The Long-Term Effect of Cattle Manure Application on Soil P Availability and P Fractions in Saline-Sodic Soils in the Songnen Plain of China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Soil Sampling
2.4. Laboratory Methods
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
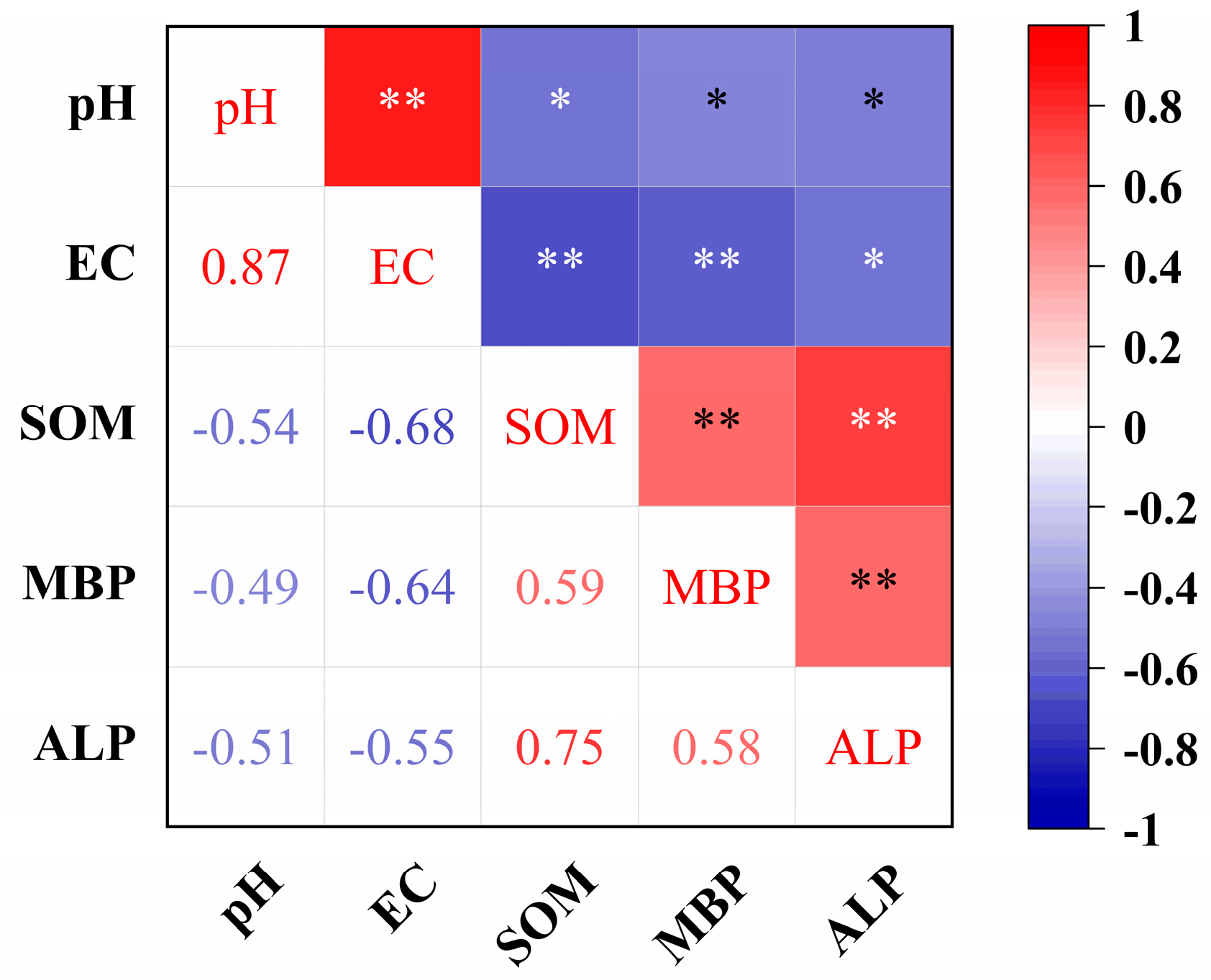
3.1. Soil pH Value and Electrical Conductivity
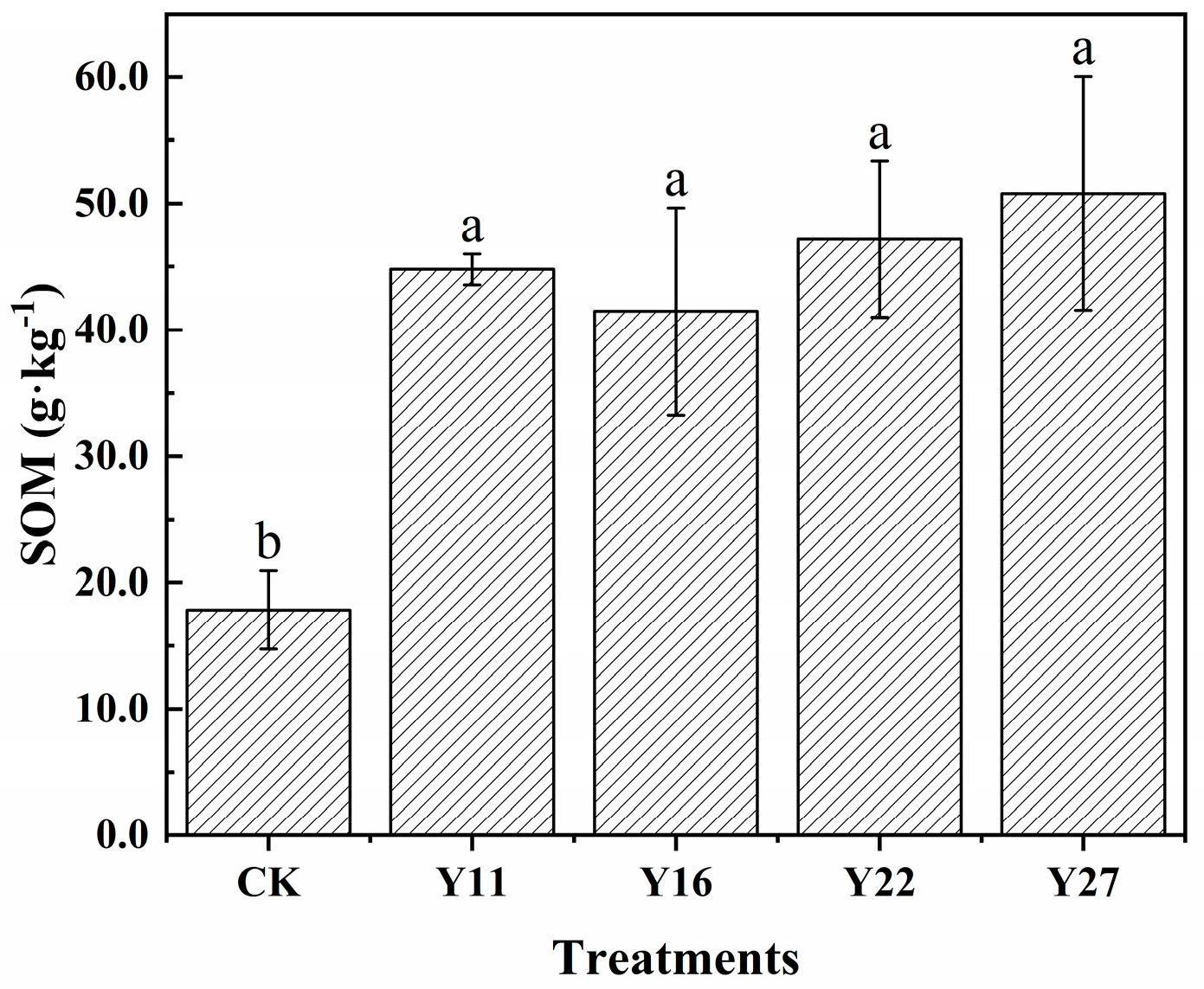
3.2. Soil Organic Matter
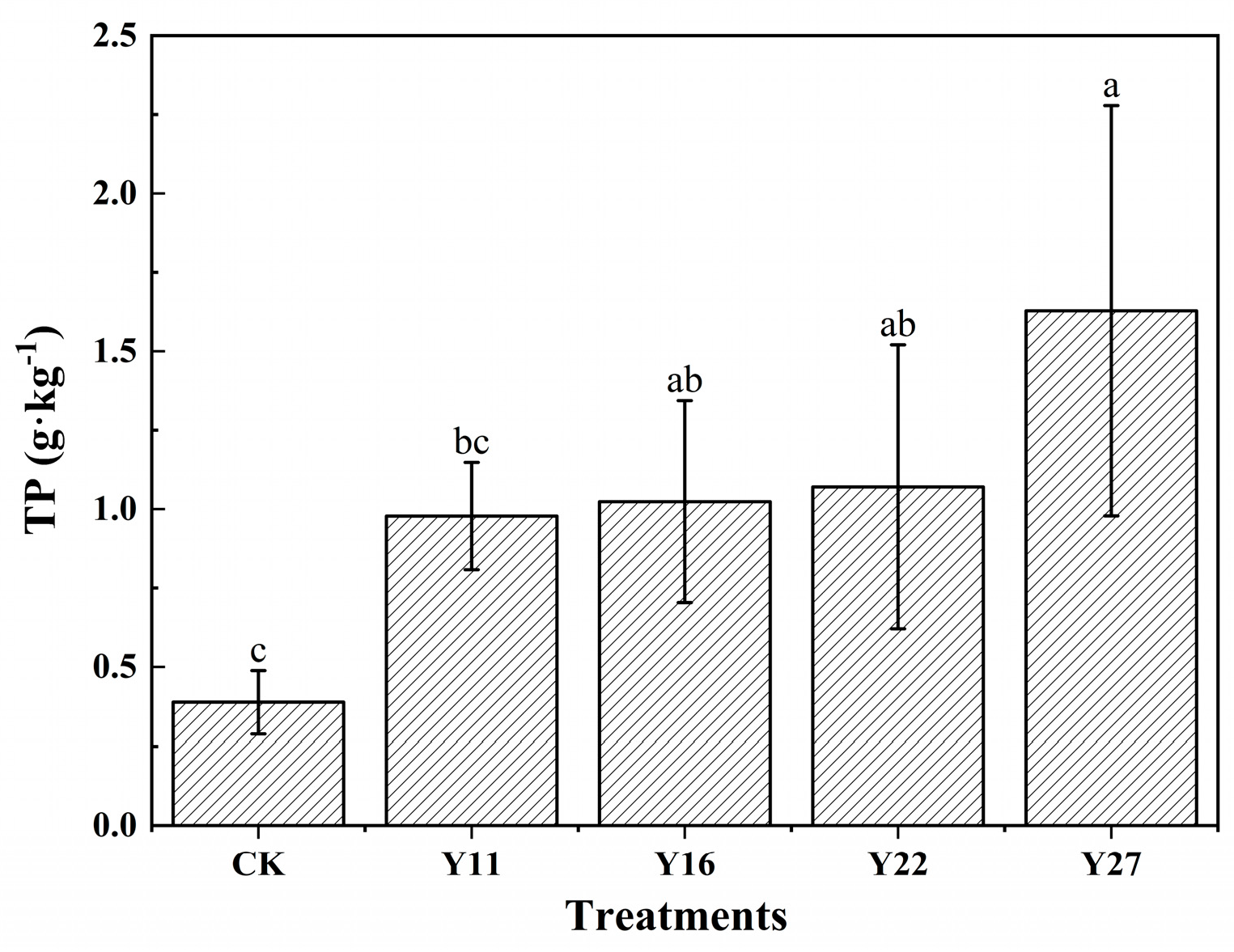
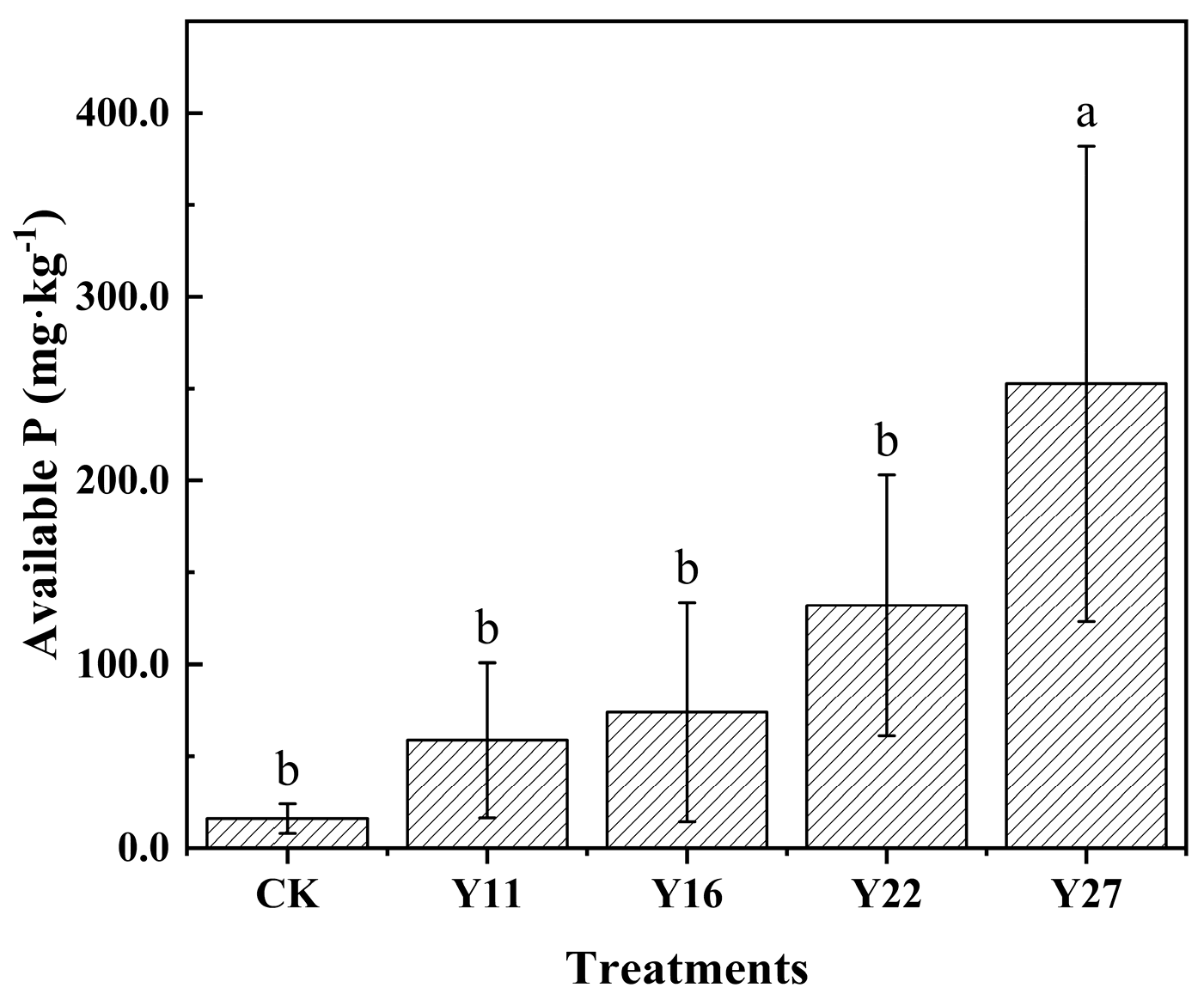
3.3. Soil Total P and Available P
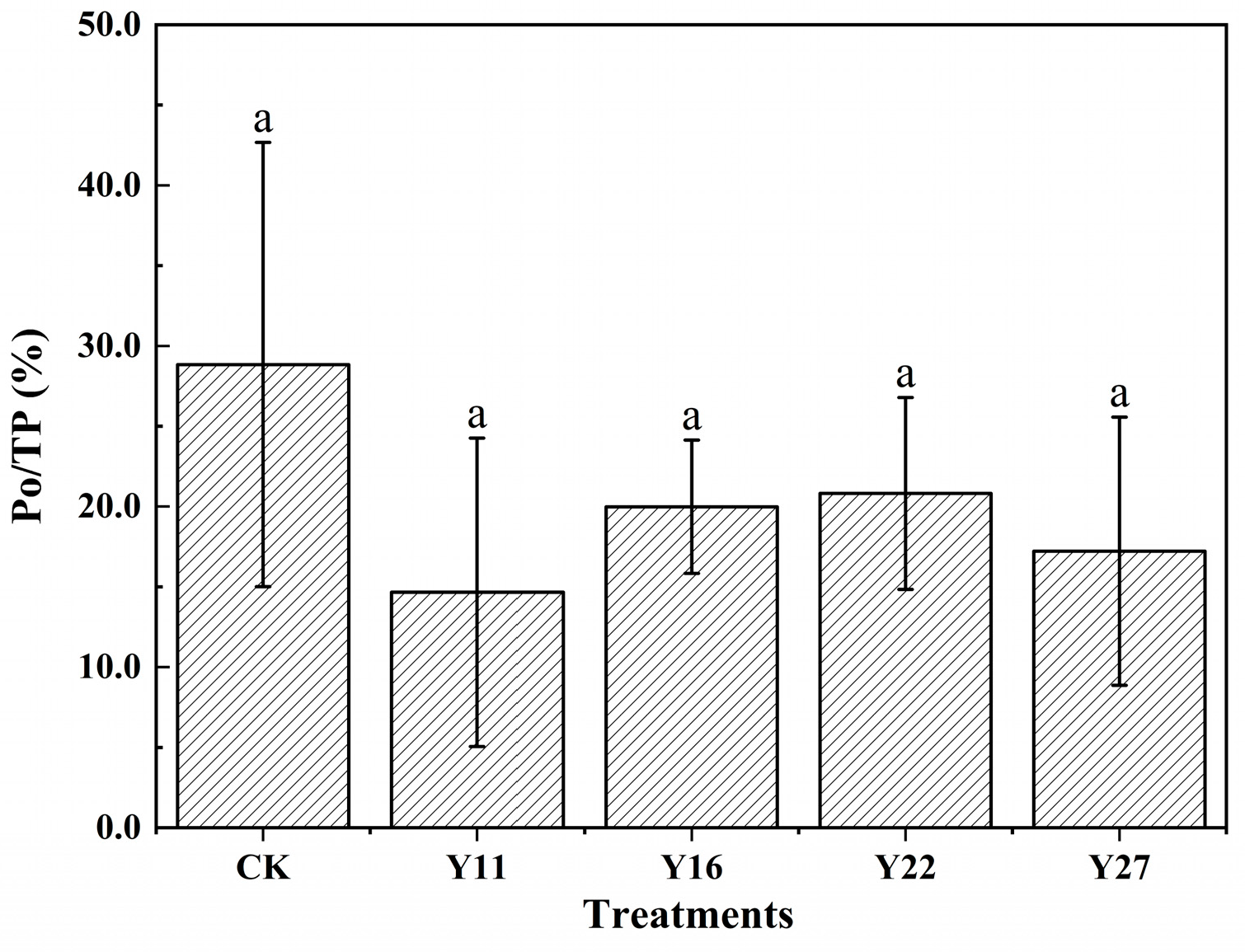
3.4. Soil Organic P and Inorganic P
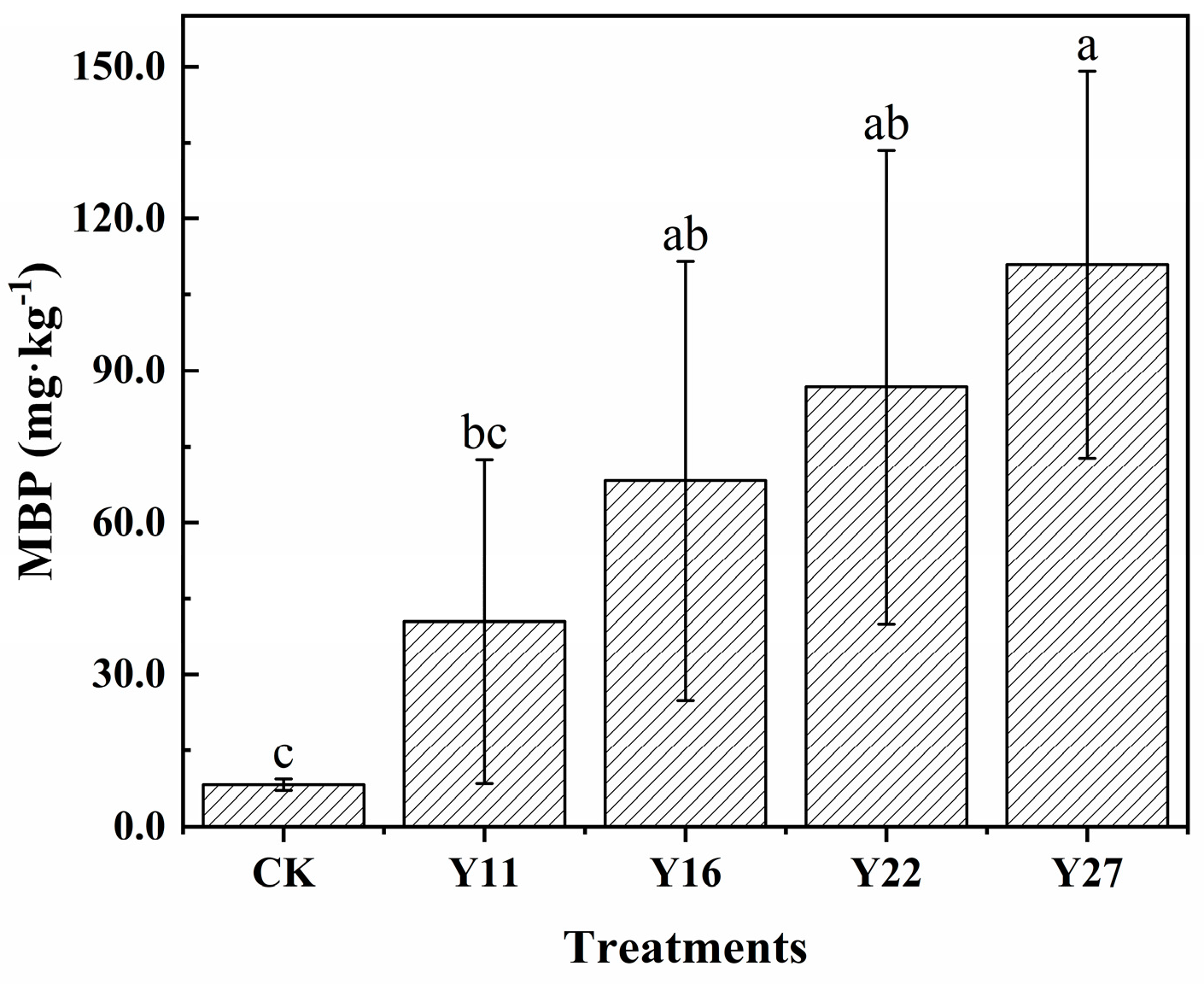
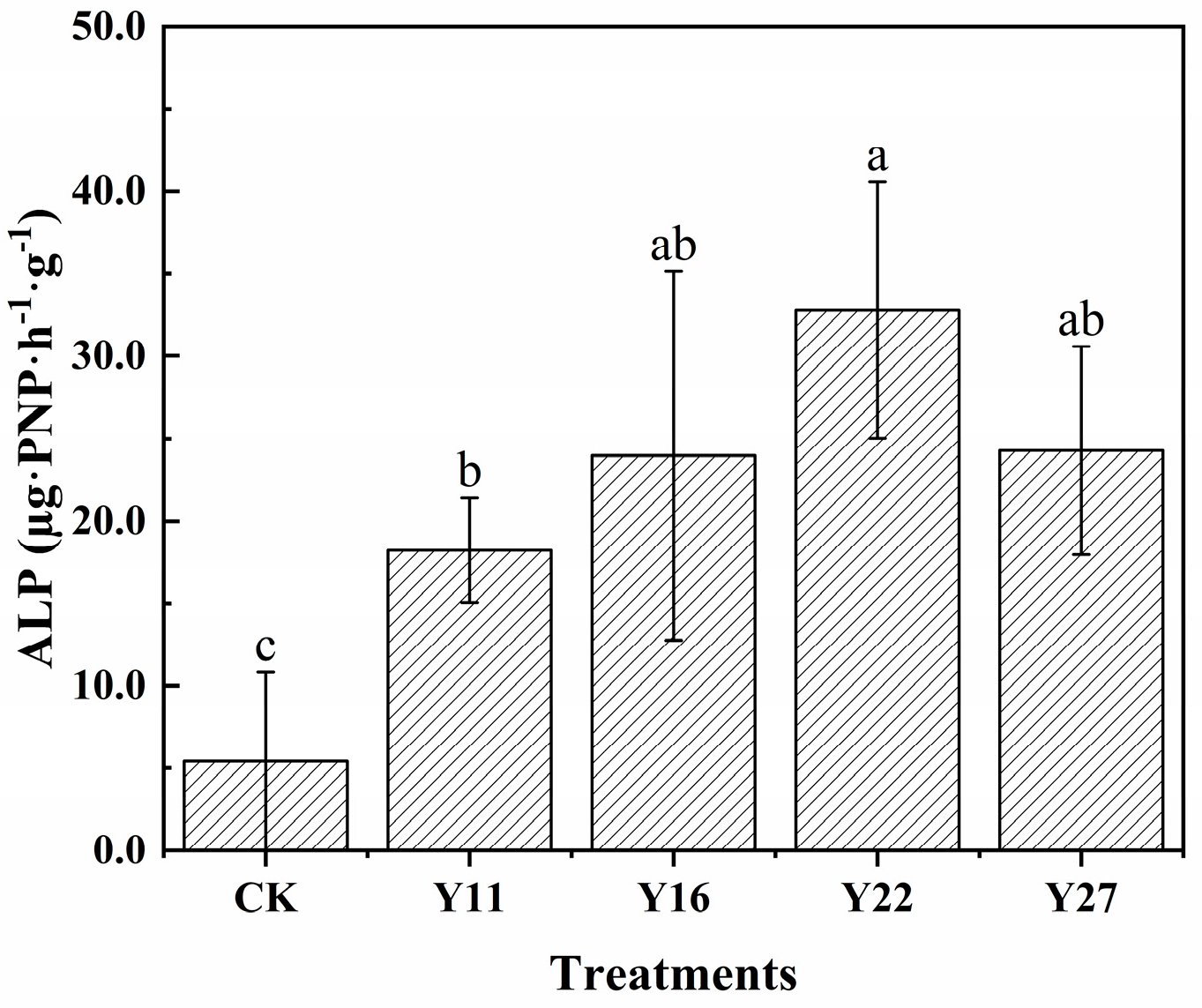
3.5. Soil Microbial Biomass Phosphorus and Alkaline Phosphatase Activity
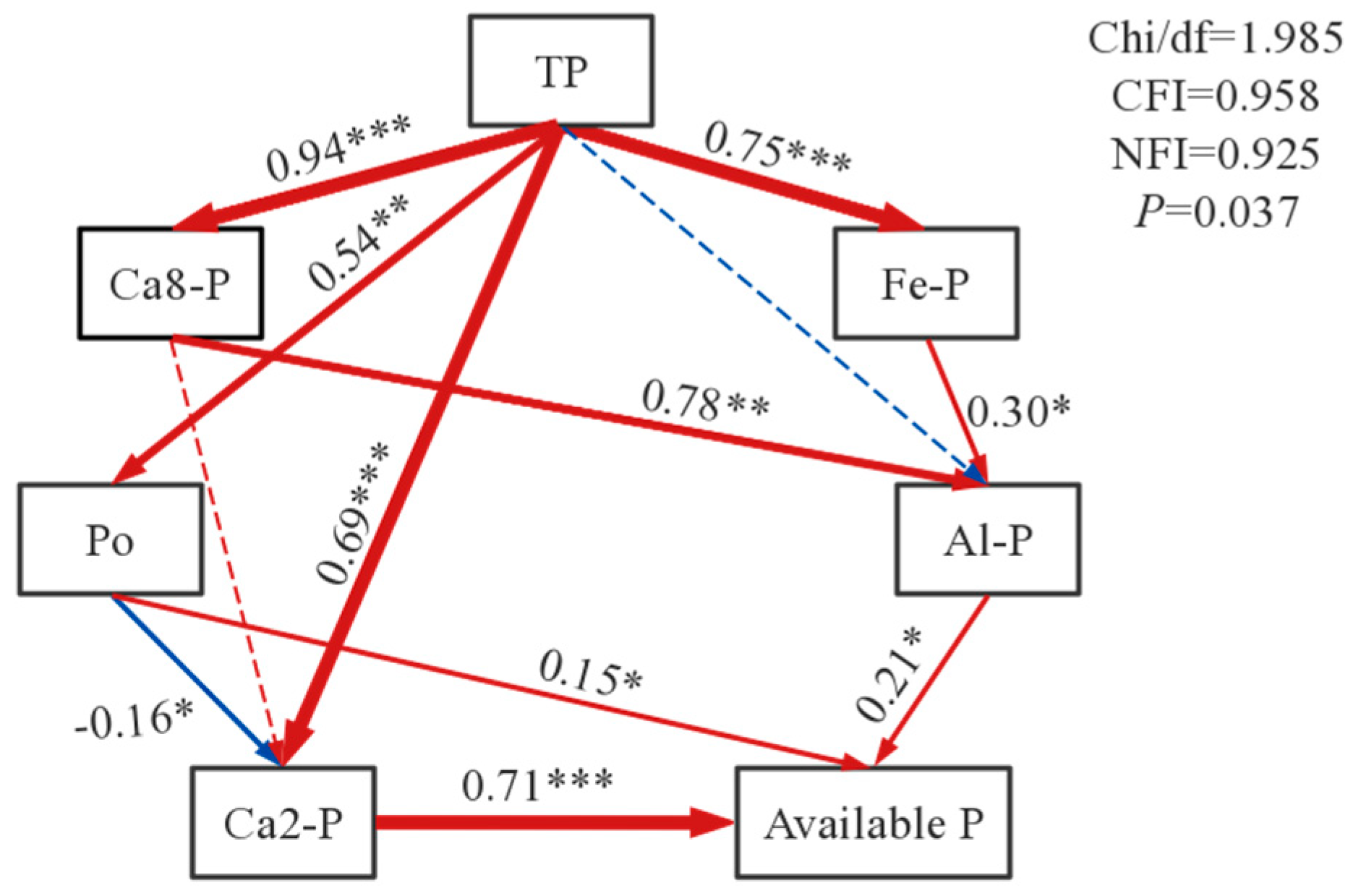
3.6. Relationships Between Total P, P Fractions, and Available P
4. Discussion
4.1. Long-Term Effect of Manure Application on Soil Properties, Microbial Biomass Phosphorus, and Alkaline Phosphatase Activity
4.2. Long-Term Effect of Manure Application on Soil Total P, Available P, and P Fractions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Lin, C.Y.; Han, Z.M.; Fu, C.B.; Huang, D.; Cheng, H.G. Dissolved nitrogen in salt-affected soils reclaimed by planting rice: How is it influenced by soil physicochemical properties? Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Peng, S.Q.; Chen, Z.; Fan, L.; Li, Y. Effect of salt vertical distribution on sulfate-affected soils deformation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 894, 165036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.H.; Tian, L.; Nasir, F.; Bahadur, A.; Batool, A.; Luo, S.; Yang, F.; Wang, Z.C.; Tian, C.J. Response of microbial communities and enzyme activities to amendments in saline-alkaline soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 135, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.S.; Yao, R.J.; Wang, X.P.; Xie, W.P.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, L.; Sun, R.J. Research on Salt-affected Soils in China: History, Status Quo and Prospect. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2022, 59, 10–27. [Google Scholar]
