Straw Returning with Decomposition Agent Enhanced Rice Yield and Decreased Yield-Scaled N2O Emissions in Tropical Paddy Fields
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sampling
2.4. Analysis
2.5. DNA Extraction and Real–Time PCR
2.6. Data and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.2. Yield and the Nutrients in Straw and Grain
3.3. Soil N2O Emissions
3.4. Soil NH4+ and NO3– Contents
3.5. Abundance of N-Cycling Functional Genes
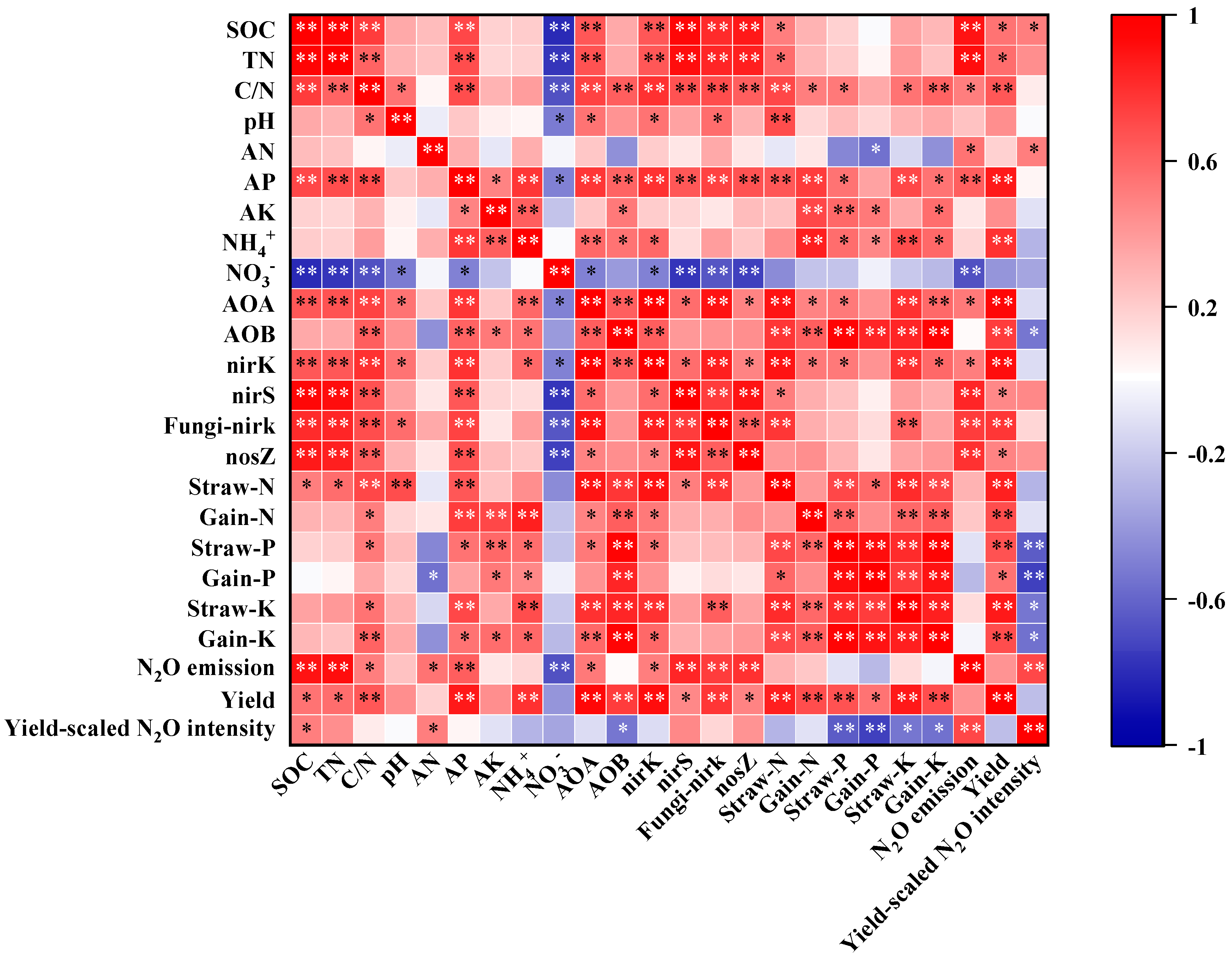
3.6. Dominant Factors Controlling Soil N2O Emissions and Rice Yield
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Returning Decomposed Straw on Soil Properties and Rice Yield
4.2. Effects of Returning Straw on Soil N2O Emissions
4.3. Effects of Returning Decomposed Straw on Soil N2O Emissions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Reay, D.S.; Davidson, E.A.; Smith, K.A.; Smith, P.; Melillo, J.M.; Dentener, F.; Crutzen, P.J. Global Agriculture and Nitrous Oxide Emissions. Nat. Clim. Change 2012, 2, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravishankara, A.R.; Daniel, J.S.; Portmann, R.W. Nitrous Oxide (N2O): The Dominant Ozone-Depleting Substance Emitted in the 21st Century. Science 2009, 326, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterbach-Bahl, K.; Dannenmann, M. Denitrification and Associated Soil N2O Emissions Due to Agricultural Activities in a Changing Climate. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2011, 3, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindlbacher, A.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Butterbach-Bahl, K. Effects of Soil Moisture and Temperature on NO, NO2, and N2O Emissions from European Forest Soils. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuhel, J.; Šimek, M.; Laughlin, R.J.; Bru, D.; Chèneby, D.; Watson, C.J.; Philippot, L. Insights into the Effect of Soil pH on N2O and N2 Emissions and Denitrifier Community Size and Activity. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 1870–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitz, A.M.; Linder, E.; Frolking, S.; Crill, P.M.; Keller, M. N2O Emissions from Humid Tropical Agricultural Soils: Effects of Soil Moisture, Texture and Nitrogen Availability. