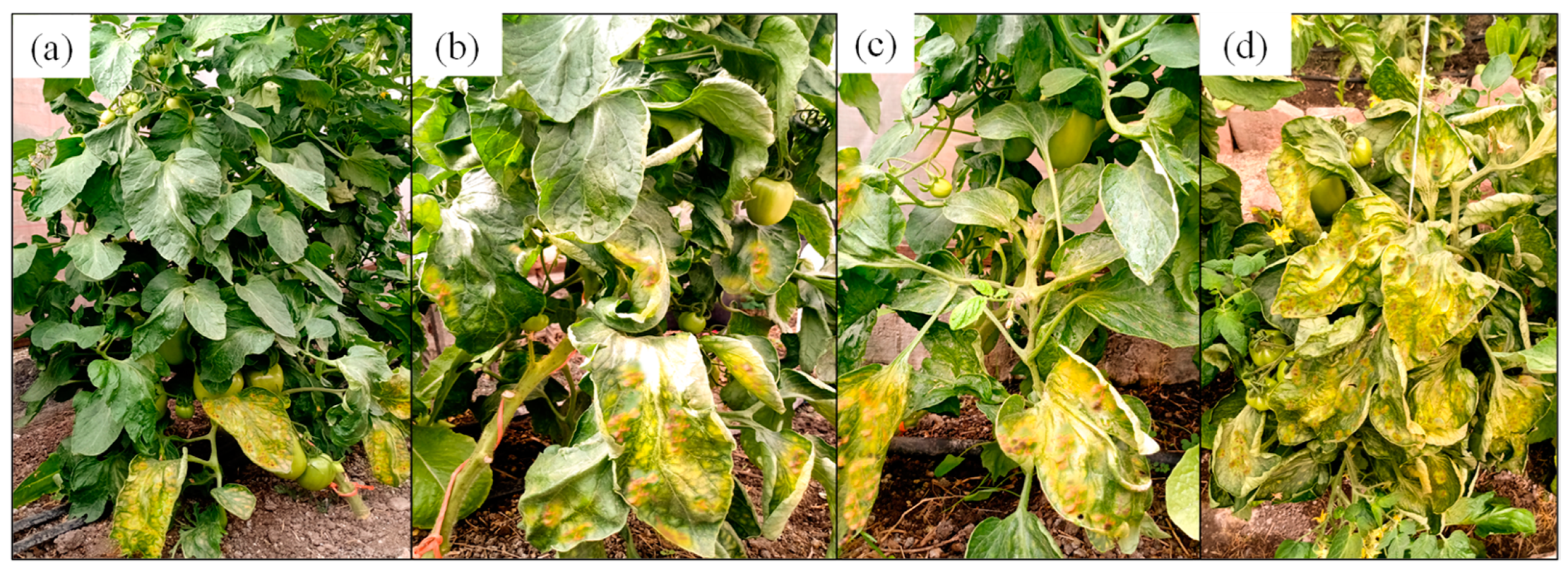
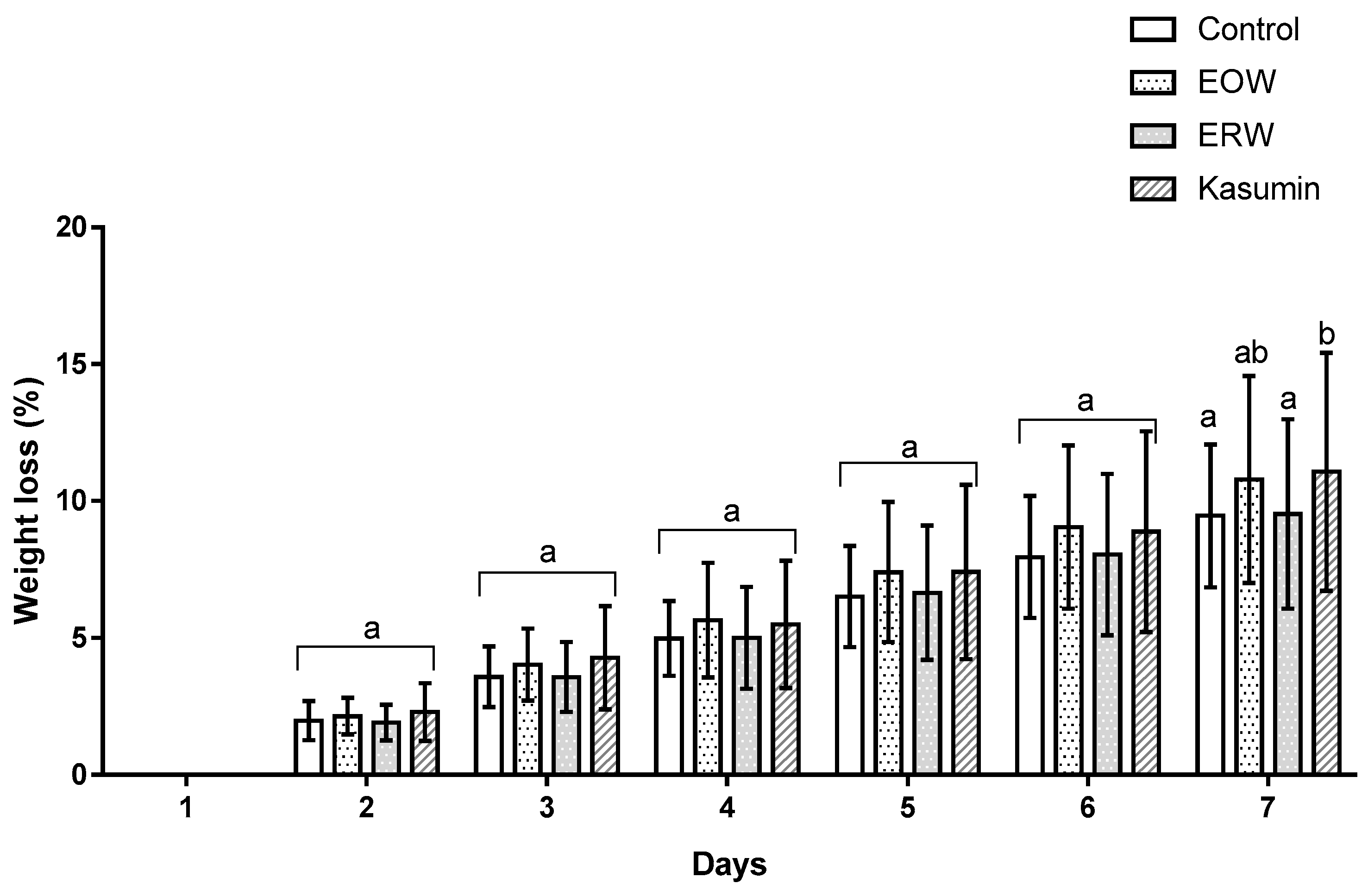

| Treatment | SD (cm) | NL | NC |
|---|---|---|---|
| EOW | 1.91 ± 0.12 ab | 14.22 ± 1.08 a | 6.78 ± 0.48 a |
| ERW | 2.07 ± 0.51 a | 14.78 ± 0.51 a | 6.50 ± 0.17 a |
| Kasumin | 1.74 ± 0.12 b | 14.67 ± 0.88 a | 7.39 ± 0.26 a |
| Control | 1.72 ± 0.10 b | 13.78 ± 0.25 a | 7.22 ±0.09 a |
| Treatment | Weight (g) | PD (cm) | ED (cm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EOW | 202.27 ± 49.39 a | 8.36 ± 0.74 ab | 6.50 ± 0.58 ab |
| ERW | 236.16 ± 42.86 b | 8.16 ± 1.53 ab | 6.92 ± 0.44 b |
| Kasumin | 205.11 ± 36.85 a | 8.15 ± 0.59 b | 6.67 ± 0.45 ab |
| Control | 223.27 ± 35.62 ab | 8.65 ± 0.67 a | 6.80 ± 0.48 a |
| Treatment | °Brix | TA (% Citric Acid) | pH | Firmness (kg/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOW | 3.58 ± 0.49 a | 0.323 ± 0.003 a | 4.44 ± 0.26 a | 2.38 ± 0.53 a |
| ERW | 3.44 ± 0.58 ab | 0.358 ± 0.003 ab | 4.53 ± 0.19 ab | 2.39 ± 0.55 a |
| Kasumin | 2.97 ± 0.49 b | 0.352 ± 0.004 abc | 4.51 ± 0.07 a | 2.33 ± 0.47 a |
| Control | 3.10 ± 0.53 b | 0.308 ± 0.004 ad | 4.60 ± 0.31 b | 2.55 ± 0.47 a |
| Treatment | L* | a* | b* | a*/b* | CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EOW | 38.10 ± 1.19 a | 26.09 ± 3.01 a | 26.13 ± 1.72 a | 1.00 ± 0.12 a | 37.03 ± 3.04 a |
| ERW | 38.36 ± 1.26 a | 24.34 ± 2.47 ab | 25.59 ± 1.51 a | 0.95 ± 0.07 a | 35.92 ± 2.13 a |
| Kasumin | 38.34 ± 1.17 a | 23.72 ± 2.68 b | 24.32 ± 4.28 b | 0.99 ± 0.13 a | 36.49 ± 3.41 a |
| Control | 38.57 ± 1.32 a | 26.27 ± 1.91 ac | 26.42 ± 1.61 ac | 1.00 ± 0.06 a | 36.58 ± 1.84 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mexicano, L.; Medina, T.; Mexicano, A.; Carmona, J.-C. Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water in Controlling Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato in Tomato Crops. Agronomy 2024, 14, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030597
Mexicano L, Medina T, Mexicano A, Carmona J-C. Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water in Controlling Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato in Tomato Crops. Agronomy. 2024; 14(3):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030597
Chicago/Turabian StyleMexicano, Lilia, Tarsicio Medina, Adriana Mexicano, and Jesús-Carlos Carmona. 2024. "Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water in Controlling Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato in Tomato Crops" Agronomy 14, no. 3: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030597
APA StyleMexicano, L., Medina, T., Mexicano, A., & Carmona, J.-C. (2024). Electrolyzed Oxidizing Water in Controlling Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato in Tomato Crops. Agronomy, 14(3), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14030597