- Tefera, B.B.; Bayabil, H.K.; Tong, Z.H.; Teshome, F.T.; Wenbo, P.; Li, Y.C.; Hailegnaw, N.S.; Gao, B. Using liquefied biomass hydrogel to mitigate salinity in salt-affected soils. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, A.E.; Poulton, P.R.; Fixen, P.E.; Curtin, D. Phosphorus: Its Efficient Use in Agriculture. In Advances in Agronomy; Spark, D.L., Ed.; Academic Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 123, pp. 177–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Pavinato, P.S.; Withers, P.J.A.; Teles, A.P.B.; Bejarano Herrera, W.F. Legacy phosphorus and no tillage agriculture in tropical oxisols of the Brazilian savanna. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 1050–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Xiao, F.; Zhang, D.; Hu, R.; Xiong, R.; Lv, W.; Yang, Z.; Tan, W.; Yu, H.; Ding, D.; et al. Organophosphorus mineralizing-Streptomyces species underpins uranate immobilization and phosphorus availability in uranium tailings. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 476, 134975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Zhan, X.Y.; Zhang, S.X.; Ibrahima, K.H.M.; Xu, M.G. Response of soil Olsen-P to P budget under different long-term fertilization treatments in a fluvo-aquic soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, L.E.Z.; Nunes, R.d.S.; de Figueiredo, C.C.; Rein, T.A. Spatial distribution of soil phosphorus fractions in a clayey Oxisol submitted to long-term phosphate fertilization strategies. Geoderma 2022, 418, 115847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiecher, T.; Fontoura, S.M.V.; Ambrosini, V.G.; Araujo, E.A.; Alves, L.A.; Bayer, C.; Gatiboni, L.C. Soil phosphorus forms and fertilizer use efficiency are affected by tillage and soil acidity management. Geoderma 2023, 435, 116495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltas, A.S.; Tavali, I.E.; Uz, I.; Kaplan, M. Monitoring the effects of pH and EC regulated drip fertigation on microbial dynamics of calcareous soil in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) cultivation under greenhouse conditions in a Mediterranean climate. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 306, 111448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, V.; Das, A.; Nayak, A.; Chawla, Y.; Dasgupta, S.; Weindorf, D.C.; Li, B.; Chakraborty, S. Digital soil mapping of available phosphorus using a smartphone-integrated RGB imaging device and ascorbic acid extraction method. Smart Agric. Technol. 