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1077–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, S.; Breitenbeck, G.A.; Faulkner, S.P. Denitrification and N2O Emission from Forested and Cultivated Alluvial Clay Soil. Biogeochemistry 2005, 73, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senbayram, M.; Chen, R.; Budai, A.; Bakken, L.; Dittert, K. N2O Emission and the N2O/(N2O + N2) Product Ratio of Denitrification as Controlled by Available Carbon Substrates and Nitrate Concentrations. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 147, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, A.A.; Madramootoo, C.; Hamel, C.; Liu, A. Denitrification and Nitrous Oxide to Nitrous Oxide plus Dinitrogen Ratios in the Soil Profile under Three Tillage Systems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 38, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Wu, X.; Yu, Y.; Luo, S.; Hu, R.; Lu, G. Effects of Mild Alternate Wetting and Drying Irrigation and Mid-Season Drainage on CH4 and N2O Emissions in Rice Cultivation. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 698, 134212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chidthaisong, A.; Cha-un, N.; Rossopa, B.; Buddaboon, C.; Kunuthai, C.; Sriphirom, P.; Towprayoon, S.; Tokida, T.; Padre, A.T.; Minamikawa, K. Evaluating the Effects of Alternate Wetting and Drying (AWD) on Methane and Nitrous Oxide Emissions from a Paddy Field in Thailand. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2018, 64, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenet, B.; Gabrielle, B.; Chenu, C.; Arrouays, D.; Balesdent, J.; Bernoux, M.; Bruni, E.; Caliman, J.-P.; Cardinael, R.; Chen, S. Can N2O Emissions Offset the Benefits from Soil Organic Carbon Storage? Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 237–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasek, A.A.; Hondzo, M.; Kozarek, J.L.; Staley, C.; Wang, P.; Lurndahl, N.; Sadowsky, M.J. Intermittent Flooding of Organic-rich Soil Promotes the Formation of Denitrification Hot Moments and Hot Spots. Ecosphere 2019, 10, e02549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gergel, S.E.; Carpenter, S.R.; Stanley, E.H. Do Dams and Levees Impact Nitrogen Cycling? Simulating the Effects of Flood Alterations on Floodplain Denitrification. Glob. Change Biol. 2005, 11, 1352–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prado, A.; Merino, P.; Estavillo, J.M.; Pinto, M.; González-Murua, C. N2O and NO Emissions from Different N Sources and under a Range of Soil Water Contents. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2006, 74, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A. Soil Water Content and the Ratio of Nitrous Oxide to Nitric Oxide Emitted from Soil. In Proceedings of the Biogeochemistry of Global Change: Radiatively Active Trace Gases Selected Papers from the Tenth International Symposium on Environmental Biogeochemistry, San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–24 August 1991; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; pp. 369–386. [Google Scholar]
- Powlson, D.S.; Glendining, M.J.; Coleman, K.; Whitmore, A.P. Implications for Soil Properties of Removing Cereal Straw: Results from Long-Term Studies 1; Wiley Online Library: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011; ISBN 0002-1962. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; Ma, W.; Zhou, B.; Yang, X.; Salah, A.; Li, C.; Cao, C.; Zhan, M.; Zhao, M. Effects of Straw-Return Method for the Maize–Rice Rotation System on Soil Properties and Crop Yields. Agronomy 2020, 10, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francioni, M.; Hoshino, Y.T.; Kishimoto-Mo, A.W. Effects of Crop Residue Incorporation on Soil-biodegradable Mulch Film Degradation in a Broccoli-sorghum Rotation System. Agron. J. 2024, 116, 94–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berhane, M.; Xu, M.; Liang, Z.; Shi, J.; Wei, G.; Tian, X. Effects of Long-term Straw Return on Soil Organic Carbon Storage and Sequestration Rate in North China Upland Crops: A Meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 2686–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Shar, A.G.; Li, S.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Tian, X. Effect of Straw Return Mode on Soil Aggregation and Aggregate Carbon Content in an Annual Maize-Wheat Double Cropping System. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Xu, Z.; Xue, Y.; Sun, R.; Yang, R.; Cao, X.; Li, H.; Shao, Q.; Lou, Y.; Wang, H. N2O Emissions from Soils under Short-Term Straw Return in a Wheat-Corn Rotation System Are Associated with Changes in the Abundance of Functional Microbes. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 341, 108217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Ding, W.; Liu, D.; He, T.; Yoo, G.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Z.; Fan, J. Wheat Straw-Derived Biochar Amendment Stimulated N2O Emissions from Rice Paddy Soils by Regulating the amoA Genes of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 113, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.S.; Hedley, M.J.; White, R.E. Processes of Soil Acidification during Nitrogen Cycling with Emphasis on Legume Based Pastures. Plant Soil 1991, 134, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chapman, S.J.; Nicol, G.W.; Yao, H. Nitrification and Nitrifiers in Acidic Soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 116, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, H.A.; Loveless, J.E. Effect of Temperature and pH Value on the Growth-Rate Constants of Nitrifying Bacteria in the Activated-Sludge Process. Water Res. 1983, 17, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cáceres, R.; Malińska, K.; Marfà, O. Nitrification within Composting: A Review. Waste Manag. 2018, 72, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, F.; Song, J.; Giltrap, D.; Feng, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, S. Crop Yield and N2O Emission Affected by Long-Term Organic Manure Substitution Fertilizer under Winter Wheat-Summer Maize Cropping System. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Senbayram, M.; Well, R.; Brüggemann, N.; Pfeiffer, B.; Loick, N.; Stempfhuber, B.; Dittert, K.; Bol, R. Nitrification Inhibitors Mitigate N2O Emissions More Effectively under Straw-Induced Conditions Favoring Denitrification. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 104, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Li, Y.; Zhu, K.; Ju, X.; Wu, D. The Divergent Role of Straw Return in Soil O2 Dynamics Elucidates Its Confounding Effect on Soil N2O Emission. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2024, 199, 109620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulla, H.M.; El-Shatoury, S.A. Actinomycetes in Rice Straw Decomposition. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 850–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helal, G.A. Bioconversion of Straw into Improved Fodder: Fungal Flora Decomposing Rice Straw. Mycobiology 2005, 33, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bani, A.; Pioli, S.; Ventura, M.; Panzacchi, P.; Borruso, L.; Tognetti, R.; Tonon, G.; Brusetti, L. The Role of Microbial Community in the Decomposition of Leaf Litter and Deadwood. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 126, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakosová, E.; Hrabák, P.; Černík, M.; Novotný, V.; Czinnerová, M.; Trögl, J.; Popelka, J.; Kuráň, P.; Zoubková, L.; Vrtoch, Ľ. Effect of Various Chemical Oxidation Agents on Soil Microbial Communities. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 314, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Wu, Y.; Peng, Q.; Wu, L.; Van Zwieten, L.; Khalid, M.S.; Younas, A.; Lin, S.; Zhao, J.; Bashir, S. The Interactive Effects of Dolomite Application and Straw Incorporation on Soil N2O Emissions. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassaei, F. Nitrous Oxide Emissions from Rice Paddy: Impacts of Rice Straw and Water Management. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2023, 42, e14066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaćimović, G.; Aćin, V.; Mirosavljević, M.; Brbaklić, L.; Vujić, S.; Dunđerski, D.; Šeremešić, S. Effects of Combined Long-Term Straw Return and Nitrogen Fertilization on Wheat Productivity and Soil Properties in the Wheat-Maize-Soybean Rotation System in the Pannonian Plain. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Naresh, R.K.; Gupta, R.K.; Panwar, A.S.; Mahajan, N.C.; Singh, R.; Mandal, A. Effect of Tillage and Straw Return on Carbon Footprints, Soil Organic Carbon Fractions and Soil Microbial Community in Different Textured Soils under Rice–Wheat Rotation: A Review. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio Technol. 2020, 19, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGill, W.B.; Hunt, H.W.; Woodmansee, R.G.; Reuss, J.O. Phoenix, a Model of the Dynamics of Carbon and Nitrogen in Grassland Soils. Ecol. Bull. 1981, 33, 49–115. [Google Scholar]