2024, 9, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jin, S.; Wang, K. Machine learning and genetic algorithm for mapping soil available phosphorus in coastal provinces in Southeast China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.; Aleinikovienė, J.; Butkevičienė, L.-M. Innovative Organic Fertilizers and Cover Crops: Perspectives for Sustainable Agriculture in the Era of Climate Change and Organic Agriculture. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gu, F.; Zhang, D.; Lin, W.; Tang, J.; Zhang, B.; Yu, X. Investigating the Two-Dimensional Distribution of Soil pH and Phosphorus in the Charosphere: A Short-Term Incubation Experiment. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Ren, L.; Wu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; Song, X.; Li, X. Saline-alkali soil amended with biochar derived from maricultural-solid-waste: Ameliorative effect and mechanism. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 368, 122134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ren, T.; Yan, J.; Zhu, D.; Liao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Cong, R.; Li, X.; Lu, J. Straw returning mediates soil microbial biomass carbon and phosphorus turnover to enhance soil phosphorus availability in a rice-oilseed rape rotation with different soil phosphorus levels. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 335, 107991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.F.; Ma, X.F.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Z.T. The long-term effects of cattle manure application to agricultural soils as a natural-based solution to combat salinization. Catena 2019, 175, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shawver, S.; Wepking, C.; Ishii, S.; Strickland, M.S.; Badgley, B.D. Application of manure from cattle administered antibiotics has sustained multi-year impacts on soil resistome and microbial community structure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 157, 108252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinasoa, S.; Rakotoson, T.; Rabeharisoa, L.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Nishigaki, T. Farmyard manure application increases lowland rice yield in phosphorus-deficient soils, but not in soils with high pH and phosphorus-fixing capacity. Field Crops Res. 2023, 296, 108906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhan, X.Y.; Wu, Q.H.; Huang, S.M.; Zhu, P.; Yang, X.Y.; Zhang, S.X. Characteristics of inorganic phosphorus fractions and their correlations with soil properties in three non-acidic soils. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 3626–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalo Filho, F.; Dias, N.d.S.; Prazeres Suddarth, S.R.; Ferreira, J.F.S.; Anderson, R.G.; Fernandes, C.d.S.; de Lira, R.B.; Neto, M.F.; Cosme, C.R. Reclaiming Tropical Saline-Sodic Soils with Gypsum and Cow Manure. Water 2020, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erich, M.S.; Fitzgerald, C.B.; Porter, G.A. The effect of organic amendments on phosphorus chemistry in a potato cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 88, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.H.; Liu, D.; Li, T.X.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zheng, Z.C. Phosphorus accumulation characteristics in Polygonum hydropiper and rhizosphere properties affected by poultry manure application. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 131, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.C.; Jiang, B.F. The method of measurement inorganic phosphorus fractions in calcareous soil. Soil 1990, 22, 101–102. [Google Scholar]
- Tabatabai, M.A. Soil Enzymes. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Weaver, R.W., Angle, S., Bottomley, P., Bezdicek, D., Smith, S., Tabatabai, A., Wollum, A., Eds.; American Society of Agronomy Publishing: Madison, WI, USA, 1994; pp. 775–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, P.C.; Powlson, D.S.; Jenkinson, D.S. Measurement of microbial biomass phosphorus in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1982, 14, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.P.; Zhao, L.; Wang, C.; Huang, H.Y.; Zhuang, M.H. Synergistic improvement of carbon sequestration and crop yield by organic material addition in saline soil: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 891, 164530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larkin, R.P. Potato Cropping System and Variety Impacts on Soil Properties, Soilborne Diseases, and Tuber Yield in a Long-Term Field Trial. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.H.; Liu, Y.; Ferreira, J.F.S.; Wang, M.M.; Na, J.; Huang, J.X.; Liang, Z.W. Long-term combined effects of tillage and rice cultivation with phosphogypsum or farmyard manure on the concentration of salts, minerals, and heavy metals of saline-sodic paddy fields in Northeast China. Soil. Till. Res. 2022, 215, 105222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaaban, M.; Wu, Y.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Peng, Q.; Lin, S.; Hu, R. Enzyme activities and organic matter mineralization in response to application of gypsum, manure and rice straw in saline and sodic soils. Environ. Res. 2023, 224, 115393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Yan, X.; Xia, X.; Liu, D.; Guo, S.; Ma, R.; Lou, Y.; Yang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, Q.; et al. Effects of the three amendments on NH3 volatilization, N2O emissions, and nitrification at four salinity levels: An indoor experiment. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 354, 120399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; de Jonge, L.W.; Moldrup, P.; Paradelo, M.; Arthur, E. Improvements in soil physical properties after long-term manure addition depend on soil and crop type. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, S.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.; Dong, H.; Dai, S.; Chai, L.; Li, H.; Lv, Y.; Li, T.; et al. Trade-offs of organic amendment input on soil quality and crop productivity in saline-alkali land globally: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Agron. 2025, 164, 127471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, S.; Gul, S.; Ziad, T.; Yunus, A.W.; Khan, R.U.; Akbar, A.; Buriro, A.H. Influence of composted manures and co-composted biochar on growth performance of saffron and soil nutrients under varying electrical conductivity soil conditions: A two-year field study. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.F.; Li, D.W.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, L.R.; Ma, X.F.; Wang, H.Y.; Wang, G.C. Soil properties and corn (Zea mays L.) production under manure application combined with deep tillage management in solonetzic soils of Songnen Plain, Northeast China. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Ran, C.; Ma, Q.; Miao, Y.; Li, S.; Lan, H.; Li, X.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Shao, X. The Application of Straw Return with Nitrogen Fertilizer Increases Rice Yield in Saline–Sodic Soils by Regulating Rice Organ Ion Concentrations and Soil Leaching Parameters. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, T.Y.; Zhao, J.J.; Liu, A.H.; Long, X.H.; Rengel, Z. Effects of soil physicochemical properties on microbial communities in different ecological niches in coastal area. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 150, 103486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.C.; Guo, S.F.; Zhai, L.M.; Pan, J.T.; Khoshnevisan, B.; Wu, S.X.; Wang, H.Y.; Yang, B.; Ji, J.H.; Liu, H.B. How long-term excessive manure application affects soil phosphorous species and risk of phosphorous loss in fluvo-aquic soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Shao, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, X. Soil enzymes as indicators of saline soil fertility under various soil amendments. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 237, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Lv, Q.; Zhang, L.; Fan, J.; Wang, T.; Meng, Y.; Xia, H.; Ren, X.; Hu, S. Converted paddy to upland in saline-sodic land could improve soil ecosystem multifunctionality by enhancing soil quality and alleviating microbial metabolism limitation. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintarič, M.; Štuhec, A.; Tratnik, E.; Langerholc, T. Specific Fertilization Practices Reveal Important Insights into the Complex Interaction Between Microbes and Enzymes in Soils of Different Farming Systems. Life 2024, 14, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Fan, M.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Hao, Z.; Yu, J.; Yang, Y.; Zuo, W.; Shan, Y.; et al. Organic Amendments Promoted Soil Agglomeration Mainly via Alleviating Abiotic Constraints and Stabilizing and Functionalizing Microbiomes in Coastal Salt-Affected Lands. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.L.; Yuan, J.H.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y. Animal manures promoted soil phosphorus transformation via affecting soil microbial community in paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.H.; Duan, Y.; Li, M.H.; Tang, C.G.; Kan, W.J.