- Abou El Nour, M.M.; Serry, S.Y. Effect of Crop Sequence, Compost and Plant Residues on Maize Yield Production, Sandy Soil Fertility and Reduce N-Mineral Fertilizer. Assiut J. Agric. Sci. 2018, 49, 141–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jin, Z.; Shah, T.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H.; Peng, S.; Nie, L. Effect of Straw Returning on Soil Organic Carbon in Rice–Wheat Rotation System: A Review. Food Energy Secur. 2020, 9, e200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devêvre, O.C.; Horwáth, W.R. Decomposition of Rice Straw and Microbial Carbon Use Efficiency under Different Soil Temperatures and Moistures. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 1773–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abro, S.A.; Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Kuyide, J.E. Decomposition Characteristics of Maize (Zea mays L.) Straw with Different Carbon to Nitrogen (C/N) Ratios under Various Moisture Regimes. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 10149–10156. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Liu, S.; Ni, G.; Rong, Q.; Huang, H.; Zhou, C.; Yin, X. Effects of Different Soil Moisture Contents on Rumen Fluids in Promoting Straw Decomposition after Straw Returning. Agronomy 2023, 13, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Ciampitti, I.A.; He, P.; Xu, X.; Qiu, S.; Zhao, S. Response of Soil Denitrification Potential and Community Composition of Denitrifying Bacterial to Different Rates of Straw Return in North-Central China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 170, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liang, Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, A.; Tan, Y.; Bol, R. Incorporating Straw into Intensively Farmed Cropland Soil Can Reduce N2O Emission via Inhibition of Nitrification and Denitrification Pathways. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeven, E.; Decock, C.; Barthel, M.; Bertora, C.; Sacco, D.; Romani, M.; Sleutel, S.; Six, J. Nitrification and Coupled Nitrification-Denitrification at Shallow Depths Are Responsible for Early Season N2O Emissions under Alternate Wetting and Drying Management in an Italian Rice Paddy System. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 120, 58–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Zhou, C.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.; Ni, G.; Yin, X. Effects of Rumen Microorganisms on Straw Returning to Soil at Different Depths. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2023, 114, 103454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lu, M.; Cui, J.; Li, B.; Fang, C. Effects of Straw Carbon Input on Carbon Dynamics in Agricultural Soils: A Meta-analysis. Glob. Change Biol. 2014, 20, 1366–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hou, H.; Sheng, R.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, H.; Wei, W. Denitrifying Communities Differentially Respond to Flooding Drying Cycles in Paddy Soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2012, 62, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.U.; Aamer, M.; Mahmood, A.; Awan, M.I.; Barbanti, L.; Seleiman, M.F.; Bakhsh, G.; Alkharabsheh, H.M.; Babur, E.; Shao, J. Management Strategies to Mitigate N2O Emissions in Agriculture. Life 2022, 12, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Li, X.L.; Xu, H.; Han, Y.; Cai, Z.C.; Yagi, K. Effects of Nitrogen Fertiliser and Wheat Straw Application on CH4 and N2O Emissions from a Paddy Rice Field. Soil Res. 2007, 45, 359–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
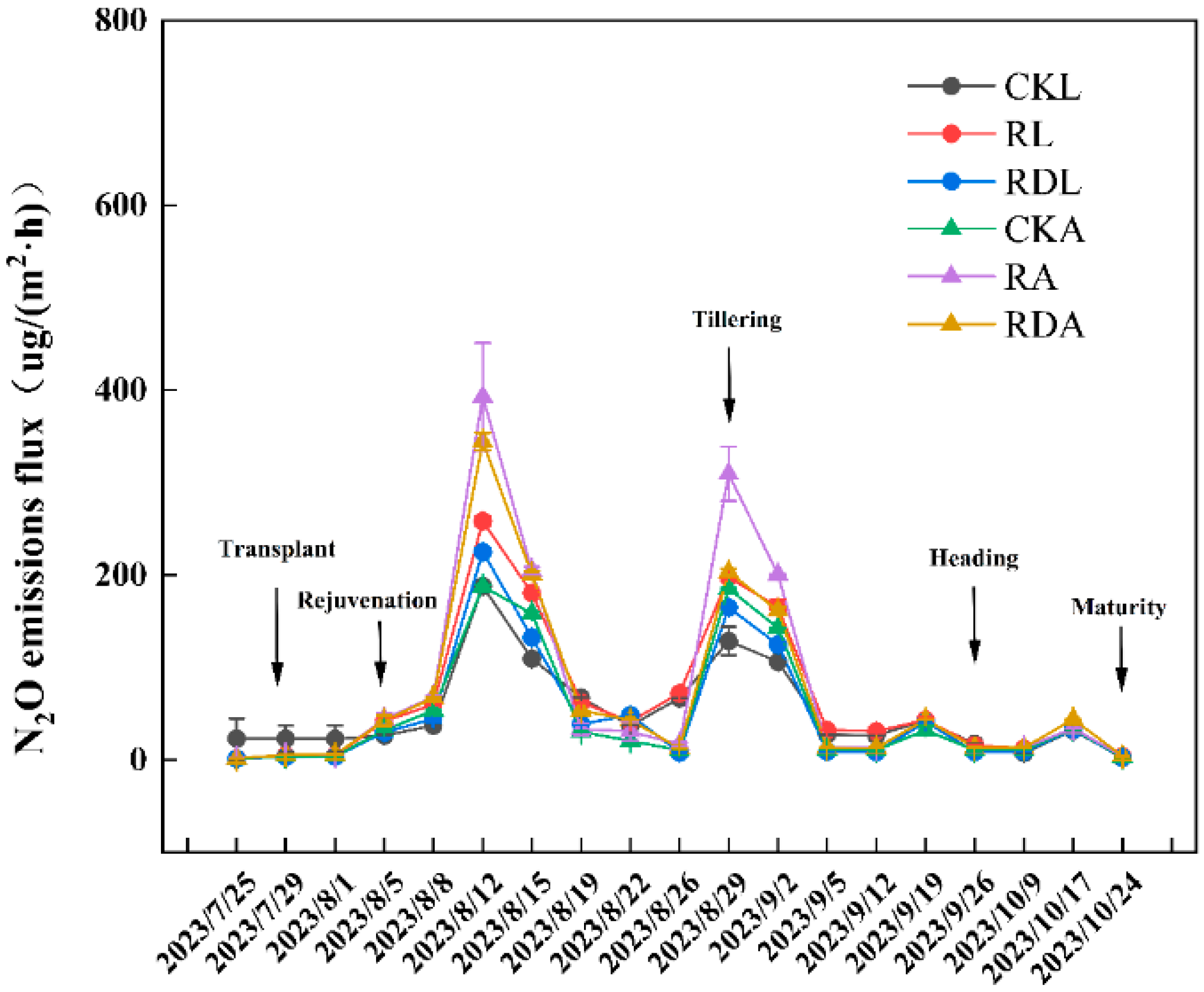
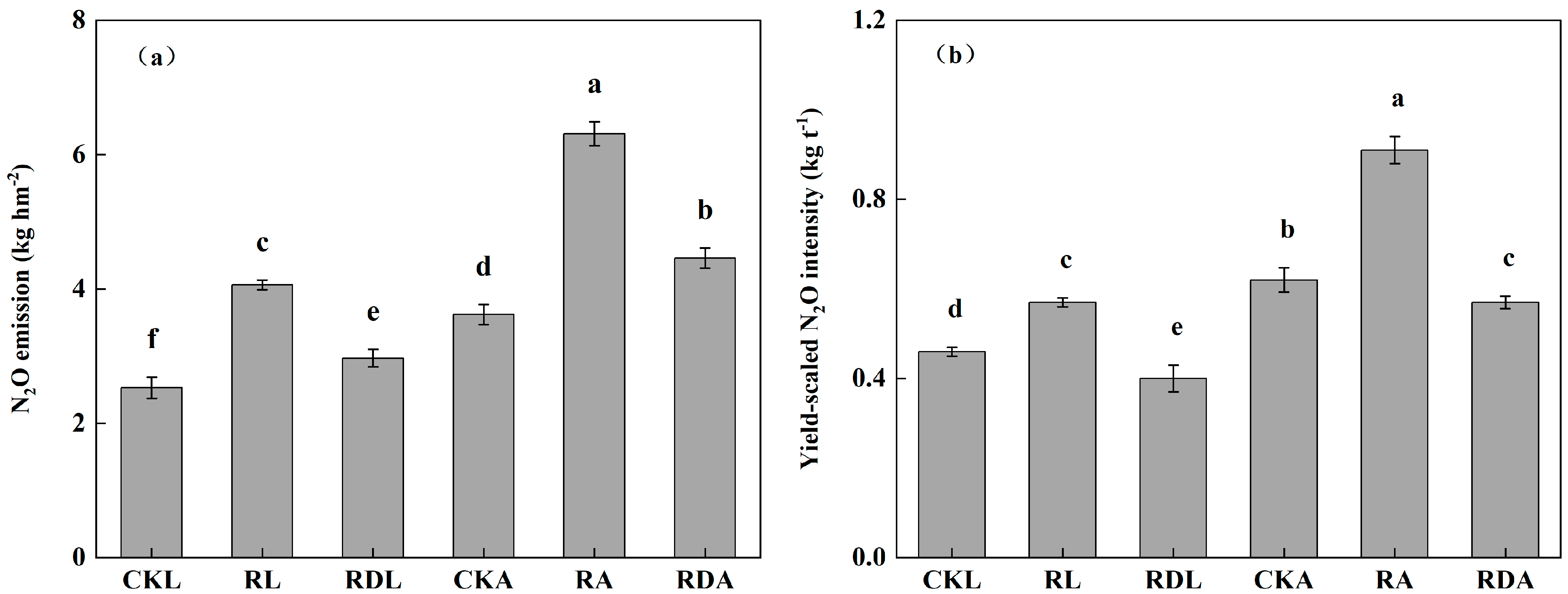

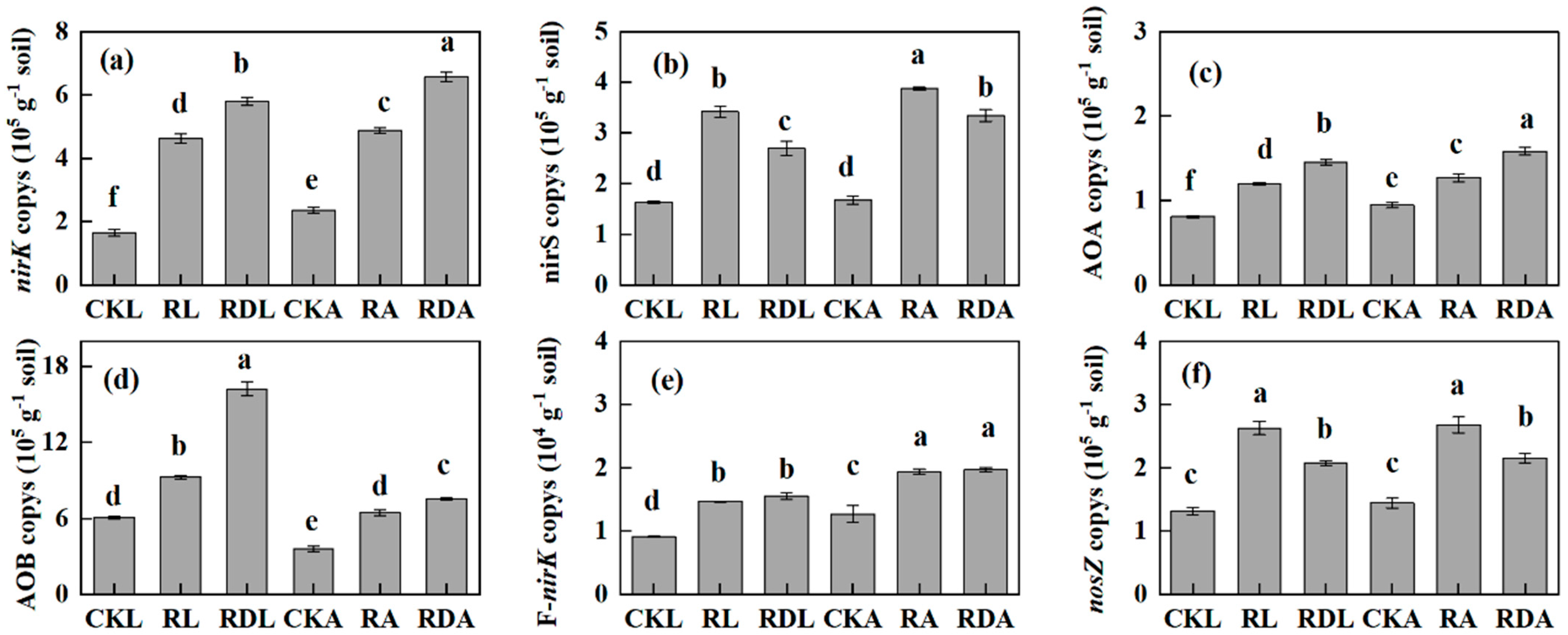
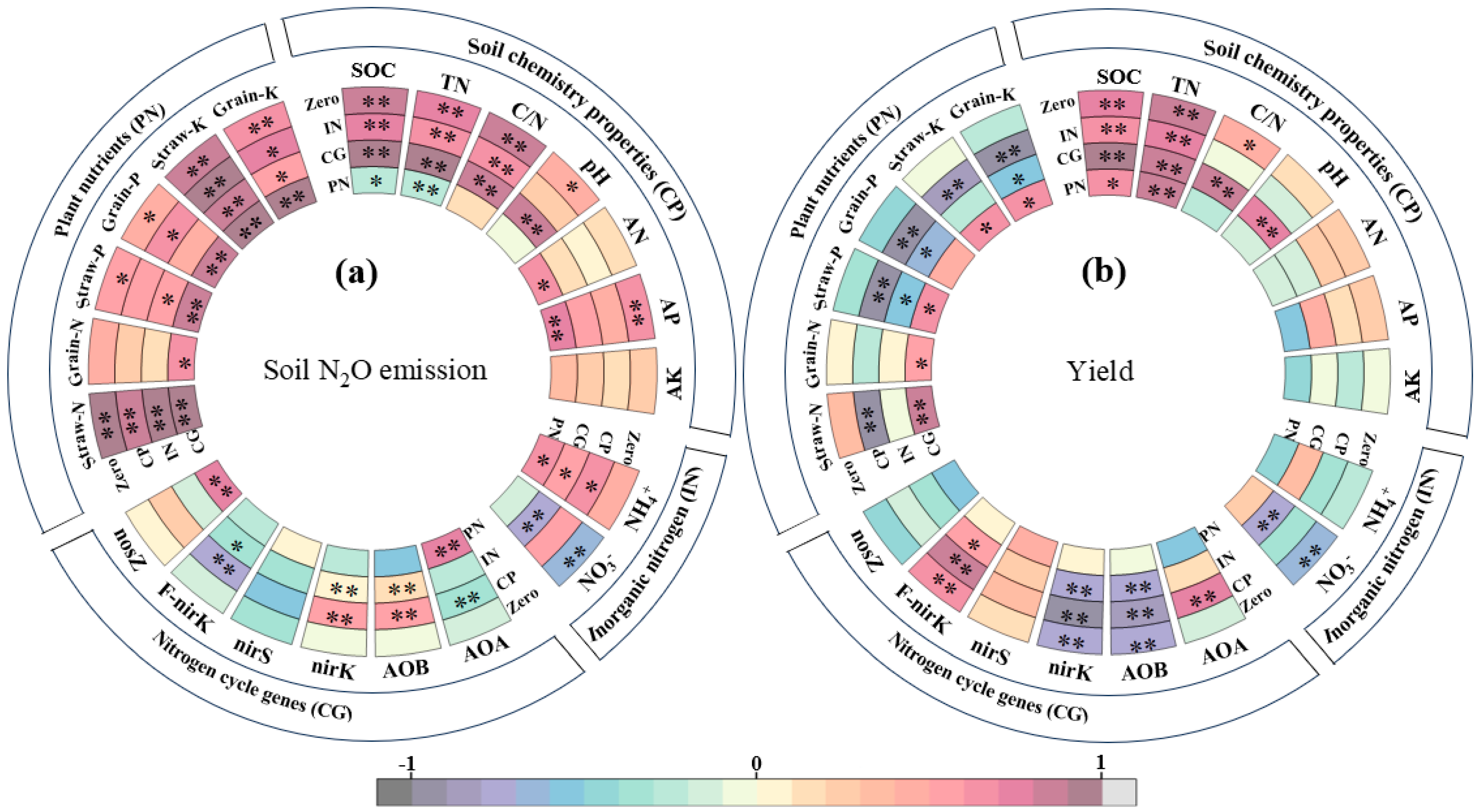
| Treatment | SOC (g·kg−1) | Total N (g·kg−1) | C/N ratio | pH | AP (mg·kg−1) | AK (mg·kg−1) | AN (mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKL | 12.1 ± 0.04 e | 0.87 ± 0.02 d | 14.0 ± 0.35 b | 5.60 ± 0.03 d | 28.5 ± 1.51 e | 44.7 ± 1.62 b | 110 ± 2.36 bc |
| RL | 18.6 ± 0.59 b | 1.17 ± 0.02 b | 15.9 ± 0.38 a | 5.70 ± 0.05 cd | 56.6 ± 2.56 b | 73.9 ± 2.49 a | 114 ± 3.31 bc |
| RDL | 16.8 ± 0.38 c | 1.05 ± 0.03 c | 16.1 ± 0.46 a | 5.95 ± 0.04 a | 45.1 ± 1.30 c | 60.9 ± 2.62 ab | 109 ± 3.07 c |
| CKA | 13.0 ± 0.44 d | 0.88 ± 0.01 d | 14.7 ± 0.61 b | 5.76 ± 0.09 bc | 41.0 ± 0.71 d | 53.4 ± 1.71 b | 123 ± 1.91 a |
| RA | 20.7 ± 0.34 a | 1.30 ± 0.01 a | 15.9 ± 0.15 a | 5.83 ± 0.02 b | 45.1 ± 0.55 c | 47.1 ± 11.1 b | 115 ± 0.41 b |