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, H.L.; Zhong, W.L.; Wu, L.F. Manure substitution improves maize yield by promoting soil fertility and mediating the microbial community in lime concretion black soil. J. Integr. Agric. 2024, 23, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfenstein, J.; Tamburini, F.; von Sperber, C.; Massey, M.S.; Pistocchi, C.; Chadwick, O.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Kretzschmar, R.; Frossard, E. Combining spectroscopic and isotopic techniques gives a dynamic view of phosphorus cycling in soil. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.L.; Chen, S.; Cui, J.Y.; Ping, H.X.; Yuan, C.P.; Chen, Q. A meta-analysis of arable soil phosphorus pools response to manure application as influenced by manure types, soil properties, and climate. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 115006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Wen, Y.; Ma, J.; Macdonald, A.; Hill, P.W.; Chadwick, D.R.; Wu, L.; Jones, D.L. Long-term farmyard manure application affects soil organic phosphorus cycling: A combined metagenomic and 33P/14C labelling study. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 149, 107959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Duan, Y.H.; McLaughlin, N.; Huang, S.M.; Guo, D.D.; Xu, M.G. Phosphorus desorption from calcareous soils with different initial Olsen-P levels and relation to phosphate fractions. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2997–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Z.; Shi, L.L.; Lu, H.B.; Shao, Y.H.; Liu, S.R.; Fu, S.L. Drought promotes soil phosphorus transformation and reduces phosphorus bioavailability in a temperate forest. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 732, 139295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| pH Value | EC/(dS·m−1) | BD/(g·cm−3) | Exc. Na+/(cmol·kg−1) | SOM/(g·kg−1) | TP/(g·kg−1) | Available P/(mg·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9.50 | 6.23 | 1.35 | 12.06 | 10.95 | 0.25 | 12.08 |
| pH Value | SOM/(g·kg−1) | Na/(g·kg−1) | N/(g·kg−1) | P/(g·kg−1) | K/(g·kg−1) | Ca/(g·kg−1) | Mg/(g·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8.42 | 590.69 | 0.41 | 13.28 | 12.02 | 15.35 | 9.77 | 4.58 |
| Soil Properties | Treatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Y11 | Y16 | Y22 | Y27 | |
| pH value | 10.07 ± 0.11 a | 8.24 ± 0.92 b | 8.55 ± 0.93 b | 8.81 ± 0.84 b | 8.06 ± 0.13 b |
| EC/(dS·m−1) | 1.45 ± 0.34 a | 0.55 ± 0.26 b | 0.55 ± 0.24 b | 0.63 ± 0.26 b | 0.45 ± 0.14 b |
| Pi | Treatments | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | Y11 | Y16 | Y22 | Y27 | |
| Fe-P | 10.77 ± 7.57 b | 18.43 ± 4.29 b | 18.26 ± 2.38 b | 31.91 ± 17.59 ab | 45.40 ± 29.46 a |
| Al-P | 27.16 ± 7.71 b | 36.88 ± 6.45 b | 39.63 ± 7.96 b | 45.72 ± 17.93 b | 74.42 ± 24.28 a |
| Ca2-P | 15.04 ± 8.68 b | 60.58 ± 54.04 b | 50.92 ± 37.53 ab | 80.45 ± 42.82 ab | 140.49 ± 64.38 a |
| Ca8-P | 11.42 ± 7.28 b | 72.89 ± 31.34 b | 81.73 ± 48.17 b | 117.46 ± 95.21 b | 248.35 ± 132.68 a |
| Ca10-P | 32.10 ± 7.68 | 36.08 ± 5.35 | 27.39 ± 3.77 | 33.06 ± 6.55 | 30.31 ± 5.17 |
| O-P | 40.63 ± 47.49 | 14.89 ± 18.77 | 55.77 ± 39.61 | 43.41 ± 22.88 | 37.51 ± 26.69 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, X.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.; Meng, Q. The Long-Term Effect of Cattle Manure Application on Soil P Availability and P Fractions in Saline-Sodic Soils in the Songnen Plain of China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123059
Feng X, Liu C, Li Y, Xu J, Zhang J, Meng Q. The Long-Term Effect of Cattle Manure Application on Soil P Availability and P Fractions in Saline-Sodic Soils in the Songnen Plain of China. Agronomy. 2024; 14(12):3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123059
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Xiaotong, Changjie Liu, Yang Li, Jiaqi Xu, Juan Zhang, and Qingfeng Meng. 2024. "The Long-Term Effect of Cattle Manure Application on Soil P Availability and P Fractions in Saline-Sodic Soils in the Songnen Plain of China" Agronomy 14, no. 12: 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123059
APA StyleFeng, X., Liu, C., Li, Y., Xu, J., Zhang, J., & Meng, Q. (2024). The Long-Term Effect of Cattle Manure Application on Soil P Availability and P Fractions in Saline-Sodic Soils in the Songnen Plain of China. Agronomy, 14(12), 3059. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14123059