| RDA | 19.1 ± 0.25 b | 1.19 ± 0.01 b | 16.0 ± 0.24 a | 5.73 ± 0.02 bc | 74.5 ± 1.06 a | 60.6 ± 14.5 ab | 127 ± 3.28 a |
| Treatment | Yield (t·ha−1) | Straw N (g·kg−1) | Grain N (g·kg−1) | Straw P (g·kg−1) | Grain P (g·kg−1) | Straw K (g·kg−1) | Grain K (g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CKL | 5.55 ± 0.28 c | 3.31 ± 0.58 c | 6.21 ± 0.38 d | 3.25 ± 0.85 c | 3.04 ± 0.48 c | 20.27 ± 1.48 c | 2.31 ± 0.18 c |
| RL | 7.08 ± 0.13 b | 4.41 ± 0.69 b | 6.76 ± 0.54 a | 3.43 ± 0.86 b | 3.09 ± 0.33 b | 21.20 ± 2.33 b | 2.56 ± 0.33 b |
| RDL | 7.41 ± 0.35 a | 5.18 ± 0.83 a | 6.37 ± 0.87 c | 3.93 ± 0.67 a | 3.26 ± 0.28 a | 22.25 ± 2.28 a | 2.76 ± 0.28 a |
| CKA | 5.89 ± 0.32 c | 3.36 ± 0.54 c | 6.31 ± 0.62 d | 3.12 ± 0.19 d | 2.62 ± 0.201 d | 19.11 ± 1.21 d | 2.19 ± 0.21 d |
| RA | 6.94 ± 0.13 b | 4.61 ± 0.26 ab | 6.25 ± 0.58 c | 3.22 ± 0.22 c | 2.82 ± 0.87 c | 20.35 ± 2.87 c | 2.32 ± 0.17 c |
| RDA | 7.85 ± 0.28 a | 4.86 ± 0.41 a | 6.41 ± 1.38 b | 3.35 ± 0.55 b | 3.06 ± 0.28 b | 22.47 ± 1.28 a | 2.47 ± 0.28 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meng, L.; Lu, Q.; Lin, T.; Dong, L.; Wu, X.; Zhuo, Y.; Yang, A.; Zhu, Q.; Meng, L. Straw Returning with Decomposition Agent Enhanced Rice Yield and Decreased Yield-Scaled N2O Emissions in Tropical Paddy Fields. Agronomy 2024, 14, 3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123060
Meng L, Lu Q, Lin T, Dong L, Wu X, Zhuo Y, Yang A, Zhu Q, Meng L. Straw Returning with Decomposition Agent Enhanced Rice Yield and Decreased Yield-Scaled N2O Emissions in Tropical Paddy Fields. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123060
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Longwei, Qiqian Lu, Tian Lin, Lu Dong, Xiaochen Wu, Yixiu Zhuo, Anfu Yang, Qilin Zhu, and Lei Meng. 2024. "Straw Returning with Decomposition Agent Enhanced Rice Yield and Decreased Yield-Scaled N2O Emissions in Tropical Paddy Fields" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123060
APA StyleMeng, L., Lu, Q., Lin, T., Dong, L., Wu, X., Zhuo, Y., Yang, A., Zhu, Q., & Meng, L. (2024). Straw Returning with Decomposition Agent Enhanced Rice Yield and Decreased Yield-Scaled N2O Emissions in Tropical Paddy Fields. Agronomy, 14(12), 3060. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123060





